Section one: Biological Molecules Summary
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What type of glucose is amylose made of
Alpha glucose
What type of glucose is amylopectin made up of
Alpha glucose
What type of glucose is cellulose made up of
Alpha Glucose
What are the two types of enzyme inhibitors
Competitive and non-competitive
How do Competitive inhibitors, inhibit enzyme action
Competitive inhibitors occupy the active site so that the substrate cannot enter the active site and form an enzyme-substrate complex
How do Non-competitive inhibitors, inhibit enzyme action
Non-competitive inhibitors occupy a binding site which is not the active site. The inhibitor alters the shape of the enzyme so that the enzyme is no longer able to function
What are the names of the Bases for DNA
thymine, adenine, guanine, cytosine
What are the names of the bases for RNA
Uracil, Adenine, guanine, cytosine
What type of sugars are in DNA and RNA
Pentose sugars:
Deoxyribose (DNA)
Ribose (RNA)
What are the enzymes present in DNA replication
DNA Polymerase and DNA Helicase
What type of replication is DNA replication
Semi-conservative
What type of Bonds hold the complementary bases together in DNA
Hydrogen bonds
How many Hydrogen bonds hold Adenine and Thymine together
Two
How many hydrogen bonds hold Cytosine and Guanine together
Three
What temperature is optimum for enzymes
37°C
What are Triglycerides made up of
1 Glycerol + 3 Fatty acids
What is a phospholipid made up of
1 Glycerol + 2 Fatty Acids + 1 Phosphate group
What are enzymes
Globular proteins which act as Catalysts within reactions
What holds first degree proteins (primary structure) together
Peptide bonds between amino acids
How does the structure of the second degree protein form? (secondary Structure)
Hydrogen bonds form between the C=O and -NH groups within the peptide chains
what Shape is a secondary protein
an Alpha Helix
What bonds hold a third degree protein together (tertiary structure)
Ionic bonds form between amino and Carboxyl groups uninvolved in peptide bonds
Hydrogen bonds which are numerous but easily broken
Disulfide bridges which are fairly strong and are therefore not easily broken
What is the structure of a fourth degree protein (quatenary structure)
Multiple peptide chains are involved and are linked together in various ways
prosthetic groups are involved
What are prosthetic groups
Non protein groups that are present within a Quatenary protein
What factors affect enzyme action
temperature
pH
Concentration of enzyme
Concentration of substrate
How does temperature affect enzyme action
As temperature increases, kinetic energy increases (molecules move more rapily and therefore collide with higher frequency)
What happens to an enzyme if the temperature is too high
The bonds holding the shape if the active site break and the enzyme denatures
how does pH affect enzyme action
A change of pH alters the shape of the acctive site
What happens if the change in pH is too drastic
If there is a significant change in pH the bonds holding the tertiary structure of the protein (which hold the shape of the active site) break, this causes the active site to become deformed and the enzyme is now denatured
What is pH
the measure of hydrogen ion concentration within a solution
how do you calculate pH
pH= -log10
what is the shape of DNA
Double helix
What does a nucleotide molecule contain
Base
Phosphate group
Pentose sugar
How stable is DNA
Very stable
Why is DNA a stable molecule
The phosphodiester backbone protects the more chemically reactive organic bases
hydrogen bonds link the organic bases forming rungs between the phosphodiester uprights
what is the name of the reaction through which monomers are joined up into polymers
Condensation
What is the name of the reaction through which polymers are broken up into their monomers.
Hydrolisation
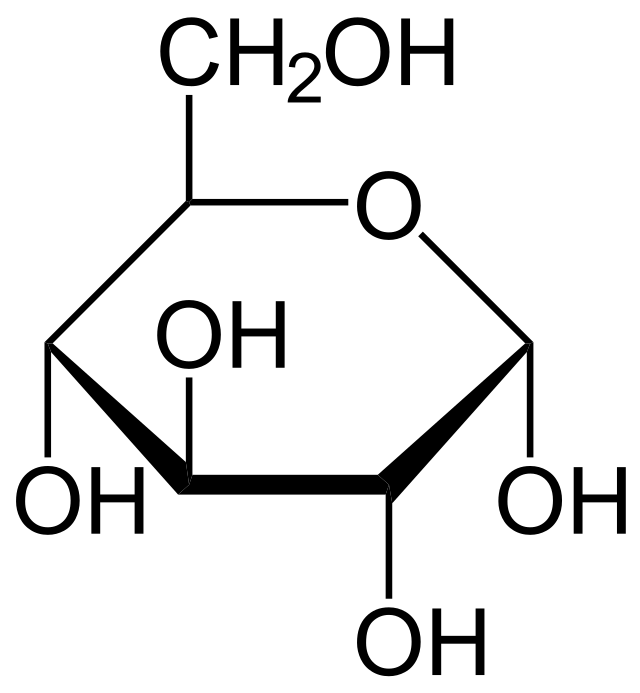
What type of glucose molecule is this
Alpha glucose
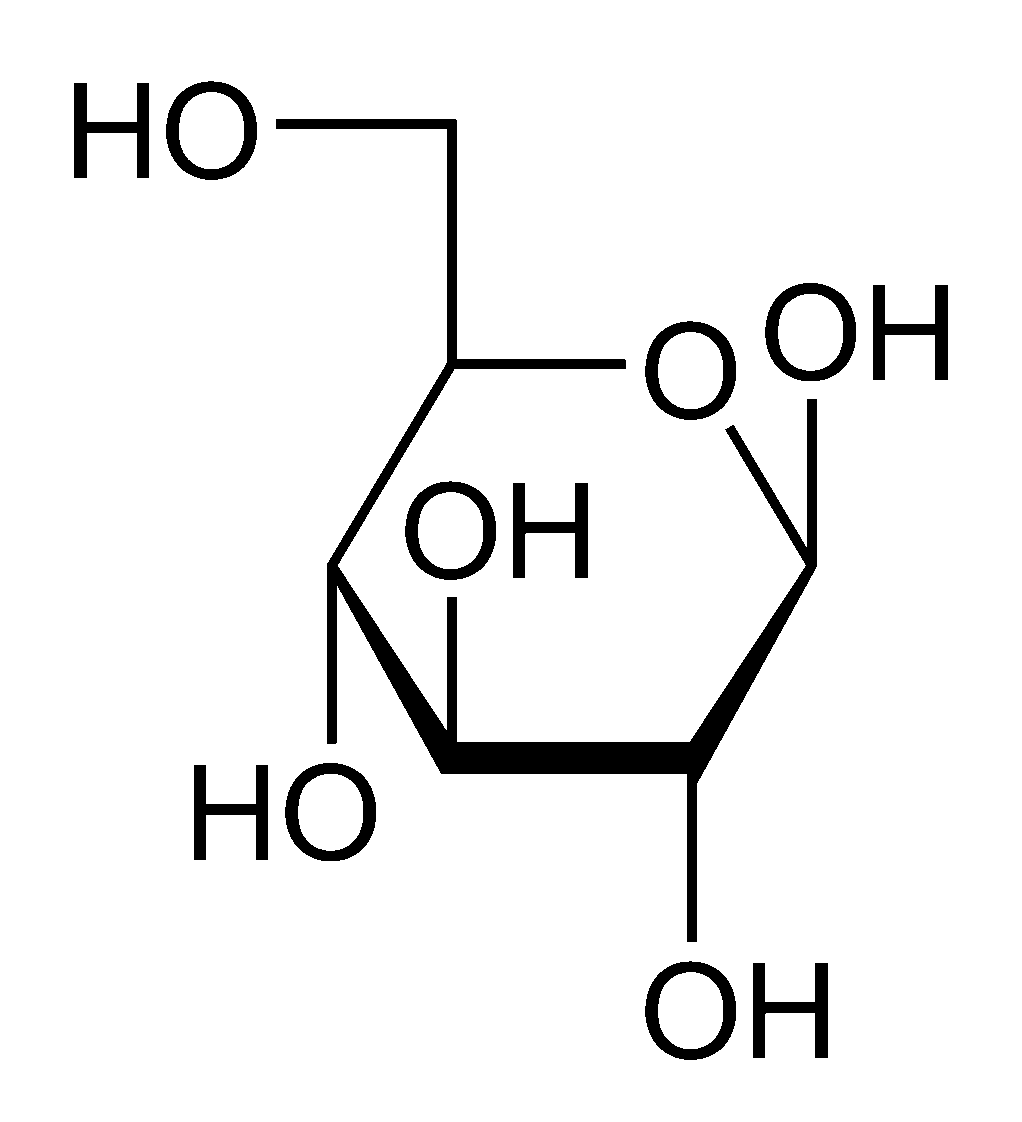
What type of glucose molecule is this
Beta Glucose
How is maltose formed
through the condensation reaction between two glucose molecules
How is sucrose formed
Through the condensation reaction between a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule
How is lactose formed
Through a condensation reaction between glucose and galactose
what do fatty acids contain
A carboxyl group
Hydrocarbon chain represented by R
What is Glycerol made up of
3 carbons
An alcohol group attached to each carbon
what is Photo Phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP from ADP within Chlorophyll organelles during photosynthesis
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP from ADP within Plant and animal cells during respiration
What is Substrate-level phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP from ADP through the transfer of Phosphate groups from donor Molecules
What does ATP stand for
Adenosine Triphosphate
What does ATP contain
Ribose
Adenine
Phosphate groups
what is the role of DNA Polymerase within DNA replication
Reforms Phosphodiester bonds between nucleotide molecules after the complementary bases have been bound together
What is the role of DNA helicase within DNA replication
Breaks down the hydrogen bonds present between complementary bases
Why is ATP used as a short term source of energy
It is not able to be stored unlike other energy sources such as carbohydrates and fats (lipids)
How does ATP release energy
through the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP
in what ways is ATP used
metabolic processes
movement
active transport
secretion
Activation of molecules
Which Polysaccharides are branched
Amylopectin and Glycogen
Which Polysaccharides are unbranched
Amylose and Cellulose
What is the order (colours) for concentration of sugars in the Benedict’s test
Blue, green, yellow, orange, Brick red
Which sugars are reducing sugars
Monosaccharides and some disaccharides
What is added and then heated with Benedict’s solution to test for non reducing sugars
Dilute hydrogencarbonate