Anatomy and Physiology Integumentary System
1/365
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
366 Terms
List the five parts of the integumentary system
skin
hair
oil and sweat glands
nails
sensory receptors
What are the six functions of the
integumentary systems
regulated body temperature
stores blood
protects body from external environment
detects cutaneous sensations
excretes and absorbs substances
synthesizes vitamin D
medical specialty that deals with the
diagnosis and treatment of
integumentary system disorders
dermatology
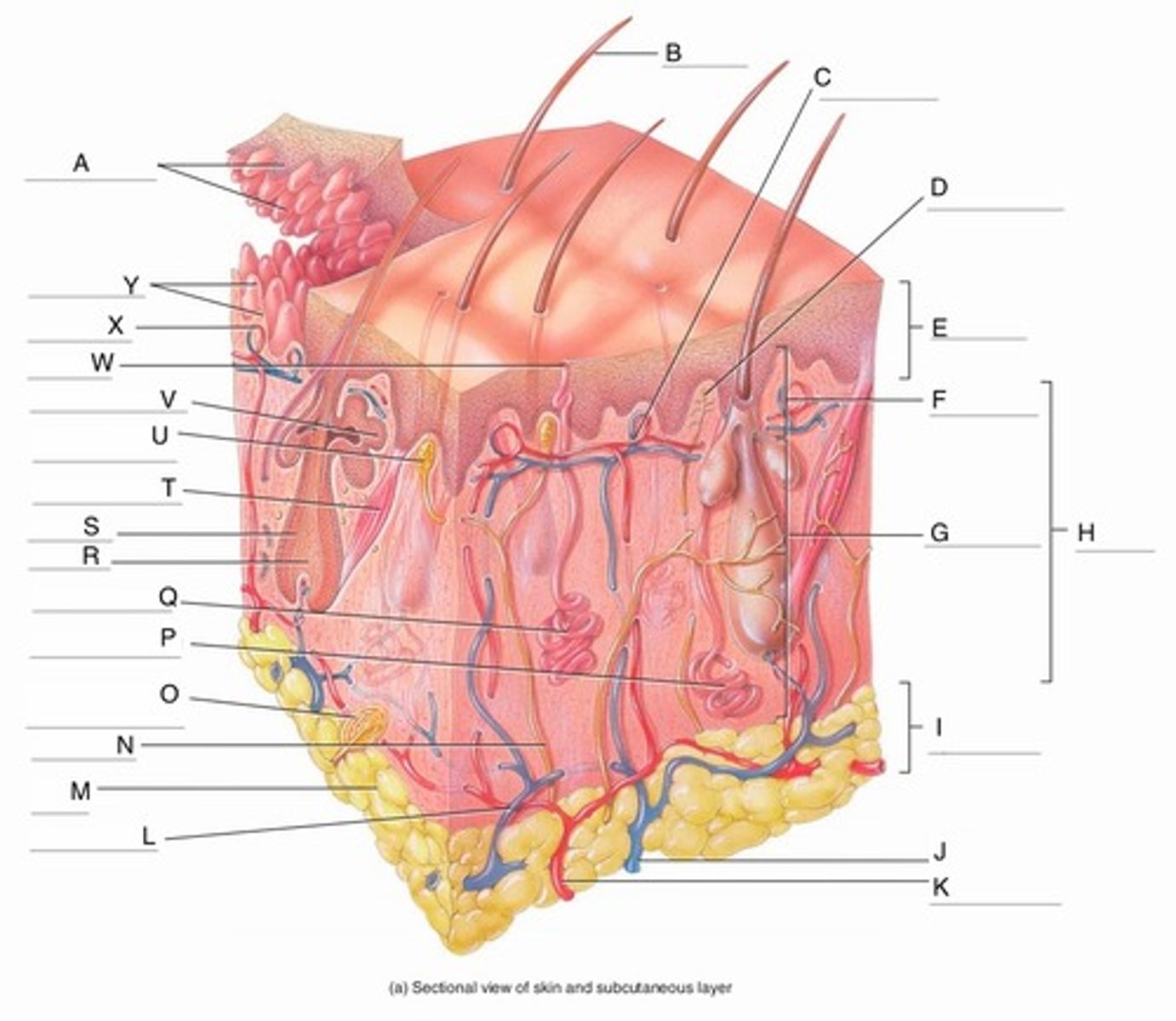
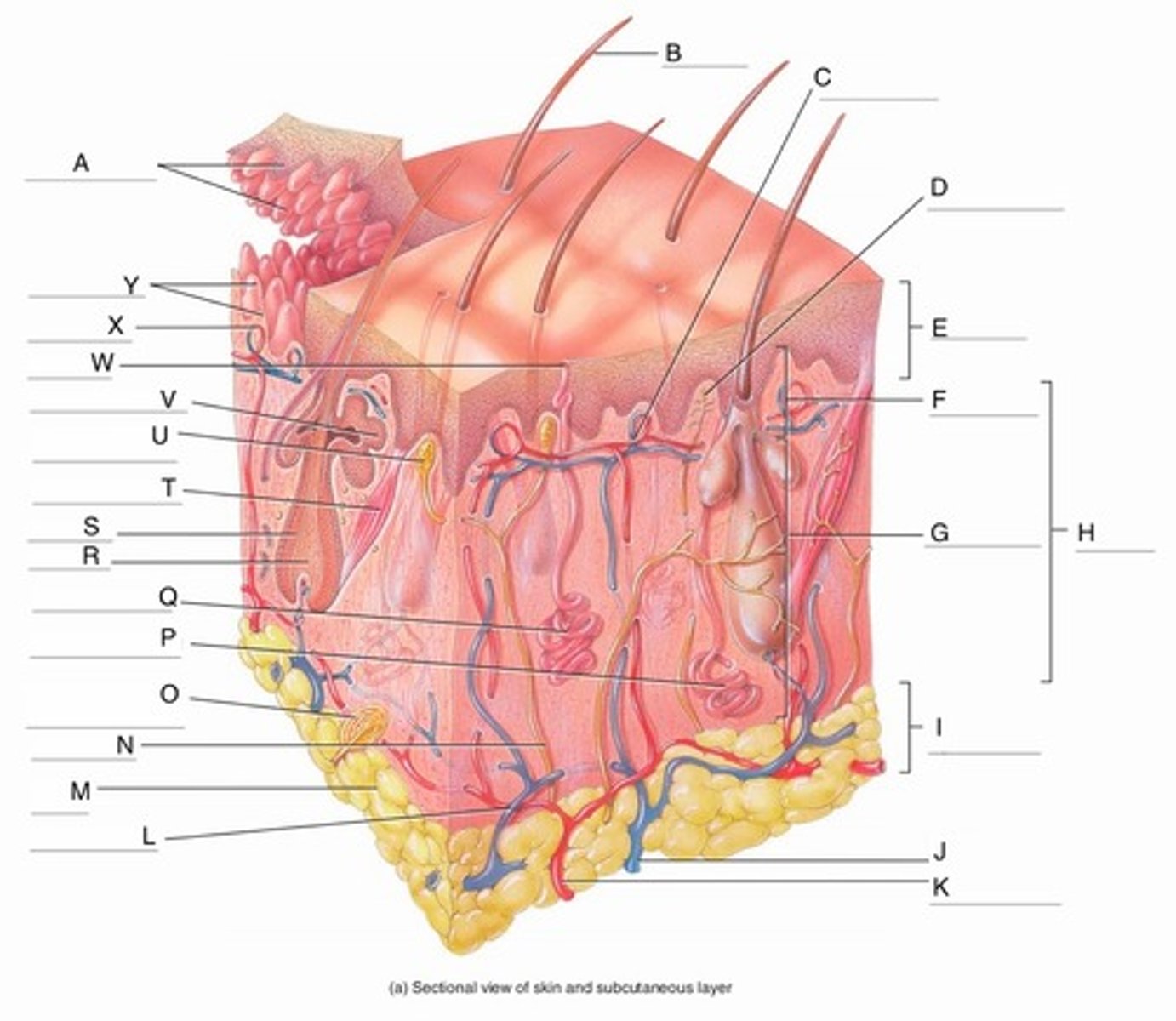
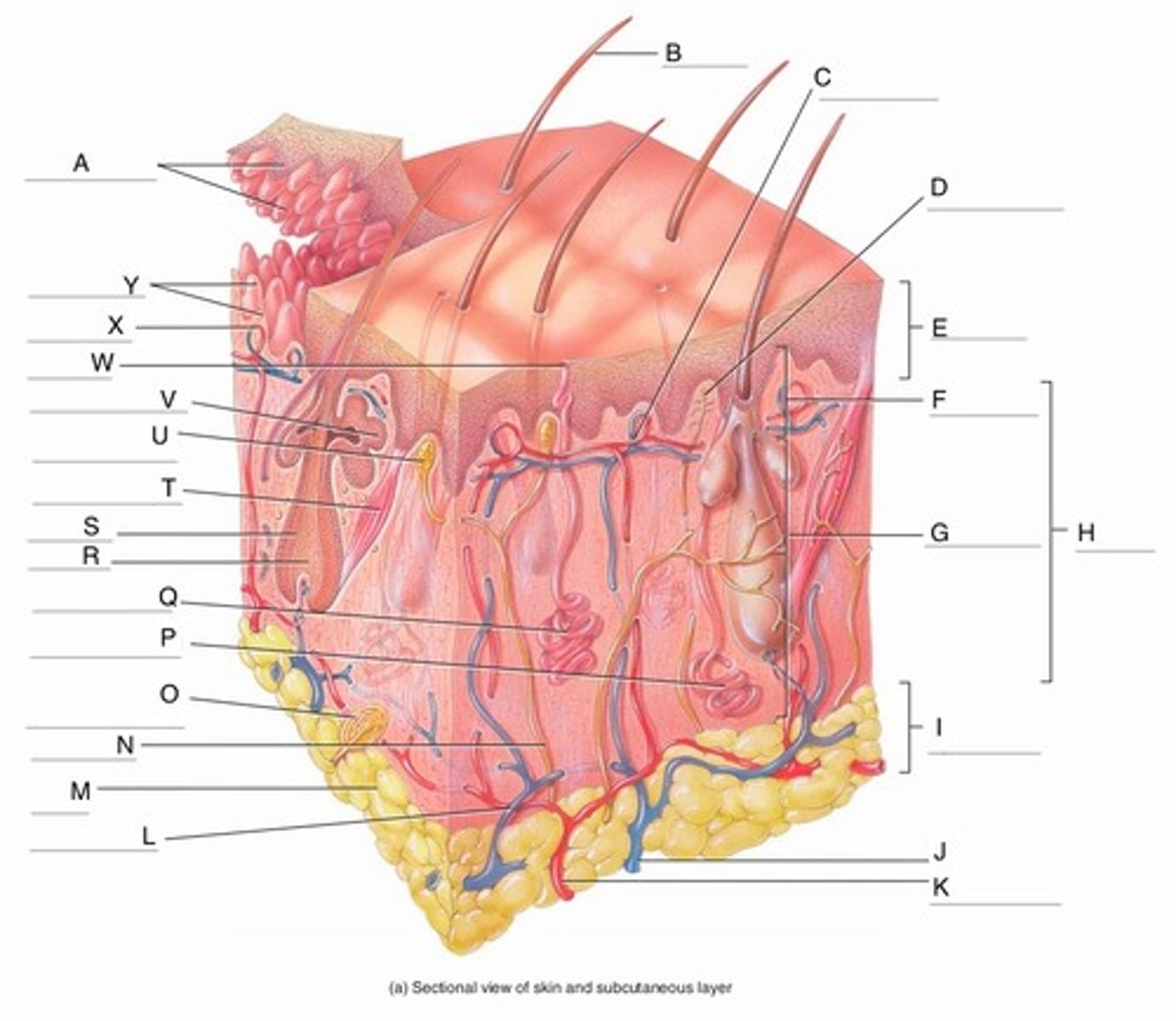
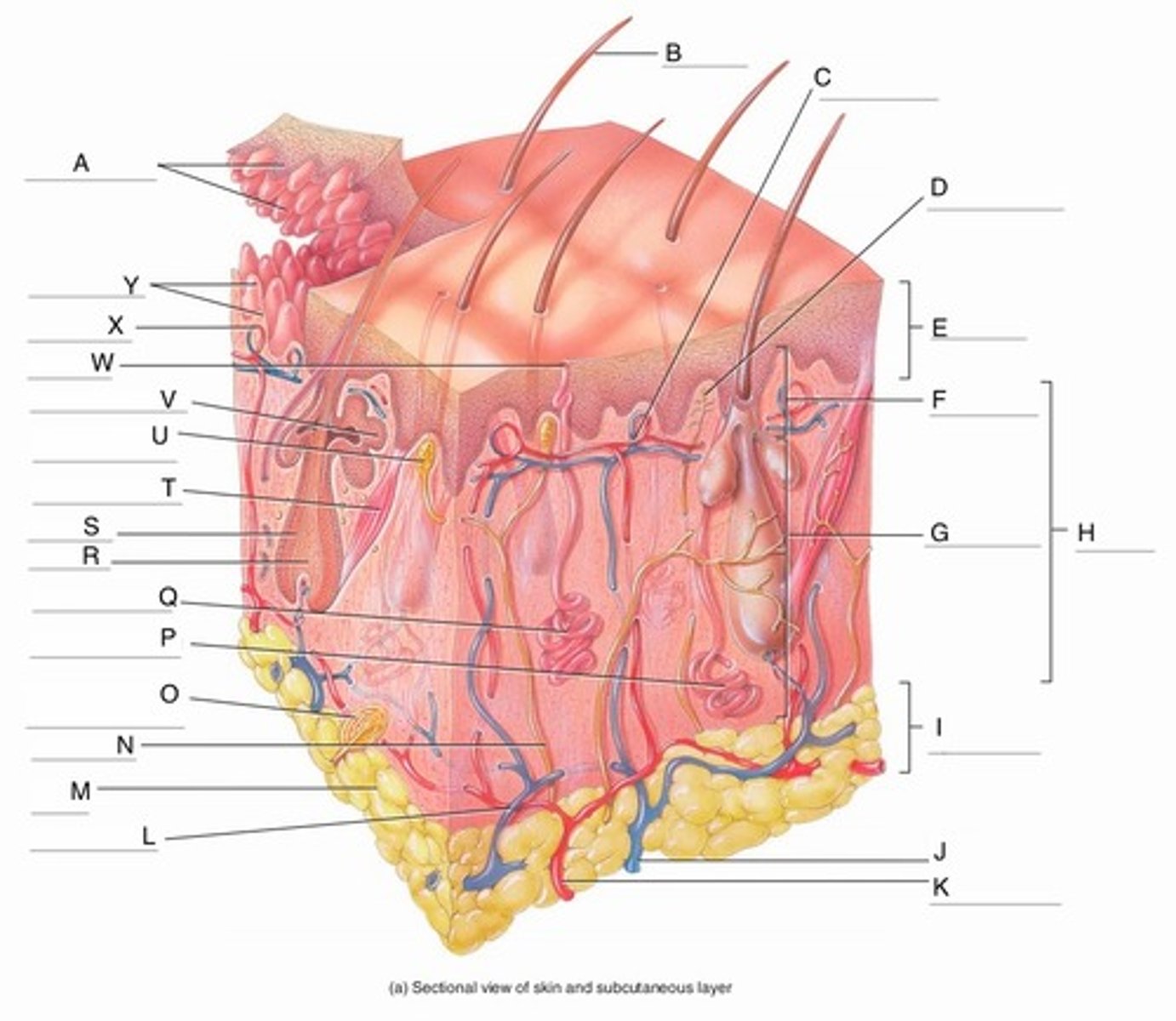
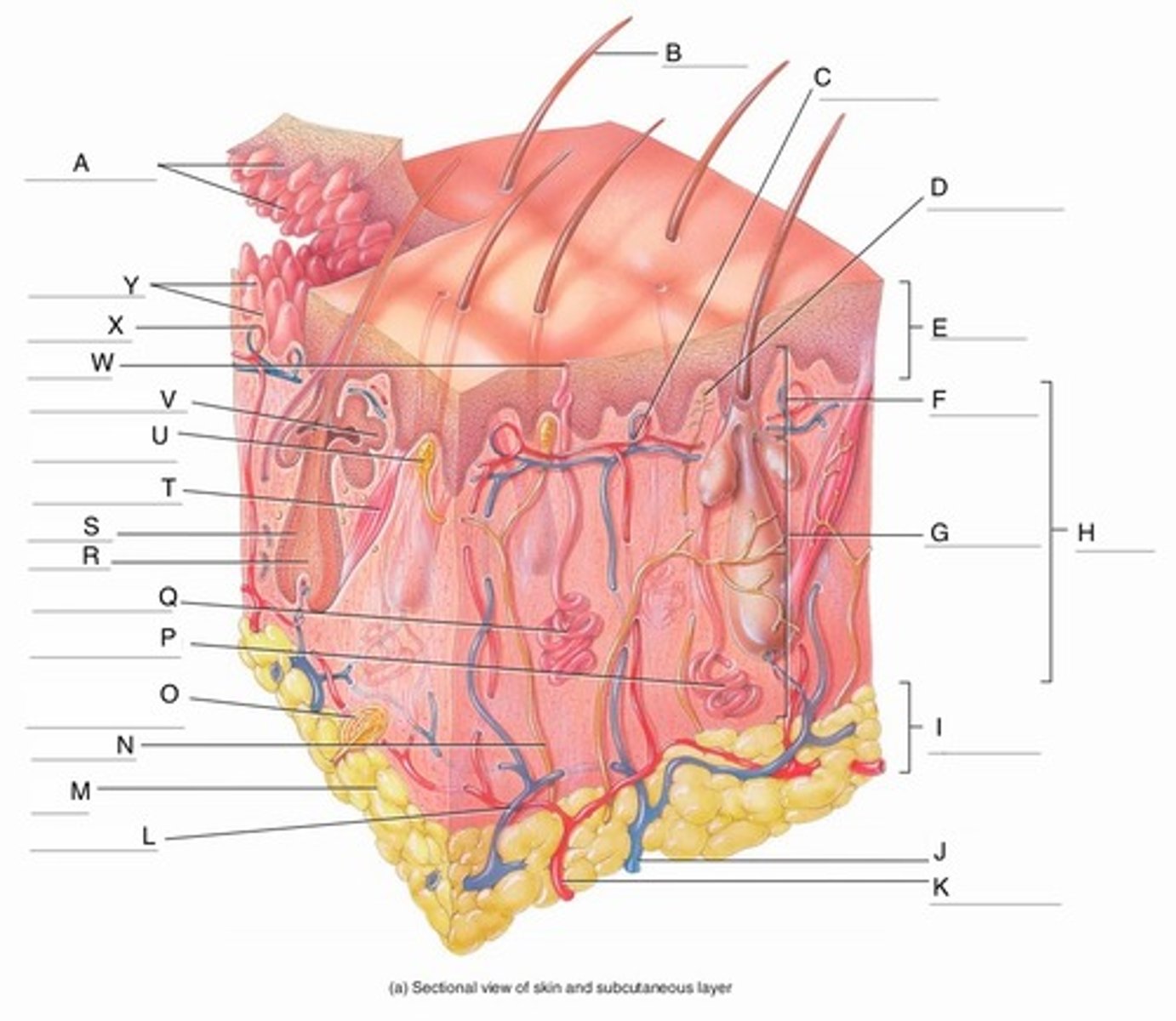
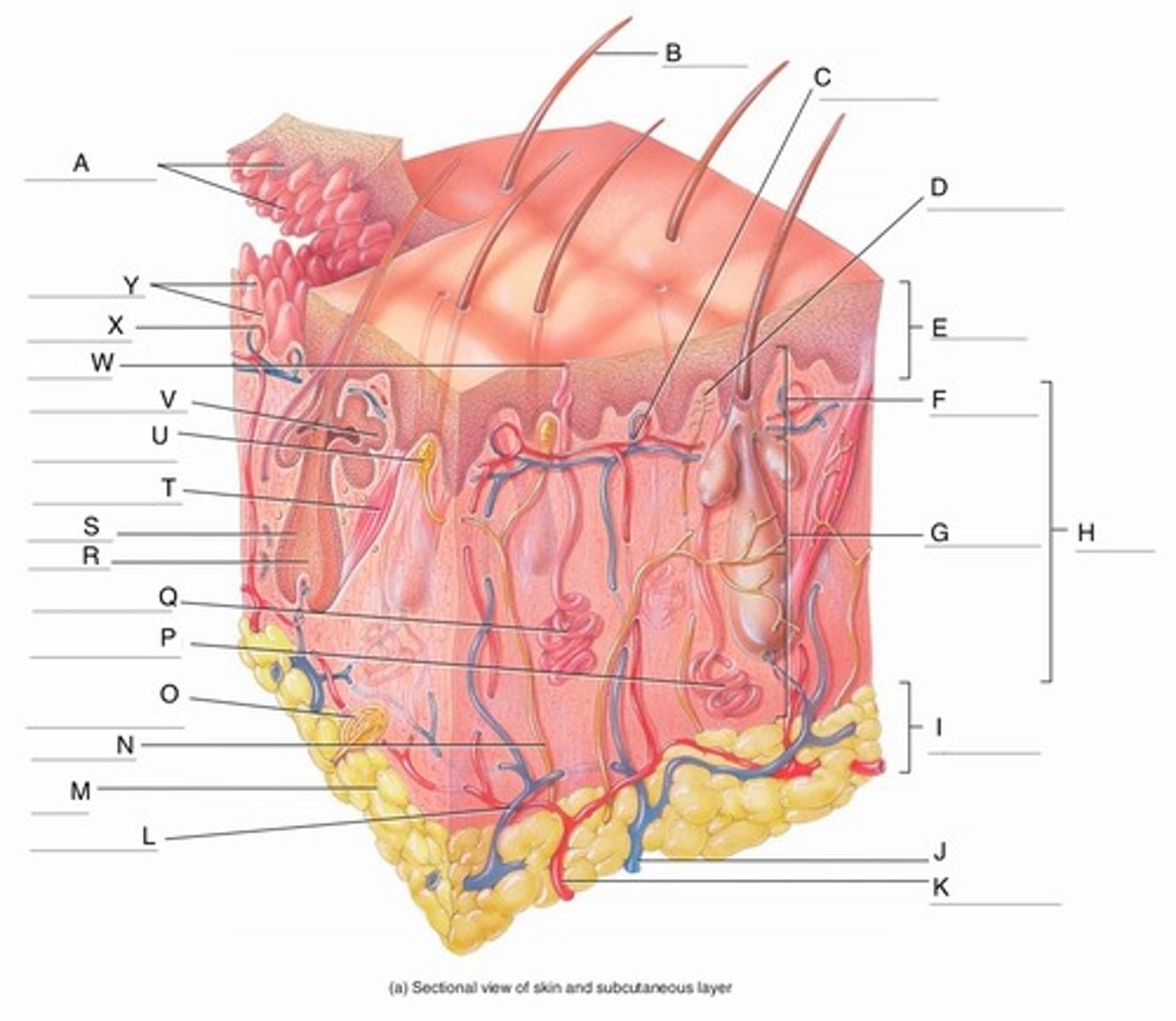
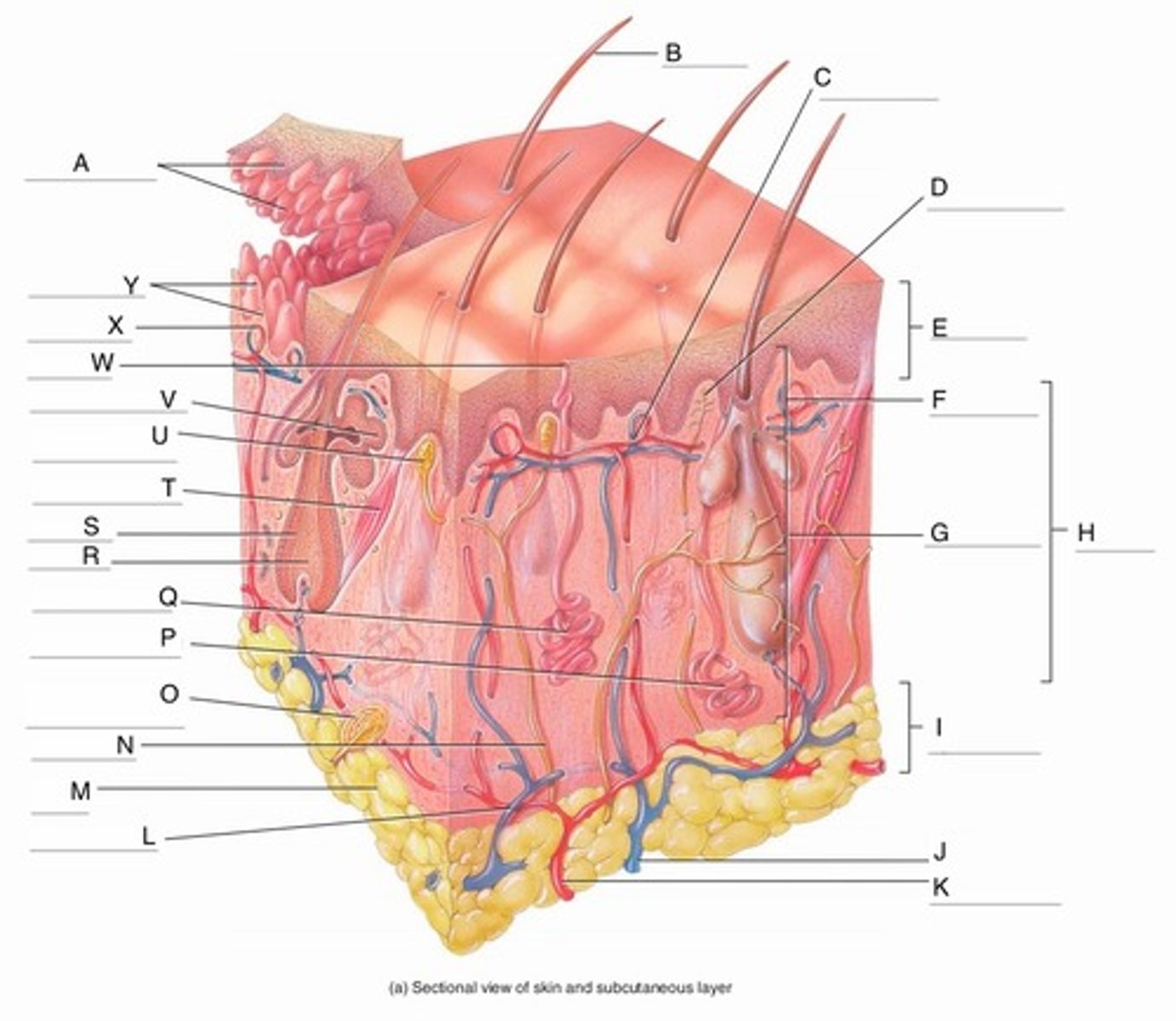
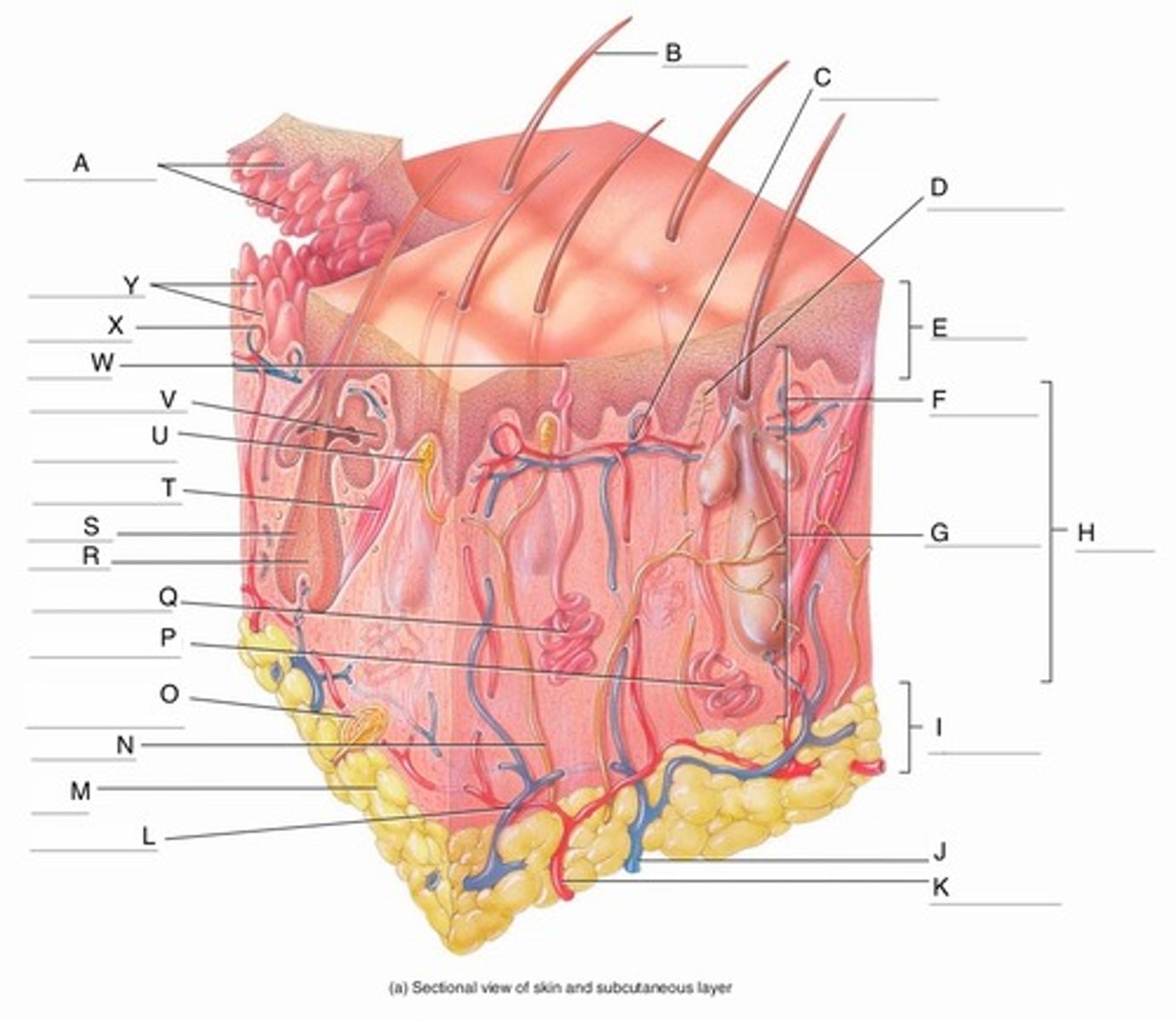
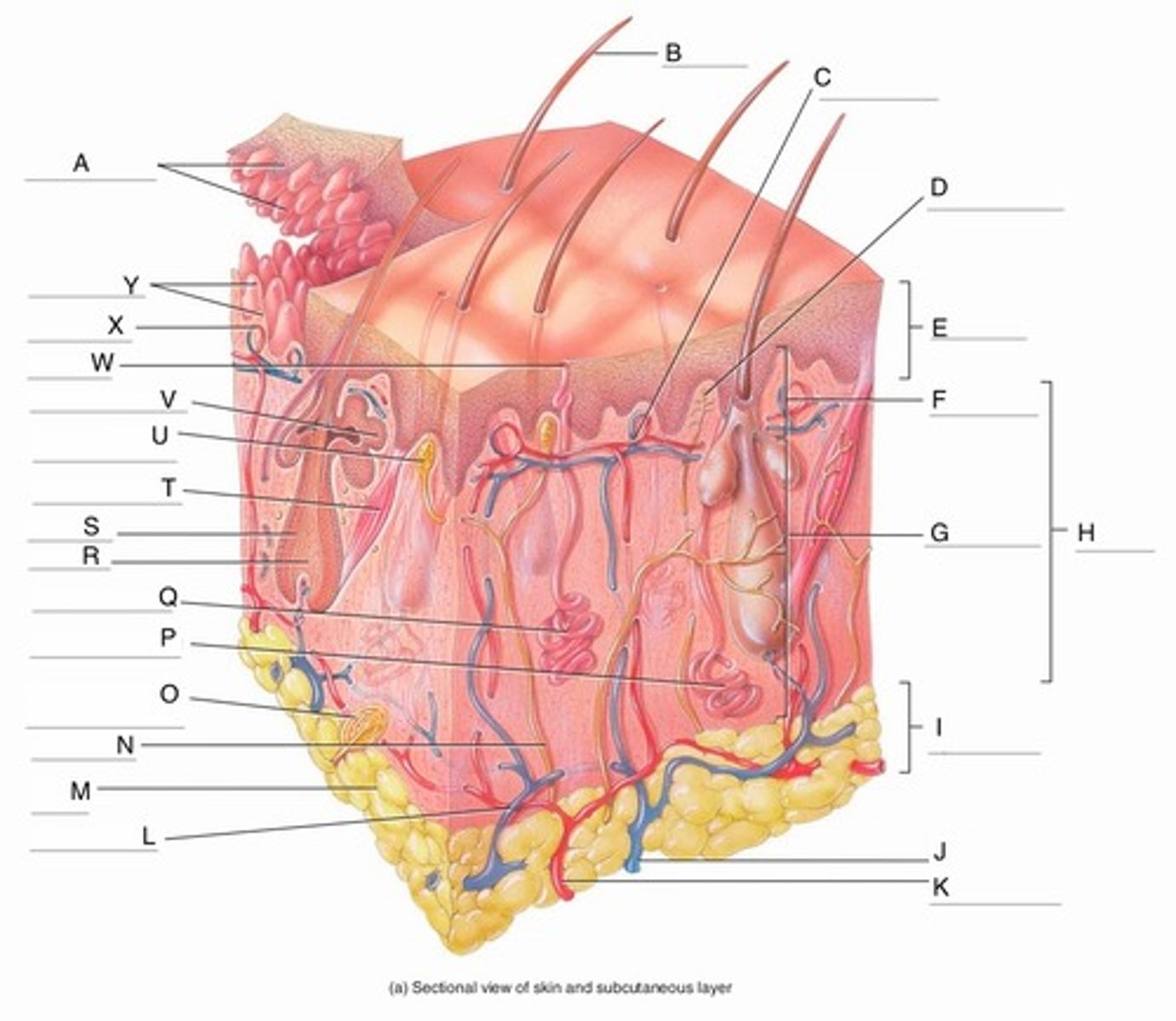
A
Epidermal Ridges
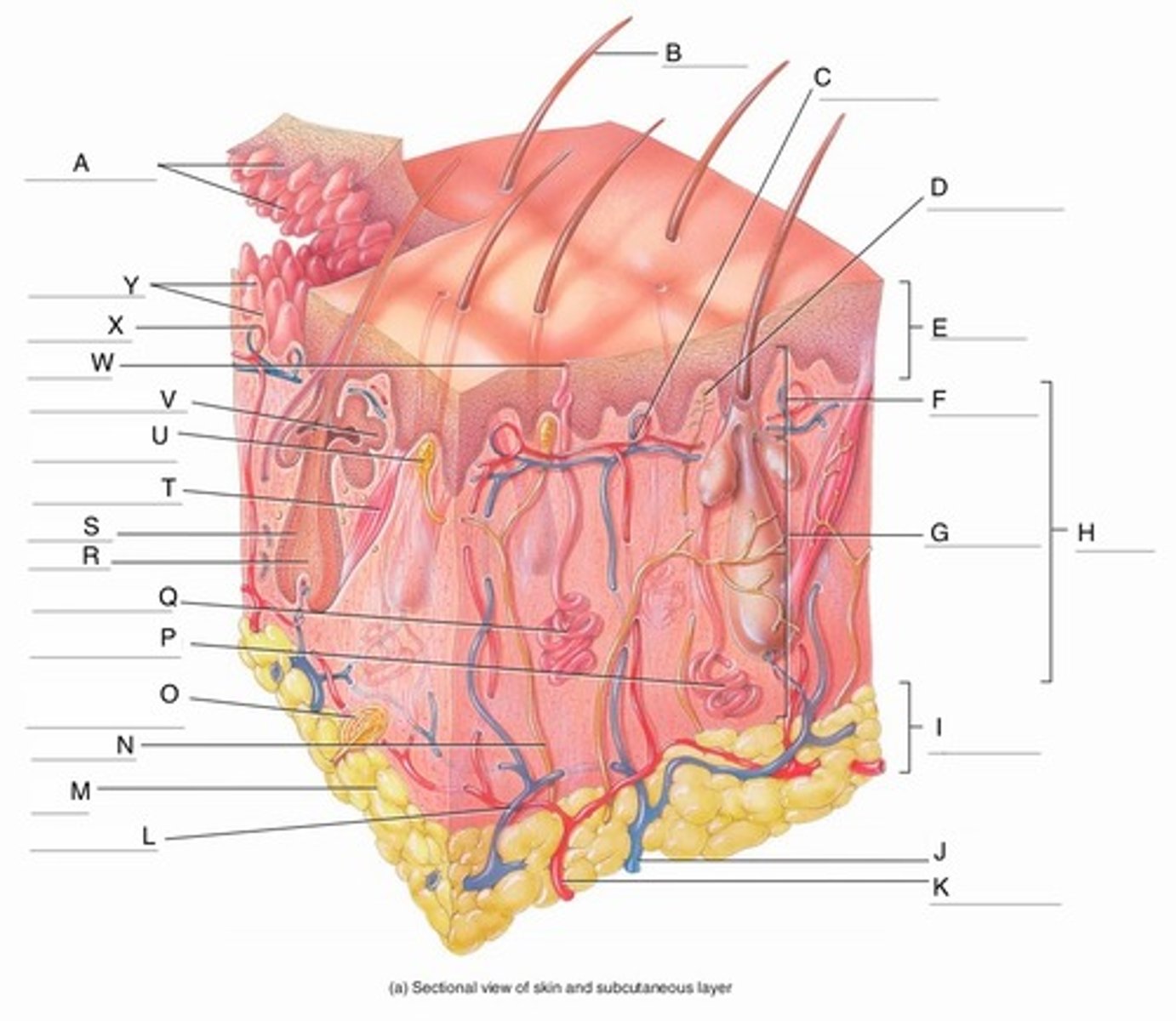
B
Hair shaft
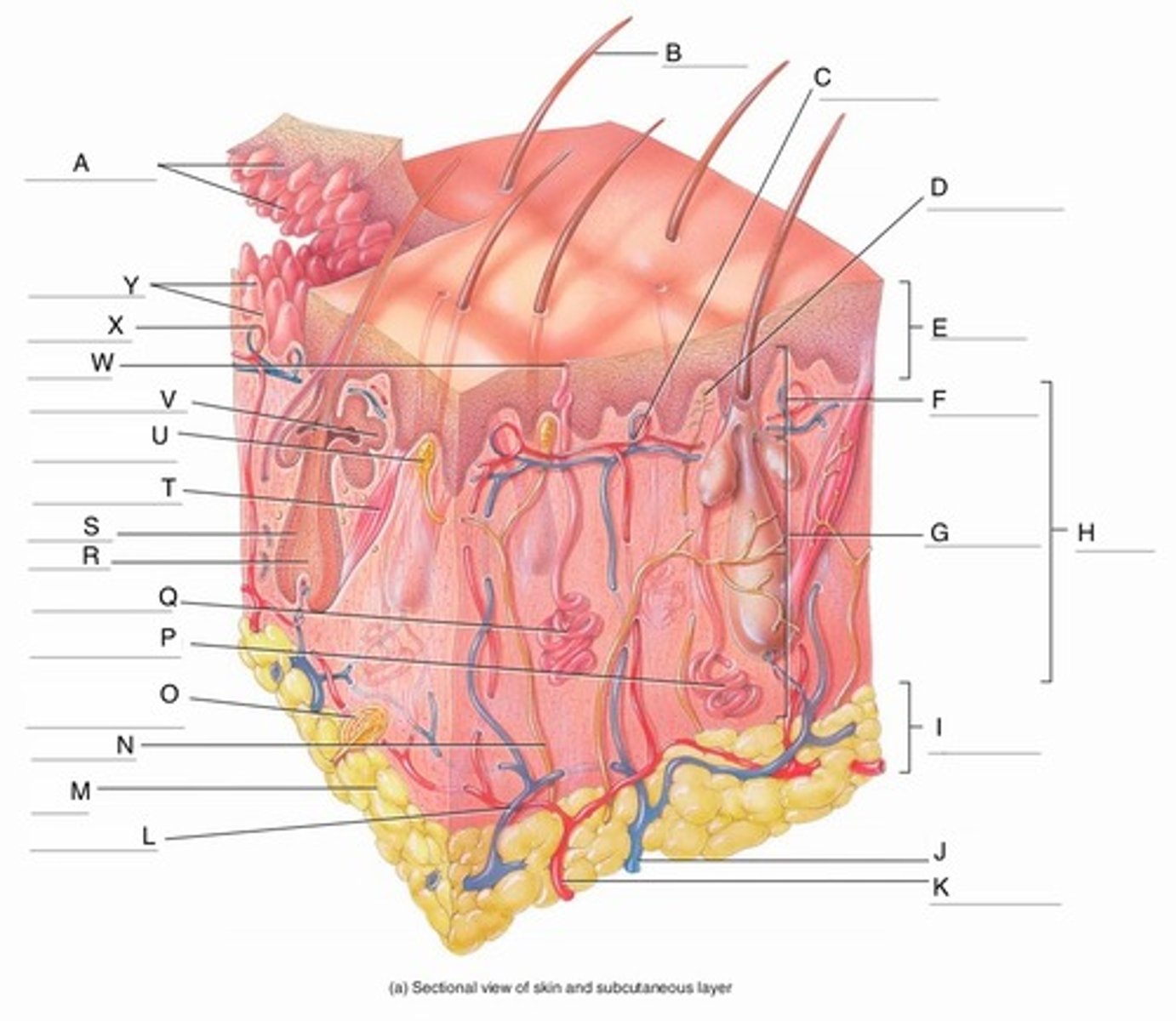
C
Papillary Plexus
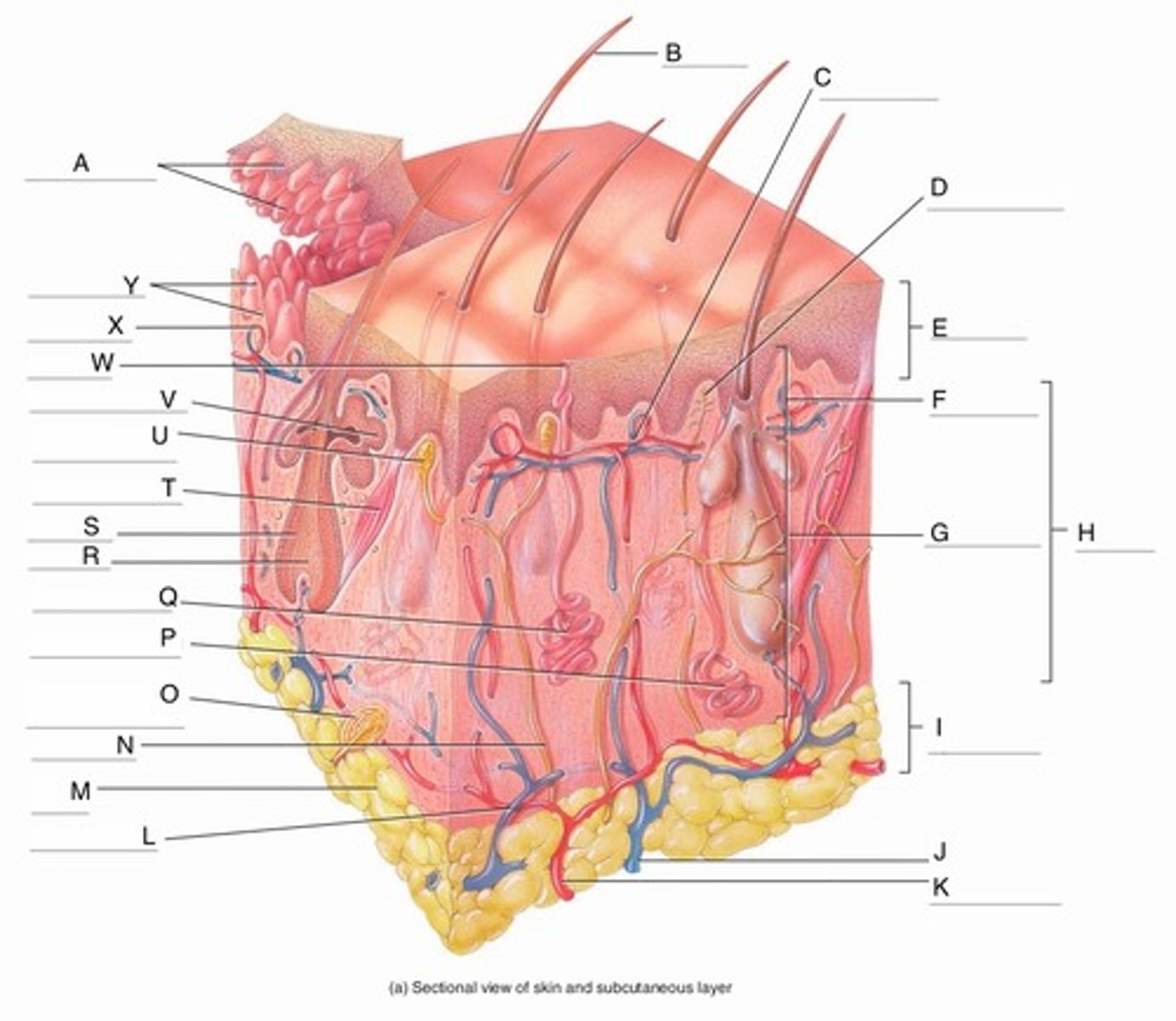
D
Free Nerve Ending
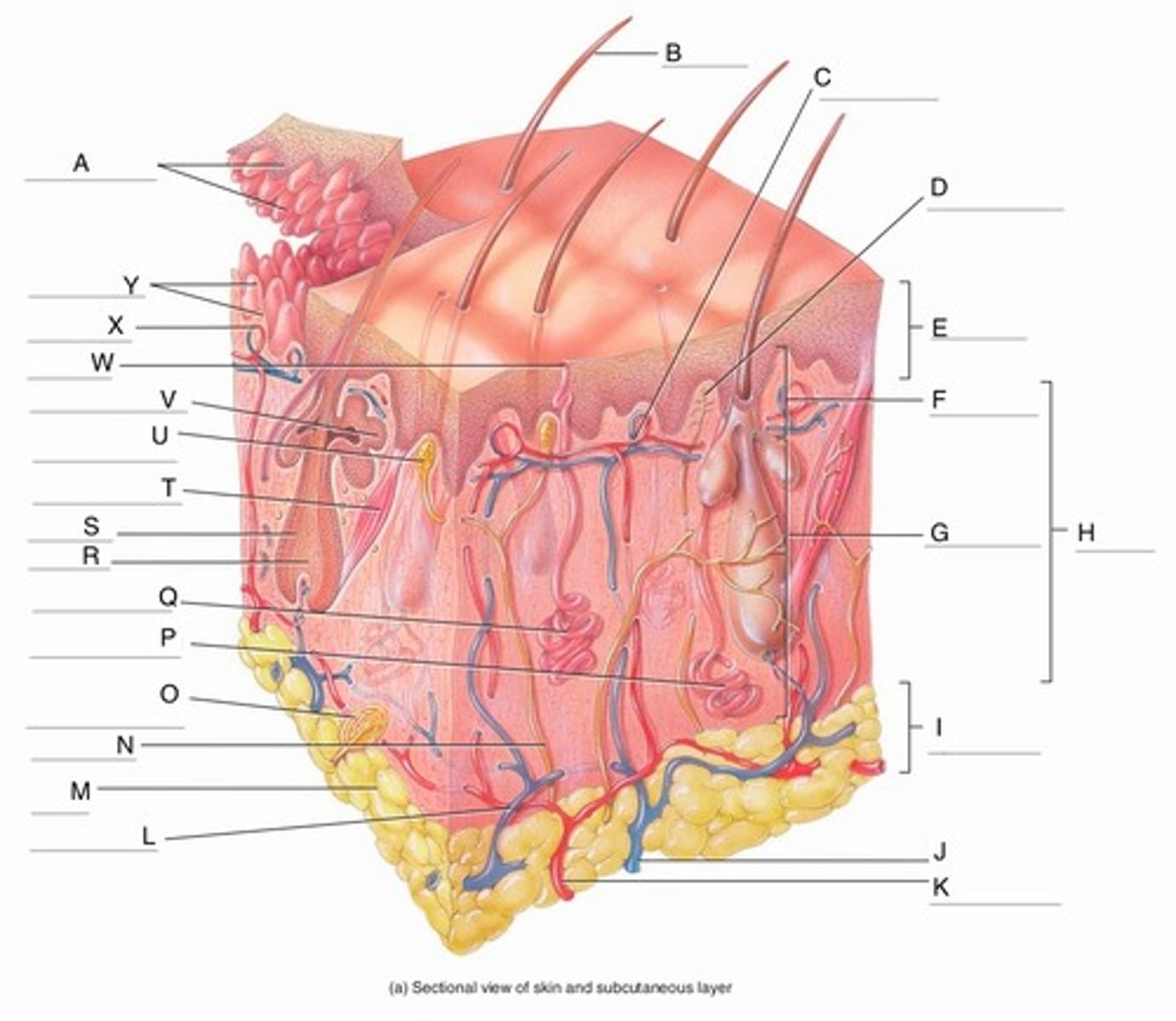
E
Epidermis
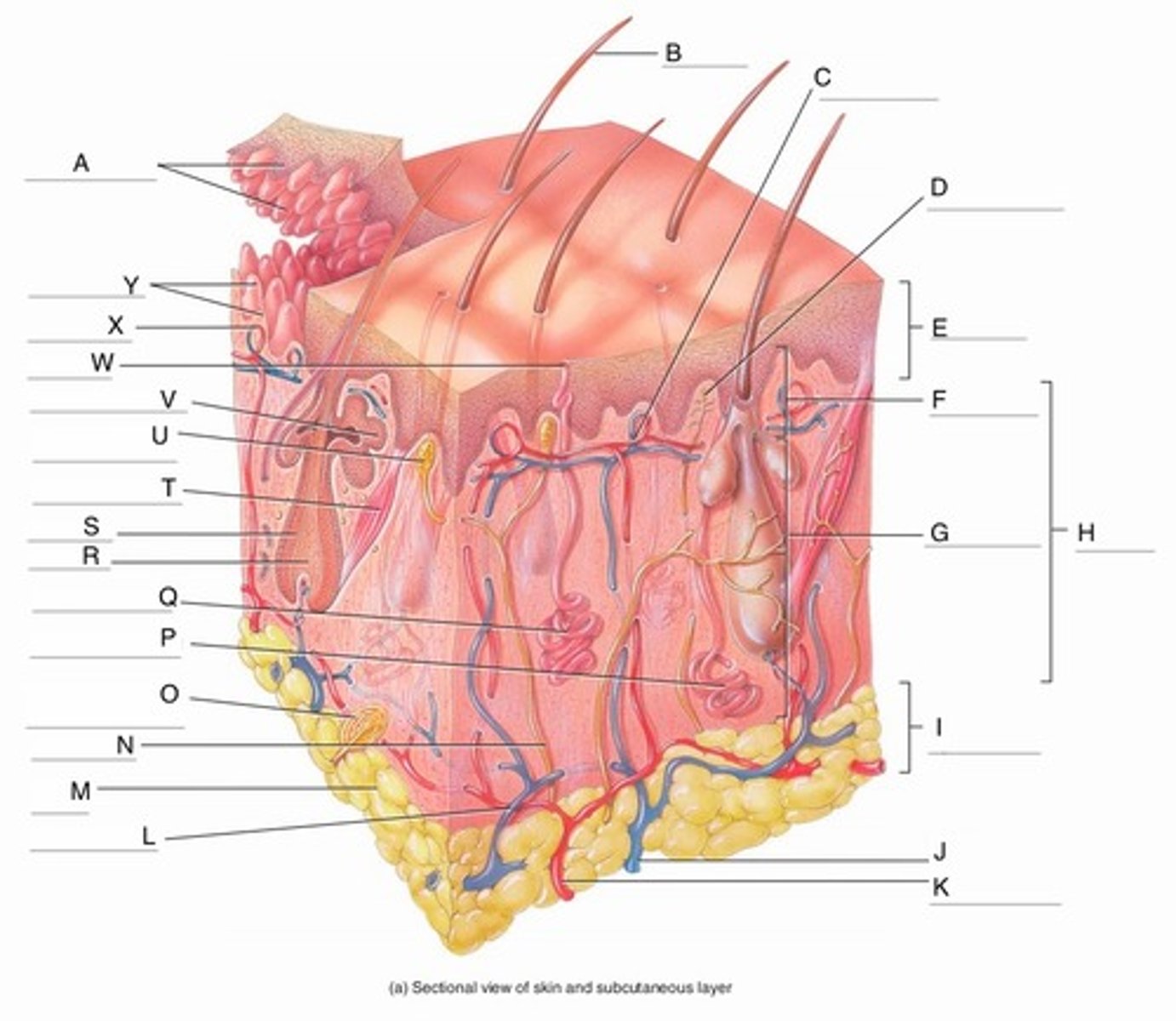
F
Papillary Region
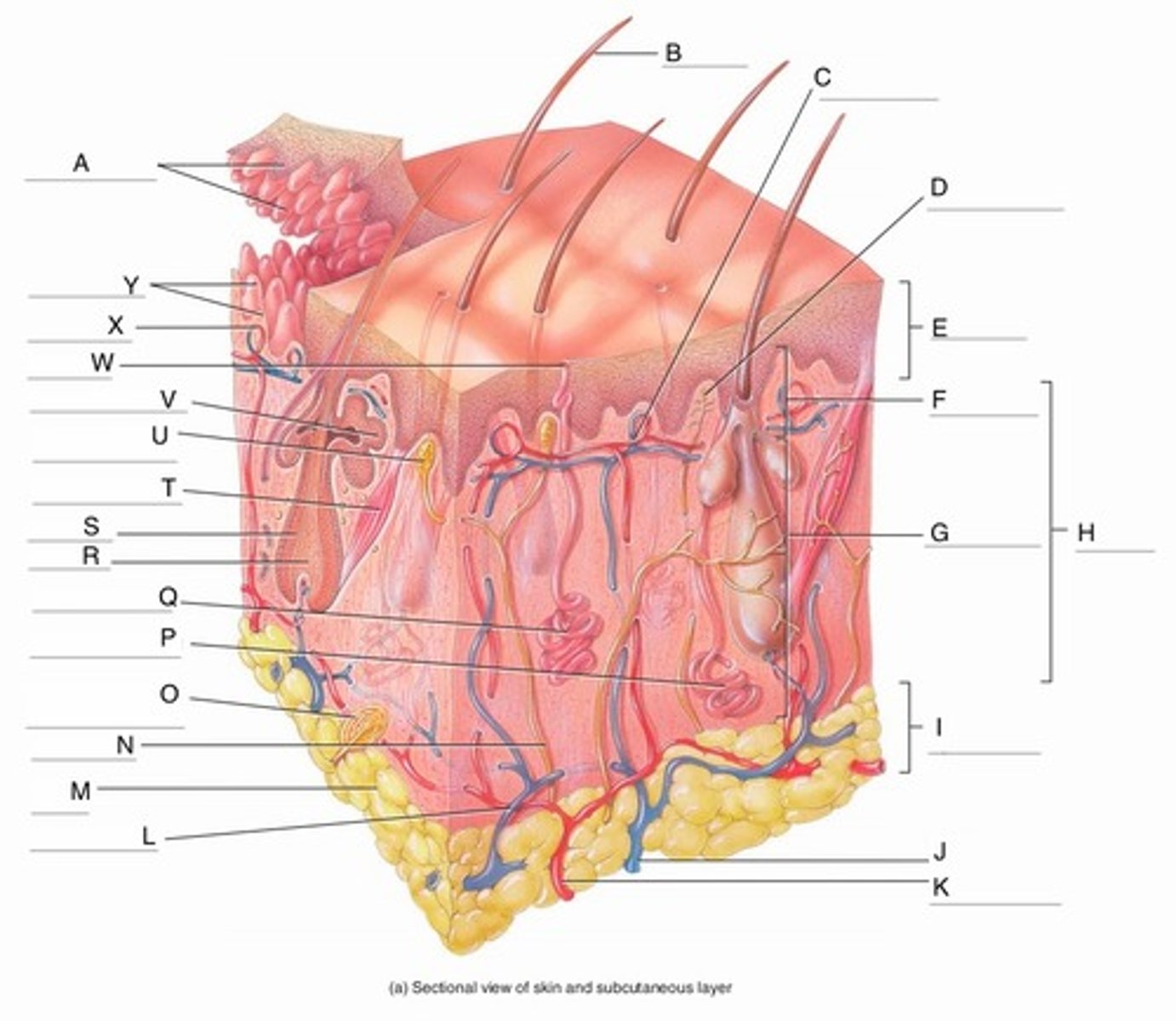
G
Reticular Region
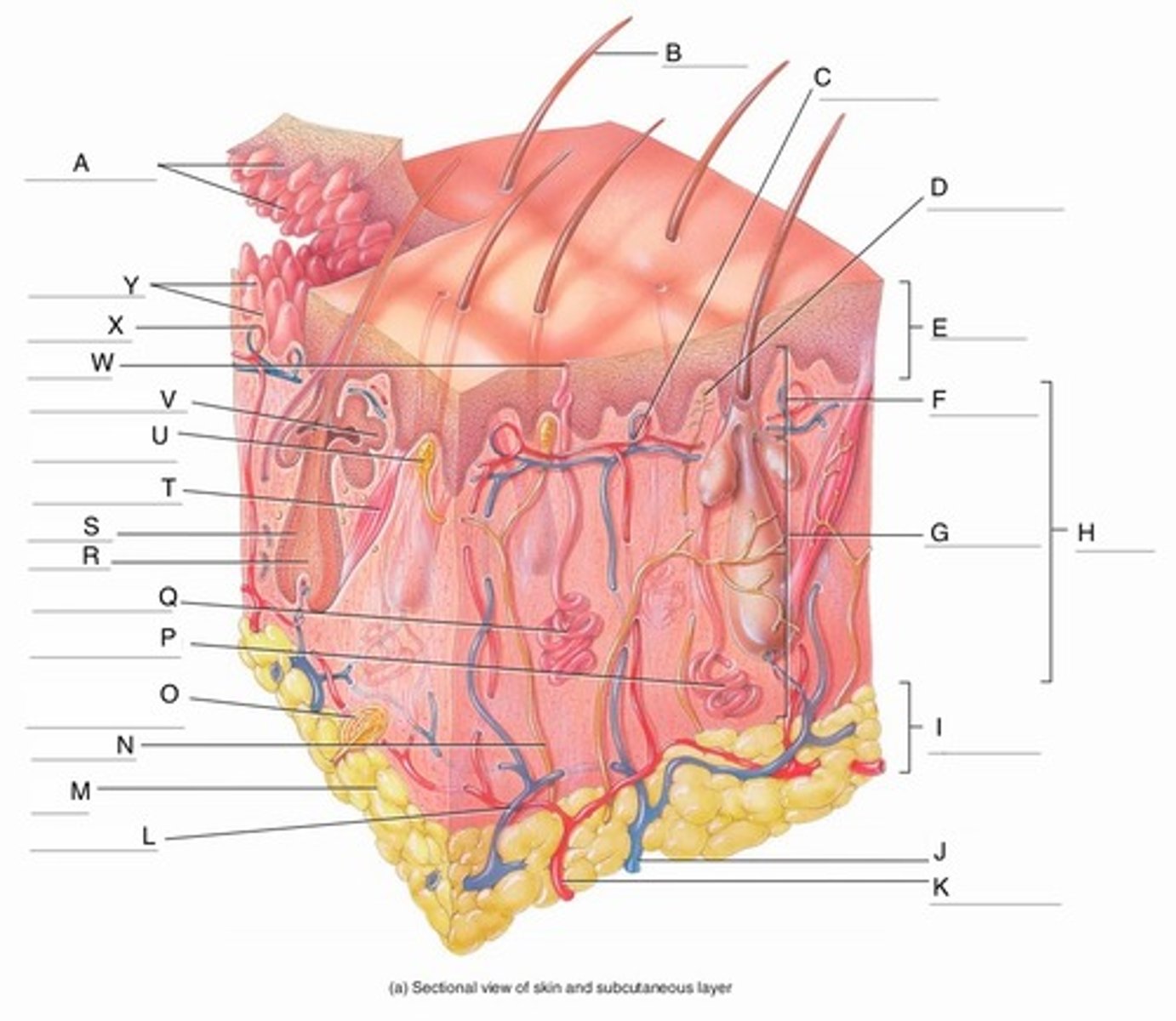
H
Dermis
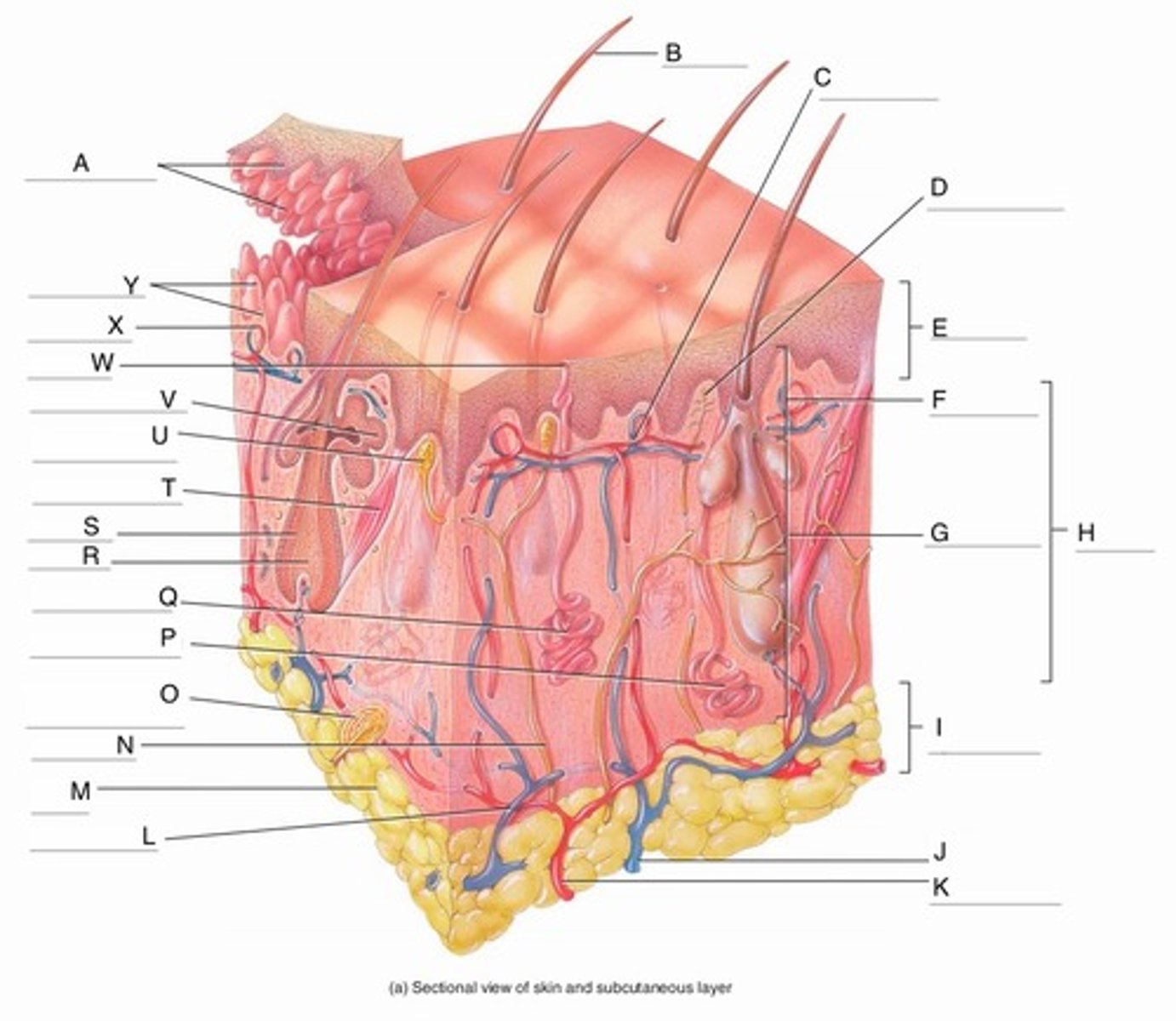
I
Subcutaneous layer
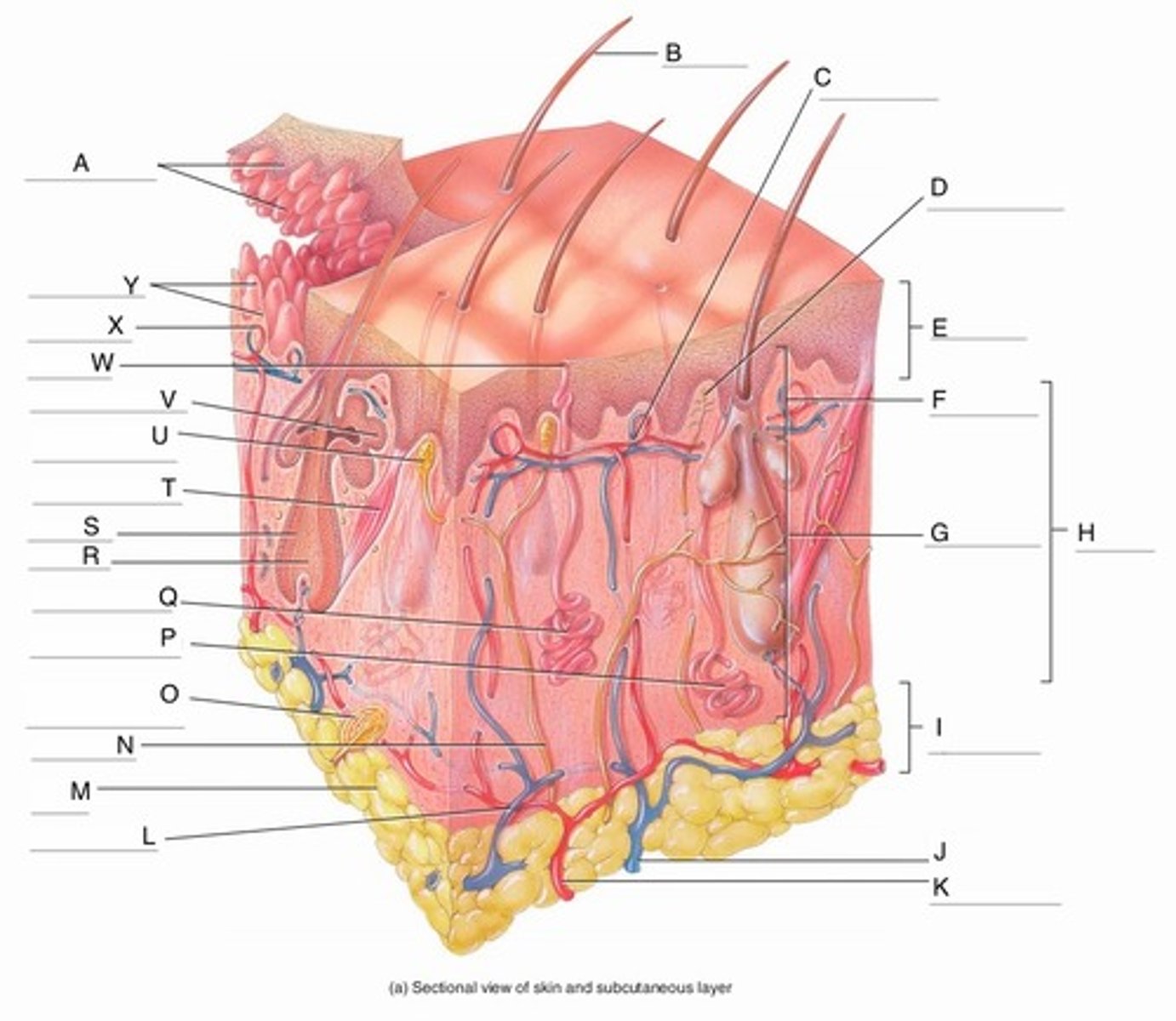
J
Vein
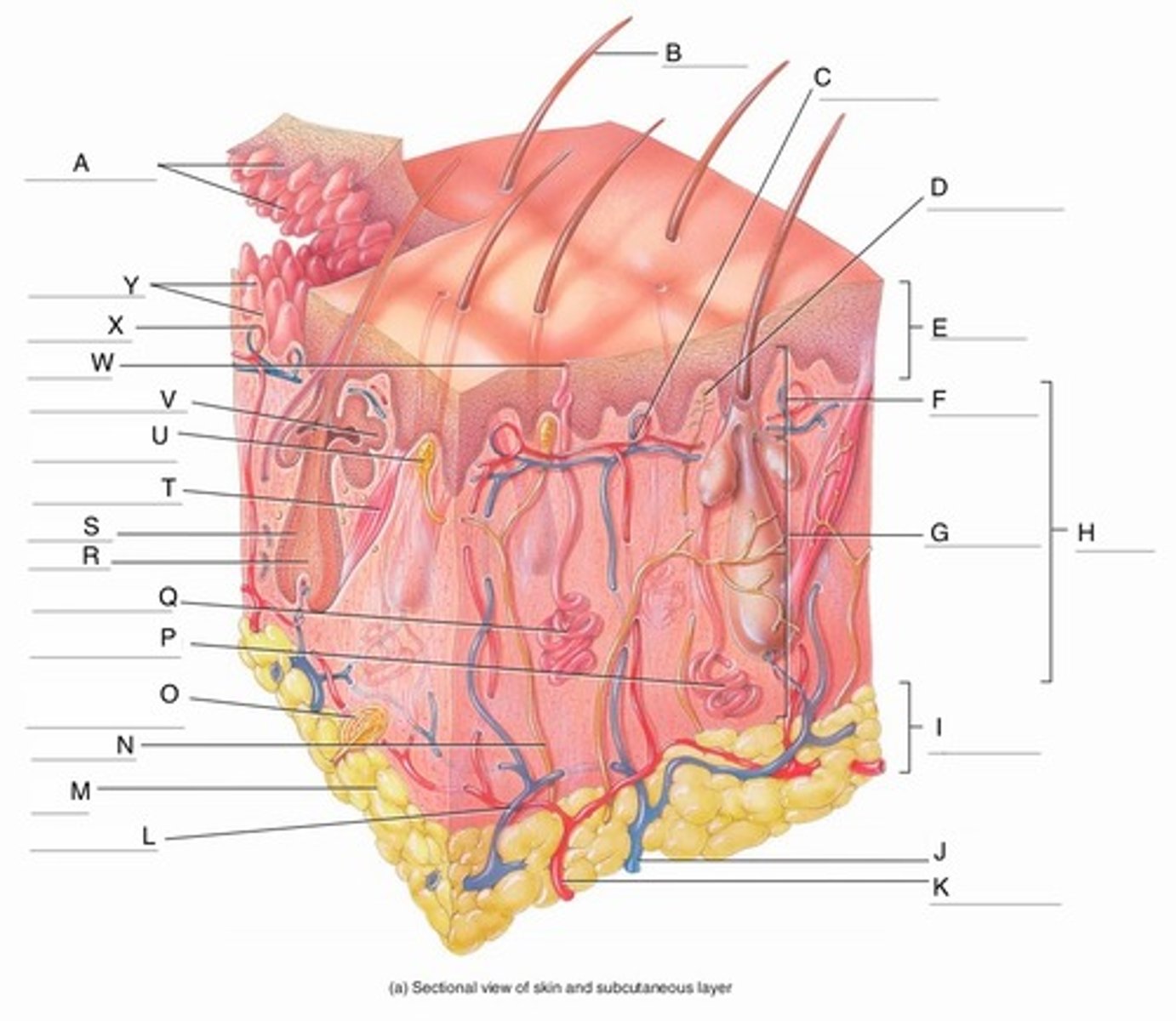
K
Artery
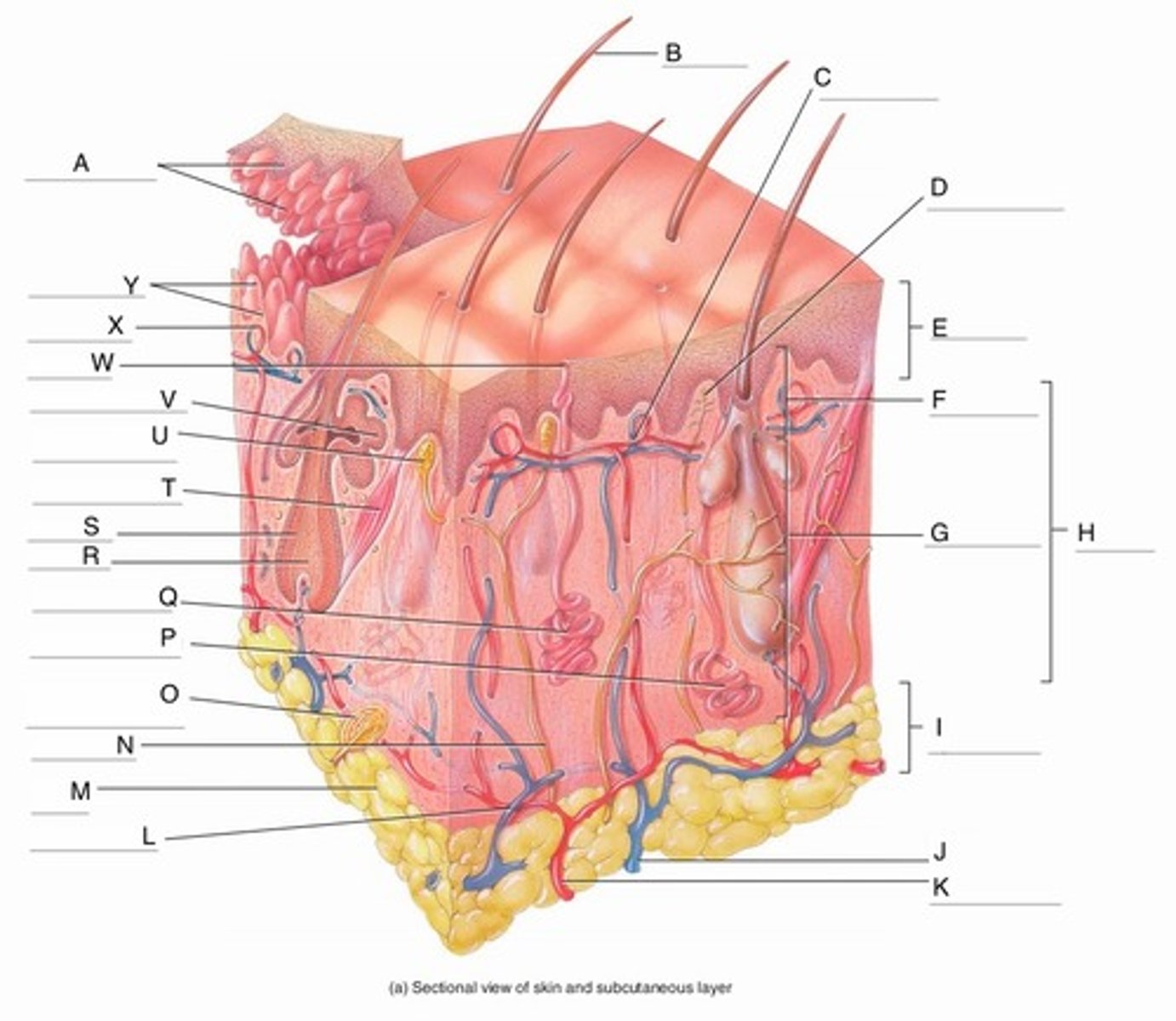
L
Cutaneous plexus
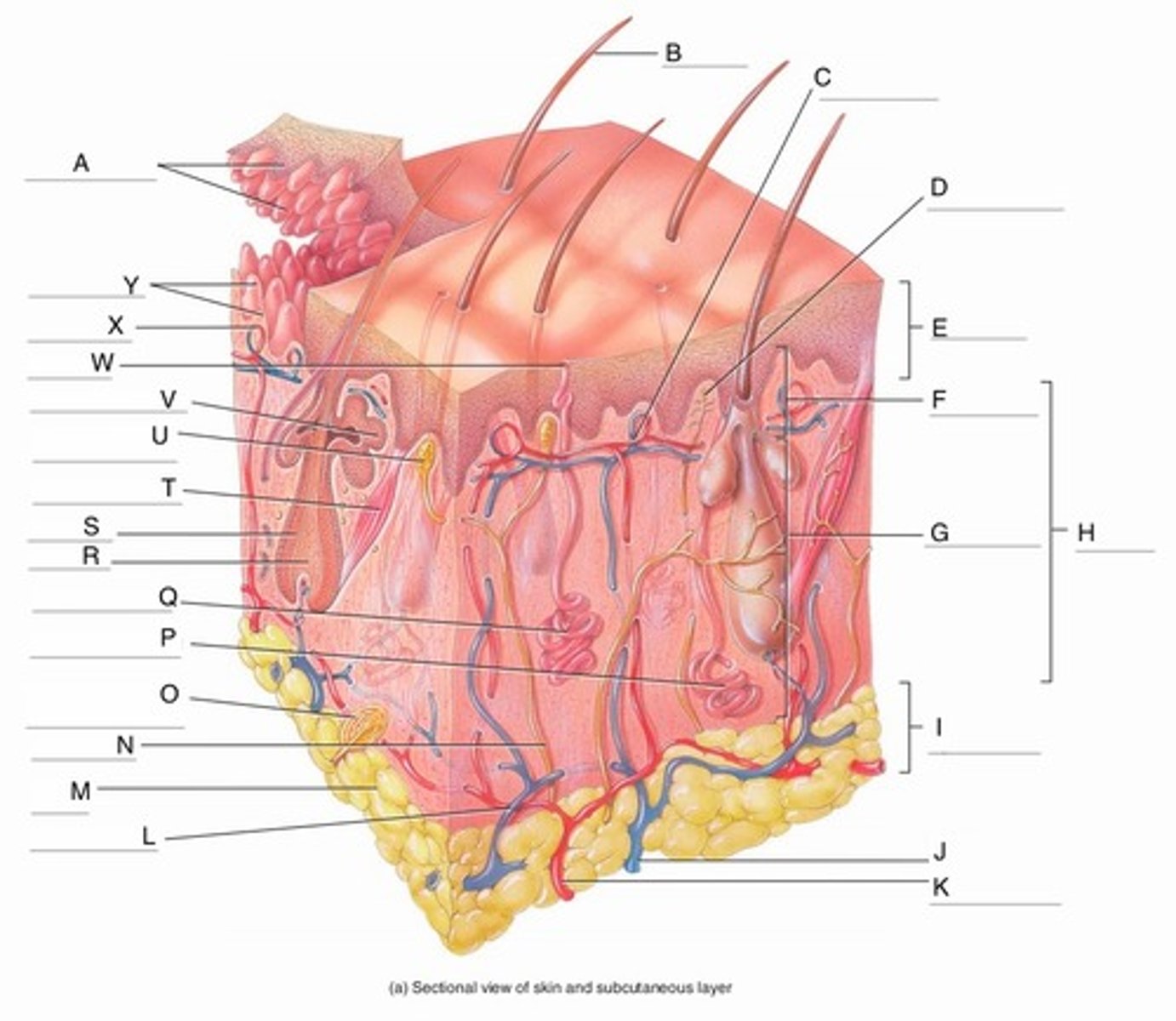
M
Adipose Tissue
N
Sensory Nerve
O
Pacinian Corpuscle
(Lamellated Corpuscle)
P
Apocrine Sweat Gland
Q
Eccrine Sweat Gland
R
Hair Root
S
Hair Follicle
T
Arrector Pili Muscle
U
Meissner Corpuscle
(Corpuscle of Touch)
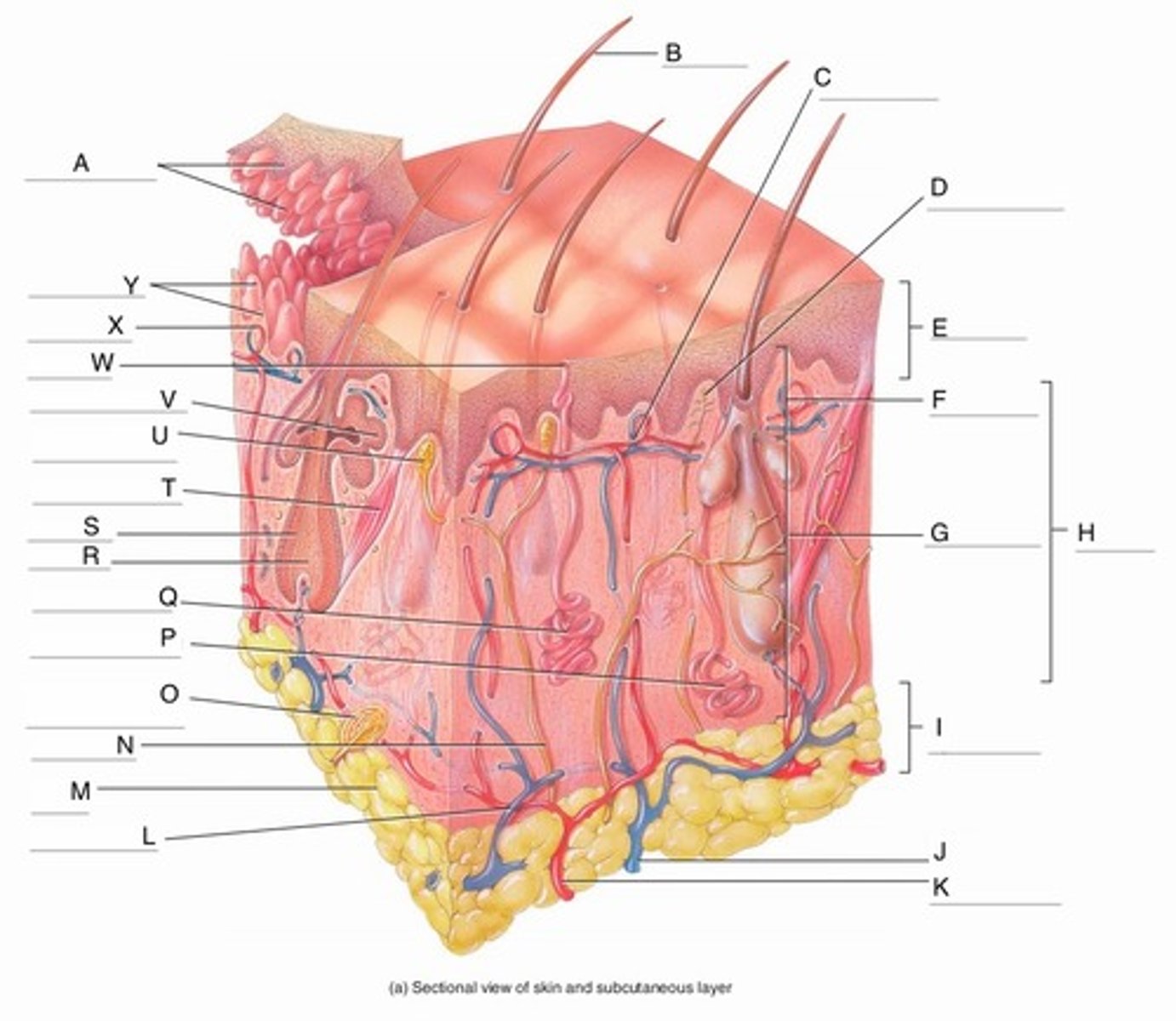
V
Sebaceous Gland
(oil gland)
W
Sweat Pore
X
Capillary Loop
Meissner corpuscle
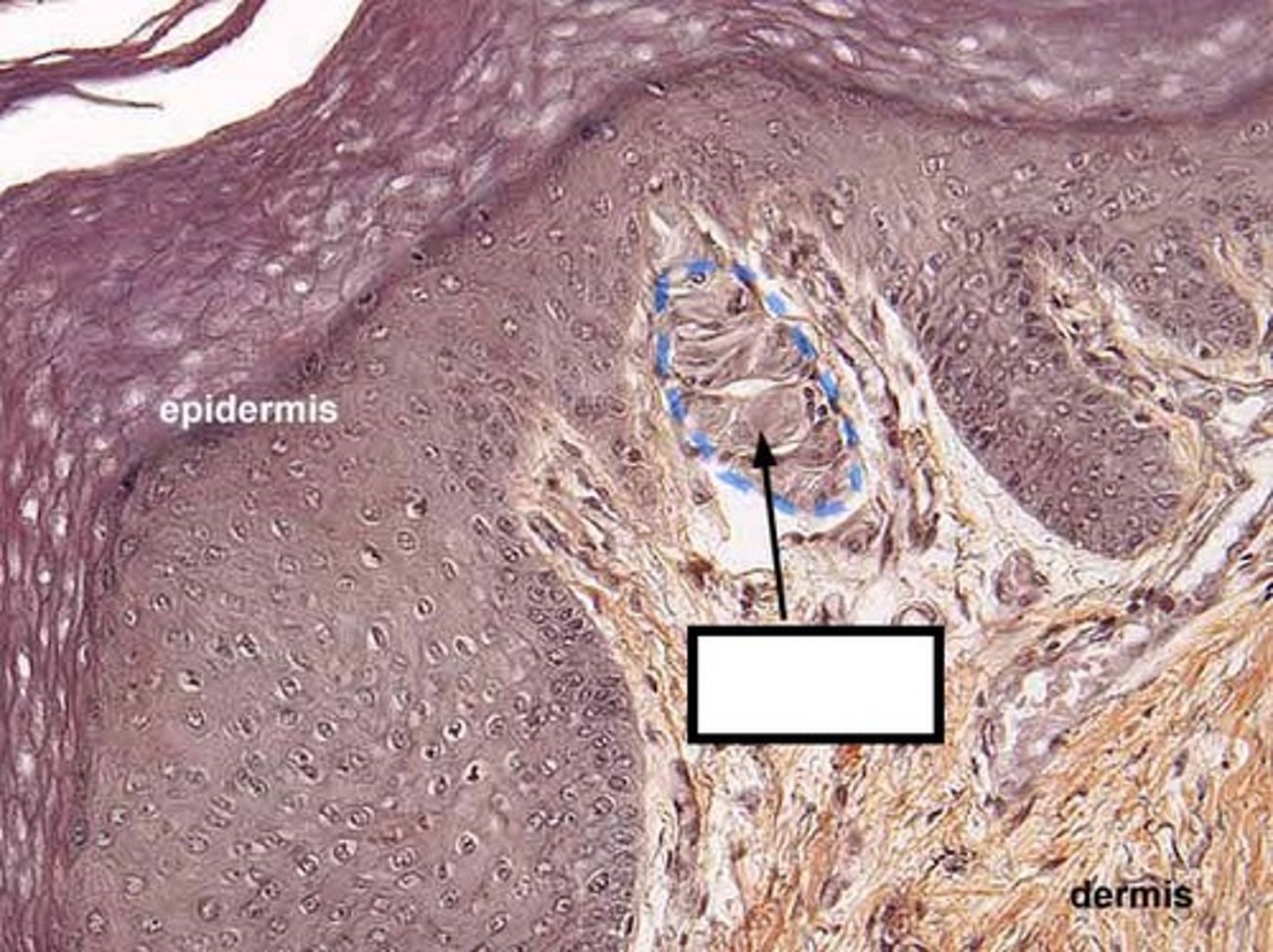
Y
Dermal Papillae
Pacinian Corpuscle (Lamellated corpuscle)
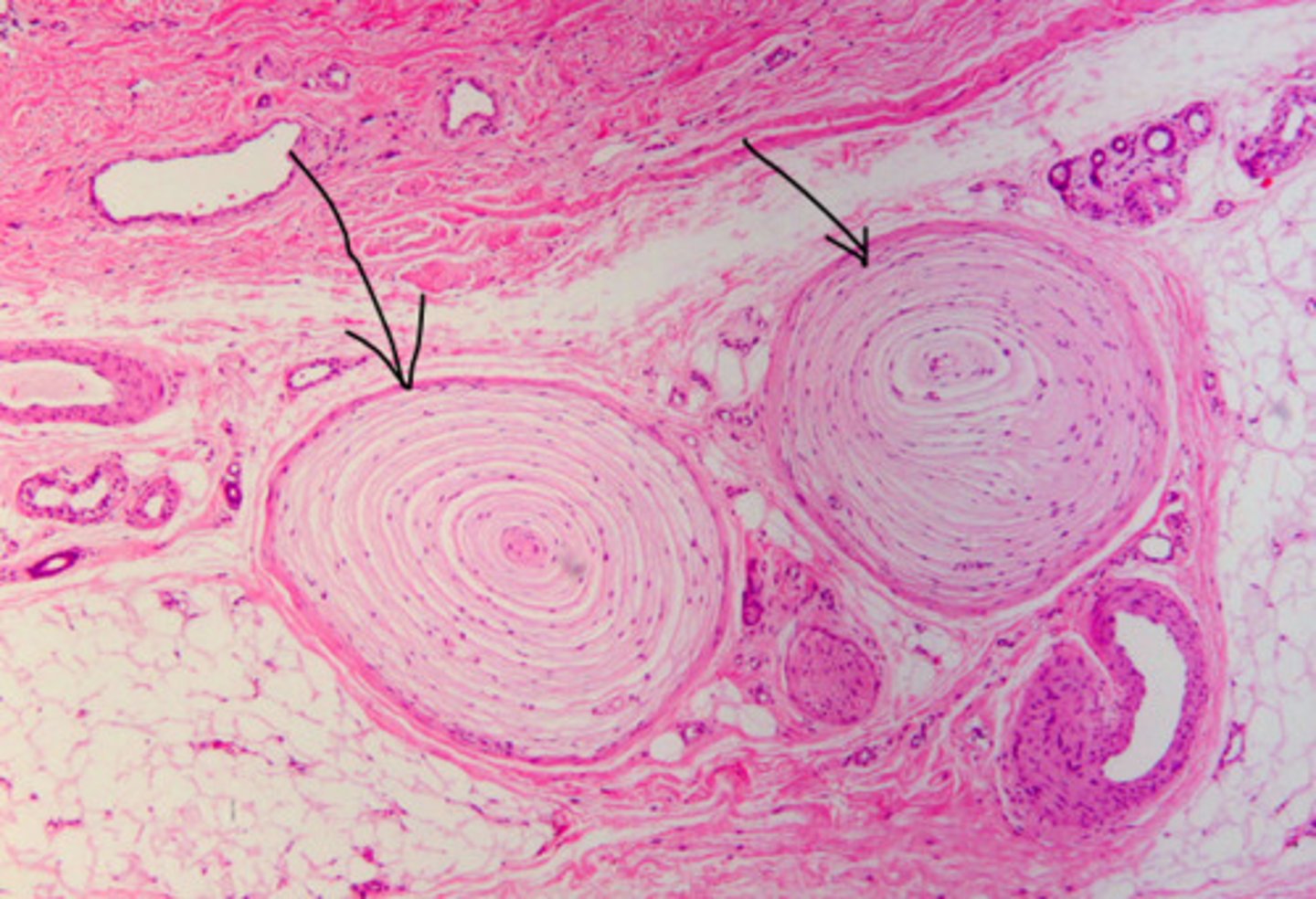
Dermis
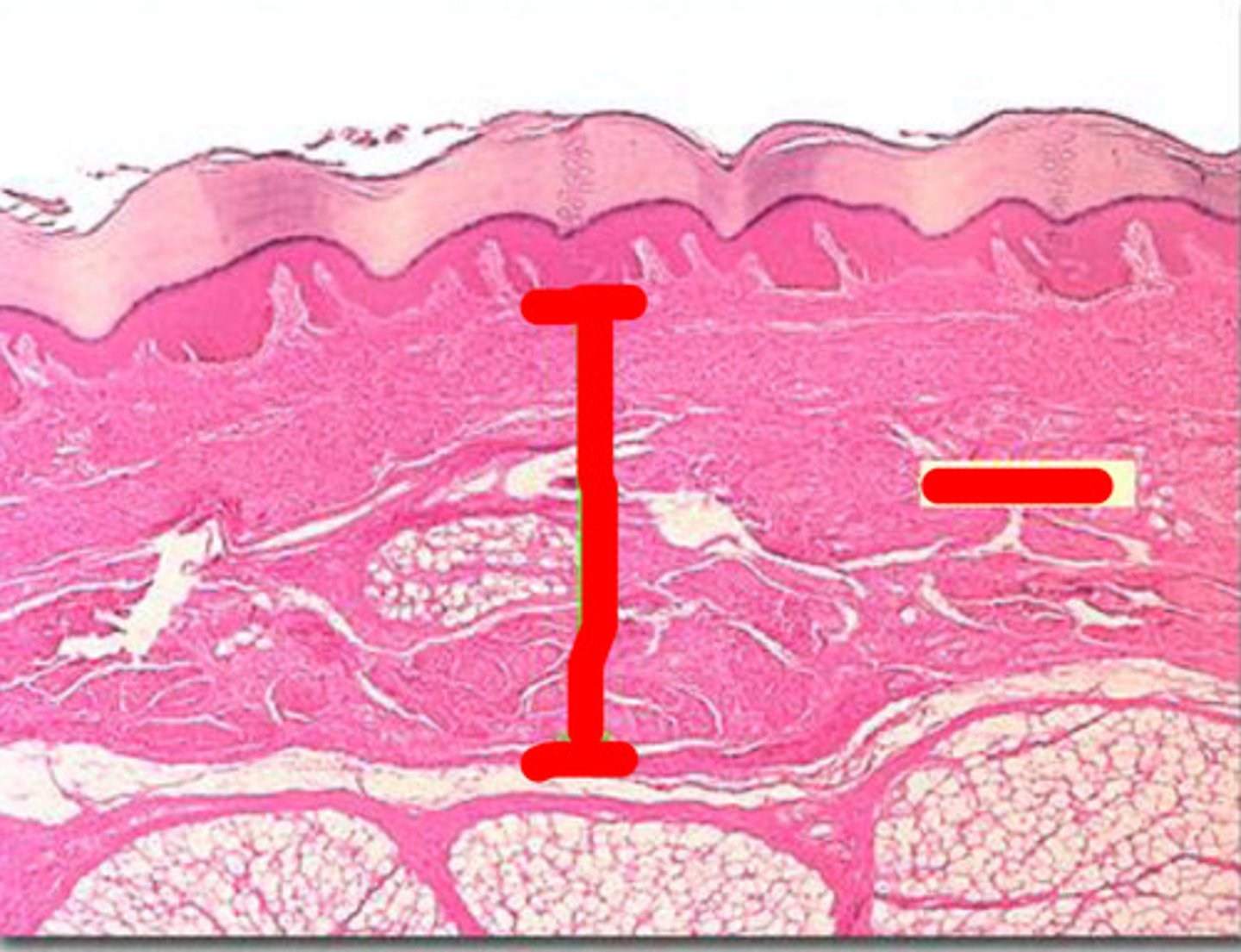
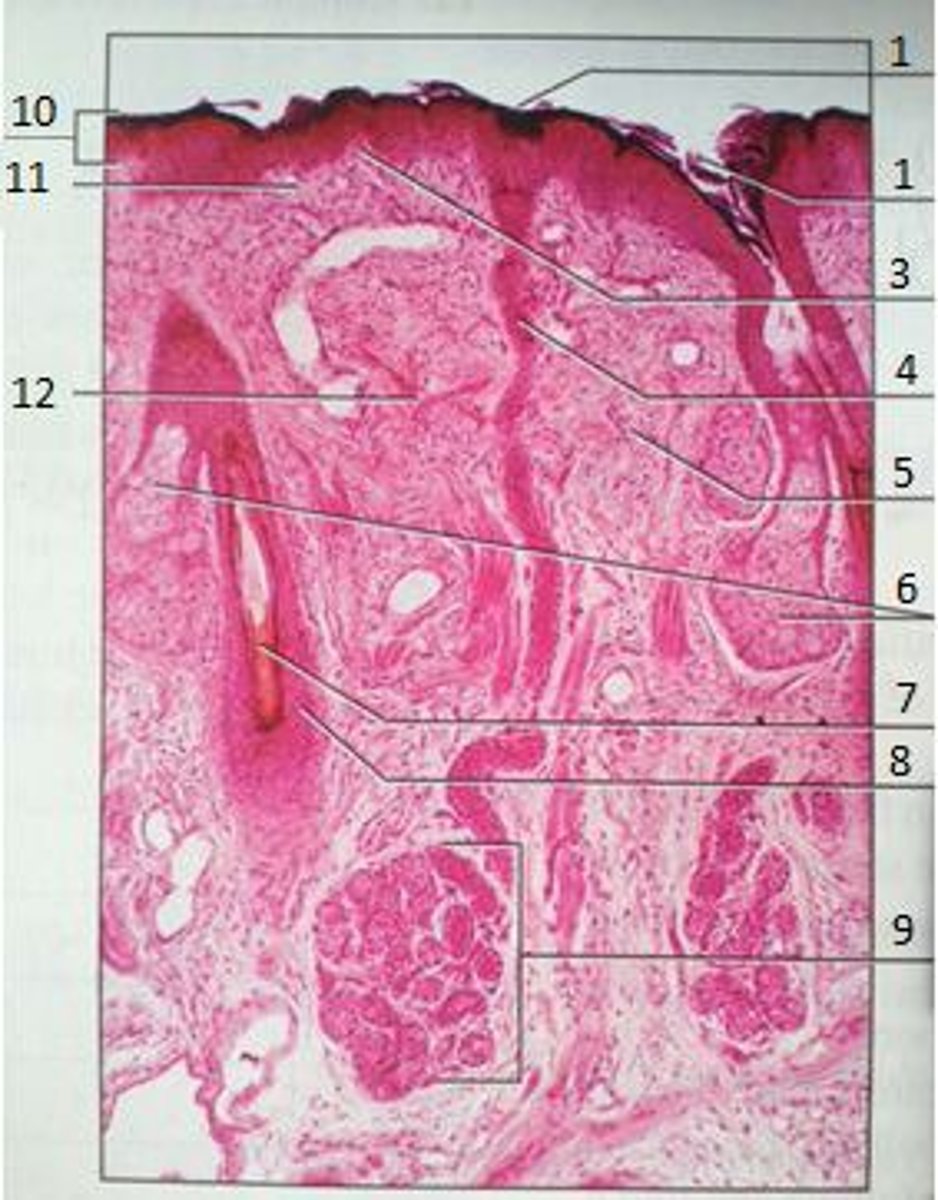
1
Pores
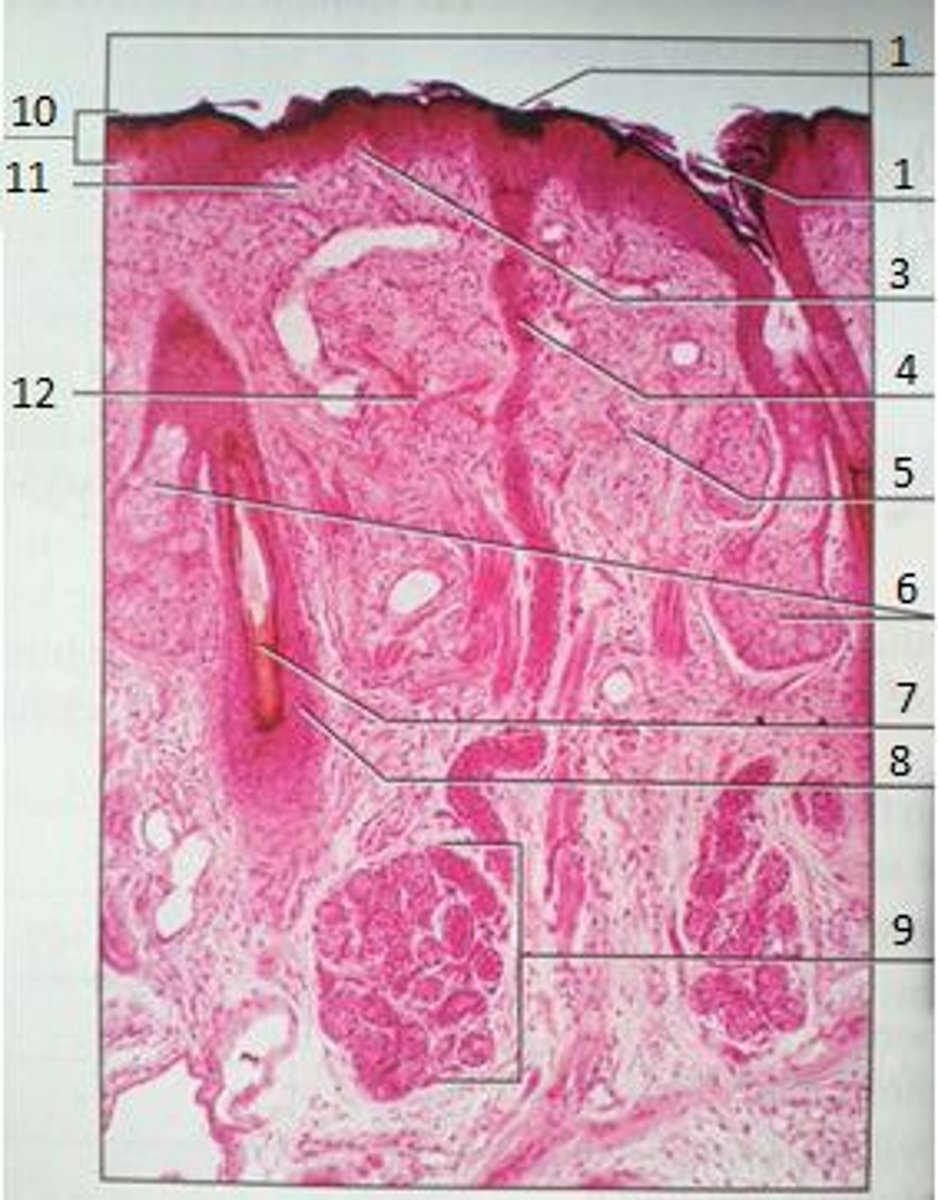
3
Papillary Region
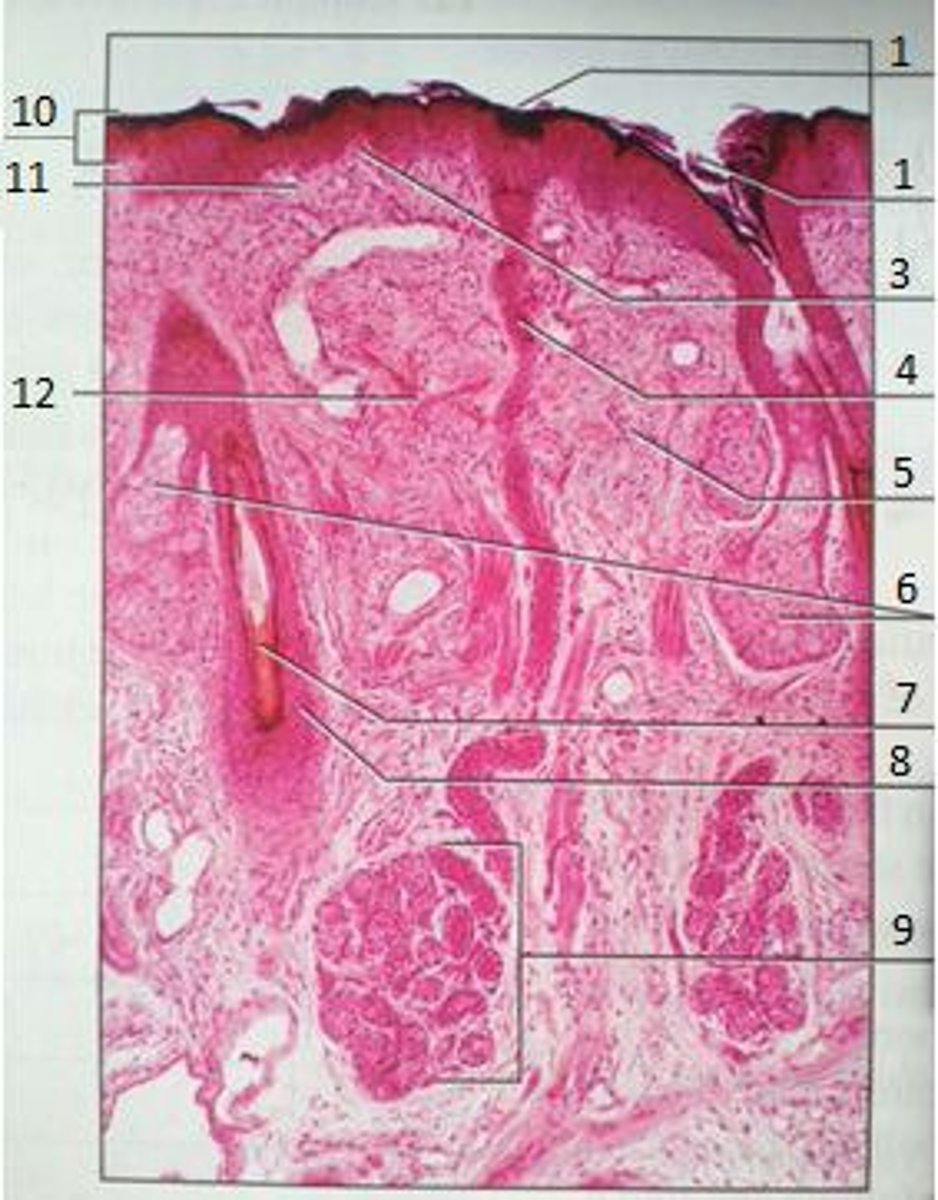
4
Eccrine Sweat Duct
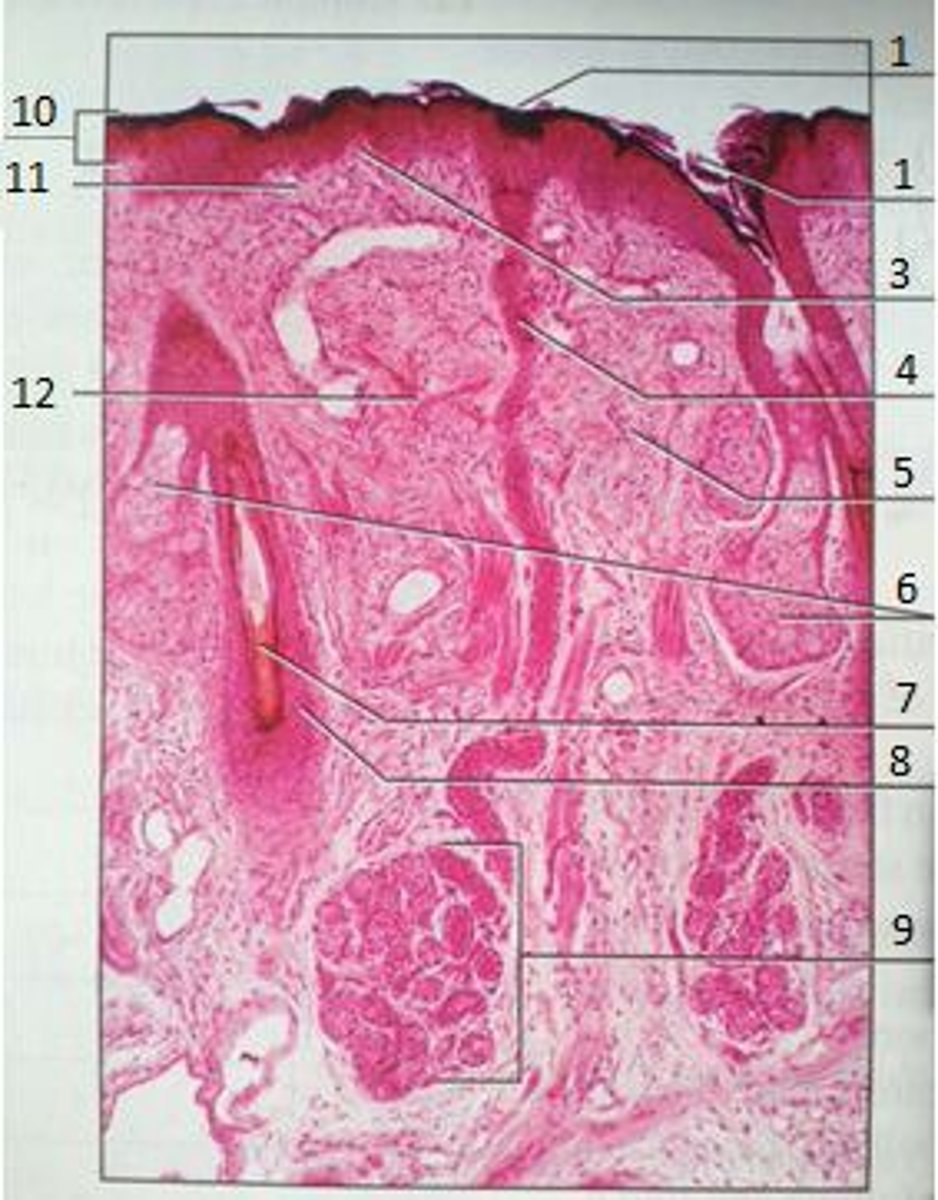
6
Sebaceous Gland
(oil gland)
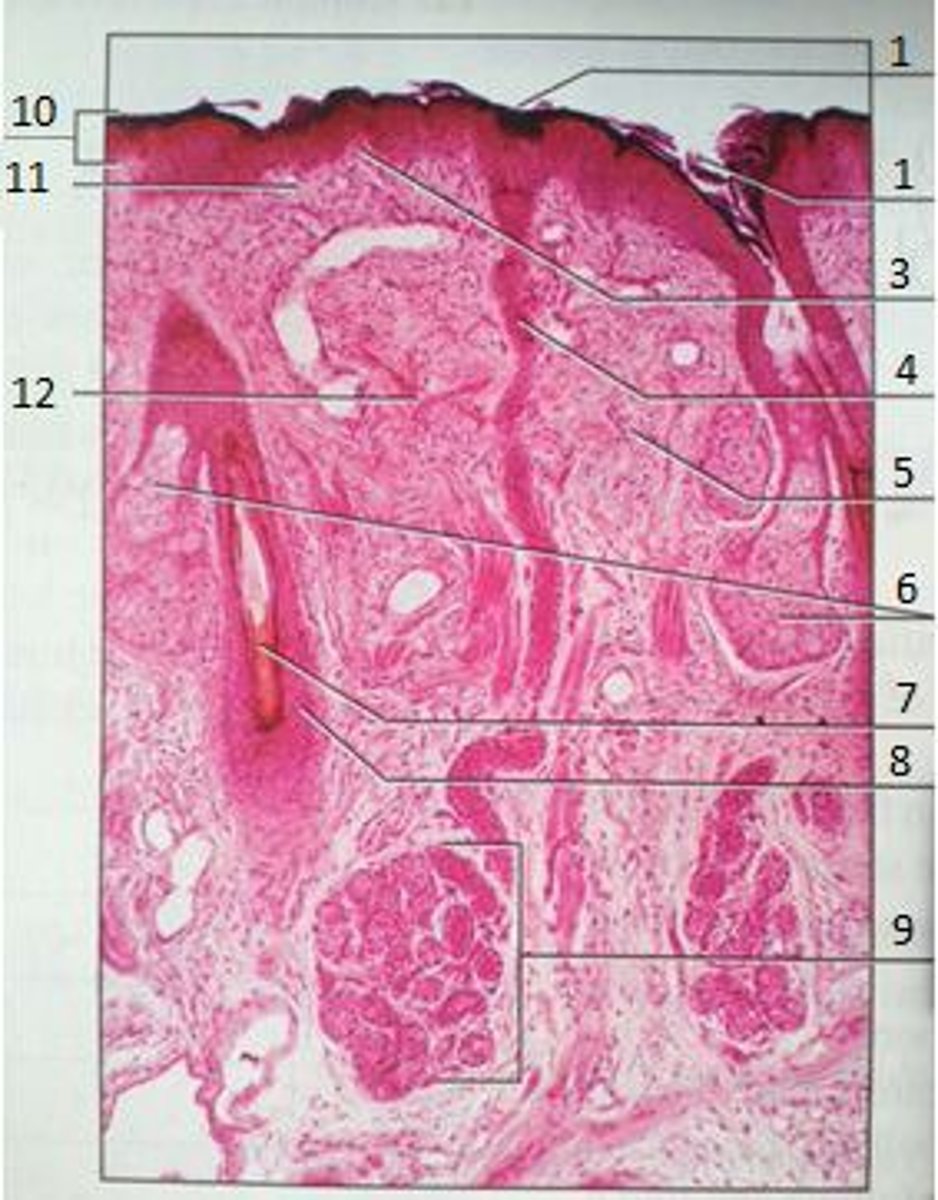
7
Hair Root
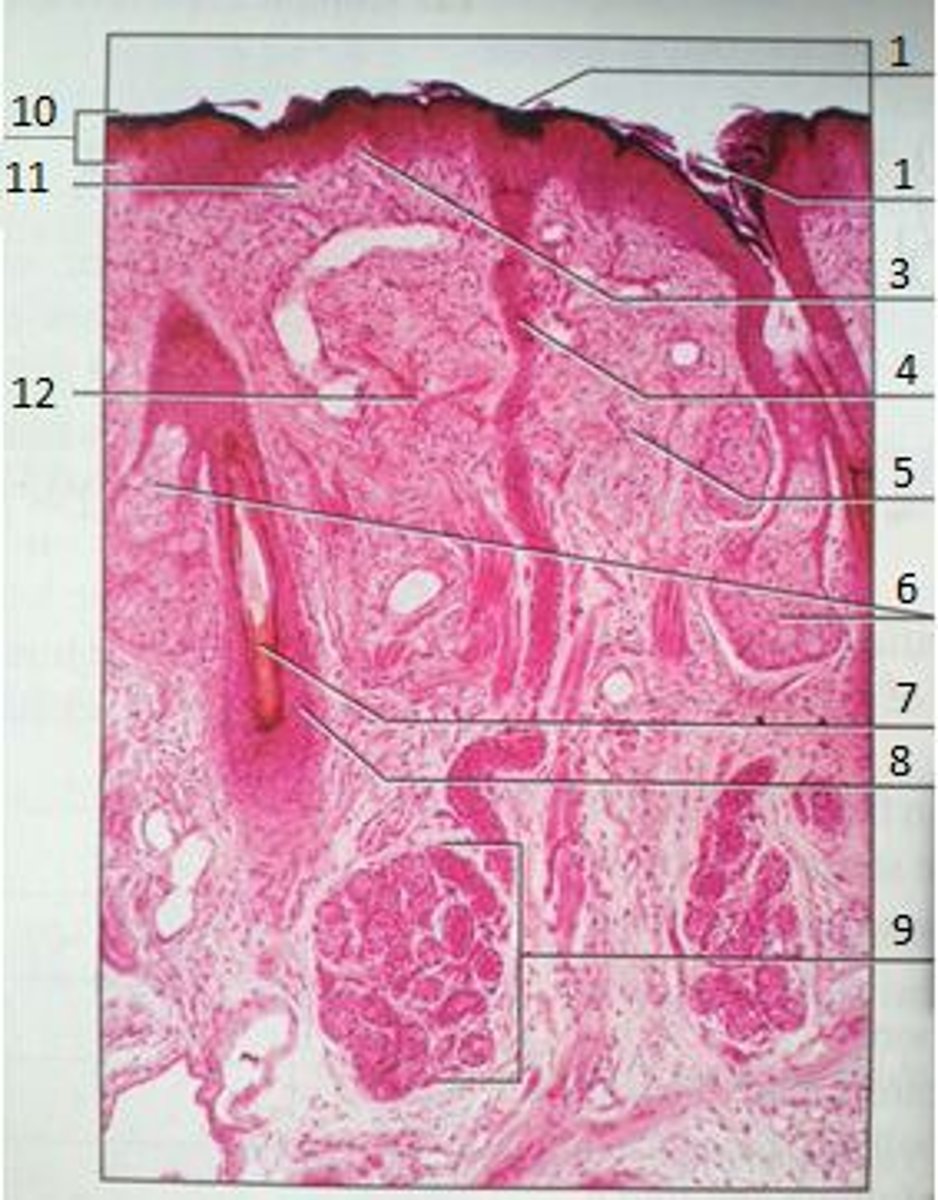
8
Hair Follicle
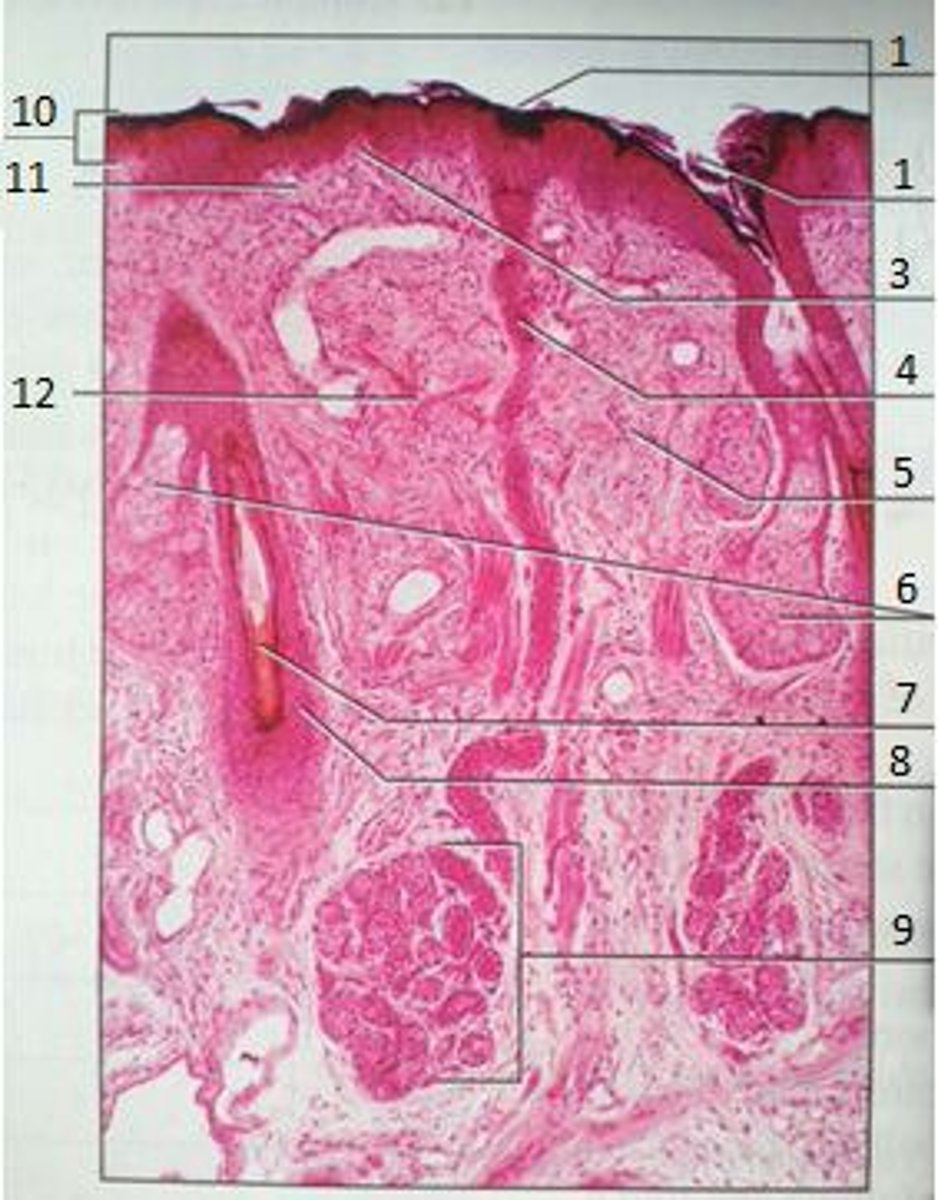
9
Eccrine Sweat Gland
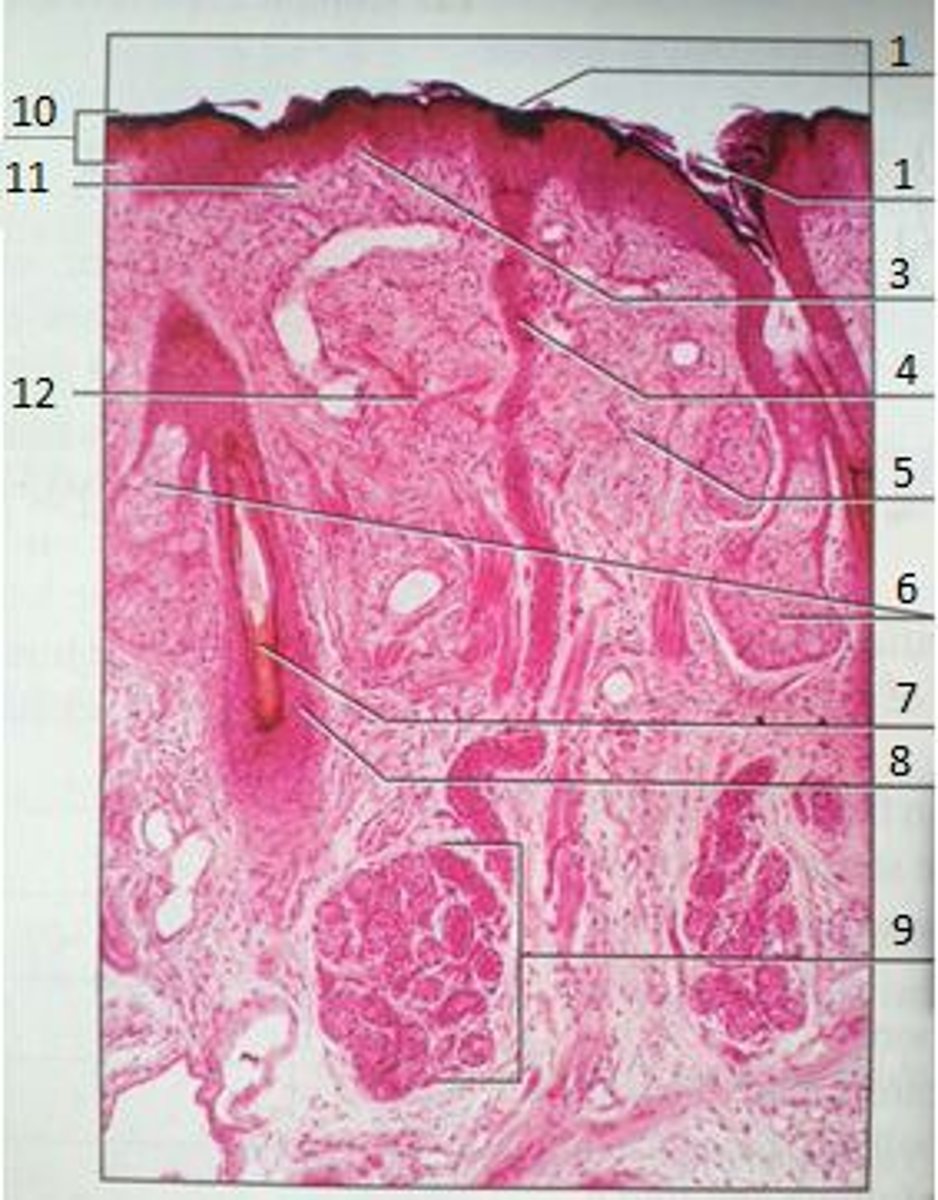
10
Epidermis
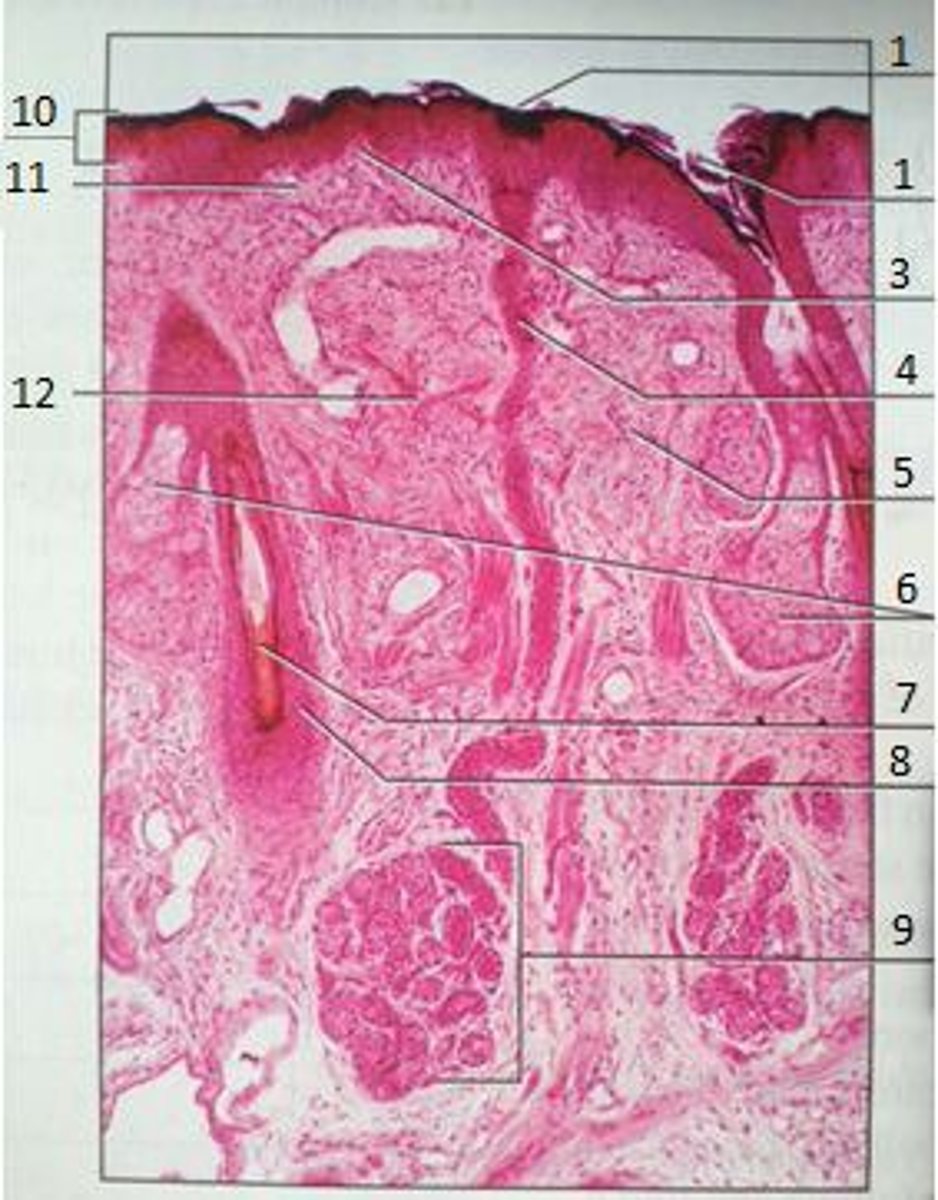
11
Papillary Region
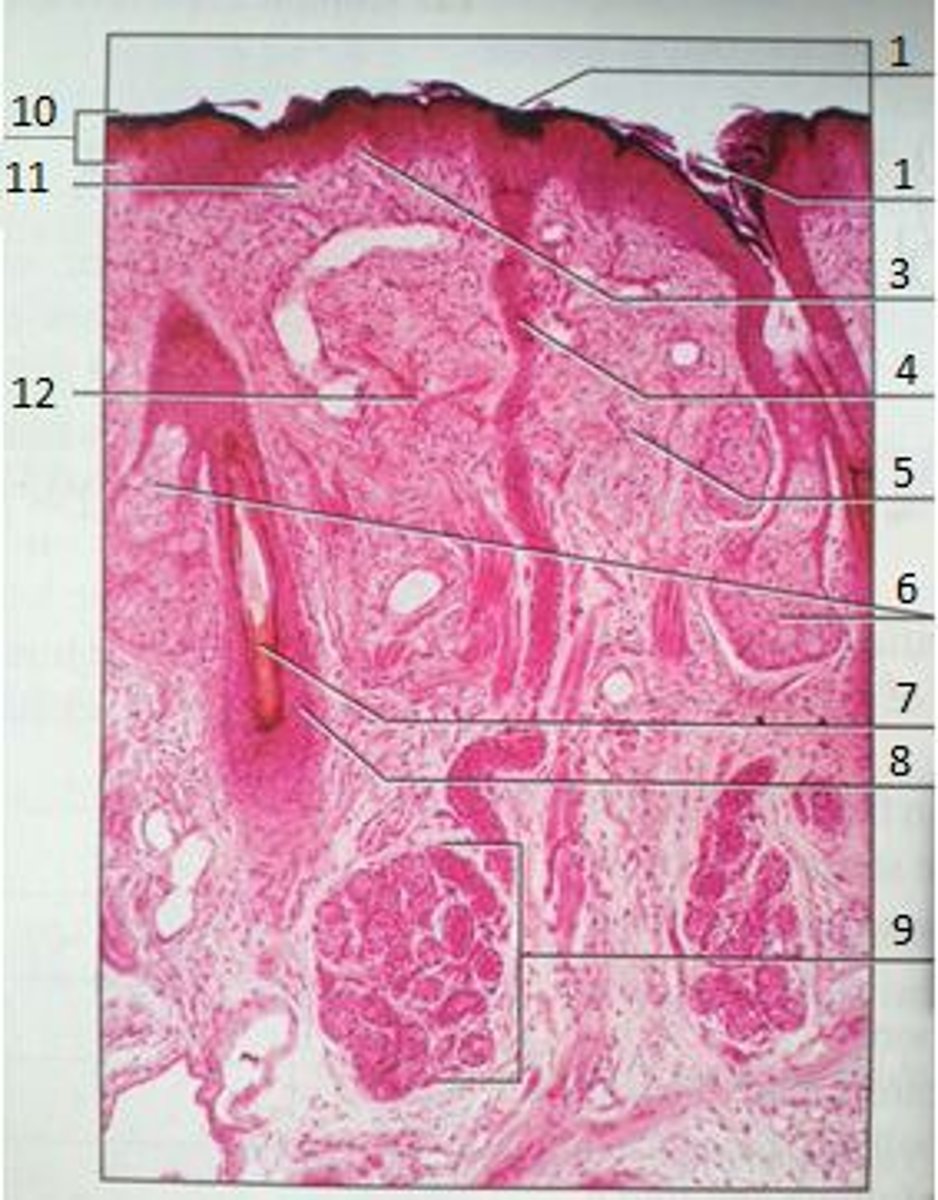
12
Reticular Region
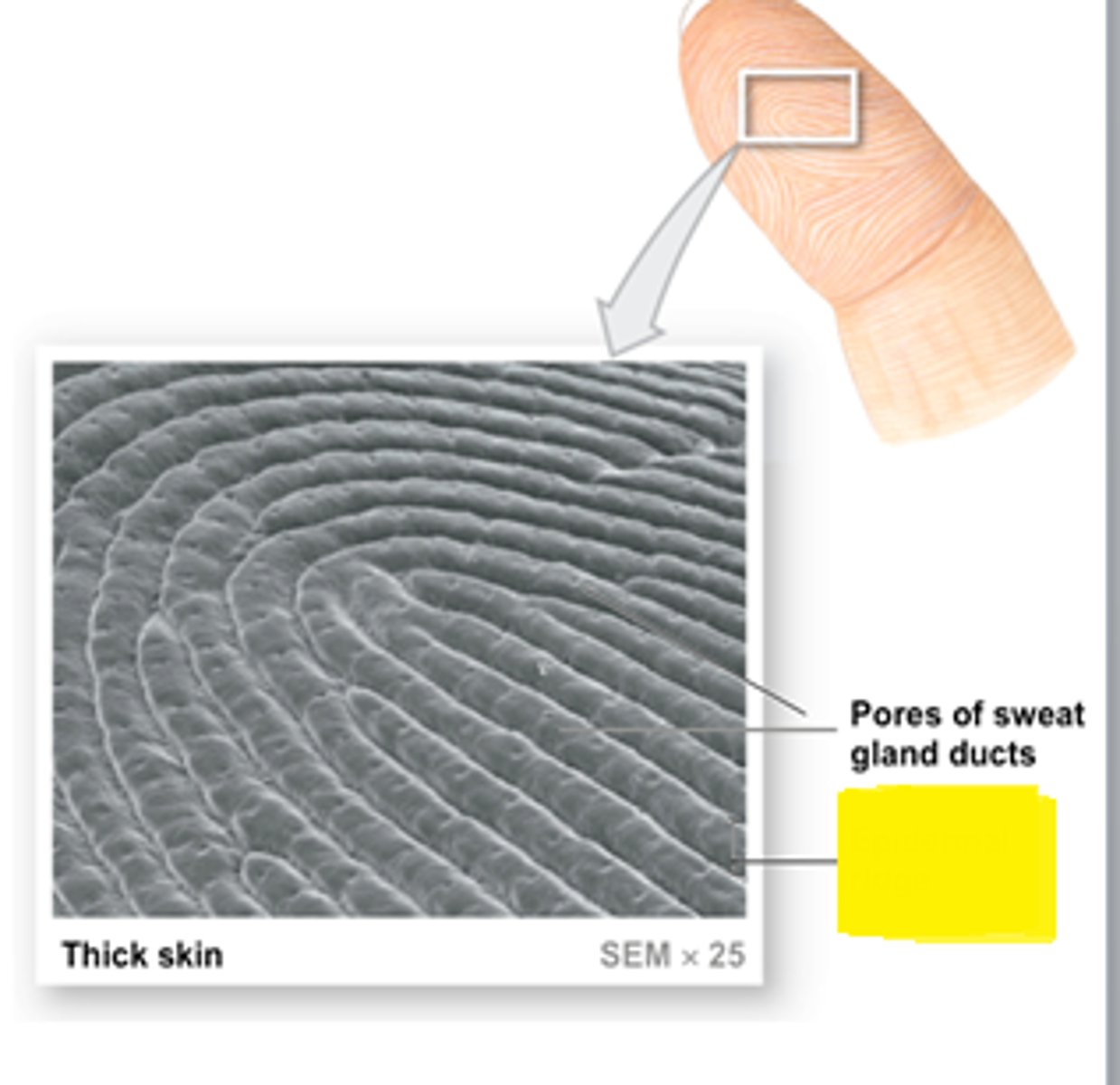
The yellow box
Epidermal Ridge
1
2
1. Epidermal Ridge
2. Corpuscle of touch (Meissner)
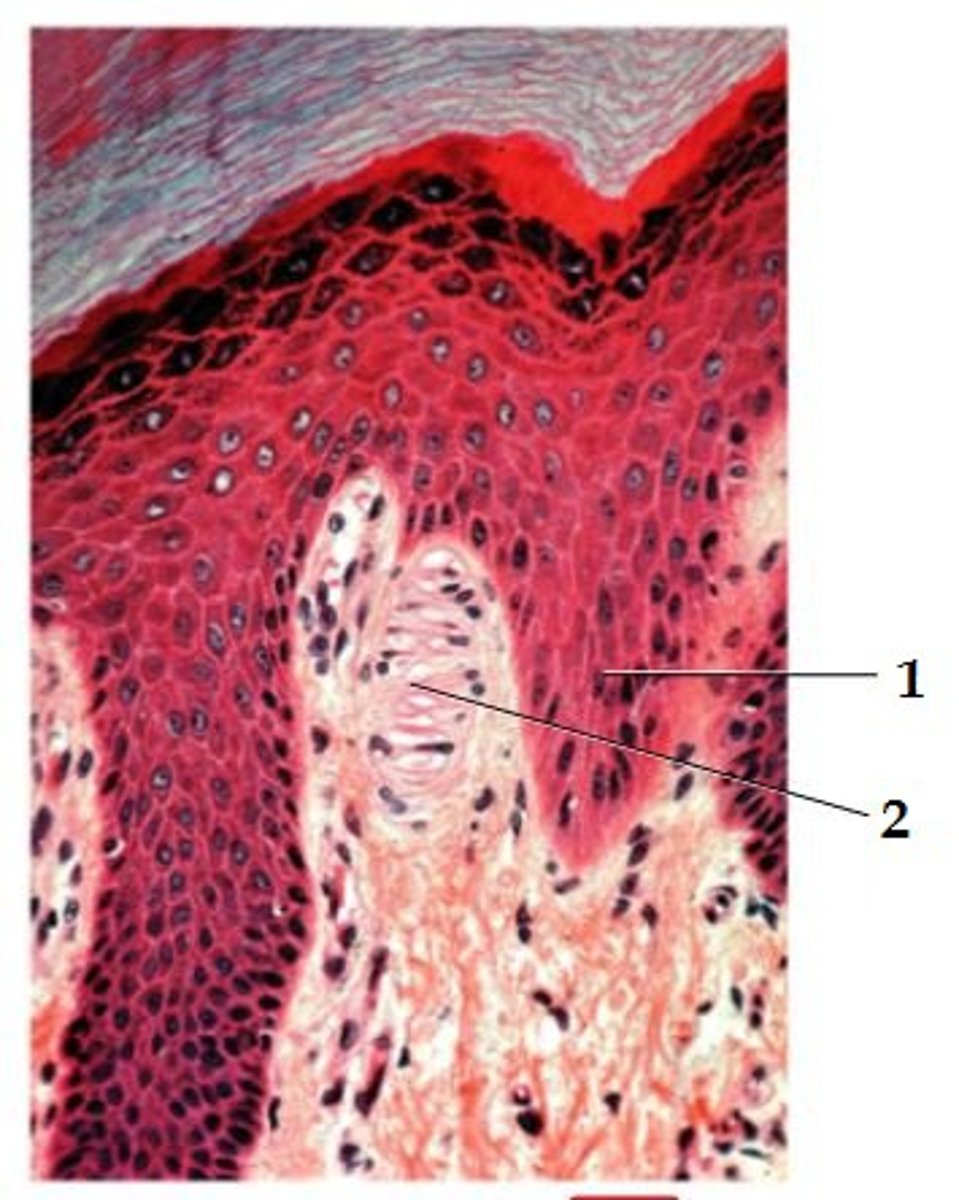
another name for skin
cutaneous membrane
how does the weight of the skin
compare to the weight of an entire adult human body?
7% of an adult body weight
what are the two main parts of the skin?
epidermis
dermis
dermis is composed of what kind of
tissue?
connective tissue
epidermis is composed of what kind of tissue?
epithelial tissue
why does a paper cut usually not bleed?
The epidermis is avascular
fibers from the dermis anchor skin to which layer?
is that layer part of the skin?
the layer is composed of what kind of tissue?
hypodermis or subcutaneous layer (subQ layer)
it is not part of the skin
areolar and adipose tissue
the hypodermis is connected to what tissue?
fascia (connective tissue around
muscles and bones)
what three things can be found in the subcutaneous layer?
adipose tissue
large blood vessels
pacinian corpuscles
epidermis is composed of what kind of tissue?
keratinized stratified squamous
epithelium
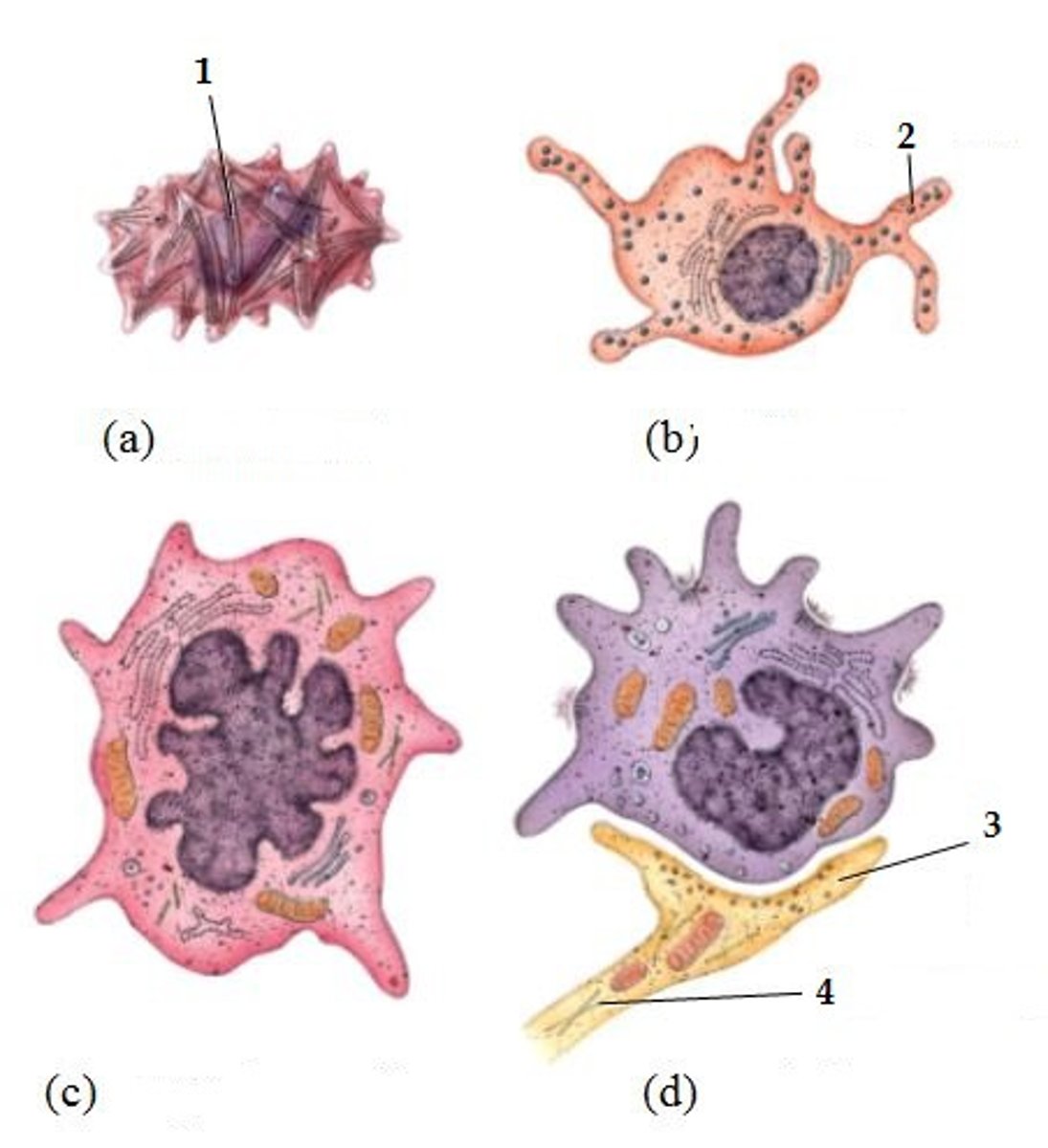
what four types of cells make up the epidermis?
keratinocytes
melanocytes
Langerhans cells
Merkel cells
what two things are produced by
keratinocytes?
what are their functions?
the protein keratin provides strength
lamellar granules provides a
water-repellant sealant
what is produced by melanocytes?
what is its function?
melanin
it gives skin its color and prevents
damage from UV light
what is the function of Langerhans cells?
activate immune responses against
microbes that invade the skin
what is the least common epidermal cell?
what is its function
Merkel cells
make up Merkel discs that sense touch
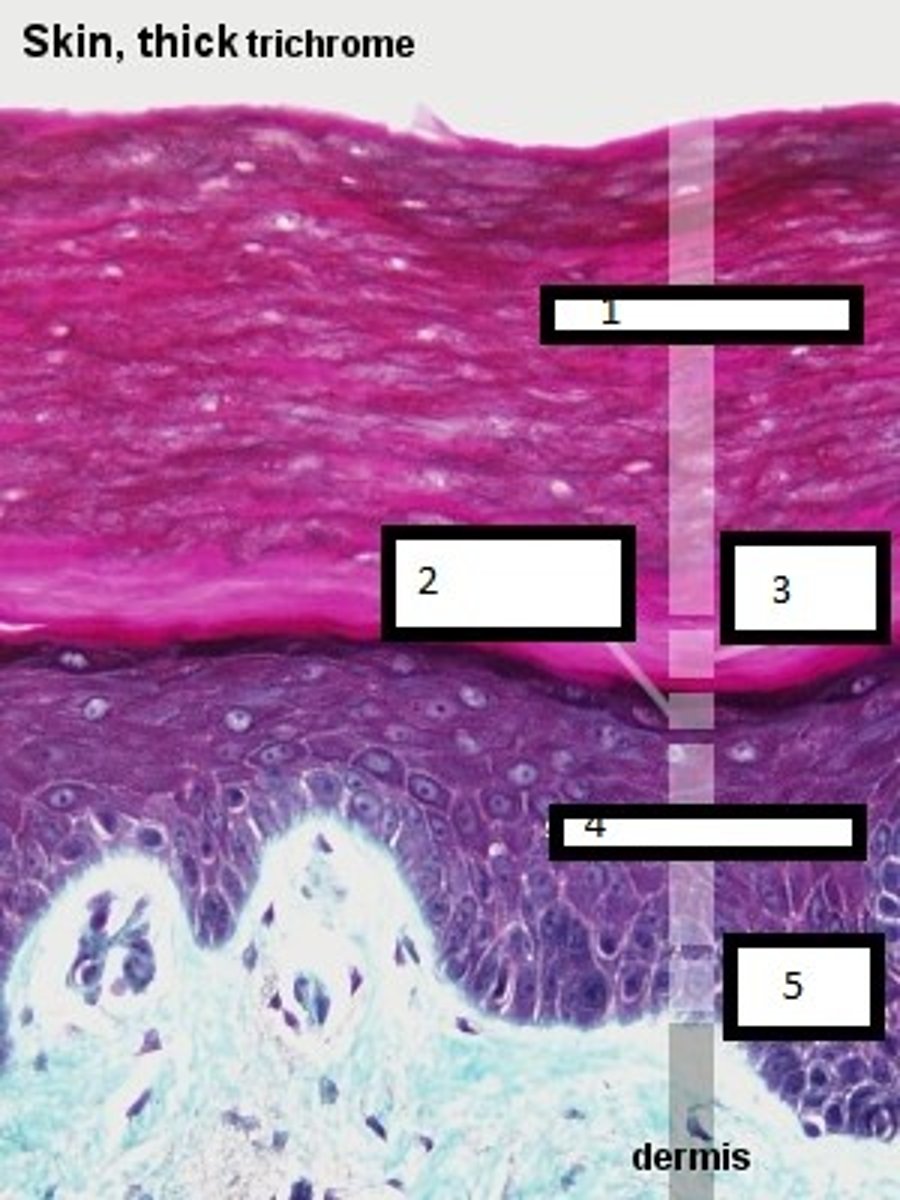
what are the four layers of the
epidermis in thin skin?
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum corneum
what additional layer is found in the epidermis in thick skin?
stratum lucidium
describe the stratum basal
a single layer of cuboidal or columnar
keratinocytes including stem cells
located deepest
melanocytes and merkel cells are scattered throughout
what are the three types of skin graft and where does the tissue come from for each?
autograft - skin comes from the person
receiving the graft
isograft - skin comes from a twin
autologous skin transplant - keratinocytes from the person
receiving the graft are cultured and the
produced skin is used
describe the stratum spinosum
keratinocytes arranged in 8 - 10 layers, becoming more flattened as they become more superficial, the keratin proteins are coarser and tightly join
adjacent cells in desmosomes.
Langerhans cells and projections of melanocytes are also present in this layer
describe the stratum granulosum
3 - 5 layers of flattened keratinocytes undergoing apoptosis, having degenerating nuclei and organelles as they move away from the dermal blood vessels
lamellar granules fuse with the plasma membrane and release lipids for water-repellant sealant
describe the stratum lucidum
4 - 6 layers flattened, clear, dead
keratinocytes that contain large amounts of keratin and thickened
plasma membranes
describe the stratum corneum
25 - 30 layers of flattened, dead
keratinocytes. The cells are extremely thin and flat and no longer contain nucleus or organelles; they only contain keratin. The cells overlap like scales on a snake.
an abnormal thickening of the stratum corneum
callus
1
stratum corneum
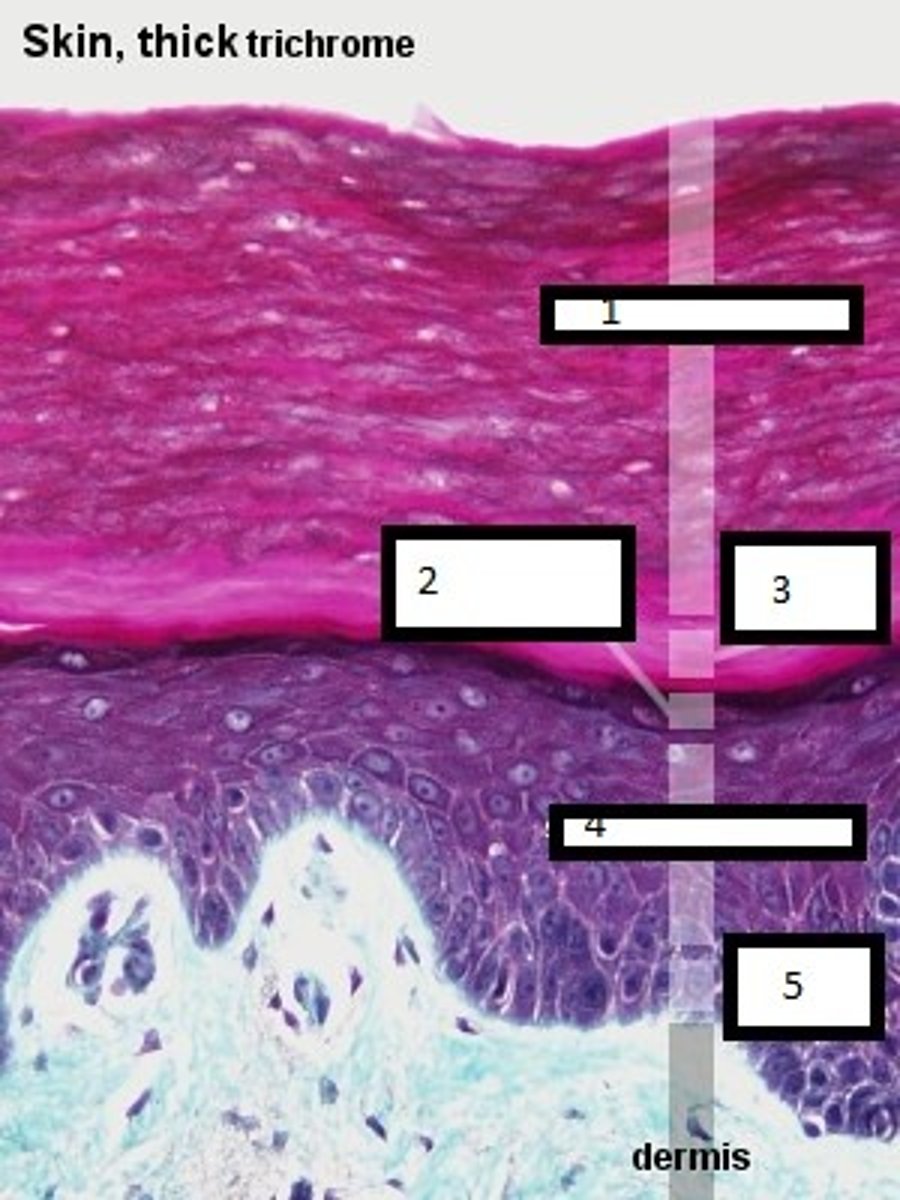
2
stratum granulosum
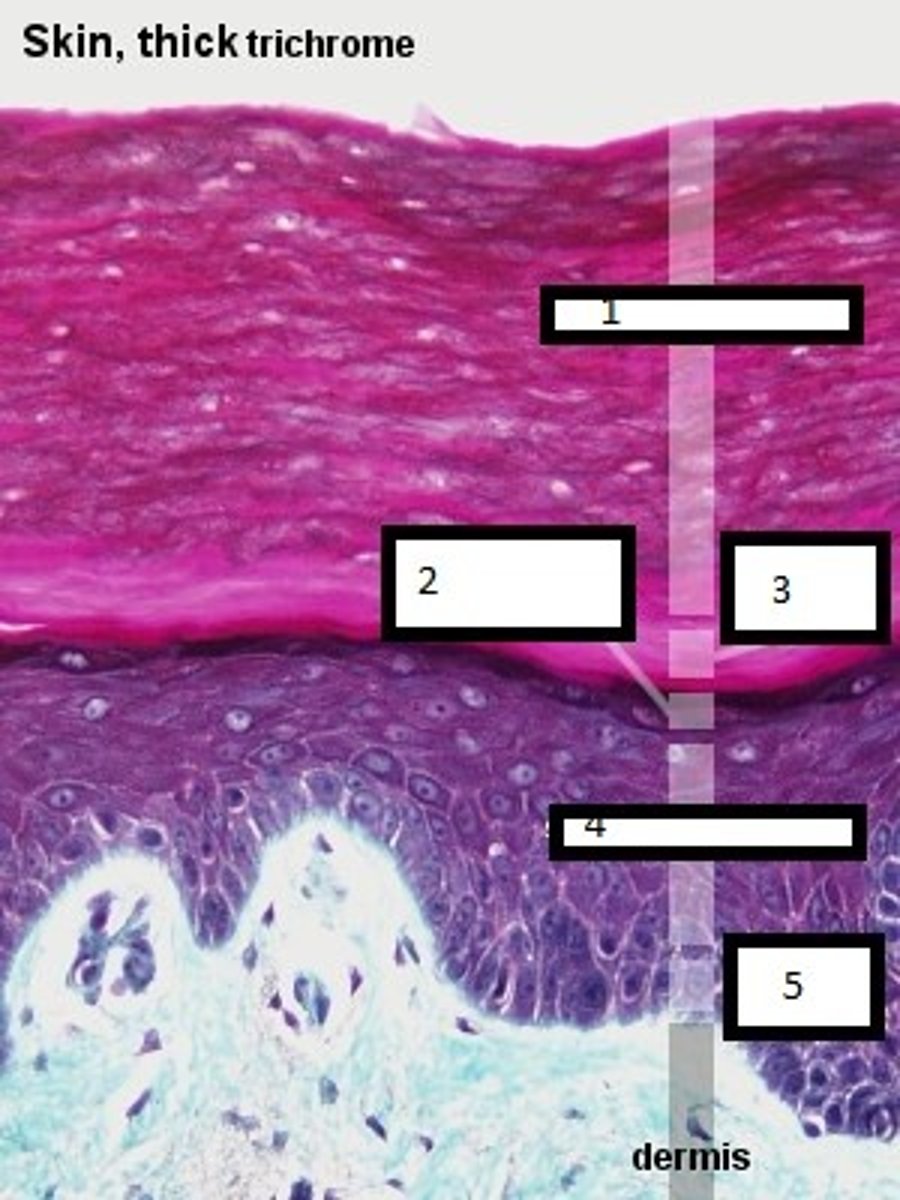
3
stratum lucidum
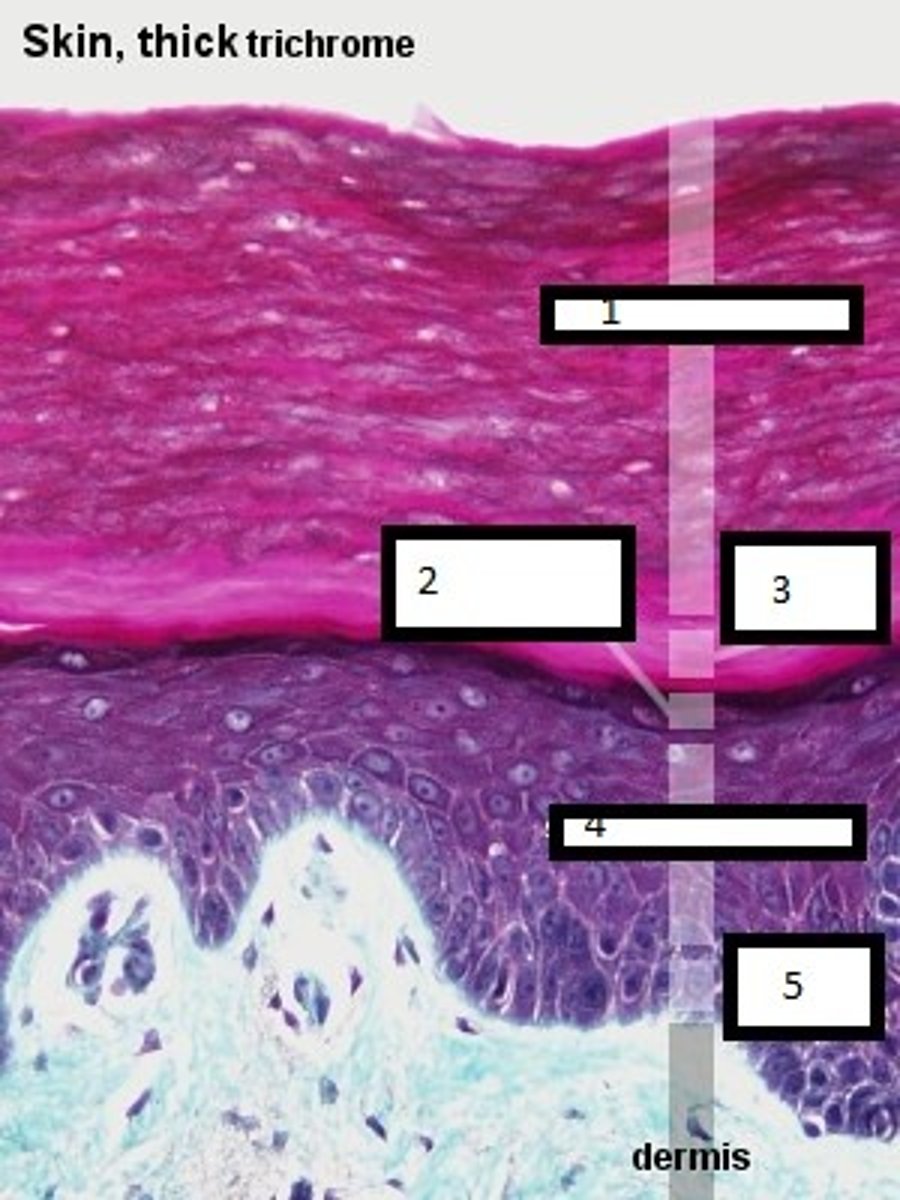
4
stratum spinosum
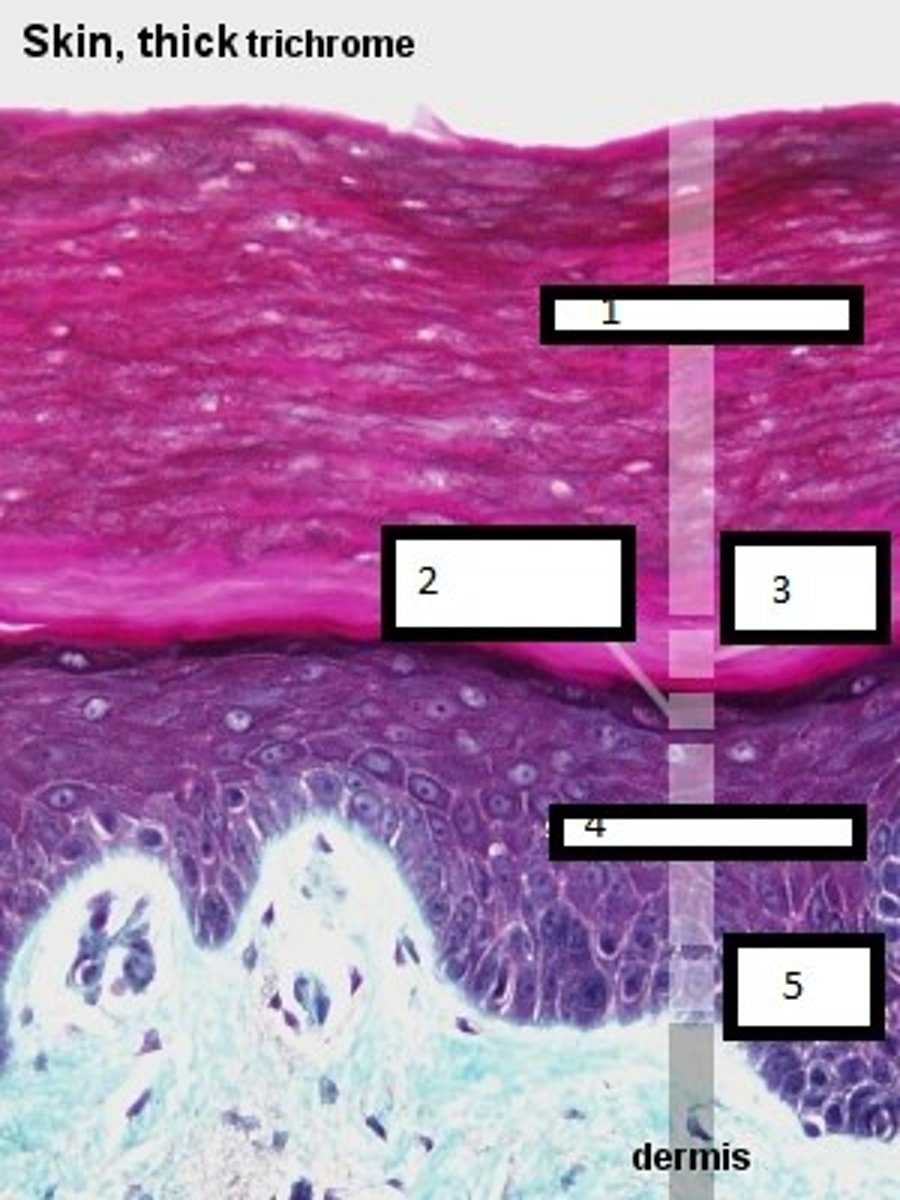
5
stratum basale
melanocyte
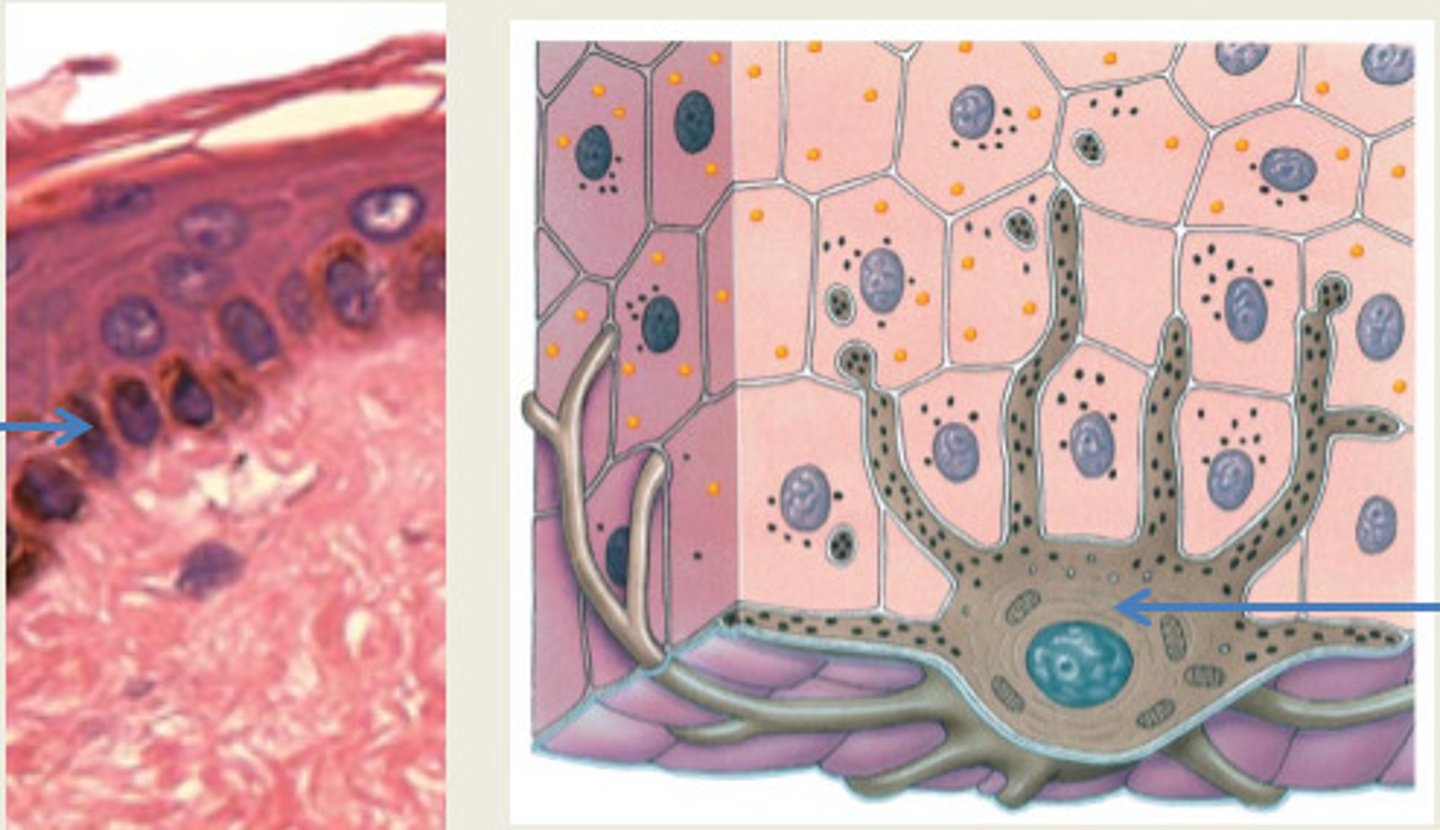
langerhans cell
A
B
C
D
A keratinocyte
B melanocyte
C Langerhans cell
D Merkel cells
the process in which cells mover from one epidermal layer to the next, accumulating more keratin as they go
keratinization
On average, how long does it take cells formed in the stratum basal to rise to the surface and become sloughed off?
4 - 6 weeks
describe the composition of the dermis
dense irregular connective tissue
containing collagen and elastic fibers
which is thicker, the dermis or
epidermis?
dermis
dried, treated dermis
leather
what kind of cells are found in the
dermis?
a few cells, predominantly fibroblasts, some macrophages, and a few adipocytes near the subQ layer
what are the two layers of the dermis?
papillary region (1/5 thickness)
reticular region (4/5 thickness)
what fibers make up the papillary
region?
thin collagen and elastic fibers
small, nipple shaped structures that project into the undersurface of the
epidermis
dermal papillae
what structures can be found in dermal papillae?
all contain capillary plexus
some contain Meissner corpuscles
some contain free nerve endings
what fibers make up the reticular
region?
thick collagen fibers and some coarse elastic fibers
what is different about the collagen fibers in the reticular region when
compared to the papillary region?
In the reticular region, collagen fibers are more course and arranged in a
netlike manner, creating a greater
resistance to stretching
what things can be found in-between the fibers of the reticular region?
blood vessels
nerves
hair folicles
sebaceous glands
sudoriferous glands
the ability to stretch
extensibility
the ability to return to original shape after stretching
elasticity
a series of ridges and grooves on the surfaces of palms, finger, soles, and toes
epidermal ridges
what creates the surface features of the epidermal ridges?
downward projections of the epidermis into the dermis between the dermal papillae of the papillary region
what causes fingerprints?
ducts of sweat glands open o the tops of epidermal ridges as sweat pores and this sweat is what forms fingerprints
what are the two functions of the
epidermal ridges?
1. increases the surface contact between the dermis and epidermis, allowing
nutrition of the dermis
2. strengthens the junction between the
dermis and epidermis
regions of the skin where the collagen fibers have a predominant direction
tension lines
(lines of cleavage)
what ware the two types of melanin and what color do they produce?
pheomelanin (yellow to red)
eumelanin (brown to black)
where are the most melanocytes found in the human body?
epidermis of the penis
nipples of the breast
areolae (area around the nipples)
face
limbs
mucous membranes
what causes the color differences
between people?
the number of melanocytes is
consistent between people
color differences are related to the amount of pigment produced by the melanocytes
melanocyte patches present in young people
freckles
accumulation of melanin due to age
liver spots