normative decision-making
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
characteristics of decision-making process
there is more than one alternative in the market
consumers need to make choices among alternatives
consumers are always trying to choose alternatives they think are the best ones
judgements
evaluations/estimates regarding the likelihood that something will happen; does not require a decision
I think car A will be more reliable than car B is an example of a ____ (judgment / decision)
judegement
I chose car A over B is an example of a _____ (judgment / decision)
decision
the consumer decision process in order
need recognition
information search
alternative evaluation
purchase
post purchase
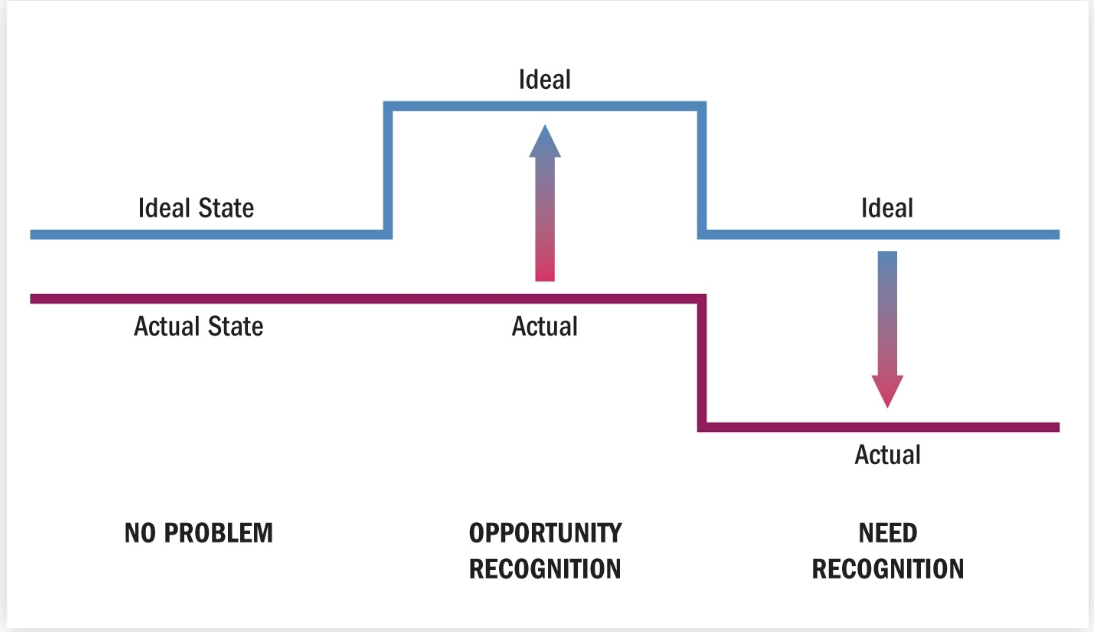
problem recognition
occurs when consumer sees difference between current state and ideal state
opportunity recognition
ideal state moves upward
need recognition
actual state declines
problem recognition graph
information search
search for available alternatives
attributes of available alternative (quality, price, etc)
search internally / externally
internal search
the process of recalling stored information from memory
external search
the process of collecting info from outside sources (media, internet, retailer)
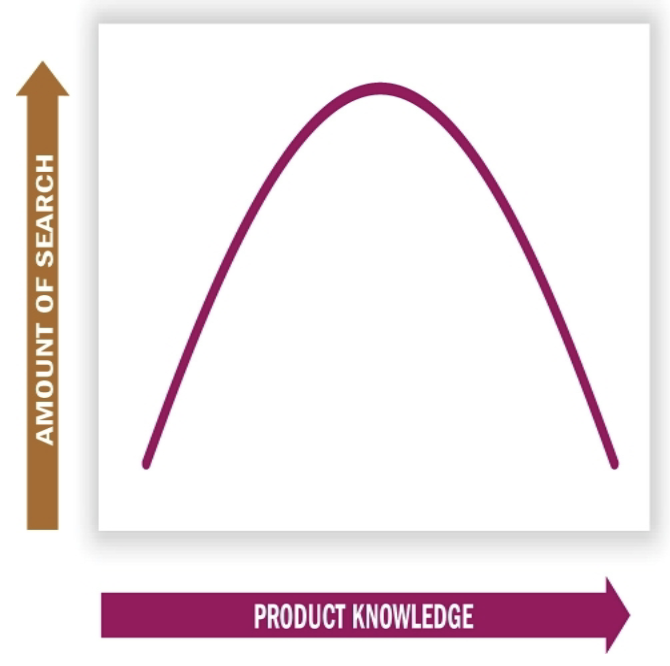
influence of consumer’s prior expertise on search
moderately knowledgable consumers tend to search more than product experts and novices
types of perceived risk
financial
performance
physical
social
psychological
what leads to search
involvement - is the decision important to consumer’s self-concept/values
perceived risk types
ease of access to information
what determines search
benefits - involvement, perceived risk
cost - difficulty of gathering the info
to make informed decision….
consumers will gather as much data as needed ; we continue to search until costs exceed utility of information search
results of searching
universal set
retrieval set
evoked set - actively considered during the choice process
inept set - aware of, but considered unacceptable
inert set - indifferent towards
decision rule
strategies used by consumers to guide decision making; sometimes use product characteristics to guide decisions
compensatory decision rule
selecting the best overall brand ; a positive score on one attribute can outweigh a negative score on another attribute
perceived risk
the subjective probability and severity of potential negative consequences associated with a purchase decision
performance risk
the risk that a product or service will not perform as expected
physical risk
the risk of physical harm or damage to oneself or others from using a product
financial risk
the risk of losing money or incurring financial losses associated with a purchase
social risk
the risk of social disapproval or embarrassment associated with using a product
psychological risk
the risk of loss of time, money, or effort associated with a purchase