Terminology and Basic Anatomy Exam (Sports Med Exam 2)
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Anatomical Position
Standing straight upright, feet facing forward, arms at the side, palms of the hands facing forward
Anterior
Front of body
Posterior
Back side of body
Medial
Body part lying near the midline of the body
Lateral
Body part lying away from the midline of the body
Proximal
Point closest towards a joint/attachment
Distal
Point farthest away from a joint/attachment
Inferior
Body part below another body part
Superioir
Body part above another body part
Superficial
Toward or on the surface
Deep
Away from the surface/internal
Supine
To lie or be placed with the anterior surface facing up (lying on your back)
Prone
To lie or be placed with the anterior facing down (lying on your stomach)
Flexion
Joint that bends or moves forward- Decreasing angle between two bones
Extension
Joint that straightens or moves backwards- increasing angle between two bones
Abduction
Moving away from the midline of body
Adduction
Moving towards midline of body
Horizontal Abduction
Moving shoulder/arm away from body
Horizontal Adduction
Moving shoulder/arm across the body
Internal Rotation
Rotation of a joint toward the middle of the body
External Rotation
Rotation of a joint away from the middle of the body
Circumduction
Movement of a part in a circular direction- typically ball and socket joints
Pronation
Rotating forearm/hand until palm is facing down/away
Supination
Rotating forearm/hand until palm is facing up/forward
Inversion
Turning or pulling sole of foot inward- pulling toe inward towards midline
Eversion
Turning or pulling sole of foot outward- pulling toe away from midline
Plantarflexion
Extending ankle/pointing toes down
Dorsiflexion
Flexing ankle/pulling toes up
Muscle
Soft tissue structure that has contractible abilities- muscles contract to create movement
Tendon
Tissue that attaches muscle to bone
Ligament
Tissue that connect bone to bone- helps secure a joint
Bone
Hard tissue that gives our body structure- place for ligaments and tendons to attach
Joint
Point of where to bones join together
Synovial
Freely moveable joint
Cartilage
Fibrous type of material that serves as cushion, joint filler, etc
Bursa
Small, fluid-filled sac located in joints; acts a cushion and reduces friction between moving parts
Nerves
Bundle of fibers that sends messages between the body and the brain to create motor movement and sensory information
Myotomes
Groups of muscles innervated by a single spinal nerve that can create movement
Dermatomes
Area of skin innervated by a single spine nerve, for transmitting sensory information like touch and pain to the brain
Acute Injury
Rapid onset resulting from a traumatic event
Chronic Injury
Slow onset, gradual development of structural damage
Hypertrophy
Increase in muscle or tissue size
Atrophy
Decrease in muscle or tissue size
Edema
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in tissue/cavities (Swelling)
Ecchymosis
Discoloration due to blood accumulation under skin/tissue (Bruising)
Inflammation
Body’s protective response to injury (or infection)
Sprain
Stretching or tearing of ligaments
Strain
Stretching or tearing of tendon or muscle
Cramp
A painful continuous involuntary muscle contraction
Contusion
Bruise- when you have a blow to the soft tissue or bone of the body
Hematoma
Swelling composed of blood, internal bleeding associated with contusion; More severe compared to a bruise/contusion
Dislocation
Displacement of a joint
Subluxation
Temporary self-reducing dislocation
Fracture
Broken Bone
Laceration
Cut through the skin
Abrasion
Scraping off a layer of skin
“-itis”
Inflammation of something
Modality
Method of apparatus for therapy
Sports Injury Rehabilitation
Typically an exercise program to assist in recovery from sports injuries
Cryotherapy
Therapy treatment using application of cold
Thermotherapy
Therapy treatment using application of heat
HOPS
Process of injury assessment/evaluation: History, Observation, Palpation, Special Tests
HOPS: History
First part of the evaluation, gather subjective information about how and when injury occured
HOPS: Observation
Second part of the evaluation, use eyes and ears to evaluate
HOPS: Palpation
Examination by touch
HOPS: Special Tests
Last stage of your injury evaluation, includes ROM, stress tests, neurological, circulatory, and functional tests
2 components of Bone
Organic (makes bone resilient) and Inorganic (makes bone hard)
Features of bone
It’s a living tissue
Has a rich blood supply (vascular)
Constantly changing tissue
Rich in minerals (iron, calcium, etc)
Functions of Bone
Provide support for the body
Protects vital organs
Provides for/assists with movement
Produces blood cells
Storage area for minerals
How many bones in the body?
206
Axial skeleton
Bones around the axis/center of body
Appendicular Skeleton
Bones found in the extremities
Long Bones
Ex: Humerus, femur
Short Bones
Cube-like shape; Ex: carpal and tarsal bones
Irregular bones
Complex shapes; Ex: facial, vertebrae
Flat bones
Thin/flat; Ex: bones found in skull
Sesamoid bones
Embedded in tendons
Bone Age differences
Babies: Large head, long trunk, short arms and legs; no knee caps
Adults: Small head, short trunk, long arms and legs
Bone Sex differences
Males: Limbs longer, broad shoulders
Females: Shorter Limbs, narrow shoulders, wide hips
Pelvic differences in Males and Females
Male: Pelvic arch narrow, long conical cavity, narrow hips
Females: Wide pelvic arch, short cylindrical cavity, wide hips
The Skull
Comprised of flat or irregular bones; serve as the brain case- specific bones that encase the brain are known as the calvarium
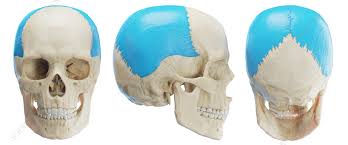
Frontal Bone
One single bone, unpaired- sits front of skull
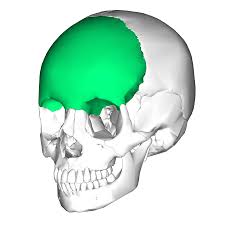
Parietal Bone
Paired on either side of the skull
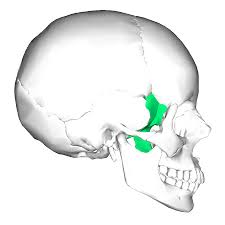
Temporal Bones
Paired on either side of the skull (Ear canal), This area is known as the mastoid process
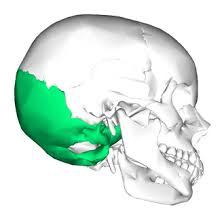
Occipital Bones
Unpaired, sits at the posterior aspect of the skull
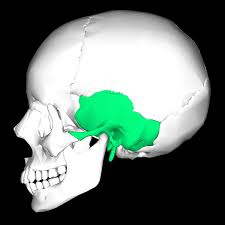
Sphenoid bone
Paired on either side of the skull, sits anterior to the temporal bones, sinuses sit here
Suture Lines
Joint between all of the skull bones, grows together as we grow older
Fontanelles aka soft sports
The space between the bones of the skull in babies
Bones that create the face
Nasal bone, zygomatic bones, maxilla and mandible
Bones that create the skull
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital, Sphenoid
Nasal bones
2 bones, create the bridge of the nose
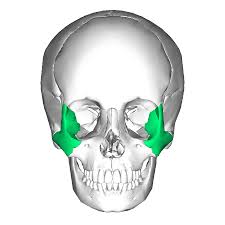
Zygomatic bone
2 bones, create the cheek bones of the face
Jaw Bones: Maxilla and Mandible
Maxilla: Mustache bone
Mandible: Jaw bone
TMJ: Temporomandibular joint
The joint between the maxilla and mandible
Sternum
AKA the breastbone, divided in 3 sections (top to bottom): Manubrium, Body, Xiphoid Process
Ribs
24 total ribs, 12 pairs
Protects heart, lungs, other thoracic organs/tissues
Makes up the thoracic cavity
Classification of Ribs
True ribs- Upper 7 ribs, connect directly to the sternum
False ribs- Ribs 8-10, connect to other ribs via costal cartilage
Floating ribs- Ribs 11-12
Parts of the Vertebrae
Spine, Transverse process, vertebral foramen, centrum (body)
Vertebral column
Consists of 5 different regions:
Cervical (7 vertebraes), Thoracic (12), Lumbar (5), Sacrum (5), Coccygeal (3-5)
Cervical region
7 vertebrae
C-1: Atlas
c-2: Axis
The atlas rests upon the axis on the odontoid process
C-7: Vertebral prominens: most prominent of the cervical vertebrae