propedeutics small animals- digestive system
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
-feeding and water: quantity, quality, appetite, thirst, mastication, salivation, swallowing
-vomit and diarrhea: quantity, quality
-management: changes in diet, foreign body
for a digestive system exploration, what type of information regarding the anamnesis should we get?
the mouth
at what part of the animal do we begin our digestive system exploration?
-lip position
-cheilitis (lip inflammation)/ wounds
-trismus (restriction of jaw movement)/ lockjaw
-difficulty opening the mouth
-sialorrhea (salivation)/ ptyalism (excess saliva)
-tongue exposition
-tumors
what do we need to observe regarding the external mouth?
hands on the jaw and mandible, fingers pressing lips toward the teeth. if the animal is dangerous, we use sedation and a gauze bandage to help
how should we open the mouth?
-mucous membranes
-tongue
-teeth
-hard palate
-soft palate
-salivary glands
-pharynx and tonsils
what should we observe when we open the mouth?
there is a congestion of blood
if the mucous membranes are red, what does this mean?
inflammation of the lips and mouth
what does stomatitis mean?
inflammation of the gums
what does gingivitis mean?
inflammation of the tongue
what does glossitis mean?
gingivitis
what is the medical term for inflammation of the gums?
benign mouth tumors
what is epulis?
malignant tumor
what is a melanoma?
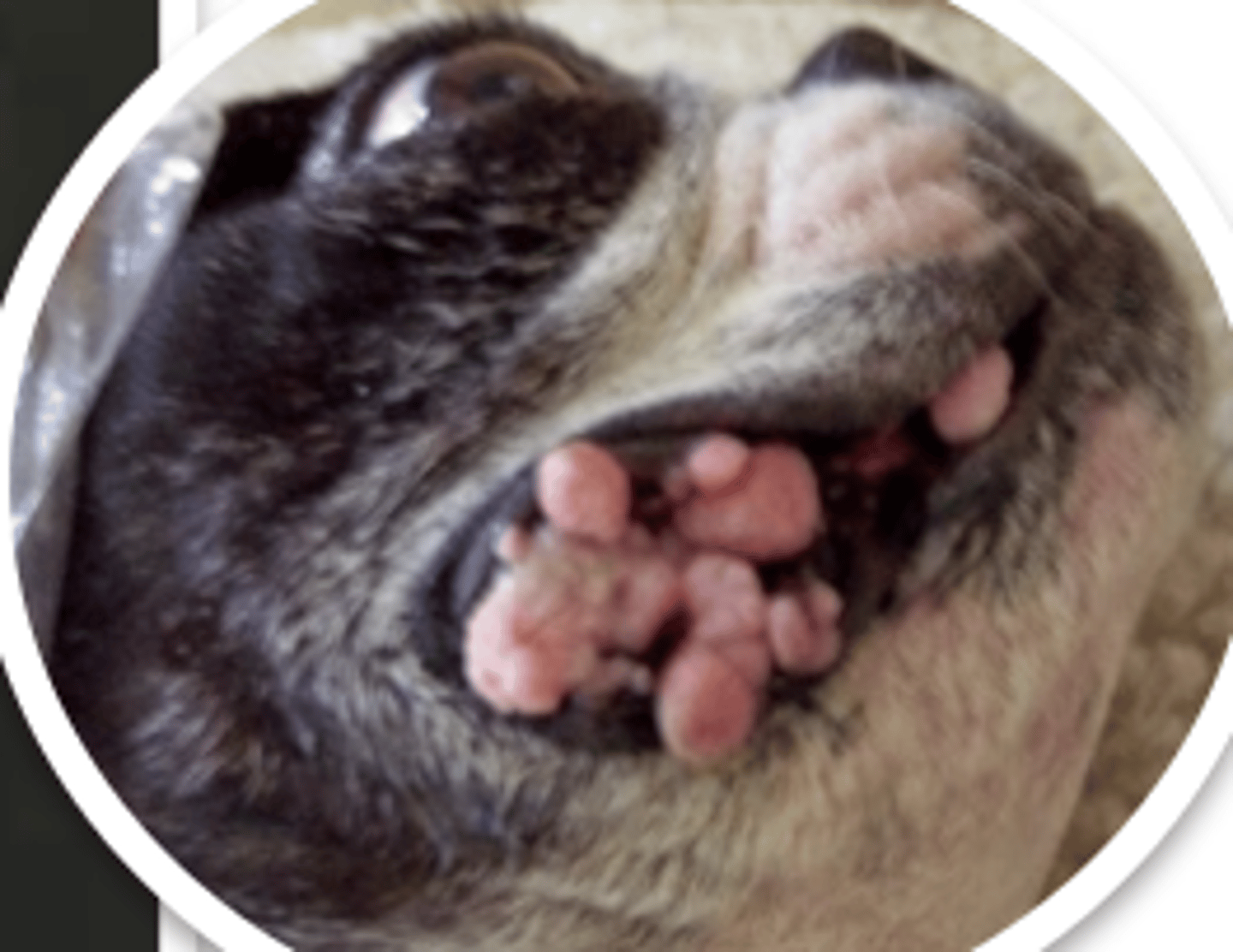
epulis
what are these called?

gingivitis
what problem does this animal have?
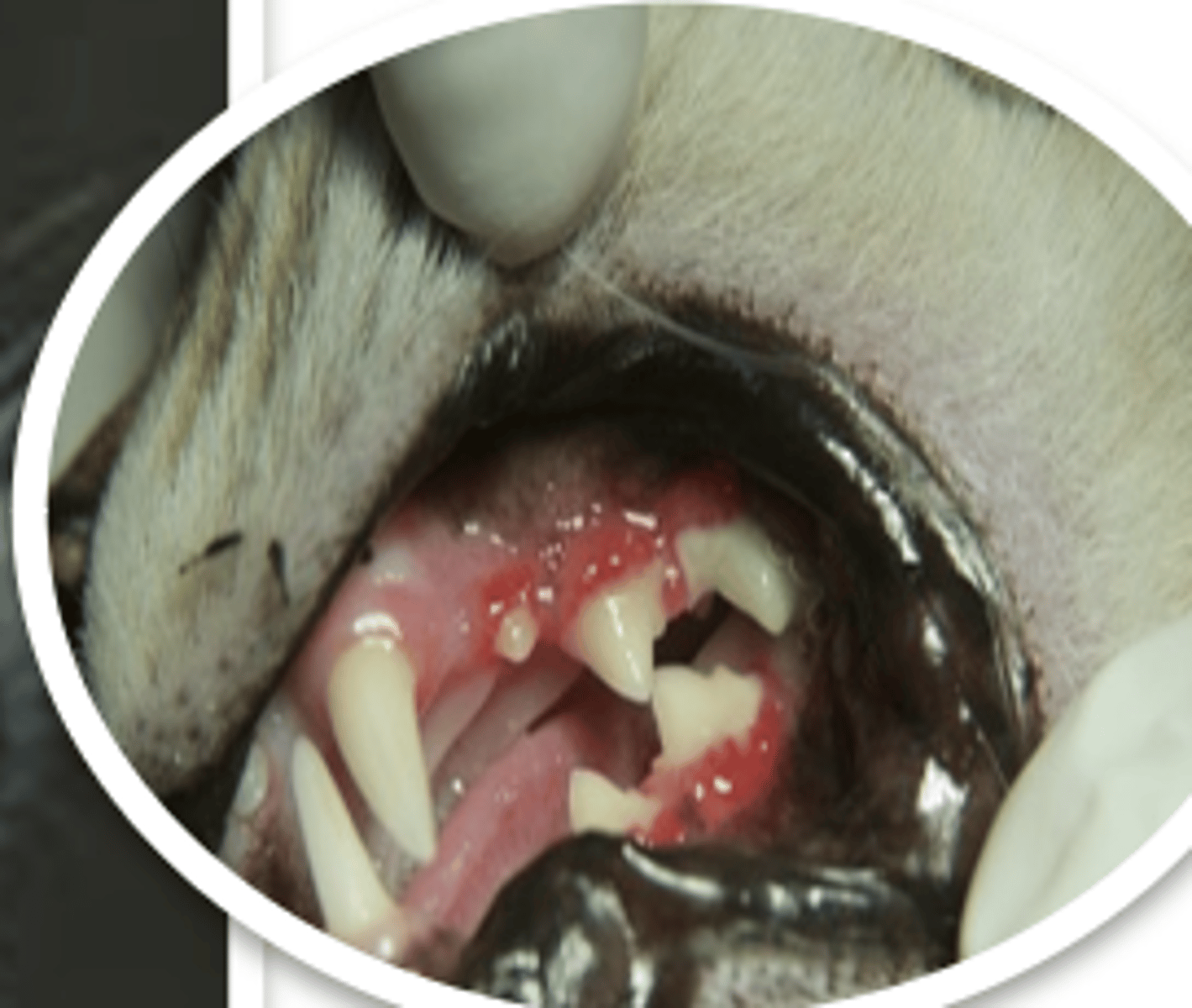
macroglossia
what is the medical term describing an excessively big tongue?
small tongue
what does microglossia mean?
XII- hypoglossal nerve
if there is paralysis of the tongue, what nerve may be injured?
brachyocephalic
the soft palate is elongated in which breeds?
halitosis
what is the medical term for bad breath?
distemper
enamel hypoplasia is a common effect of what disease?
an often chronic gum disease characterized by inflammation and infection of the structures that support the teeth, including the gums (gingiva), alveolar bone, cementum, and periodontal ligaments
what is periodontitis?
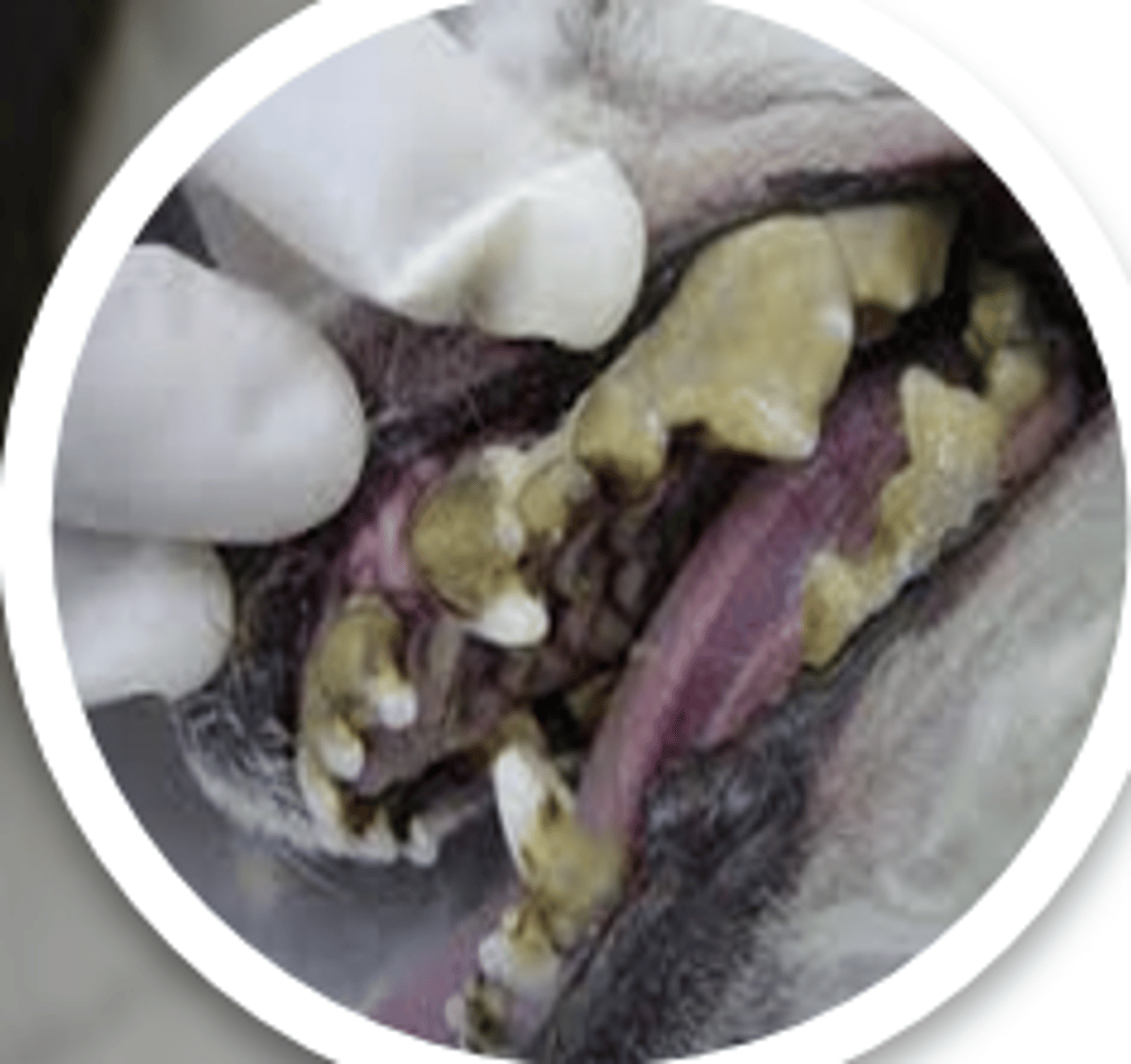
tartar buildup
what is creating this abnormal tooth color?
parotid, submandibular, sublingual, zygomatic
what are the 4 important salivary glands?
less saliva production/ dry mouth
causes: dehydration, drugs, panting, mouth breathing
what is hyposialia and what might cause it?
excess production of saliva
what is ptyalism?
-stomatitis, gingivitis, or glossitis
-foreign body
-drugs
-intoxications
what might cause ptyalism?
drooling- excess saliva production that leads to saliva uncontrollably leaking from the mouth
what is sialorrhea?
mandible fracture, foreign body, facial paralysis
what can cause sialorrhea?
inflammation of the salivary glands
what is sialadenitis?
the accumulation of saliva in a localized area due to the obstruction, trauma, or damage to a salivary gland duct (could be due to a foreign body)
what is a sialocele/mucocele?
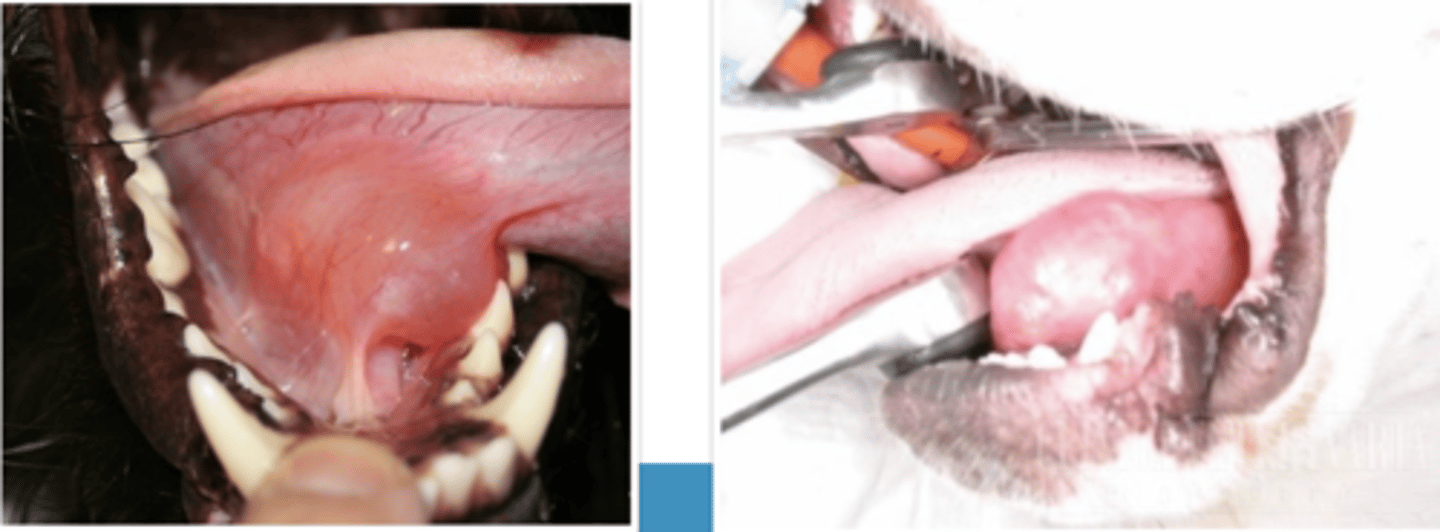
a mucocele of the sublingual gland, under the tongue
what is a ranula?
a ranula
what is this?
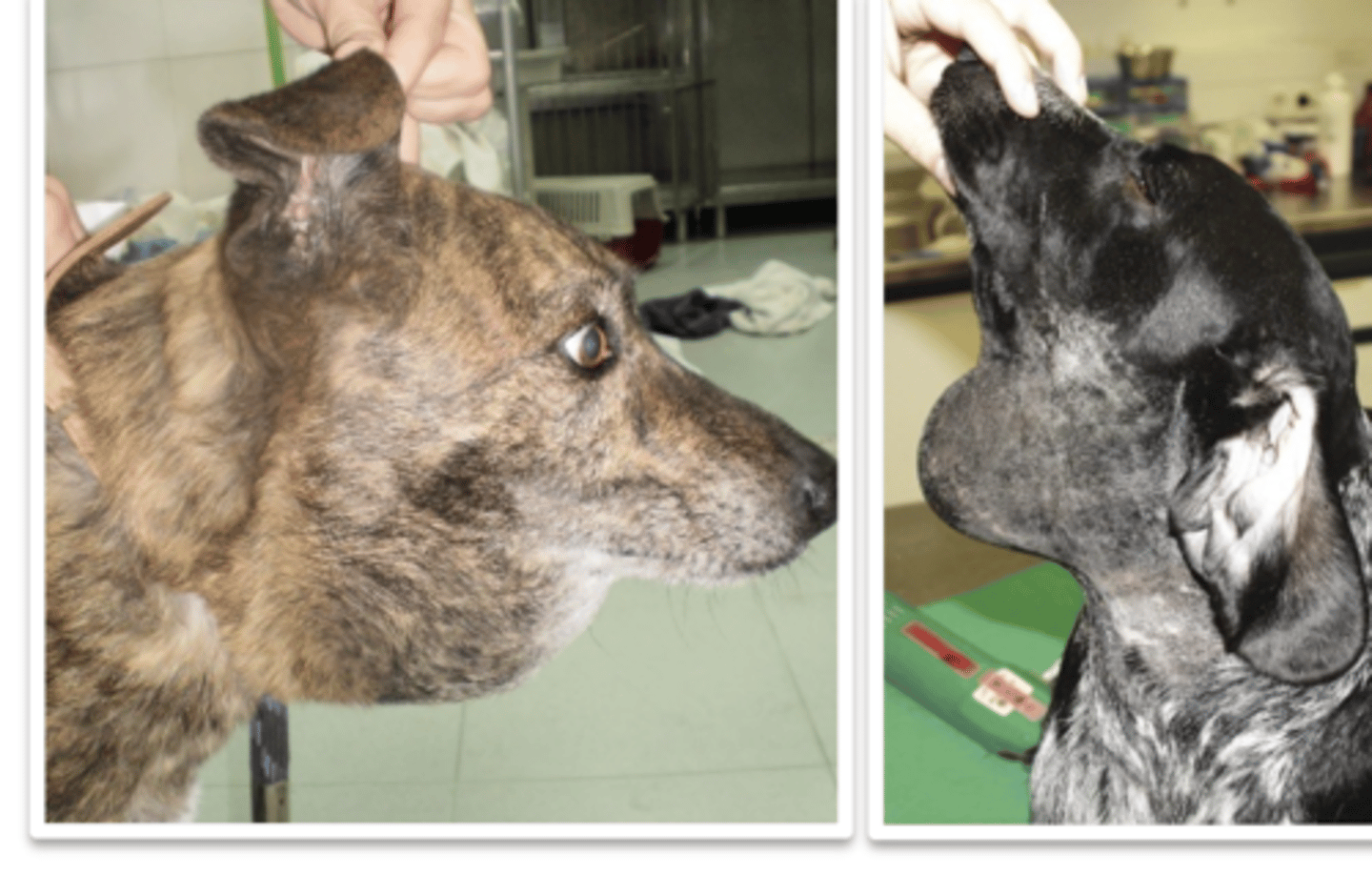
sialadenitis
what is the problem?
-inflammation
-neoplasias
-foreign body
-pharynx reflex
what do we check for in the pharynx and tonsils?
probing- tests acid levels
endoscopy
how do we inspect the esophagus internally?
epigastrium- xiphoid region
mesogastrium- flanks and umbilical region
hypogastrium- inguinal and prepubian region
what are the 3 divisions of the abdomen?
food, tumor
if the abdomen is generally increased in size and it feels solid, what could be inside?
ascites (liquid in peritoneal cavity), pyometra (womb infection)
if the abdomen is generally increased in size and it feels liquid, what could be the problem?
hernia, tumor, bruises, abscesses, edema, heart problems, hyperproteinemia
if the abdomen is increased in size but only in a certain area (localized), what could be the problem?
solids- food, tumors
liquids- ascites, pyometra
gas
what could be the issue?
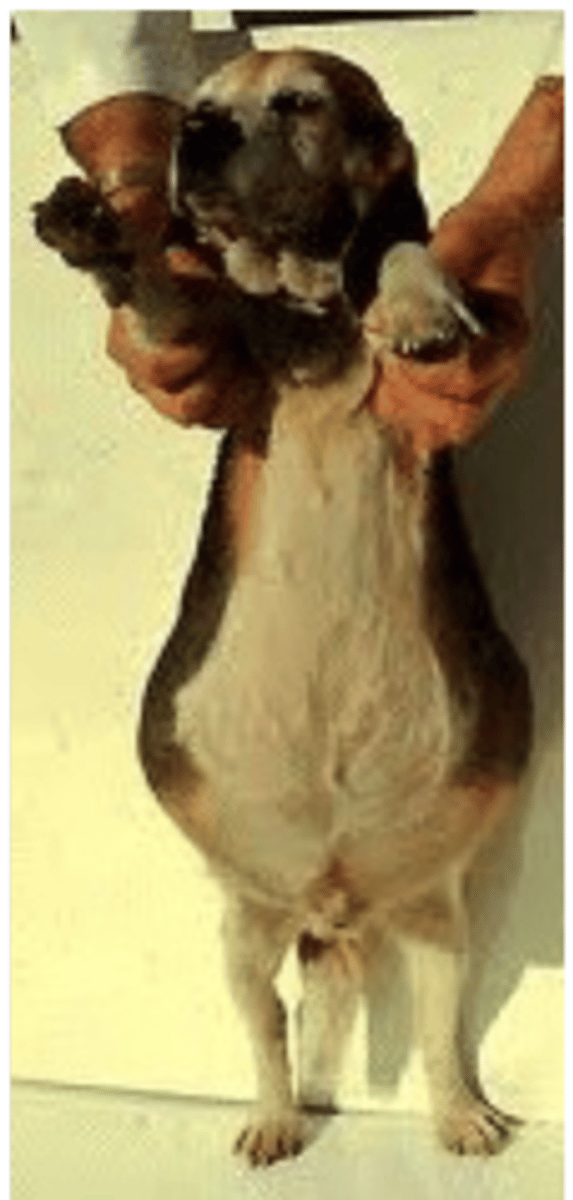
visceras, feces, tumors, tension
what can we feel when palpating the abdomen?
-peritonitis
-gastric or intestinal meteorism
-foreign body
-gastritis
-hepatitis
-pancreatitis
what issues might cause increased abdominal wall tension?
bladder and intestines
in normal conditions, what organs can we palpate in the abdominal region?
palpation and ausculation
and percussion- hit the abdomen on one size with the other hand on the other side, if there is fluid we feel the "abdominal fluid wave"
how do we check for free fluid in the abdominal cavity?
the liver
what is being percussed?
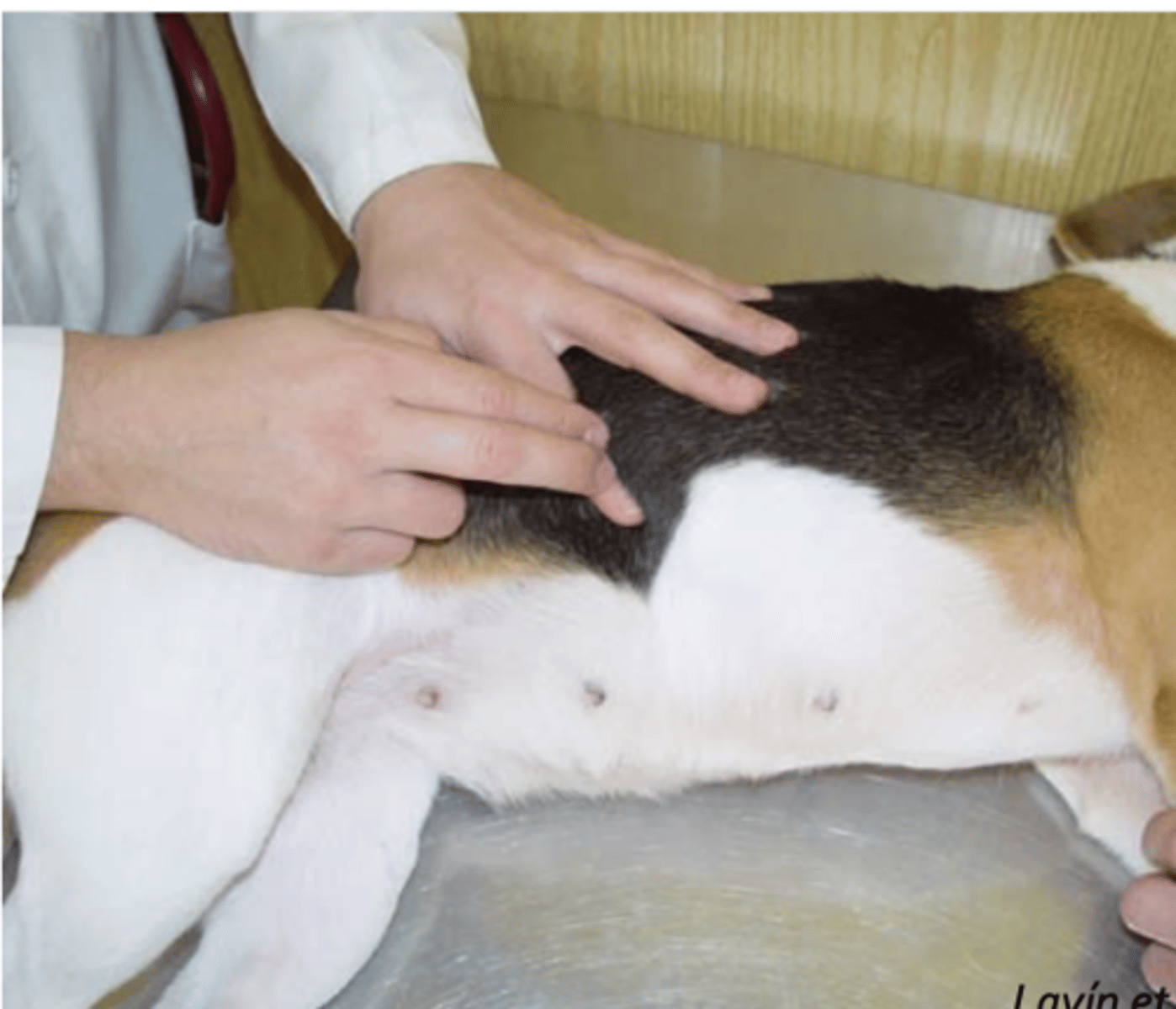
3-4 each minute
what is the normal amount of borborigms to hear when auscultating the abdominal cavity?
-hypermotility
-enteritis
-diarrhea
if there is an increased amount of borborigms per minute, what might be the cause?
-hypomotility
-paralytic ileum
-constipation, obstruction, impaction
what might be causes of a decreased amount of borborigms?
with the index or little finger
how do we palpate the anus?
-sphincter (agenesis, tonicity)
-rectal mucous (tumors, polyps)
-prolapse
-prostate
-anal glands (fistulas)
what should we evaluate when performing a rectal exam?
a rectal exam
what is the vet doing?
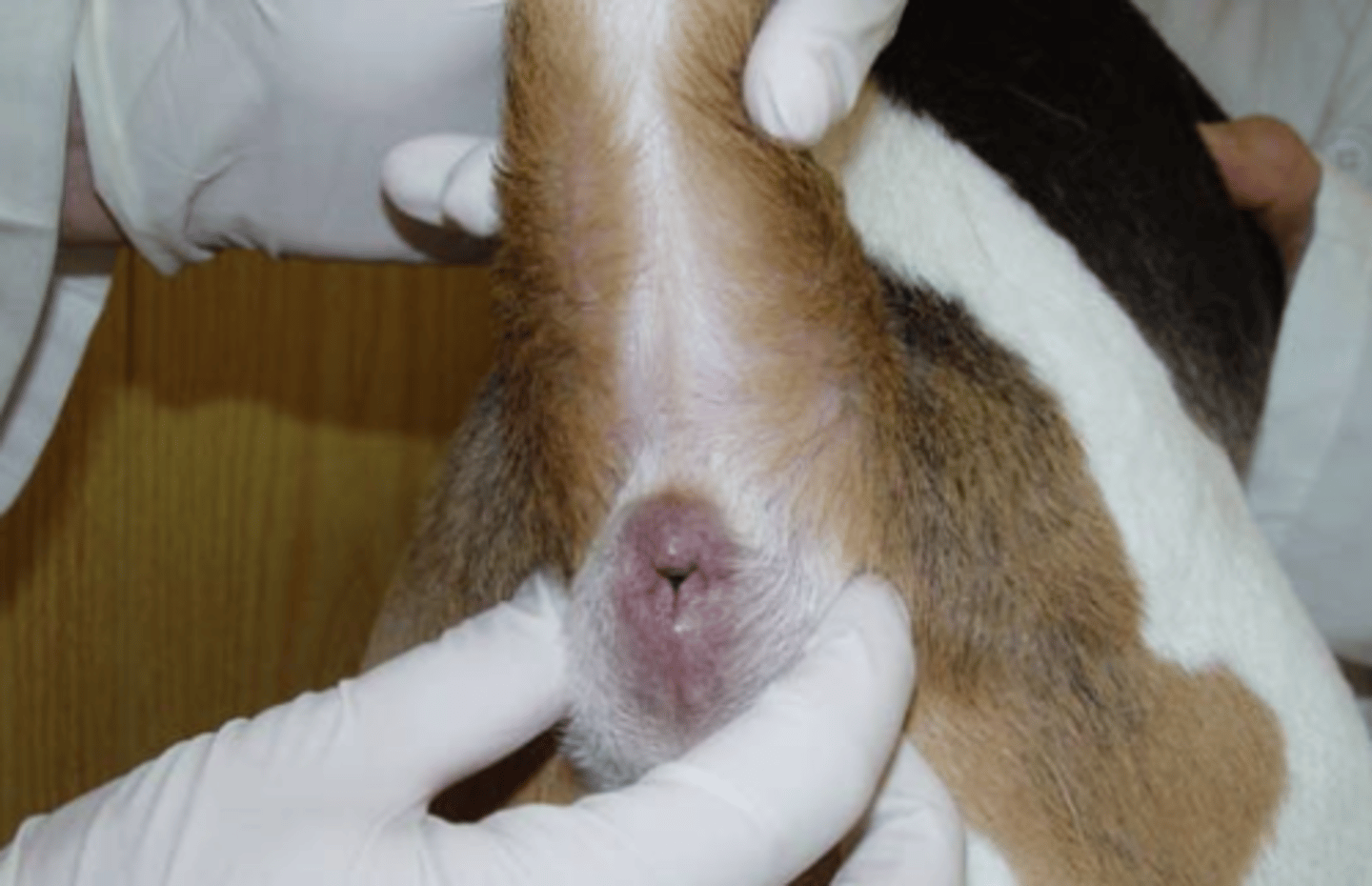
rectal prolapse
what is the issue?
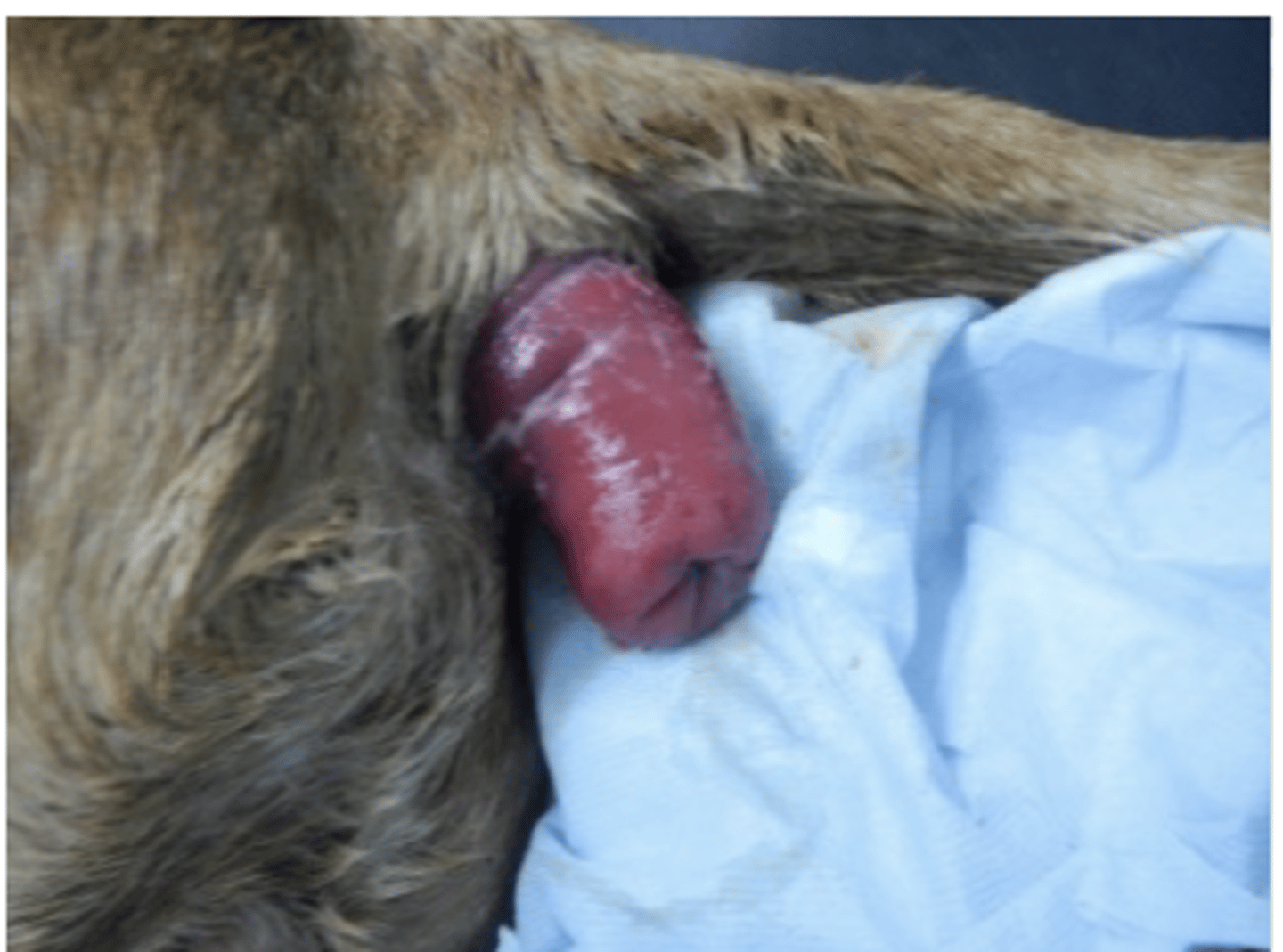
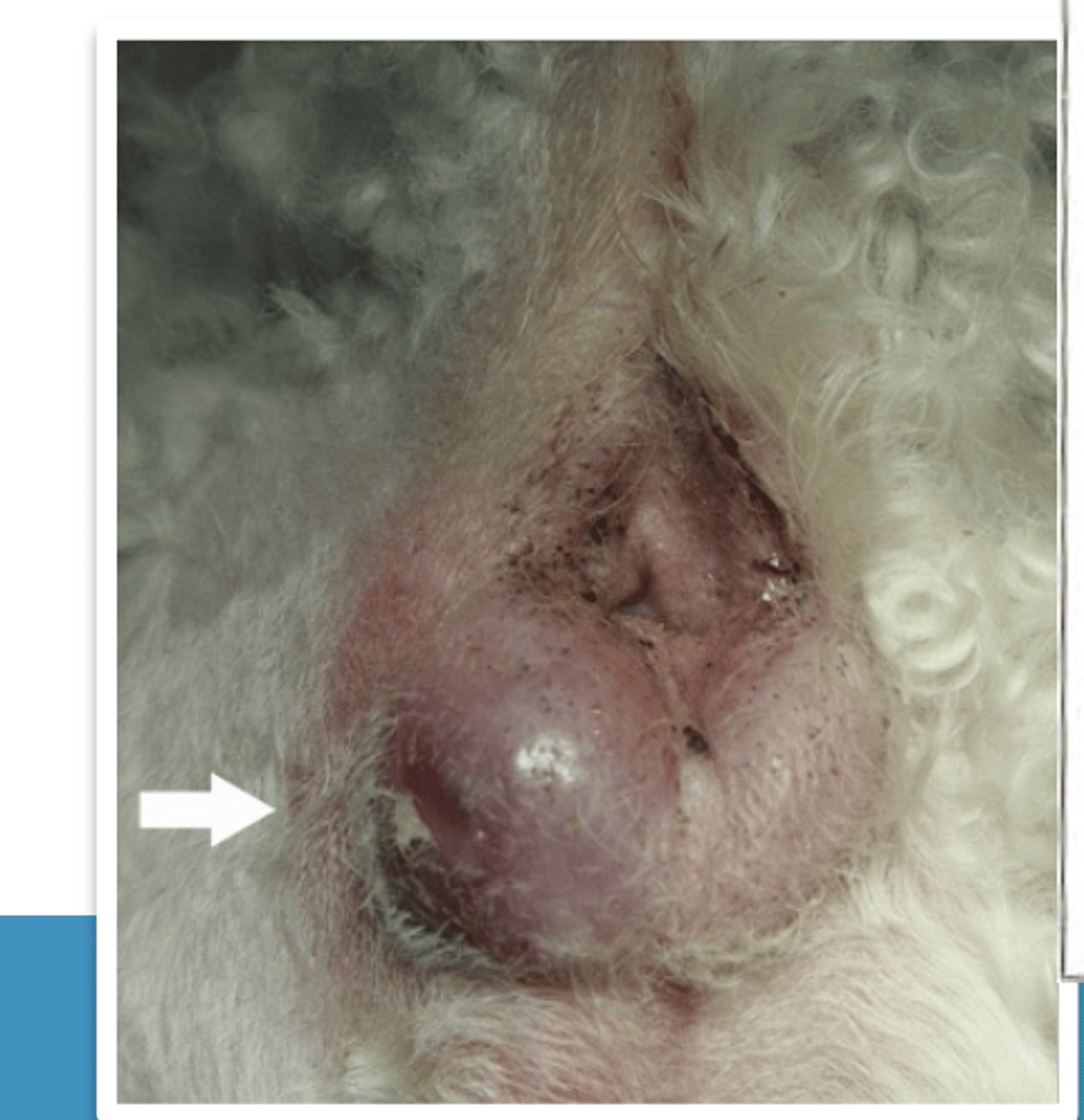
anal gland inflammation
what is this issue?
a procedure where we make an incision into the abdominal wall to access the abdominal cavity
what is a laparotomy?