NUTR 201: Final Exam SDSU
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Nutrition
ingestion, digestion, absorption, metabolism, and storage
Food Science
food analysis, sensory analysis, food chemistry, and product development and testing
Classes of Nutrients (6)
carbs, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water
Phytonutrients
nutrients in PLANT FOODS
Zoonutrients
nutrients in ANIMAL FOODS
Function of nutrients
- Provide energy for metabolism
- Build and repair body tissues
- Help regulate body processes
calorie
energy required to increase the temperature of one gram of water by 1*C
Calorie
dietary calorie
1 Calorie = ___ kilocalorie = ___ calories
1 kilocalorie; 1000 calories
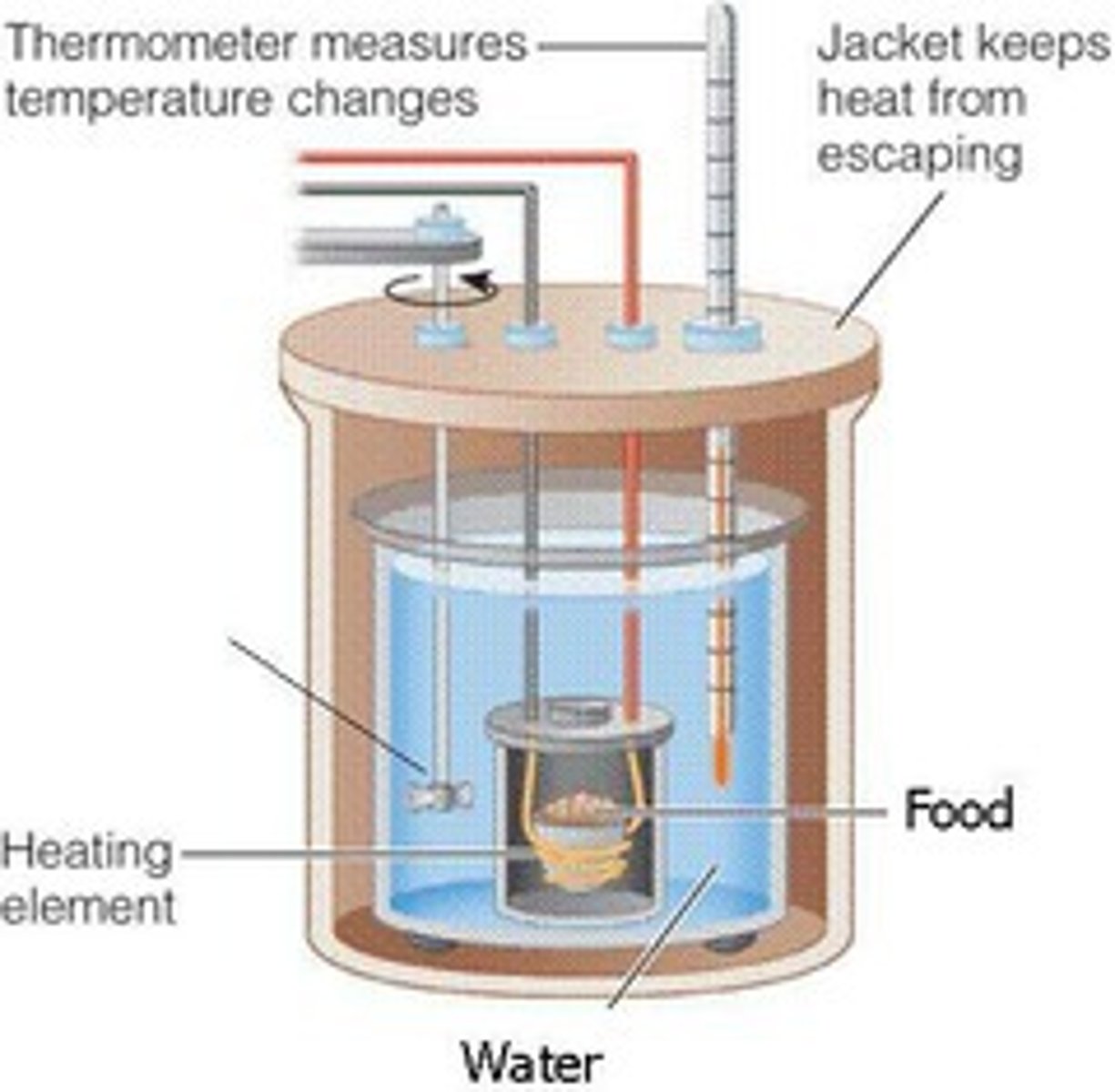
Bomb calorimeter
an instrument that measures the heat energy released when foods are burned, thus providing an estimate of the potential energy of the foods
kcal/g for carb, fat, protein, and alcohol
carb - 4kcal/g
fat - 9kcal/g
protein - 4kcal/g
alcohol - 7 kcal/g
Macronutrients
Fat, Protein, and Carbs
- required in large amounts
Micronutrients
vitamins and minerals
- required in small amounts
Nonessential nutrients
can be made by body
Essential nutrients
cannot be made by body
Top 10 Leading Causes of Death in United States
1. heart disease (28%)
2. cancer
3. stroke
4. chronic lung disease
5. accidents
6. diabetes mellitus
7. pneumonia and influenza
8. alzheimer's disease
9. kidney disease
10. blood infections
Major Diet Related Diseases
1. coronary heart disease
2. stroke
3. diabetes mellitus
4. hypertension
5. obesity
6. certain forms of cancer
7. osteoporosis
8. liver disease
9. mental health
4 Principles for Avoiding Malnutrition
1. variety
2. balance
3. moderation
4. nutrient density
Dietary Guildlines for Americans
1. healthy eating pattern across the lifespan
2. focus on variety, nutrient density, and amount
3. limit calories from added sugar, saturated fats, and reduced sodium
4. shift to healthier food and beverage choices
5. support healthy eating patterns for all
Consume less than ____% of calories per day from added sugars.
10%
Consume less than ____% of calories per day from saturated fats.
10%
Consume less than ______mg of sodium per day.
2300mg
Alcohol: Only ___ drink(s) per day for women.
1
Alcohol: Only ___ drink(s) per day for men.
2
Adults should at least spend ______ minutes of moderate intensity physical activity each day.
150 minutes
Adults should spend _____ days or more of muscle strengthening exercises per week.
2 or more days
Children (6-17 y/o) should spend at least ____ minutes doing physical activity per day.
60 minutes
Leading Reasons for Food Selection in US
flavor and cost
RDA
Recommended
Daily Allowance
- for nutritional needs of practically all healthy persons
AI
Adequate Intake
- used when evidence isn't considered good enough to call it an RDA
EAR
Estimated Average Requirement
- meet needs of the average person, can help establish the RDA (is 2 standard deviations above)
UL
Tolerable Upper Intake Level
- the level we should not exceed
EER
Estimated Energy Requirement
- takes sex, age, weight, height, and physical activity level into account
AMDR
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range
- carbs = 45-65%
- fat = 20-35%
- protein = 10-35%
Nutrition Label Requirements
- list of Ingredients
- serving size
- servings per container
- amount per serving (total calories, calories from fat, total fat, saturated fat, trans fat, sodium, cholesterol, total carbs, dietary fiber, sugars, protein, Vitamin A & C, calcium, and iron)
Changes to new food labels
- adding added sugars
- removing Vitamin A & C
- adding Vitamin D & potassium
- removing calories from fat
Voluntary on Nutrition Labels
- kcal from sat/polyunsat/monounsat fat
- soluble fiber
- insoluble fiber
- sugar alcohols
- other carbs and micronutrients
- Daily Value
- Reference Daily Intakes
- ingredients that may cause reactions in food sensitive consumers
Food Label Claims by FDA
- health
- nutrient content
- structure function
"Low calorie"
40 calories or fewer per serving
"Reduced calorie"
at least 25% lower in calories than regular food
"Calorie free"
fewer than 5 calories per serving
"Trans fat free"
less than 0.5 g trans fat and less than 0.5 g of saturated fat per serving
Pesticides
1. avoid direct contact
2. most fruits and vegetable have no pesticides or negligible amounts within safe limits for adults
3. fish from contaminated waters may contain high levels of pesticides
"100% organic"
- made with 100% organic ingredients
- USDA logo can be used
"Organic"
- minimum 95% ingredients are organic
- may include USDA logo
"Made with organic ingredients"
- 70%-94% is organic
- cannot use USDA label
ingredient panel only*
- less 70% organic
- organic can only be used on ingredient panel
How to eat food on a budget?
1. get unpackaged whole food
2. sales, but not unhealthy choices
3. deals and groupons online before you go
4. farmers market
5. buy seasonal and local foods
6. meal prep
7. choose the right supermarket
Quackery
1. big business
2. sales people use questionable scientific info
3. expected benefits are trivial compared to extravagant claims (no legitimate basis)
Where can you find accurate information regarding nutrition?
- books on nutrition (textbooks)
- scientific journals (important not to overinterpret)
- governmental agencies (USDHHS, USDA, FDA, etc)
- scientific organizations (AND, ASN, etc)
- nutrition professionals
Processed food
1. prevents spoilage
2. some food enriched or fortified
3. some nutrients may be lost
4. problem is the excessive use of highly refined products
Purpose of additives in food
1. flavor
2. enhanced color
3. improve texture
4. preserve the food
- must be generally recognized as safe (GRAS) to earn FDA approval
Digestion
breaking down macronutrients to yield nutrients ready for absorption
Absorption
movement of nutrients from intestinal tract to the circulation
Upper GI Tract
- oral cavity
- esophagus (LES)
- stomach (pyloric sphincter)
gastroesophageal sphincter
- separates the esophagus from the stomach
- closes to prevent the stomach contents from re-entering the esophagus
Lower GI
- small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
- large intestine/colon (cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid)
- rectum
Accessory Organs
liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Role of the Stomach
- mixing
- secretion of gastric juices:
1. HCL= protein denaturation and kills bacteria
2. pepsin
3. mucus for protection
4. intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption)
- production of hormones
Secretions of pancreas
- enter at duodenum
- biocarbonate = increases pH
- enzymes = breakdown protein, fats, and carbs
role of small intestine
Secretions of gallbladder
- enter duodenum
- bile acids = made in liver and allow fat digestion and absorption
role of small intestine
Role of the Large intestine
- water absorption
- electrolyte absorption
- bacterial action (fermentation, some vitamin production, probiotics v. prebiotics)
Probiotics
beneficial live bacteria found in certain foods or supplements
Prebiotics
special form of dietary fiber that acts as a fertilizer for the good bacteria in your gut
The rate at which food leaves the stomach is influenced by...?
- volume
- consistency
- composition of chyme
Amount of time between ingestion of food and its elimination?
24-72 hours
- fiber moves faster
Factors affecting transit time of food out of the body
- composition of diet
- illness
- certain medications
- physical activity
- stress/emotions
Major mechanisms of Absorption
- diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
- active transport
Energy Metabolism
chemical reaction involved in breakdown, synthesis, and transformation of energy yield nutrients
Metabolic Pathways
a series of enzymatic reactions that converts one biological material to another
Catabolic
breaking down molecules
Anabolism
synthesis of molecules
Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions
- reversible
- enzymes
- many types
- cofactors / coenzymes often assist enzymes
Enzymes
catalysts that speed of chemical reactions
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
- provides energy needed for biosynthesis, muscle contractions, active transport
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of chemical reactions that transfer electrons and 4 hydrogen ions from reducing agents along protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane producing ATP
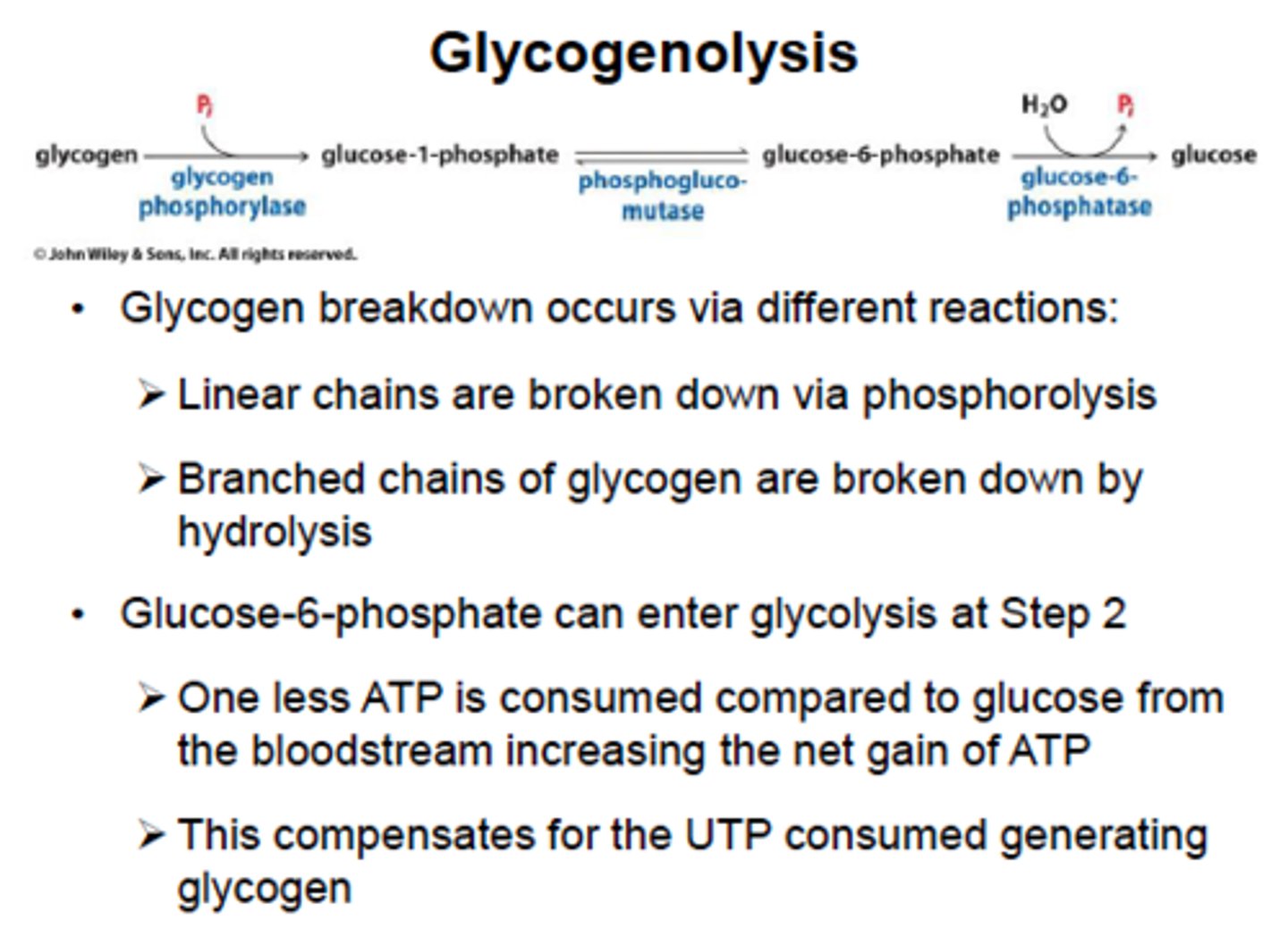
Glycogenolysis
start with glycogen,
end with individual glucose molecules
Glycolysis
breakdown of glucose to pyruvate or lactate
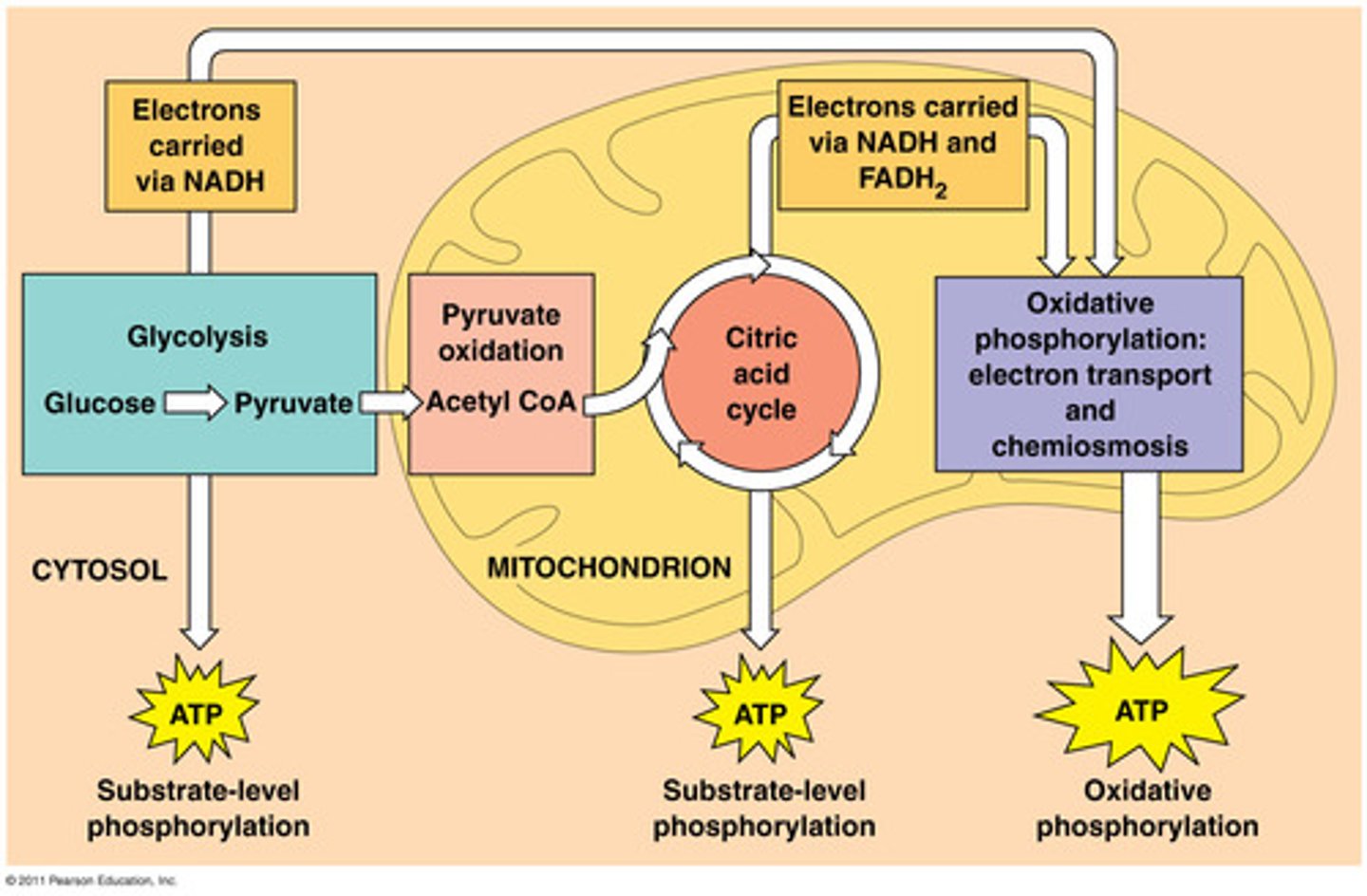
Kreb Cycle
Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA)
- major pathway used during aerobic conditions
- forms guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and reduced coenzymes (NADH + H+ and FADH2)
Fat Catabolism
breakdown of triglyceride molecules into glycerol and fatty acids when available energy sources are low
- lipolysis is followed by beta-oxidation
Lipolysis
the breakdown of fats and other lipids by hydrolysis to release fatty acids
Beta Oxidation
breakdown of fatty acids
Protein Catabolism
- first broken down to amino acids
- supplies <10% of daily ATP
- transamination
- deamination
- krebs cycle
- election transport chain
Transamination
transfer of amino group from an amino acid to alpha ketoacid
Deamination
removal of amino group from an amino acid to produce alpha ketoacid
Anabolic Pathways
- gluconeogenesis
- glycogenesis
- lipogensis
- ketogensis
- protein synthesis
Gluconeogenesis
formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources
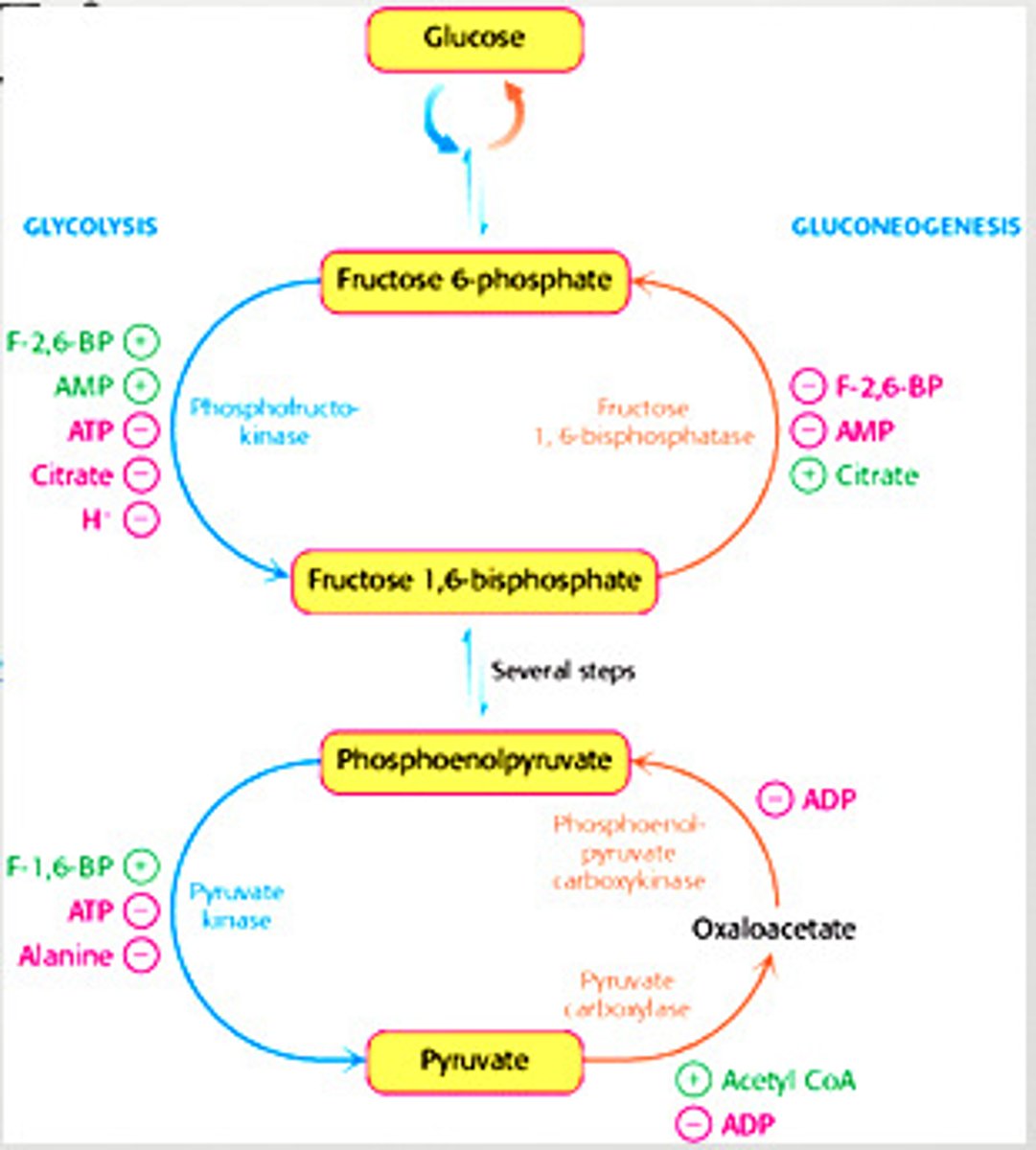
Glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose
Lipogenesis
excess glucose or amino acids make triglyceride (fatty acids or lipids)
Ketogenesis
- usually occurs at higher rates during starvation, consumption of a low carbohydrate diet, or during uncontrolled diabetes
- accumulation of acetyl coA results in ketones
Protein synthesis
- transcription: DNA --> RNA
- translation: RNA --> protein
Where do carbs come from?
photosynthesis
Monosaccharides
glucose, galactose, fructose
- ready for absorption from the gut without further digestion
Disaccharides
lactose = galactose and glucose
maltose = glucose and glucose
sucrose = fructose and glucose
Complex Carbs (polysaccharides)
starch - storage form in plants
glycogen - storage form in humans
non-digestible fiber
Insoluble Fiber
cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin
- wheat and other plant foods
Soluble Fiber
pectins, gums, beta-glucans
- fruits, most grains, beans
What are primary sources of digestible carbohydrates?
grains, fruit, and vegetable
- other sources: dairy, protein, and sweets
Dietary Goals of Carbs
1. AMDR: 45-65% calories
2. RDA: 130g/d & an
upper limit for sugar of 10%
3. Daily Reference Value is 300g
4. Fiber: RDA 25g women and 38g men
Absorption of Carbs
- almost all monosaccharides
- glucose and galactose by active transport
- fructose by facilitated diffusion
- fructose and galactose are converted to glucose in liver and used or sent into blood stream
- glucose metabolized by liver or sent through bloodstream to other tissue/cell (most important physiologically and RBC love)