Bio 1 chapter 5-6 test prep
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
List and explain the 4 things ecologist use to study populations
growth rate-how the population’s #’s are changing.
population density- # of individual per unit area.
range/population distribution-how individuals in a population are spread across an area.
age structure- # of male and female individuals in a area for each age.
3 things that affect a population's growth
migration
birth rates
death rates
immigration vs emigration?
immigration is when individuals from another area come to a new area. emigration is when individuals leave a area.
exponential growth vs logistic growth?
Exponential growth is population growth with an steadily accelerating rate, while logistic growth is the growth rate that slows and levels off at a carrying capacity.
what event caused the exponential growth of the world's population and when was this?
The industrial revolution, 500 years ago.
what is carrying capacity?
the maximum population size of a species that an environment can sustainably support over time
density dependent vs density independent limiting factors: definition and examples?
Definition: Environmental factors whose effects on a population change with the population's density. As a population grows, the impact of these factors increases.
Examples: Competition, Preditation, Disease and Parasitism, overcrowding, herbivory.
Definition: These are factors that affect a population's size, but their impact is not determined by the population's density.
Examples: Natural disasters, Extreme weather, Pollution, and Habitat destruction.
Malthus and the principle of population
Malthus's principle of population, argues that population grows exponentially while food production increases at an arithmetic rate. This imbalance leads to a struggle for existence, with "positive checks" like famine, disease, and war inevitably keeping the population in check with the means of subsistence
3 steps of demographic transition
both birth and death rates are high and population growth is slow
death rates fall while birth rates remain high, causing rapid population growth
where birth rates start to decline while death rates stay low, causing population growth to slow
habitat vs niche
A habitat is the physical environment where an organism lives, while a niche is the organism's functional role or "job" within that habitat
habitat vs microhabitat vs microbiome
A habitat is the larger physical environment where an organism lives, a microhabitat is a small, specific area within that habitat with unique conditions, and a microbiome is the entire community of microorganisms that live in a particular environment
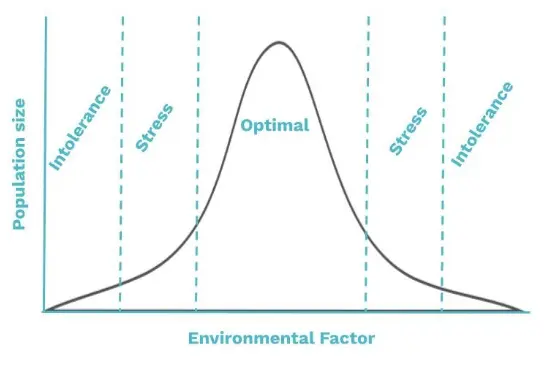
tolerance and the chart used
Tolerance is an individual's ability to survive and reproduce under different circumstances.
The use the chart of tolerance:
Competitive Exclusion Theory
two species with identical ecological niches cannot coexist in the same habitat indefinitely because one will inevitably outcompete the other for the same limited resources
Keystone species
an organism that has a large impact on its ecosystem and maintaining its structure and balance.
3 main types of symbiosis: examples and explain
mutualism- when the two individuals in the symbiotic relationship both benefit. EX. sea anemonie and clown fish. Sea anemonie provides a place for the clown fish to live and the clown fish then feeds the sea anemonie with it waste.
commensalism- when the one individual in the symbiotic relationship benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.EX. barnacles and whales, barnacles get place to live and eat and whales are unfazed.
parasitism- when an individual benefits off another individual causing harm. EX. tape worms and humans. tape worms eat our nutreints and leave none for us.
primary vs secondary succession
Primary succession begins on land without soil, such as after a volcanic eruption, and takes a very long time (1000+ years) to establish life. Secondary succession occurs in an area that was previously inhabited but has been disturbed, such as by a forest fire or hurricane, and is much faster (50-200 years) because soil and some life remain.
pioneer species
a species that is first to inhabit an area.
climax community
a stable, mature ecological community that represents the final stage of natural succession.