PNB 2264 Lab Practical #2 Study Guide
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
What is a muscle twitch?
A single contraction in a relaxation cycle observed in a musculoskeleton fiber
What is summation?
Applying multiple stimulus within a short duration (especially when effect from a previous stimulus has not completely disappeared) an increase in contractile force is visible
What is tetanus?
When muscle fiber contraction reach a point where they remain constant. When the stimulus frequency increases, the muscle fibers don't have time to relax and their contractile forces fuze together
What is muscle fatigue and why does it occur?
The decline in ability of a muscle to generate force. It occurs because of conduction failure, lactic acid buildup, and inhibition of cross bridge cycling
What is the first step of cross bridge cycling?
Cross bridge formation: phosphorylated myosin head attaches to an actin myofilament
What is the second step of cross bridge cycling?
the power stroke:
1) ADP and Pi are released from the myosin head
2) Myosin head changes to bend, low-energy state
3) Shape change pulls the actin towards the M line
What is the third step of cross bridge cycling?
Cross bridge detachment: ATP attaches to myosin, breaking the cross bridge
What is the fourth step of cross bridge cycling?
Cocking of the myosin head: attached ADP is hydrolyzed by myosin ATPase into ADP + Pi, bringing it back to a high-energy state
As you increase voltage to the muscle fibers, describe how they respond to the increased stimulus
As the voltage is increased, the muscle contractions will increase up to a certain point
What is the Maximum Excitation Voltage?
The stimulus voltage at which the response no longer increases
What is supra maximal voltage?
A stimulus that has the strength significantly above that required to activate all the nerve or muscle fibers in contact with the electrode; used when response of all the fibers is desired
What is the all-or-none phenomenon?
The strength at which a nerve or muscle fiber responds to a stimulus is independent of the strength of the stimulus. If the stimulus exceeds the threshold potential, the nerve or muscle fiber will give a complete response; otherwise, there is no response
In light of the all-or-none law of muscle contraction, how can you explain graded potential?
The all-or-none phenomenon regarding muscle contractions involves the idea that no matter how intense the stimulus, as long as membrane potential reaches threshold, an action potential will fire without variations to the intensity.
Graded response on the other hand involves muscles responding with different degrees of force due to recruitment of multiple motor units, stimulus intensity, frequency and length-tension curve. All of these things acting together give a graded response of the muscle fibers
What is muscle recruitment?
Activation of additional motor units to accomplish an increase in contractile strength in a muscle.
The higher the recruitment, the stronger the muscle contraction will be.
How does resting fiber length affect muscle tension?
If you have a very stretched out muscle, there will be little crossover between filaments leading to very little force being generated
Optimal length is when you have maximum cross bridges between thin and thick filaments
Too much overlap is not good or effective
Which sacromere represents optimal muscle length and will generate he strongest tension shown in the length-tension curve?
Sacromere C
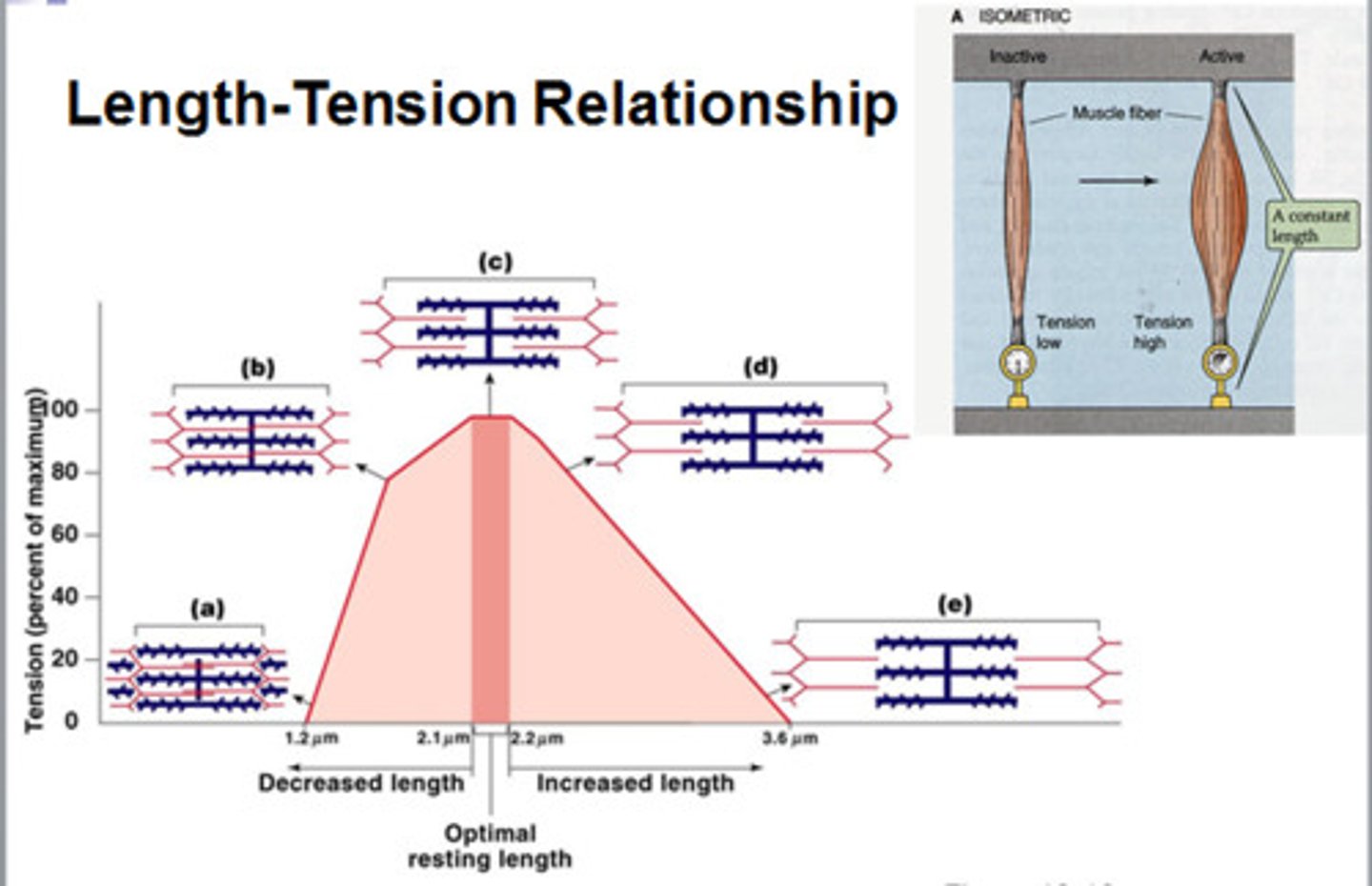
The strength of a single skeletal muscle fiber twitch:
a) is increased with fiber stretch up to some optimal length
b) is increased by stimulus magnitude up to some maximum
c) is unaffected by stimulus frequency
a) is increased with fiber stretch up to some optimal length
A single muscle twitch:
a) lasts much longer than a single action potential
b) lasts for about the same time as a single action potential
c) lasts for a much shorter time than a single action potential
a) lasts much longer than a single action potential
In a whole skeletal muscle:
a) motor units are all of the same size
b) motor units have different excitatory thresholds
c) each motor unit consist of a single nerve axon supplying one muscle fiber
b) motor units have different excitatory thresholds
The strength of contraction of a whole skeletal muscle:
a) is unaffected by stimulus frequency
b) is increased by stimulus magnitude up to some maximum
c) is not dependent on the total number of muscle fibers
b) is increased by stimulus magnitude up to some maximum
Summation occurs:
a) when a supra maximal stimulus is given
b) when the muscle fiber is stretched
c) when stimuli are delivered rapidly enough so that the muscle fiber does not relax completely between stimuli
d) when two or more motor units are activated at the same time
c) when stimuli are delivered rapidly enough so that the muscle fiber does not relax completely between stimuli
Fatigue in the isolated muscle can occur from:
a) lactic acid buildup
b) elevated extracellular K in T-tubule from repeated depolarization
c) buildup of ADP and Pi that directly inhibit cross-bridge cycling
d) all of the above
d) all of the above
Muscle tetanus:
a) results from muscle fatigue
b) results when stimulus frequency is so high that there is no time for relaxation between stimuli
c) never occurs in the intact animal
d) cannot generate a contractile force as strong as during muscle summation
b) results when stimulus frequency is so high that there is no time for relaxation between stimuli
Why is it that in a state of rigor mortis, the muscles are highly contracted and difficult to manipulate?
There is a lack of ATP which leads to myosin heads to be firmly attached to the actin filament binding site
What is membrane potentials resting condition under normal circumstances?
-40 to -75 mV
When are action potentials formed and what are they used for?
Formed when the membrane is depolarized. They are used to transmit information from one part of the cell to another
What prevents voltage gated Na+ channels from closing?
Batrachotoxin
What causes voltage gated Na+ channels from opening (irreversible)?
Tetrodotoxin
The intracellular and extracellular concentration are the same for cation A. The resting membrane potential is -70 mV. What is the net driving force for A during the resting stage?
a) no net driving force
b) move from intracellular to extracellular
c) move from extracellular to intracellular
c) move from extracellular to intracellular
What is stimulus artifact?
Cause by the spread of part of the stimulus voltage to the recording electrodes
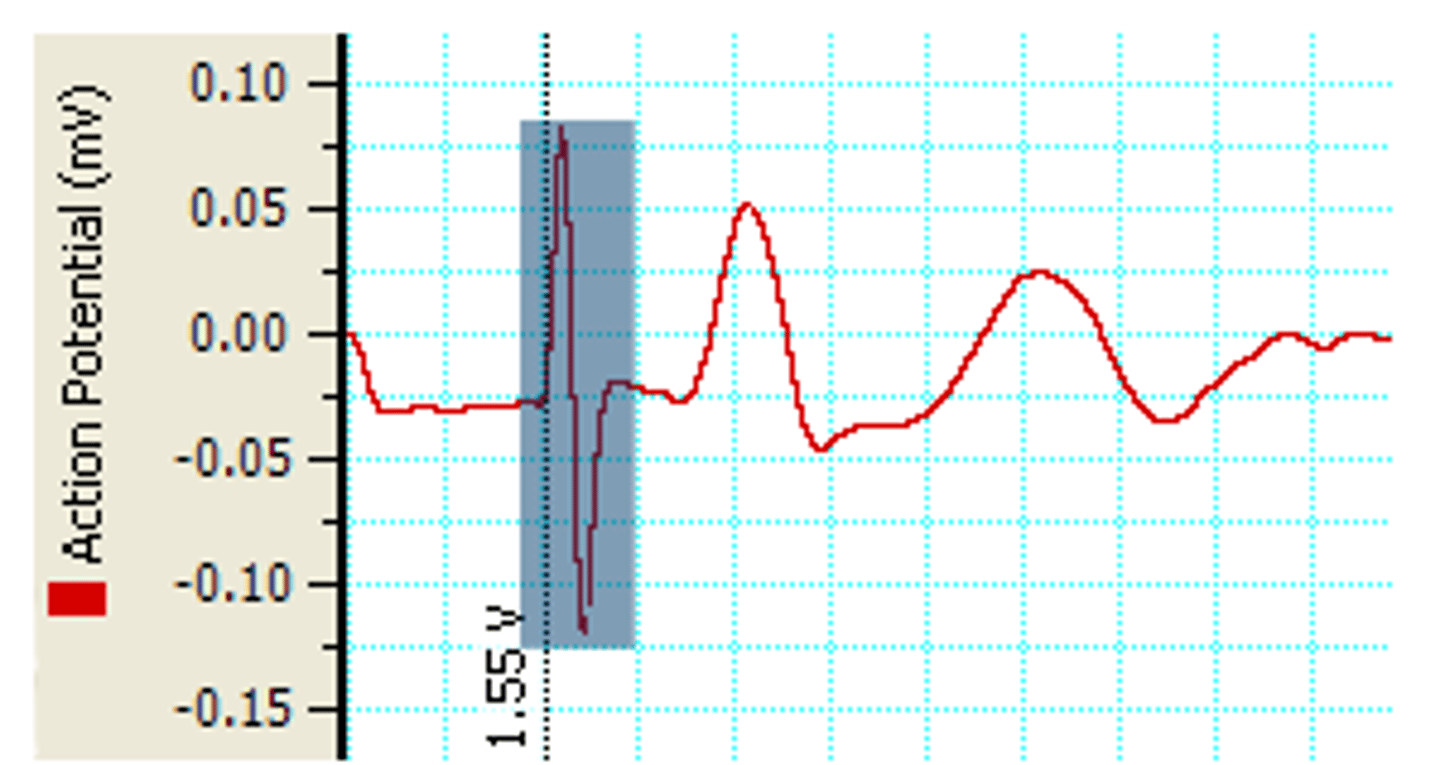
What is the threshold voltage?
The voltage at which a response is first seen
What does the delay from the stimulus artifact to the nerve impulse response reflect?
The time taken for the action potential to travel from the stimulating electrode
What is the basic formula used for calculating conduction velocity?
Distance/Time
What is the formula used for calculating the conduction velocity by the absolute method of a single distance and its corresponding latency period?
Distance 1/Latency Period 1 (or Distance 2/Latency Period 2)
What is latency period?
The time between the beginning of the stimulus artifact to the beginning of the recorded action potential
What is the formula for calculating conduction velocity by the difference method?
(D1-D2)/(LP2-LP1)
What is refractory period?
The largest interval at which a second spike in action potentials cannot be evoked
Why do we observe in biphasic waveforms recording?
This is caused by the electrodes picking up the propagating action potential. Recorded is the electric potential difference between bipolar electrodes. The reading is due to the voltage difference between two recording electrodes while AP propagate through the axon. The recording indicate the propagation of an AP, but does not reveal the different phases of an AP
How would the recording change is we switched the positions of the negative and positive recording electrodes in the earthworm lab?
The biphasic waveform would show an inverse graph
What is the anatomy of an earthworm?
Ventral Nerve Cords:
-median giant axon
-lateral giant axons
How does the medial giant fiber's larger diameter effect the velocity of APs?
It will send AP faster since it has a greater diameter and since it is located centrally
How does the lateral giant fiber's smaller diameter effect the velocity of the APs?
It will send AP slower since it has a smaller diameter
Which of these statements is true about action potentials?
a) can be generated while voltage-gated Na+ channels are already opened or inactive
b) it's easier to fire another action potential during absolute refractory period
c) stronger stimulation is needed to generate another action potential during relative refractory period
d) if giving a stronger stimulation, you can observe a bigger action potential
c) stronger stimulation is needed to generate another action potential during relative refractory period
What would a biphasic waveform look like if you doubled the distance between the two recording electrodes?
The upward and downward bumps will be separated by a flat line.
What would a biphasic waveform look like if you removed the negative electrode?
One negative deflection or a flat line
What would a biphasic waveform look like if you removed the ground electrode?
The signal will be very prone to noise and will not be interpretable
What would a biphasic waveform look like if the AP propagated past the positive electrode first?
An inverse waveform where the downward curve will show up first
What is an earthworm giant axon composed of?
individual cells, one in each segment, linked through gap junctions to its neighbors in adjacent segments
This is an extracellular recording, what does the dip in the line of the highlighted box represent?
The charge at the positive recording electrode is more negative compared to the negative recording electrode
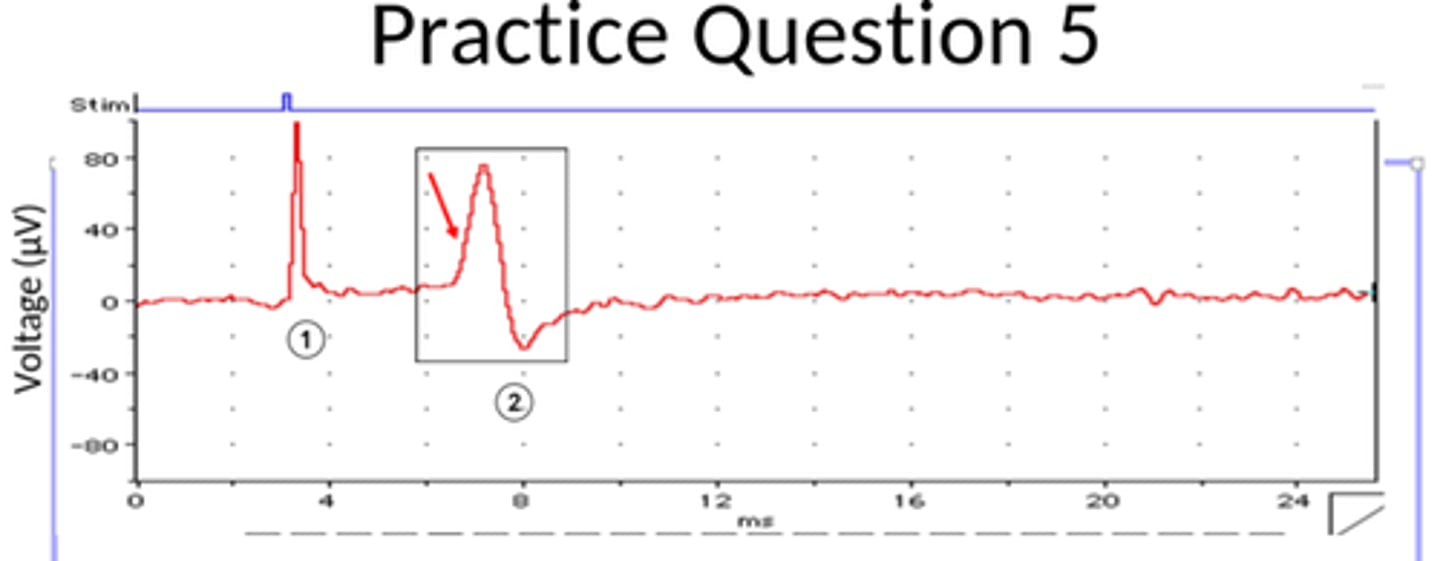
What is the consequence of the biphasic nature of the action potential recorded extracellularly?
The use of two extracellular electrodes speed some distance apart to record the potential
What do the two lateral giant nerve fibers behave as?
A single fiber because of the extensive cross-bridge connections between them
During the refractory period of the experiment, AP generated from the first stimulus always appears before the stimulus artifact generated by the second stimulus in your recording
True or False?
False
What could be the reasoning behind obtaining results in no signal or poor signal?
-Worms were drowned
-Recording pan is filled with ringers solution when ensuring the worm is fully anesthetized
-The contact between the recording pins and the worm is poor (dirty pins, electrodes are not pinned through the worm)
-The head of the earthworm is not touching both stimulating electrodes
What happens when you move the recording electrodes away from the stimulating electrodes?
The AP generated happens much later on
What is absolute refractory period?
The period immediately following the firing of a nerve fiber when it cannot be stimulated no matter how great a stimulus is applied. Na+ channels being to recover from inactivation
What is relative refractory period?
In order to get a response following the firing of a nerve fiber, a stronger than normal stimulus must be applied to elicit neuronal excitation while the Na+ channels are recovering from inactivation
What is a reflex and what are the different classifications of reflexes?
A rapid, predictable motor response to a stimulus that is unlearned, unpremeditated, and involuntary.
Classified:
-Somatic; involving a skeletal muscle contraction
-Autonomic; activation of smooth and cardiac muscle
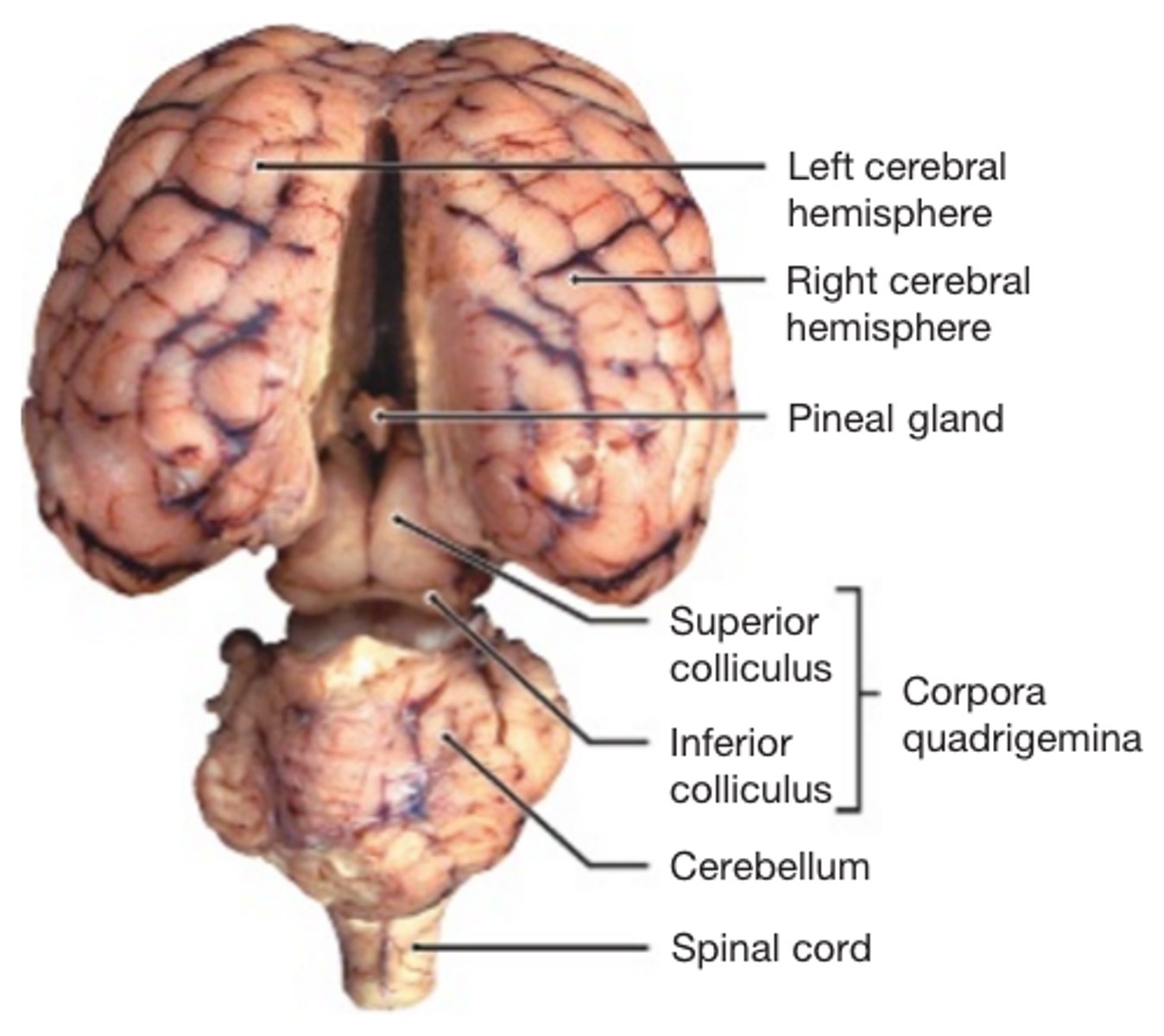
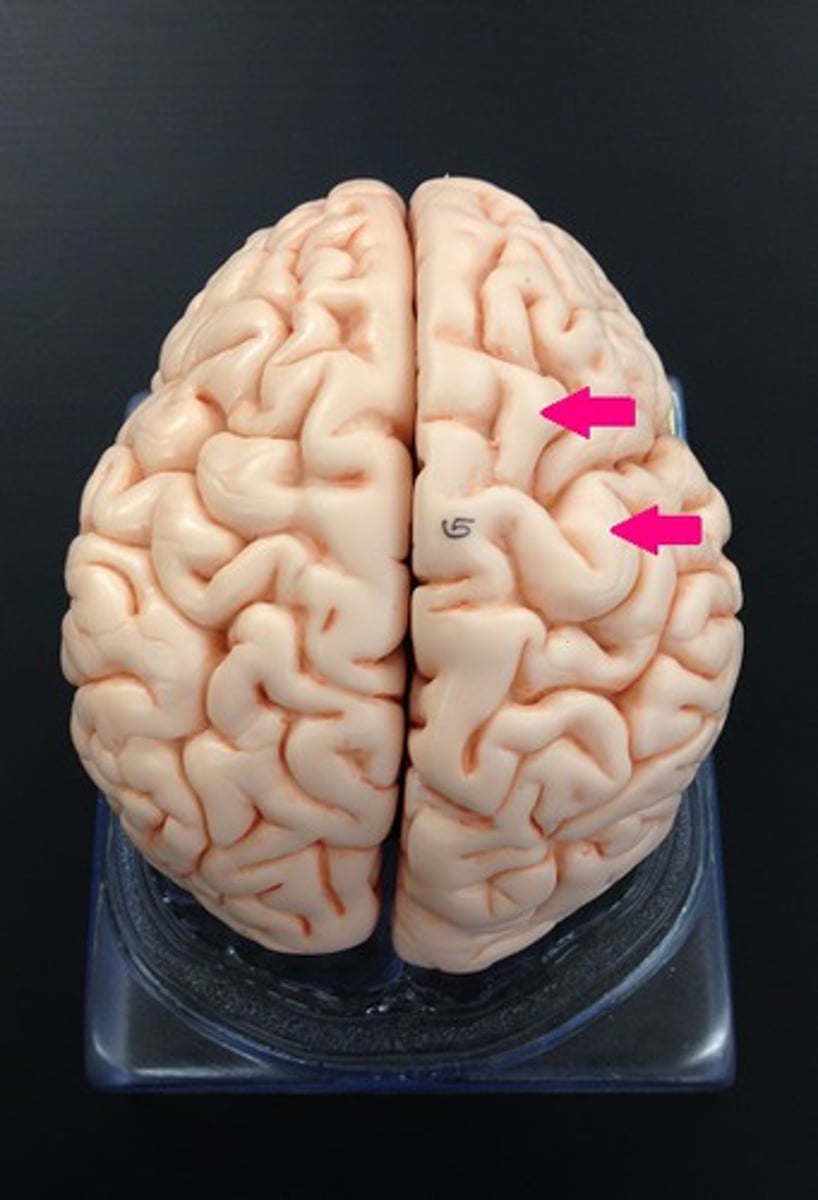
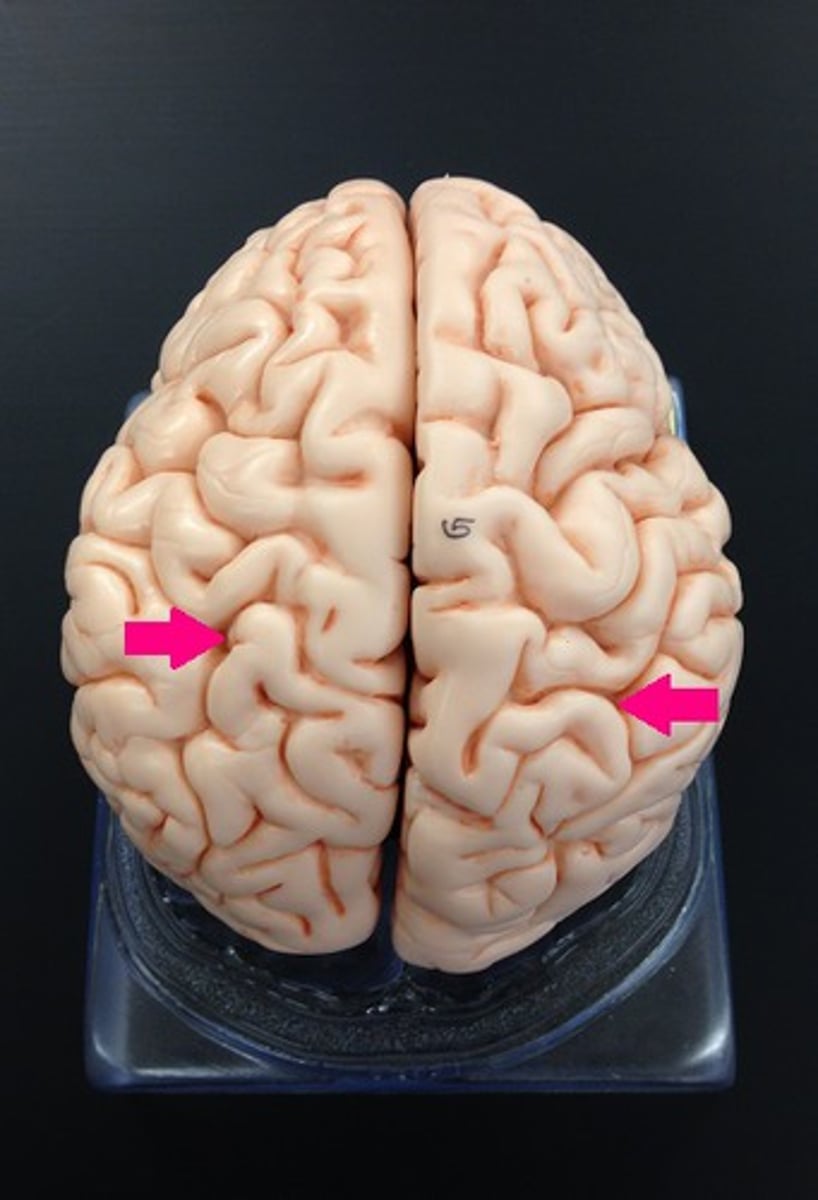
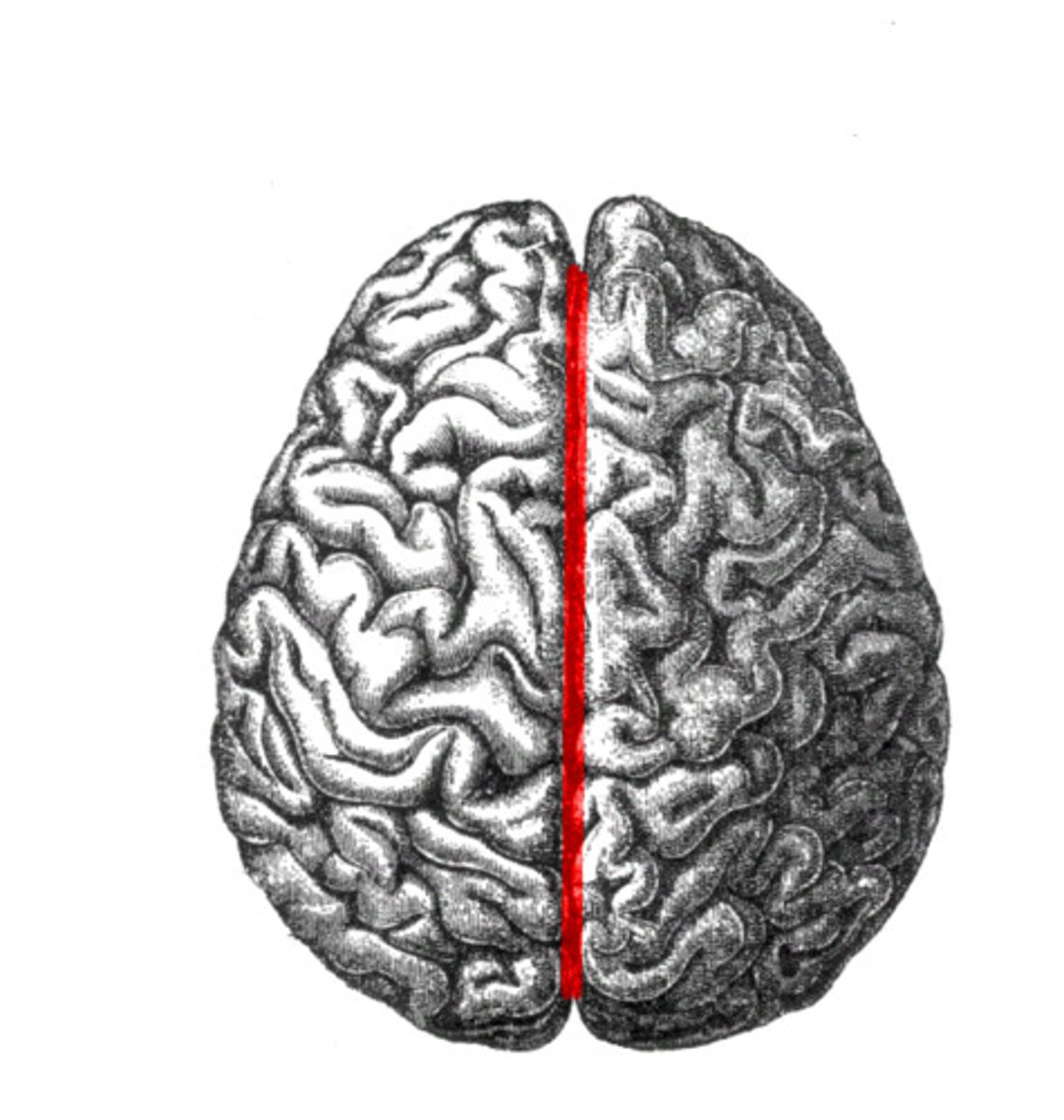
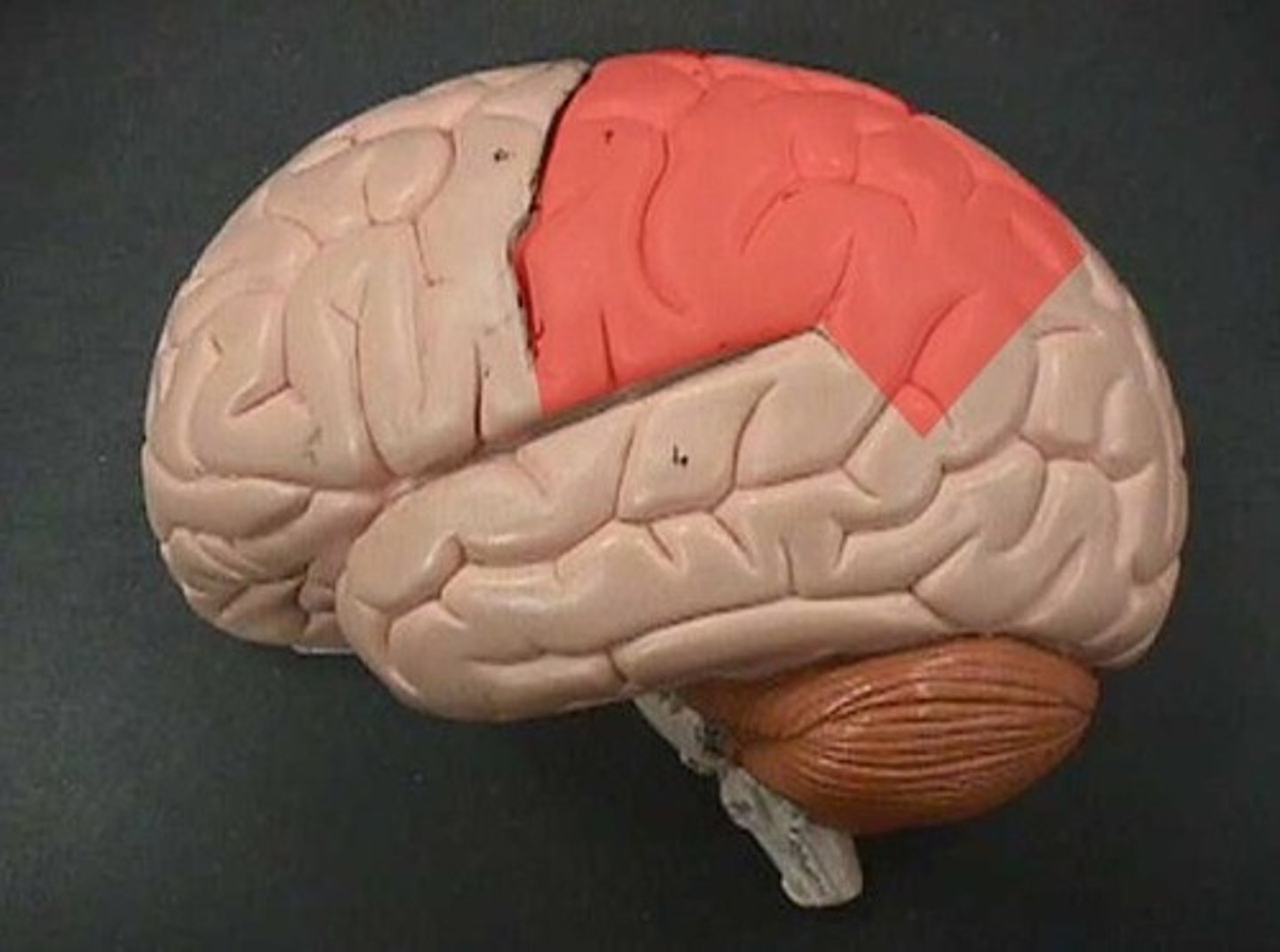
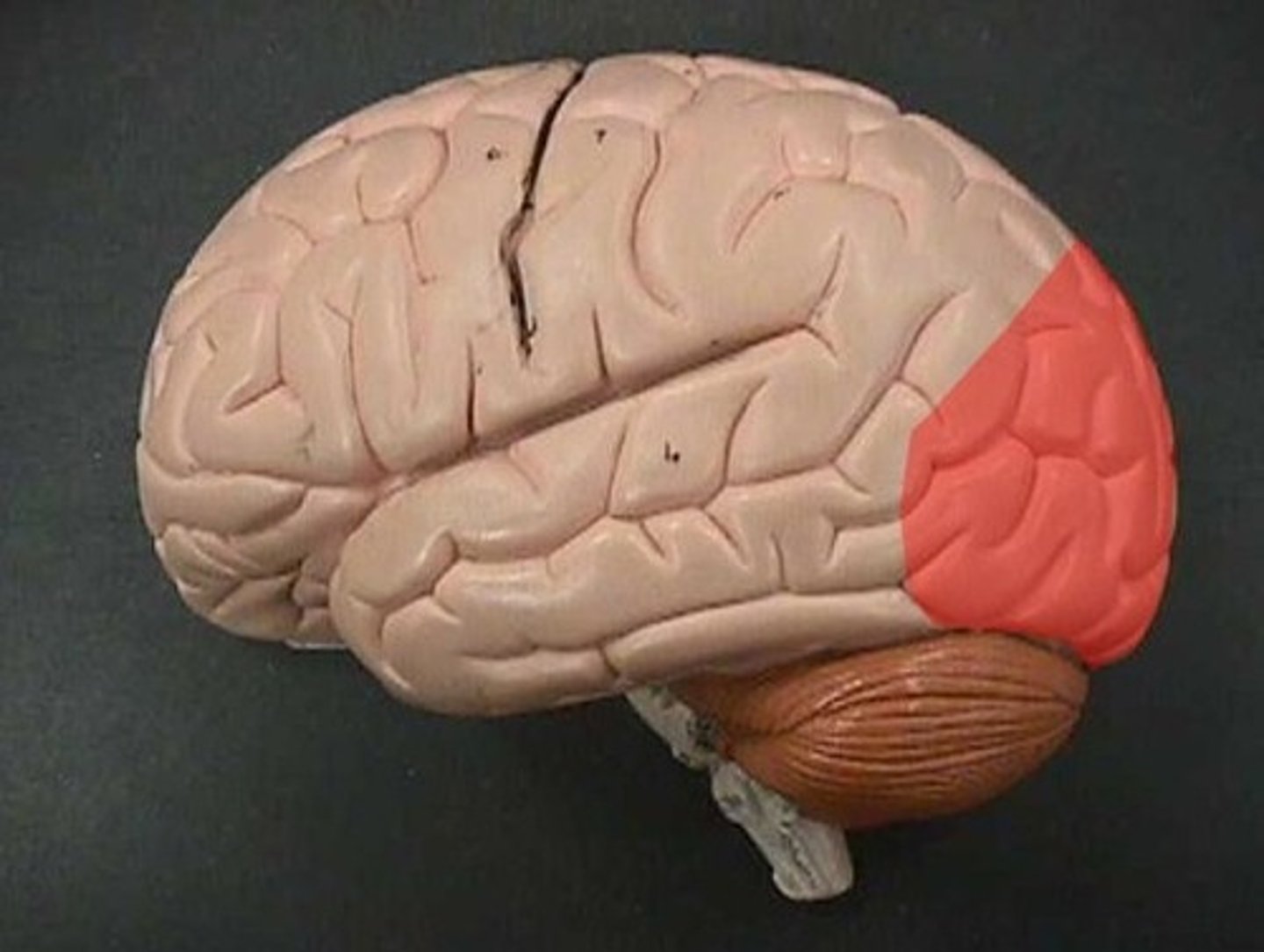
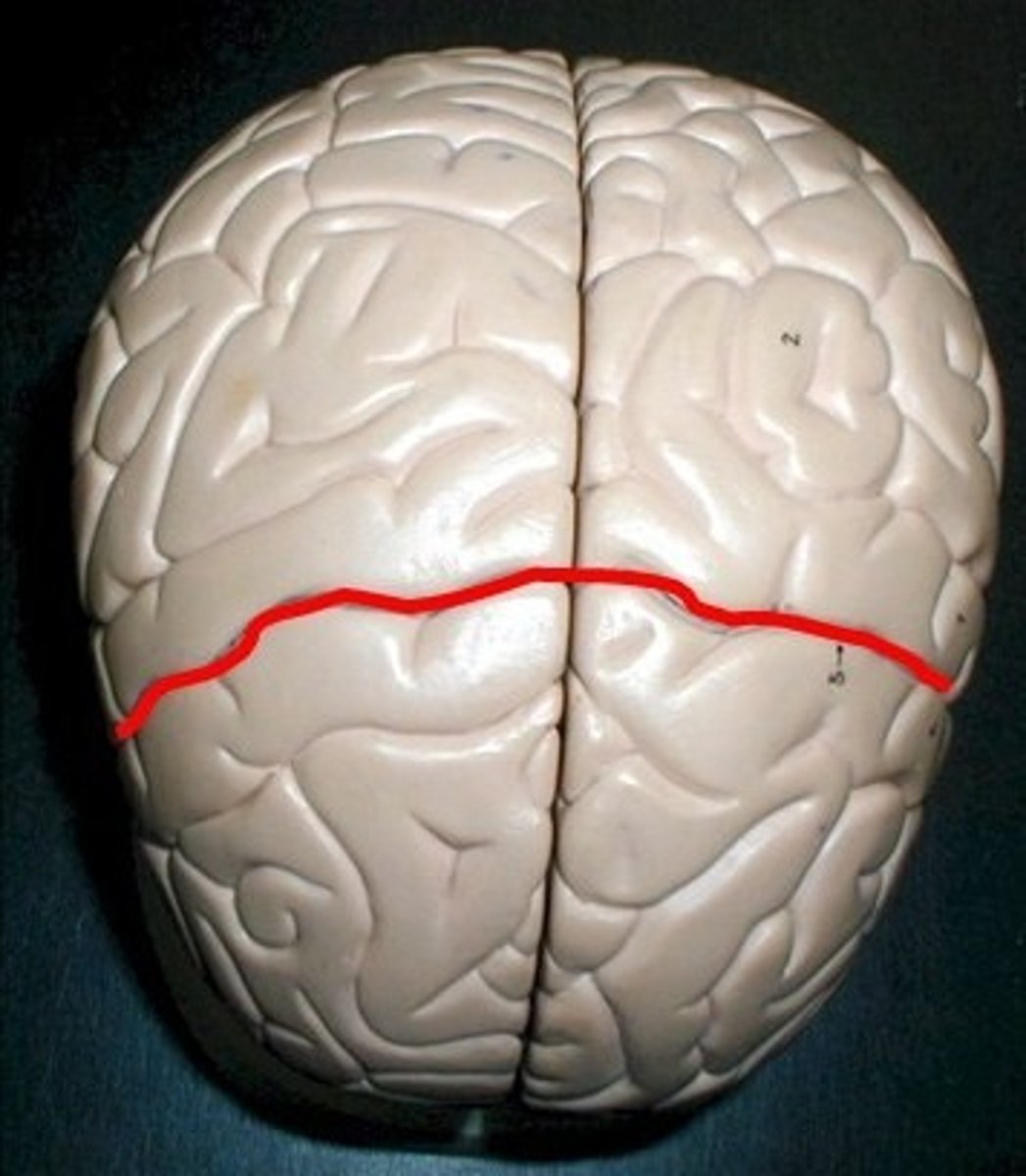
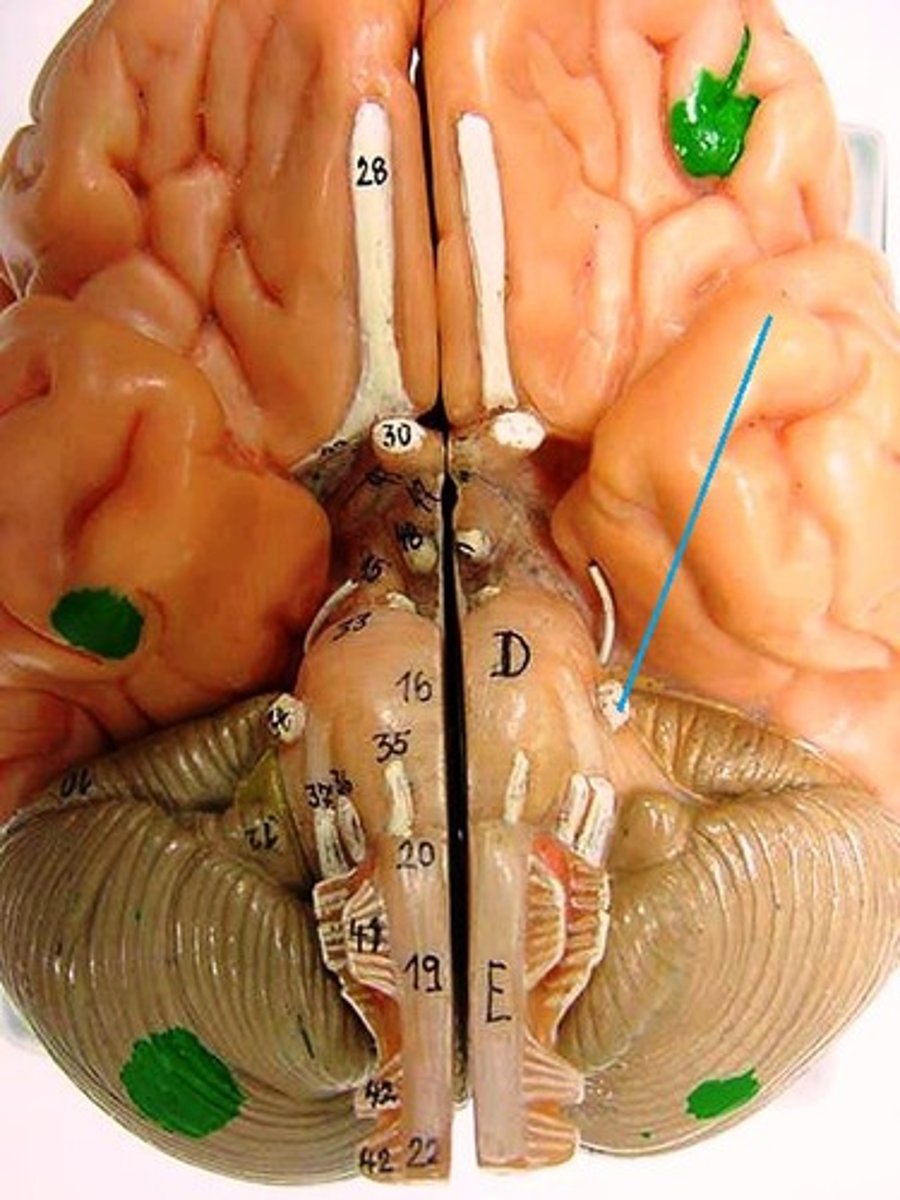
Superior Dorsal View of brain
Gyri
Sulci
Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure
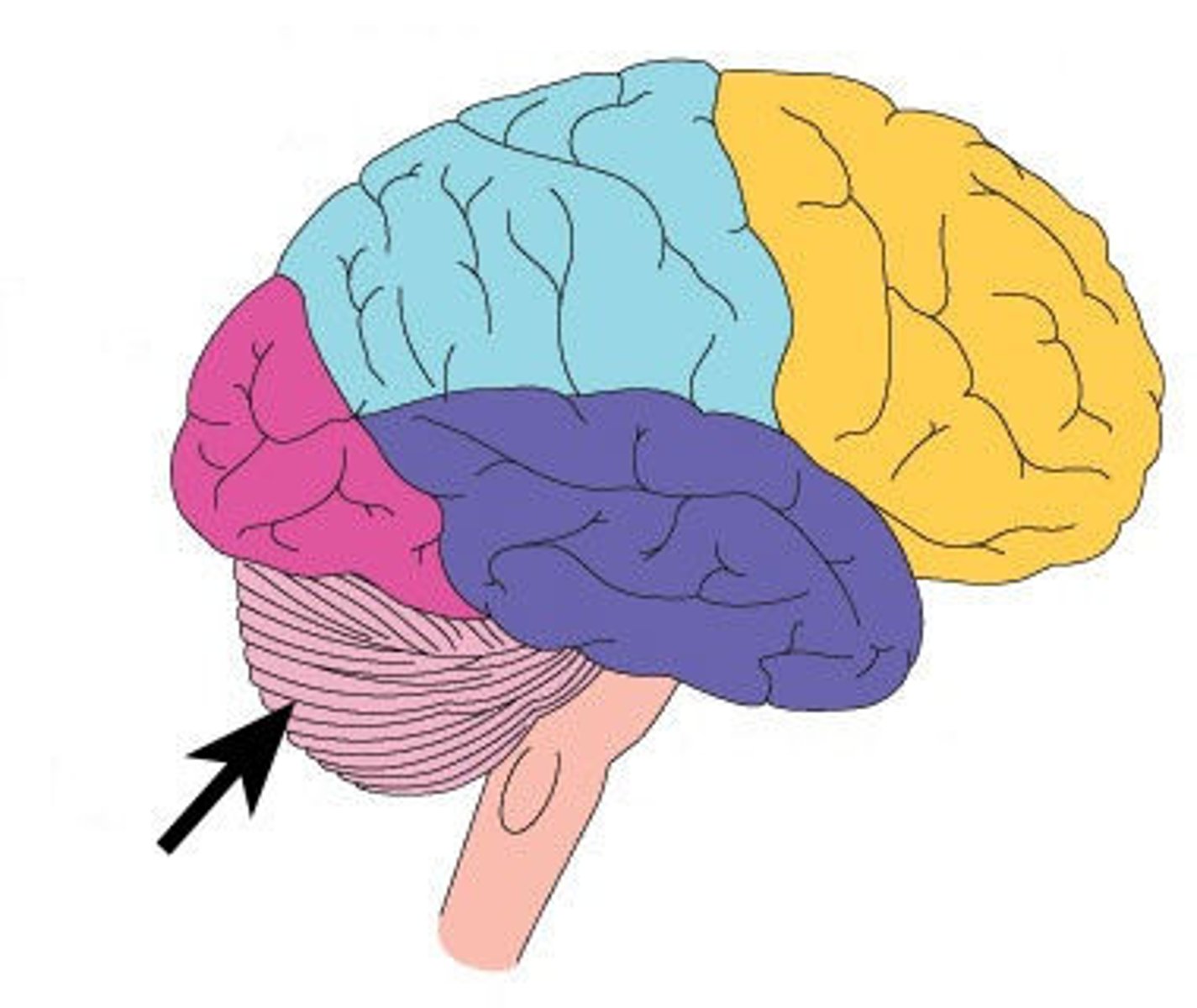
Frontal Lobe
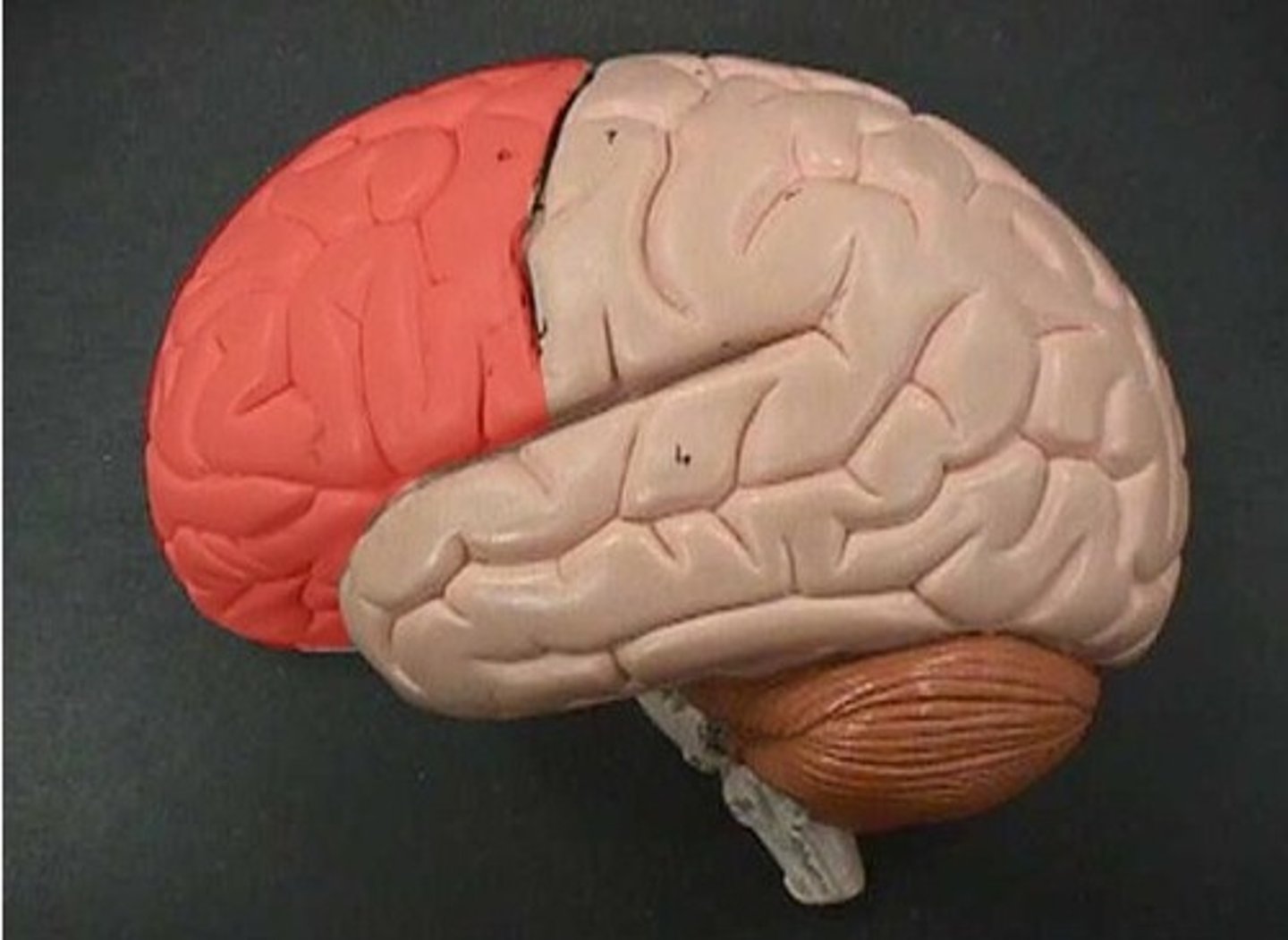
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
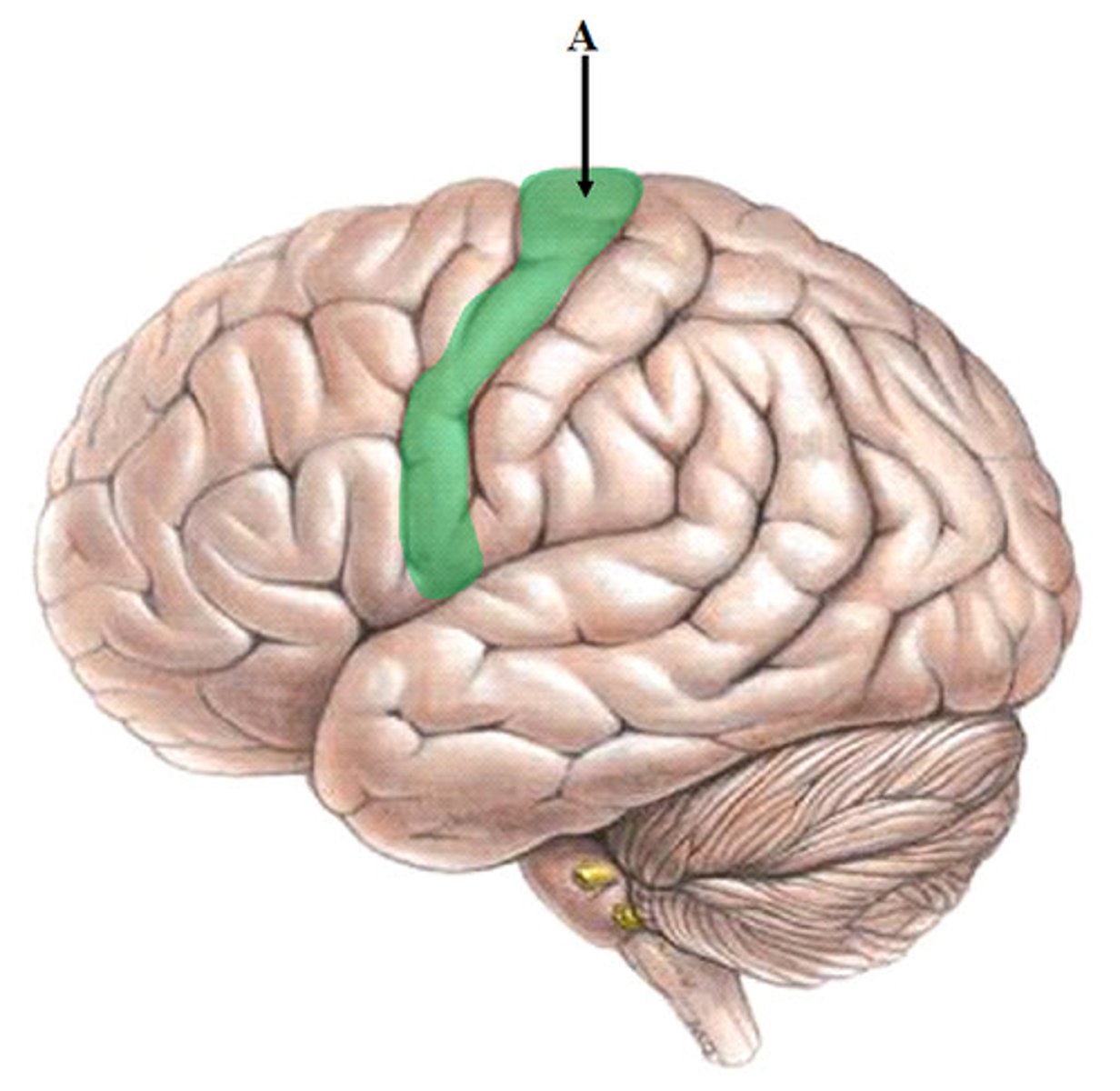
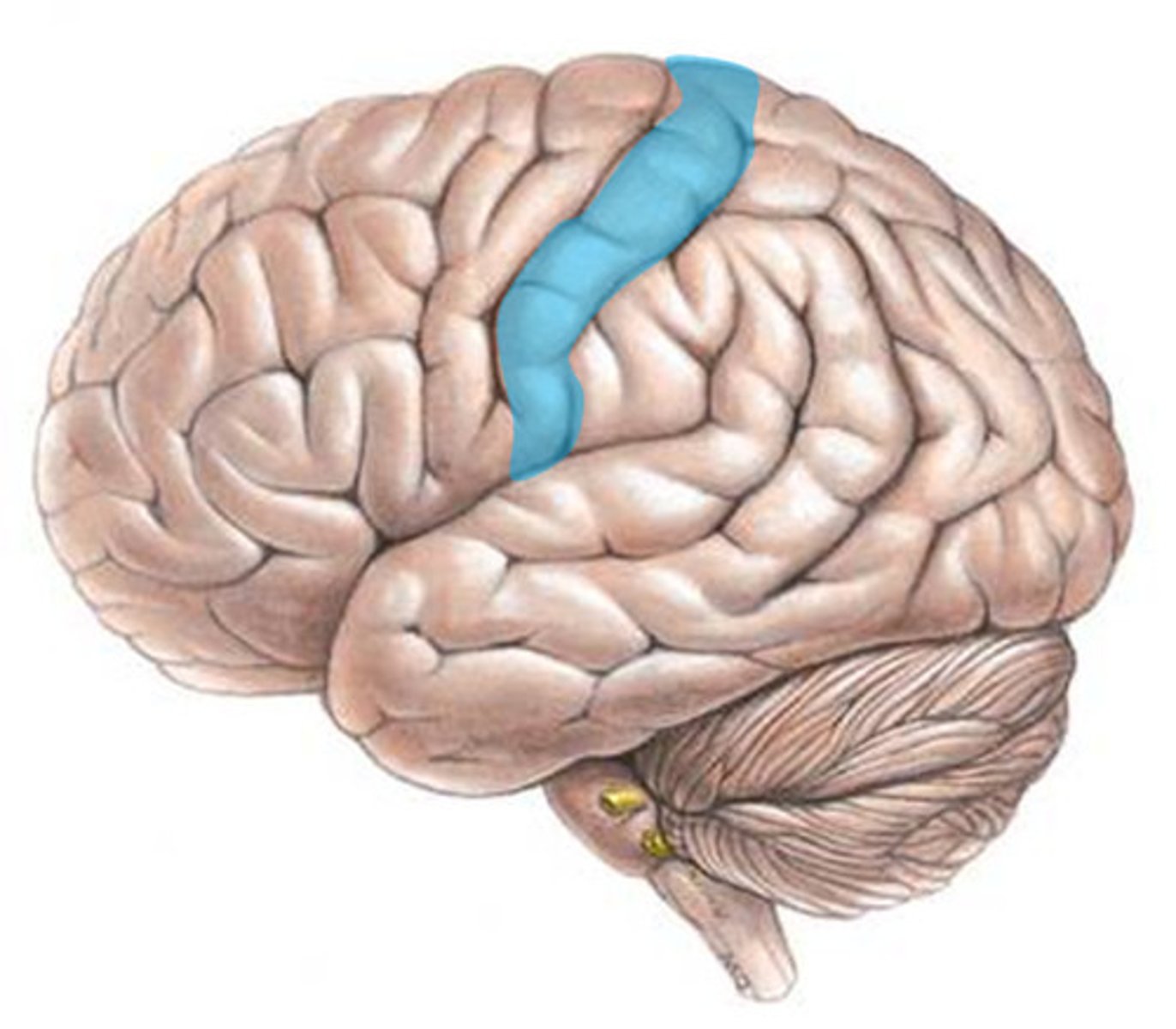
Central Sulcus
Lateral Sulcus
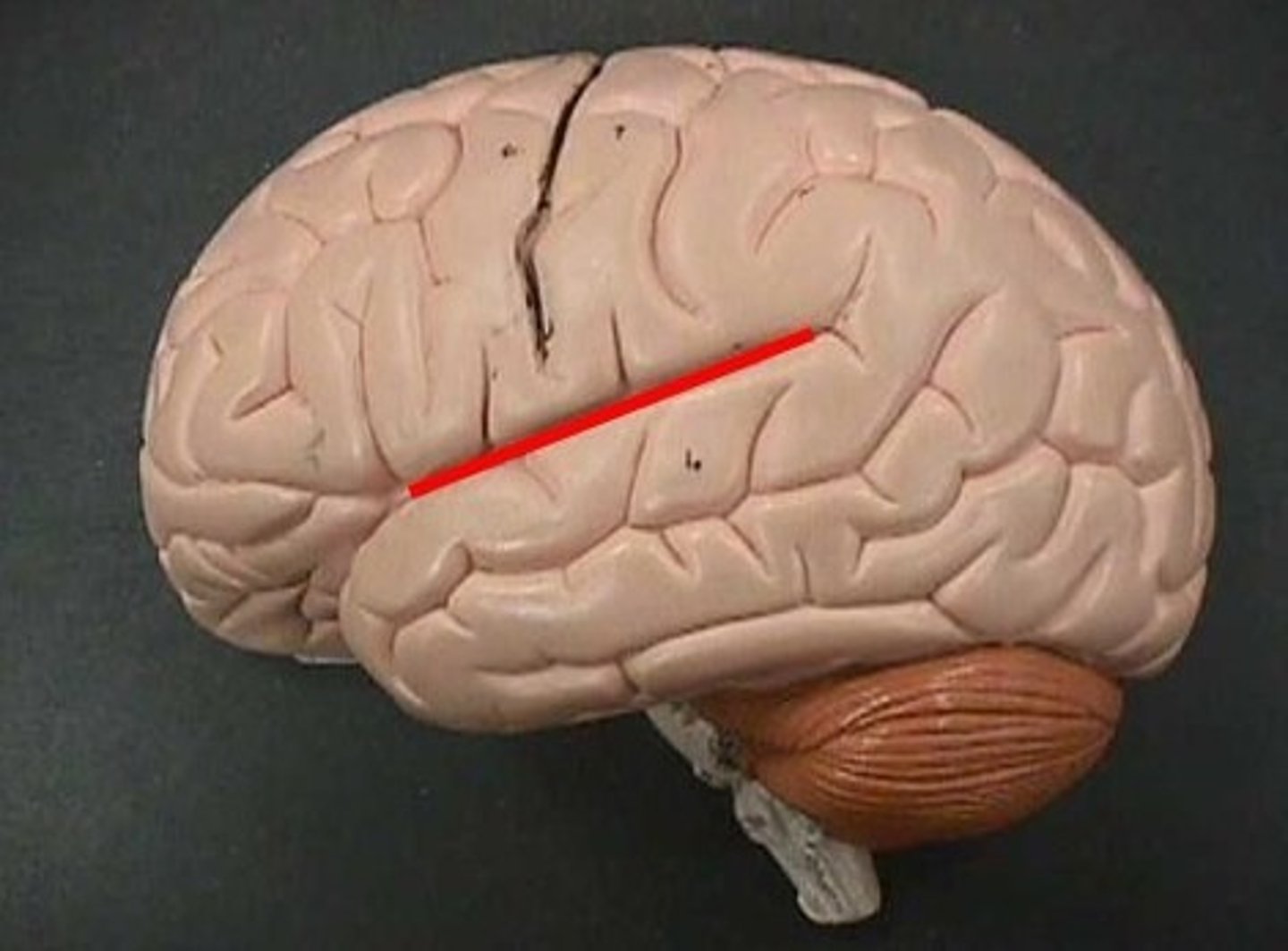
Somatomotor Area
Somatosensory Area
Cerebellum
Olfactory Bulb
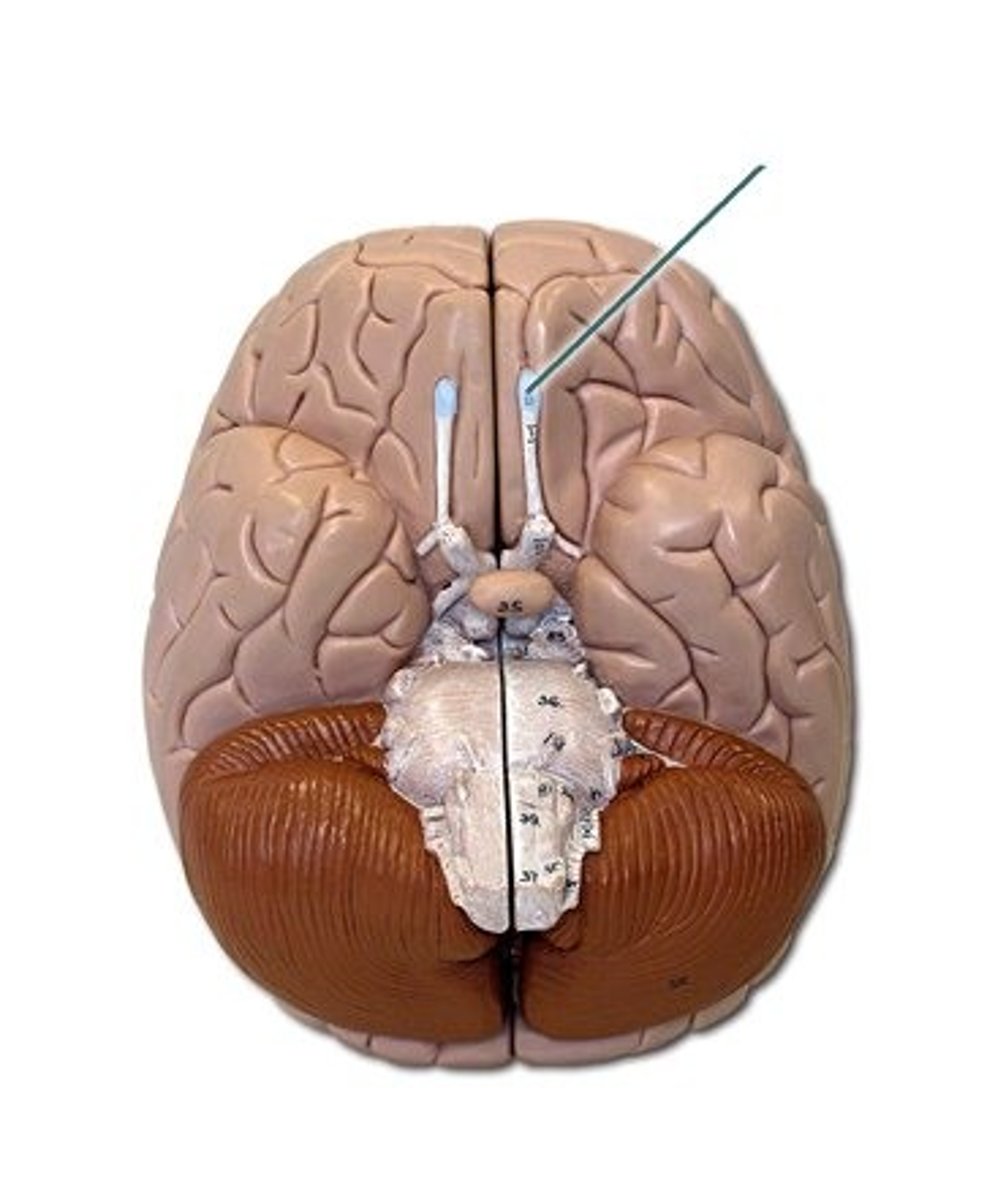
Optic Chiasm
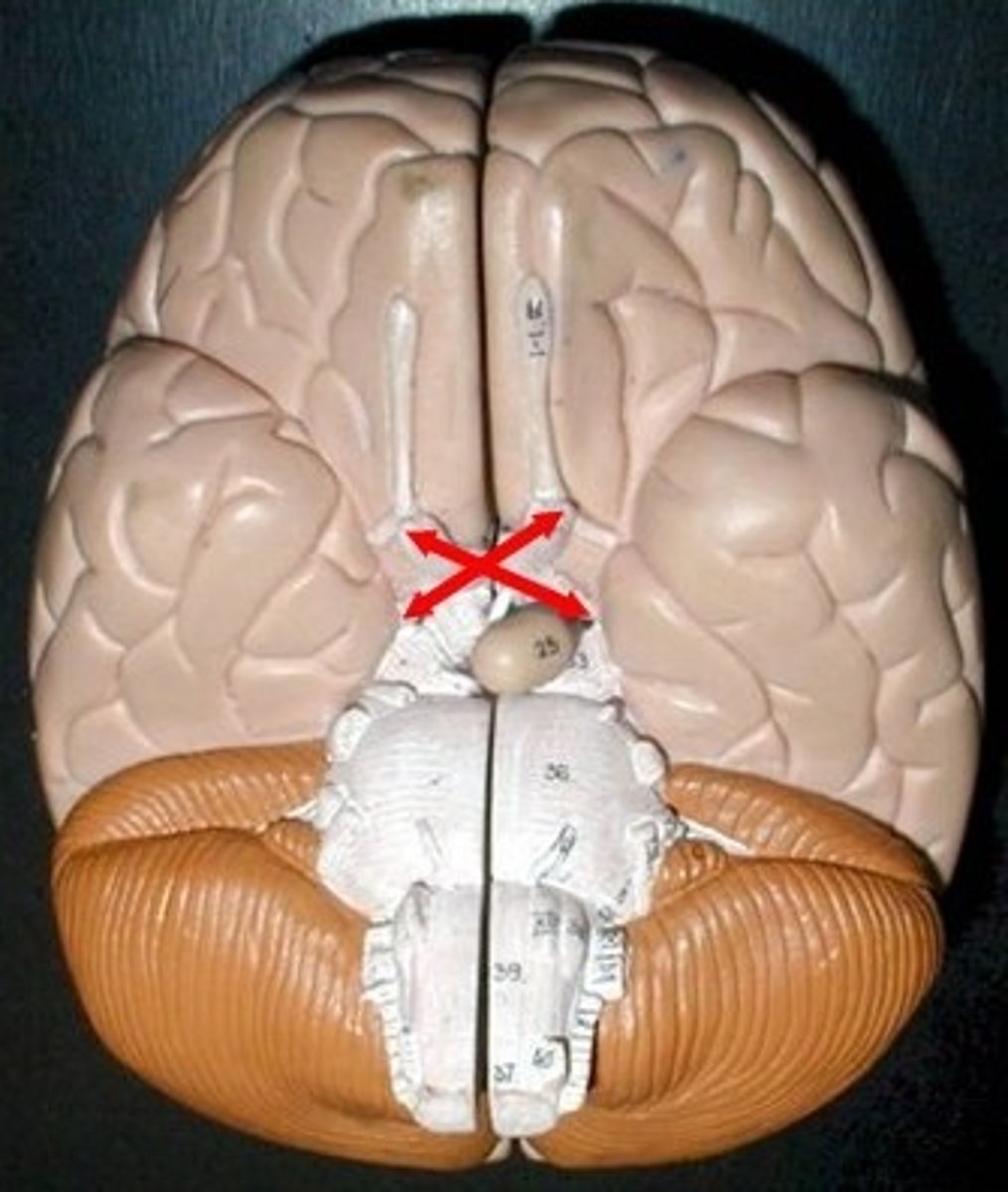
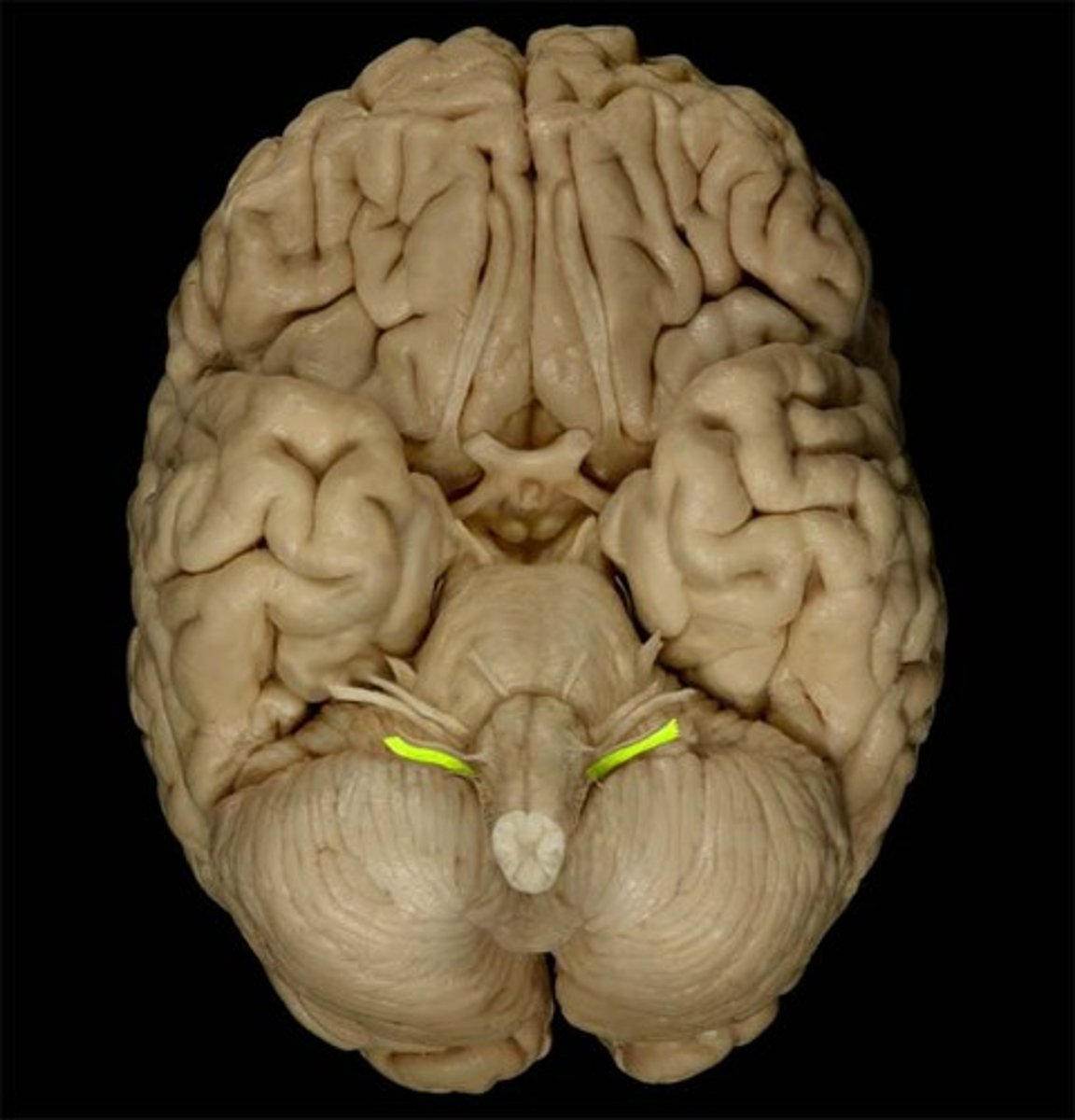
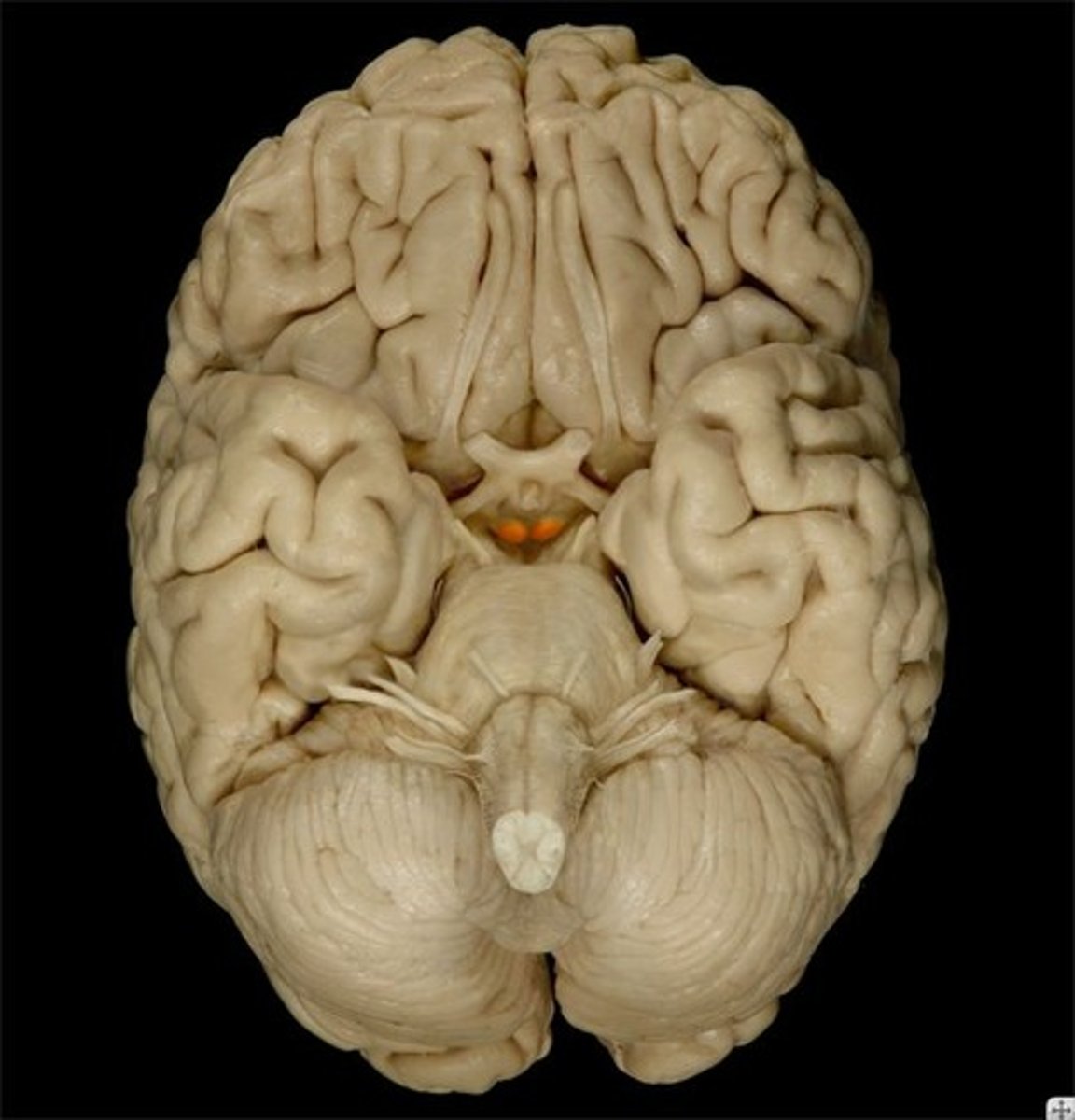
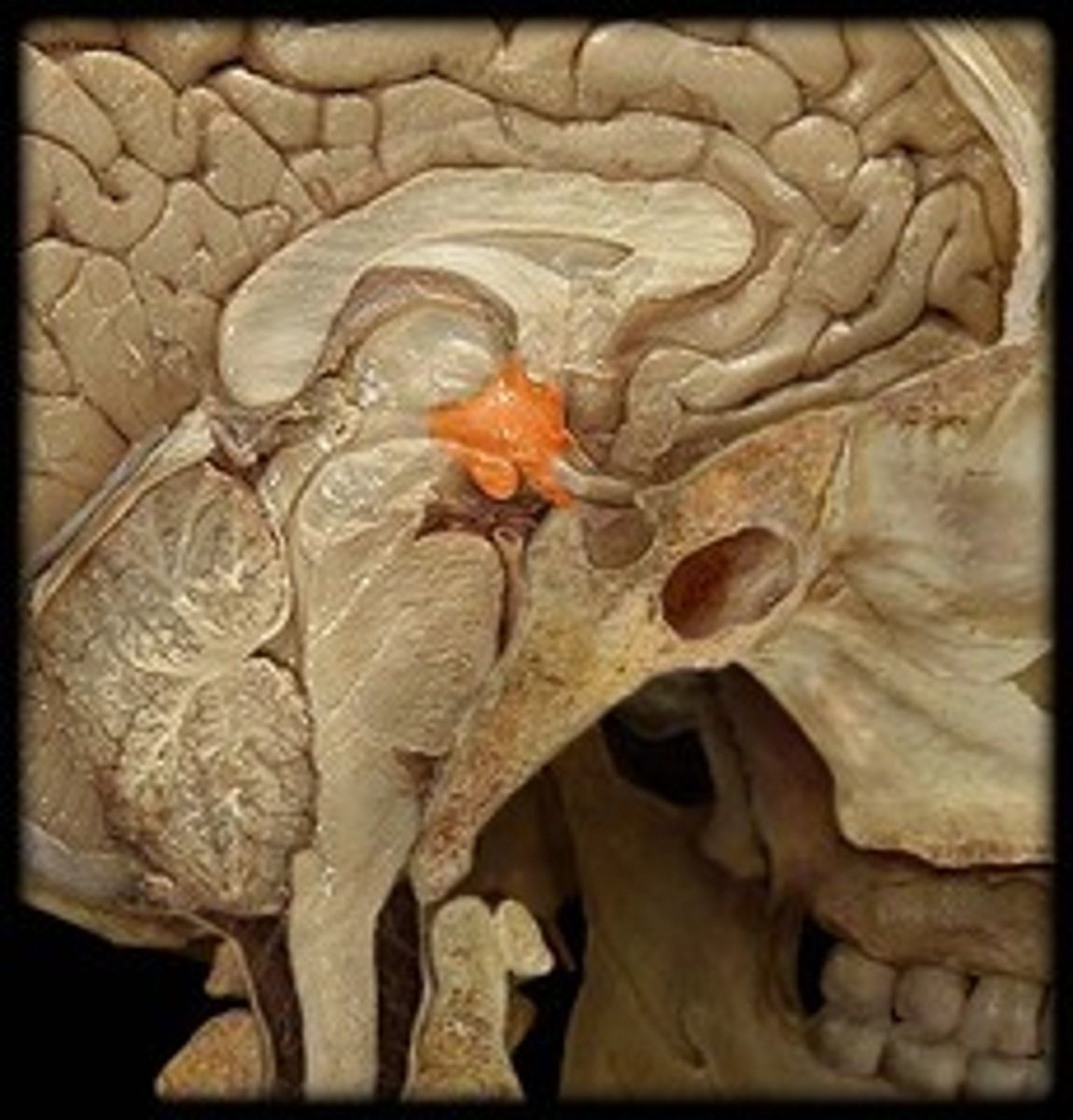
Mammillary Bodies
Pons
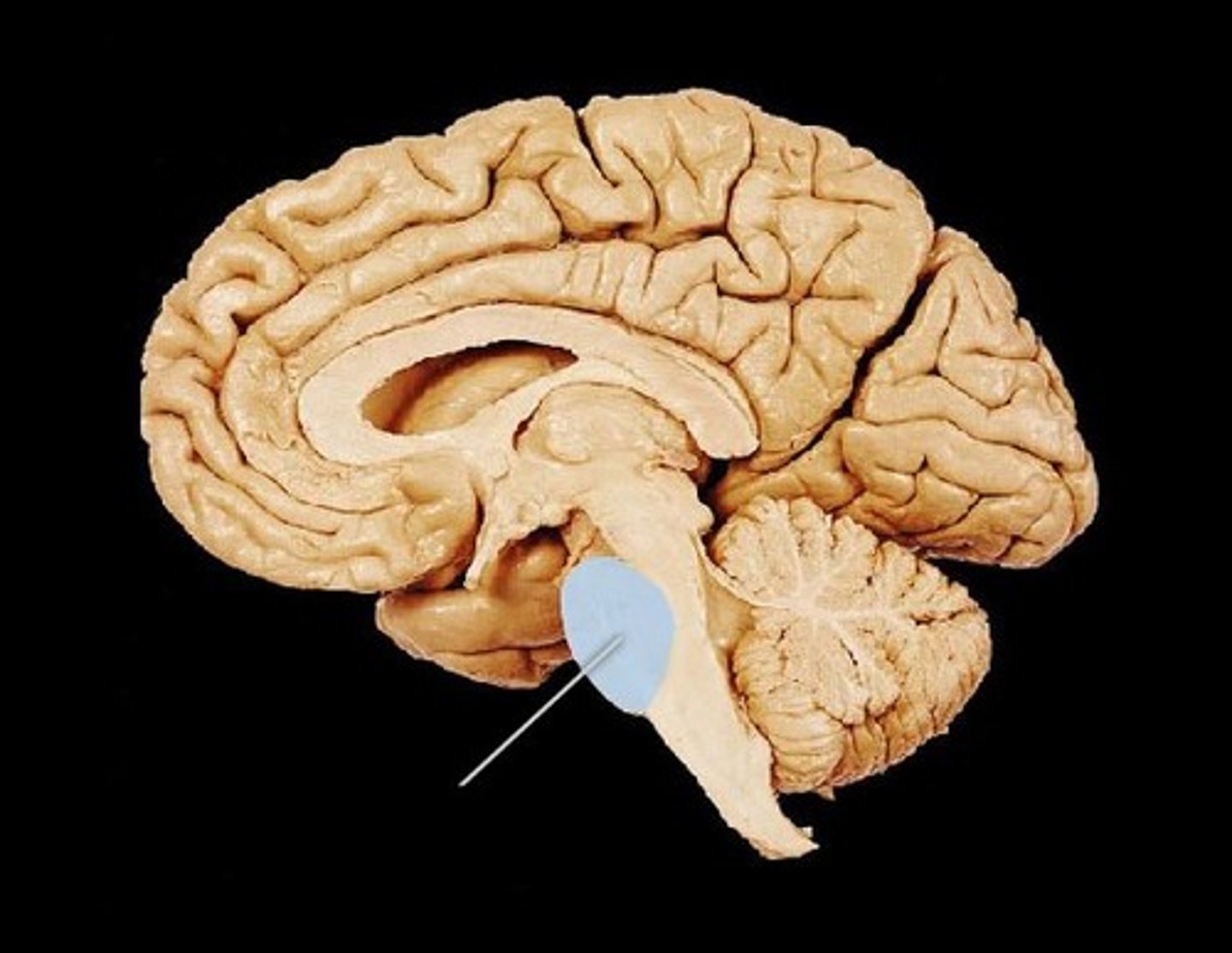
Medulla Oblongata
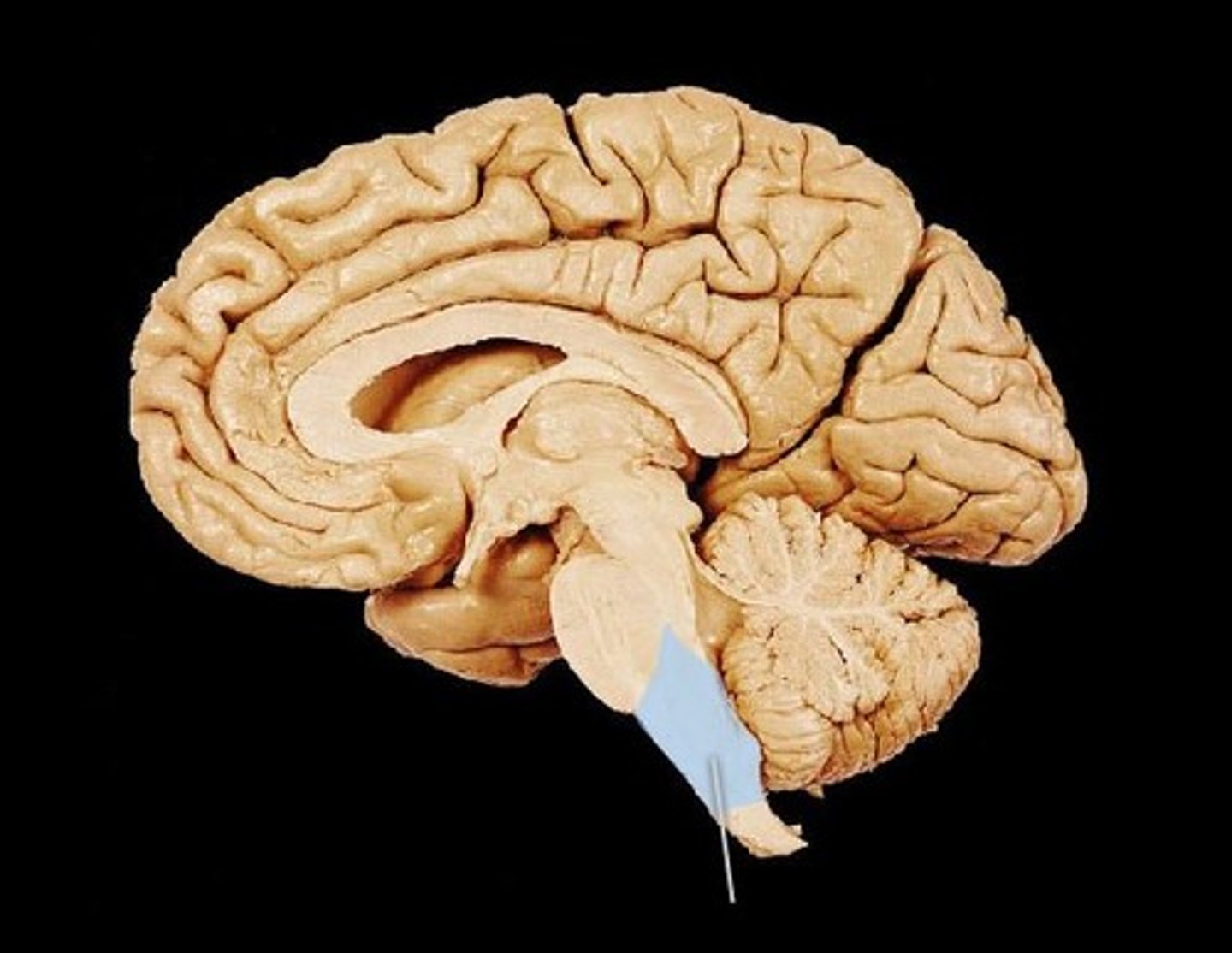
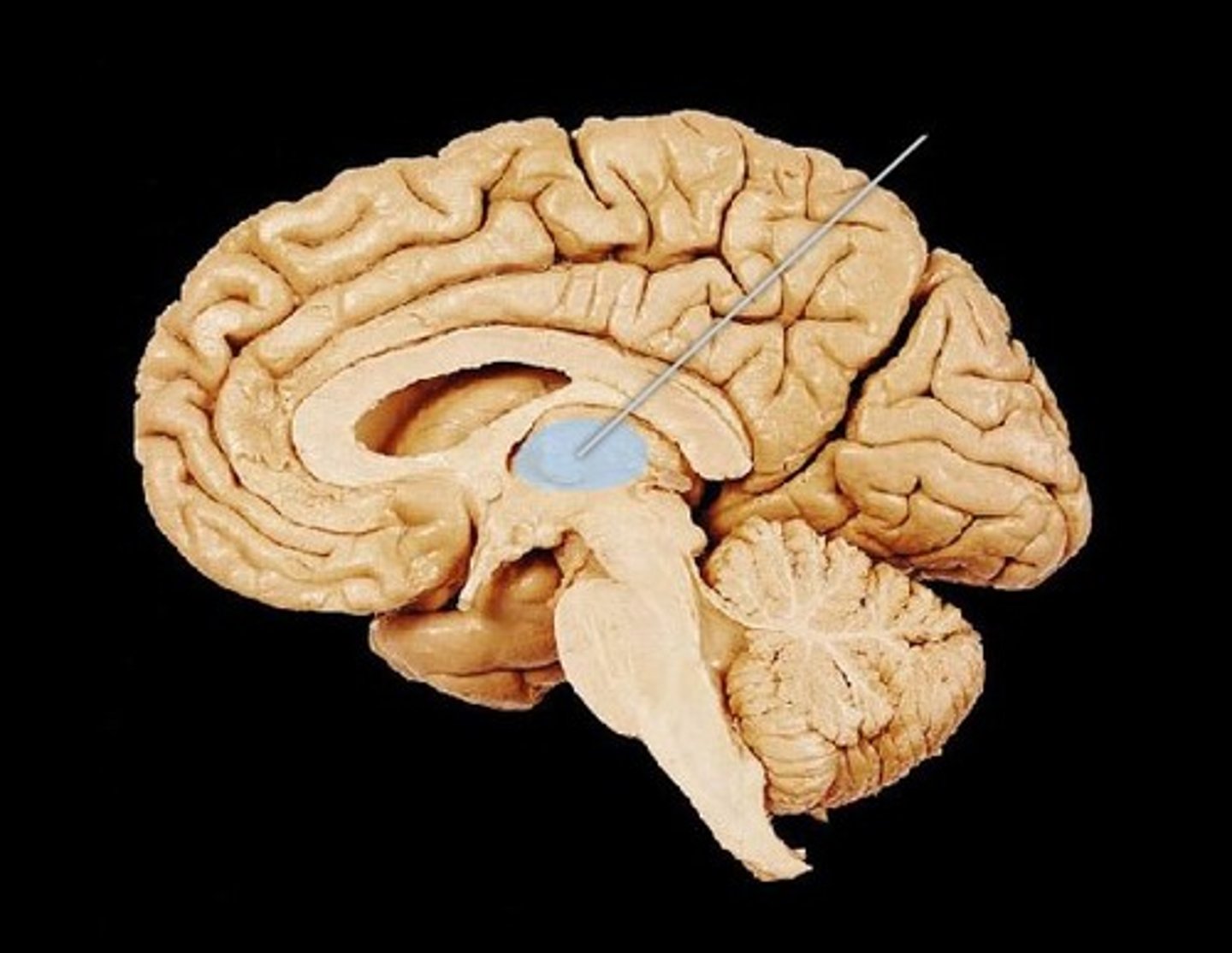
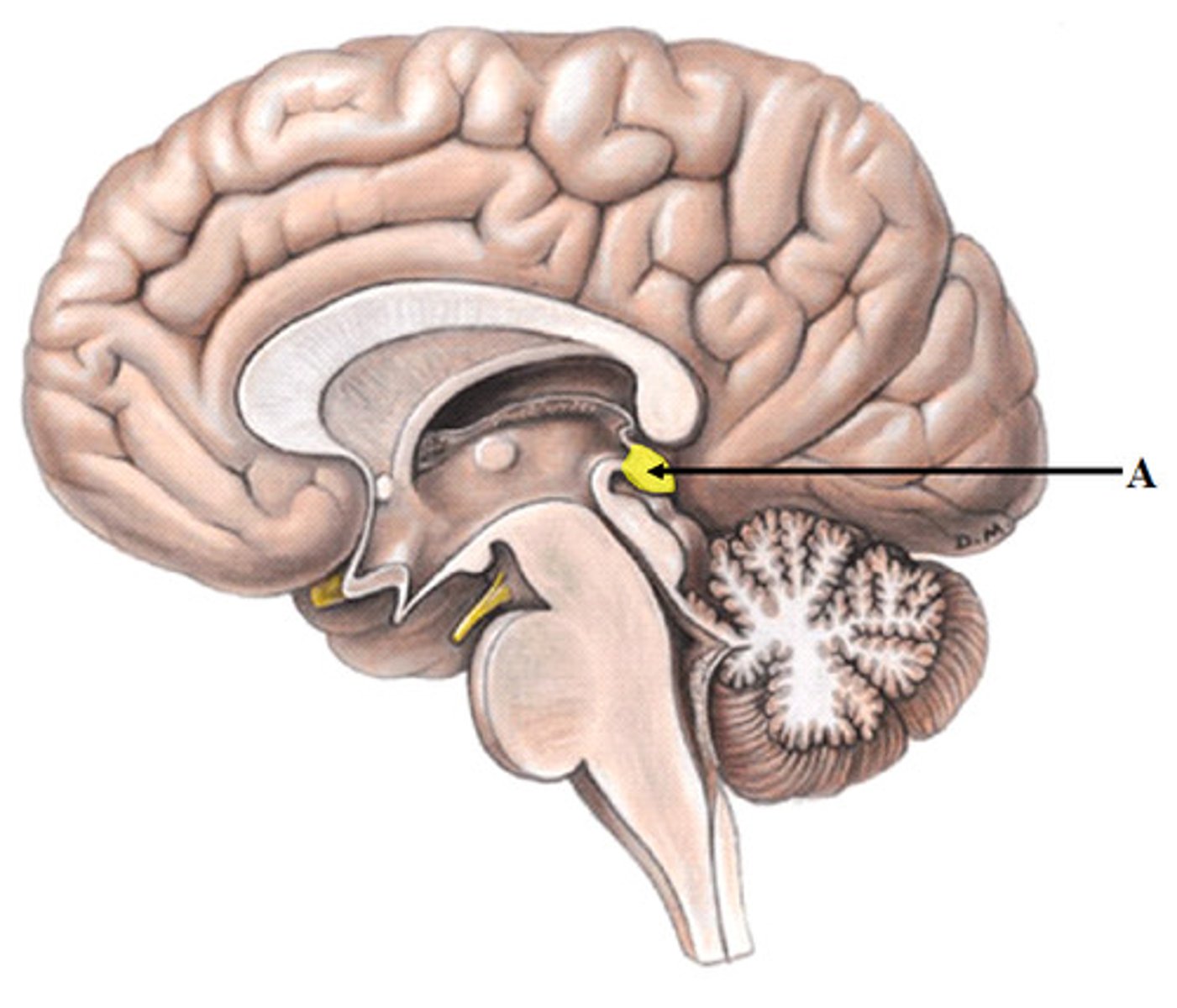
MIdsagittal View of brain
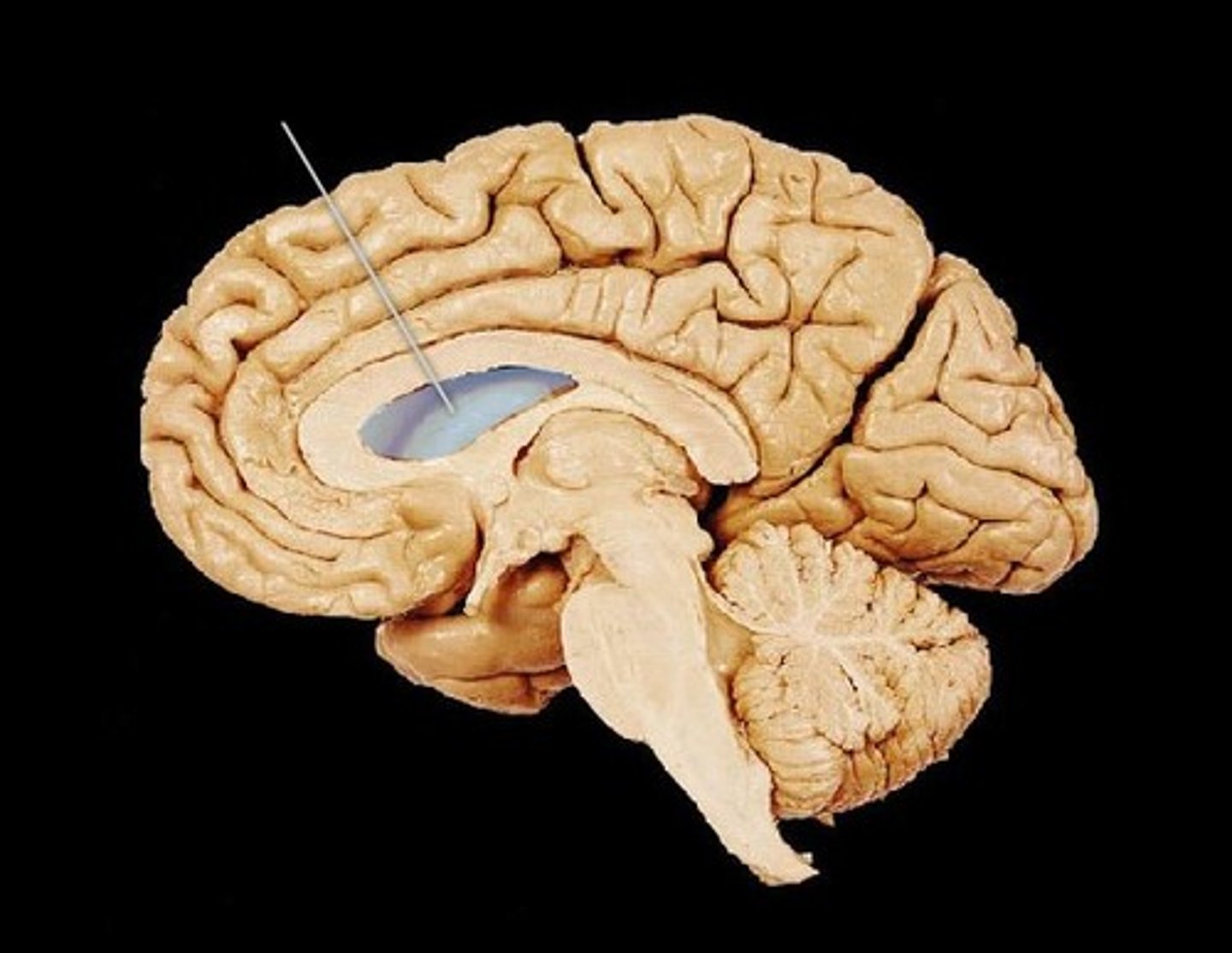
Lateral Ventricle
Third Ventricle
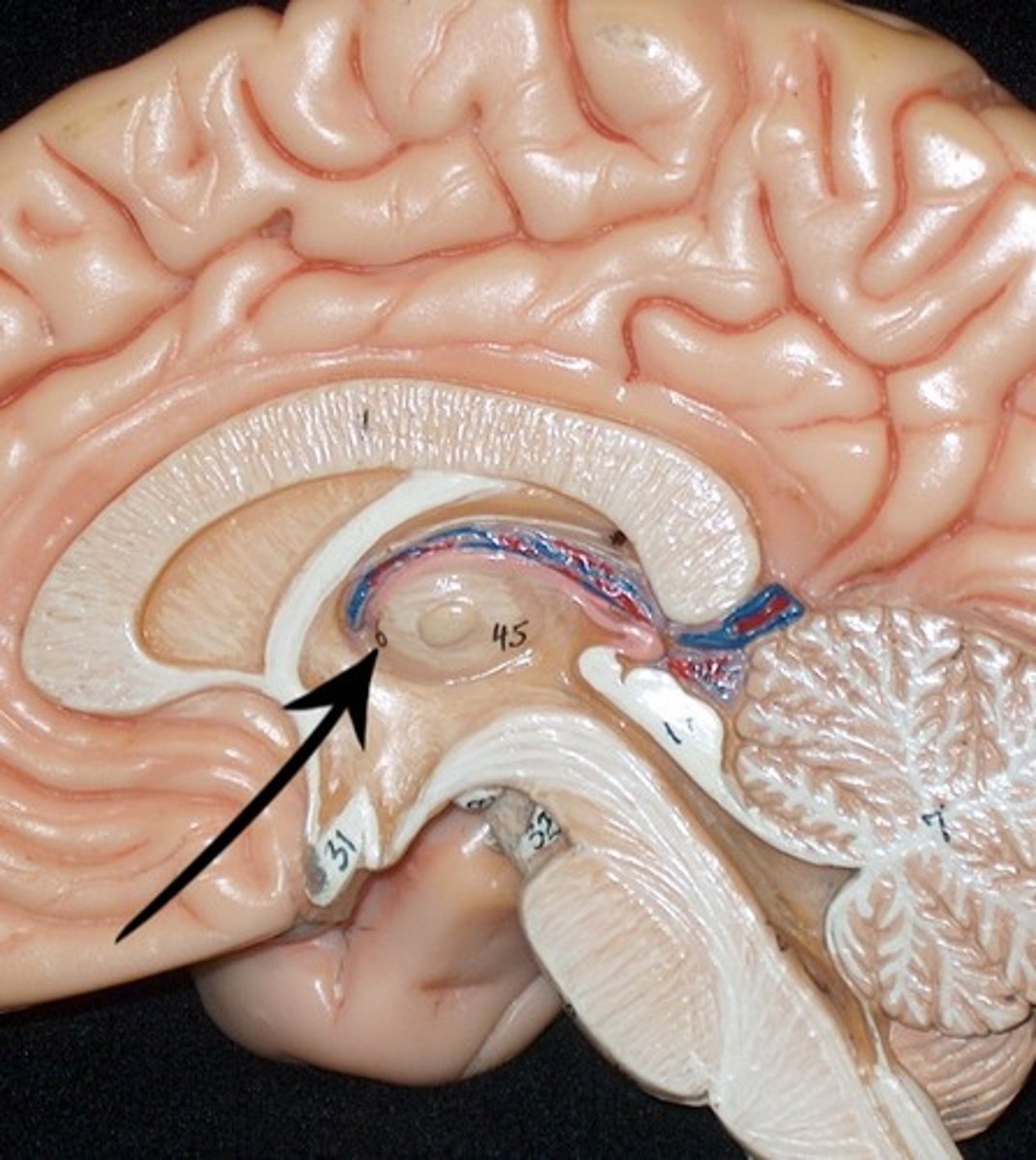
Cerebral Aqueduct
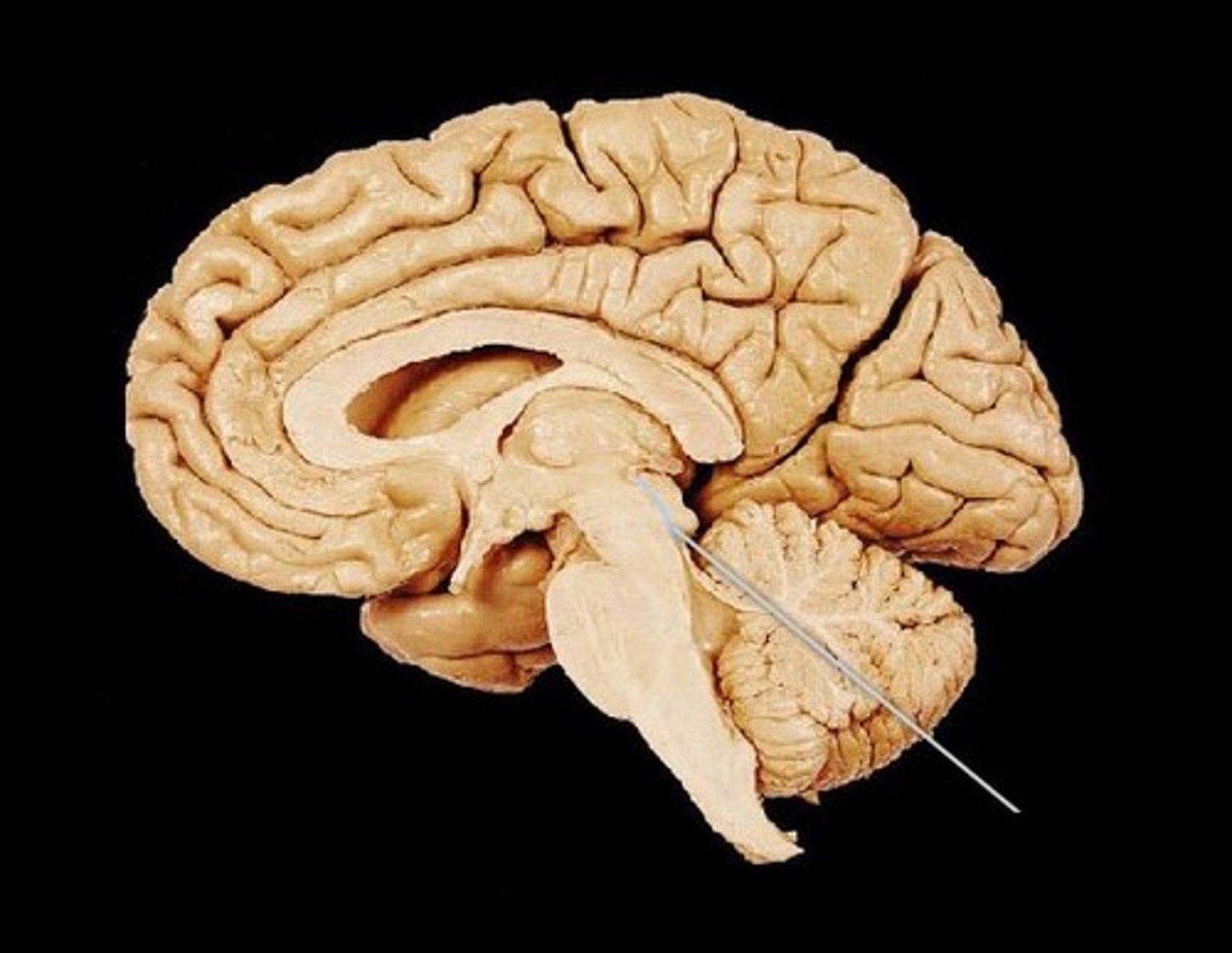
Forth Ventricle
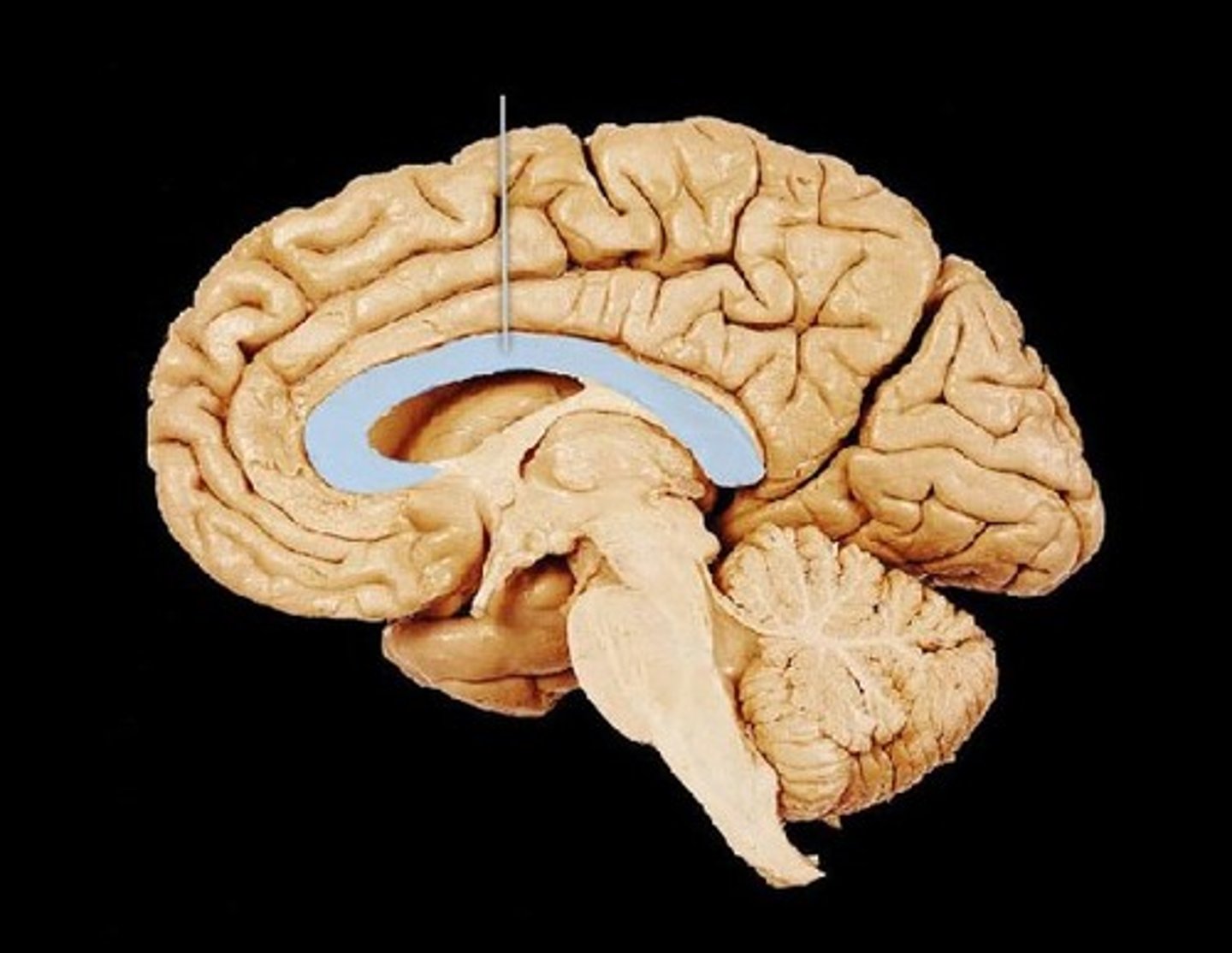
Corpus Callosum
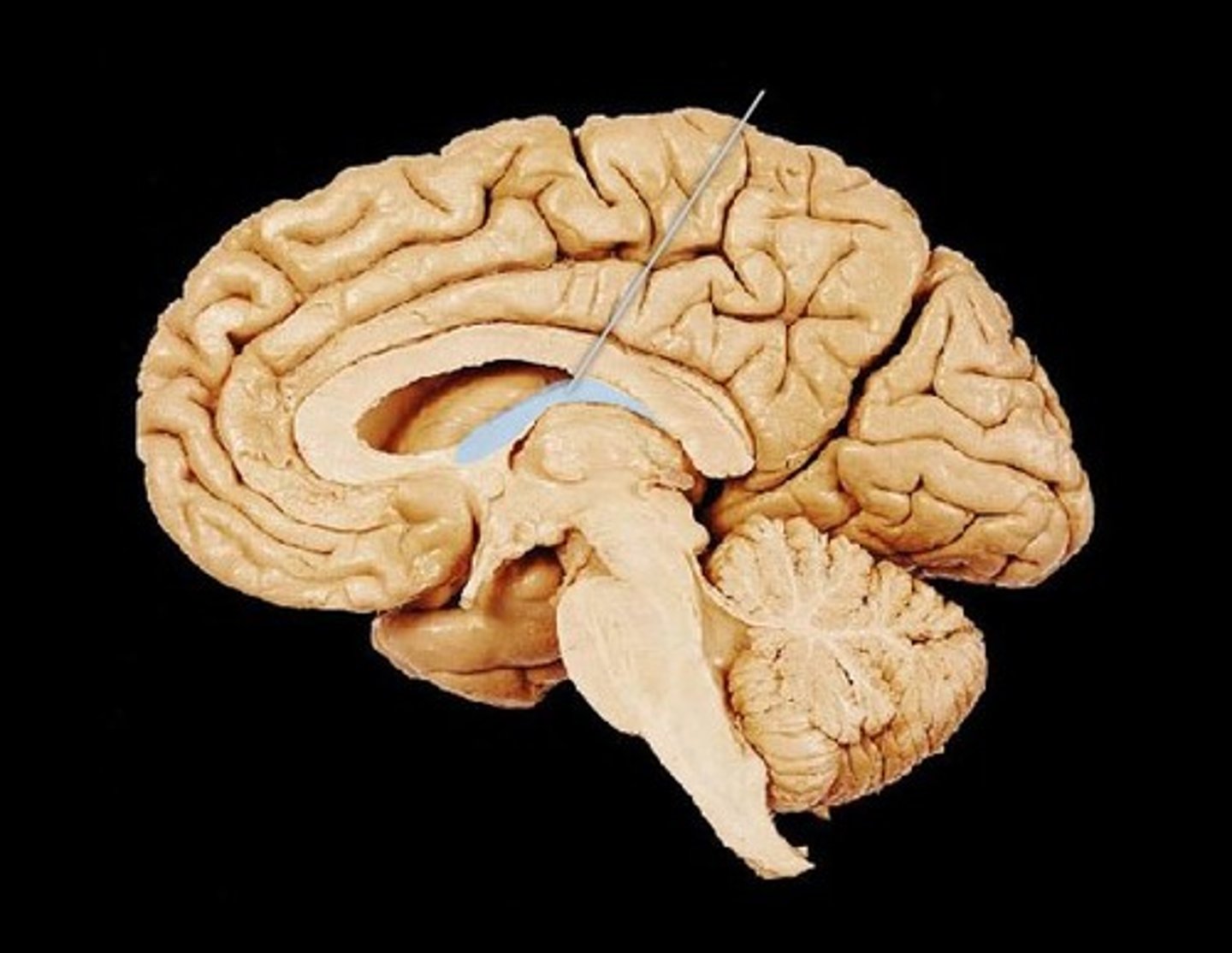
Fornix
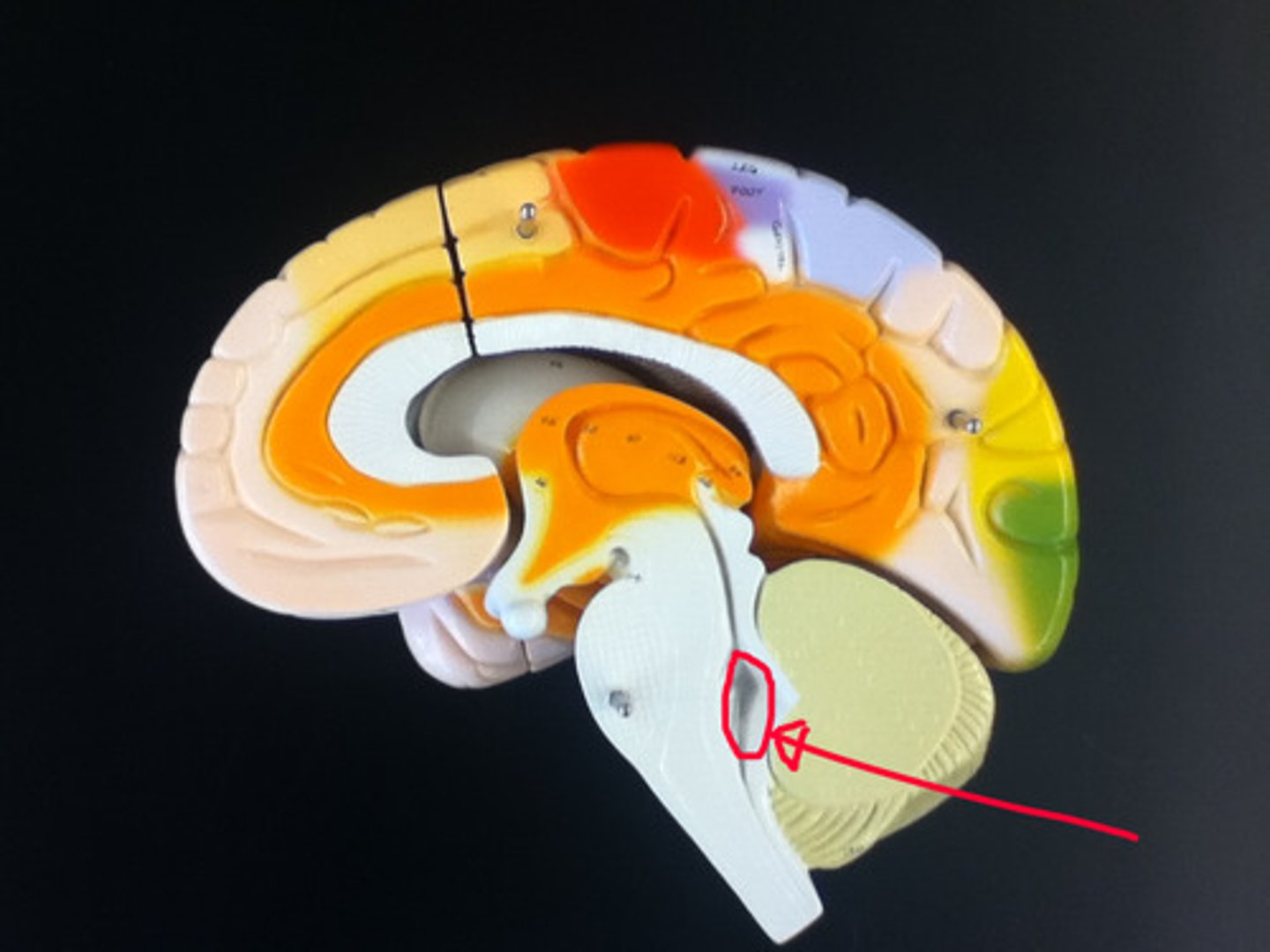
Thalamus
Pineal Gland
Superior Colliculi
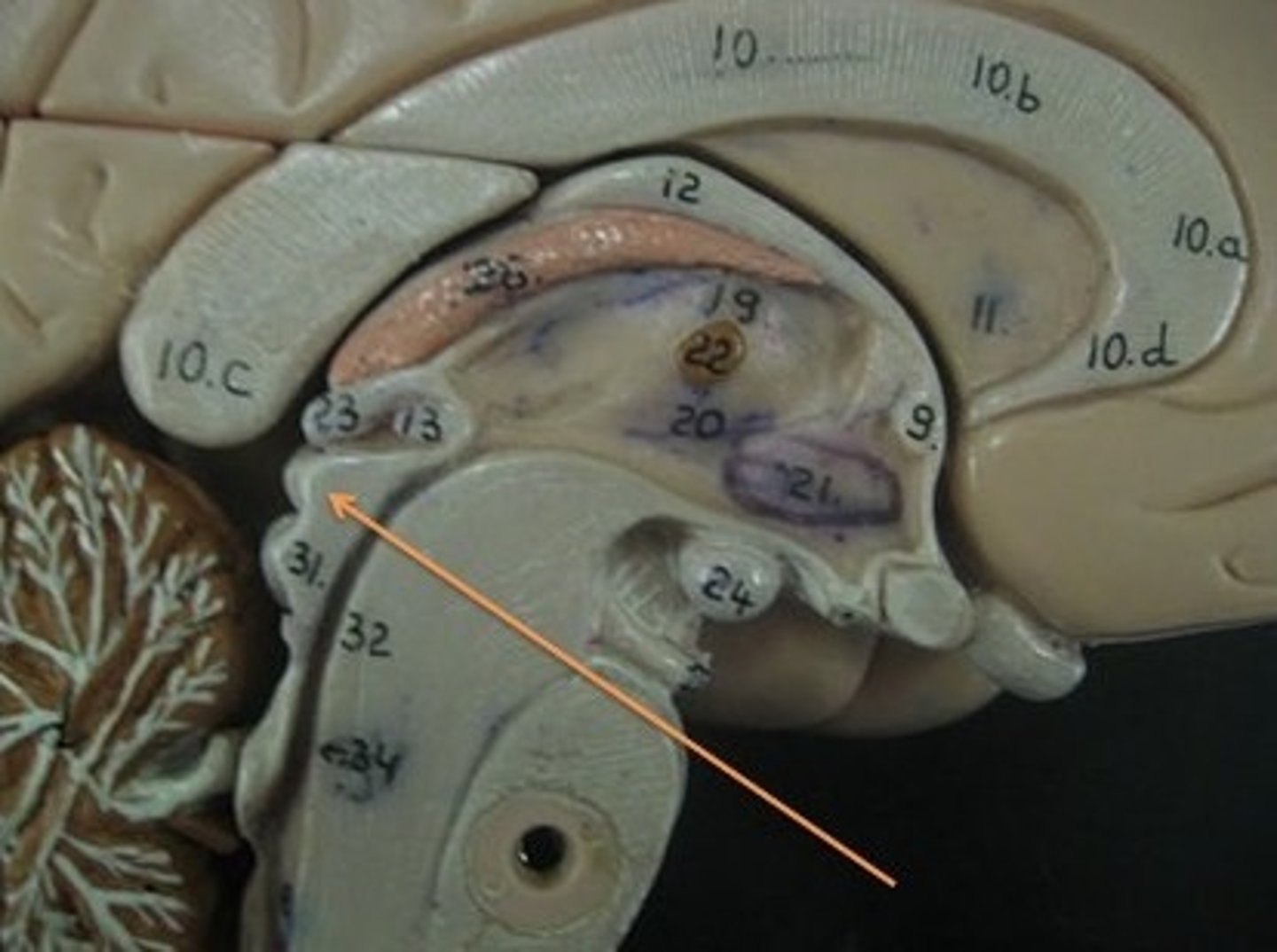
Inferior Colliculi
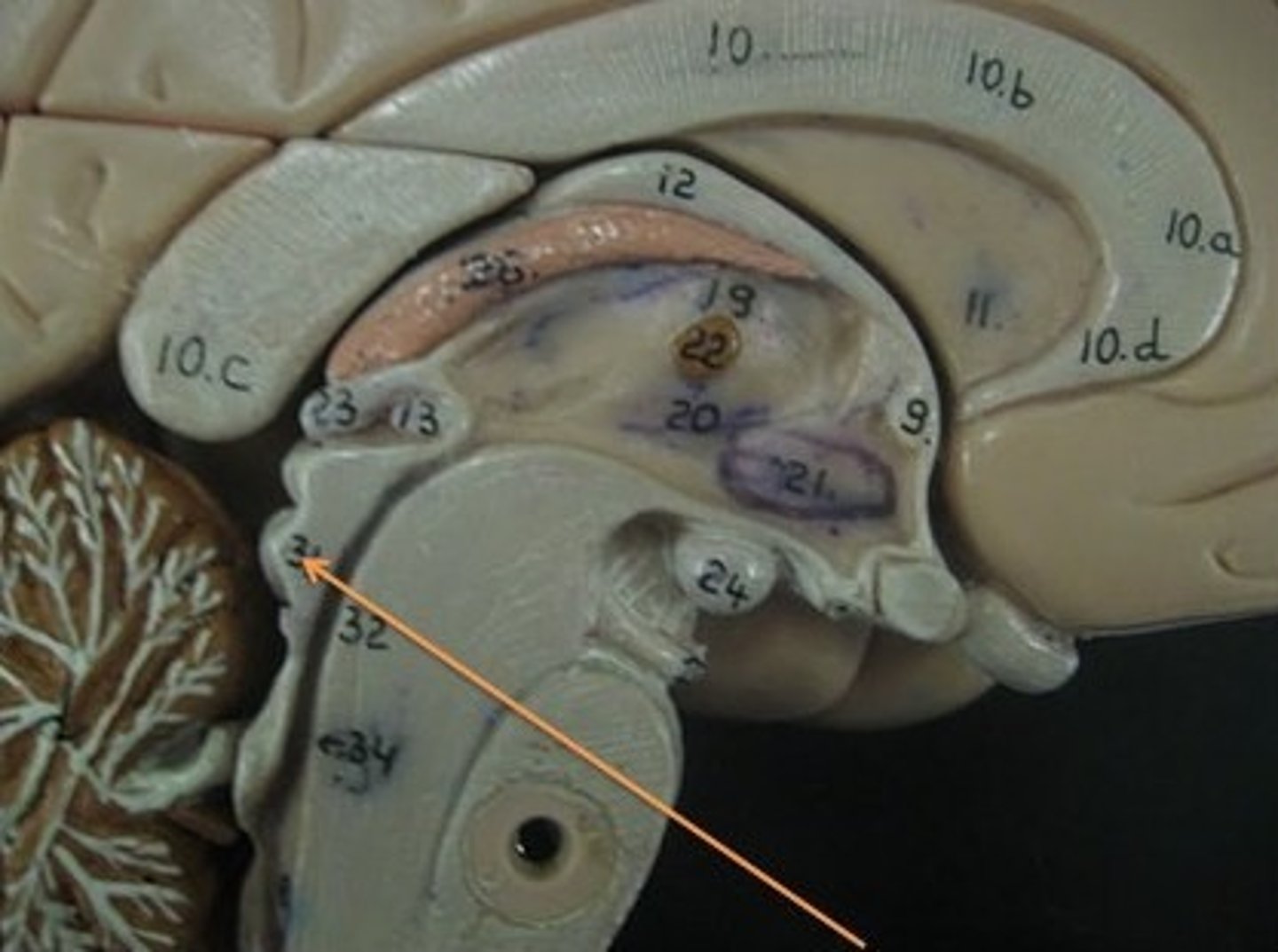
Midbrain
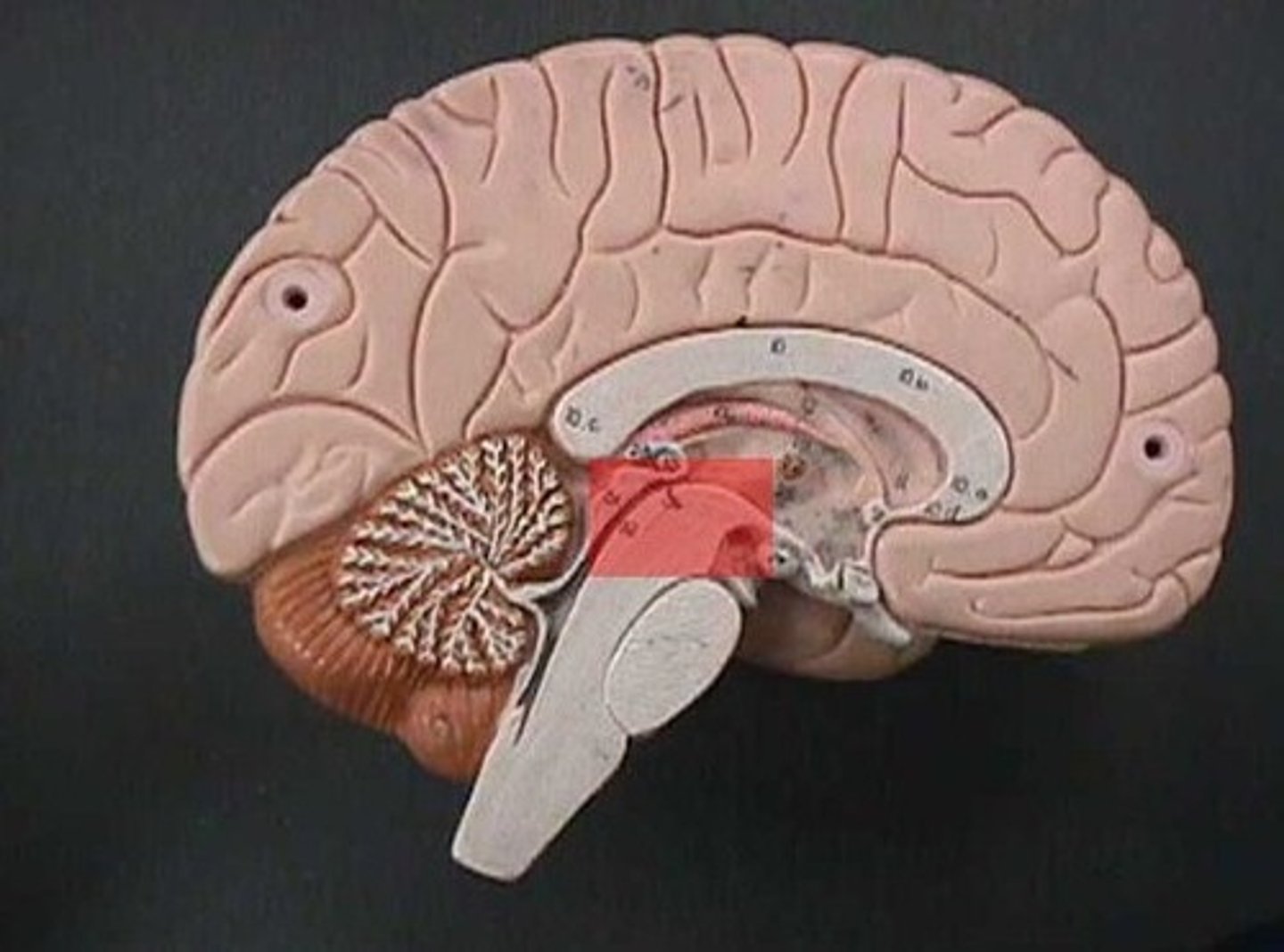
Hypothalamus
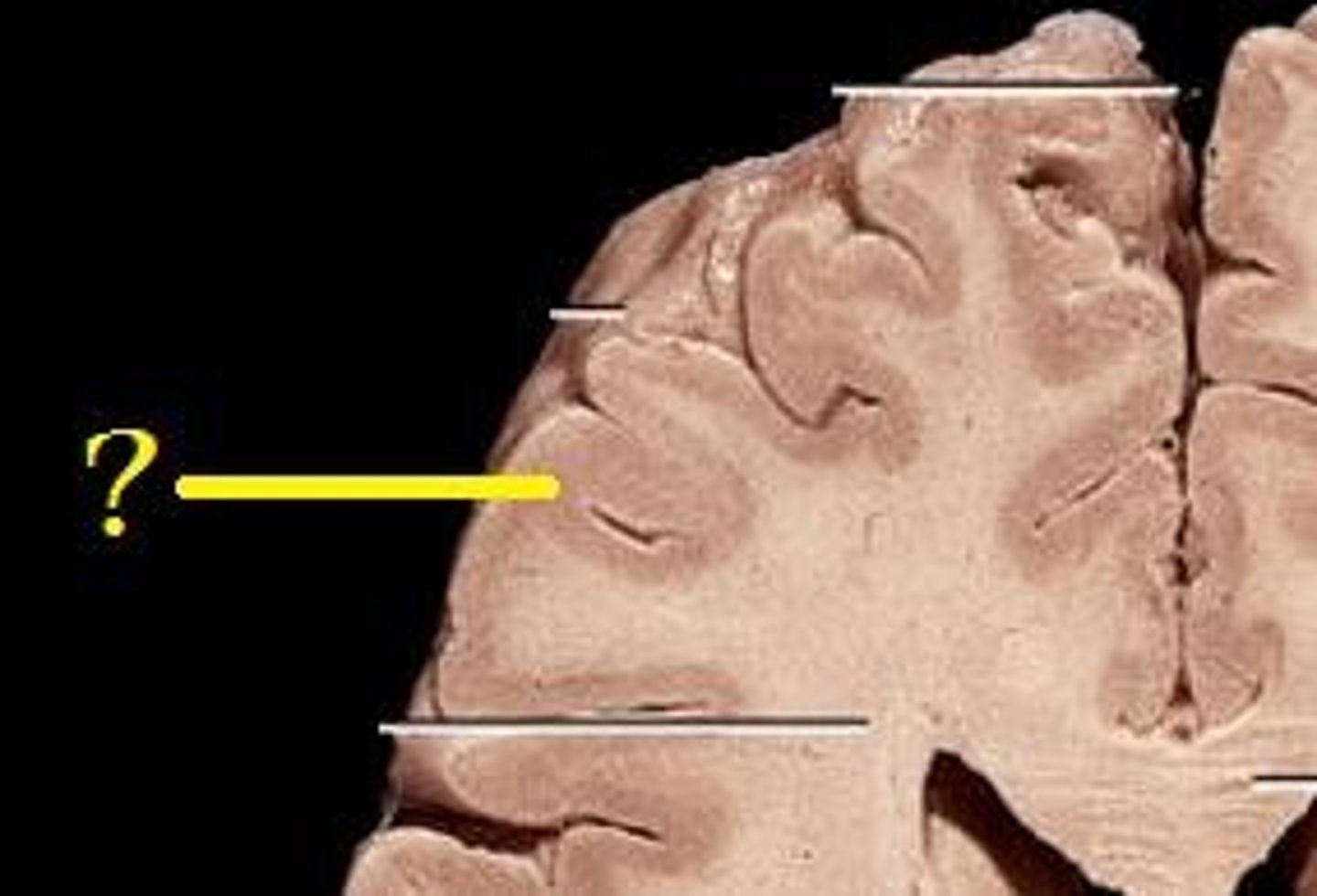
Cerebral Cortex Gray Matter (nerve cell bodies)
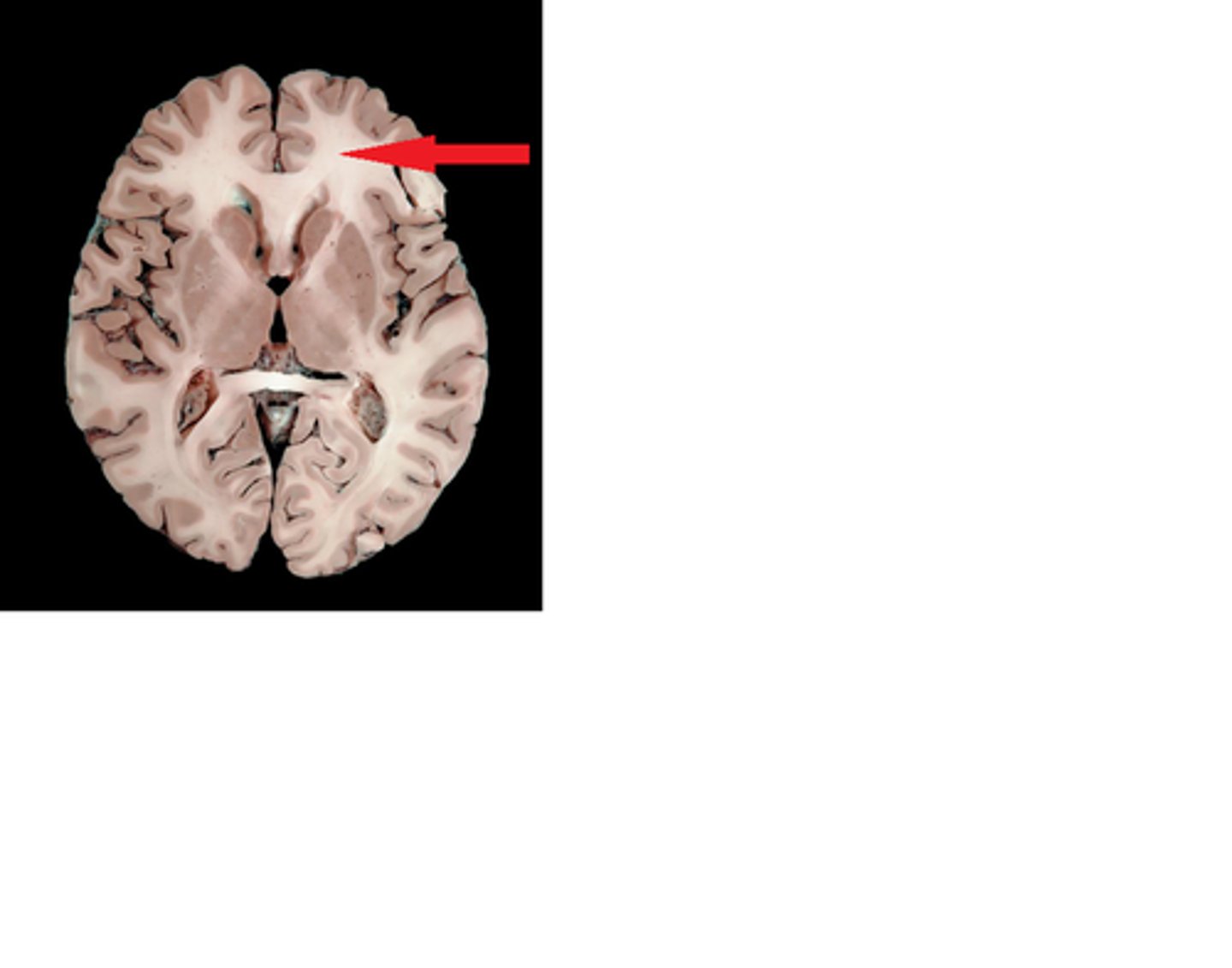
White Matter (myelinated nerve fibers)
What are all of the Cranial Nerves?
1. Olfactory
2. Optic
3. Oculomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Trigeminal
6. Abducens
7. Facial
8. Vestibulocochlear
9. Glossopharyngeal
10. Vagus
11. Accessory
12. Hypoglossal
Olfactory Nerve
Function: special sensory- smell
Location: Telencephalon
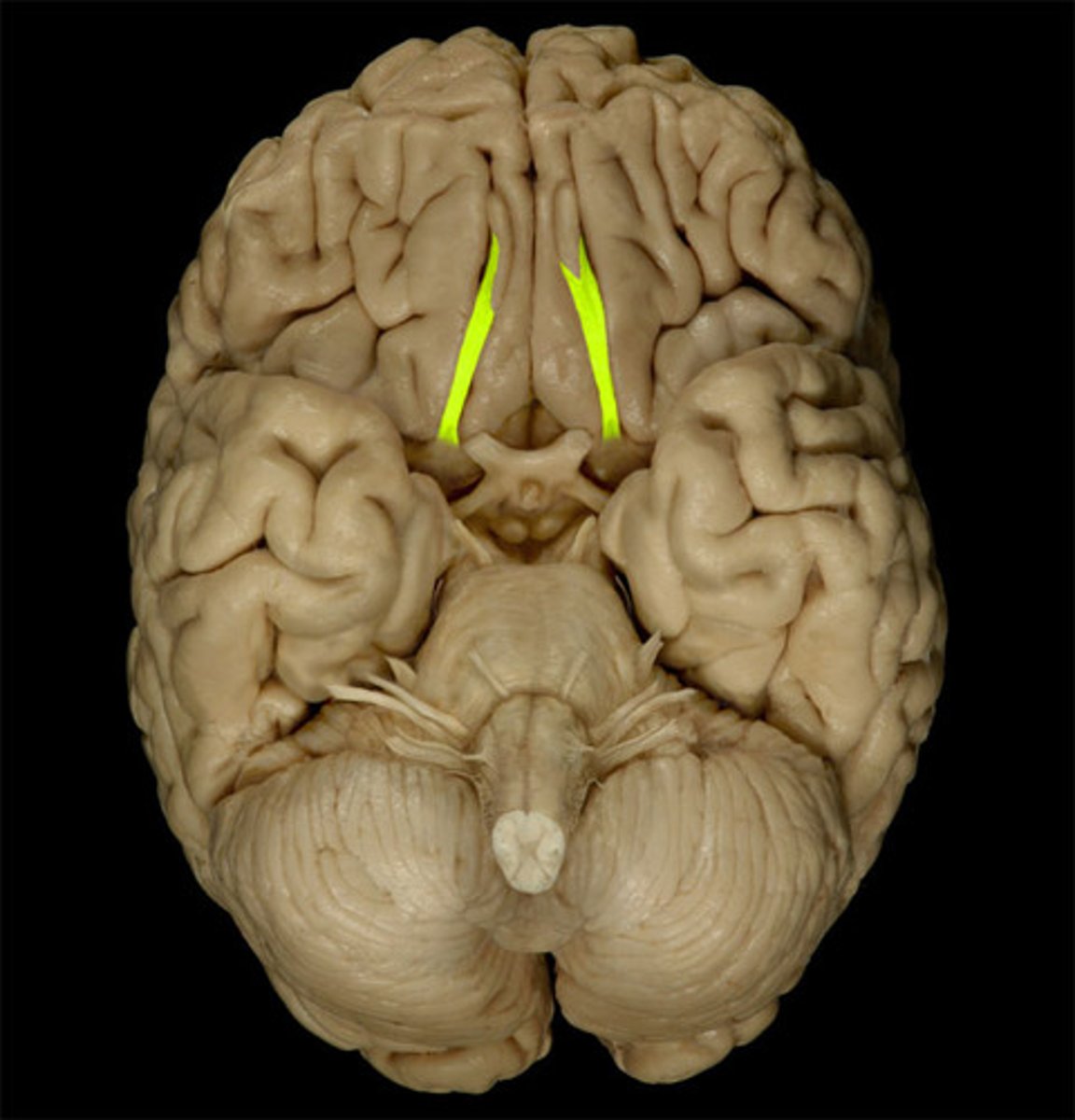
Optic Nerve
Function: special sensory- vision
Location: Diencephalon
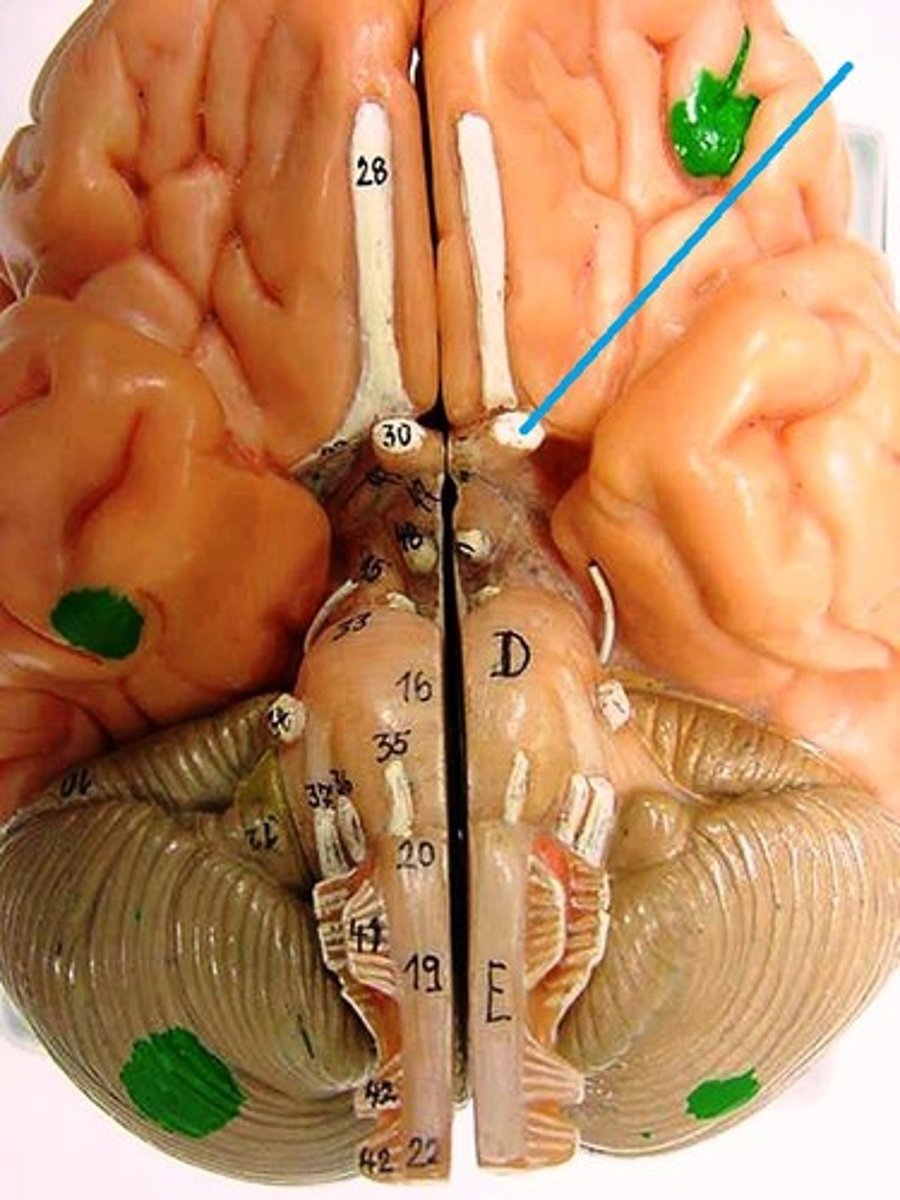
Oculomotor Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement; lid elevation, pupil contraction, lens shape
Location: Midbrain
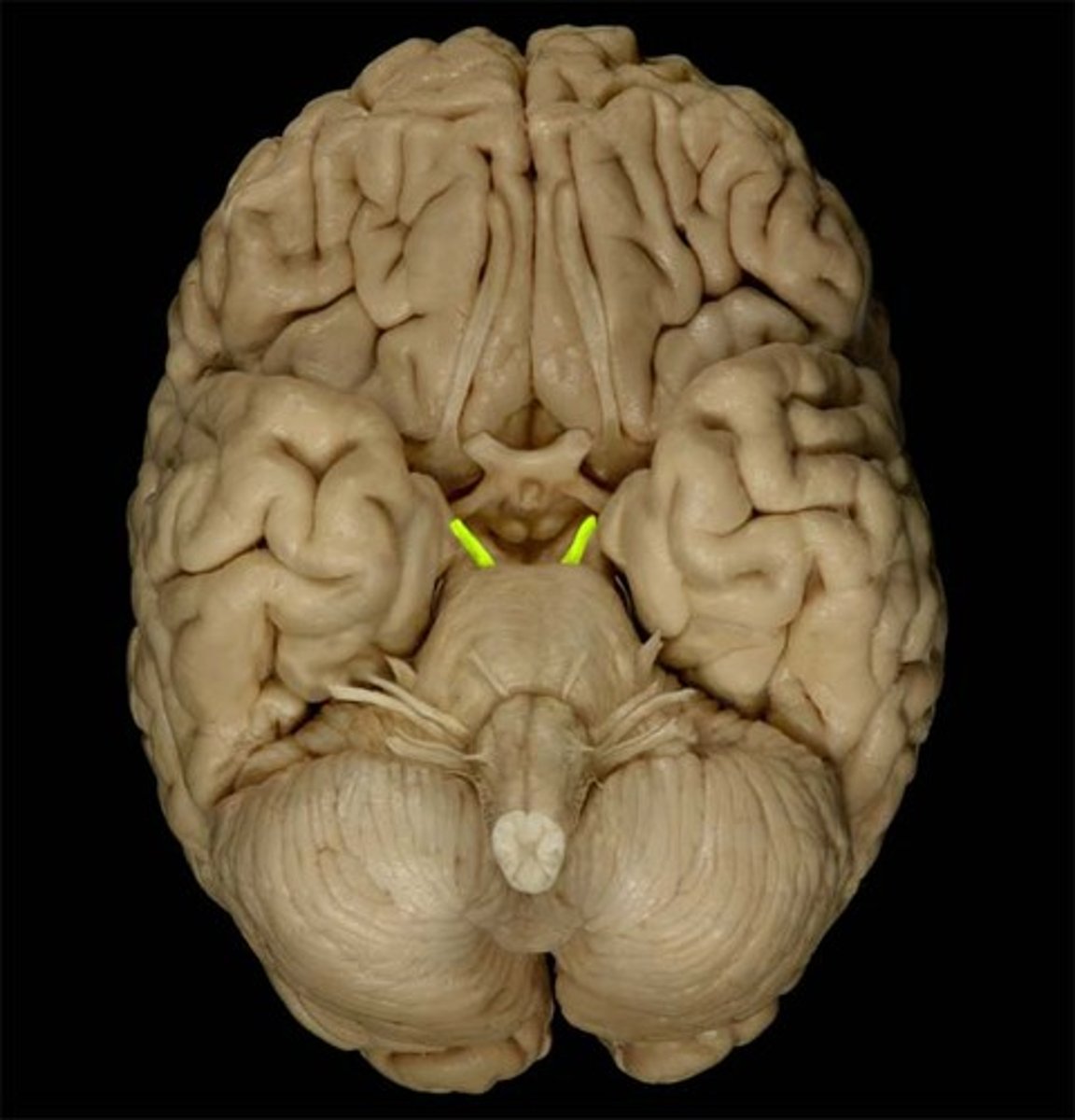
Trochlear Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement (downward and inward)
Location: Midbrain
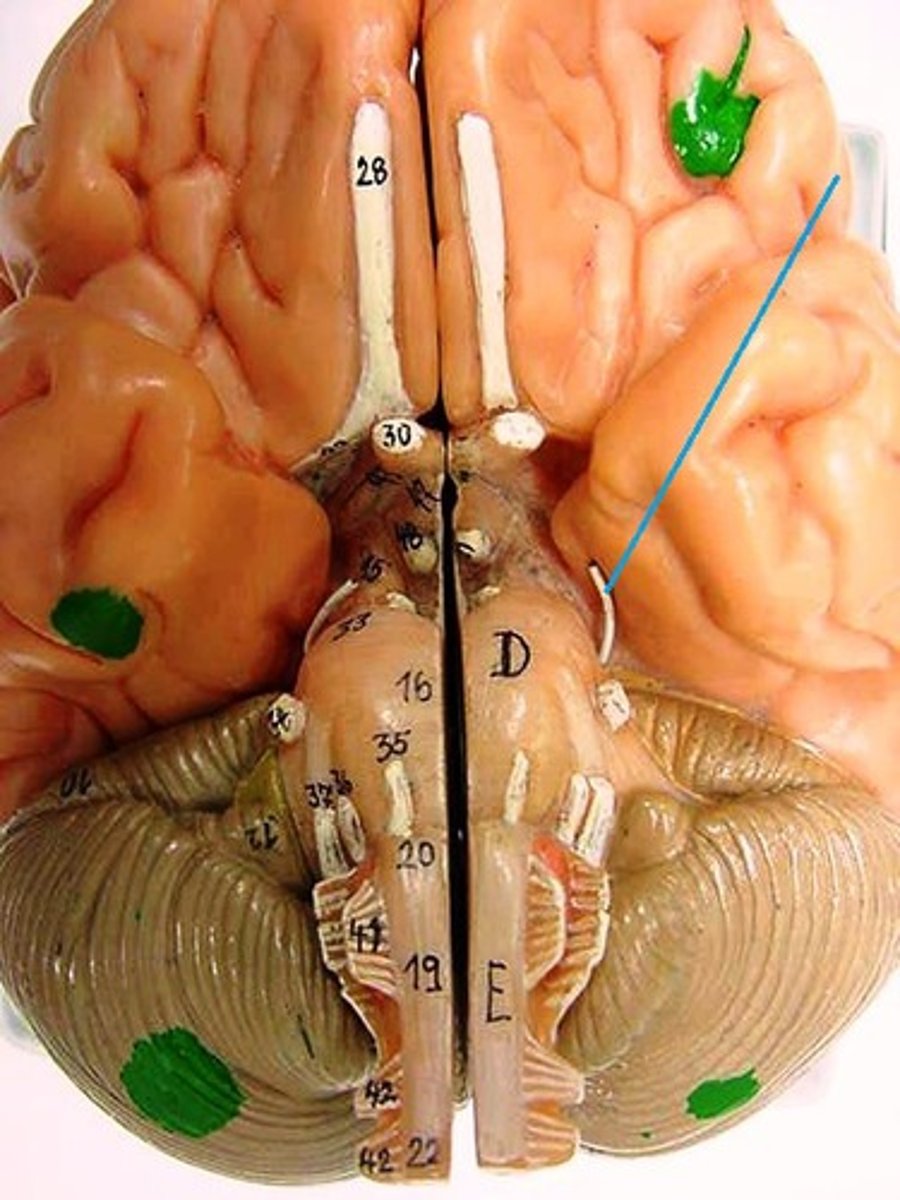
Trigeminal Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, general sensory)- mastication, touch, pain, temperature
Location: Pons
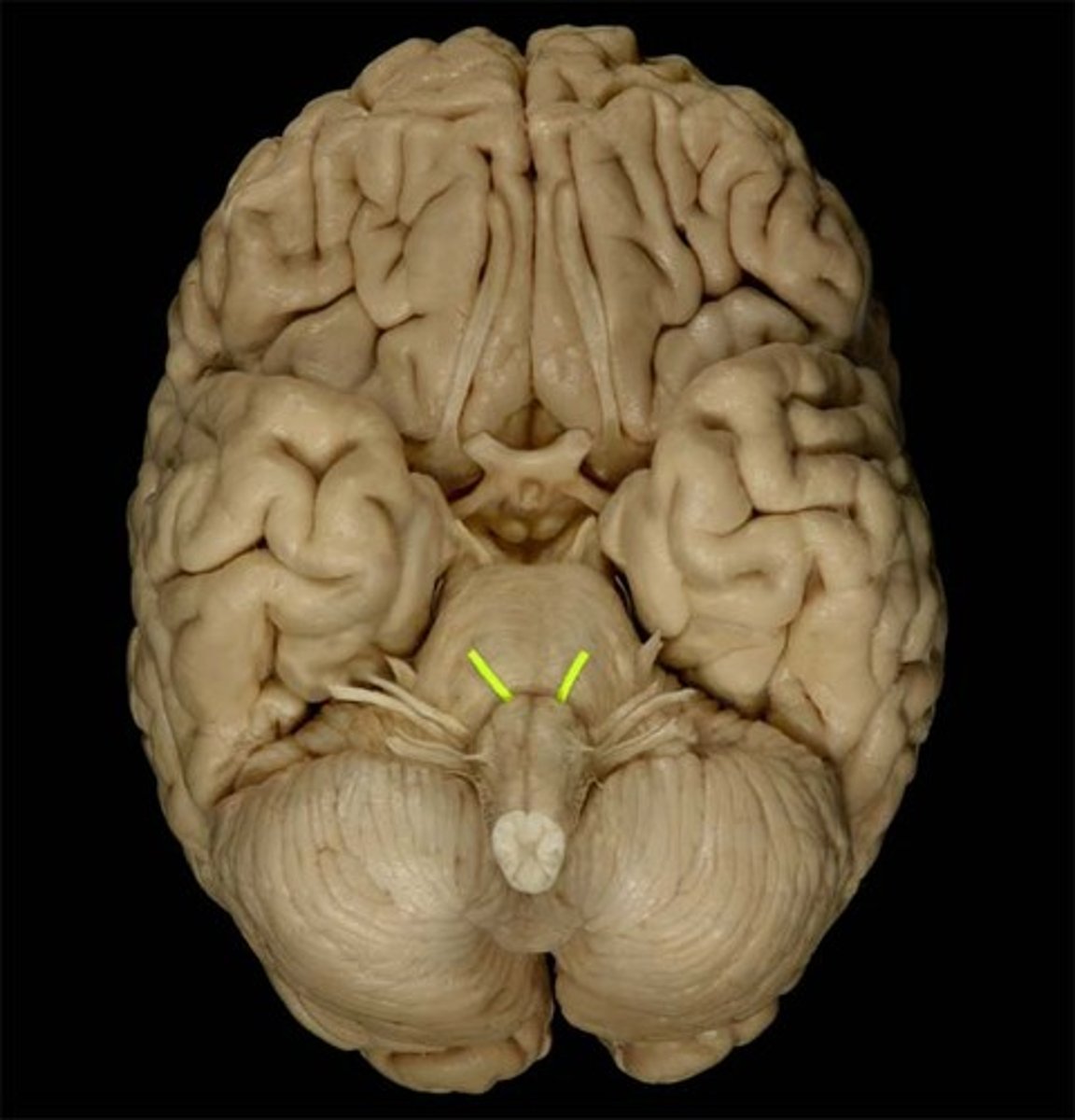
Abducens Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
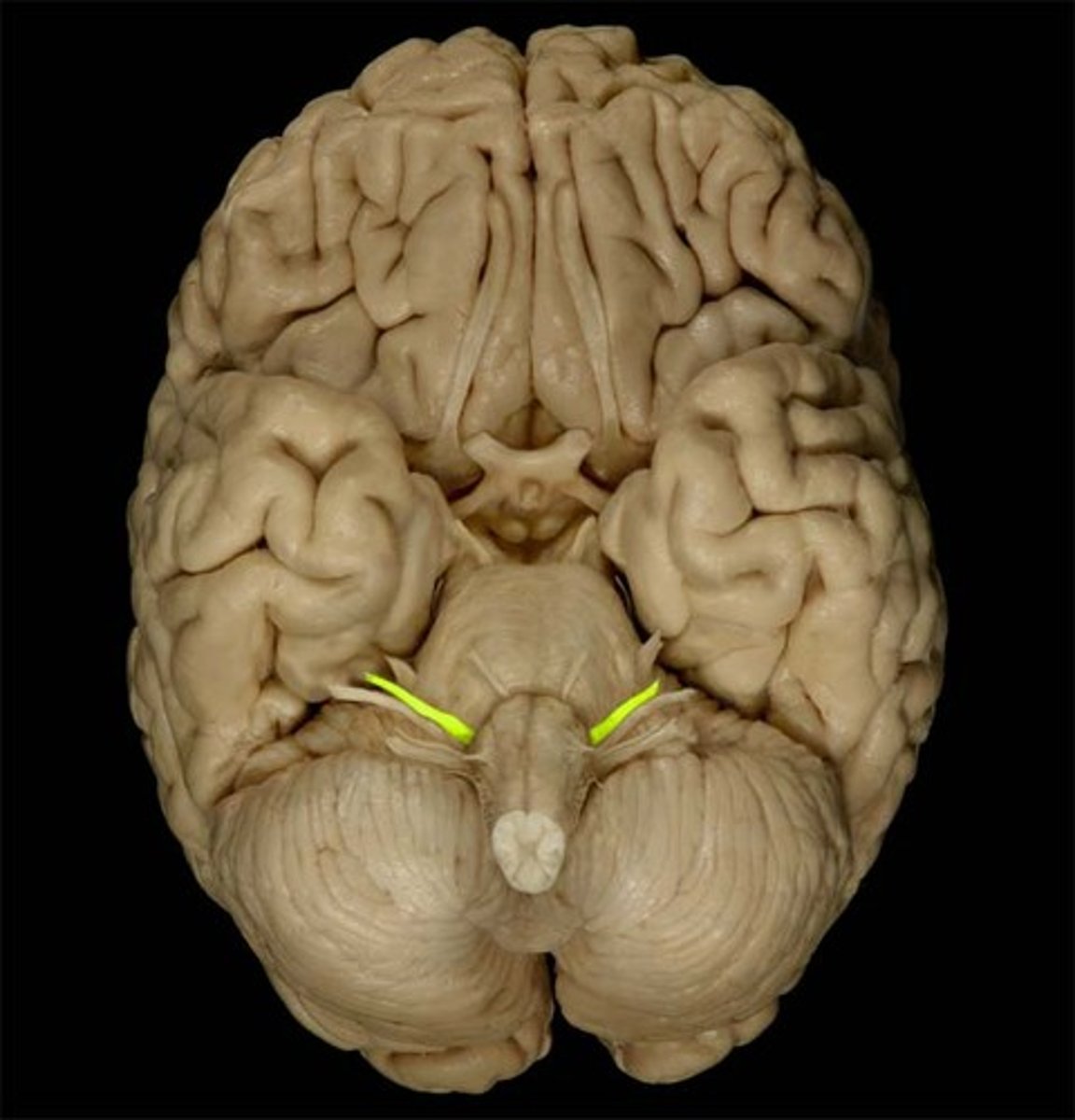
Facial Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, general sensory)- facial expression, lip articulation, taste on anterior tongue, secretion of saliva and tears
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
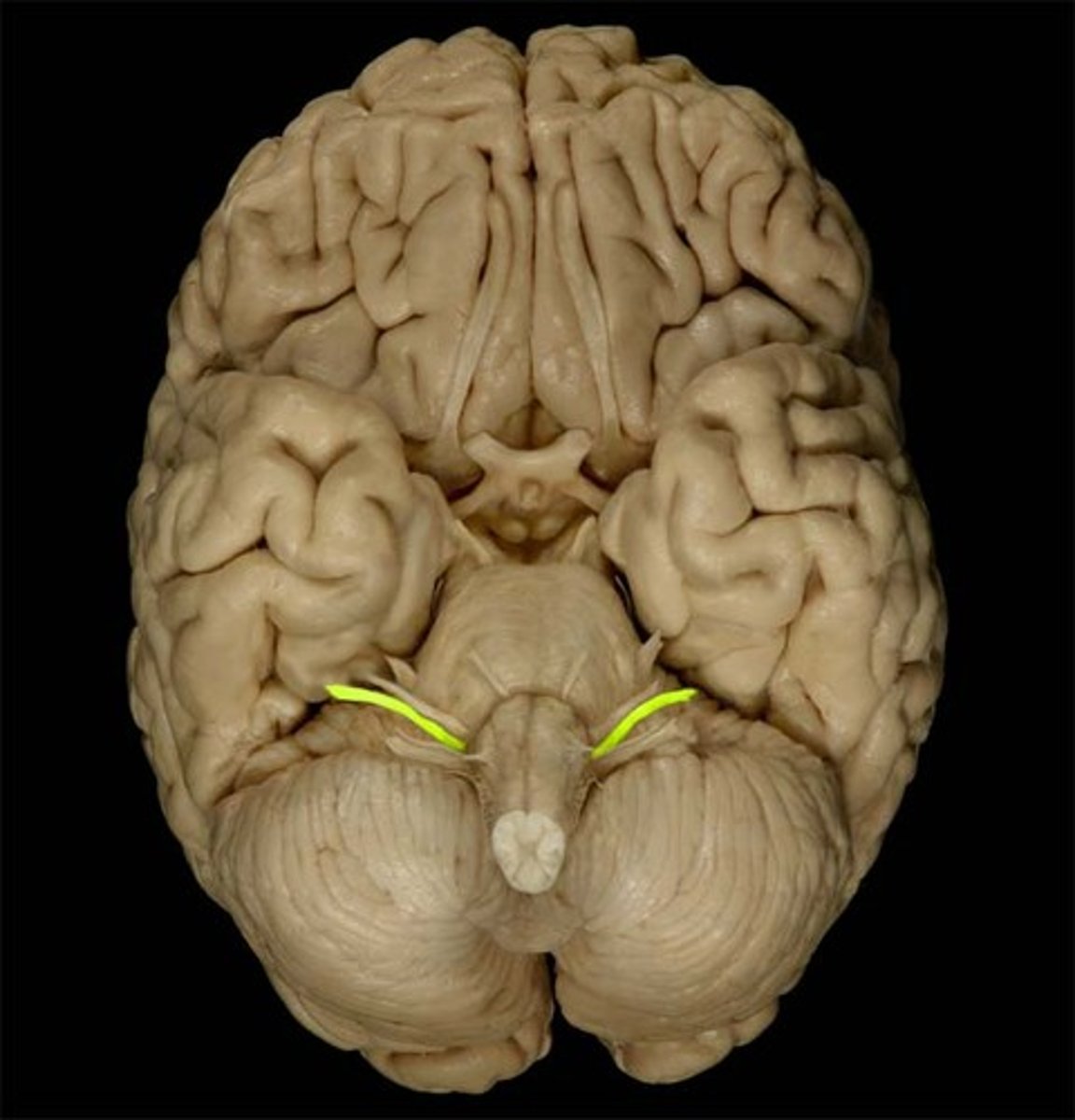
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Function: special sensesory- hearing and balance
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, visceral sensory, general sensory)- taste on posterior of tongue, gag reflex, swallowing
Location: Medulla
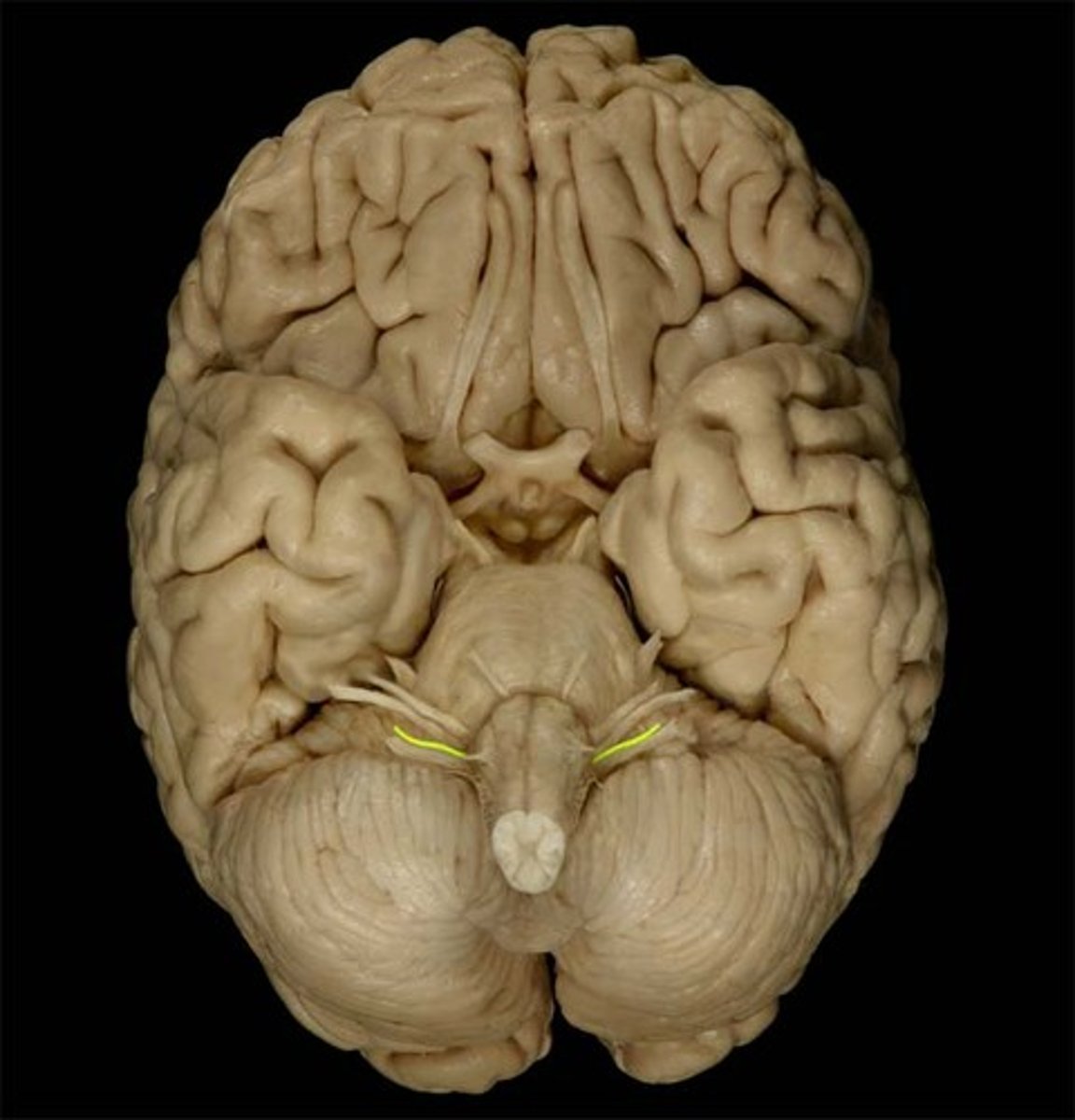
Vagus Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, visceral sensory, general sensory)- visceral muscle movement (heart, lungs, intestines)
Location: Medulla