PNB Practical #2
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
where does stimulus for muscle movement travel (5 steps)
- stimulus in cerebral cortex
- upper motor neuron
- action potential travels down corticospinal tract
- lower motor neuron
- skeletal muscle
on average 1 lower motor neurons innervates ___ skeletal muscle fibers
150
eye movements: 1 lower motor neuron innervates ____ muscle fibers
10-15
biceps brachii: 1 lower motor neuron innervates up to ____ muscle fibers
2000
if a single nerve fiber is stimulated, it will always give ...
a maximal response
3 steps of power stroke
- Ca2+ release from SR and binds to troponin
- tropomyosin shifts, exposing the myosin binding sites
- ATP is hydrolyzed triggering the contraction
what triggers the calcium release from SR
action potential
What is the I band of the sarcomere
contains only thin filaments (actin)
what is the H zone of the sarcomere
Contains only thick filament (myosin)
what is CapZ on sarcomere
the edge of the sarcomere
what is titan in the sarcomere
spring for myosin
what terminates muscle contraction
Calcium ATPase (SERCA) pumps calcium back into SR which reduces available calcium
isotonic contractions maintain ..
constant tension in the muscle as the muscle changes in lengths
2 types of isotonic contractions and what they do
- concentric: muscle shortens
- eccentric: muscle lengthens
contraction of ___ muscle causes relaxation (lengthening) of its ___ muscle
- agonist
- antagonist
(this is why in the lab when the bicep was stimulated on the graph the triceps were not & vice versa)
what is reciprocal activation
contracting muscle relaxes, antagonist contracts
what is coactivations
during reciprocal activation there is minor involuntary activity in the agonist muscle to provide support for the joint
what are isometric contractions
contractions in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change
- co contraction
(triceps and biceps are stimulated on the graph at the same time)
what is EMG and what does it measure
Electromyography -> electric muscle graph
- measures electrical activity of skeletal muscle
device = electromygraph
data = electromyogram (EMG)
in the lab where we lifted weights, where were the electrodes put
1) first, only biceps
2) then, biceps and triceps
what is powerlab
perform data acquisition, signal conditioning and pre-processing
"SIGNAL CONDITIONING"
raw EMG vs Inegrated EMG
Inegrated EMG - an average of the raw EMG -> used for analysis oft he data
4 important aspects of electrode placement
- ensure good electrical contact
- away from tendon
- avoid hairy areas
- ground electrodes should be placed as far away as possible from the recording electrodes
when holding different weights did you record an increase of EMG activity
yes
what does the largest amplitude in the recording mean
- recruited additional motor units (and therefore muscle fibers)
in the data where the forearm is extended, how will bicep and triceps look on the graph
biceps: less amplitude
triceps: more amplitude
is co contraction isometric or isotonic
isometric
is a wall sit co contraction or reciprocal activation
co contraction
is a plank isometric or isotonic
isometric
is a push up isometric or isotonic
isotonic
Put these events in chronological order
A. Ach release into synaptic cleft.
B. Action potential propagates along axon of motor neuron
C. Ach receptor binding leading to Na+ influx into the motor endplate
D. Calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in fluxes into the cytosol and binds to troponin in the muscle fiber
E. Muscle contraction
F. Ca++ influx through voltage-gated channels in the axon terminal at neuromuscular junction
BFACDE
Monitoring of EMG of patients during spinal cord or brain surgery can prevent _______
- paralysis of patients after surgery
we utilized ___ to measure the electical activity of the muscle
- EMG
we are utilizing a ________ to measure muscle tension
- force transducer
what do twitch, summation, unfused tetanus, and tetanus look like on a graph
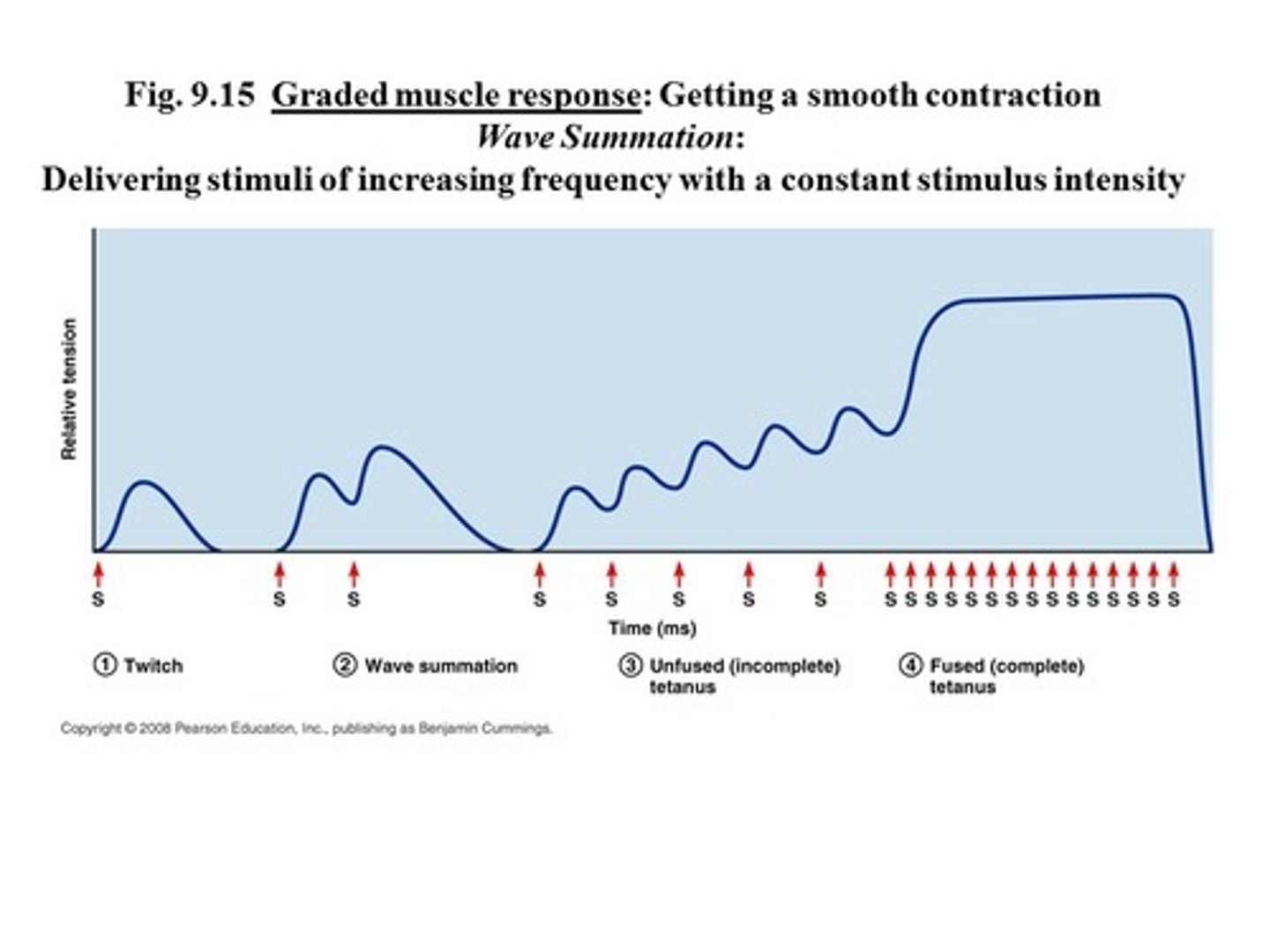
what is the relation between summation and unfused tetanus
summation leads to unfused tetanus
what does the voltage from the stimulator mimic
the activation of motor units
what does the increase of the voltage stimulator do
- more muscle fibers are stimulated -> increased muscle contraction of the muscle
relationship between motor units and muscle and the all or none idea
motor unit = all or none
muscle = variable activation via recruitment
what is on ring stand 2
- stimulator connected to machine
why is the zero- and 5-gram measurement important
- used in calibration table
- calibration gives a baseline measurement
what was changed to achieve tetanus
frequency of stimulation
what was changed to achieve maximal contraction
higher amplitude of contraction
3 causes of muscle fatigue
- build up of molecules from lactic acid (ADP, PI, MG2+, H+)
- H+ competes with Ca2+ in binding with tropomyosin
- conduction failure (lack of power stroke)
In a state of rigor mortis, muscles are highly contracted and difficult to manipulate. Why does this phenomenon occur?
A) Excess stimulation from motor neuron
B) no stimulation from motor neuron
C) Lack of ATP
D) Lack of Calcium
C) Lack of ATP
why does rigor mortis go away
decomposition of tissue
what are the fibers within an earth worm
1 medial fiber (larger)
2 lateral fibers (smaller)
how do lateral fibers differ from the medial giant fiber in terms of threshold conduction
- lateral fibers have a higher threshold and slower conduction
in giant fibers (medial fibers) nerve cells are electrically ____________, so each giant fiber can _______________________
- coupled through gap junctions
- behave as if a single axon
what is the difference between intracellular and extracellular recordings
intracellular = direct
- records voltage potential across the membrane and is more accurate
extracellular = indirectly
- records potential changes at membrane surface
-requires electrode placement near excitable cell
in the earth worm lab are we recording intracellularlly or extracellularly
extracellularly
if the stimulating electrode is placed on the left, what are the electrodes next to it from left to right
- ground electrode
- negative electrode
- positive electrode
how is the calculation made using the electrodes
potential differences between 2 recording electrodes
- charge @ positive electrode - charge @ negative electrode)
in the earth worm data, there is a quick, tall amplitude before a second one that is a little shorter and wider:
- what is the first one and what is the second
- stimulus artifact
- biphasic wave
in the recruitment of the lateral fiber what will we see
see all or nothing response
when an initial stimulus is sent what does it cause
cause action potential to propagate down the medial giant fiber
what does a stronger stimulus cause
cause recruitment of the lateral fibers
what is important to do when you are recording to ensure the signal you are seeing is real and not noise
use overlay data mode and not "solo"
what is the absolute refractory period
Na+ channels are inactivated
- not stimulus will reopen the channels to allow Na+ in and depolarize them membrane
what is the relative refractory period
some of the Na+ channels are still inactivated but some have reopened
- however: the membrane potential is more negative making it difficult to depolarize
- needs a high stimulus
how to calculate velocity using the absolute method
V= D1/LP1
D1 - distance 1
LP1 = latency period 1
how to calculate velocity using the difference method
V = (D2-D1)/(LP2-LP1)
D = distance
LP = latency period
how to tell the dorsal view vs anterior view and head vs tail
- head is closer to clitellum (chunky tag piece
- dorsal = darker
how is the earthworm oriented in this lab
- dorsal side up
- stimulator on head
what can the biphasic wave be described as
an extracellular recording that only shows the AP propagation along the fiber
what is the latency period for the medial and lateral axons
medial: from stimulus artifact to beginning of first biphasic wave
lateral: from stimulus artifact to beginning of second biphasic wave
increasing the voltage of stimulation will __ the stimulus artifact and ___ the amplitude of the action potential
- why?
- increase
- not change
Amplitute of AP depends on properties of ion channes and it is not affected by stimulation strength (all-or-none)
when two stimuli are applied to a neuron and only one response is observed, you can conclude the neuron is in
refractory period
in the brain where is white matter compared to gray matter
white is deeper to gray matter
what is cranial nerve I and is it sensory, motor, or both?
olfactory
- sensory
what is cranial nerve II and is it sensory, motor, or both?
optic
- sensory
what is cranial nerve III and is it sensory, motor, or both?
oculomotor
- motor
what is cranial nerve IV and is it sensory, motor, or both?
trochlear
- motor
what is cranial nerve V and is it sensory, motor, or both?
trigeminal
- both
what is cranial nerve VI and is it sensory, motor, or both?
abducens
- motor
what is cranial nerve VII and is it sensory, motor, or both?
facial
- both
what is cranial nerve VIII and is it sensory, motor, or both?
vestibular
- sensory
what is cranial nerve IX and is it sensory, motor, or both?
Glossopharyngeal
- both
what is cranial nerve X and is it sensory, motor, or both?
Vagus
- both
what is cranial nerve XI and is it sensory, motor, or both?
accessory
- motor
what is cranial nerve XII and is it sensory, motor, or both?
hypoglossal
- motor
is the fissure of the spinal cord in the dorsal or ventral side
ventral
what is the path of the patellar reflex arc
- sensory receptor in agonistic muscle
- sent to dorsal root
- sent to internode that connects to 2 motor neurons
- one neuron is sent to agonist muscle
- one is sent to antagonist muscle
what is the Jendrysik maneuver
- enhances tendon reflex by clasping hands together and pulling as hard as possible
- person should look somewhere else and think of other things
what is it called when there are only 2 neurons in the reflex arc
monosynaptic
what is it called when a reflex arc contains an interneuron ascending the spinal cord
polysynaptic
what are the 5 endocrine tissues in our body
- pituitary gland
- thyroid gland
- parathyroid gland
-pancreas
- adrenal gland
what is the thyroid gland responsible for
metabolism
what are the cells found in the thyroid and why are they important
follicular cells
- produce thyroglobin that is a precursor of thyroid hormones
- contain T3 and T4
- increases metabolic rate
what is the thyroid hormone pathway and what is produced in each place
TRH produced in hypothalamus
-TSH produced in anterior pituitary
- T3/T4 produced in thyroid
what are 3 important aspects of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
- increase metabolism of carbohydrate, fats, and proteins
- increase O2 consumption
- produce heat
what are 3 important aspects of Propylthiouracil
- PTU interferes with iodination process during the production of thryroglobin
- decreases thyriod function (hypothyroidism)
- decreases O2 consumption
what are the 3 different groups in the rat experiment
- control group
- thyroid hormone
- PTU
in step 1 of the rat lab, how do we determine mL of O2 consumed
total O2 consumed across all trials/ (total time in seconds/60)
-> 3 trials x5mL per trial / (total time in seconds/60)
based on ours it was
15ml/(total time in seconds/60)
in step 2 of the rat lab, how do we determine the amount of air inhaled using mL of O2 consumed
Use O2 consumption rate from step 1 / 0.21
- atmosphere is 21% oxygen
in step 3 for the rat lab how do we normalize for mass of the mouse
calculated O2 consumption rate (Step1)/ mass of mouse in grams
what are the 4 zones of the adrenal gland
- zona glomerulosa (mineral corticoids)
- zona fasciculata (glucocoritcuts)
- zona rectularis (sex hormones)
- adrenal medulla (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
what is the iris
colored part of the eye that opens and closes the pupil
what is the pupil
hole at center of the eye that allows light to enter
what is the retina
inner most layer of the eye and composed of multiple specialized optic cells