RADT142- Electromagnetism (wk9)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Who invented the first battery (voltaic pile) made of copper/zinc layers? How does it work?
Alessandro Volta
When you attach a wire to the battery/voltaic pile, current is produced.
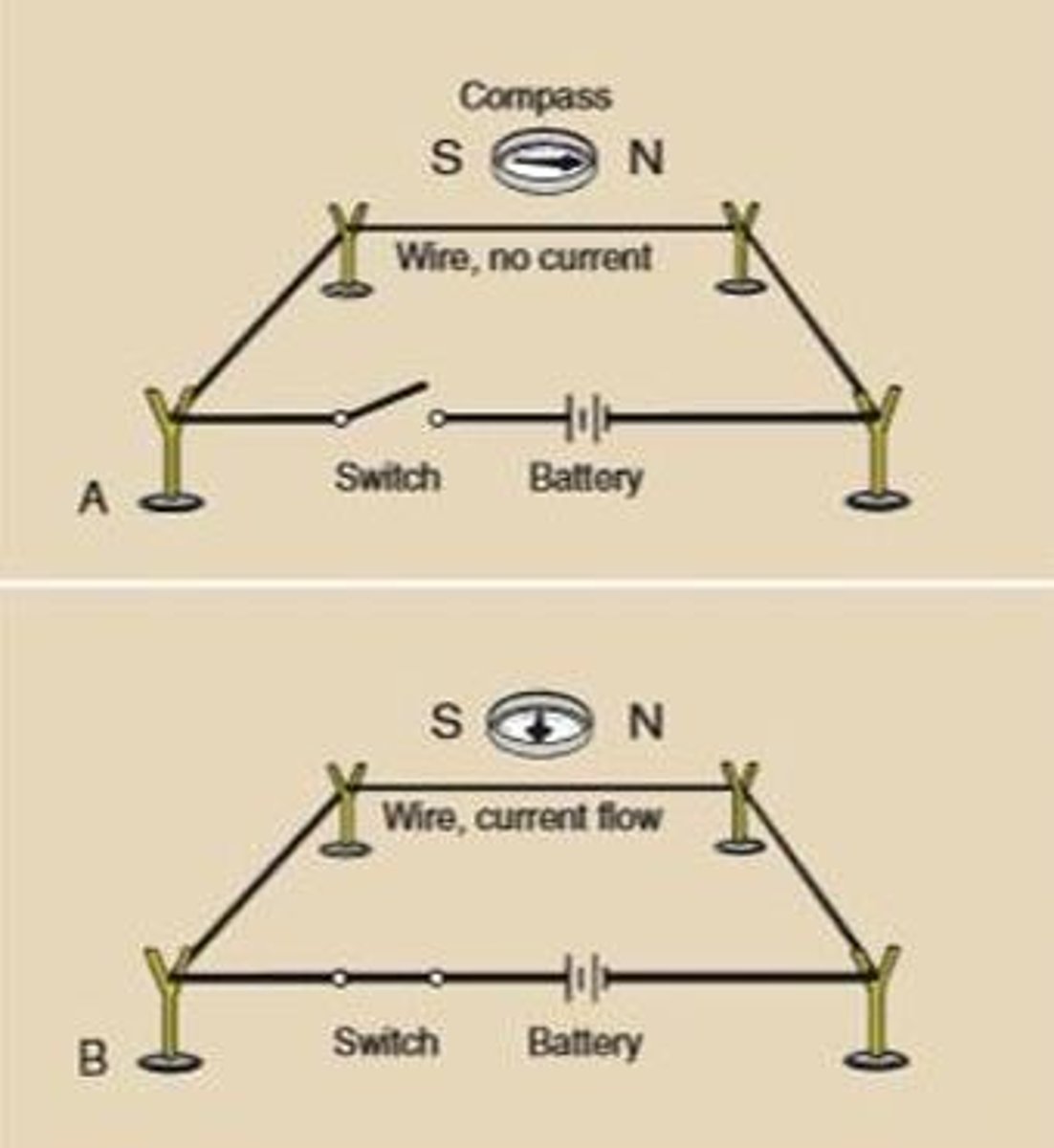
What did Hans Christian Oersted discover? Describe how it affects a compass.
Electric current produces a magnetic field
1. Without a current flow, compass points North
2. Applying a current flow, compass follows the current
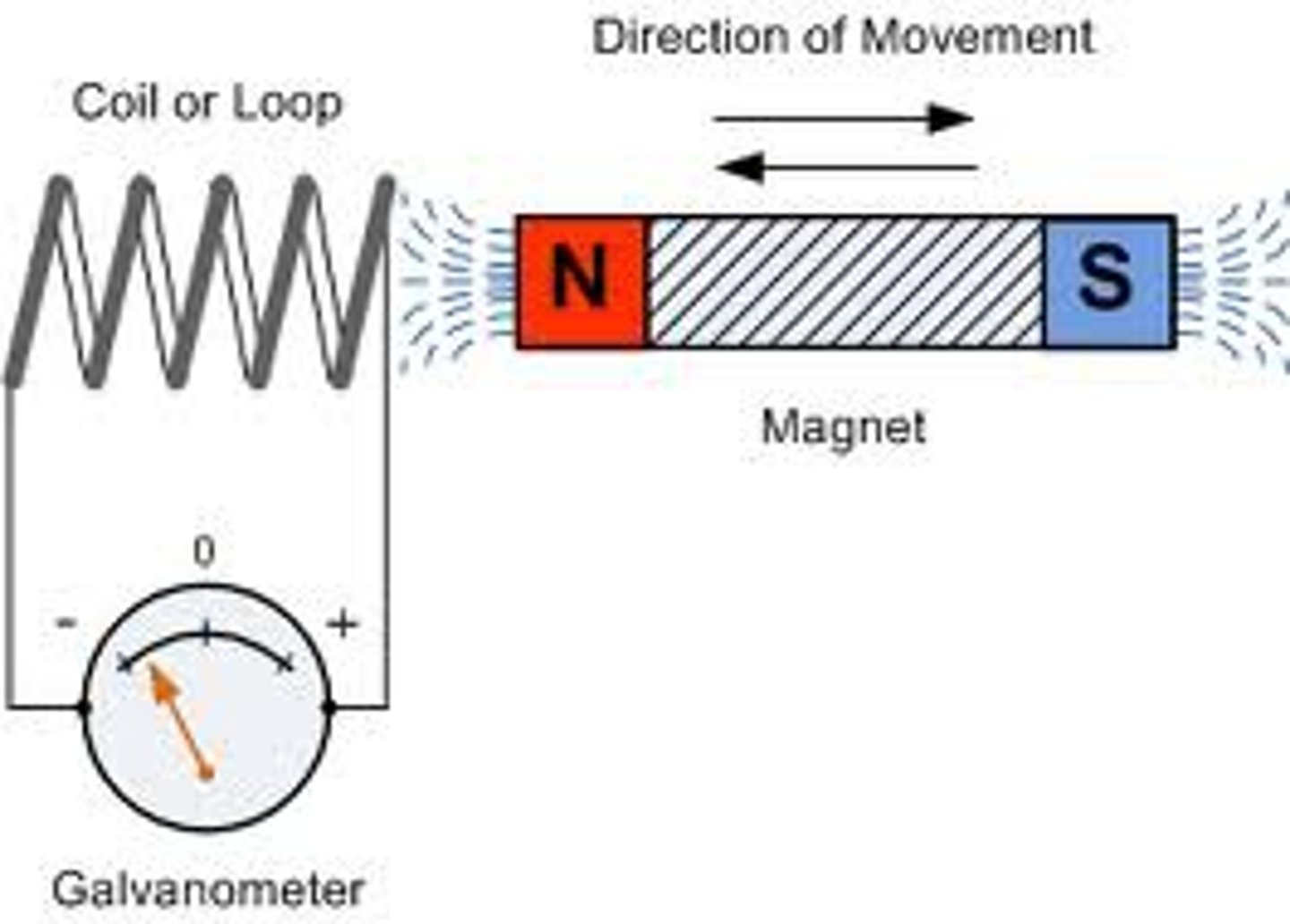
What was Michael Faraday's contribution to electromagnetism?
He found that a current is induced by moving a magnet (magnetic field.)
What is Faraday's Law of Magnetism? (electromagnetic induction)
When you move a magnetic field across a conductor or move a conductor across a magnetic field, it generates electromotive force (EMF, voltage, potential difference).
What is electromagnetic induction?
production of electric current by changing a magnetic field around it
What factors control the magnitude of induced current and their relationship with current (if applicable)?
1. Strength of Magnets (Direct relationship)
2. Speed of motion/velocity of the magnetic field (Direct relationship)
3. Direction of motion/angle of the conductor to magnetic field (90 deg to magnetic field = most current (I); ie perpendicular makes most current and parallel motion is least current)
4. Shape of conductor (more coils/loops/turns = more current)
- straight = least current
- medium coils/loops/turns
- many coils/loops/turns = highest current production
Describe the right thumb rule.
Grip a wire with your right hand
1. Thumb - direction of the current (runs positive (North) to negative (South))
2. Fingers curl in the direction of the magnetic field (counter clockwise)

What is a helix? Solenoid?
Helix = coil of wire
Solenoid = helix/coil of wire with a current
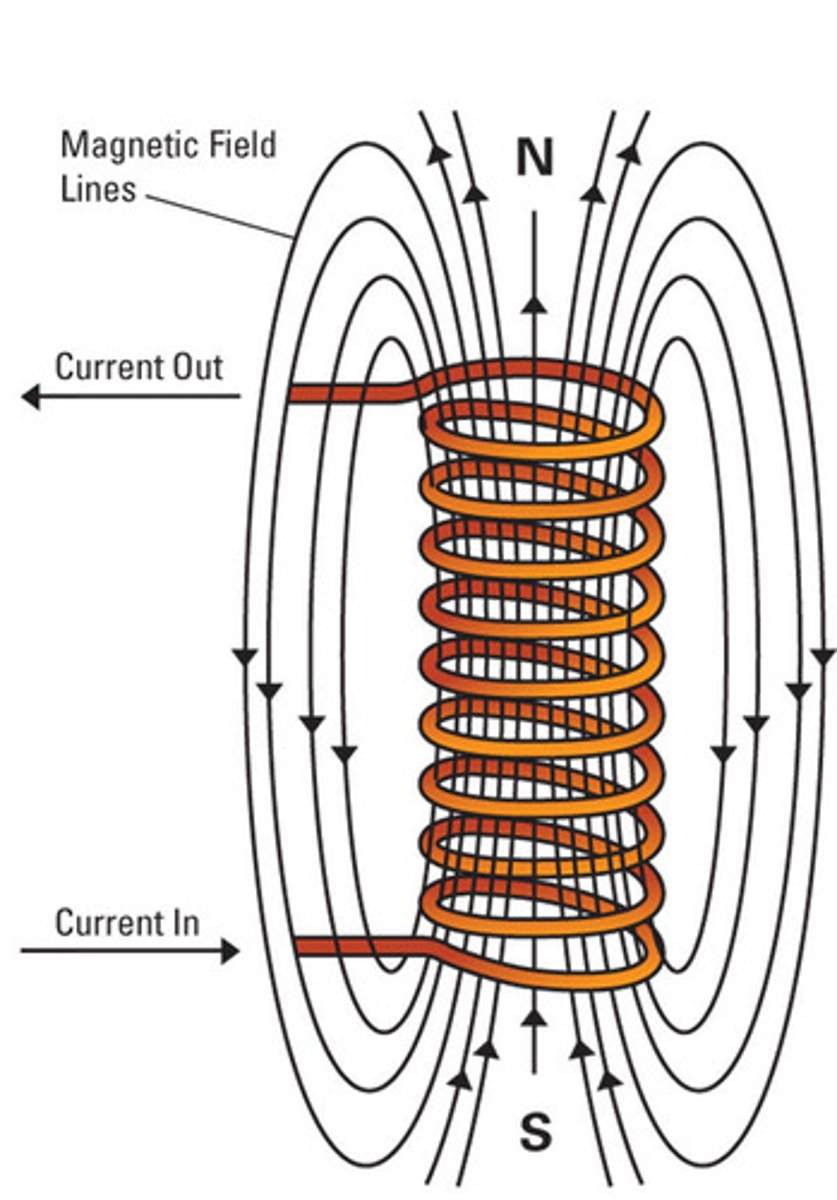
Current flows from ___ to ___
North (+) to South (-)
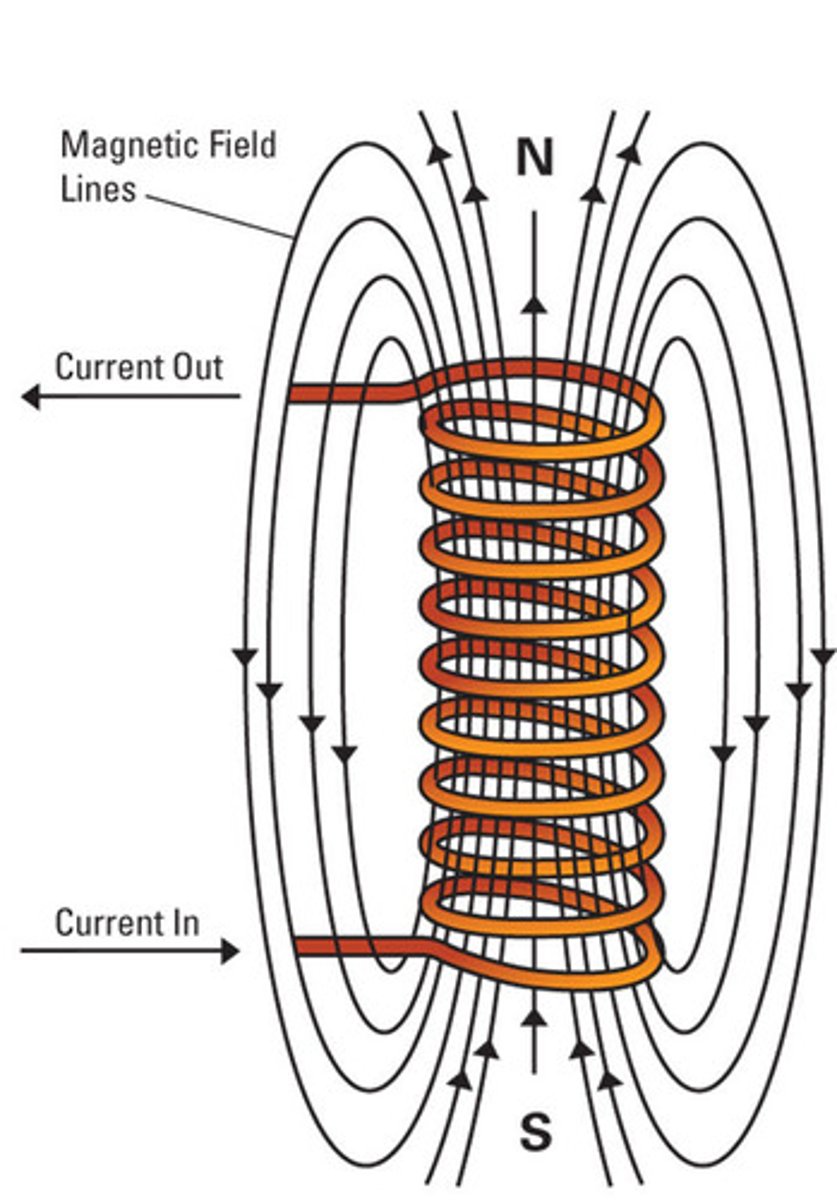
What is an electromagnet?
A solenoid with an iron core
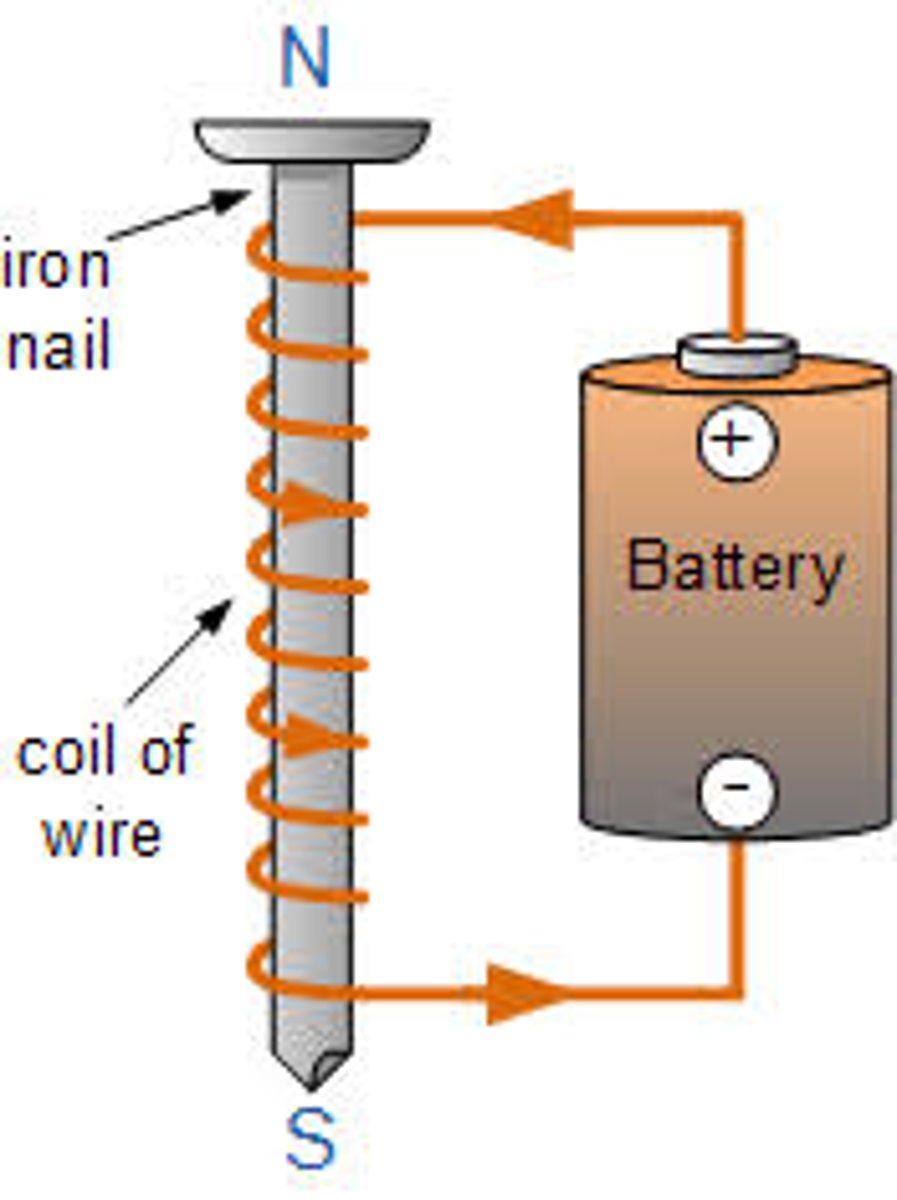
What is the relationship between ferromagnetic material and magnetic strength?
direct relationship; increase ferromagnetic material, increase magnetic strength
What is Lenz Law of Electromagnetism?
the induced current flows in the opposite direction of the applied current that produced it (it tells us the direction**)
- as energy increases-> magnetic field increases so much that it creates another magnetic field in the opposite direction
-Back EMF or Principle of self induction
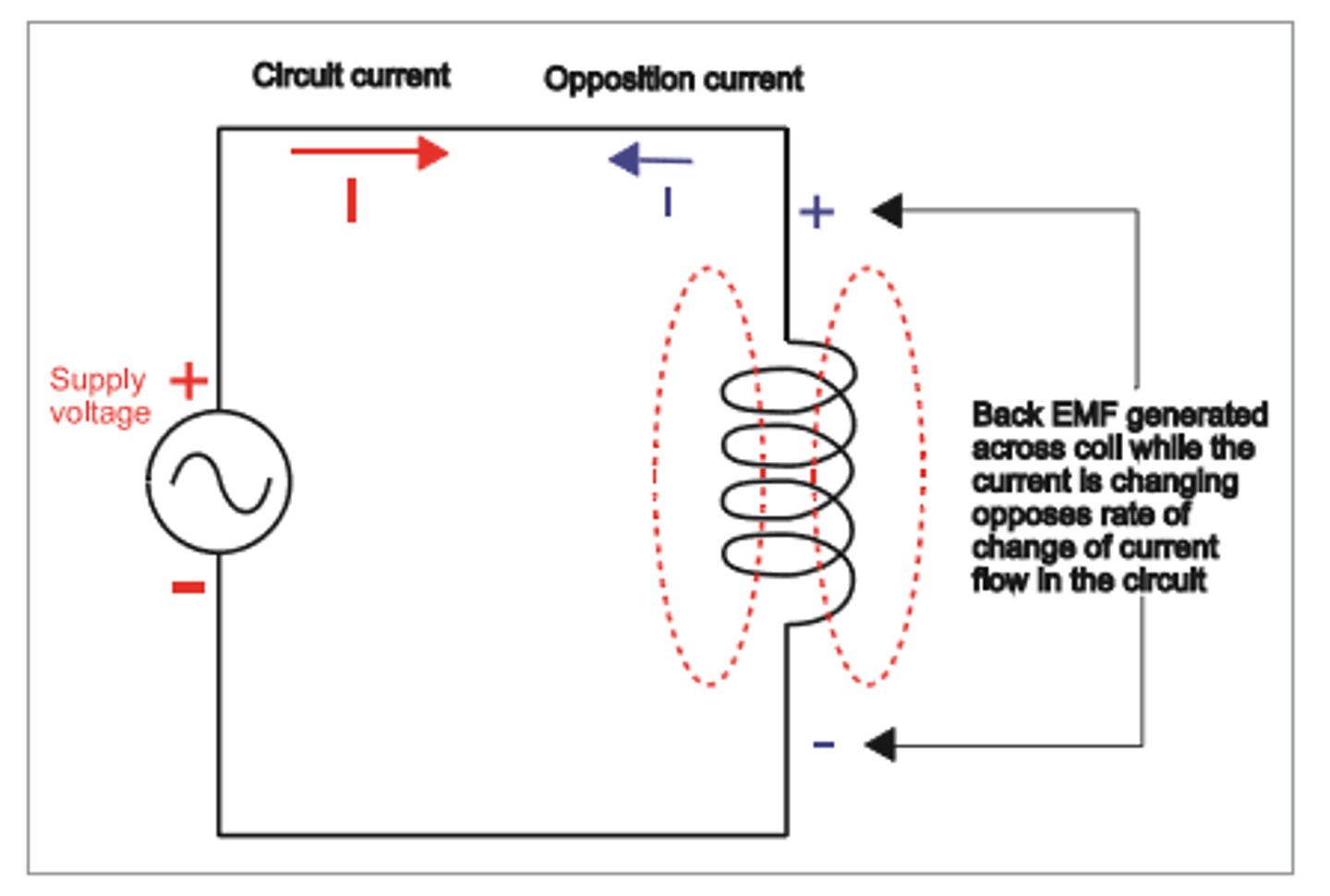
What is self induction?
the induction of opposing EMF in a single coil by its own changing magnetic field (induction in the same circuit); when a circuit changes current its magnetic field needs to account for the change so it induces an opposing EMF
What is mutual induction?
magnetic field induces a current in a nearby helix
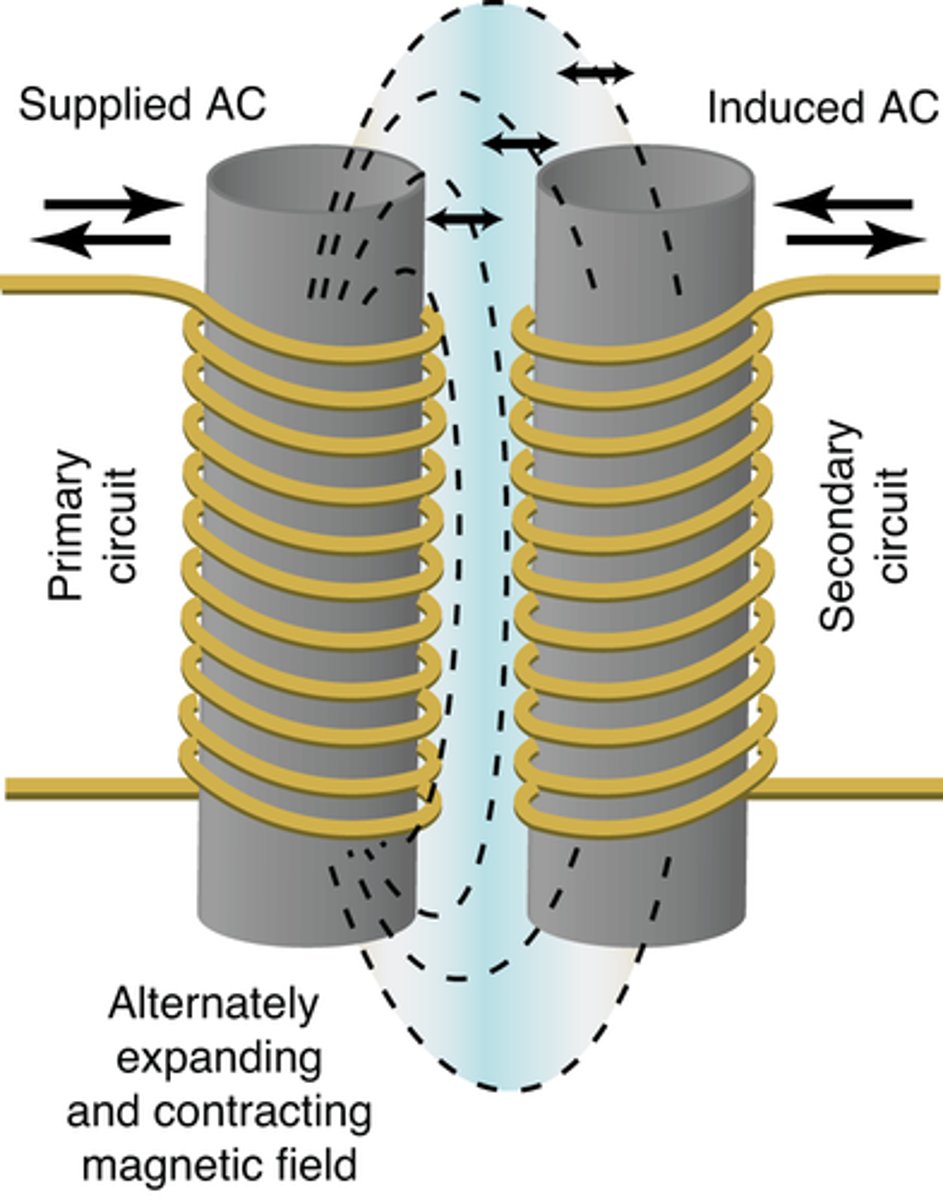
The magnetic field of primary coil will cause the secondary coil's induced current to flow in the ___ direction due to mutual induction.
opposite

Every magnet has two poles: ______ and ______
Like poles put together will store energy as ____ energy
When released of one another, the energy will be converted into ____ energy
North and South poles; potential, kinetic
Generator converts ___ energy to ____ energy
Motor converts ___ energy to ___ energy.
Generator converts MECHANICAL energy to ELECTRICAL energy
Motor converts ELECTRICAL energy to MECHANICAL energy.
What does alternating current generator graph look like?
0-90deg equilibrium to peak (+) = perpendicular to magnetic field
90 to 180 peak (+) to equilibrium = parallel to magnetic field
180 to 270 equilibrium to valley (-) = perpendicular to magnetic field
270 to 360 valley (-) to equilibrium = parallel to magnetic field
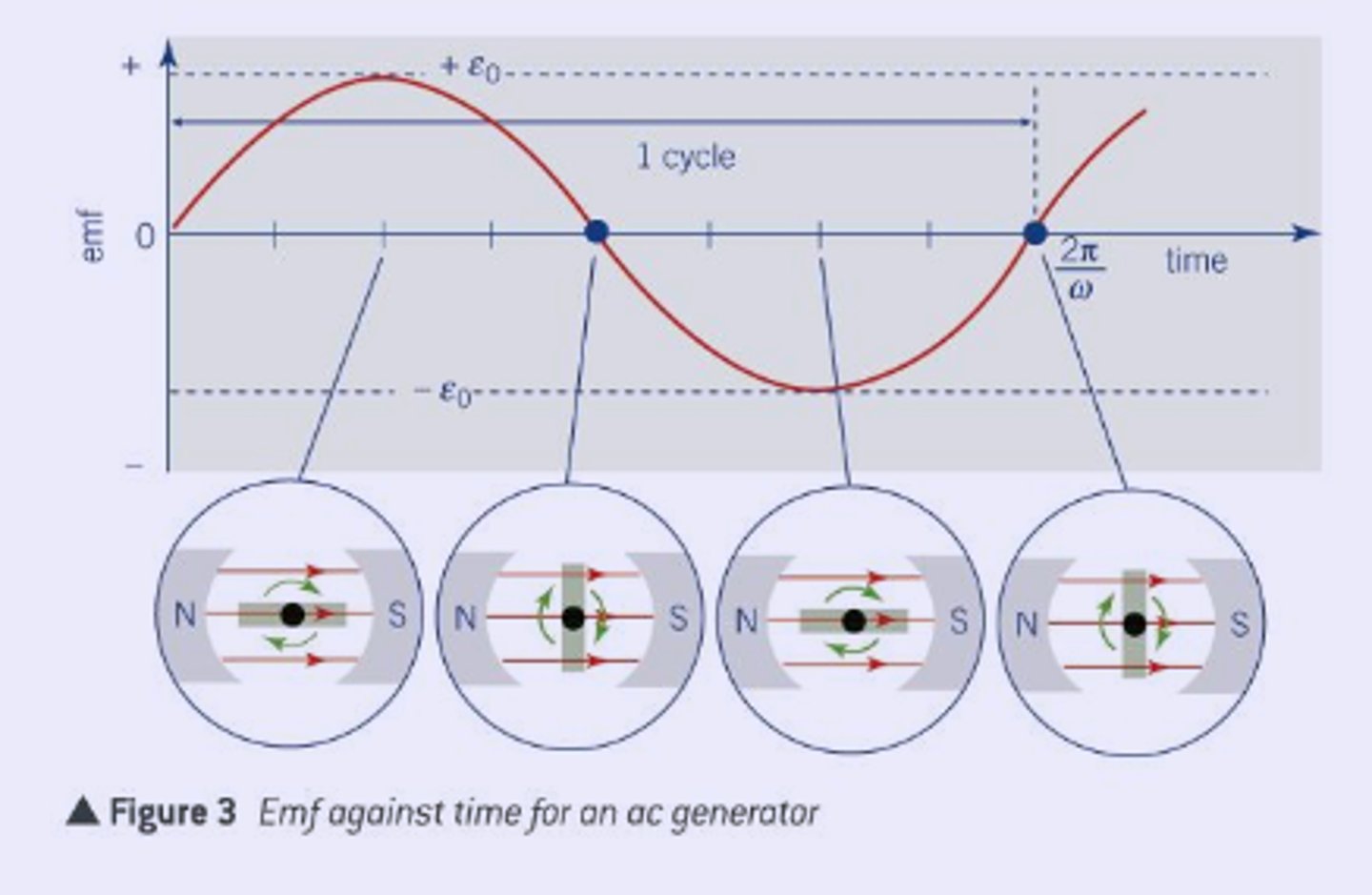
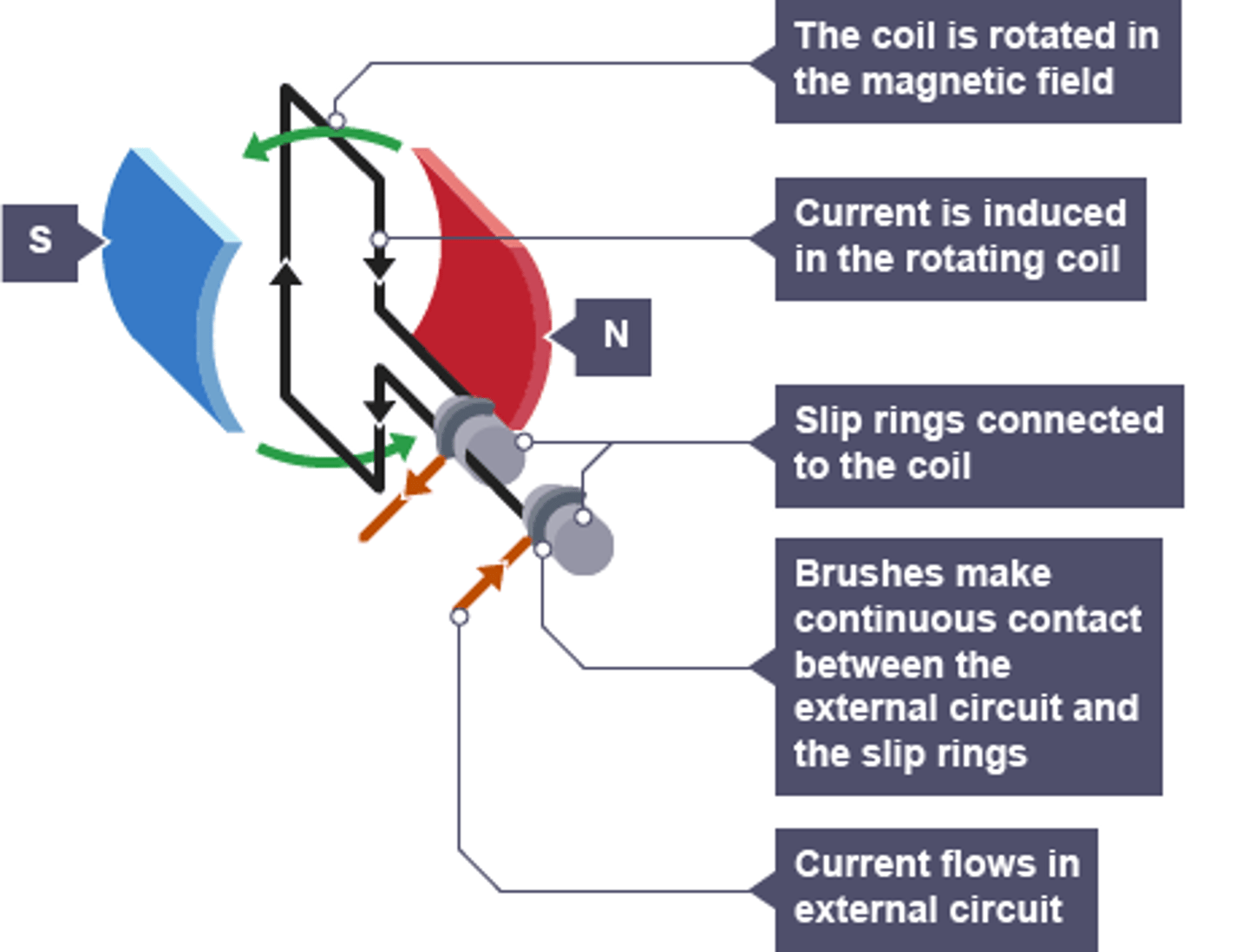
How does alternating current generator work? include parts of a generator
Parts of generator - armature, slip ring, brush
Ac generator converts MECHANICAL energy into ELECTRIC energy. Armature rotates coil of wire in a magnetic field generating an alternating EMF(voltage) and current (Faraday's Law). The voltage is collected at the slip rings and sent out to the brushes. Circuit must be closed for the current to alternate.
Current reverses every ___ turn in the alternating current generator
half
Types of motors (2)
1. Synchronous
2. Induction
What is a synchronous motor?
coil rotates at the same frequency as current (60Hz); used in timing circuits in older machines; rotor rotates at same speed as the rotating magnetic field produced by stator
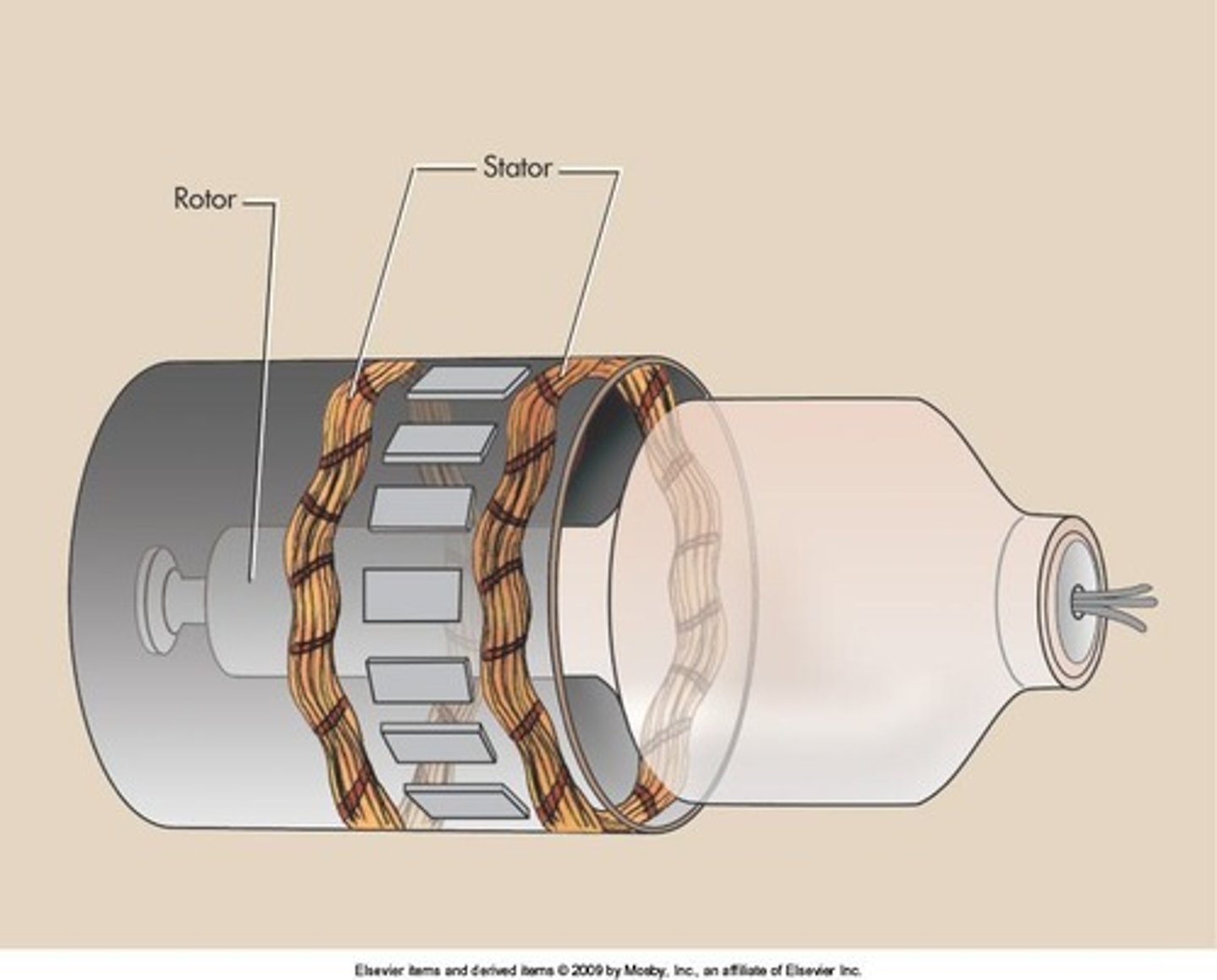
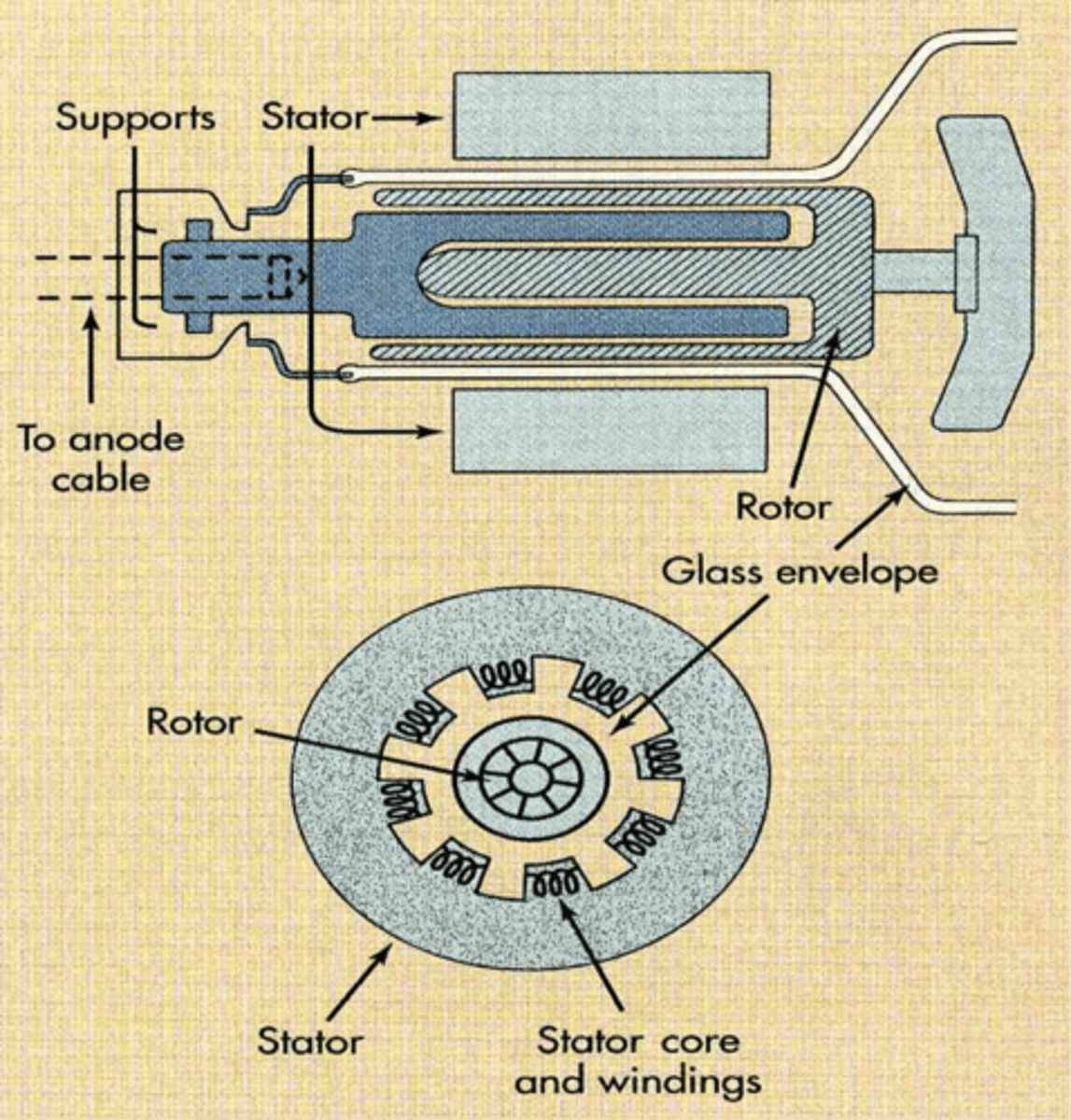
What is the difference between stator and rotor?
stator - stationary part (fixed magnet) of motor/generator that creates a magnetic field to make rotor turn in a motor or in a generator it is the stationary armature where voltage is induced
rotor - rotating part inside the stator that rotates due to the magnetic field produced by stator
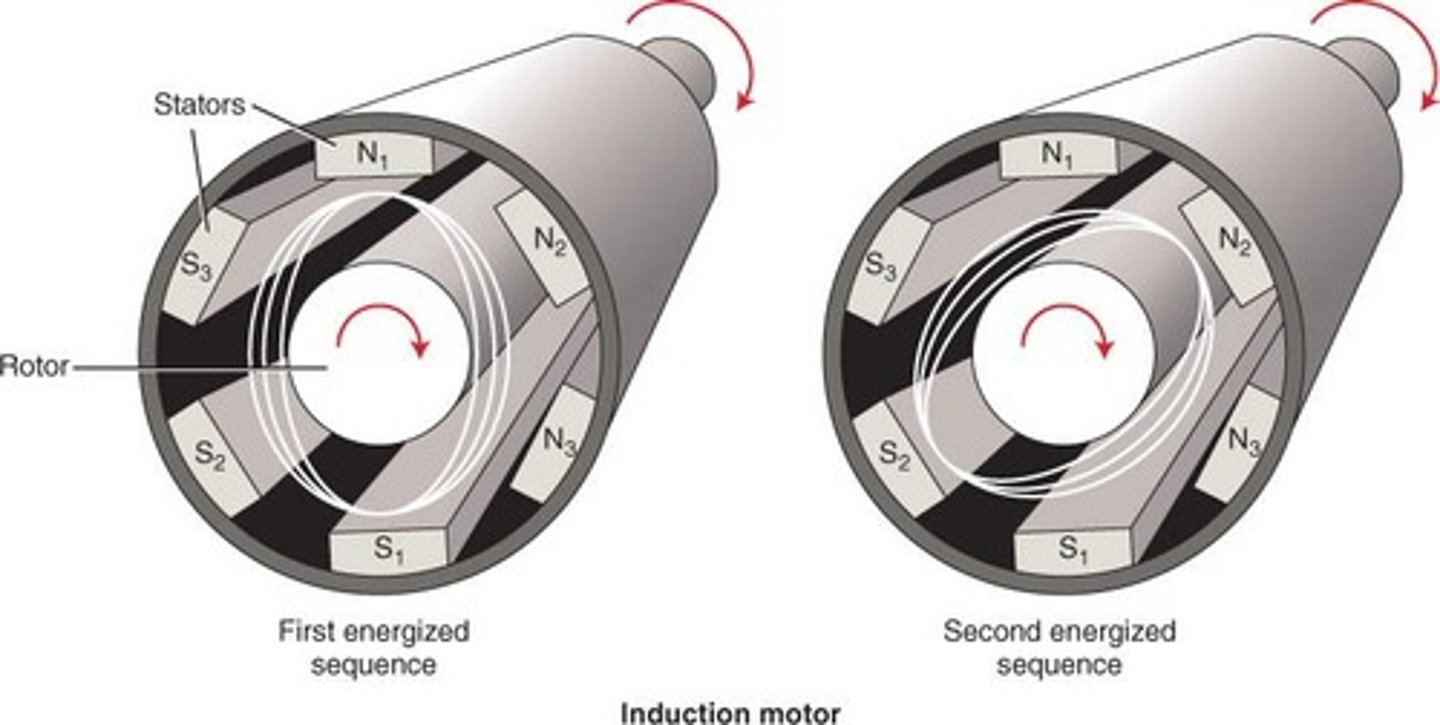
What is an induction motor?
uses electromagnets (stator) to create magnetic field to (rotor) interact with current's magnetic field
- used to rotate anode in x-ray tube
Rotor ___ anode in x-ray tube as e- hit the focal spot on focal track.
rotates
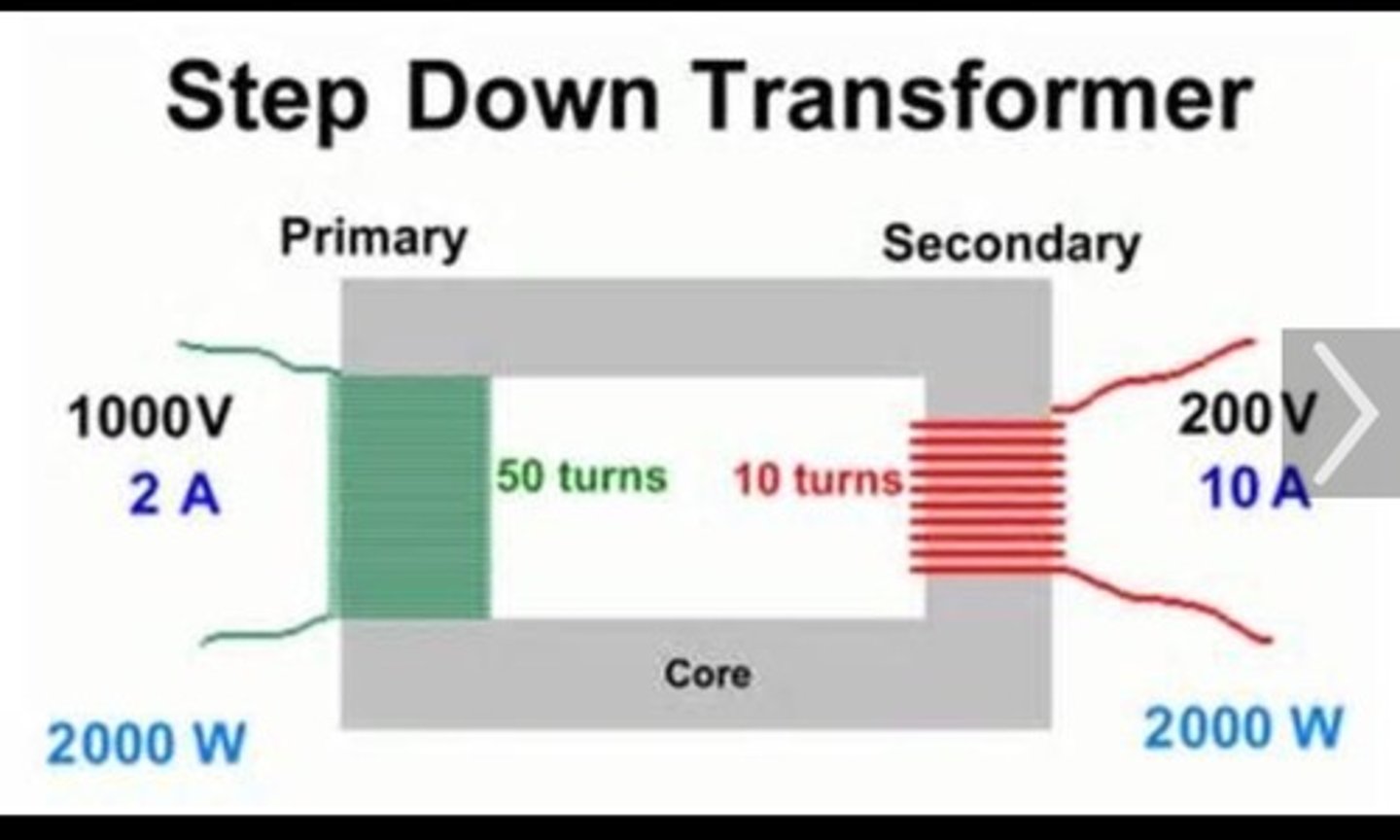
What are 2 types of transformers and what is their function?
step up and step down transformer are used to change the magnitude of current and voltage
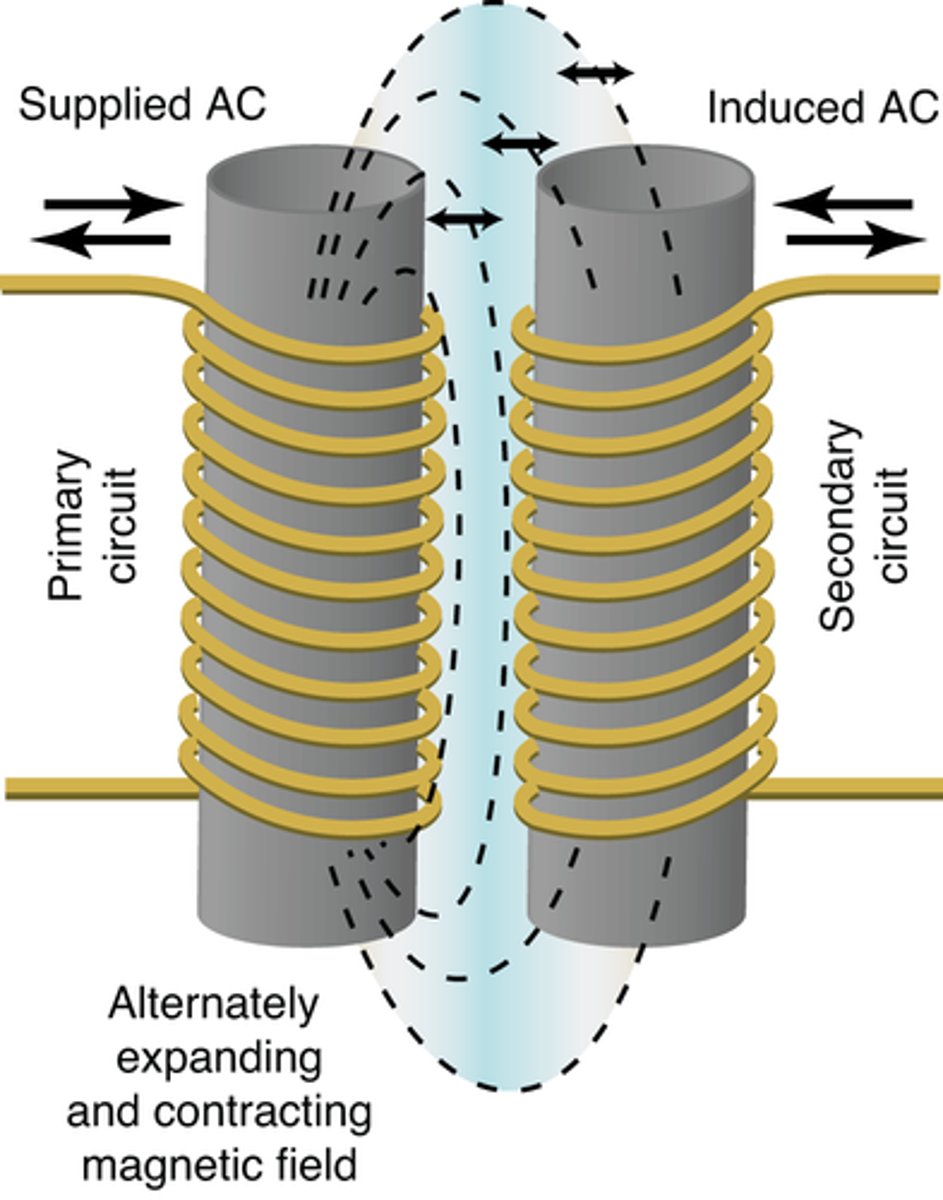
Transformers operate on the principle of ___ induction, where the changing electric current in the primary coil induces a changing current in the secondary coil.
mutual
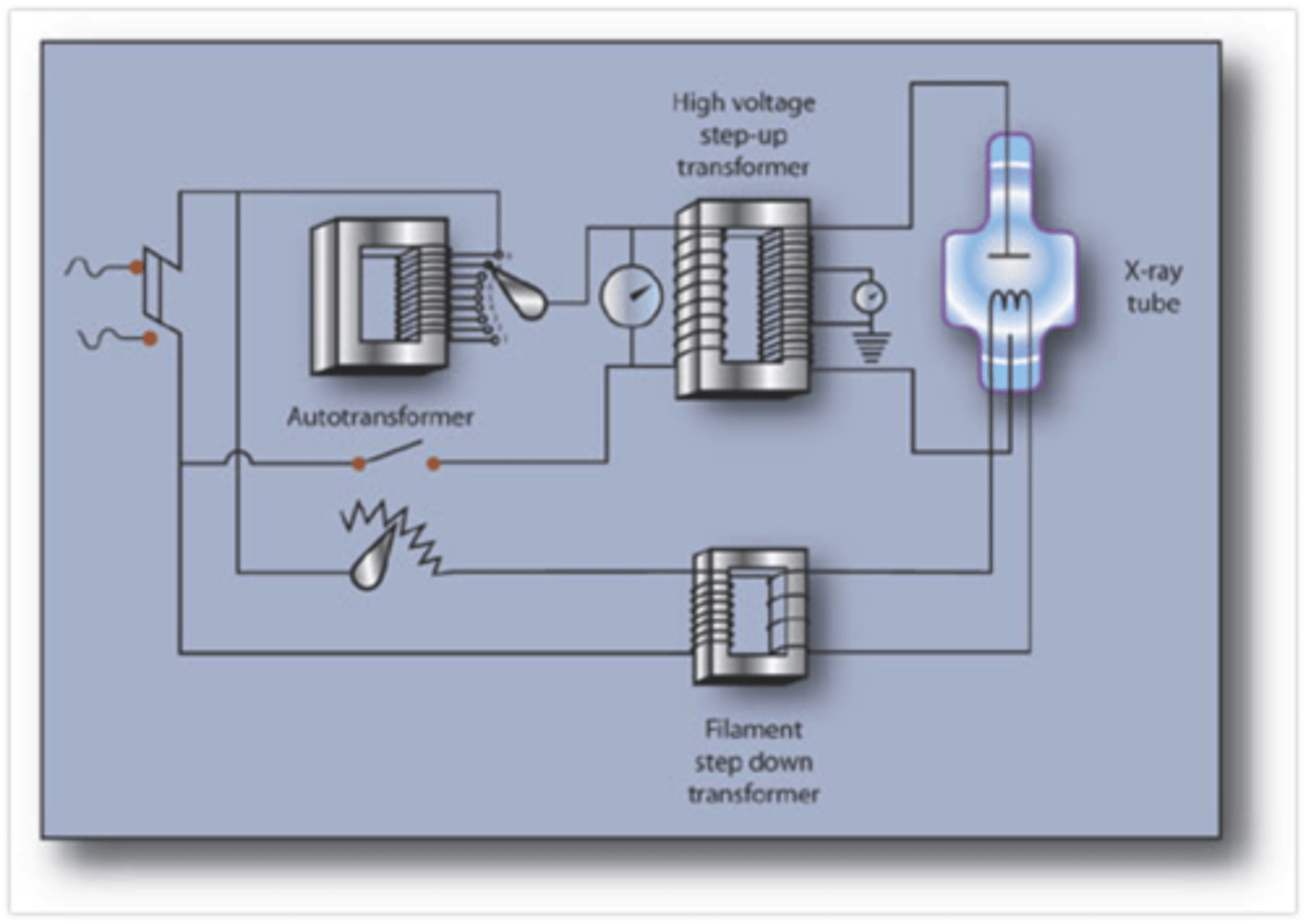
Where is step up and step down transformer found in the x-ray tube?
1. Step Up - found in tube circuit (High Voltage Transformer(HVT))
2. Step Down - found in the tungsten filament circuit (used for thermionic emission)
What are parts of transformer? (3)
1. input side (primary coil)
2. output side (secondary coil)
3, core (metal rod)
What transformer uses self induction? How does it work?
Auto transformer uses self induction by utilizing one coil, which acts as primary and secondary coil
How does a mutual induction transformer work? Give examples of mutual induction transformers.
a change in voltage/current in secondary coil is caused by the change if voltage/current in the primary coils; examples step up and step down
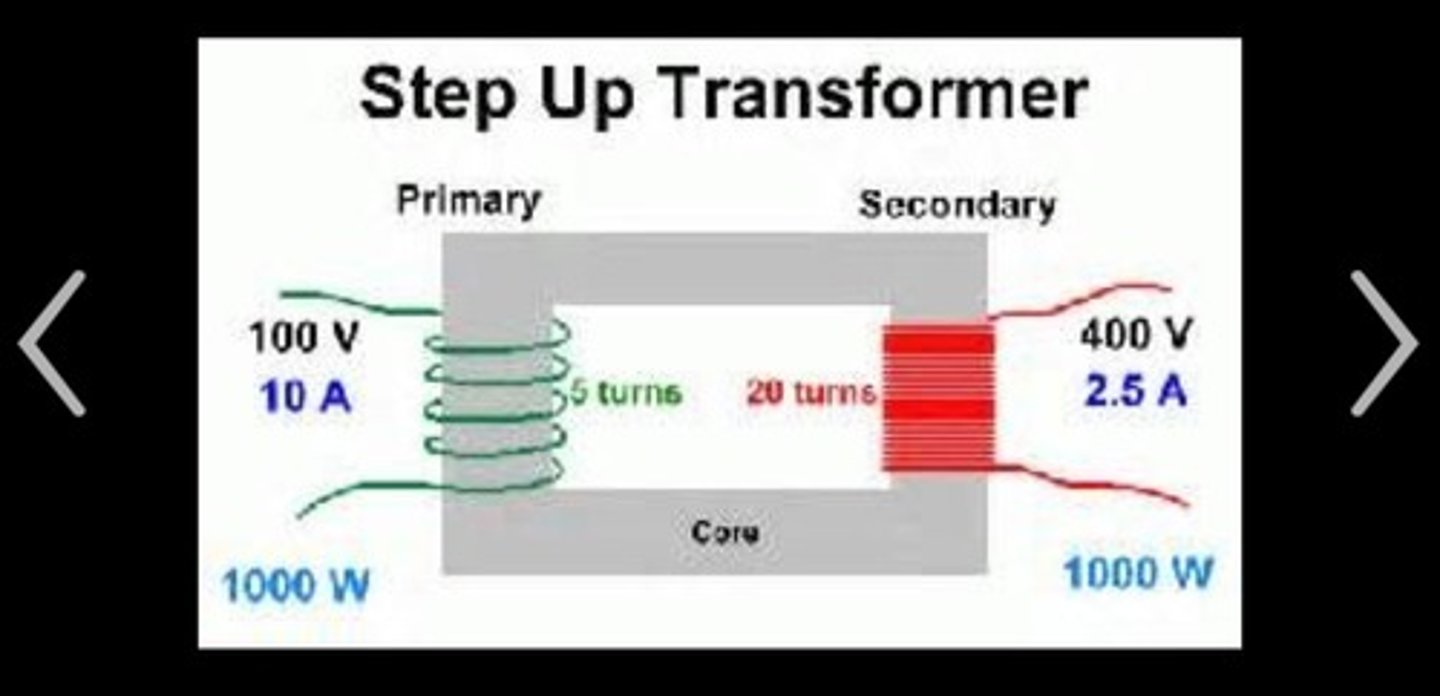
True/False - Step up transformer has 2 coils where the primary power has less coils than the secondary power. (ie. secondary coil has more turns than primary coil) --> induced EMF is higher in secondary(coil ratio = primary has fewer turns , secondary has more turns)
true
True/False - In step down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary coil which means that the induced EMF of the secondary coil is lower than the primary. (coil ratio = primary has fewer turns , secondary has more turns)
true
What is the transformer law of voltage?
Vp/Vs=Np/Ns
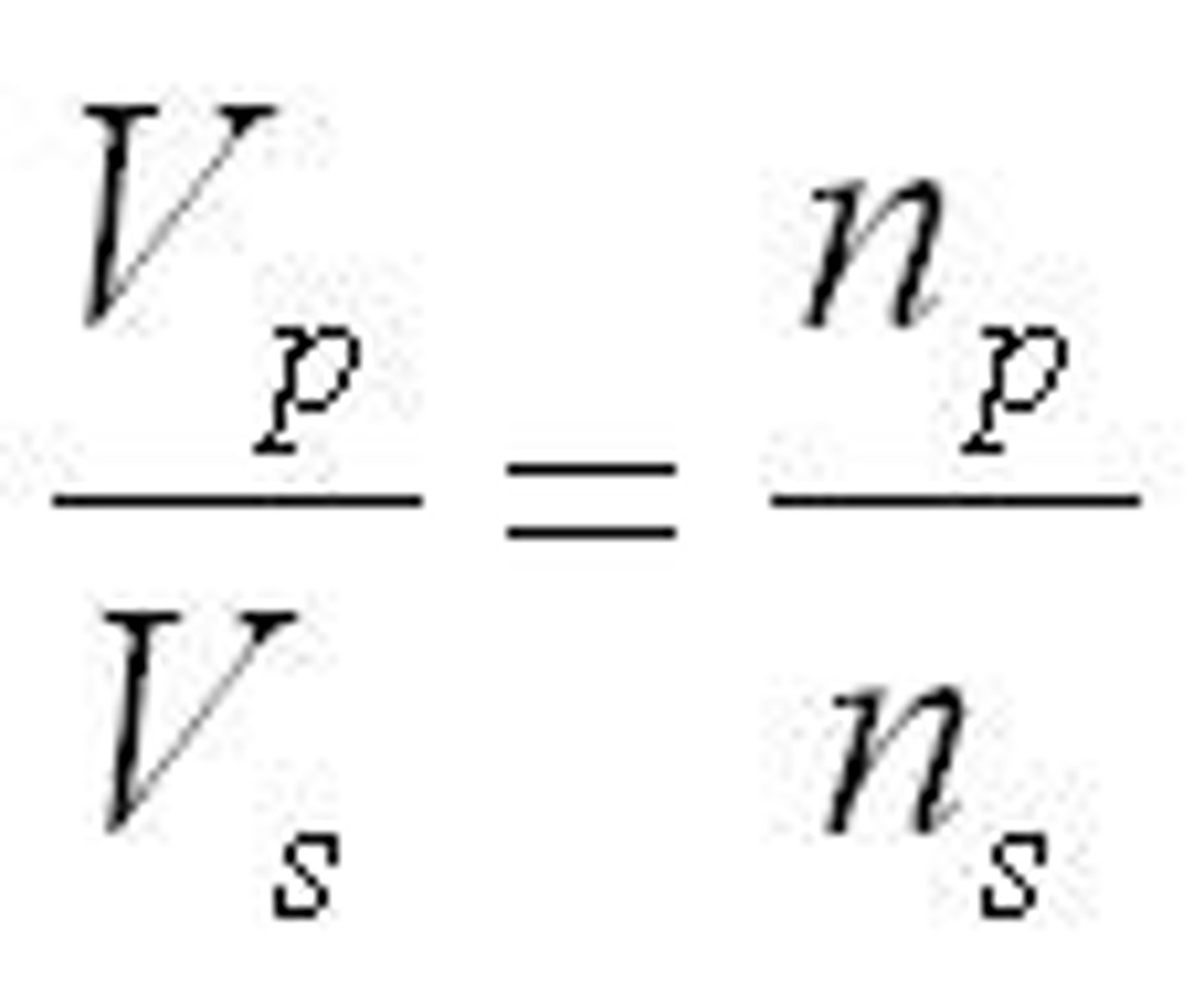
The primary side of a step up transformer has 500 turns and the secondary side has 1000 turns. If the voltage on the primary side is 200, what is the voltage on the secondary side?
500/1000=200/x
x=400V
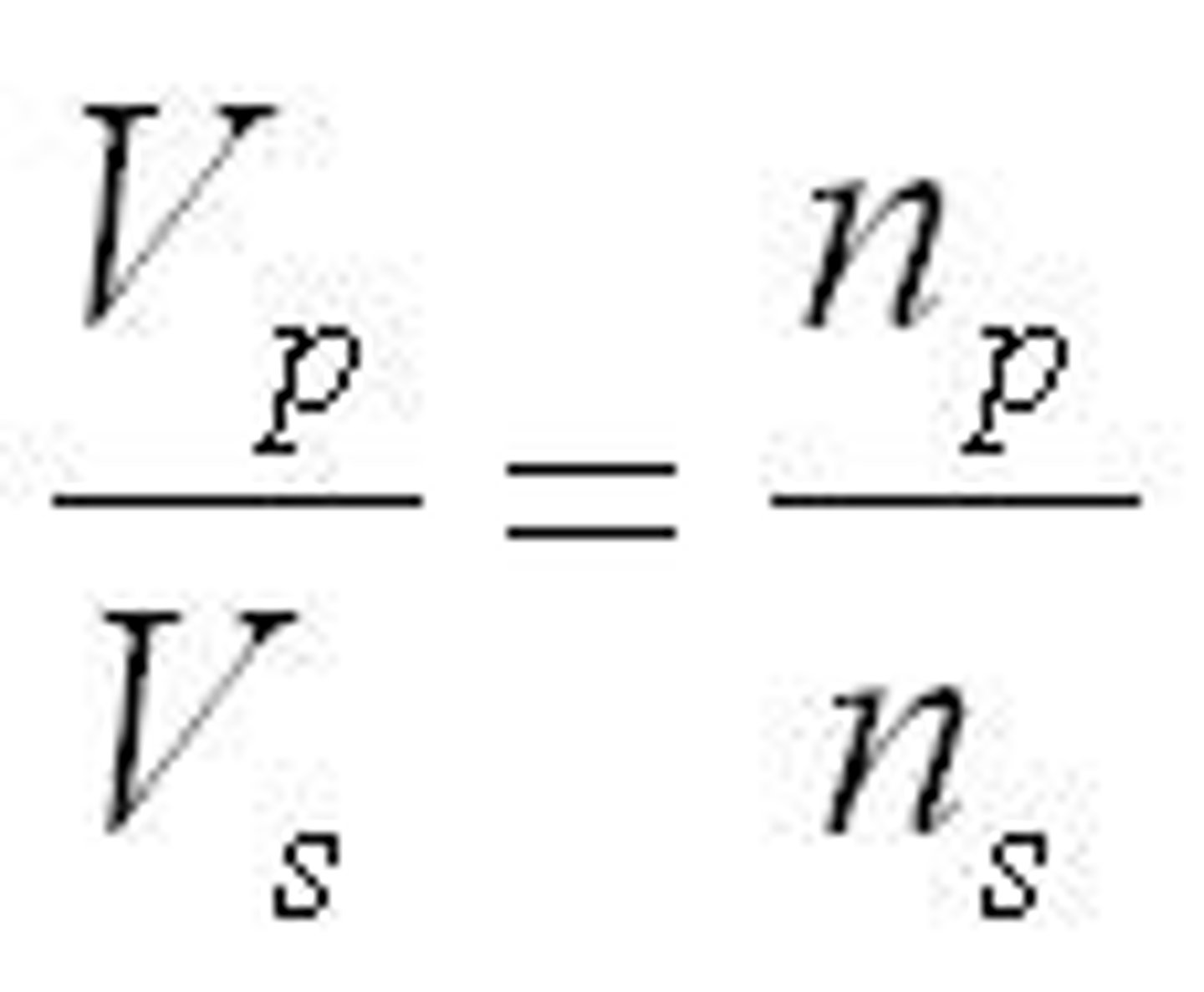
The primary side of a step up transformer has 100 turns and the secondary side has 300 turns. If the voltage on the primary side is 110V, what is the voltage on the secondary side?
100/300=110V/x
x=330V
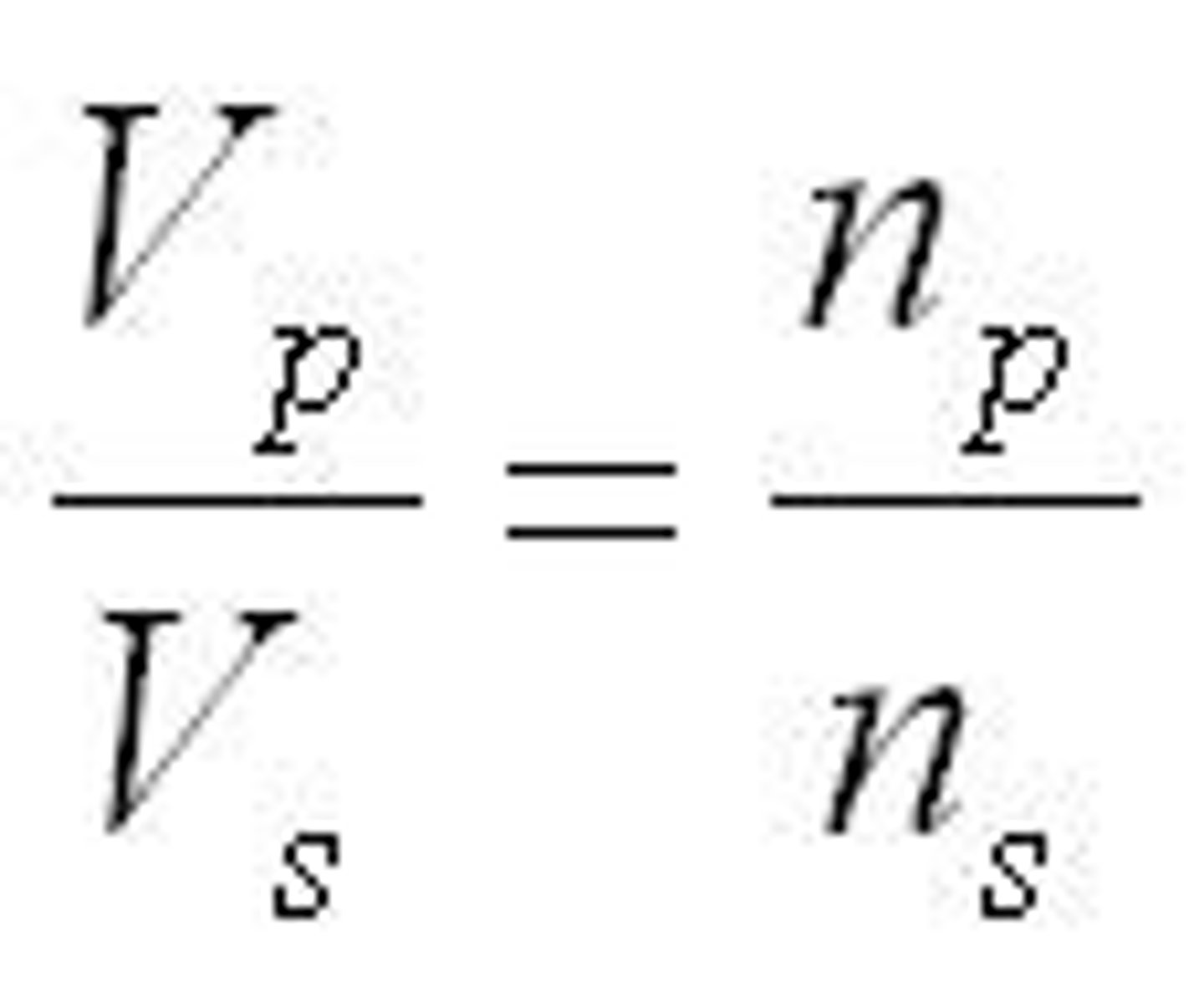
What is transformer law on amperage?
Is/Ip = Np/Ns

If the number of turns on the primary side is 50 and the number of turns on the secondary side is 150 and the amperage at the input is 10 A, what is the amperage on output?
x/10=50/150
x=3.33A
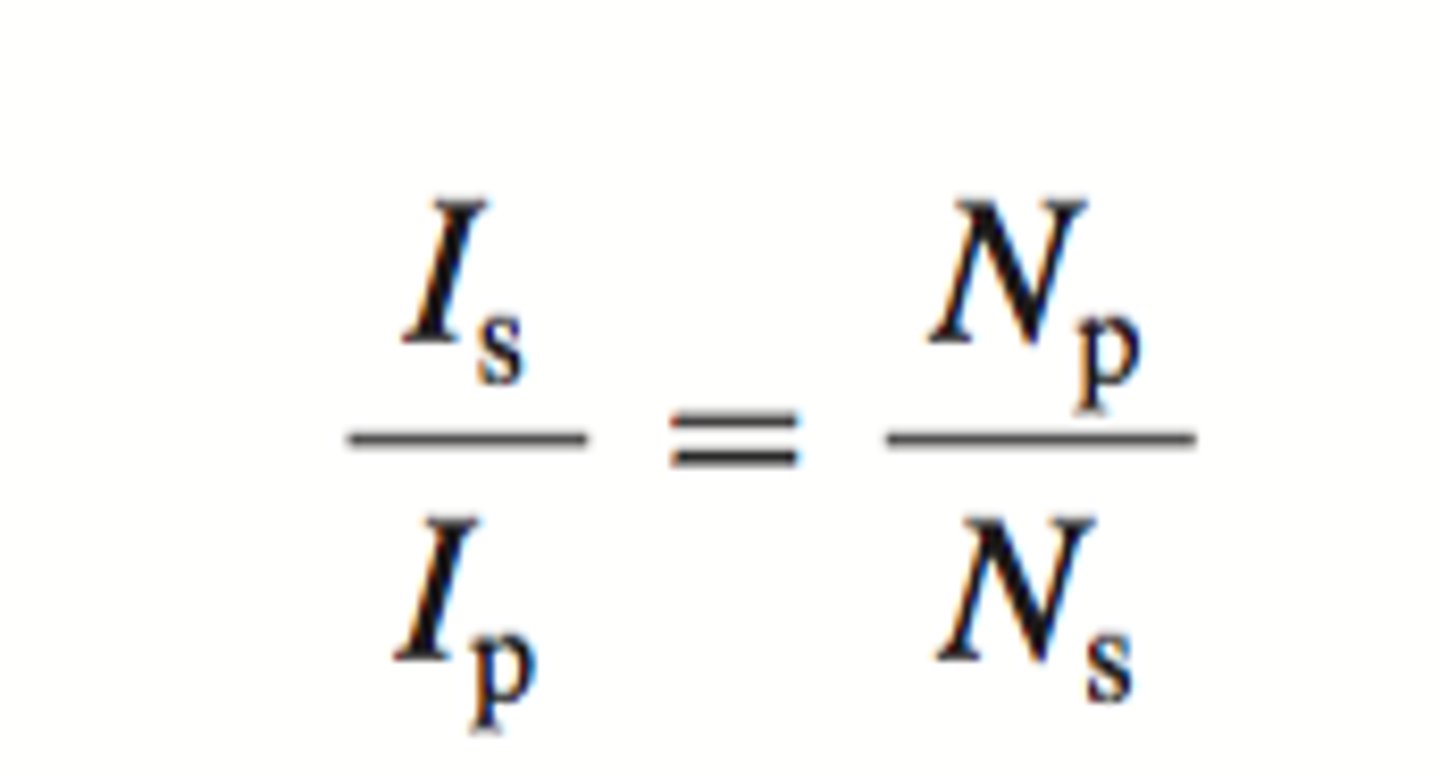
What are the power losses we get from transformer? (3)
1. Copper has low conductor resistance
2. Hysteresis (lag) - loss of energy as heat when current flips direction which causes the magnetic field it induced to flip direction (alternating current); the resistance converts energy into heat
3. Eddy Current (stronger/faster the changing magnetic field = larger Eddy current = less efficient x-ray production)
- swirling currents in core
-minimized by lamination of plates
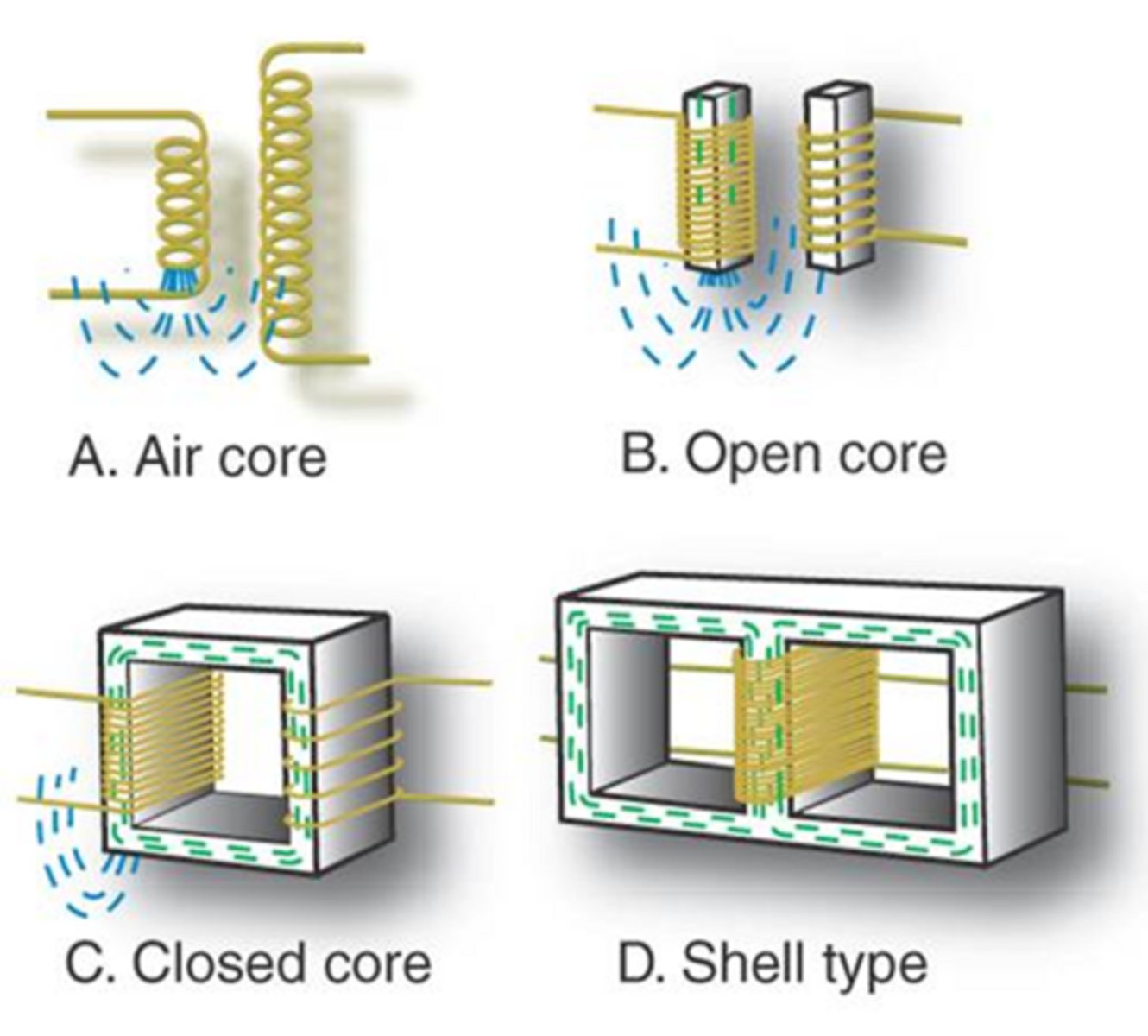
What are the 4 types of transformer constructions? (name from most leakage/less efficient to least leakage/most efficient)
1. Air Core (Most leakage/least efficient)
2. Open Core
3. Closed Core
4. Shell Core (Least leakage/most efficient)
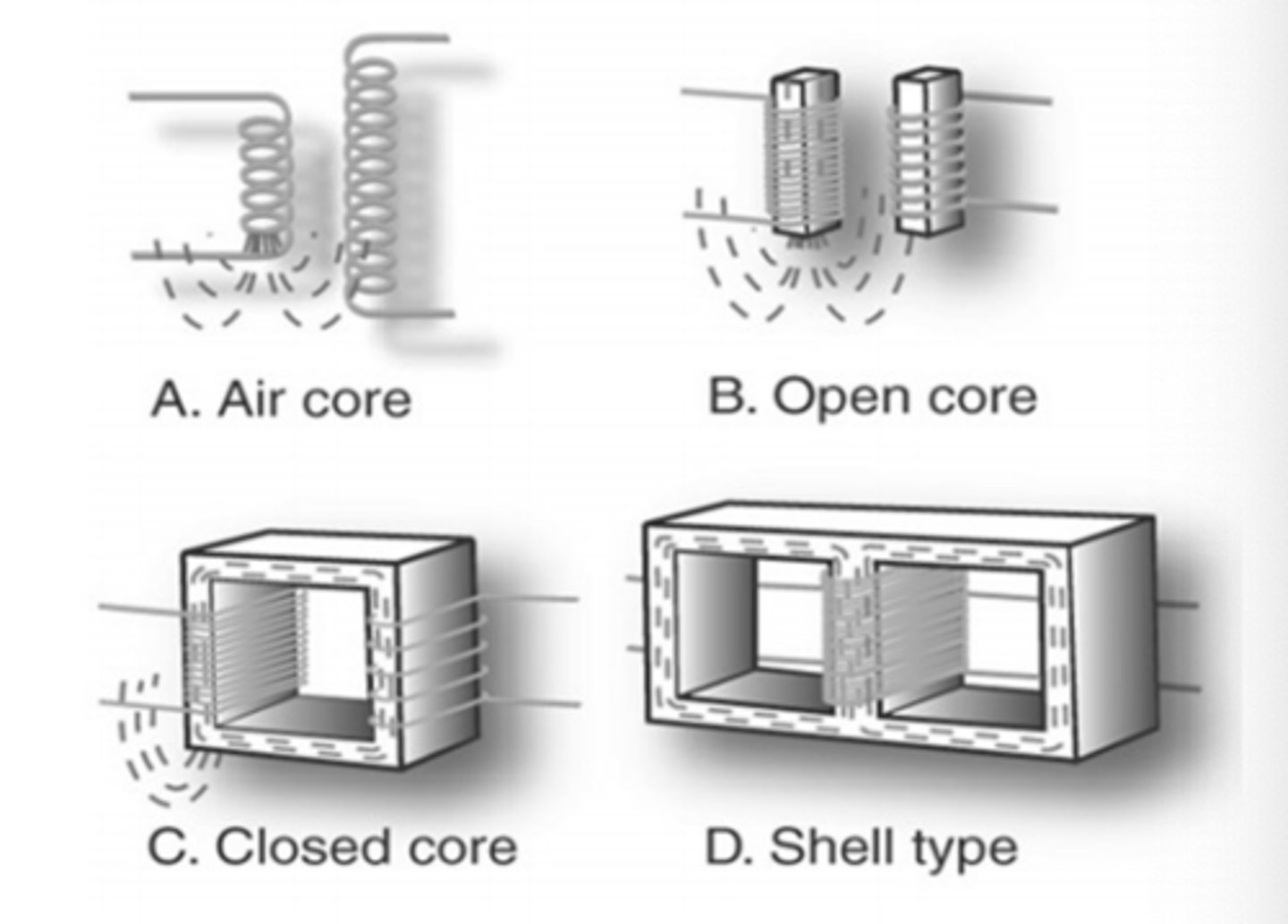
Describe open core, closed core and shell core transformers.
1. Open core - iron core inserted, leakage influx
2. Closed core -continuous path, minimal leakage, laminated core
3. Shell - most advanced, winding is insulated and is what we use for x-ray tube
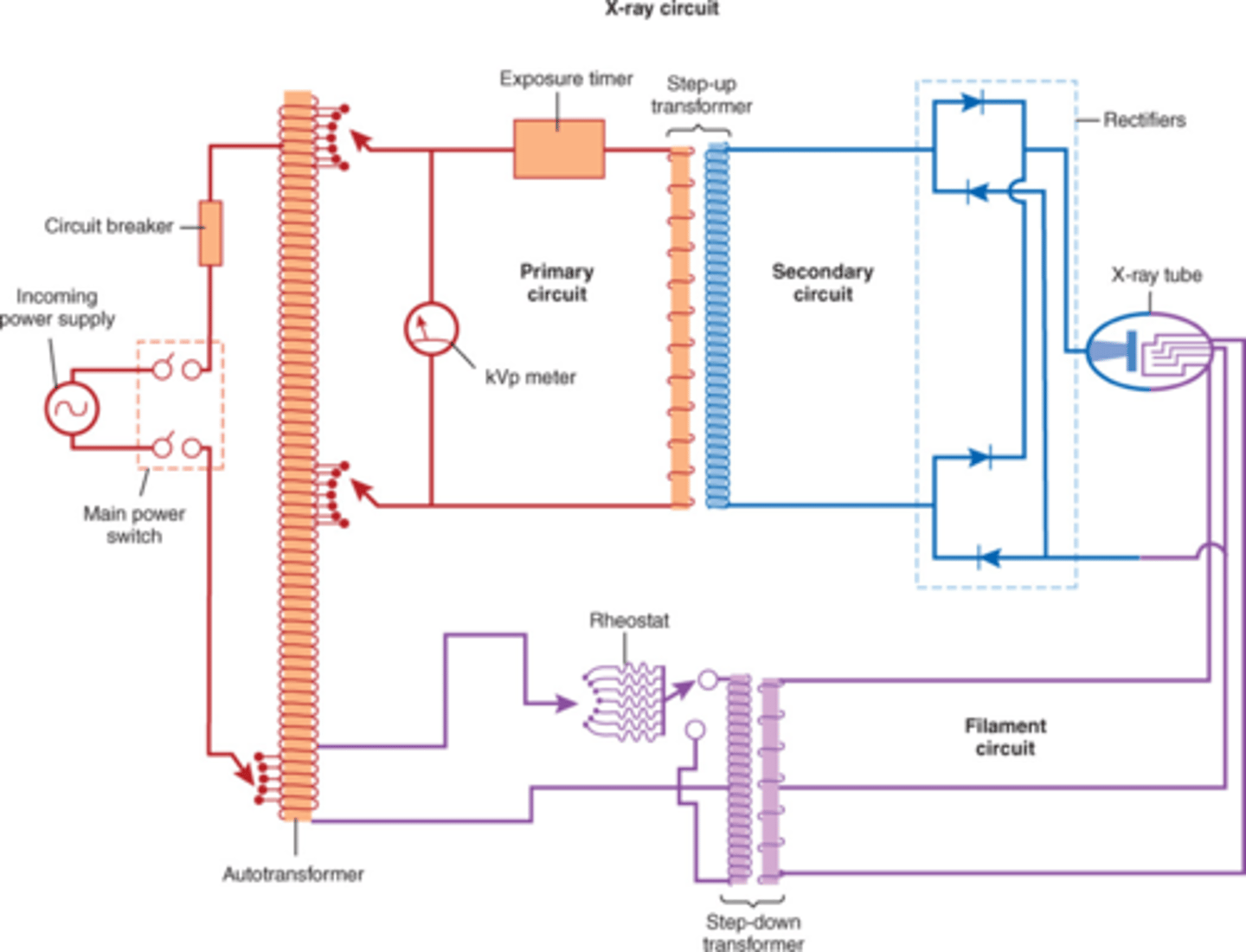
Locate the autotransformer, step up/step down transformer in the x-ray circuit
autotransformer is in between incoming AC power supply and step up transformer (it selects the kVp and works through self induction)
the step up transformer in the tube circuit (High Voltage Transformer(HVT)); works on mutual inducion
the step down transformer is at the filament; works on mutual induction