Naming Alcohols and Properties
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are alcohols?
Alcohols are organic compounds containing -OH as the functional group.
What is the general formula for alcohols?
CnH2n+1OH.
State the general rule for naming alcohols.
Start with the name of the alkane.
Add the suffix ending “-ol”.
If necessary, use a number to indicate which carbon atom is bonded to the hydroxyl group.
If it contains 2 hydroxyl groups, use the suffix ending “-diol”.
If it contains 3 hydroxyl groups, use the suffix ending “-triol”.
State one characteristic of the of the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group in alcohols.
The alcohol functional group is very polar.
Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, whereas hydrogen and carbon have low electronegativities. This results in the oxygen atom having a partially negative charge and the hydrogen a partially positive charge.
Compare the boiling points of some simple primary alcohols to the equivalent alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
The boiling point of an alcohol is always much higher than that of the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
The boiling points of the alcohols increase as the number of carbon atoms increases.
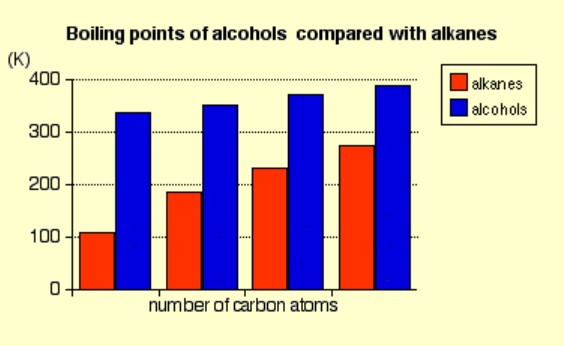
Explain why the boiling points of alcohols is greater than the equivalent alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
Alkanes are non-polar ∴ only Van der Waals forces act between alkane molecules. Van der Waals forces are weak and do not require a lot of energy to break ∴ they have low boiling points.
Because alcohols are polar (due to the hydroxyl functional group), they can form both Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds to each other ∴ they contain strong intermolecular forces which require a large amount of energy to break ∴ they have high boiling points.
What does volatility refer to?
How readily a molecule turns to a gas.
Which compound is more volatile: alcohols or alkanes?
Alkanes- because alcohols have higher boiling points than alkanes, they are less volatile.
Are alcohols soluble in water?
Yes.
Explain why alcohols are soluble in water.
The OH group in the alcohol can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Explain why larger alcohols (alcohols with longer hydrocarbon chains) are less soluble in water.
As the chain length increases, solubility decreases.
This is because longer chain alcohols have more non-polar hydrophobic regions (hydrocarbon chains) in addition to their hydrophilic hydroxyl group.
The hydrophobic effect begins to overcome the hydrophilic effect, and water solubility is lost.