L11 E2 Quasi Experimental design and MUE
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Scientific Evidence pyramid and where Quasi @
Systemic review/meta analysis
RCT
Non RCT (quasi)
Observational
Qualitative
Pretest-post test description
Dependent variable measurement taken b4 and after intervention
Non eq control group design
Participant groups not randomized, so have differences at baseline
Have control and study group where you compare histories, retrospective
Time series design
Large series of observation made on same variable consecutively over time
Interrupted time series and multiple time series designs description
Is like pretest/post test with MULTIPLE measurement b4 and after (so more in between)
Regression Discontinuity Design
used to determine causal effects of interventions by assigning threshold
Retrospective expost facto design
Studying cause and effect relationships through retrospective search
How are Quasi designs related (3)
ALL subtype aim to estimate a causal relationships btw intervention and its outcomes
ALL rely on stat adjustments to reduce bias and enhance validity
Intervention is NOT RANDOMIZED at each design
4 Times to use Quasi
Classic study design not feasible or ethical
investigator can't implement control group or randomize groups
Small sample size
not enough funding
Selection bias definition
Patients have difference between groups
Confounders and control techniques
Systematic error in way data is collected, creates false associations
Historical bias definition
Events that occur during study period that could influence outcome of the results
ex. covid
Reporting bias
Publishing only positive results and ignoring negative ones
Temporal ambiguity definition
Undermine validity of prediction by overemphasizing features close to outcome of interest
Hawthorne effect
participants' behavior changes as a result of their knowledge of being in a study
Detection bias
Differences in how outcomes are measured in groups
Maturation bias definition
Changes in participants with passage of time
How to minimize selection bias, and reporting/detection bias

MUE definition
Performance/investigative improvement method focused on evaluating medication-use processes and improving patient or system outcomes
Can explore different processes and is quite flexible

Why do MUE? (3)

MUE vs DUE/DUR
MUE emphasis on improving patient outcomes and QOL
DUR: ongoing systematic assessment to ensure appropriate medication utilization at individual patient level
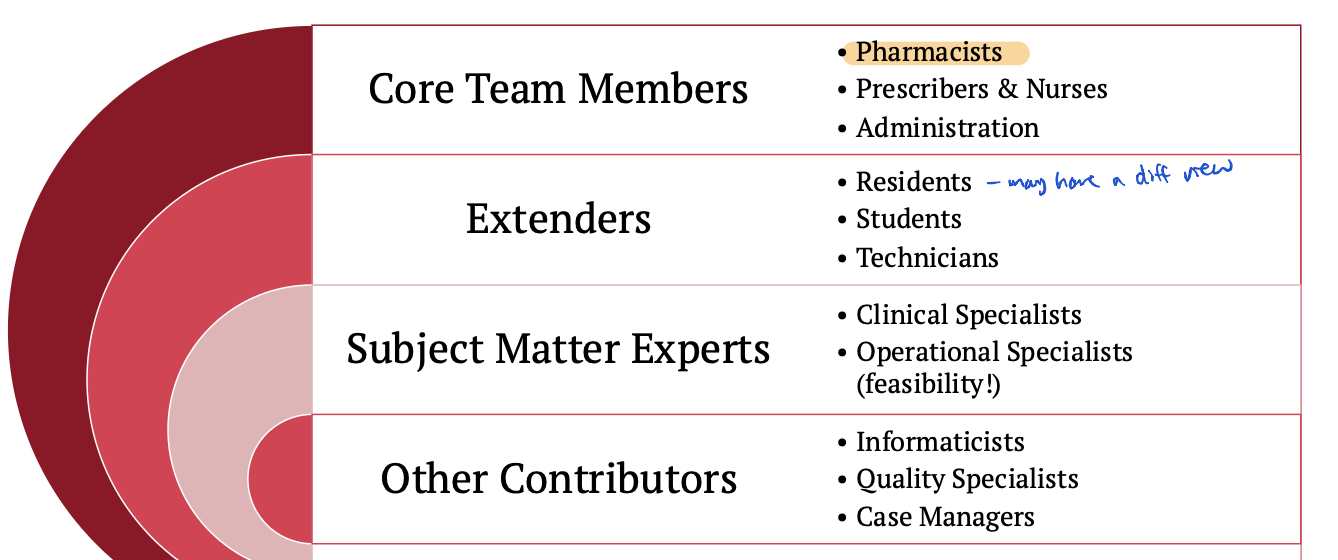
MUE team members
core team member
extenders
subject matter experts
other contributers
Objectives of MUE (8)
Evaluate medication for safety/efficacy outcome, Reduce inappropriate prescribing
practice standardization, Promoting guideline adherence
Support interdisciplinary medication management,
Support research for med alternatives, Evaluate new indications, Inform formulary decisions
Retrospective vs prospective MUE
Retrospective: look back, identify areas for improvement
Pros: Good for new drugs or processes (designed before a med is utilized), allow for real time monitoring (conducted while medication use)
5 parts of MUE life cycle
Design MUE
collect/analyze data
implement change plans
Assess effectiveness
Follow up/change/further research
Defining MUE 6 possible parts
Objective
Type of MUE
study design
setting and population
sample size
develop process for data collection
Criteria and collect data 6 things to consider when
Eligibility criteria
Endpoints
variables
measuring parameters
Is data collection possible
MUE external validity?
Analysis for MUE
Garbage in=garbage out: want high quality data
Analyze against standards
Any trends found?
Analysis inform improvement
Disseminating results for MUE
What stakeholders gotta share to?
COLLABORATE
4 parts of follow up for MUE
Document changes and write new processes
Ensure results is shared with ALL affected people
Set times for re evaluation
Ensure culture doesn't revert back
Mue Challenges (4)
Data availability/extractility
TIme constraints/urgency of MUE results
Garbage in=garbage out
Need to make sure variable descriptions are clear and measurable
4 MUE things to keep in mind
Interdisciplinary coordination
set clear objectives
schedule meeting check ins with other disciplines
REMEMBER STAKEHOLDERS
MUE 8 limitations
Lack of organization, poor communication, no follow up
data integrity
Evaluation method disrupts patient care
Lack of scope, Lack of education, Lack of hard wired corrective actions