9.0: CPU and Motherboard
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AAAA LINDOL SAKLOLO!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
System Unit (Chassis)
Case that contains all of the internal hardware (e.g. motherboard, hard disk drive, memory)
Motherboard
“System board”
Main circuit board
Many electronic components (e.g. processor and memory) are attached here.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
“Processor”
Brain of the Computer
calculates and processes information for the computer to function or perform a task.
heatsink
Covers the motherboard’s CPU socket
Absorbs heat from the CPU
fan
Dissipates the heat
Chipset
Controls communication between the CPU, memory, storage, and other peripherals
Random Access Memory (RAM)
“Main memory”
Temporarily stores data whenever the computer performs operations.
Hard Disk Drive
Long-term storage
Power Supply/AC adapter
Converts electricity from the outlet (AC 120 or 220 volts) to a type of power (DC 5-15 volts) that the computer can use.
Expansion slots
Allows users to add various types of expansion cards or adapter cards.
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
Input/output pathway connecting the CPU via the expansion slots to the peripheral devices
Serial Advance Technology Attachment (SATA)
Connects drive disk controllers/host bus adapters with mass storage devices
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS battery)
Keeps all information intact when the entire system is shut down.
Prevents reconfiguration when the PC is off.
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Connects devices like keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage for data and charging.
Storage/Disk Port
Ports such as SATA or M.2 used to connect internal and external storage devices for data storage and retrieval
Network/Communication Ports
Ethernet or Wi-Fi
Connects to networks, enabling internet access and exchange between devices.
Audio Port
3.5 mm jacks, optical ports
Used for audio input and output
Video Port
Transmits video signals to displays like monitors and projectors
Power Port
Used for supplying electricity to devices and charging batteries
Processor
Interprets and caries out basic instructions that operate a computer
On large computer systems, its actions extend over many separate chips and multiple circuit boards.
Microprocessor
On a personal computer system
All its functions are usually on a single chip
Multicore processor
A single chip with two or more cores.
Control Unit
Component of the processor that directs and coordinates most of the operation of the computer
Interprets each instruction made by a program > initiates the appropriate action to carry out said instruction
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Performs arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logic operations (greater than, less than, equal to)
Machine Cycle
Fetching, Decoding, Executing, Storing
Fetching
Obtaining a program instruction or data item from memory
Decoding
Translating the instruction into signals the computer can execute
Executing
Carrying out commands
Storing
Writing results back to memory
Register
Small, high-speed storage
Temporarily hold data and instructions
Program Counter
keeps track of the program sequence, by storing the address of the instruction currently being executed.
Instruction Register
Stores the instruction itself to be executed
Accumulator Register
Holds the results of a calculation
Memory Buffer Register
Stores the data being transferred to and from the immediate access storage
Memory Address Register
holds the address of the memory location to be accessed
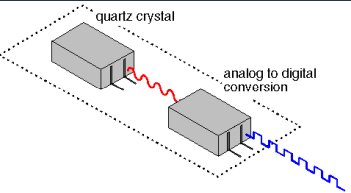
System Clock
Controls timing of all computer operations
Generates regular electronic pulses or ticks that set the operating pace of components of the system unit
Superscalar
Processors can execute more than one instruction per clock cycle
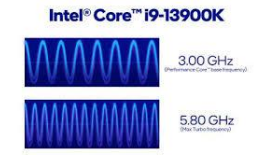
Clock Speed
Measured by no. of ticks per second
Gigahertz (billions of cycles)
The faster, the more instructions the processor can execute per second