River landforms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
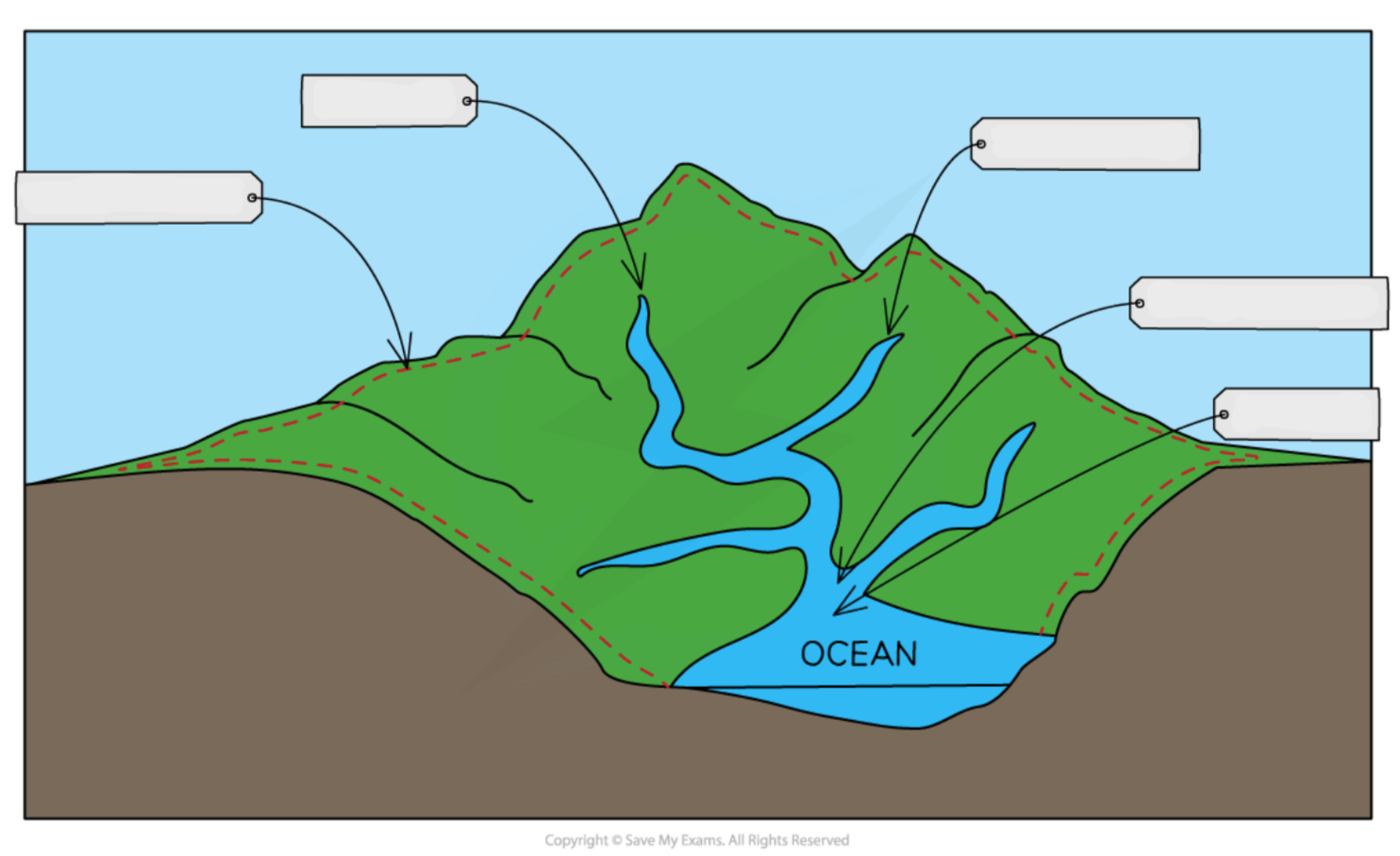
Label this drainage basin diagram
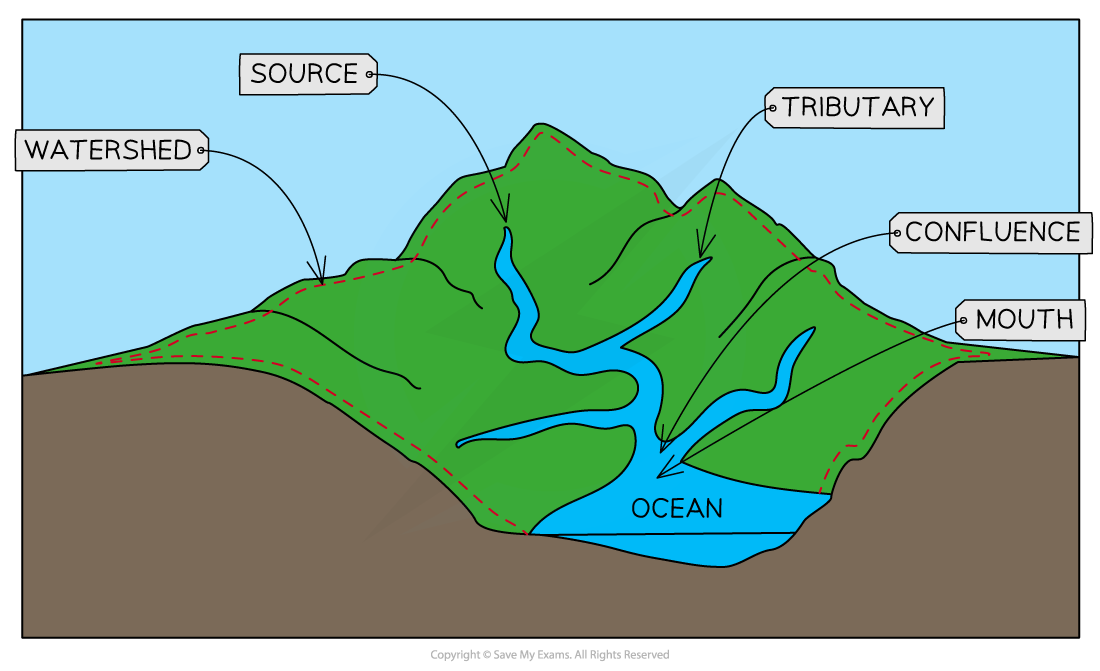
What is a drainage basin?
An area of land drained by 1 river & all its tributaries
What is the source?
Where the river starts
What is the mouth?
Where the river enters the sea or lake
What is the river channel?
Where the river flows
What is a tributary?
A small stream that flows into a larger stream / river
What is a confluence?
Where 2 tributaries join
What is a watershed?
The boundary of a drainage basin
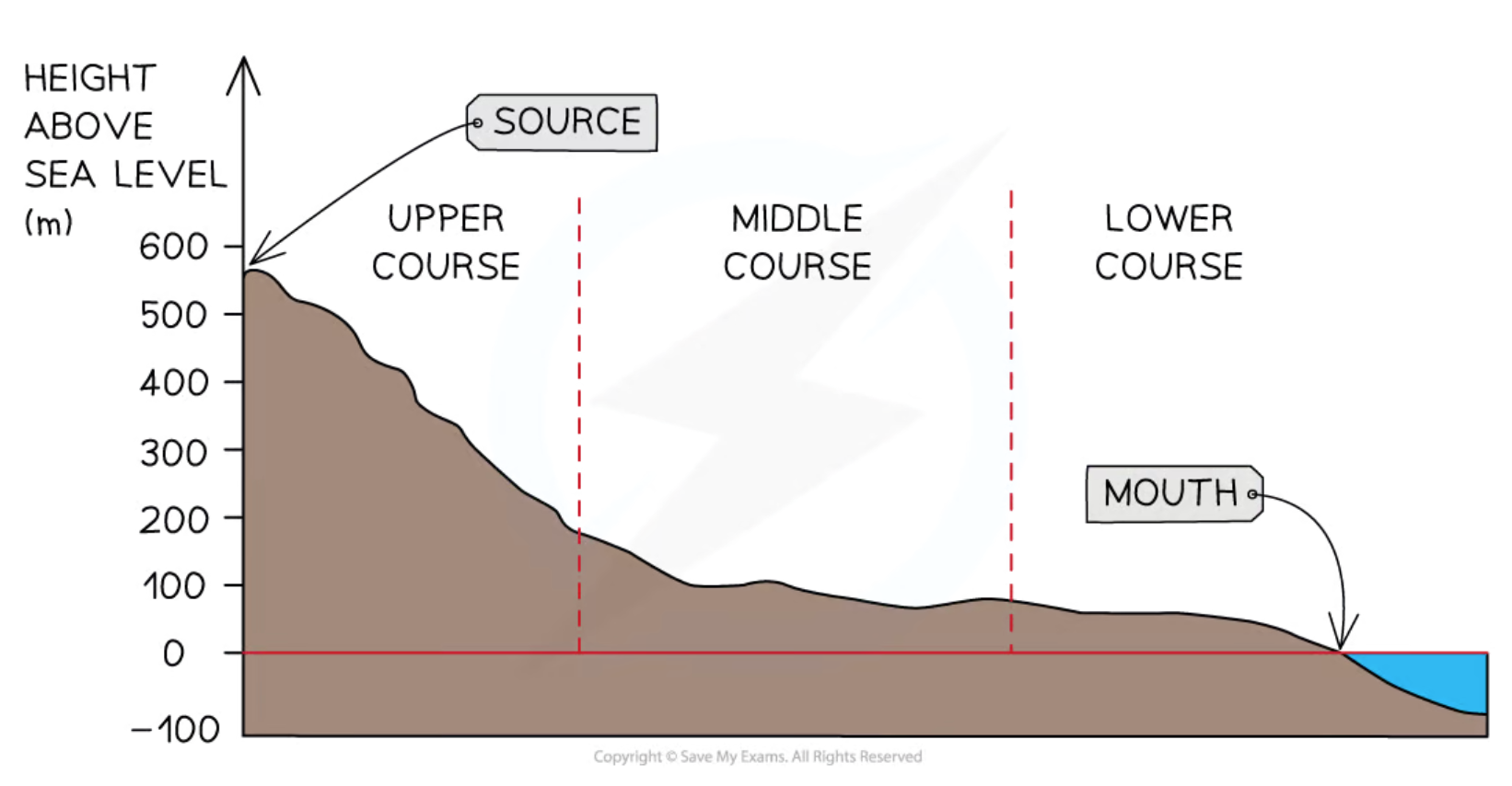
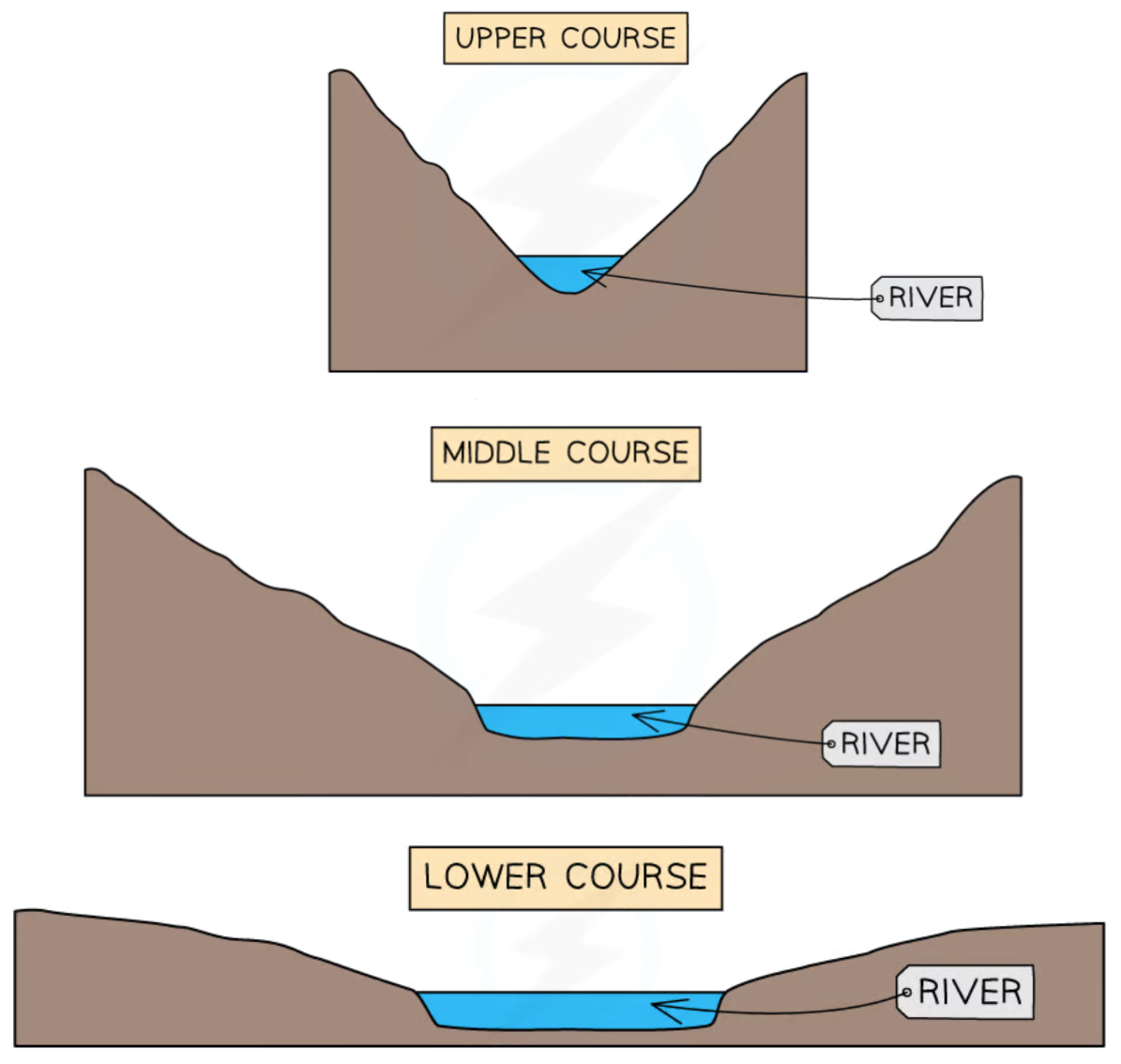
What are the 3 stages of a river?
Upper course
Middle course
Lower course
What are the defining features of the upper course?
→ River is narrow & shallow
→ Large & angular load
→ Traction is the main transportation type
→ Low velocity & discharge
→ Waterfalls, gorges, v-shaped valleys
What are the defining features of the middle course?
→ River is getting wider & deeper
→ Load is getting smaller & more rounded
→ Suspension is the main transportation type
→ Medium velocity & discharge
→ Meanders, ox-bow lakes, flood plains, levees, eyots
What are the defining features of the lower course?
→ River is wide & deep
→ Fine & rounded load
→ Solution is the main transportation type
→ High velocity & discharge
→ Estuaries, more sinuous meanders
What is the long profile of a river?
A diagram that shows how the river channels gradient changes downstream
How does the long profile change downstream?
The channel gradient decreases
What is the cross profile of a river?
A diagram that shows the cross-section of a river channel
How does the cross profile of a river change downstream?
The cross-section gets wider
How are v-shaped valleys formed?
Vertical erosion occurs when a small river rapidly flows downhill, creating a notch
Hydraulic action & abrasion erode the sides of the notch
The sides become exposed to freeze-thaw weathering which loosens rock & sediment
Some rock & sediment fall into the river & are transported downstream, widening the river channel & creating v-shaped valleys
How are waterfalls formed?
Water flows over a top layer of hard rock & a bottom layer of soft rock
Hydraulic action & abrasion cause the soft rock to erode away first as it is less resistant, leaving an overhang of hard rock
Eventually, the overhang of hard rock collapses into the plunge pool, causing the waterfall to retreat up the river & leave behind a gorge
How are meanders formed?
Erosion occurs on the outer bend because the water flows faster & has more energy, creating river cliffs
Deposition occurs on the inner bend because the water flows slower & has less energy, creating slip-off-slopes
Erosion & deposition work together to make the river channel more sinuous which thus makes meanders
How are ox-bow lakes formed?
Lateral erosion causes the outer bends of a meander to become closer together
This forms a neck which narrows due to erosion
During high flow conditions (flood), the meander neck breaks through
The river now flows through the quicker & more direct route, bypassing the old meander
Sediment is deposited due the decrease in river energy, sealing off the old meander & forming an oxbow lake
How are floodplains formed?
During a flood, water displaces onto the surrounding land
Sediment is deposited onto to the flooded land since the river loses energy
This creates a flood plain which expands overtime due to meander migration & deposition on the inner bend
How are levees formed?
During a flood, the river loses energy & so deposits sediment
The larger sediment is deposited first at the channel edges & the finer sediment is deposited last at the outer parts of the floodplain
After many floods, this builds up a raised ridge on the river bank, known as a levee