AP Macro unit 4 and 5
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Bond
Certificate of in debt that specifies the obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond
stock
claim of partial ownership with a firm/ business
Financial intermediaries
institutions allow savers to provide funds directly to borrowers
mutual funds
sells shares and uses the funds to buy stocks and bonds
liquidity
the ease in which an asset can be accessible and turned into cash
rate of return
net gain or loss of an investment over a specified period of time
risk
the chance that an investment’s outcome actual gains are different than expected
GDP formula
Y=C+I+G+NX
closed economy
a closed economy loses international trade (NX).
Y=C+I+G
Y-C-G
Is the total income that remains after paying for consumption and government purchases
national savings
also equals investment
savings = investments
Savings formula
S=(Y-T-C)+(T-G)
Private saving
amount of income a household has left after paying taxes and consumption
Y-T-C
Public saving
amount of tax revenue the government has left after paying its spending
T-G
budget surplus
T>G; Taxes are greater than government spending. S>0
Budget deficit
T<G; Government spending is greater than tax revenue; S<0
Nominal Interest rates =
real interest rates + Inflation
Real Interest rates =
Nominal Interest Rates - Inflation
If inflation is greater than expected inflation,
real interest rates will decrease
If inflation is less than expected inflation,
real interest rates will increase
Fiat money
serves as currency
No other purpose
US Dollar
Commodity Money
can perform the function of money
gold or oil
M1
High liquidity
Currency, transaction accounts, and travelers’ checks.
M2
medium liquidity
Savings Accounts, Certificates of Deposit and other Liquid assets.
M3
Low Liquidity
Accounts from M2 that are above 100,000$
medium of exchange
Money is used to buy goods and services without complications of bartering.
Unit of account
Money is used to measure values of goods and services.
Store of value
Money is used to preserve or save purchasing power for future consumption.
Fractional Reserve Banking
Banks accept deposits and are required to to hold a small fraction of what is deposited
Money multiplier
1/reserve requirement
Demand for moeny inverse
People demand a certain amount of money.
The inverse relationship is as interest rates go down, demand for money goes up and vice versa
Shifters of Demand in the Money Market
Price Level
Real GDP
Transaction Costs
Supply for the money market
The Supply of Money will remain constant compared to the change in nominal interest rates.
It will only change based on the FED’s monetary policy.
how to increases money supply/expansionary monetary policy
Decrease Discount Rate
Decrease reserve ratio
buy bonds
decrease the federal funds rate
how to decrease money supply
increase discount rate
increasereserve ratio
sell bonds
increase the federal funds rate
Investment demand
the desired quantity of investment spending by firms across the country.
inverse relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of investment demanded.
the quantity demanded will decrease or increase based on the monetary policy.
Expansionary Policy (Easy Monetary Policy)
This policy increases money supply and real GDP output
Contractionary Policy (Tight Monetary Policy)
This policy decreases the money supply and real GDP output.
Recessionary Gap
Fed Reserve will increase money supply
Inflationary gap
Fed Reserve will decrease money supply
Loanable funds market
is a market perpetuated by borrowers and savers.
Borrowers demand the loans while saver supply them.
The market is in equilibrium when the real interest rate adjusts to a point where the amount of borrowing equals the amount of saving.
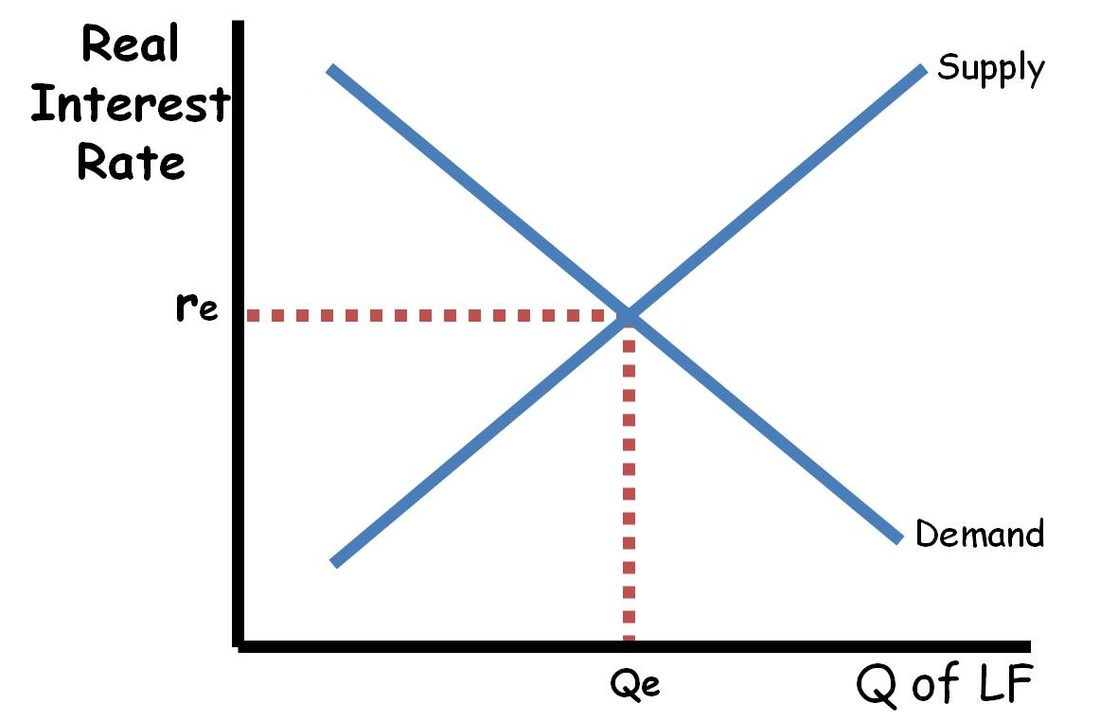
Demand of loanable funds market
When real interest rates increase, quantity for loanable funds demanded decreases.
When real interest rates decrease, quantity for loanable funds demanded increases.
Supply of loanable funds market
When real interest rates increase, the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases.
When the real interest rates decrease, quantity of loanable funds supplied decreases.
Shifters of demand in the loanable funds market
Foreign Demand for Domestic Currency
All Borrowing, Lending and Credit
Deficit Spending - This will increase borrowing.
Expectations for the Future
Shifters of supply in the loanable funds market
Savings Rate
Expectations for the Future
Lending at the Discount Window
Foreign Purchases of Domestic Assets
Interest rates
The proportion rate of a loan that one is charged based on a percentage of a loan over a period of time
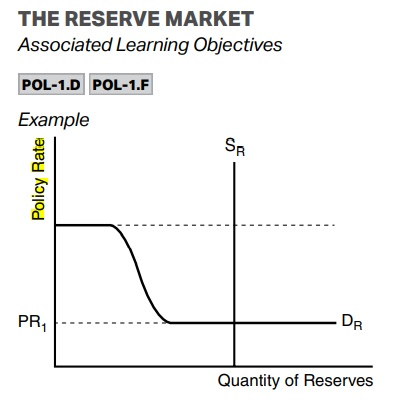
reserve market
Ample Reserves: When the Federal Reserve pays IOR (Interest on Reserves) that is higher than the Federal Funds Rate so banks will place their reserves in the central bank.
Limited Reserves: When the Discount Rate is cheaper than the Federal Funds rate.
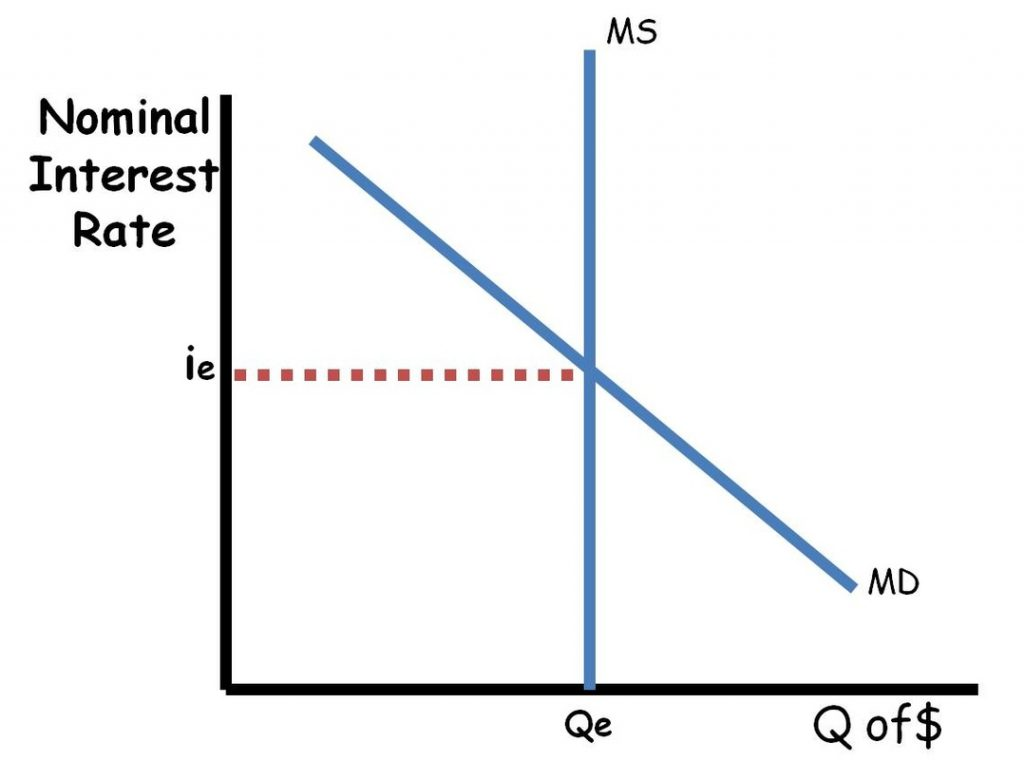
Money market
The money market graph shows how the supply of money and the demand for money interact to determine the equilibrium nominal interest rate. It includes a vertical money supply curve, controlled by the central bank, and a downward-sloping money demand curve, influenced by factors like income and interest rates. Changes in the money supply (a shift of the vertical curve) directly impact interest rates, as a shift to the right lowers rates and a shift to the left raises them.
Fiscal Policy for a recessionary gap
Actions: Government spending increases, Taxes decreased
Results: Leads to AD increase
Monetary policy for recessionary gap
Actions: Reserve Ratio decrease, Discount rate decrease, or Buy bonds
Results: Leads to an increase in the money supply which lowers interest rates which will increase AD
No policy for recesionary gap
Actions: Wages will drop
Results: SRAS will increase
Fiscal policy for inflationary gaps
Actions: Government spending decreases, Taxes increased
Results: Lead to AD decrease
Monetary policy for inflationary gaps
Actions: Reserve Ratio increase, Discount rate increase, or Sell bonds
Results: Leads to a decrease in the money supply which raises interest rates which will decrease AD
No policy for inflationary gap
Actions: Wages will increase
Results: SRAS will decrease
Money growth formula
M*V=P*Y
M = Money
V = Velocity of Money
P = Price
Y = Real Output
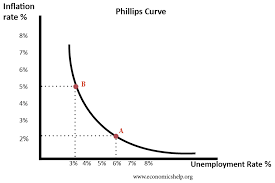
The Phillips Curve
Inflation Rate and Unemployment Rate are inverse
Demand pull inflation
Either caused by Consumer Demand increasing or Government Deficit Spending increasing
Cost push inflation
Decrease in production due to an increase in costs. Labor, Natural Resource Shortages
Wage price spiral
Prices of Goods go up, Need Higher Wages, Higher Labor Costs, Less goods, price increase, Higher Wages, Higher Labor Costs, Less goods, Higher prices
Fiscal Stimulus
Use of expansionary fiscal policy, Increase in government spending, decrease in personal taxes, or increase in income transfers.
Fiscal restraint
Use of contractionary fiscal policy, Decrease in government spending, increase in personal taxes, or decrease in income transfers.
Government revenue
Total income gained by the government at all levels through taxes.
Goverment Expedentures
Total spending payments towards discretionary and non-discretionary purchases.
Budget surplus
This takes place when government revenues exceed government expenditures. Tax Revenues > Government spending
Budget Deficit
This takes place when government spending exceeds government tax revenue. Government Spending > Tax Revenues
National debt
All deficits accumulated over the course of multiple years
Crowding out
This is an economic theory that takes place when the public sector spending can eliminate or lessen the private sector spending.
Economic growth
Economic Growth is critical for raising the standard of living (Real GDP per Capita). This is completed through the advancement of:
Technology
Amount of Physical Capital
Amount of Human Capital
How does our Economy Grow through Public Policy?
Increase Education Spending
Increase Infrastructure Spending
Promotion for innovation