Ch. 11: Muscles of the Body
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Skeletal muscles
produce movements (Ex. Blinking of an eye, standing on tiptoe, swallowing food. etc.")
Consist of fascicles
Fascicles
arranged in different patterns
Fascicle arrangement
tells about action of a muscle
Types of fascicle arrangements
Parallel, Convergent, Pennate, Circular, Fusiform, Multipennate, Bipennate, Unipennate
Parallel arrangement
fascicles run parallel to the long axis of the muscle
Strap-like - sternocleidomastoid
Fusiform - biceps brachii
Convergent Arrangement
Origin of the muscle is broad
Fascicles converge toward the tendon of insertion
Ex. pectoralis major
Pennate Arrangement
Unipennate, Bipennate, & Multipennate
Unipennate Arrangement
fascicles insert into one side of the tendon
Bipennate Arrangement
Fascicles insert into the tendon from both sides
Multipennate Arrangement
fascicles insert into one large tendon from all sides
Circular Arrangement
Fascicles are arranged in concentric rings
Surrounds external body openings
Ex. Orbicularis oris and Orbicularis oculi
Sphincter
general name for a circular muscle
Lever
a rigid bar that moves
Fulcrum
a fixed point
Effort
applied force at one end
Load
resistance, is between the effort and fulcrum
Movements of skeletal muscles involve leverages such as
Lever, Fulcrum, Effort, Load
Bones
act as levers
Joint
act as fulcrums
Muscle contraction
provides effort
Load
bone, overlying tissue, and anything lifted
Fulcrum, Effort, Load
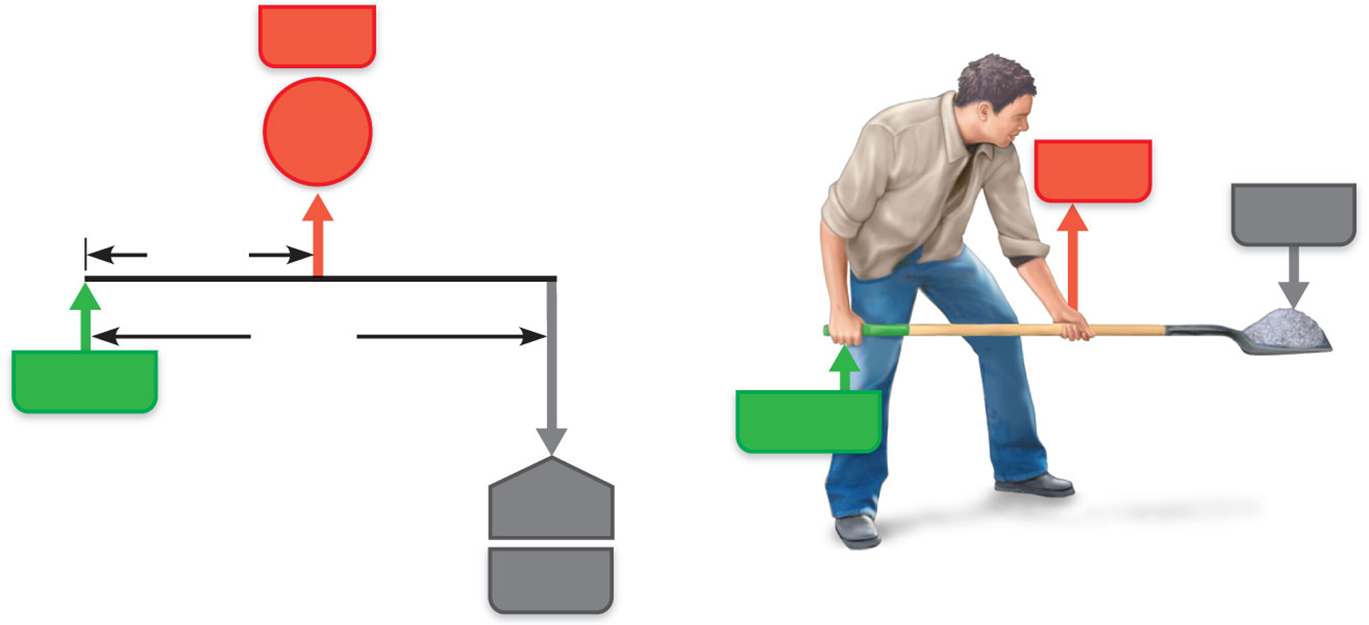
Levers allow a given effort to- (bone-muscle relationships)
move heavier loads and move loads farther
Mechanical advantage- (bone-muscle relationships)
moves a large loas over small distances
Mechanical disadvantage- (bone-muscle relationships)
allows a load to be moved over a large distance
A First-class lever system
raises your head off your chest. The posterior neck muscles provide the effort; the atlanto-occipital joint is the fulcrum; and the weight to be lifted is the facial skeleton.
Second-class lever system
is exerted when you stand tip-toe. The effort is exerted by the calf muslces pulling upward toward the heel: the joints of the ball of the foot are the fulcrum: and the weight of the body is the load.
A Third-class lever
can be when you’re flexing your forearm by the biceps brachii muscle. The effort is exerted on the proximal radius of the forearm; the fulcrum is the elbow joint; and the load is the hand and distal end of the forearm.
Muscles organized into four groups
Musculature of the visceral organs, pharyngeal arch muscles, axial muscles, limb muscles
Musculature of the visceral organs
includes smooth and cardiac muscle, develops from splanchinic mesoderm
Pharyngeal arch muscles
includes skeletal muscles of the pharynx, muscles of the head and neck
Extensors
muscle mass dorsal to limb bones
Flexors
muscle mass ventral to limb bones
Extensors of the upper limb
triceps brachii, extensor digitorum
Flexors of the upper limb
biceps brachii, flexor carpi radialis
Extensors of lower limb
quadriceps femoris, tibialis anterior
Flexors of the lower limb
hamstrings, gastrocnemius
Prime mover (agonist)
has major responsibility for a certain movement
Antagonist
opposes or reverses a movement
Synergist- helps the prime mover
by adding extra force, and by reducing undesirable movements
Fixator
a type of synergist that holds a bone firmly in place
A muscle that crosses of the posterior side of joint produces extension
example: latissimus dorsi
A muscle the crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces flexion
example: pectoralis major
Dense fibrous connective tissue divides limb muscles into
compartments
Muscles in opposing compartments are
agonist and antagonist pairs
Head muscles
Temporalis, Masseter
Facial muscles
Epicranius, Frontal belly, Orbicularis oculi, Zygomaticus, Orbicularis oris
Neck muscles
Sternohyoid, Sternocleidomastoid, Platysma
Shoulder muscles
Trapezius, Deltoid
Thorax muscles
Pectoralis minor, Serratus anterior, Pectoralis major, Intercostals
Abdomen muscles
Rectus abdominis (abs), Internal oblique, Transversus abdoominis, External oblique
Arm muscles
Triceps brachii, Biceps brachii, Brachialis
Forearm muscles
Pronator teres, Brachioradialis, Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus
Pelvis/Thigh muscles
Iliopsoas, Pectineus
Thigh
Tensor fasciae latae, Sartorius, Adductor longus, Gracilis, Rectus femoris, Vastus lateralis, Vastus medialis
Leg
FIbularis longus, Extensor digitorum longus, Tibialis anterior, Gastro cnemius, Soleus
Pharyngeal constrictors
squeeze food into the esophagus
Head Movement
Sternocleidomastiod
Spelnius capitis and splenius cervicis
Erector Spinae group
largest of the deep back muscles
Lateral and anterior abdominal wall formed by
external oblique, internal oblique, transverses abdominis
Deltoid
large shoulder/arm muslce
Pectoralis major
large chest muscle
movements of the scapula
Trapezius, levator scapulae, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor
Latissimus dorsi
large triangle shaped back muscle
Levator scapulae
goes from scapula up the neck to the cranial bones
Thenar muscles
ball of thumb muscle