Inferential statistics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Difference between descriptive and inferential statistics
Descriptive:
Allows us to draw conclusions about differences/ correlations through use of graphs and averages.
Inferential:
Allows us to say whether difference/ correlation is significant through the use of statistical tests.
How to complete a sign test
After collecting interval data from both conditions of the IV, collate data into a table.
Cross out any data that is unchanged between the two conditions.
Mark down the sign of difference between the conditions for each participants data (+ or -)
Identify the less frequent sign (+ or -) and count how many there are → this is the calculated S value
Using the table of critical values, compare your calculated value to it.
Identify the level of probability (most likely will be p<0.05) and whether or not the hypothesis is directional (1 tailed) or non-directional (2 tailed) → use this and your calculated value to determine whether or not the data is significant.
Either accept or reject the experimental and null hypothesis.
(If data is significant, reject null and accept experimental and vice versa for non-significant data.)
What to do if test is significant at a significance level of p<0.05?
Reject null hypothesis and accept experimental hypothesis because there is 5% probability or less than the difference in results occurred due to chance.
What to do if test is not significant at a significance level of p<0.05?
Accept null hypothesis and reject experimental hypothesis because there is 5% probability or less that the difference in results occurred due to chance.
Type I error
False positive
Rejecting null hypothesis when it should have been accepted because it was actually a chance finding.
→ when the level of significant is too lenient e.g. p>0.20
Type II error
False negative
Accepting the null hypothesis when it should have been rejected because the IV did affect the DV.
→ when the level of significance is too strict e.g. p<0.001
In what situation would a psychologist use a stricter level of significant such as p<0.01?
drug trials
treatment for mental disorders
situations which may never happen again
→ researcher needs to be more confident and eliminate the probability of chance affecting the results as much as possible.
Choosing statistical tests table
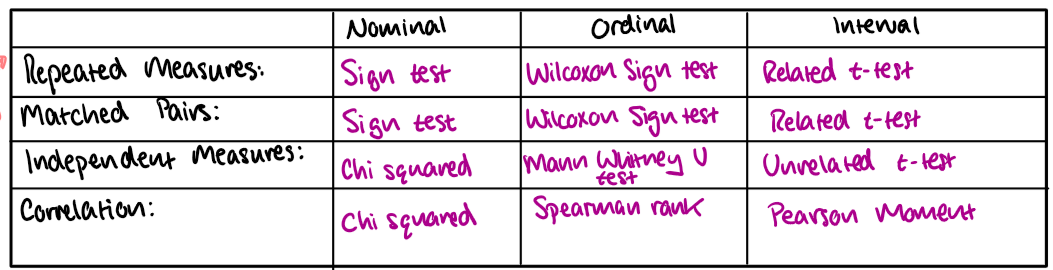
What statistical test should I use to test? Repeated measures design and nominal data
sign test
What statistical test should I use to test? Repeated measures design and ordinal data
wilcoxon sign test
What statistical test should I use to test? Repeated measures design and interval data
related t-test
What statistical test should I use to test? matched pairs and nominal data
sign test
What statistical test should I use to test? matched pairs and ordinal data
wilcoxon sign test
What statistical test should I use to test? matched pairs and interval data
related t-test
What statistical test should I use to test? independent measures and nominal data
chi squared
What statistical test should I use to test? independent measures and ordinal data
mann whitney U test
What statistical test should I use to test? independent measures and interval data
unrelated t-test
What statistical test should I use to test? correlation and nominal data
chi squared
What statistical test should I use to test? correlation and ordinal data
spearman rank
What statistical test should I use to test? correlation and interval data
pearson moment