Chapter 1 Radiology Technology
1/186
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not finished yet !
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
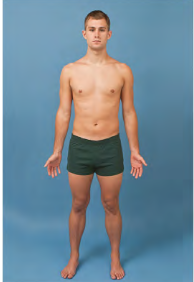
Anatomic Position
Palms forward
Hands forward
Standing up straight
Facing us
Arms slightly abducted from body
Toes forward
How we position x-rays to be viewed?
We don’t take x-rays in anatomic position but we present the x-rays in anatomic position.
Splitting the body into left and right halves.
Sagittal plane
Splitting the body into Anterior and Posterior portions. (Mid-coronal: equal portions)
Coronal plane
Not parallel to Sagittal, Coronal, or Horizontal plane.
Oblique plane
must also include a qualifying term that indicates which way it is rotated, such as medial or lateral rotation ( For projections )
Otherwise known as Axial. Transverse plane splitting the body into Superior and Inferior portions.
Horizontal plane
Radiograph
A processed image of a patient's anatomic part(s), as produced by the action of x-rays on an image receptor
Radiograph vs. X-ray film
Radiograph - includes the recording medium and the image.
X-ray Film - x-ray film specifically refers to the physical piece of
material on which a latent (non-processed) radiographic image
is stored.
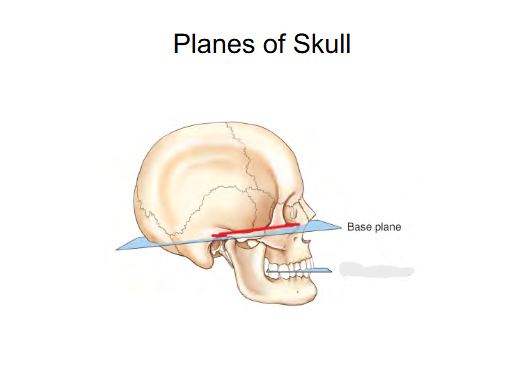
Planes of Skull
Base plane
Occlusal plane
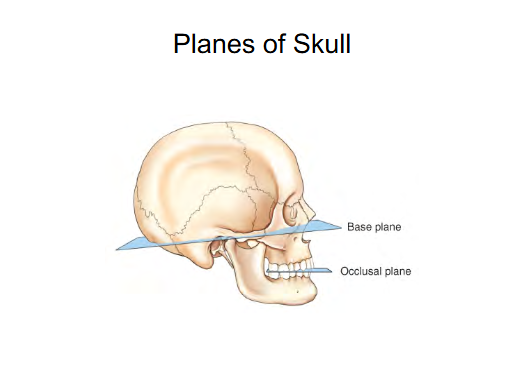
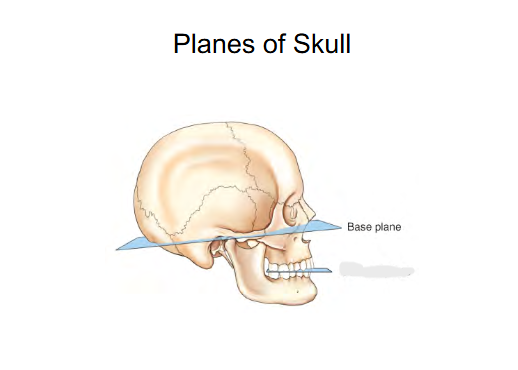
Base Plane
Connects Interorbital margin to External Auditory Meatus (ear canal) (EAM).
Helps position the head
sometimes is called the Frank-fort horizontal plane
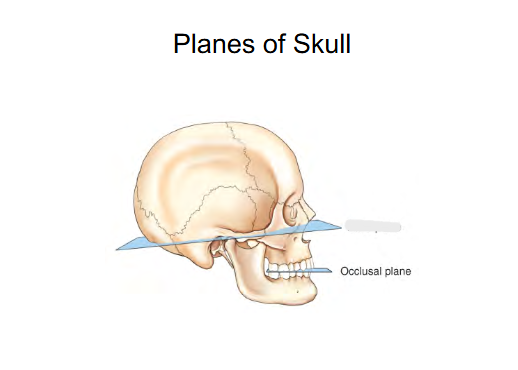
Occlusal Plane
Plane when teeth are together .
Positioning purposes for Cervical spine
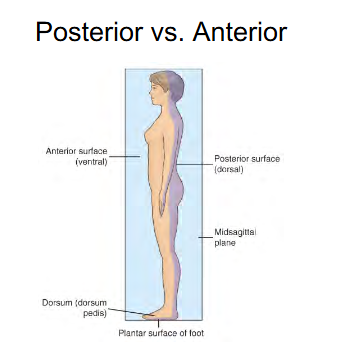
Top of feet
Dorsum ( Dorsum Pedis )
Anterior/Ventral
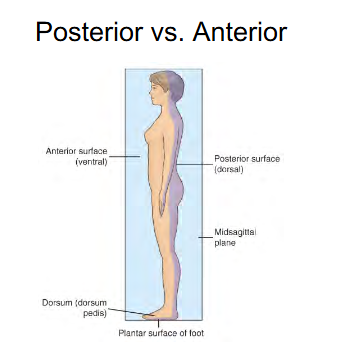
Bottom of feet
Plantar surface of foot
Posterior/Dorsal
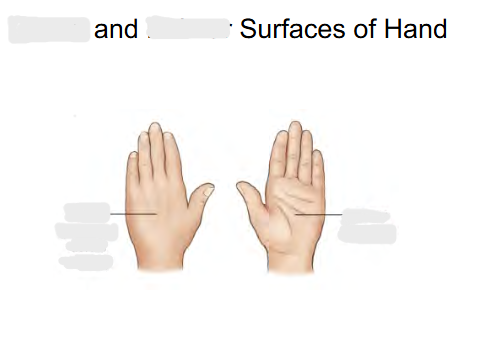
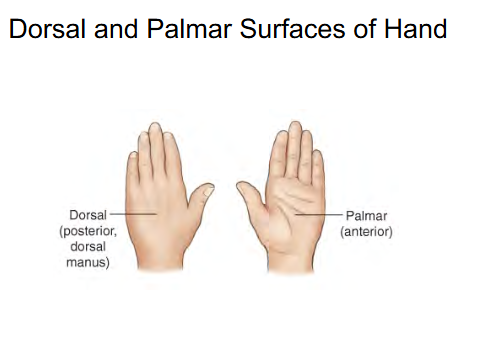
Front of hand surface called:
Palmar ( Anterior )
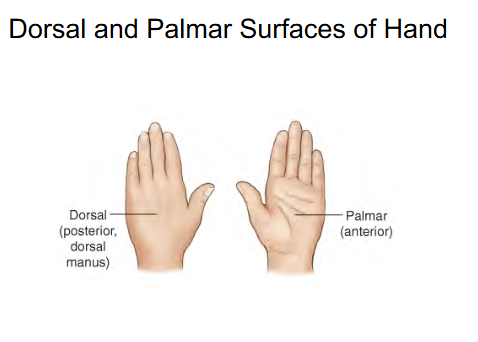
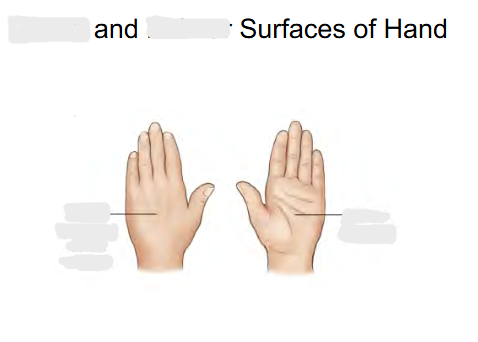
Back of hand surface called:
Dorsal
Posterior
“ Dorsal Manus “
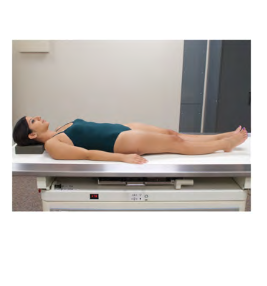
General body position:
Laying on your back facing upward
Supine
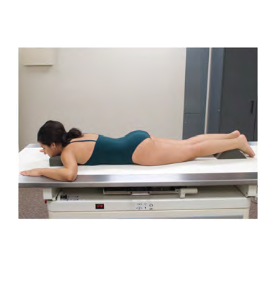
General body position:
Laying on your belly
Prone
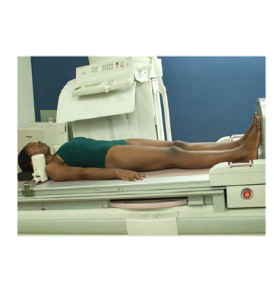
General body position: recumbent position with the body tilted with the head lower than the feet.
Head is slightly lower than feet
important for patients feeling faint
Trendelenburg
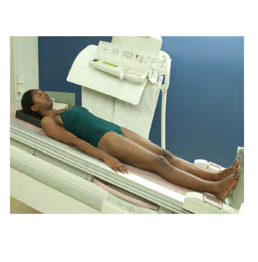
General body position: recumbent position with the body tilted with the head higher than the feet.
Head is higher than feet
Upper GI exams if patient can’t stand up
Fowler ( can be known as : Reverse Trendelenburg )

General body position: Patient is upright
Erect
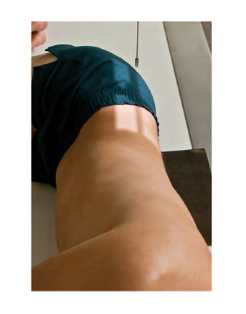
General body position:
Lying down in any position
Recumbent

General body position:
Patient is Supine w/ hips and knees flexed. Thighs abducted and rotated externally. ( Position for a pap smear/urinary )
Lithotomy
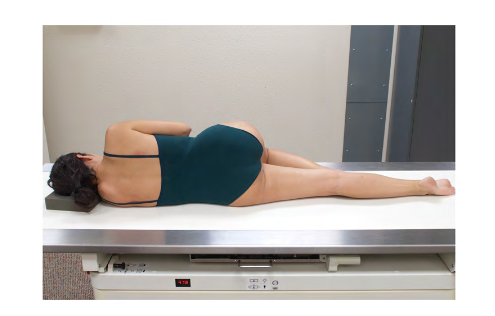
General body position : recumbent oblique position with the patient lying on the left anterior side, with the right knee and thigh flexed and the left arm extended down behind the back.
Position for Barium Enema
Modified Sims position

What position is this?
Right Lateral Erect

What position is this?
Right Lateral Recumbent
What position is this?
Left Posterior Oblique
What position is this?
Left Posterior Oblique
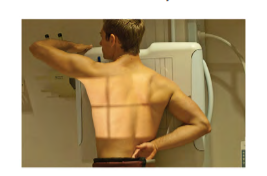
What position is this?
Right Anterior Oblique

What position is this?
Right Anterior Oblique
Body Position:
How is the body positioned? How is the patient positioned?
Projection:
Describes the path or direction of the central ray
Breakdown into two things (Body position)
What part of the body is touching first? Is it Anterior or Posterior.
Is it right or left side touching?
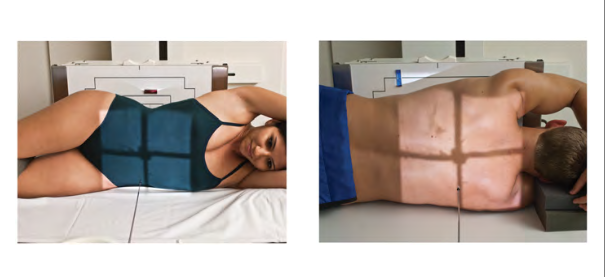
What position term is this?
Patient lying down
Horizontal beam
Decubitus (Decub) Position

Position : ?
Projection: ?
Position: Left Lateral Decubitus
Projection: AP projection
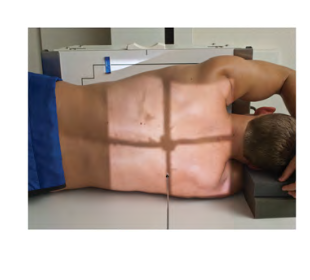
Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Right Lateral Decubitus
Projection: PA projection
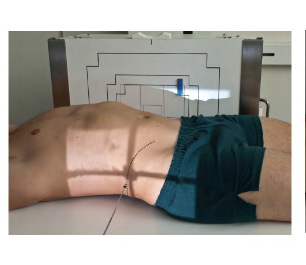
What Position is this? ( Look how patient is with IR )
Laying supine with Horizontal beam
Dorsal Decubitus
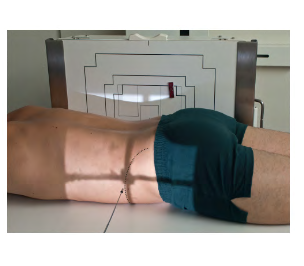
What Position is this? ( Look how patient is with IR)
Laying Prone with Horizontal beam
Ventral Decubitus
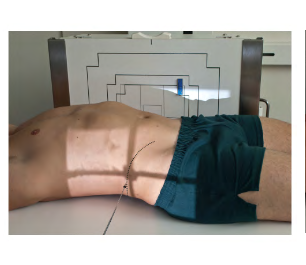
Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Dorsal Decubitus
Projection: Left Lateral
( Left Lateral Dorsal Decubitus)
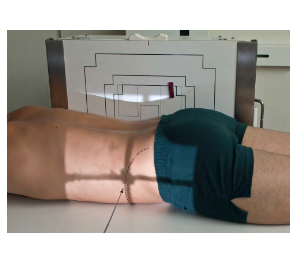
Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Ventral Decubitus
Projection: Right Lateral
( Right Lateral Ventral Decubitus )
How does x-ray beams come out of the x-ray tube?
Fan shaped and use the straightest portion of x-ray beam to the center of the body part.

Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Medial Oblique Foot
Projection: AP
-Always add what side ( Ex: Right AP Medial Oblique Foot)

Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Lateral Oblique Hand
Projection: PA
-Always add what side ( ex: Right PA Lateral Oblique Hand)
Tube angle or patient angle more than 10 degrees
Axial
Hand, foot or Limb turned or held so palm/sole facing downwards
Pronated

Position: ?
Projection: ?
Position: Oblique elbow
Projection: AP medial
( Right AP Medial Oblique Elbow )

Entering Lateral aspect ( the thumb side) and exiting the medial aspect
Lateromedial
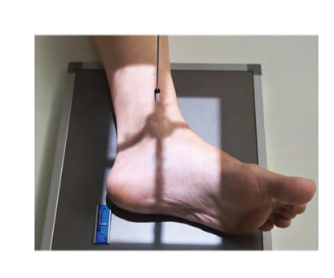
Entering the Medial aspect of ankle and exiting the Lateral aspect of the ankle.
Mediolateral
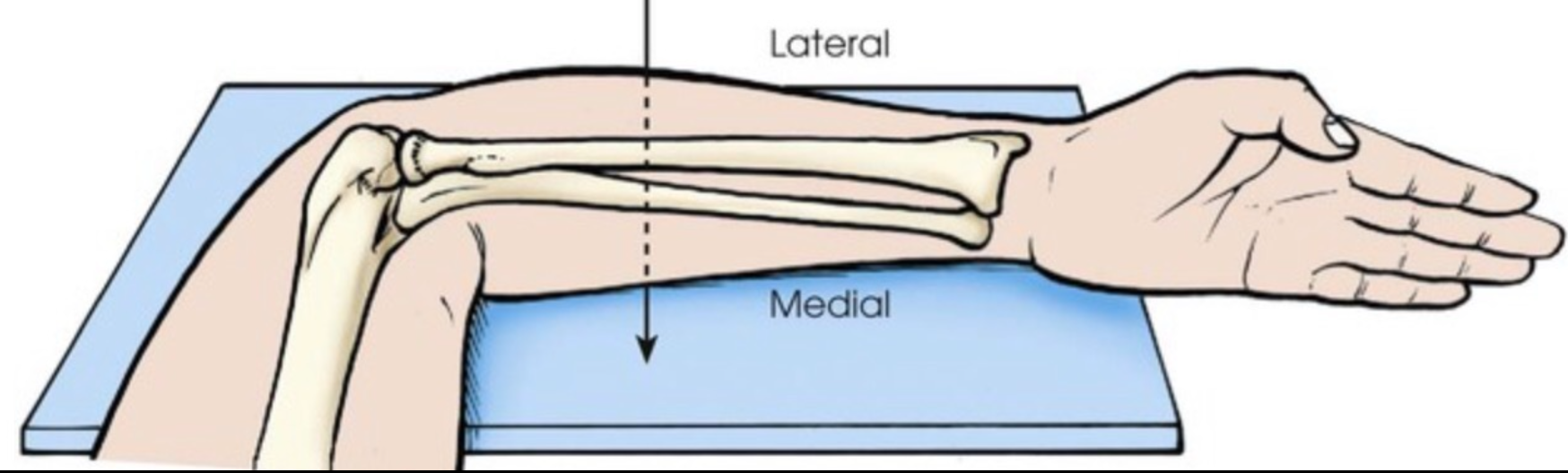
Better example of Lateral and Medial . It’s based off of anatomic position
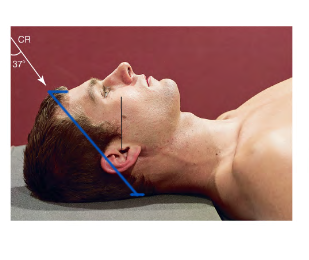
Special Projection Terms:
AP Axial (semiaxial) Projection
37 degree angle = Axial
Enters Anterior exits Posterior
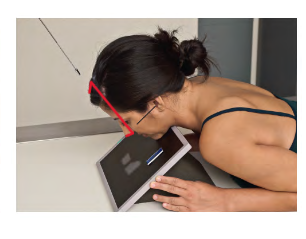
Special Projection terms:
Axial (superoinferior) Projection
Tube is angled = Axial
Enters Superior exits Inferior
Inferosuperior Axial Projection
Enters Inferior exits Superior = Inferosuperior
Angled more than 10 degrees = Axial
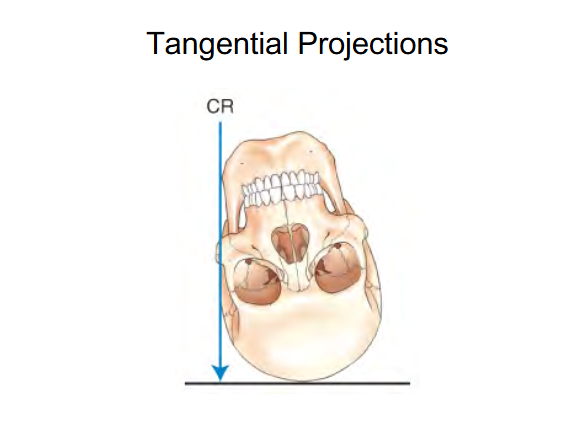
The beam (CR) is touching a curve or surface at only one point .
Image shows Tangential projection of Zygomatic arches
“Skims” Zygomatic arches
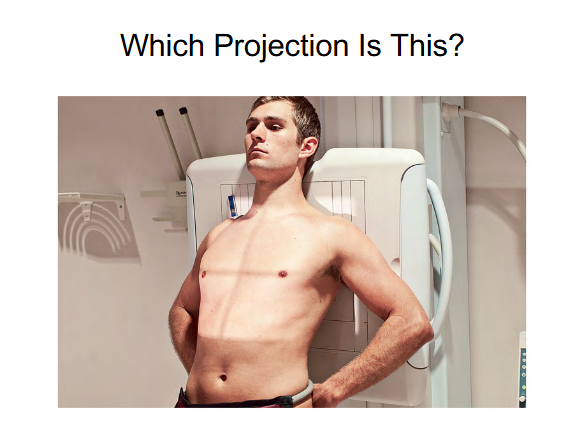
Projection: AP Axial
Leaning shoulders back
Angling the patient = Axial
Answer = AP Axial Lordotic Position

Answer = Trans Thoracic Lateral Projection
Trans ( Across the thoracic)
Thoracic Lateral ( Patient is in Lateral )
( if we want to add position it would be Right Lateral )
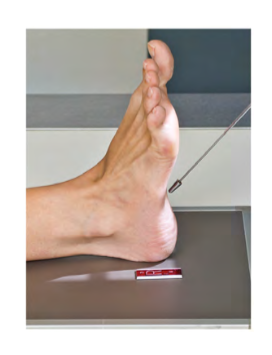
Name this projection?
Planodorso projection of foot or PA proj. of foot
more specific “Axial Planodorso projection of the Calcaneus ”
Bottom of foot= Plantar
40 degree angle = Axial
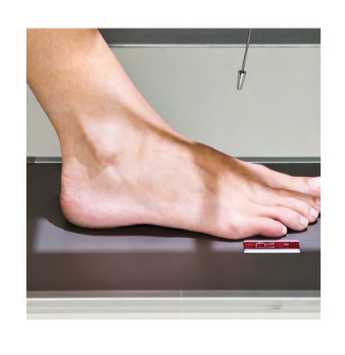
Name this projection?
Dorsoplantar or AP proj. of foot
Top of foot: Dorsum
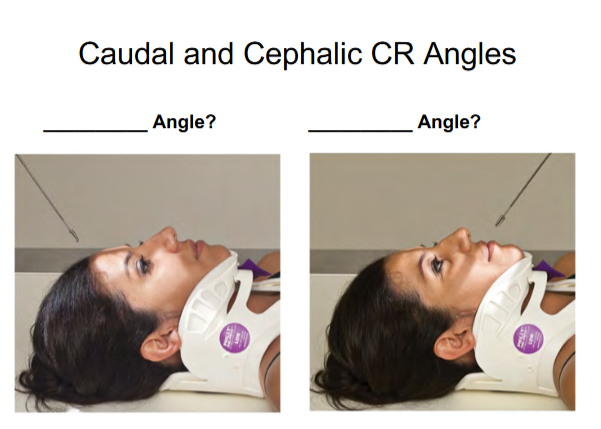
Caudad Angle
Towards the feet
image 1
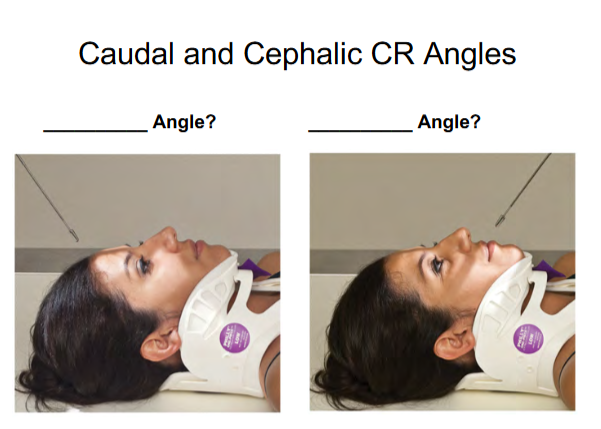
Cephalic Angle
Towards the head
image 2
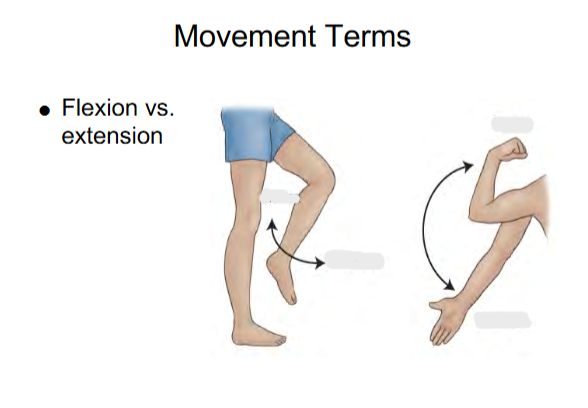
Flexion
Flexion decreases the angle of the joint
Flexion for legs
Bend leg
Flexion for arms
Bend Elbow
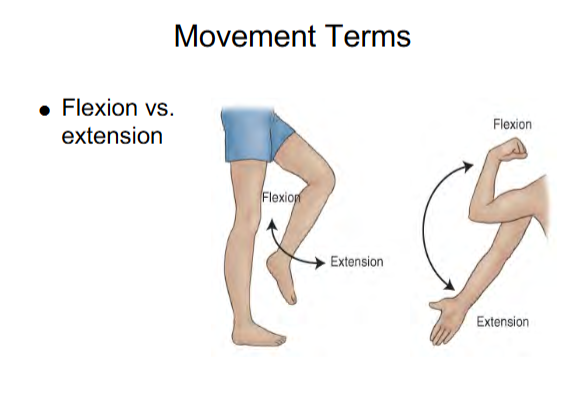
Extension
Extension increases the angle
Extension for legs
Straighten leg
Extension for arms
Straighten arm
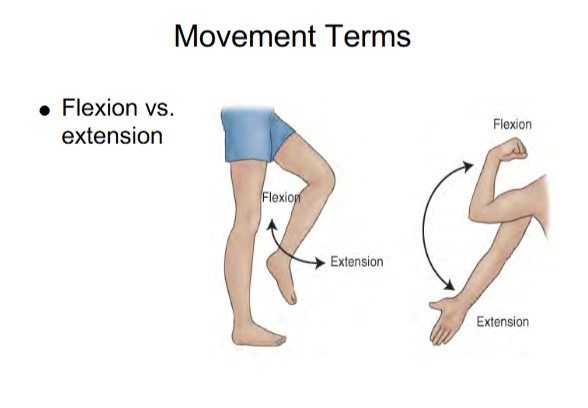
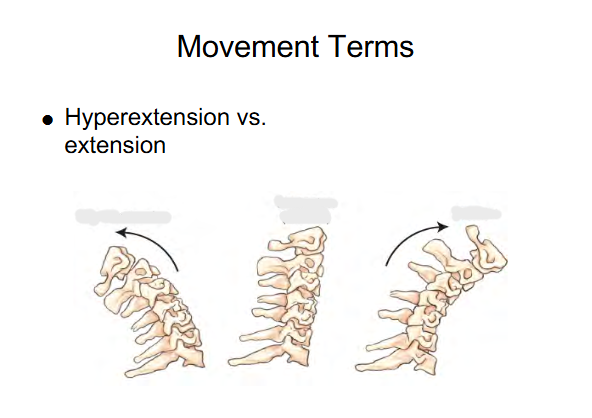
Image 1 : Hyper-extension beyond the straight or neutral position
Image 2 : Extension ( Neutral )
Image 3 : Flexion ( chin to chest )
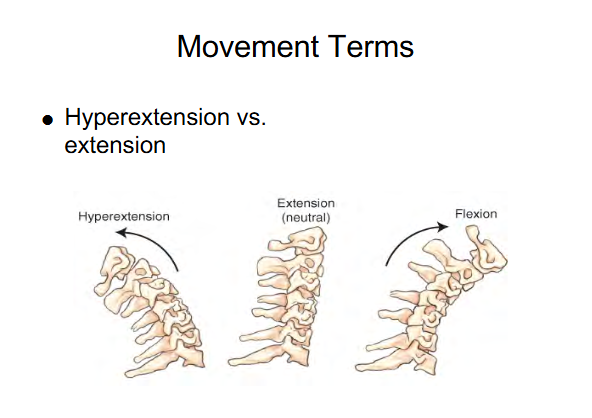
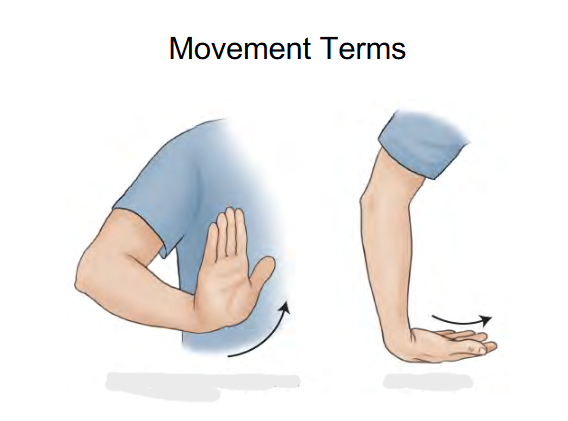
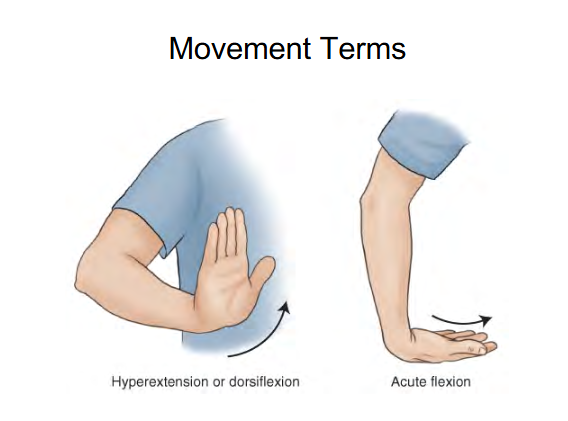
Image 1 : Hyperextension or Dorsiflexion
lifting up hand to the air
Image 2: Acute Flexion
Moving Fingers downwards wrist
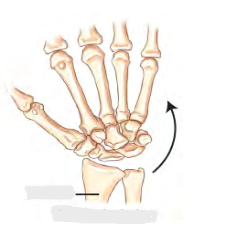
Movement term
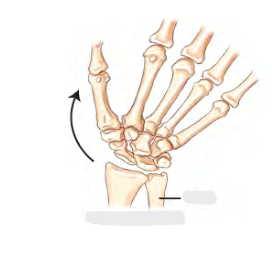
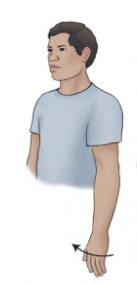
Ulna Deviation
Moving hand towards Ulna (Pinky side)
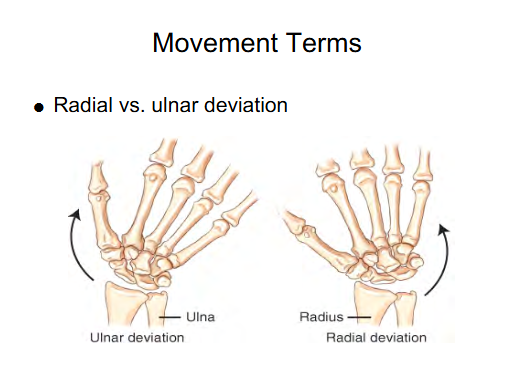
Movement term
Radius Deviation
Moving hand towards Radius ( Thumb side)
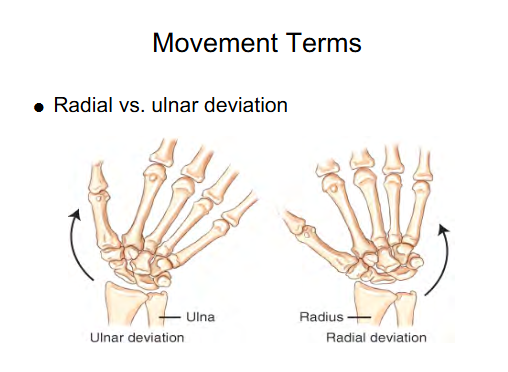
Movement term for foot
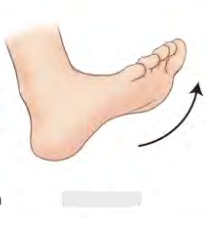
Dorsiflexion
90 degrees
Toes up
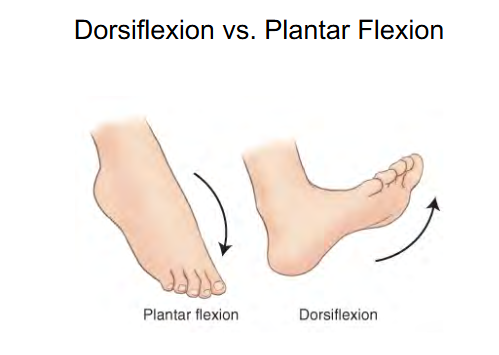
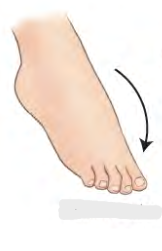
Movement term for foot
Plantar flexion
180 degrees
Toes hanging down
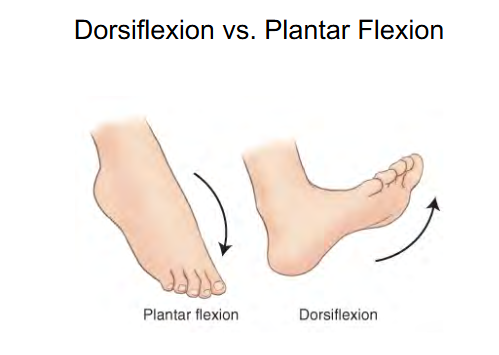
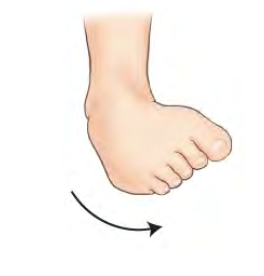
Stress movement of ankle joint
Inversion ( Varus ) inward stress movement
Big toe up , pinky toe down
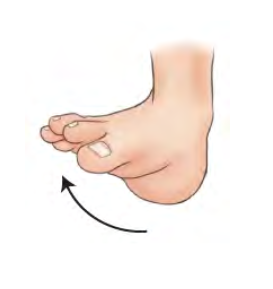
Stress movement of ankle joint
Eversion (Valgus) outward stress movement
Big toe down , pinky toe up
What type of rotation ?
Medial rotation
is a rotation or turning of a body part with movement of the anterior aspect of the part toward the inside, or median plane.

What type of rotation?
Lateral rotation
is a rotation of an anterior body part toward the
outside, or away from the median plane.
Movement term
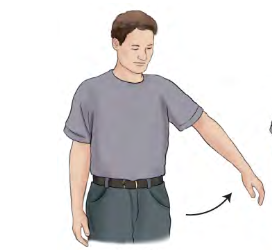
Abduction
Away from
Movement term
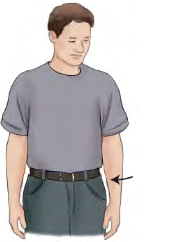
Adduction
towards
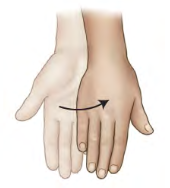
Movement term
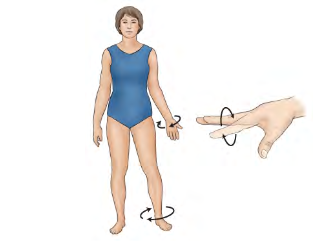
Pronation
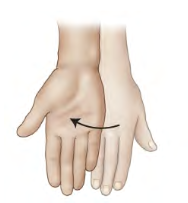
Movement term
Supination
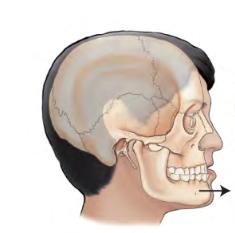
Movement term
Protraction
movement forward from a normal position
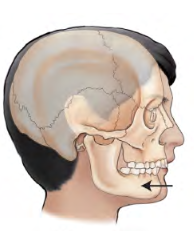
Movement term
Retraction
movement backward or the condition of being drawn bac k.
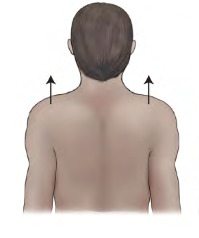
Movement term
Elevation
lifting, raising, or moving of a part superiorly.
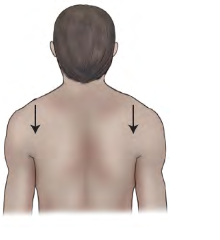
Movement term
Depression
letting down, lowering, or moving of a part
inferiorly.
Movement term
Circumduction movement
Circular movement at a joint
Combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
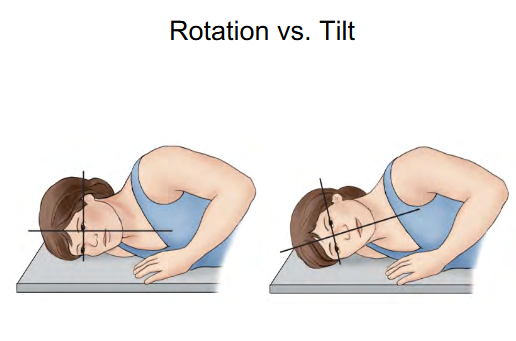
Difference b/w Rotation and Tilt
Rotation: Stays parallel with IR
Tilt: Midsagittal plane is no longer parallel to IR
Midsagittal has a slant to it
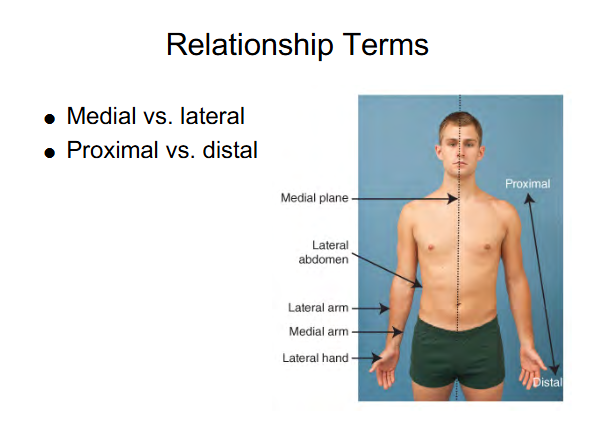
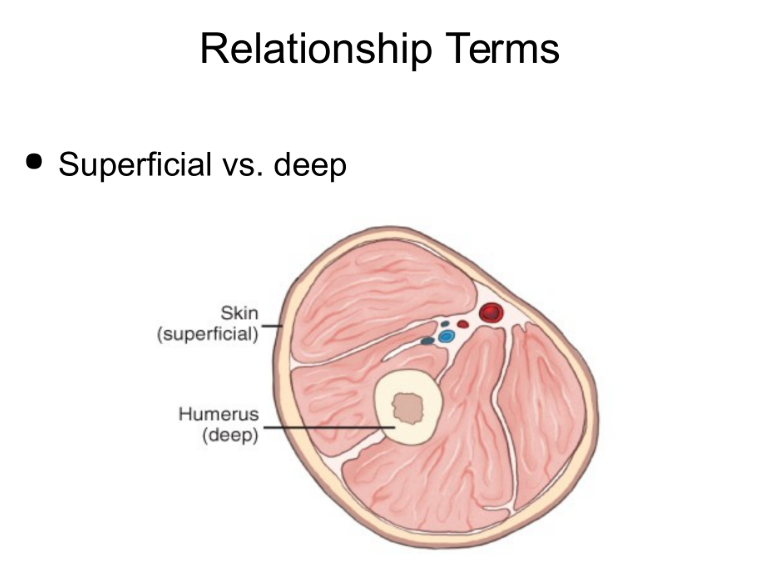
Relationship terms
Superficial vs Deep
Superficial - nearer the skin surface
Deep - The more interior you get to the body part (arrow points at Humerus compared to Skin)
Radiographic view definition
View as describes body part as seen by IR or other recording medium such as Fluoroscopic screen.
Positioning accuracy
All pertinent anatomy demonstrated
Multiple images aligned on IR
Collimation ( only want light field on anatomy you want)
Rotation ( depends on what you want to create)
Central Ray ( CR) ( Want the straightest beam at body part)
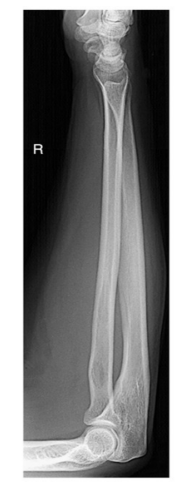
Evaluation criteria
Anatomy demonstrated: Elbow and wrist joints both included
Position: No rotation at wrist and elbow joints
Exposure: Optimal exposure factors
Image markers: “R” marker visible
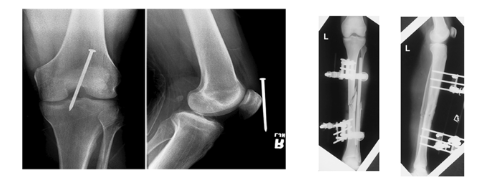
Positioning Rules and Principles
MINIMUM TWO VIEWS/PROJECTIONS
Anatomic structures superimposed ( Placed or laid on top of each other)
Localization of lesions or foreign bodies ( For example the nail near the knee)
Determination of alignment of fractures ( For example: the alignment of the tibia )
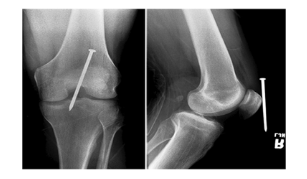
1 x-ray done straight on ( PA or AP) → Nail seems deep
1 x-ray 90 degree from that projection for true lateral → Nail adjacent to knee after true lateral
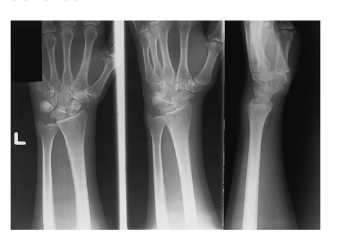
Positioning Rules and Principles
MINIMUM THREE PROJECTIONS/VIEWS
when joints are in prime interest area
AP or PA
Lateral
Oblique
Long bones are required how many projections?
Two
AP
Lateral
Joints in a prime interest area how many projections?
Three
AP or PA
Lateral
Oblique
Exceptions to Positioning Rules
Postreduction upper and lower limbs ( Ex: Wrist in a cast usually three views but it’s fractured. Only 2 views (PA and lateral ) to check alignment.
Pelvis study projection unless hip injury is suspected ( Ex: Usually 1 view unless trauma which you want 2 views.)
Abdomen (KUB) One x ray supine when usually 2 x-rays 90 degrees from each other.
Viewing radiographs?
patient is facing the viewer, with the patient in the anatomic position
Limbs in anatomic position
Hands & feet are digits up.
Human body 10 systems
(l) skeletal
(2) circulatory
(3) digestive
(4) respiratory
(5) urinary
(6) reproductive
(7) nervous
(8) muscular
(9) endocrine
( l0) integumentary
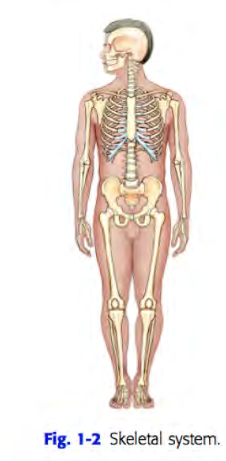
Skeletal system
includes the 206 separate bones of the body and their associated cartilages and joints
structures that make up the passageway from the exterior to the
alveoli of the lung interior include
nose
mouth
pharynx
larynx
trachea
bronchial tree.
urinary system includes
organs that produce, collect, and eliminate urine.
kidneys
ureters
bladder
urethra
function of the nervous system
regulate body activities with electrical impulses that travel along various nerves
muscular system, which includes all muscle tissues of the body,
is subdivided into three types of muscles:
Skeletal
smooth
cardiac
Most of the muscle mass of the body is skeletal muscle
striated and under voluntary control
Smooth muscle
involuntary
is located in the walls of hollow internal organs such as blood vessels, the stomach , and intestines.