Bio 113- Unit 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Features of evaluation of a claim
evidence- quantitative info (numbers)
source- scientific study that has been published in peer review journal
mechanism- scientific explanation for what is going on
why is the process of science reliable?
self corrective (mistakes caught bc scientists scrutinize each other’s work)
peer review
conclusions always subject to change based on new evidence
experiments are designed to disprove hypothesis
objective hypothesis testing
belief perseverance
tendency to cling to a belief even if evidence supports the contrary
hypothesis
what they hypothesize is happening
significant difference
null hypothesis
what they hypothesize is not happening
no significant difference
prediction
what we expect to measure if the hypothesis is correct
the null is rejected
dosage, duration, and measurement
testing the hypothesis
null is rejected if prediction is correct
null fails to be rejected if prediction is incorrect
experimental group
receives the experimental treatment
negative control group
has the same conditions as the experimental group except for the experimental treatment
scientific consensus
When multiple scientists test their predictions using experiments, and they all agree with one another
sample size that will provide the most accurate mean
little variation (we want this!)= bigger sample size
we take a subset of the population that will be reflective of the population
sample
subset of the population that has been measured
standard deviation
how close the majority of the population sits to the mean
measure of the variation of the sample
what curve will have the smallest standard deviation
narrow curve= less variation in measurements (this is what you want)
standard error
tells us about how the standard deviation relates to sample size
we want standard error to be low
statistically significant
significant difference (wasn’t due to chance)
*= indicates statistically significant difference
the more * you see on a graph= the more confident you can be that the difference is truly significantly statistically different
reject the null hypothesis
scientific theory
a hypothesis that describes a widespread phenomenon in nature that has been tested many times and in those times the null was rejected
cell theory
all living things are made up of cells
chromosome theory of inheritance
dna is the heritable material that gets passed from parent to offspring
the theory of evolution
the population of organisms change over time
most controversial
natural selection
the process by which species change over time
occurs when individuals within a population vary in characteristics that are heritable
in a particular environment, certain versions of these heritable characteristics help individuals survive and reproduce more often than others
where does variation come from in natural selection
mutations
random mistakes in DNA replication
arise by chance
the more something replicates/reproduces, the more mutations/variation is generated
understanding evolution by natural selection is critical for medicine
antibiotic resistance bacteria
atoms
nucleus in center
electrons move around the nucleus in orbitals
orbitals are grouped into levels called electron shells
valence shell
the outer shell
atom is most stable when its valence shell is filled
nonpolar covalent bond
equal sharing of valence electrons between atoms in a covalent bond
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons between atoms in a covalent bond
ex/ water
unequal charge
electronegativity
strength at which an atom’s nucleus pulls electrons
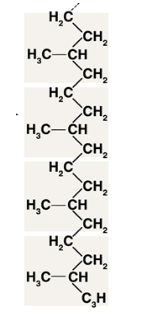
Macromolecule
lipids
consist of C-H bonds
nonpolar
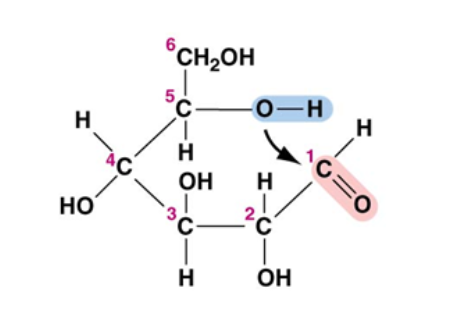
Macromolecule
Carb
consist of C=O groups bonded to -OH groups with some C-H bonds
polar
ex/glucose

Macromolecule
Nucleic acids
consist of nucleotides; phosphate group, sugar, nitrogenous base
polar
which macromolecules will dissolve in water
carbs and nucleic acids bc they are polar
phospholipids
lipids that make up the cell membrane
have a nonpolar region (the tail) and a polar region (the head)
form lipid bilayers in water
cell membrane (lipid bilayer): hydrophilic heads interact with each other, with water, and with other polar molecules- hydrophobic tails don’t interact with anything
which molecules would get through cell membrane on own
non polar and small molecules bc not attracted to polar heads
O2, CO2, N2
H2O: small and polar: wont get through on its own usually bc it will interact with polar head, but a very small amount can due to small size
glucose/sucrose: large and polar (can never get through on it’s own)
Ions: can’t get through on own bc of their charge but they are small
saturated lipid
hydrocarbon chains consist of only single bonds between carbons
long
unsaturated lipid
hydrocarbon chains have one or more double bonds
short
has curves
greater permeability
decreased temp and effect on lipid movement
slows lipid movement= hydrophobic tails in center to pack closer together
at very low temps= lipid bilayers solidify
Would you expect a fly that lives in Antarctica to have more saturated or unsaturated phospholipids in their cell membranes compared to a fly that lives in the hot desert?
fly that lives in arctic would have more unsaturated phospholipids
cold temps= decrease permeability
there needs to be more unsaturated lipids to increase permeability
cystic fibrosis
disease caused by a defect of membrane transport
genetic disease
primary symptom: mucus is think and sticky (blocks airways and interferes with digestion and absorption)
causes very early death
people with CF= genetic mutation which makes the chloride protein channel nonfunctional (Cl- can’t move from inside the cell to outside of the cell)
why does Cl- need a protein channel to get through cell membrane?
Cl- is an ion= can’t get through cell membrane on own
gets stuck to polar heads
diffusion
solutes move from high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached
the cell membrane must be permeable to that solute
osmosis
water moves from low solute concentration to high solute concentration until equilibrium is reached
there must be a concentration difference for water to move
is there a connection between diffusion and osmosis?
yes
Concentration of Ca in a cell is higher inside than outside the cell, the cell
pumps Ca from inside the cell to outside the cell, now there is more Ca outside
the cell.
the water moves from inside to outside because water will move towards the higher solute concentration. Water always follows solutes.
outside solution is hypertonic to the inside
hyper= more
Higher solute concentration outside the cell than inside you can say the outside is hypertonic compared to the inside
cell will shrink
water moves from inside to outside
outside solution is hypotonic to the inside
hypo= less
if there is a higher solute concentration inside the cell than outside, the outside is hypotonic compared to the inside
water moves from outside to inside
cell expands and bursts
isotonic
outside and inside solute concentration are equal
no change in the cell
simple diffusion
diffuse directly through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient (from high to low)
facilitated diffusion
uses a protein channel to diffuse through the cell membrane down concentration gradient (high to low)
doesn’t require energy
active transport
move through cell membrane against their concentration gradient (low to high) through protein channel
uses energy
primary active transport
protein pump moves ions against their concentration gradient
ATP is used
secondary active transport
uses electrochemical energy
in the same cotransporter
what are proteins made of?
amino acids (building blocks)
primary structure
sequence of animo acids
secondary structure
spirals or folds
alpha-helix or beta-pleated sheets
tertiary structure
complex 3D shape
gives the protein the function
quaternary structure
not a real structure
multiple tertiary structures forming one complex
what is an enzyme
tertiary proteins
speed up rate of chemical reactions
work by acting as catalysts
destabilize bonds in substrates (reactants) and lower the activation energy required for a reaction to start
active site
reactants enter and products leave
induced fit
the substrate induces a slight change in shape of the enzyme so that it can fit perfectly
allosteric inhibition
when a regulatory molecule binds somewhere other than the active site
competitive inhibition
reversible
inhibitor molecule directly binds on the active site
reversible
only returns to 100% of its function in competition
reversible
adding a phosphate group to inactivate (or activate) the enzyme
increasing reactant concentration
irreversible
peptide bond is cut
metabolic pathway
a specific molecule is altered in a series of steps that results in a final product