Transition Metals
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Describe how TM form ions
Lose 4s electrons before 3d electrons
Name and describe the 2 odd transition metals
Copper and Chromium
More stable with half full 4s orbital so donate a 4s electron into the 3d subshell
Define transition metal
Metal that can form one or more stable ions with an incomplete d subshell
Describe Zn and Sc
They are d block elements as their outer electron is in a d subshell
But they aren't transition metals as they don't form a stable ion with an incomplete d subshell
Describe the 4 main characteristics of TM
- Catalysts
- Variable Oxidation States
- Form complex ions
- Coloured compounds
These arise due to the incomplete d subshell
Define complex ion
central metal ion surrounded by ligands
Define ligand
molecule or ion that forms a coordinate bond with a transition metal by donating a lone pair of electrons
Define monodentate ligand
molecules or ions that can donate one electron pair to the central metal ion to form one coordinate bond
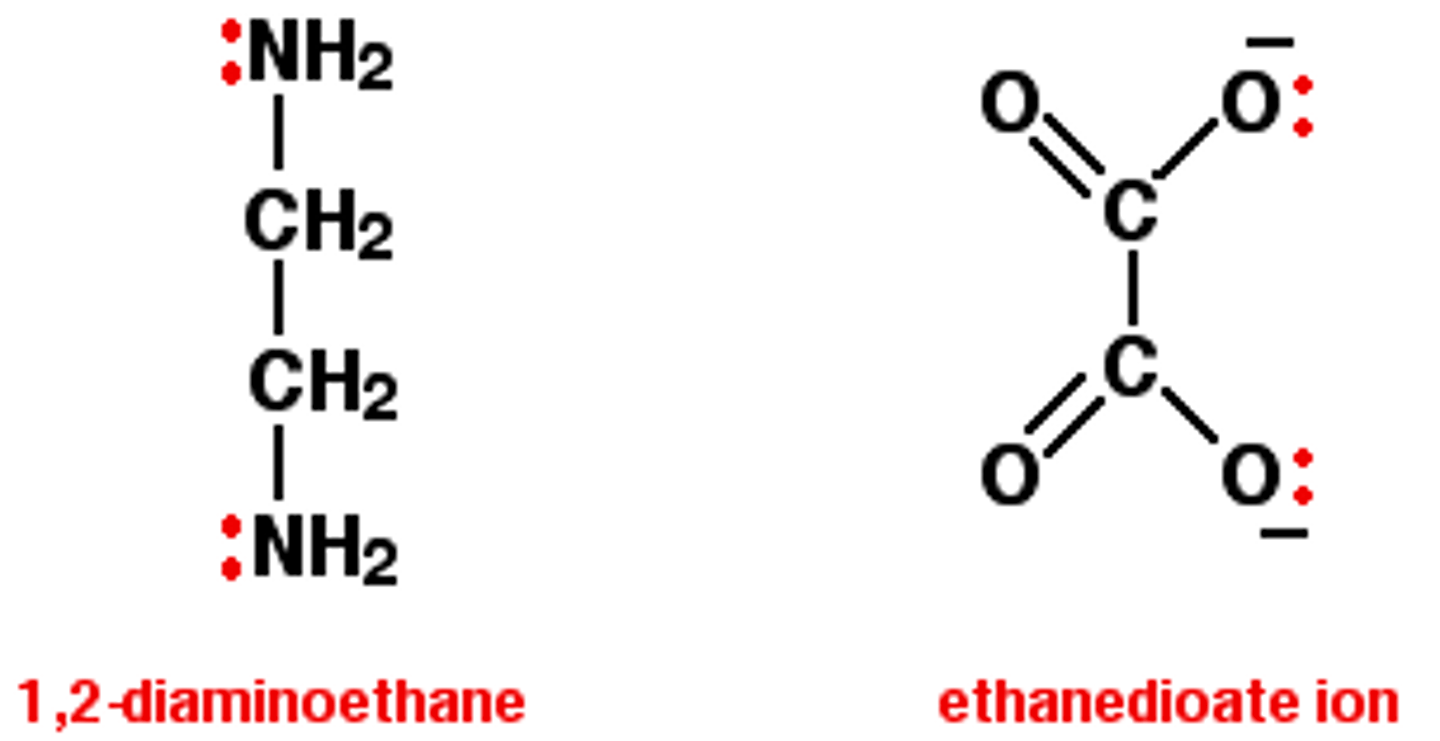
Define bidentate ligands
molecules or ions that have two atoms that each donate an electron pair to the central metal ion to form two coordinate bonds
Give examples of bidentate ligands
Define multidentate ligand
molecules or ions that have more than 2 atoms that can each donate an electron pair to the central metal ion to form more than 2 coordinate bonds
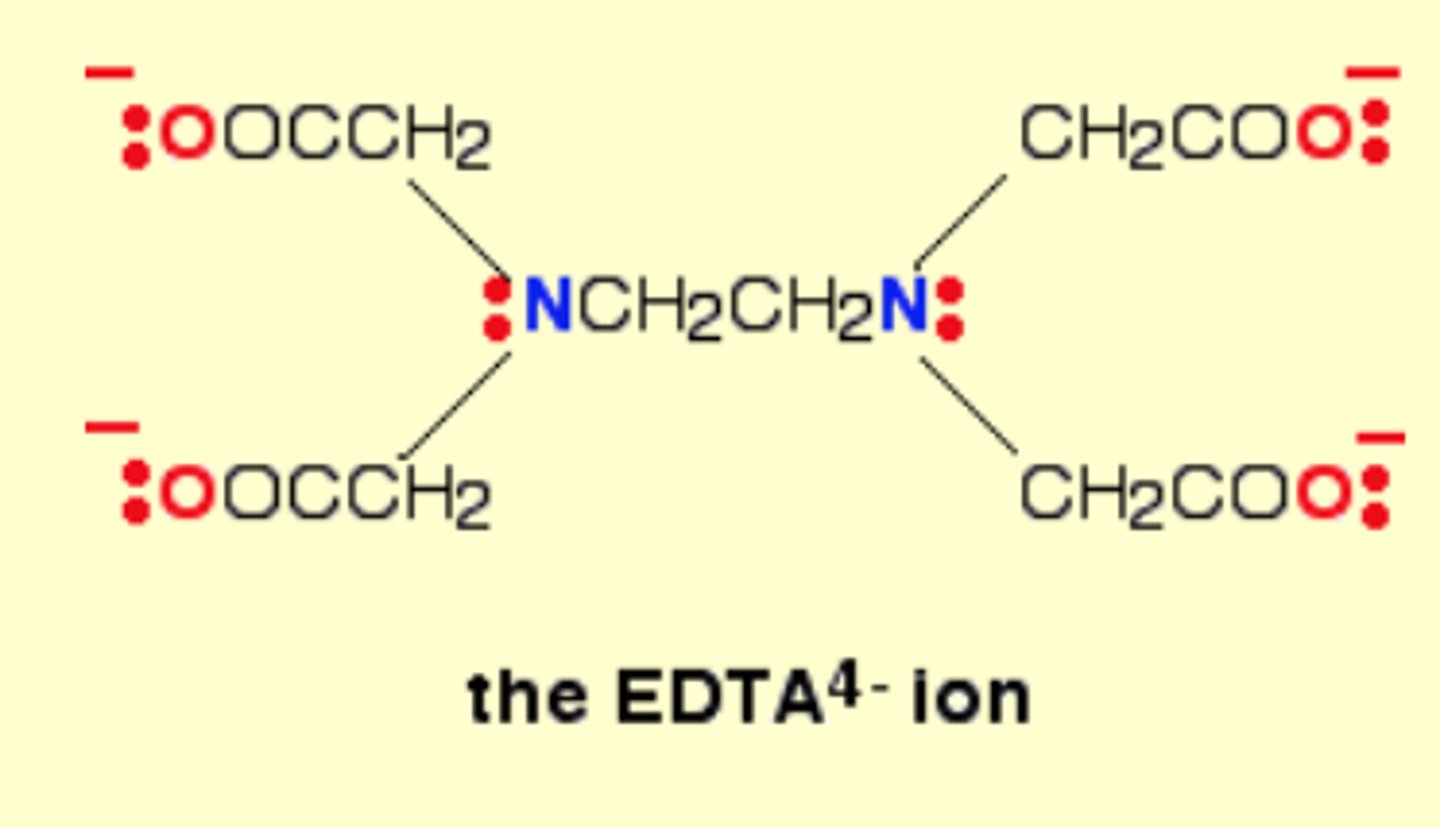
Give an example of a multidentate ligand
EDTA4-
Has 6 atoms that can each donate 1 lone pair to the central metal ion
Can form 6 coordinate bonds with a metal ion
Define coordination number
The number of coordinate bonds to the central metal atom/ ion
(NOT the same as the number of ligands)
What are the 4 main complex ion shapes?
- Octahedral
- Tetrahedral
- Square Planar
- Linear
Compare the ligands Cl- , H2O and NH3
Cl- is larger than H2O and NH3 so would have a different shape
Describe the (expected) shape complexes with H2O or NH3 ligands
Octahedral
Describe the (expected) shape complex with Cl-
Tetrahedral
Describe the reaction of Cobalt Salts with excess ammonia
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 ⇌ [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
Pink ---> Light brown
Coord Num 6 ---> 6
Shape Octahedral ---> Octahedral
Describe the reaction of Copper(II) salts with excess ammonia
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4NH3 ⇌ [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ + 4H2O
Blue ---> Deep/ Dark Blue
Coord Num 6 ---> 6
Shape Octahedral ---> Octahedral
Describe the reaction of Cobalt salts with conc HCl
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ⇌ [CoCl4]2- + 6H2O
Pink ---> Blue
Coord Num 6 ---> 4
Shape Octahedral ---> Tetrahedral
Describe the reaction of Copper Salts with conc HCl
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ---> [CuCl4]2- + 6H2O
Blue ---> Yellow/ Green
Coord Num 6 ---> 4
Shape Octahedral ---> Tetrahedral
Describe Haemoglobin
Haem group with Fe2+ complex
Coord num 4
Electrons originate from lone pair of N for Fe - N bond
Oxygen and water bind interchangeably in a reversible reaction
Carbon monoxide can substitute for oxygen so is considered toxic
What is the chelate effect?
Substitution of monodentate ligand with bidentate or multidentate ligand leads to a more stable complex
Why are transition metals ions coloured?
Due to the incomplete d subshell
How do colours of transition metals arise?
- Transition metals absorb certain frequencies of visible light
- This causes d electrons to be promoted to higher energy level
- The remaining colours of light are transmitted
Why are aqueous copper (II) ions blue in colour?
- Cu(II) ions absorb certain frequencies of visible light
- d electrons are promoted
- Blue light that remains is transmitted
Give the first equation for energy gap
∆E = hv
∆E is energy gap in joules
h is Plancks constant = 6.63 x10^-34 Js
v is frequency of light absorbed in Hz
Give the equation for v (frequency of light absorbed)
v = c / λ
v is frequency of light absorbed in Hz
c is speed of light = 3 x10^8 ms^-1
λ is wavelength of light in m (usually given as nm so convert)
Give the overall equation for Energy gap
∆E = h c / λ
What factors affect colour of transition metal complexes?
- Change in coordination number
- Change in ligand
- Change in oxidation state
No question on colorimetry
Define stereoisomers
Same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
What stereoisomers can form from square planar complexes with 2 different ligands
Cis and Trans
Cis is next to each other
Trans is opposite
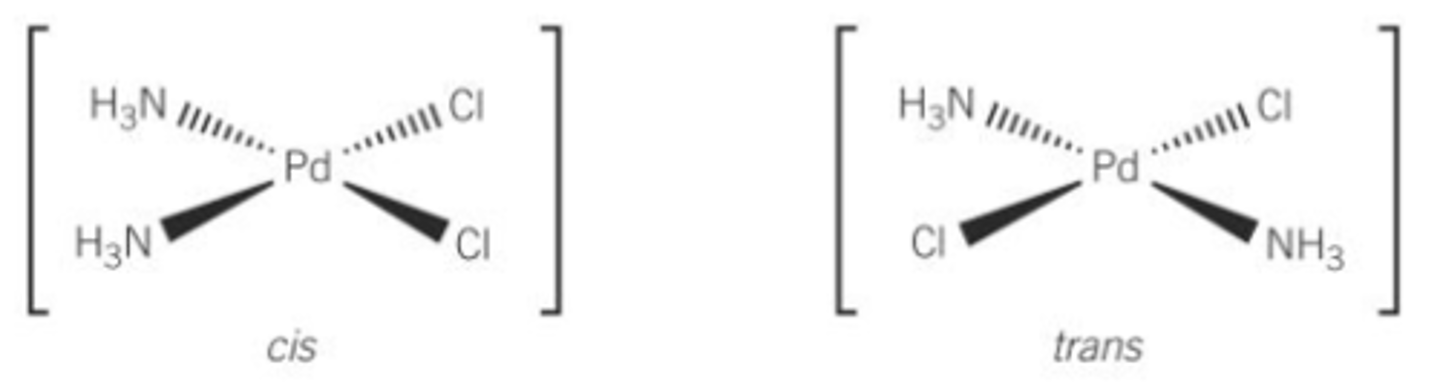
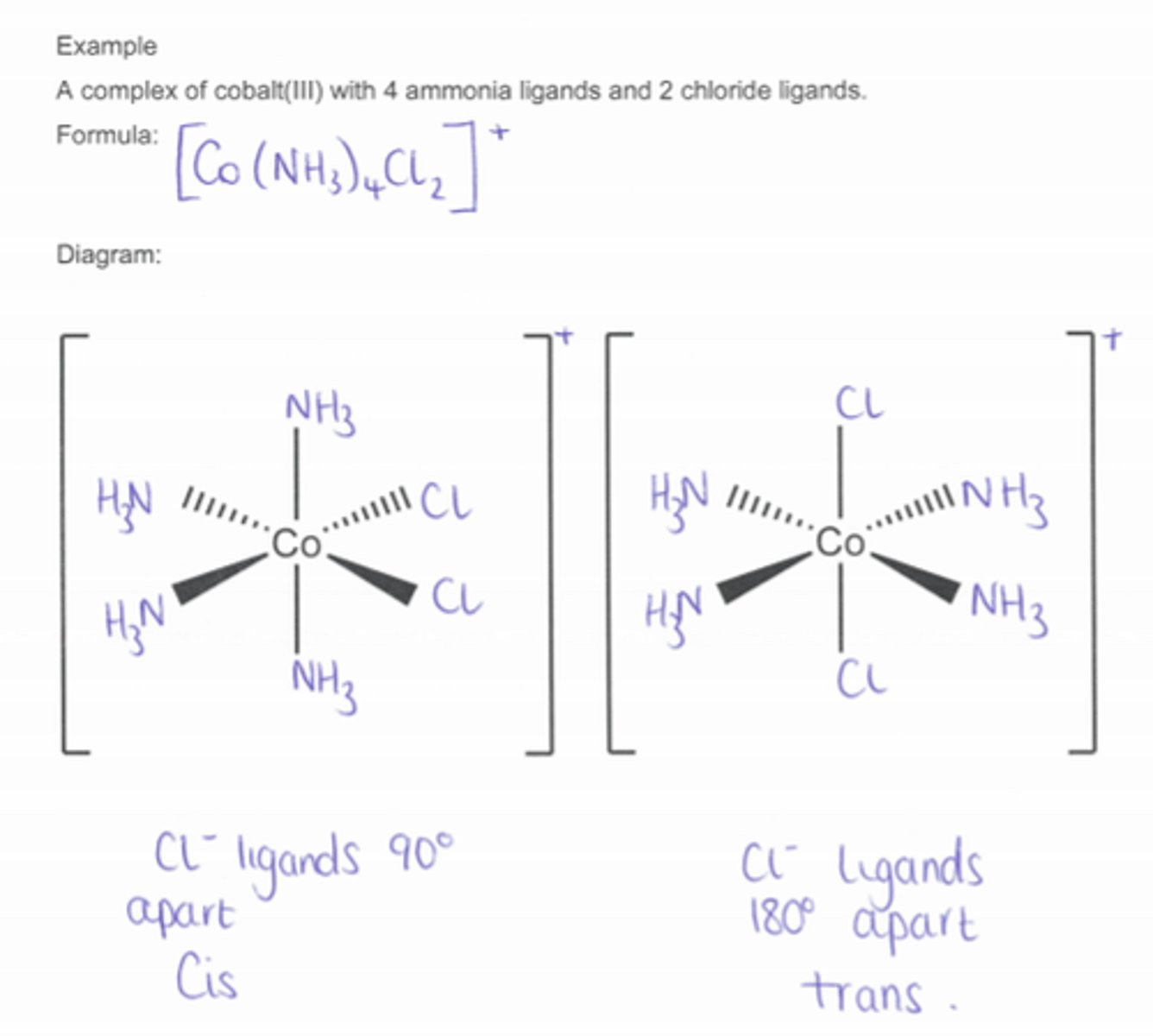
Describe stereoisomerism of octahedral complexes
2 different ligands 2 of one and 4 of the other
Describe optical isomers
non superimposable mirror images
Bidentate ligand optical isomers
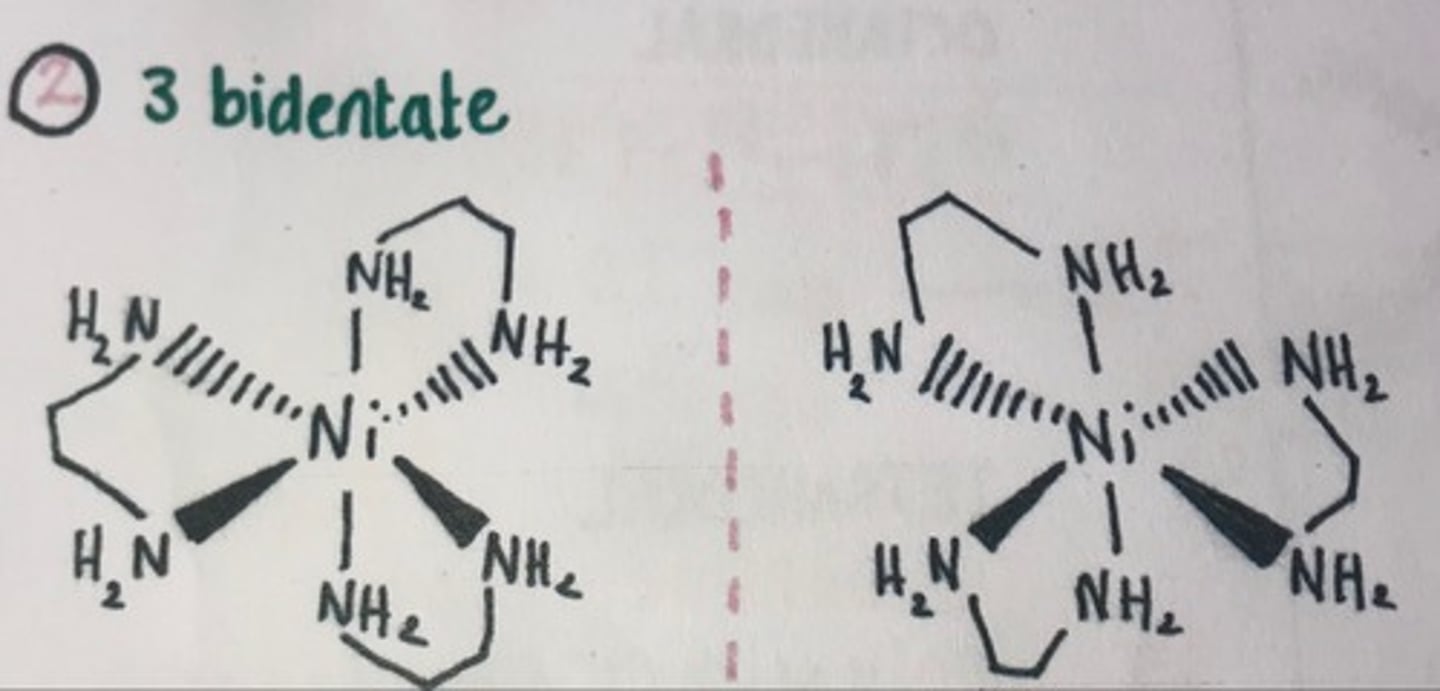
Describe the isomerism of octahedral complexes with 2 monodentate and 2 bidentate ligands
Show Cis- Trans and Optical isomerism
Describe catalysts
- Speed up rate of reaction without being used up
- Provide an alternate reaction pathway of lower activation energy - leads to more frequent successful collisions
What is the effect of catalysts on ∆H?
No effect
Only reduces Ea
Why can transition metals act as catalysts?
Due to variable oxidation states
What are the 2 types of catalysts transition metals can act as?
- Heterogeneous
or
- Homogeneous
Define Heterogeneous catalysis
a catalyst in a different state/phase to the reactants
Why is a thin layer of metal used on a support medium for the catalyst?
- Increases SA
- Reduces costs
Give the steps involved in heterogeneous catalysis
- Adsorption (stick)
Reactant molecules adsorb onto the transition metal surface
- Chemical reaction
Bonds weaken/break - reaction takes place - new bonds form
- Desorption
Products desorb (unstick/vacate) the catalyst surface
Describe catalyst poisoning
Heterogeneous catalysts work when the reactants adsorb to the catalyst surface
Impurities in the reactants can bind to the active sites to block the reactants
We say the catalyst has been poisoned
This reduces efficiency as the surface area is reduced as active sites are blocked
The catalyst may need replacing or regenerating - poisoning can be minimised by purifying the reactants
Give the equations for the contact process
Vanadium oxide is the heterogenous catalyst
SO2 + V2O5 ---> SO3 + V2O4
V2O4 + 0.5O2 ---> V2O5
Overall: SO2 + 0.5O2 ---> SO3
Define Homogenous catalysis
Catalyst in the same state/phase as the reactants
Give the reaction between S2O8 2-(aq) and I-(aq)
without the catalyst
S2O8 2- + 2I- ---> 2SO4 2- + I2
Reaction is slow as both reactants are negative so repel
Give the reaction between S2O8 2-(aq) and I-(aq)
with the catalyst
2Fe2+ + S2O8 2- ---> 2SO4 2- + 2Fe3+
2Fe3+ + 2I- ---> I2 + 2Fe2+
Steps can occur in either order with either Fe2+ or Fe3+ being the catalyst
Define autocatalysis
the catalyst for the reaction is a reaction product
Give the reaction between MnO4- and C2O4 2-
[Manganate(VII) ions and ethanedioate ions]
2MnO4- + 5C2O4 2- + 16H+ ---> 2Mn 2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
Both reactants are negative so reaction is initially very slow
For the reaction of MnO4- and C2O4 2-
Describe the rate of reaction of time
Initially very slow as it is uncatalysed
As Mn2+ is being formed the rate increases rapidly - catalysed
Rate decreases at the end of the reaction as reactant conc decreases
Give the mechanism for the reaction of MnO4- and C2O4 2- with the catalyst
2MnO4- + 5C2O4 2- + 16H+ ---> 2Mn 2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
4Mn 2+ + MnO4- + 8H+ ---> 5Mn 3+ + 4H2O
2Mn 3+ + C2O4 2- ---> 2Mn 2+ + 2CO2
Mn3+ is the intermediate
Give the oxidation states, colour and ions for all the Vanadium ions
VO2 + +5 Yellow
VO²+ +4 Blue
V³+ +3 Green
V²+ +2 Violet
Describe Tollens reagent
[Ag(NH3)2]+
Aldehyde warmed with tollens reagent gives silver mirror
Aldehyde oxidised to carboxylic acid
Silver ions in tollens are reduced to solid silver
Equation for reduction of Tollens reagent
[Ag(NH3)2]+ + e- ---> Ag(s) + 2NH3
Describe redox potentials
Measure of how easily an ion or atom is to reduce to a lower oxidation state
More positive redox potential means more likely to be reduced so less stable ion
Redox potential is same as standard electrode potential under standard conditions in aqueous solution
Which complex is stronger oxidising agent and why?
[Co(H2O)6]2+
[Co(H2O)6]3+
3+ is smaller and more highly charged so gains electrons more readily
Give the half equation for Manganate ions
MnO4- + 8H+ 5e- ---> Mn2+ + 4H2O
Give the half equation ethanedioate ions?
C2O4 2- ---> 2CO2 + 2e-
How can conc of MnO4- ions be measured in its reaction with ethanedioate ions?
MnO4- ions are pink/purple colour