Biology: Cell Energy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
ATP
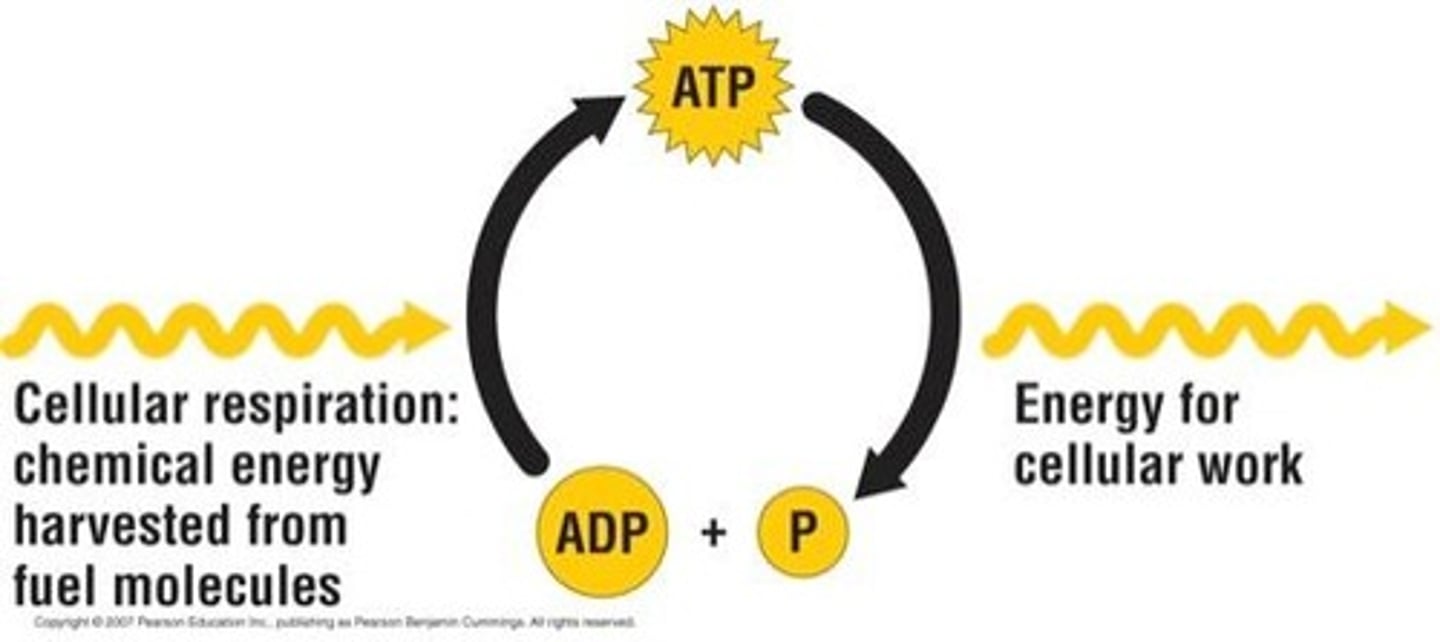
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work, 3 phosphates
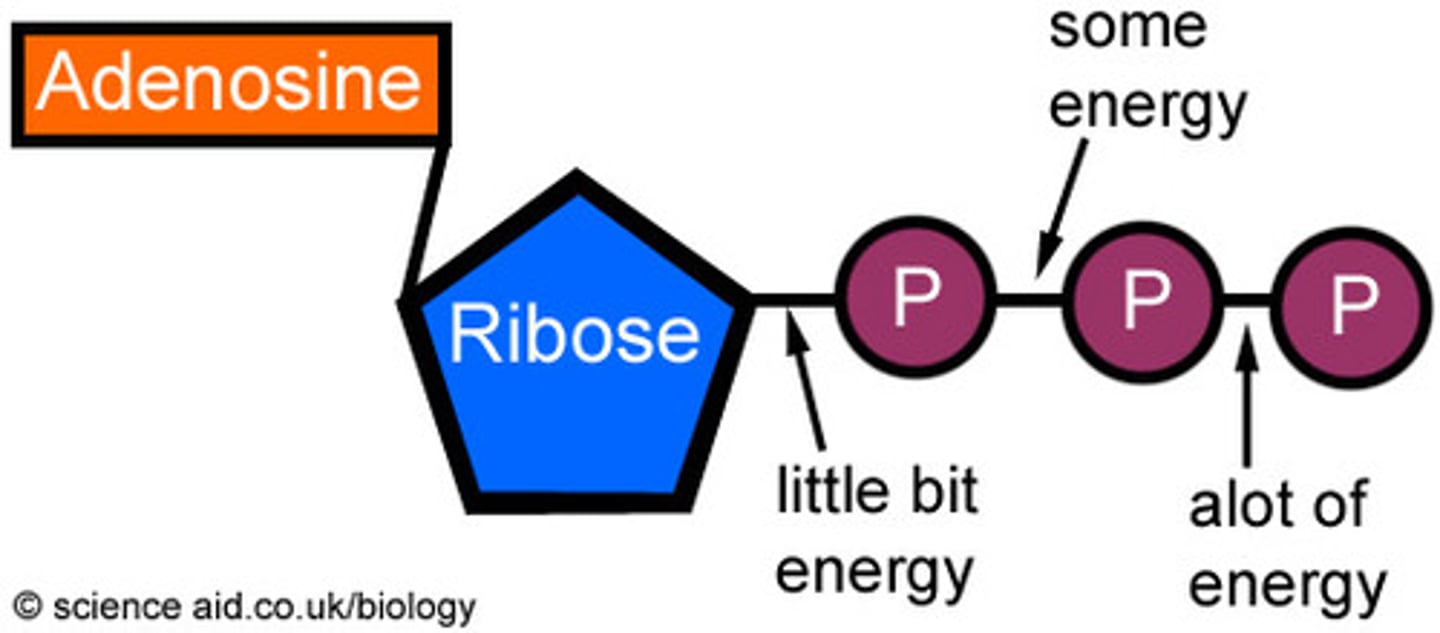
ADP
a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate group, 2 phosphates
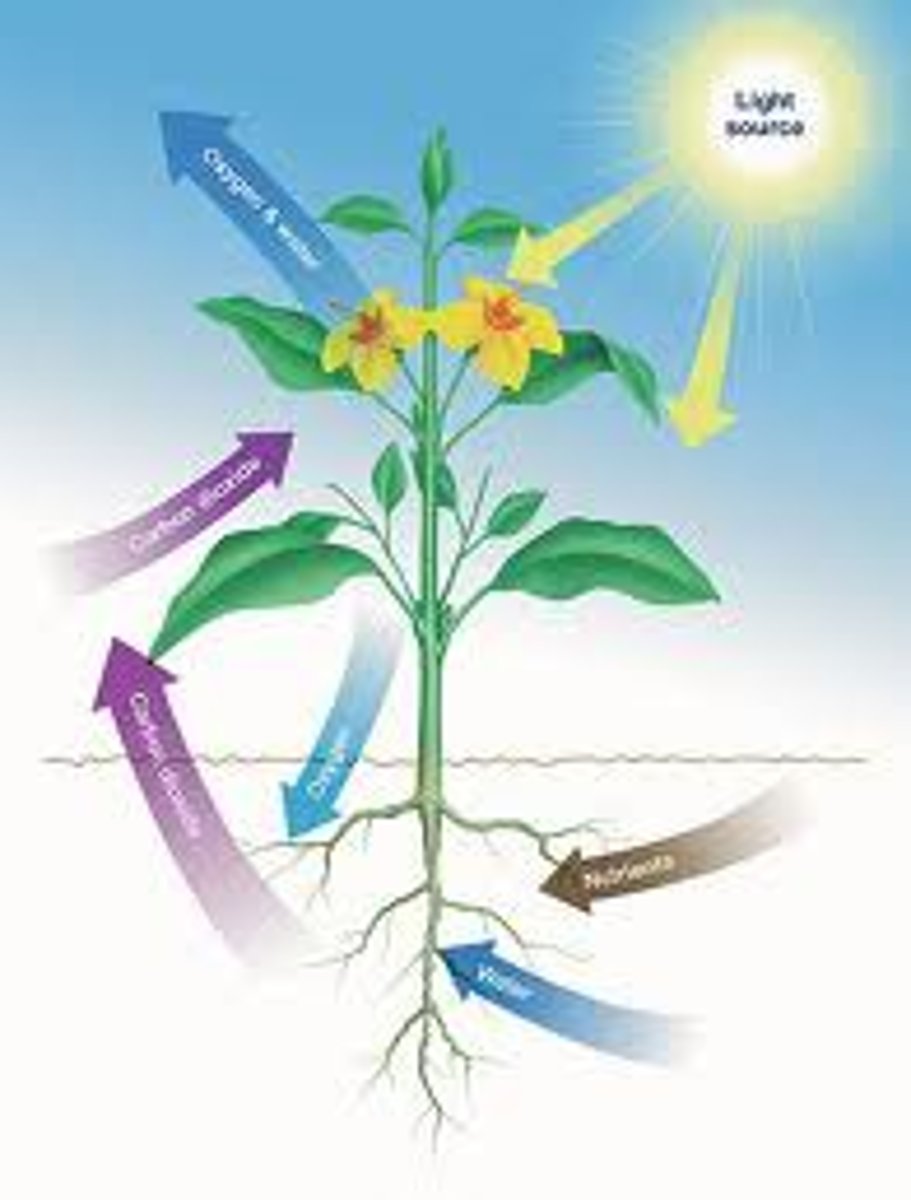
autotroph
an organism that collects energy from sunlight or inorganic substances to produce food
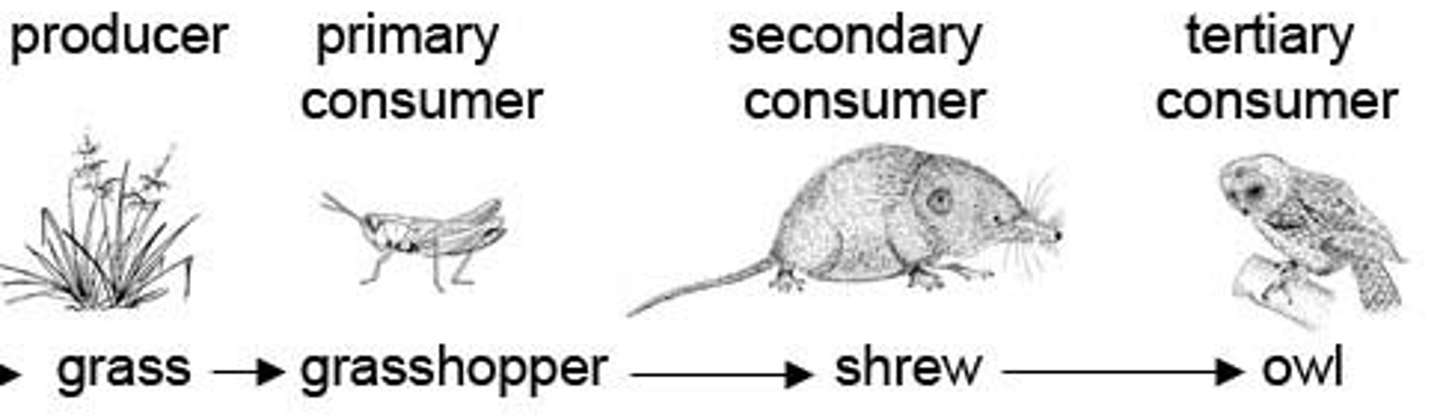
producer
an organism that makes its own food, autotroph

heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer

consumer
organism that relies on other organisms for its energy and food supply; also called a heterotroph
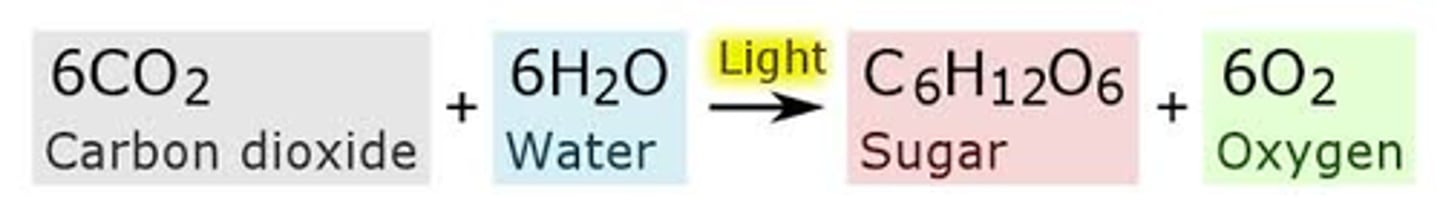
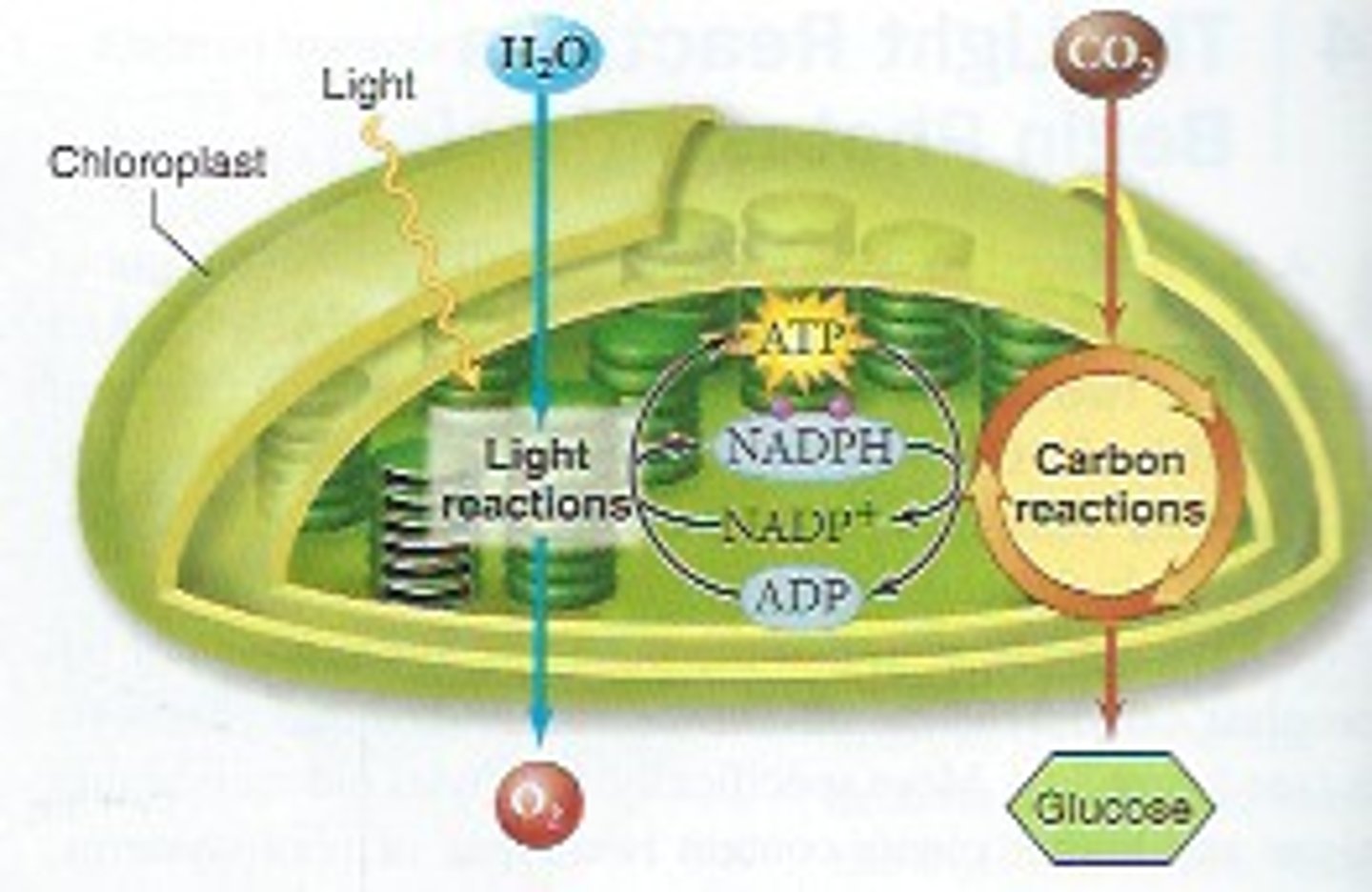
photosynthesis
process by which plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars (glucose)
chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria, necessary for photosynthesis (absorbs light energy, reflects green light)

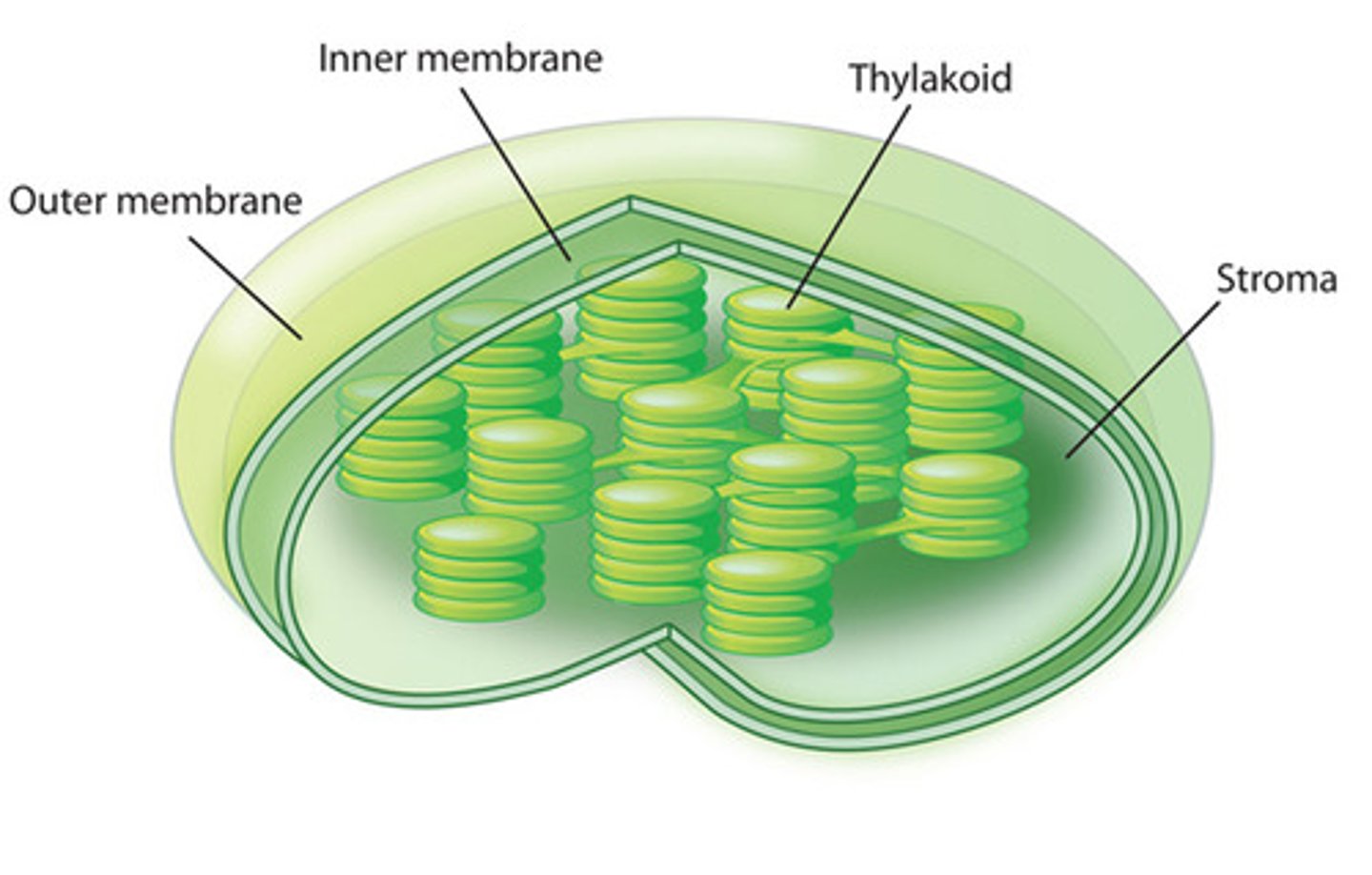
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy (sight of light reactions)
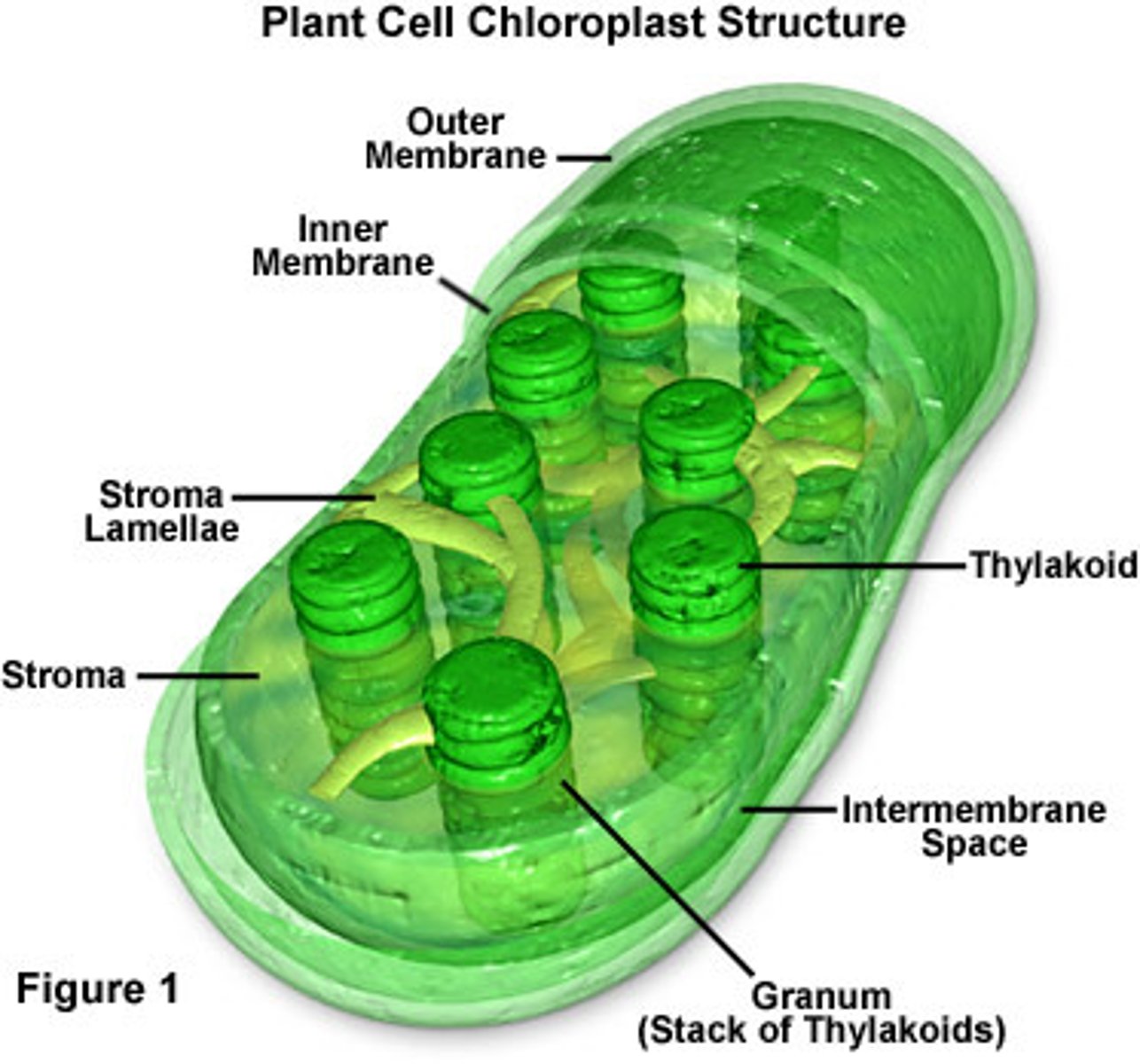
grana
a stack of thylakoids within a chloroplast (light dependent reactions occur in grana, a stack of thylakoids)
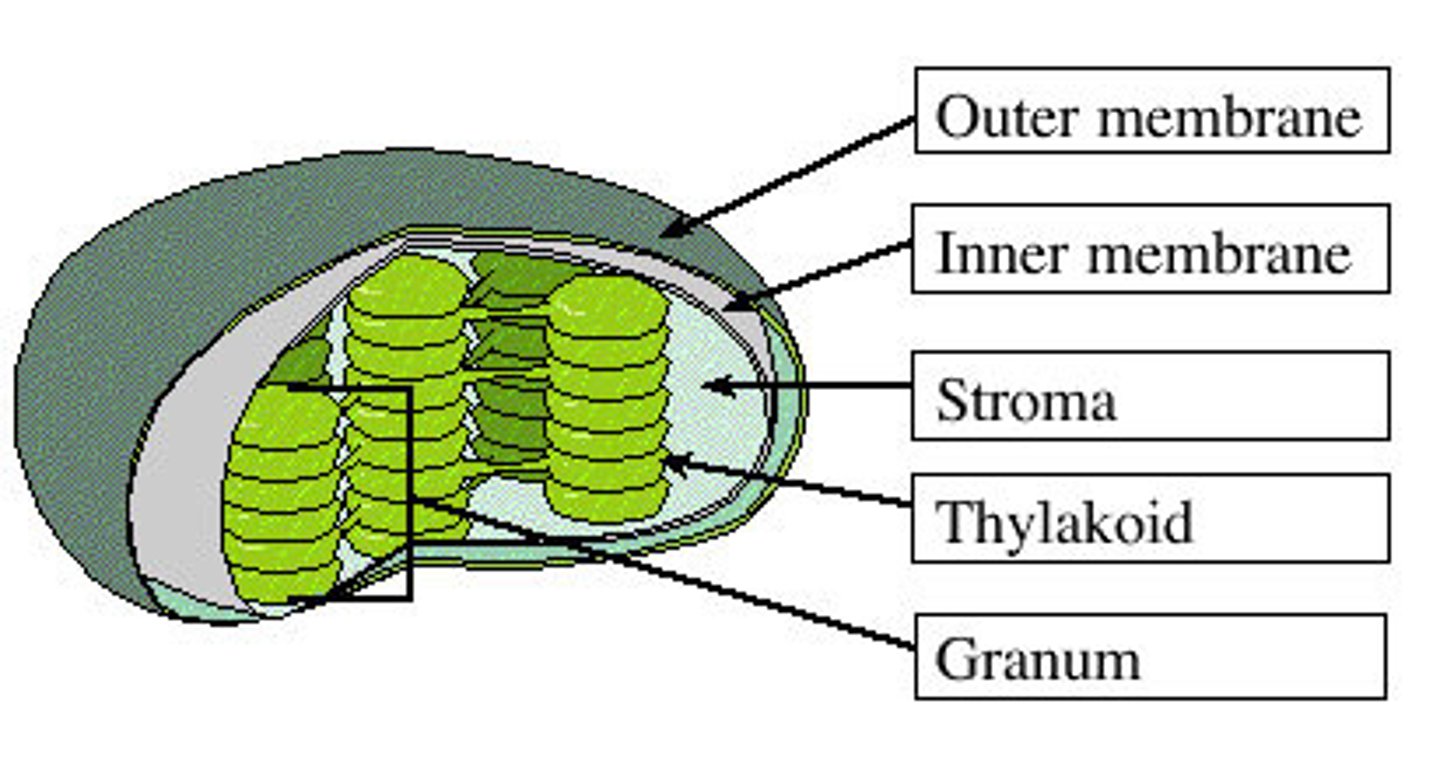
stroma
In plants, the liquid solution that surrounds the thylakoids in a chloroplast. (light independent reactions/Calvin cycle happens here)
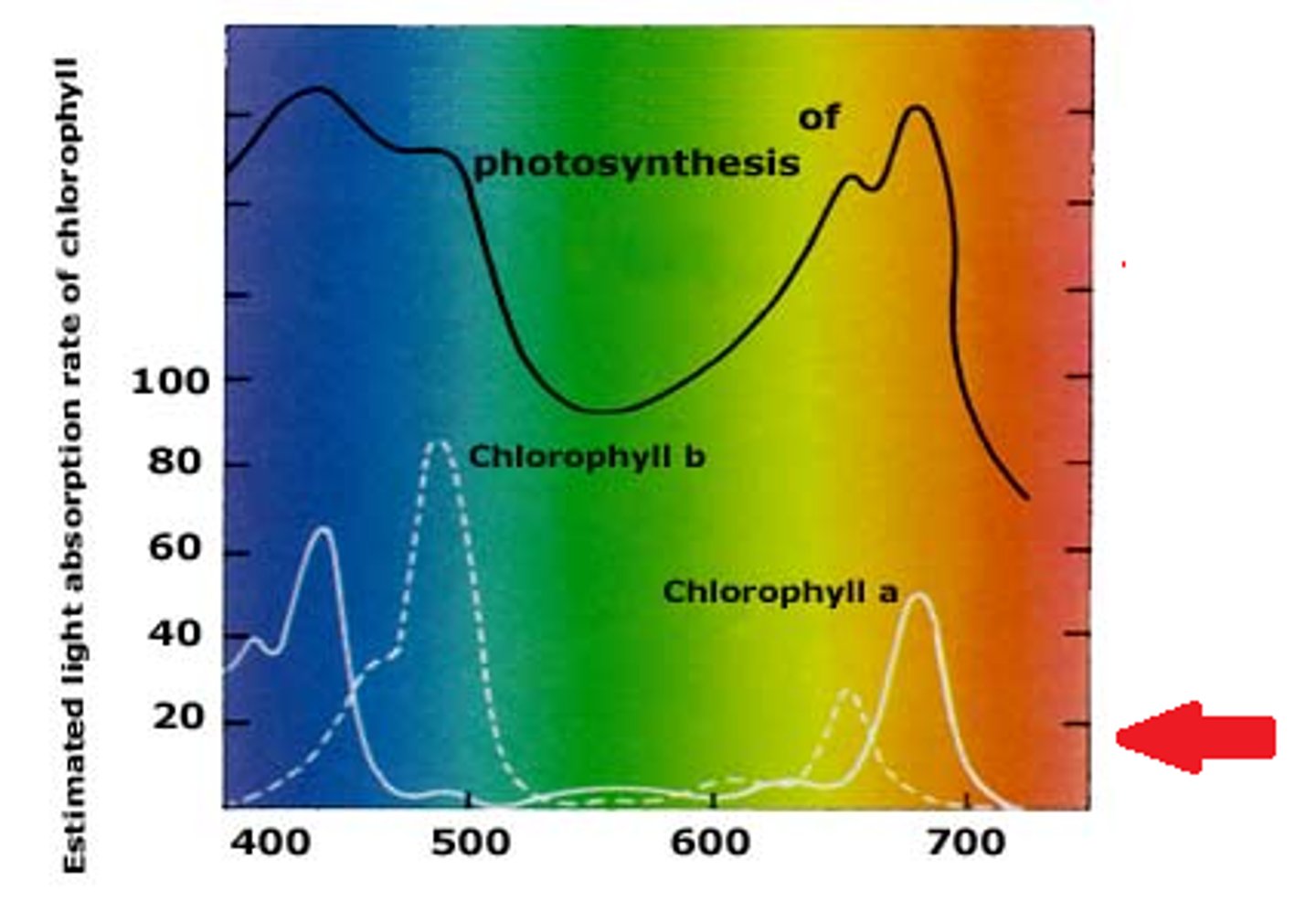
chlorophyll absorption spectrum
a graph showing the amount of light absorbed by Chlorophyll pigments at various wavelengths
reactants
the elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction (inputs: left of arrow)
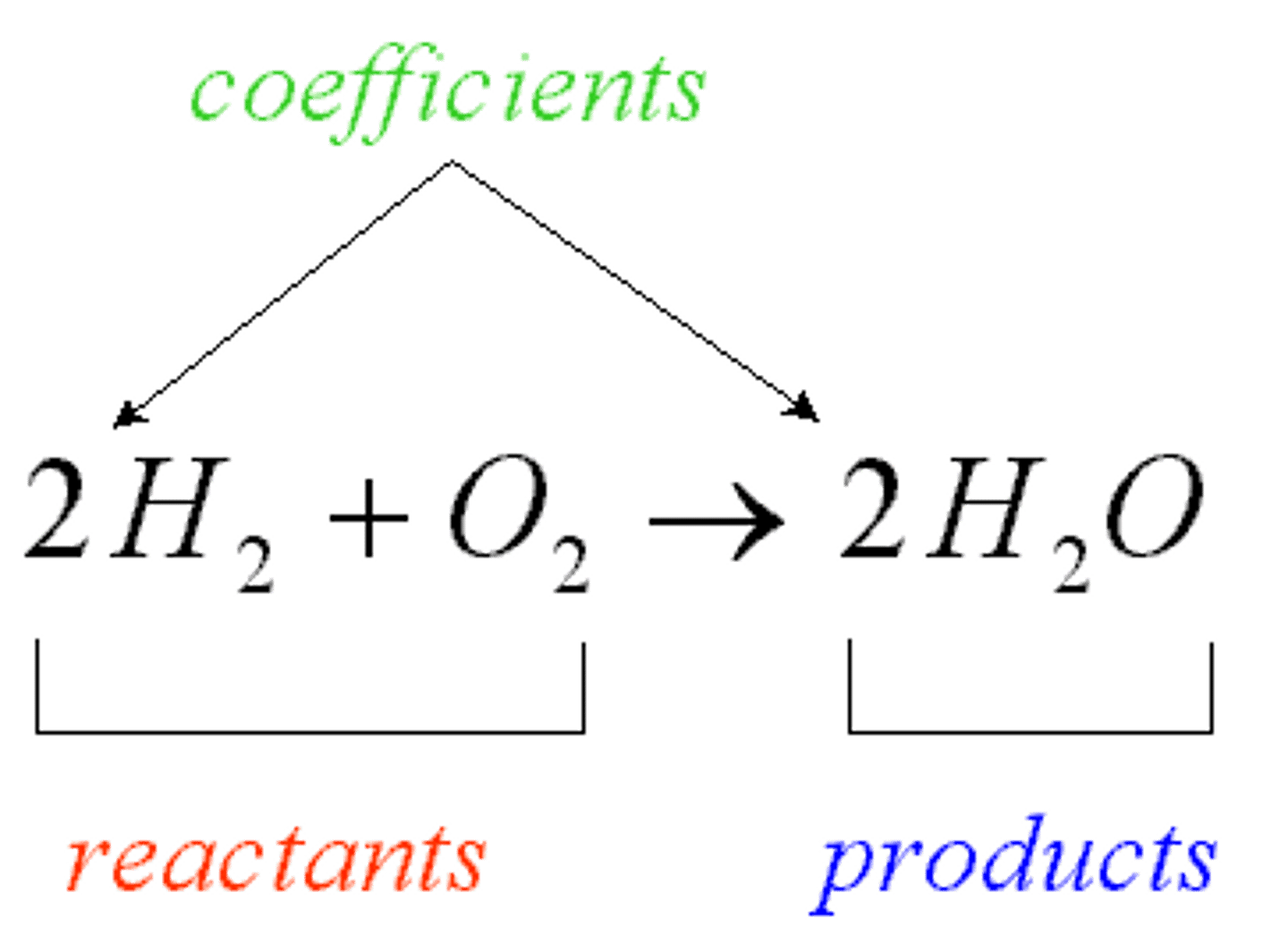
products
the elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction (out puts: right of arrow)
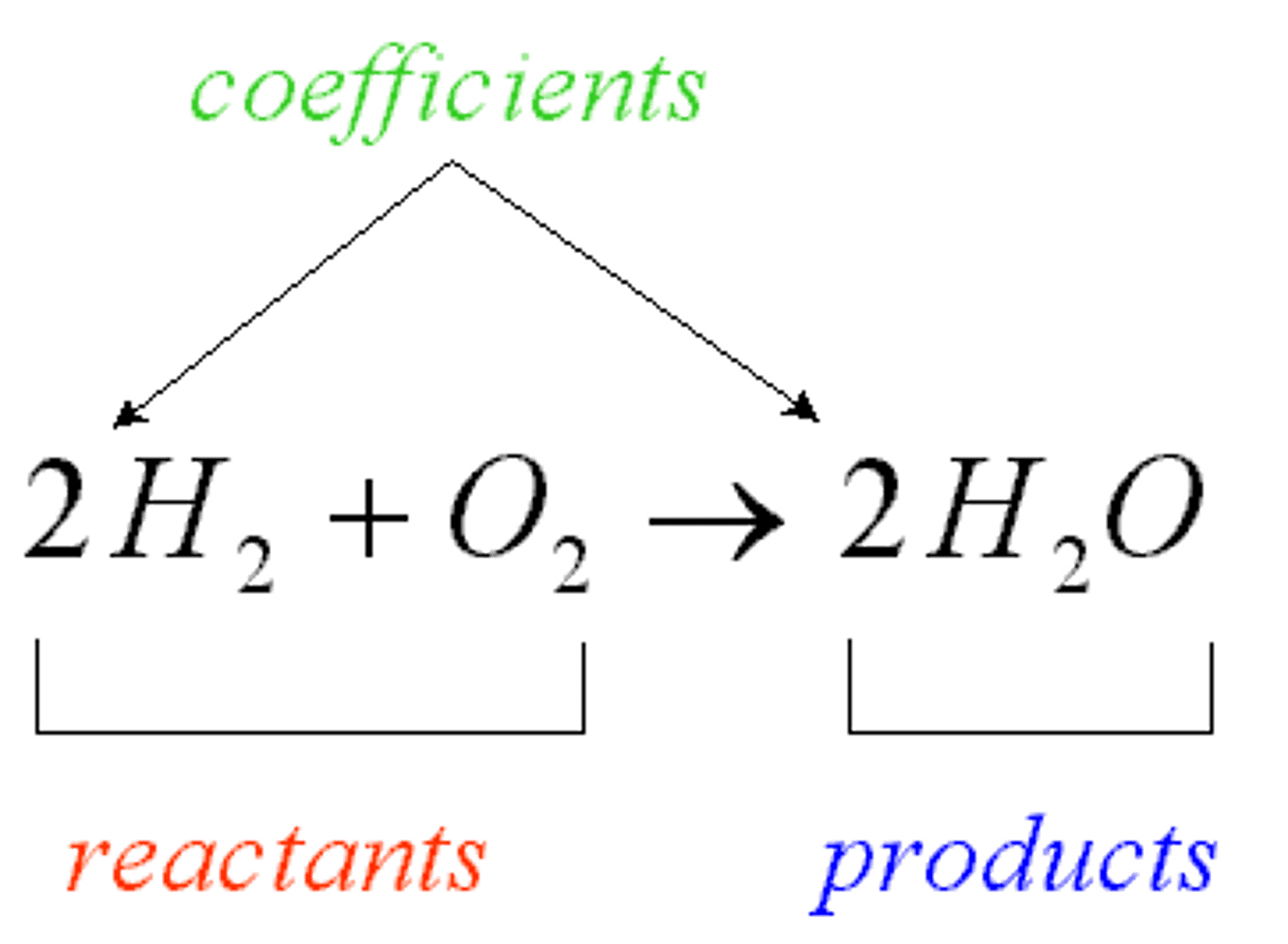
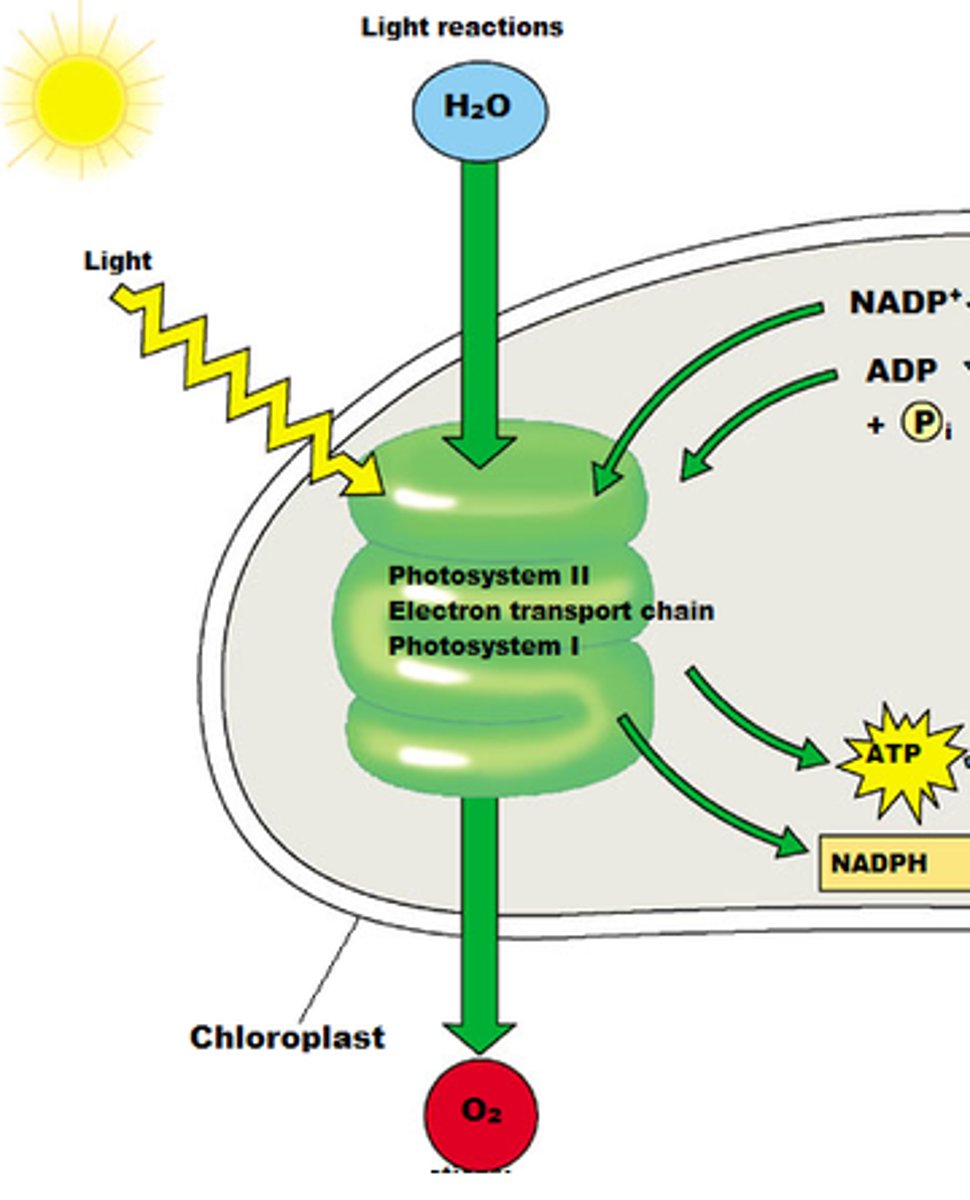
light dependent reactions
set of reactions in photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH (energy source for Calvin Cycle/light independent reactions)
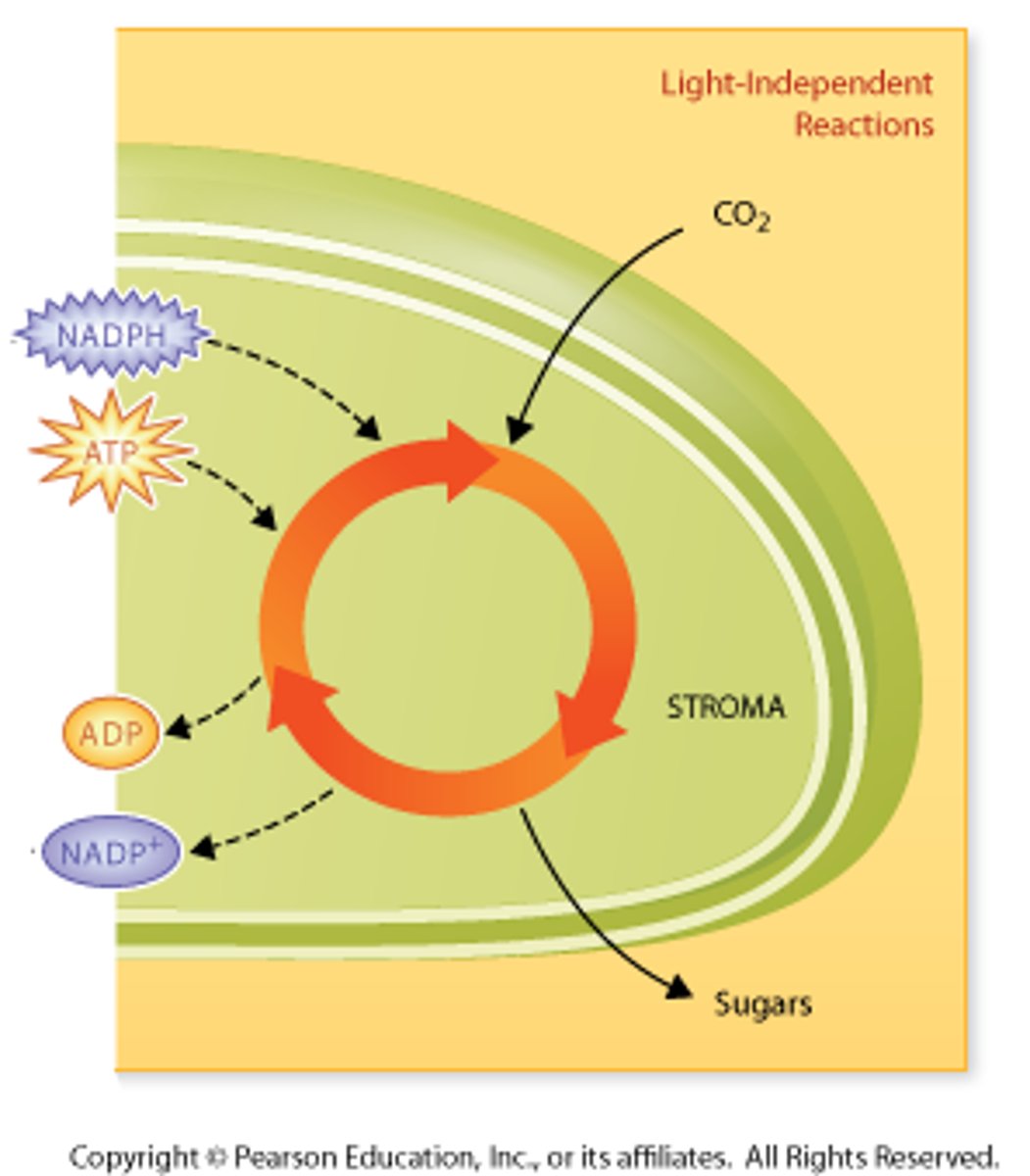
light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle or dark reactions)
second stage of photosynthesis; uses ATP and NADPH from light reactions to assemble sugars (glucose) from water and CO2, Calvin Cycle
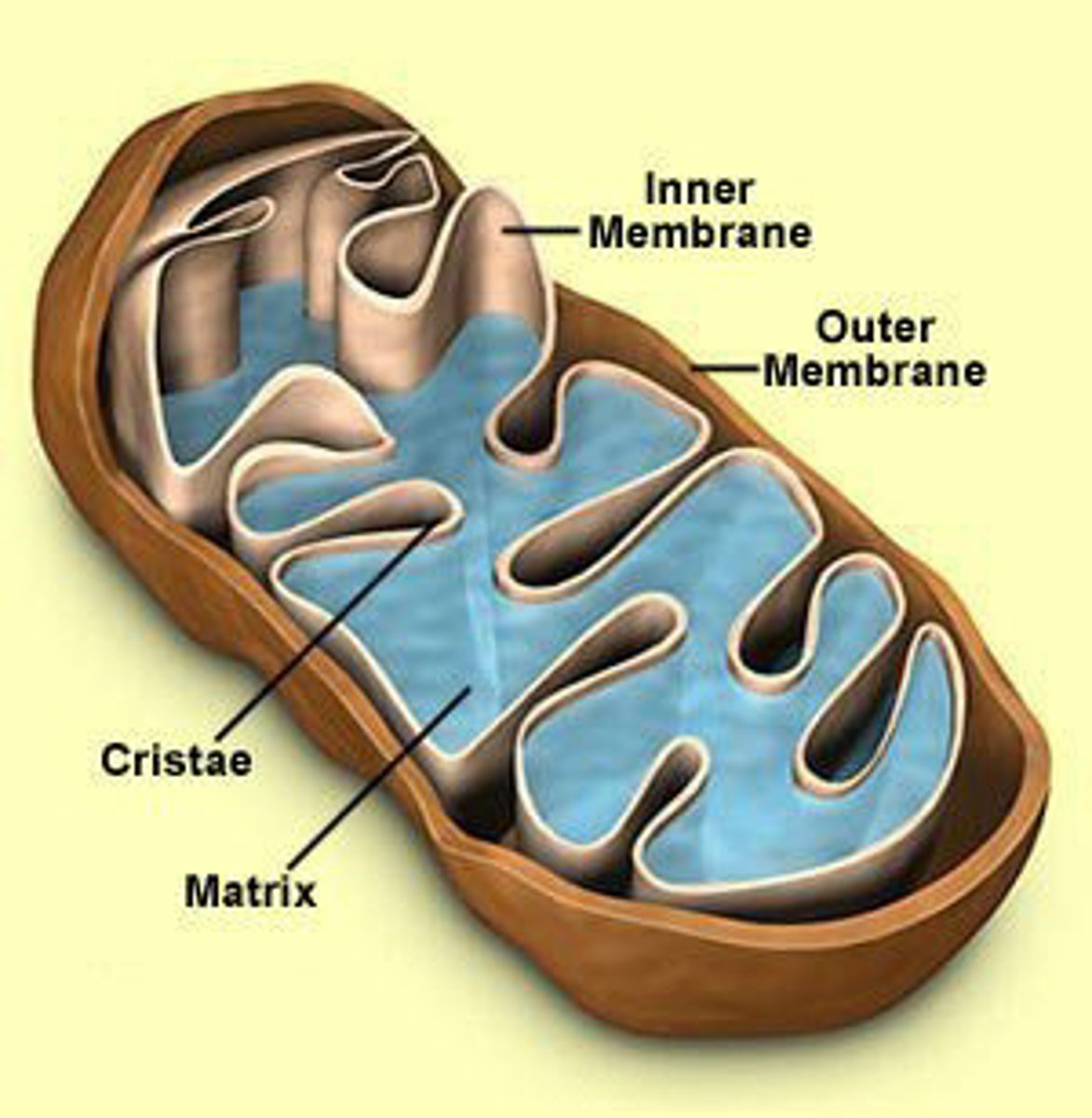
cellular respiration
process that releases energy (36-38 ATP) from glucose in the presence of oxygen, happens in mitochondria of eukaryotes and cytoplasm of prokaryotes

mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, (found in plants and animals) organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production during cellular respiration, Krebs Cycle and ETC happen here!
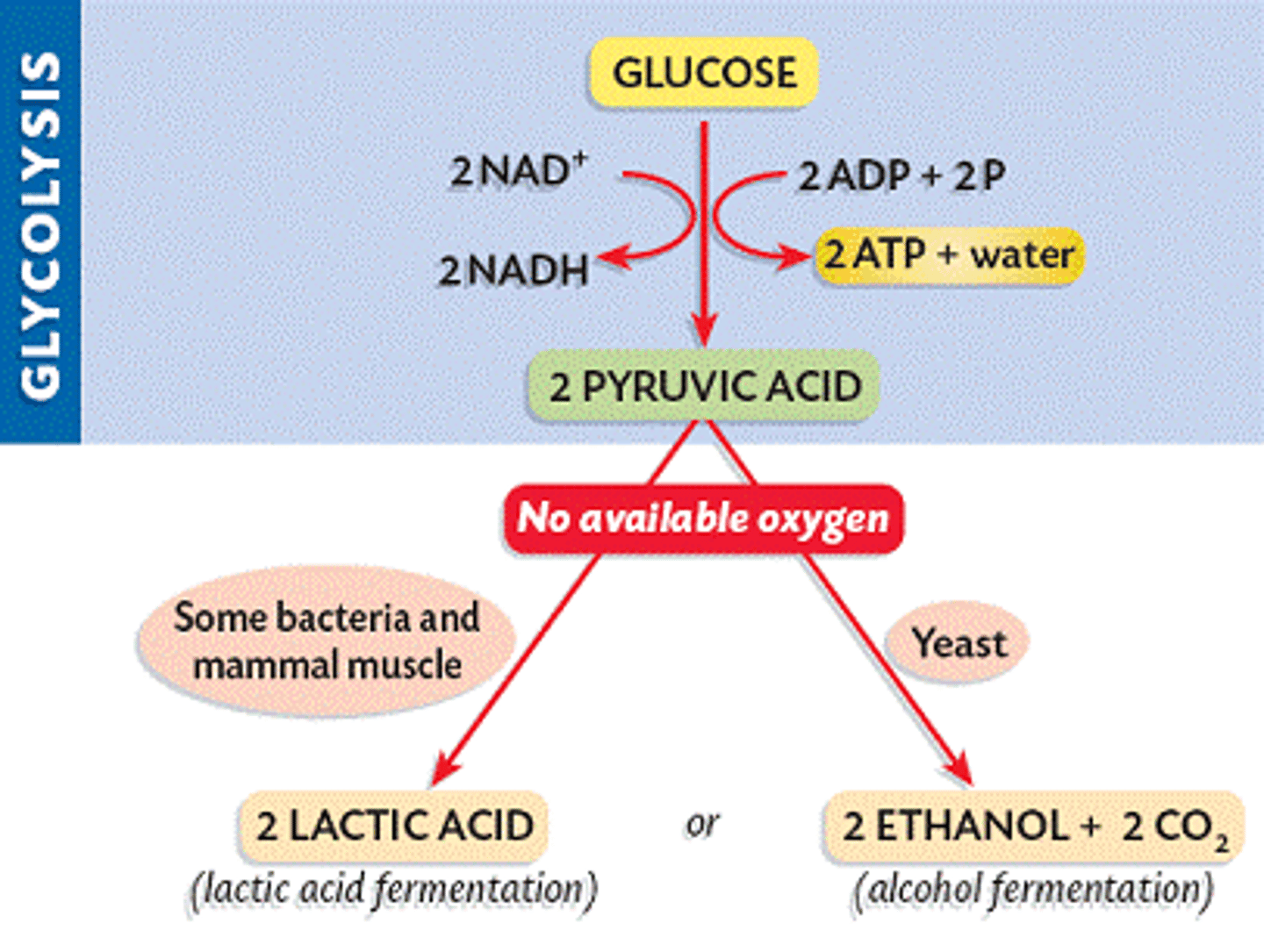
lactic acid fermentation
anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product and 2 ATPs (occurs when demand for oxygen greater than supply)
alcoholic fermentation
anaerobic process used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce CO2 and ethyl alcohol and 2 ATP molecules (also used when little or no oxygen present)
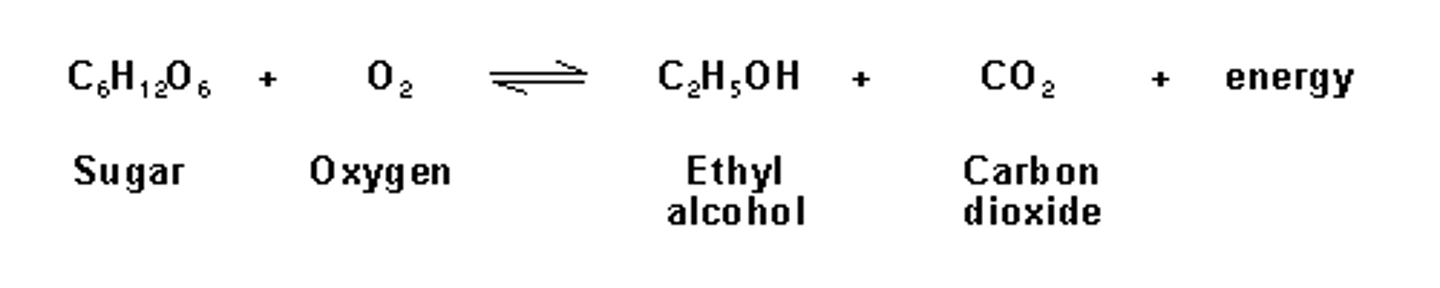
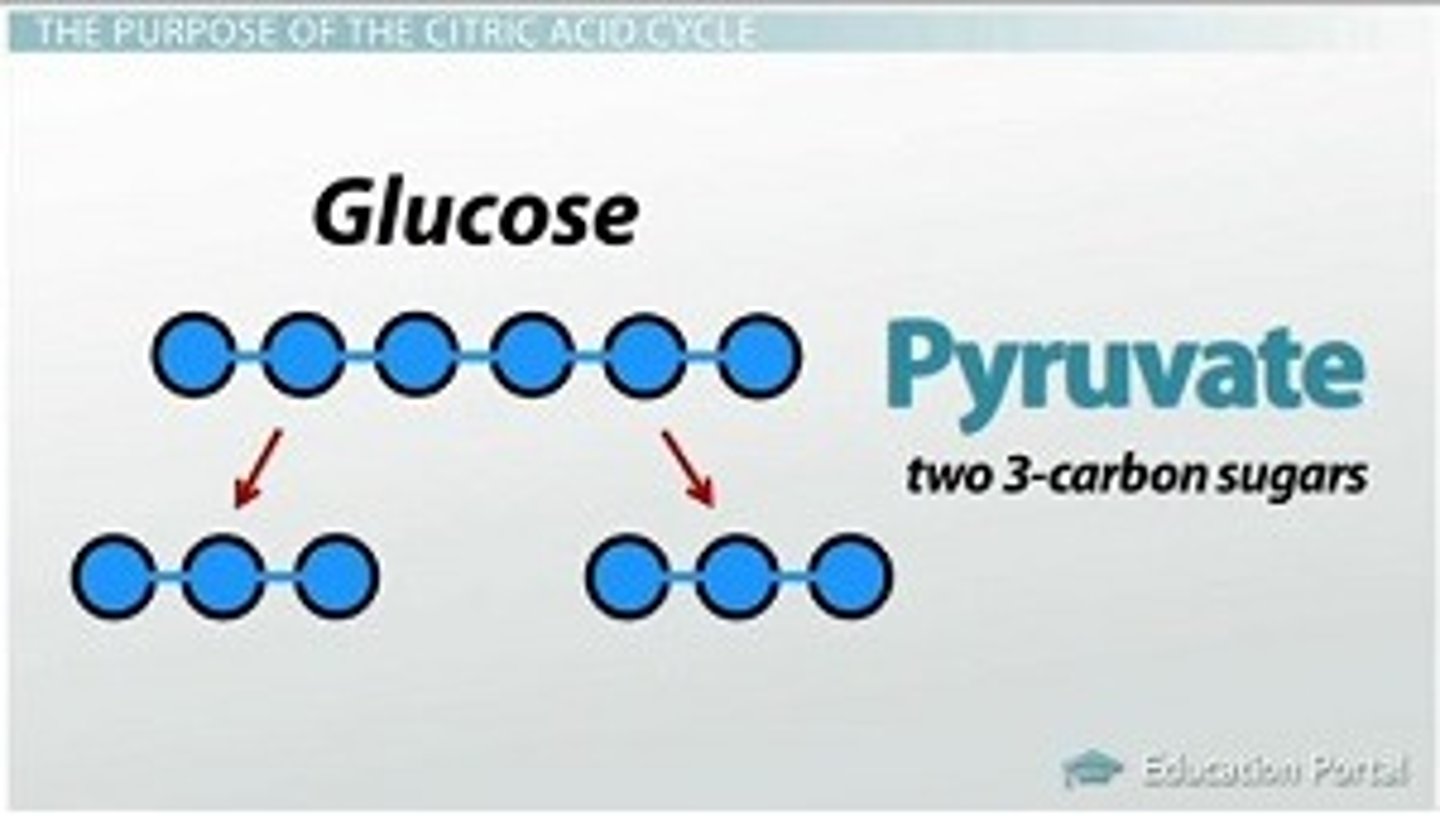
Glycolysis
1st step of aerobic AND anaerobic respiration (fermentation) , occurs in cytoplasm; splits one glucose into 2 pyruvic acids, makes 2 ATP and NADH
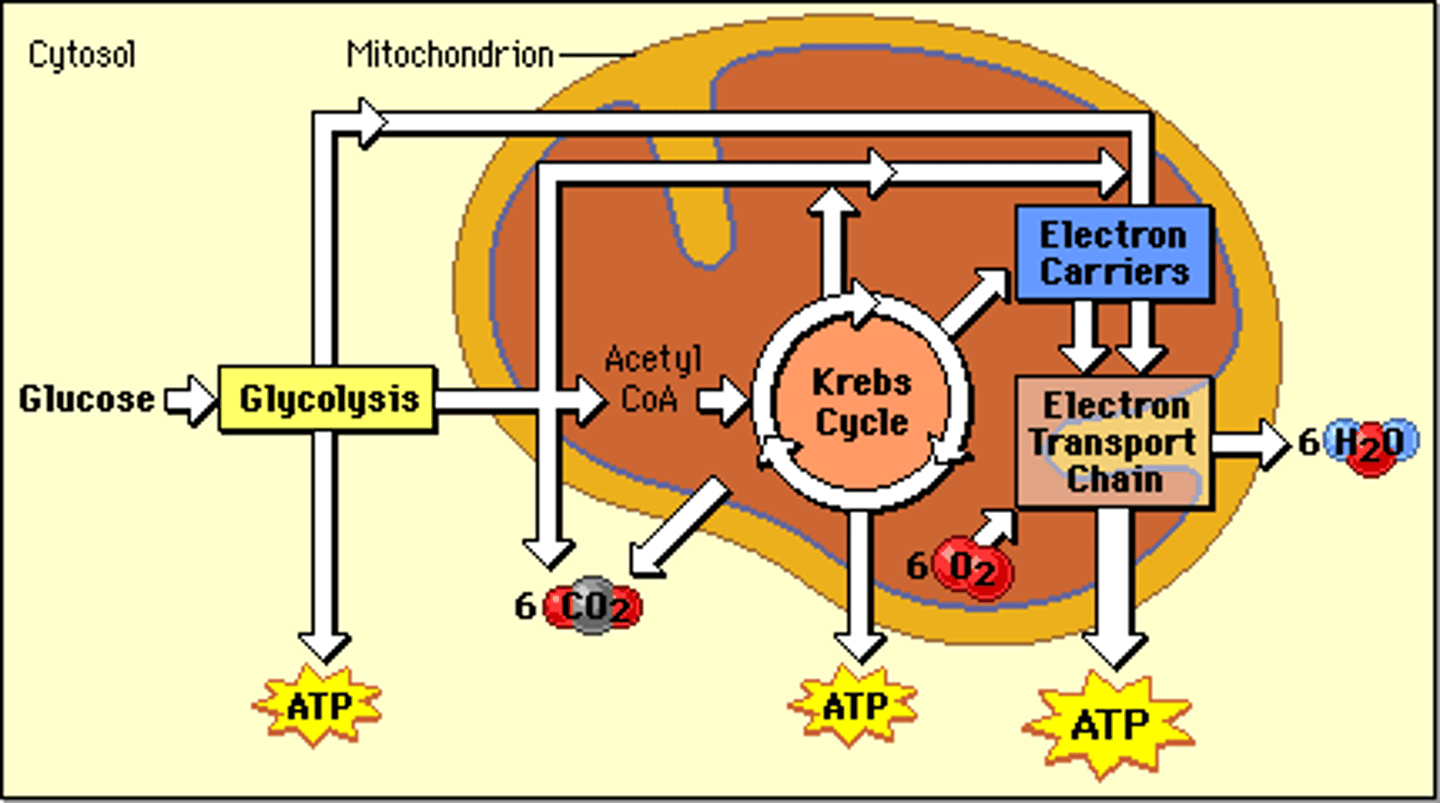
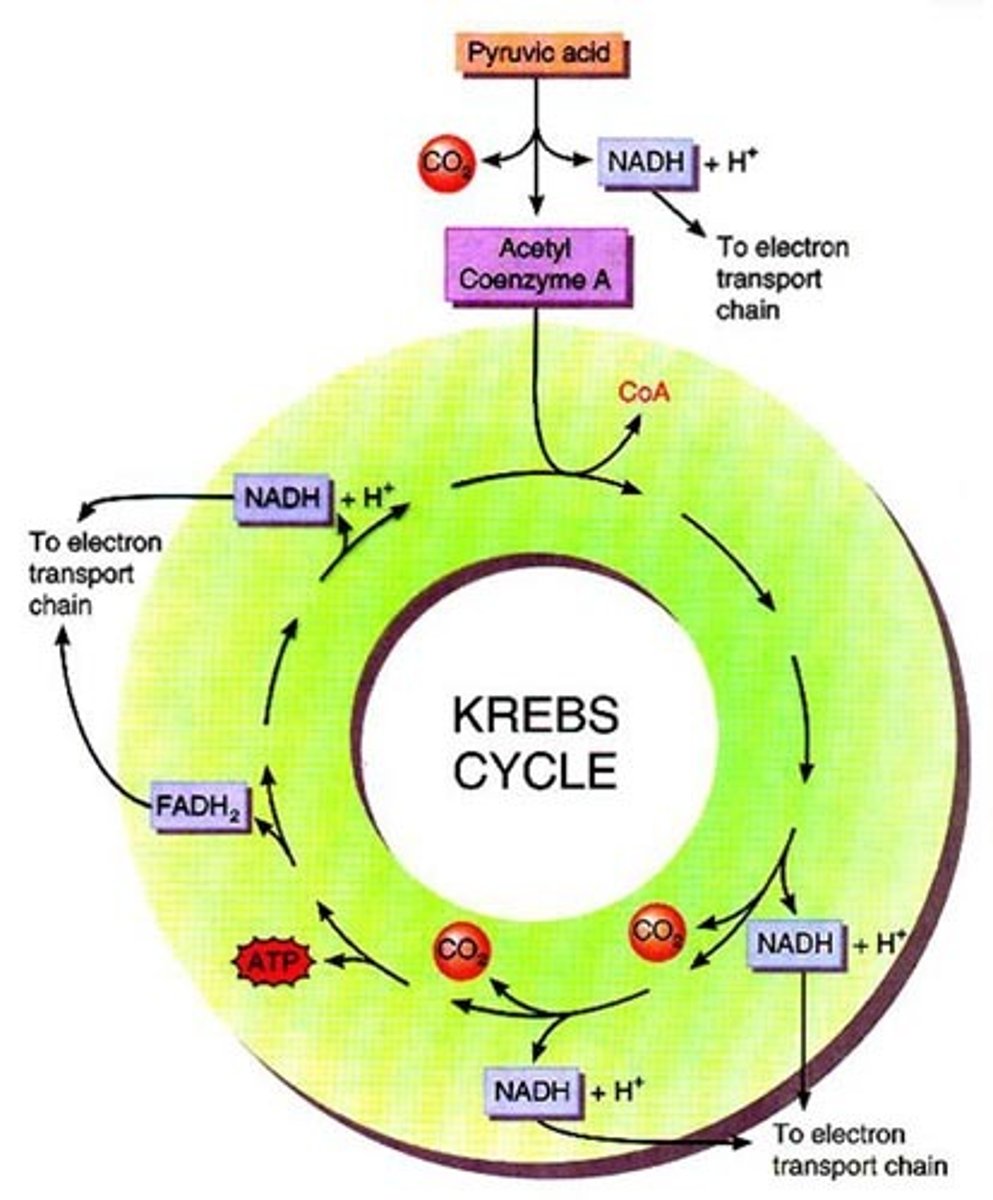
Kreb's cycle (citric acid cycle)
2nd step of aerobic respiration, occurs in mitochondria, acts on the pyruvates produced by glycolysis ( makes 2 ATP per glucose molecule)
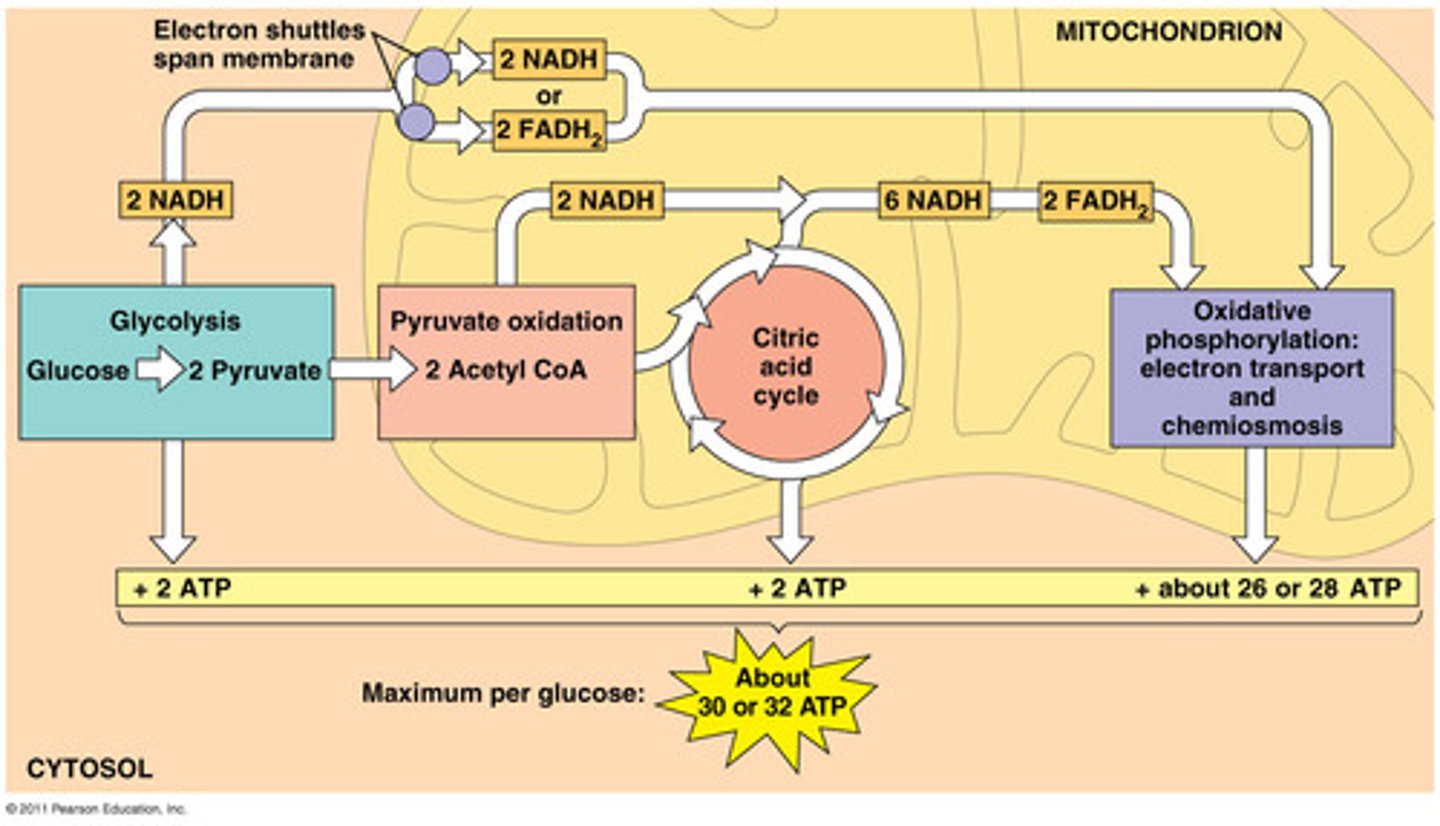
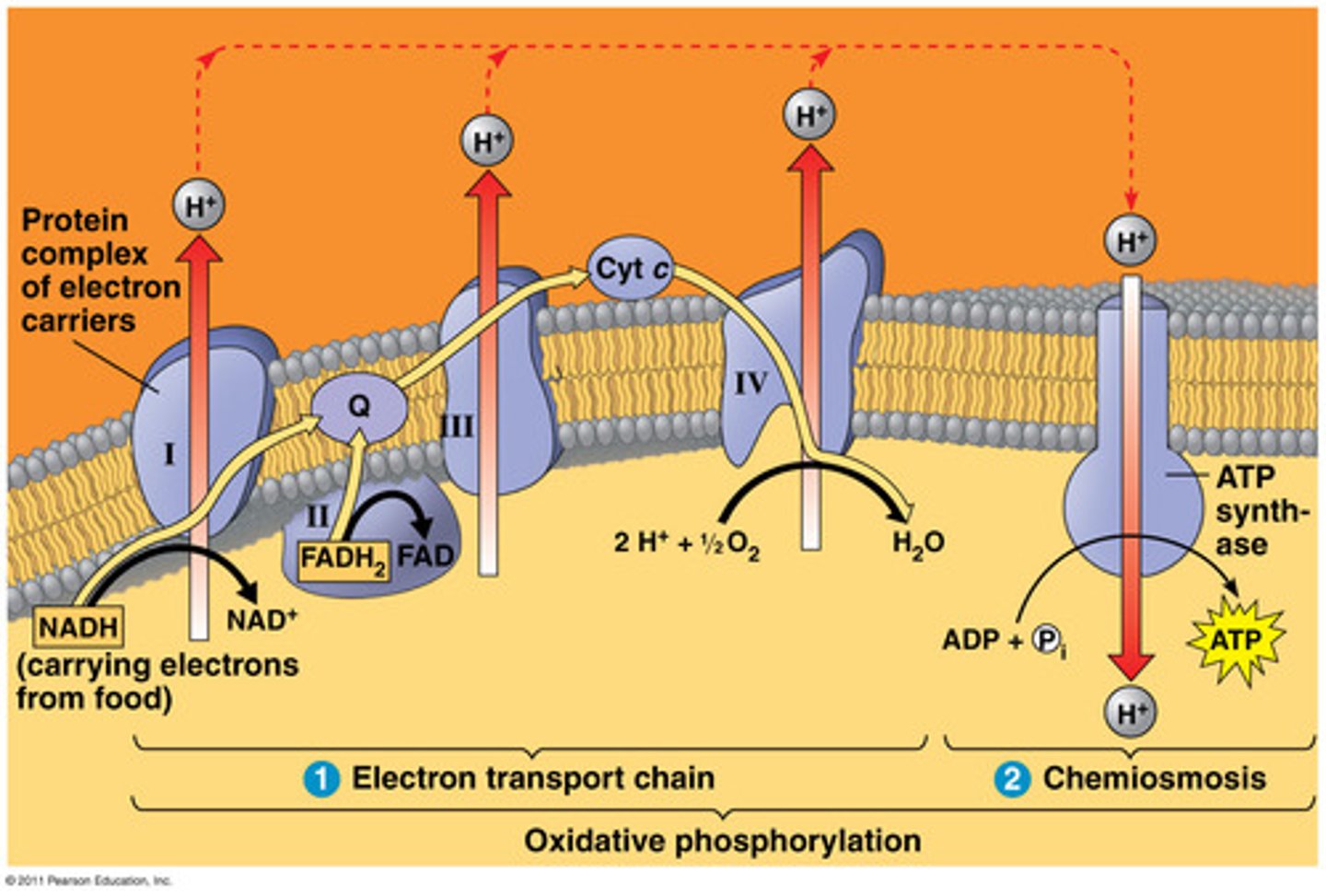
electron transport chain (ETC)
3rd step of aerobic respiration uses the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP for cell to use as energy (32 ATP per glucose molecule)
aerobic
process that requires oxygen

anaerobic
process that does not require oxygen, the 2 kinds of anaerobic respiration are lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermenation
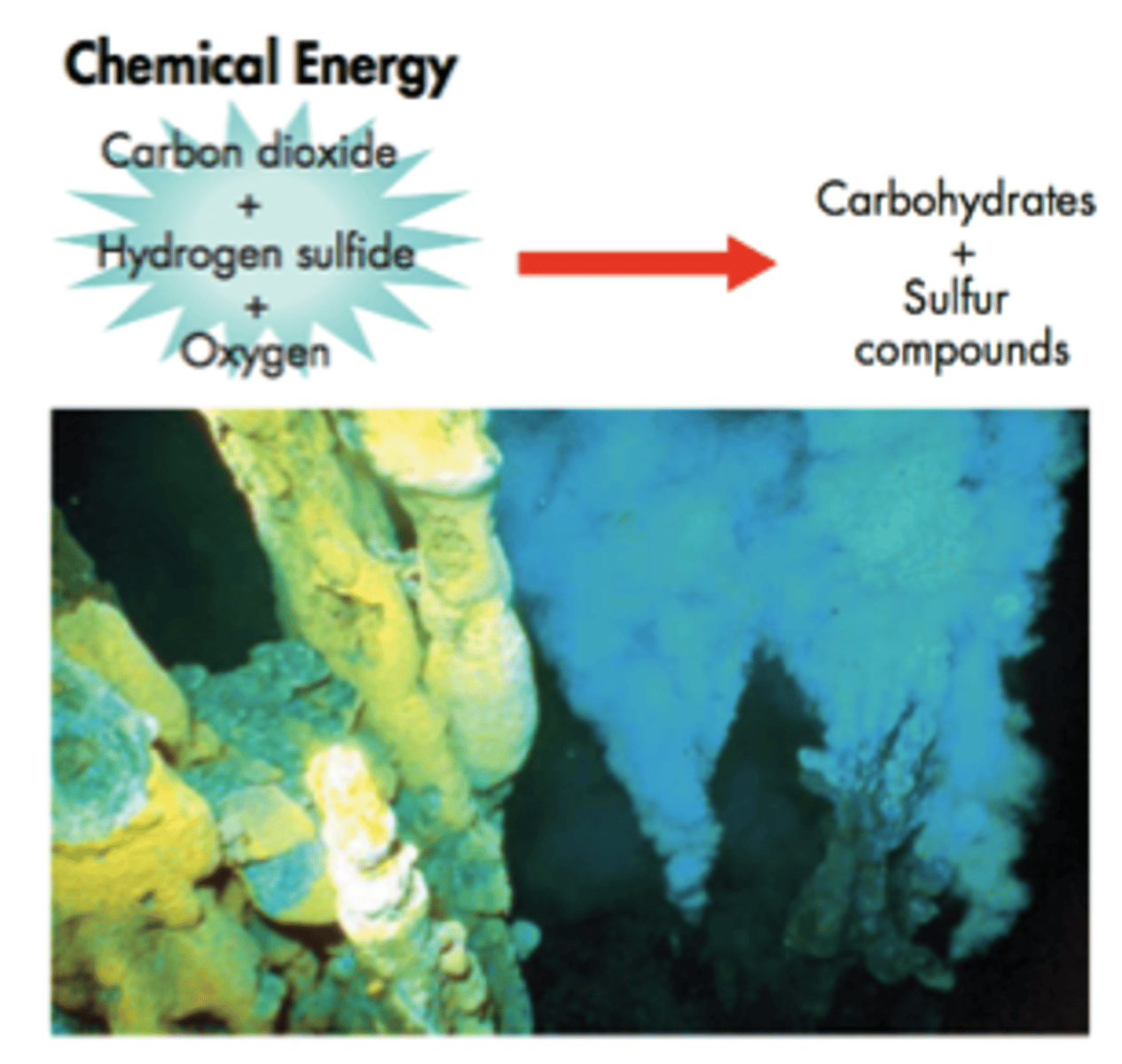
chemosynthesis
process by which ATP is synthesized by using chemicals as an energy source instead of light
FADH2
electron carrier produced during the Krebs cycle, reduced to FAD
NADPH
electron carrier, (energy storage molecule)
reduced form of NADP+
pyruvate
Three-carbon compound that forms as an end product of glycolysis (spliting of glucose molecule) .
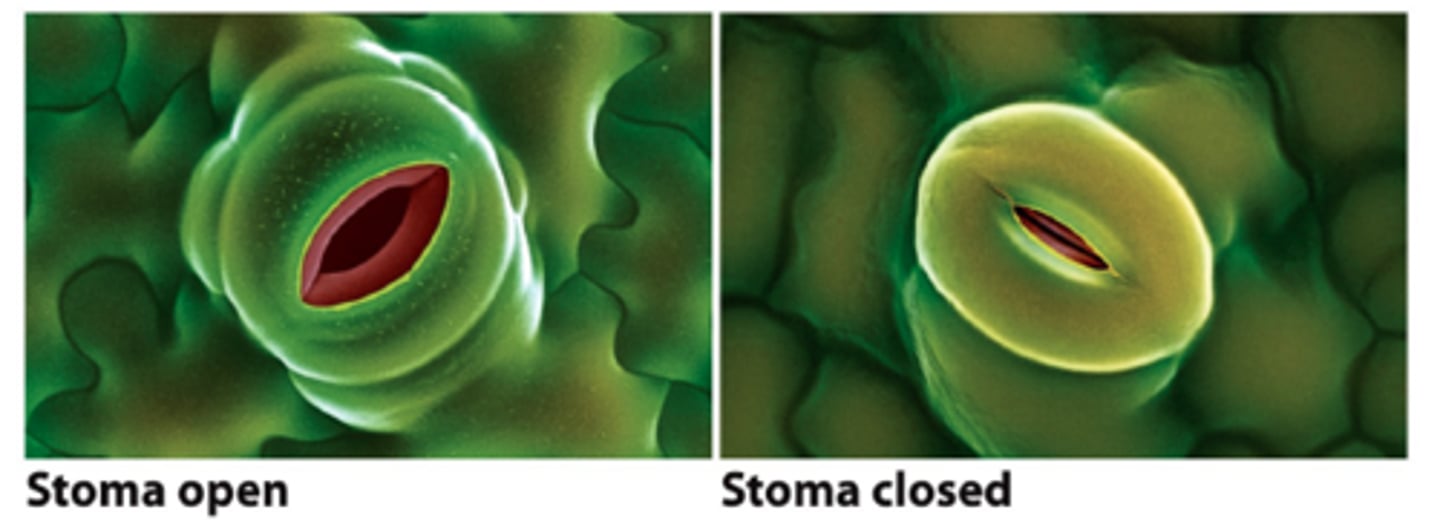
stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
Not studied (31)
You haven't studied these terms yet!