Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
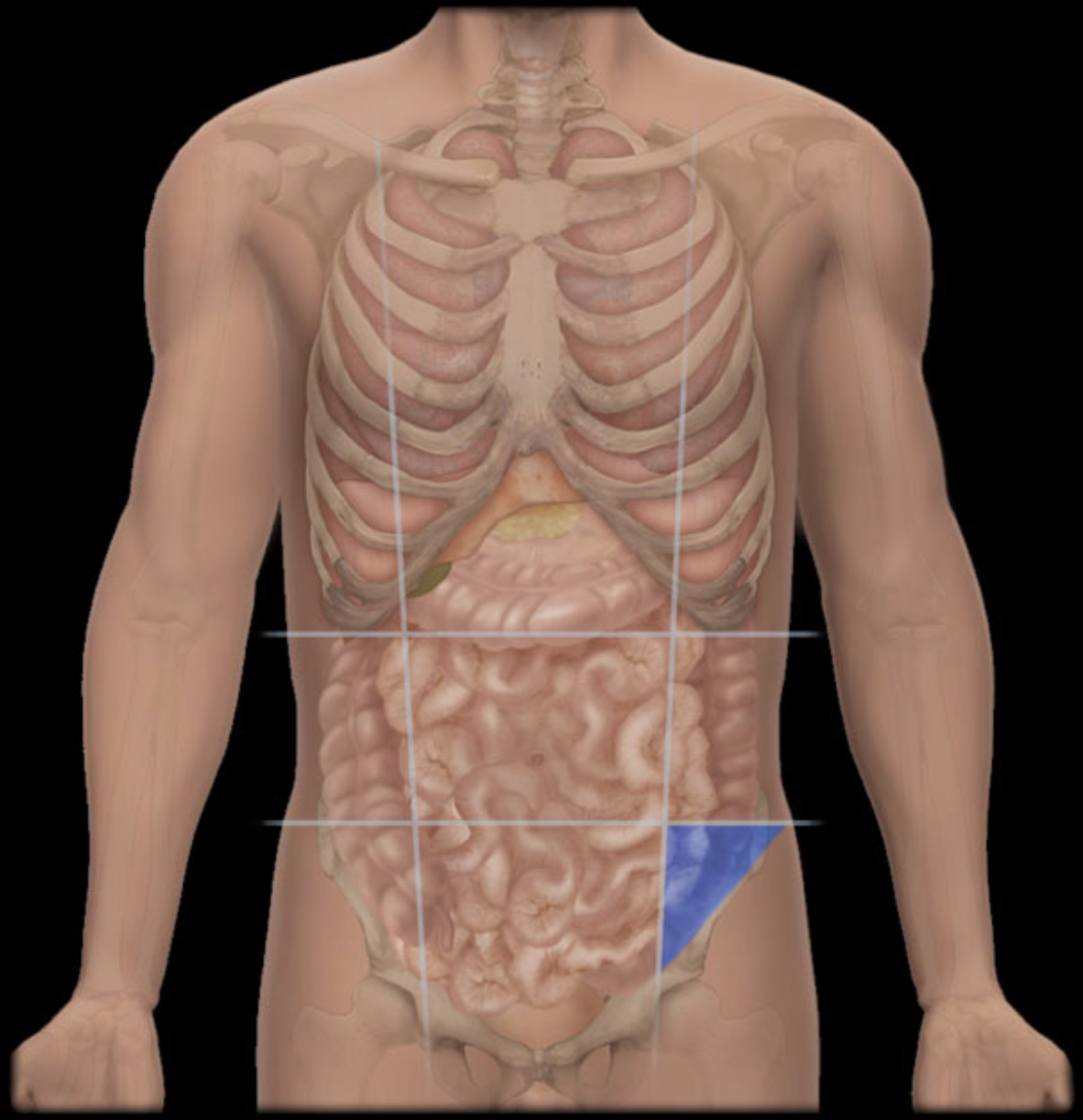
Name the abdominal region shown.
Left inguinal region
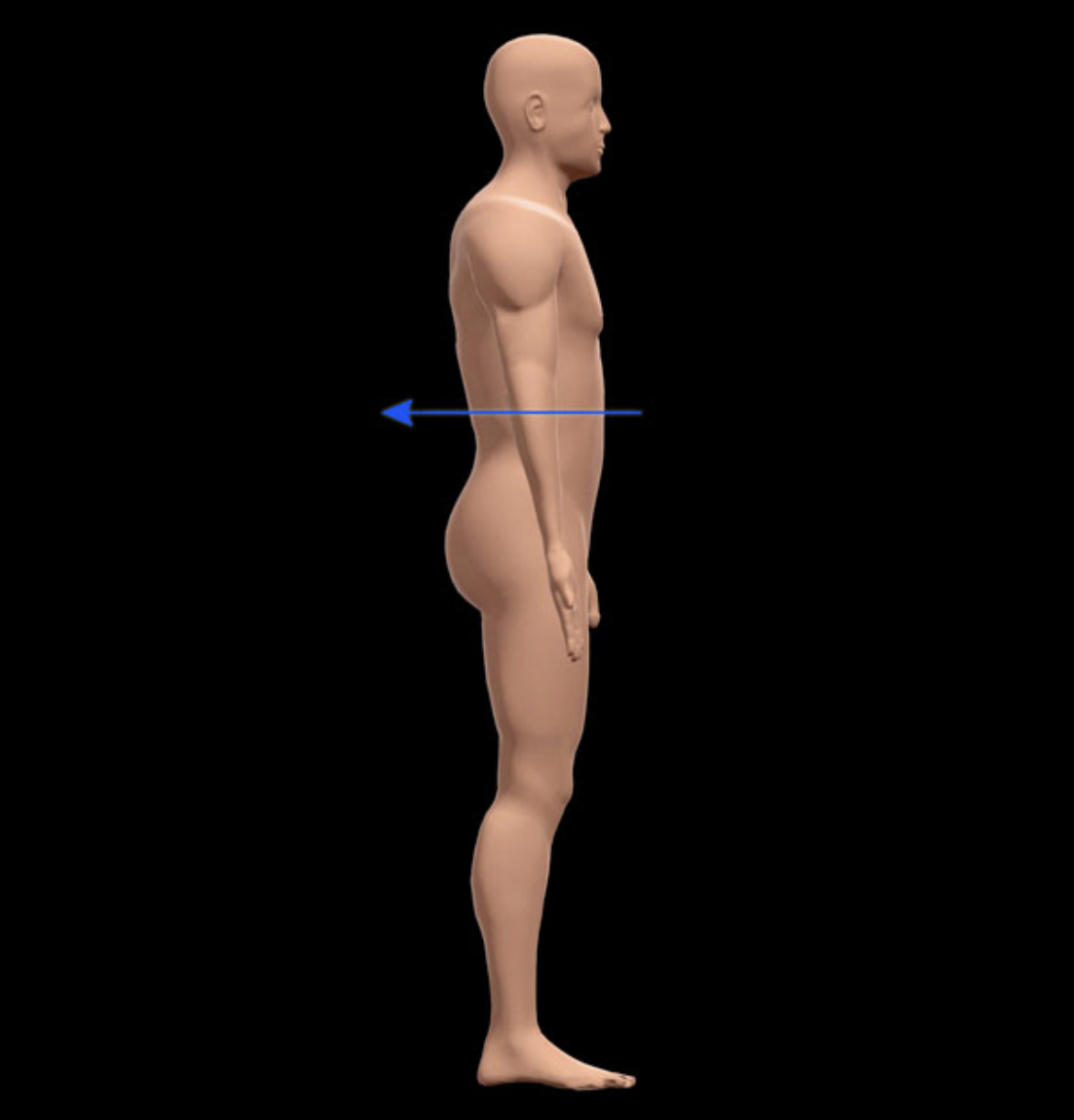
Name the directional term indicated.
Posterior
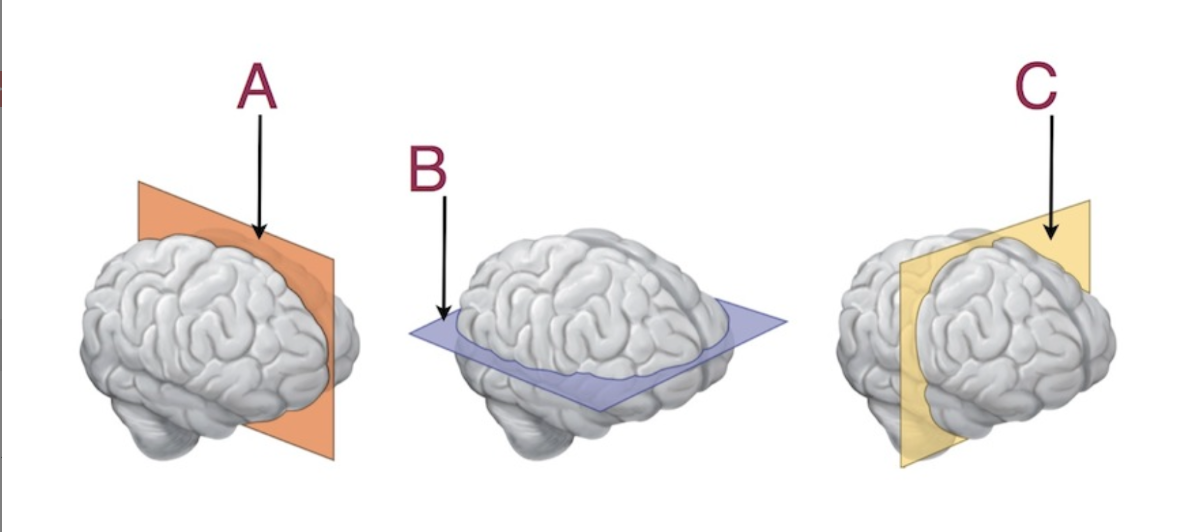
The letter C represents a:
Coronal Section
Which of the following blood pH values in a patient indicates an alkalosis?
pH 7.8
A triglyceride consists of:
3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
The atoms of the isotopes of a particular element vary in the number of:
Neutrons
Which of the following is an element?
Carbon
Glucose is:
A molecule
Hydrogen bonds form between molecules containing ____ bonds; the hydrogen bond is between a hydrogen atom of one molecule and a partially ____ charged atom of another.
Polar covalent; negatively
What type of reaction occurs during protein synthesis to produce the primary structure of a protein?
Dehydration synthesis
Carbon can form ___ covalent bonds
4
Hemoglobin in blood, collagen in tendons, and enzymes in the digestive system are all examples of:
Proteins
A person has alkalosis if the blood pH:
Rises above 7.5
In a covalent bond:
Atoms share a pair or more of electrons
Which of the following is the most abundant inorganic substance in the body?
Water
Generally, a chemical buffer is described as:
A weak acid and weak base that helps prevent big changes in pH
Glycogen is stored in the liver and ____.
Skeletal muscles
Nucleic acids include:
RNA and DNA
An enzyme is _____.
Protein that speeds up chemical reactions without being changed or depleted
A protein consists of:
More than 200 amino acids
Glycolysis is an examples of:
Catabolism
A polar covalent bond is created when ______.
Atoms within the bond do not have the same pull on the shared electron, and as a result the electron spends more time around one atom relative to the other atom within the bond
The first electron shell of an atom can hold a maximum of:
2 electrons
Two questions must be answered to determine whether a substance will diffuse across a cell membrane. One is whether a concentration gradient exists for that substance. The other question is:
Is the cell membrane permeable to the substance?
If a liter of 0.9% saline is infused into a patient, where will most of the water volume end up?
Evenly distributed between intracellular and extracellular fluid
Which of the following is an example of osmosis ocurring in the body?
Water being drawn into blood vessels from interstitial fluid
If a number of human cells were placed in a beaker of pure water, the solution would be called:
Hypotonic
Which of the following enters cells by facilitated diffusion?
Glucose
Facilitated diffusion:
Involves membrane protein molecules
Active transport:
All of the above are true
(Requires ATP, involves membrane protein molecules, transports substances from low concentration to high concentration)
By which of the following processes does a white blood cell engulf a foreign particle?
Phagocytosis
During the process of diffusion:
Molecules move from a region of high concentration to one of low concentration
The plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane because it:
Lets only certain molecules pass through
Which of the following form the basic structure of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
The mitochondria contain enzymes for the chemical reactions involved in:
The citric acid cycle only
The dense mass of ribonucleic acid found within the nucleus is the:
Nucleolus
The lysosomes of cells contain many:
Digestive enzymes
All of the following refer to the plasma membrane of a cell except:
The phospholipids exist in a single layer
The endoplasmic reticulum may be described as a:
Series of membrane-lined channels in the cell’s cytoplasm
The mitochondria of the cell are best known as the organelles where:
Energy is released from food molecules
One strand of a DNA molecule contains the bases AATGCGTCA. Which of the following is the sequence of bases on the other (complementary) strand of DNA (reading left to right)?
TTACGCAGT
Which statement is accurate?
a. Human cells contain 46 genes; another name for a gene is a nucleosome.
b. DNA is made up entirely of genes; a chromosome is the uncondensed form of chromatin.
c. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA constitutes a gene; DNA and associated proteins from chromatin.
d. Each nucleotide in a gene is bound by hydrogen to the next nucleotide in the sequence; chromatin is a nitrogenous base.
c. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA constitutes a gene; DNA and associated proteins form chromatin
During transcription:
A RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read and copied
The term “transcription” refers to:
A messenger RNA complementary copy being made of DNA
What type of reaction occurs during protein synthesis to produce the primary structure of a protein?
Dehydration synthesis
Cytokinesis usually begins before ____ ends.
Telophase
The replication of the DNA molecule during interphase occurs during the:
S- phase
Translation occurs in the:
Cytosol
DNA synthesis occurs during which part of the cell cycle?
S- phase
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that binds DNA< but is unable to bind RNA. This best displays the enzyme characteristic of:
Substrate specificity
The term “codon” refers to:
A three-base sequence of mRNA
Which of the following shows the correct sequence of mitosis?
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase