Chapter 10 - Muscle Tissue
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2 PHYL 141
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Skeletal Muscle
long fused cells
multiple nuclei
visible striations
voluntary
connected to skeleton
Smooth muscle
spindle shaped
single nuclei
no visible striations
no voluntary movement
located in organs and vessels
Cardiac Muscle
branced and interconnected
single nuclei
visible striations
not voluntary
only in the heart
Organization of muscle fibers from smallest to largest
myofilaments, myofibril, muscle fiber, fascicle, muscle
Muscle fibers
made of myofibrils wrapped in sarcolemma
have dark (A bands) and light (I bands) portions
Endomysium
muscle fibers are wrapped in this
Perimysium
muscle fibers (with endomysium) are bundled and wrapped in this.
now called a fascicle
Epimysium
Outermost layer, covering the entire muscle
fascicles are wrapped in this
Motor Unit
functional unit of a muscle
composed of a single motor neuron and all the muscle cells it stimulates
sends a signal that causes muscle fibers to contract simultaneously
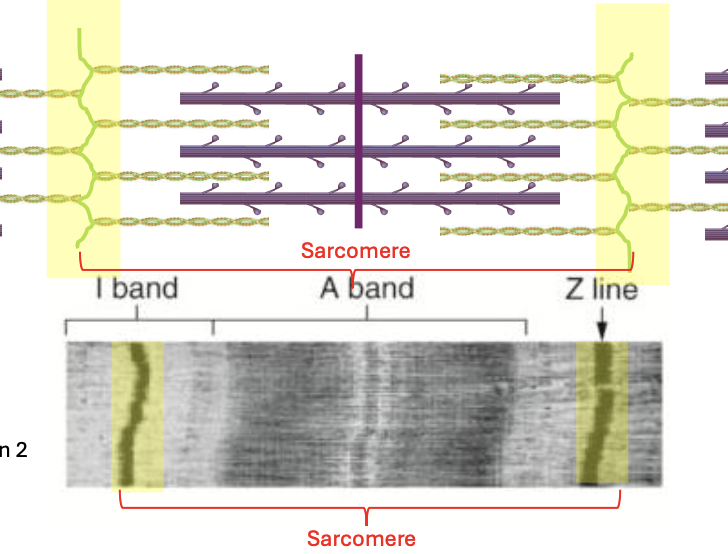
Sarcomere
Part that contracts when moving muscle
individual unit of contraction
makeup myofibril
Components of sarcomere
A band
I band
H zone
Z line/disc
M line
A band
contains both thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments
more static area
Zone of overlap: regions where thin and thick filaments overlap (this can change with contraction)
I Band
contains only thin filaments (actin)
good indicator of how much more space you have for contraction
Z line/Z disc
anchors for actin
forms the actual function part for muscle
sarcomere is between 2 of this
M-line
region that holds myosin together
very little zone of overlap
H Zone
region that contains only myosin, no actin
m line is the center of this
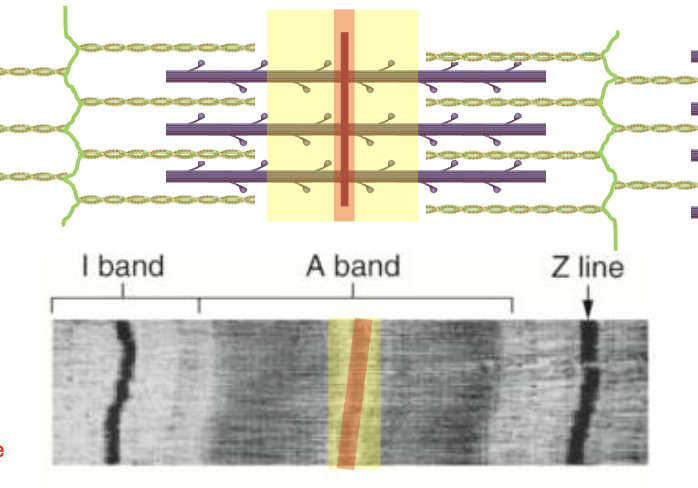
H zone

I Band

A band

M line
Z line/Z disc
Neuromuscular Junction Excitation
neuronal action potential
acetylcholine release
Na+ enters the cell
Sarcoplasmic reticulum Caa2+ release
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
releases Ca+ to initiate muscle contractions
energy for cells are produced here (smooth ER for muscles)
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter/stimulus for muscles (action potential)
A neuron will secrete ths across a synaptic cleft
Action Potential
change in electrical charge that occurs in a neuron when a nerve impulse is transmitted
depolarization and repolarization
Resting potential
initial phase
naturally allows for the movmeent of more K+ ions across membrane
generally netaive
muscles return to after their electrical potential was charged
Depolarization
Na+ into the cell
Neurotrasmitter released —> cell becomes permeable to sodium
Repolarization
K+ ions out
cell becomes permeable to K+ again
T-tubules
incaginations of membranes that allow the electric flow to get deep into the cell
ACH causes Na+ to enter the cell through voltage gated chanels
Na+ entering near the Sarcoplasmic reticulum (via t-tubules) causes Ca2+ release
Myofibrils
composed of repeating units called sarcomeres
thick (myosin) filaments and thin (actin) filaments
Tropomyosin and troponin
Thick and Thin filaments contribution to contraction
Myosin grabs onto actin
Myosin pulls actin inward causing contraction
Troponin
Locks tropomyosin in place; when Ca2+ binds to it, it releases tropomyosin
Tropomyosin
prevents myosin binding to actin
Steps of Contraction
ATP hydrolyzes into ADP + P powering the myosin head
Myosin binds to actin (cross bridge formation)
Myosin puylls actin inward towards the center (power stroke)
ATP binds to myosin cuasing it to detach from actin
Contraction
tightening and shortening of a muscle fiber to generate force
Twitch
singular muscle contraction
Tension
force generated by muscle contractions
strength
Ideal Sarcomere length
80-120% resting length
tension = strength
produces maximum tension
Decreased sarcomere length
below 80%
zone of overlap increases until thin filaments have nowhere else to go
strength is decreased
Increased Sarcomere length
above 120% at resting length
produces reduced tension due to lack of concentraction
Zone of overlap reduces until no overlap occues which results in no tension
Motor Unit Recruitment
Fewer = less force, more control
More = more force, less control
Isotonic Contraction
force generated by changing muscle length
Isometric Contraction
force generated while maintaining muscle length
Concentric contraction
Type of isotonic contraction
muscles shorten
flexion
Eccentric contraction
type of isotonic contraction
muscles lengthen
extension
Fast Twitch
Type IIx
Low efficiency
anaerobic
low ATP
highest speed of shortening
Slow twitch
type I
aerobic
low/slowest speed of shortening
large ATP
high efficiency