HW9: Infective Endocarditis, Cardiac Tumors, Thrombus Quiz
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
29/29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is Infective Endocarditis?
microbial infection of the epicardium
microbial infection of the endothelial layer
microbial infection of the serous pericardium
microbial infection of the myocardium
microbial infection of the endothelial layer
What are the most common microbes or pathogens that cause Infective endocarditis?
Bacteria staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus viridans
myocarditis
Viral infection
HIV/AIDS
Bacteria staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus viridans
The signs and symptoms associated with Infective Endocarditis include all the following, EXCEPT:
flu-like symptoms; fever, night sweats, chills
Osler's nodes
negative blood culture
Fever of unknown origin
SOB, CP, tachycardia
new or changed murmur
negative blood culture
All the following are some risk factors associated with contracting Infective endocarditis, EXCEPT:
open wound
infected needle
heart disease complications
cardiac devices/catheters
dental procedure
cardiac imaging
cardiac imaging
All the following are some complications associated with Infective endocarditis, EXCEPT:
structural cardiac valve changes
All of these
embolism
heart failure
prosthetic valve dysfunction
acute/chronic valvular regurgitation and stenosis
All of these
Patients most at high risk of contracting Infective endocarditis include all the following, EXCEPT:
IV drug users
History of infective endocarditis
some serious congenital heart diseases and repaired congenital heart disease
prosthetic valve recipients
CAD
CAD
All the following are some echo findings associated with Infective endocarditis, EXCEPT:
hypokinetic LV function
thick, shaggy, swinging or pedunculated valvular appearance
probable valvular regurgitation
structural or hemodynamic cardiac changes
possible pericardial effusion
hypokinetic LV function
Cardiac tumors are categorized as primary, secondary, benign and malignant.
True
False
True
A myxoma is described as all the following, except:
usually mobile and moves with blood flow. (Pedunculated)
capable of detaching from stalk and becoming an embolism.
capable of producing physiologic MS or TS, and MR or TR
most common primary malignant cardiac tumor
usually attached by a ‘stalk’ to the interatrial septum
most common primary malignant cardiac tumor
A cardiac Lipoma is an encapsulated, well defined tumor composed of mature fat cells.
True
False
True
Some facts about a Papillary Fibroelastoma include all the following, except:
highly mobile mass; capable of embolism, stroke, valve dysfunction, arrhythmias, sudden death
closely resembles the chordae tendineae
most common malignant valvular tumor
Aortic valve, LVOT, anterior MV leaflet – most affected
most common malignant valvular tumor
What cardiac pathology does this represent?
Aortic valve vegetations
Thickened /calcified aortic valve
Thrombus
Fibroelastoma
Aortic valve vegetations
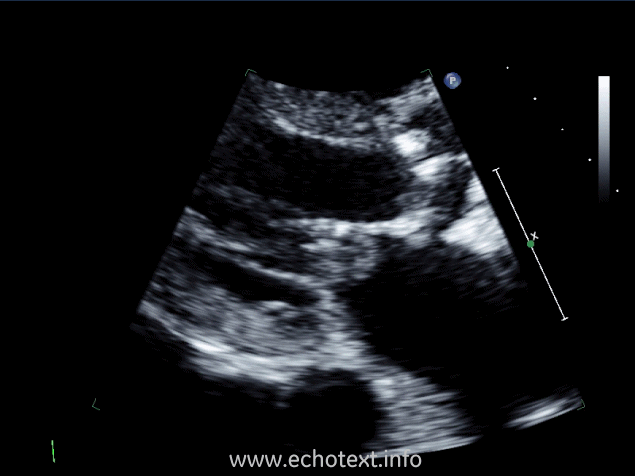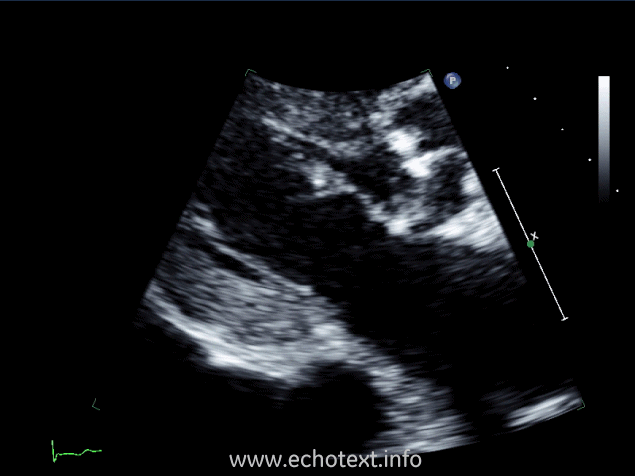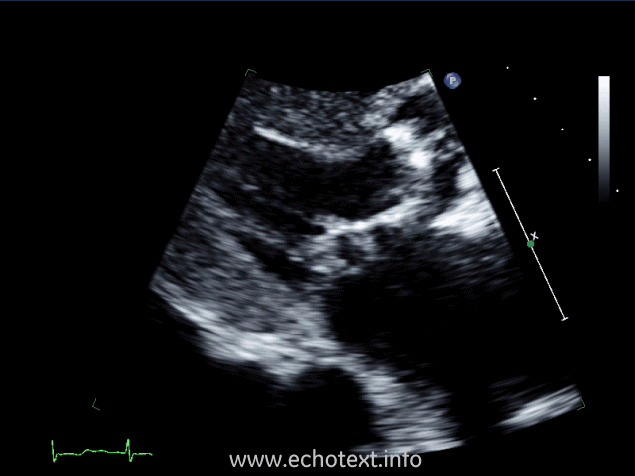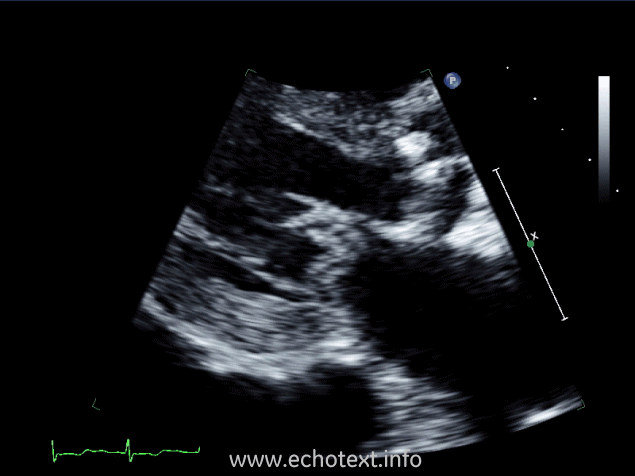
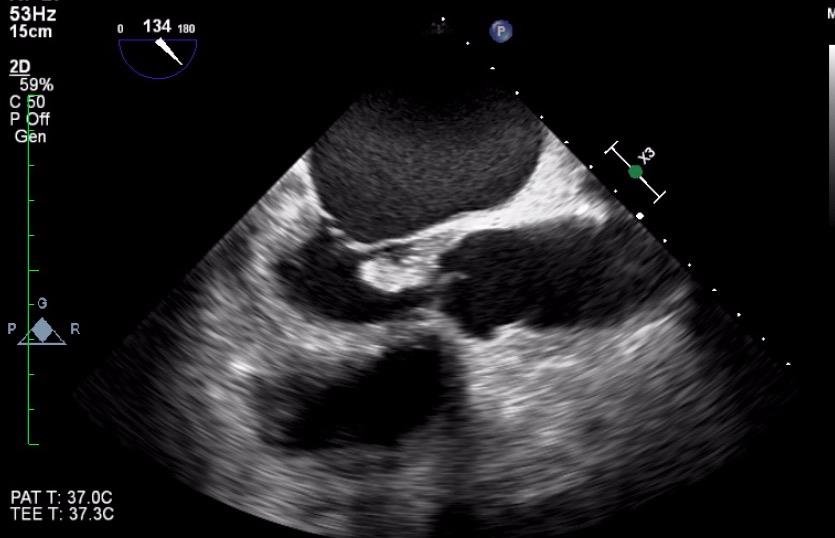
Which cardiac pathology is shown below?
Mitral annular calcification and AS
Mitral valve endocarditis and AS
Mitral stenosis
Constrictive pericarditis and AS
Mitral valve prolapse and AS
Mitral valve endocarditis and AS
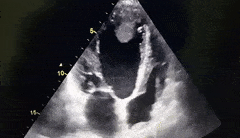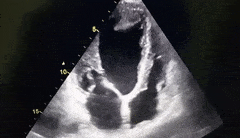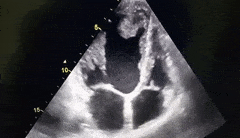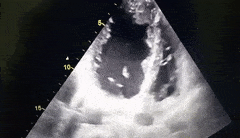
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
LA thrombus
Metastatic tumor
LV myxoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
LV Apical thrombus
LV Apical thrombus
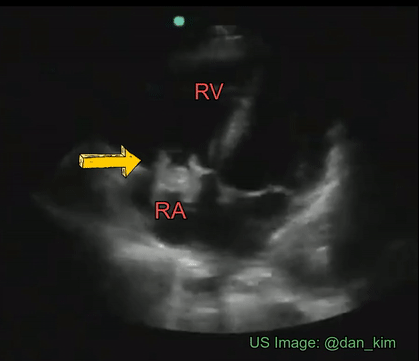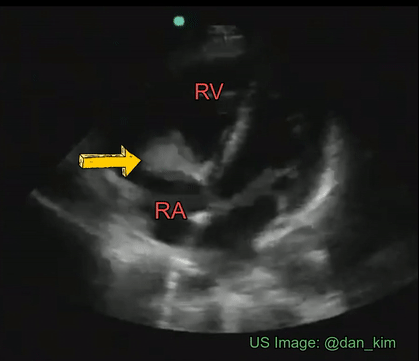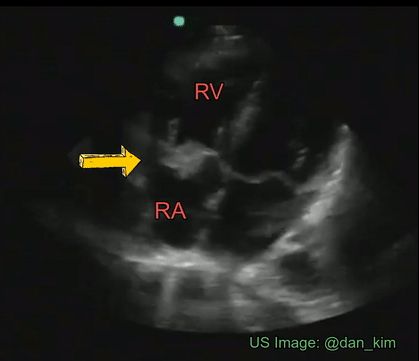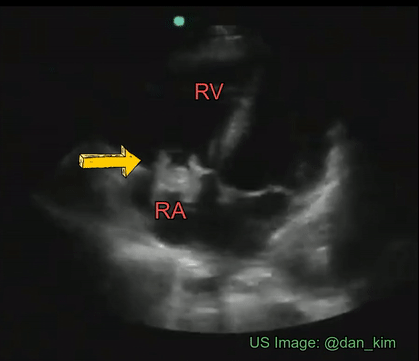
Identify the cardiac pathology demonstrated in the image.
Right atrial myxoma
Mitral stenosis
Tricuspid endocarditis/vegetation
Tricuspid stenosis
Tricuspid endocarditis/vegetation
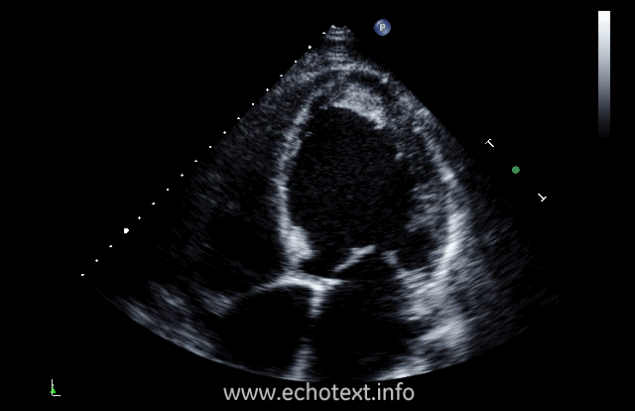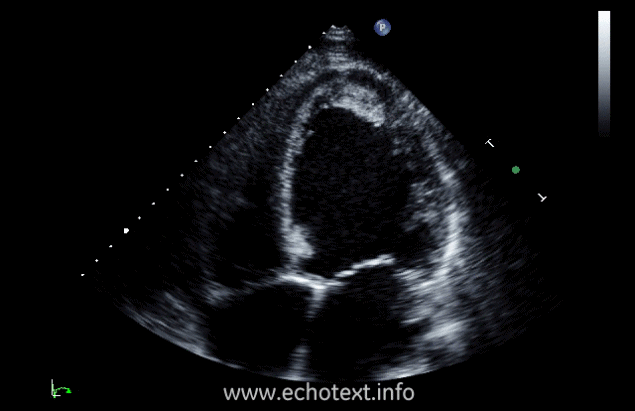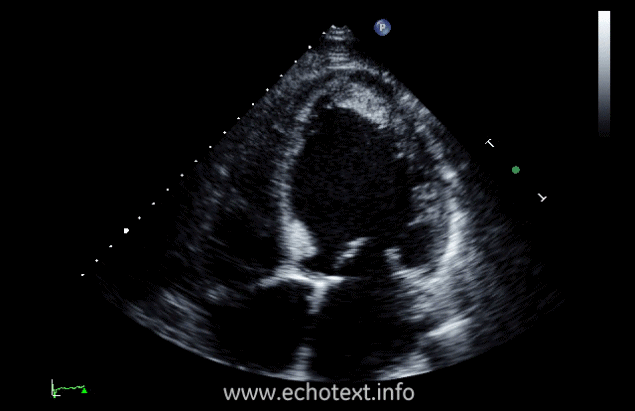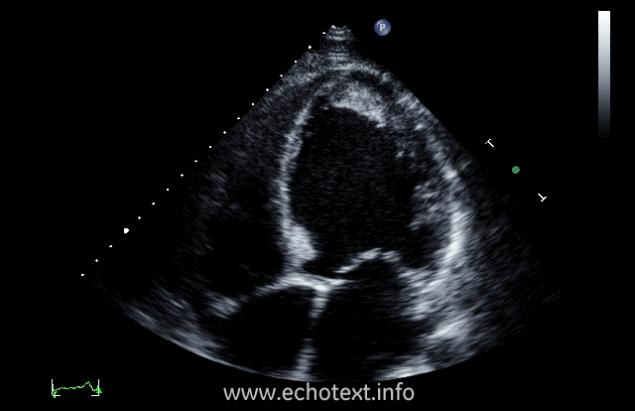
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
Non-compaction cardiomyopathy
Metastatic tumor
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
LV Apical thrombus
LV Apical myxoma
LV Apical thrombus
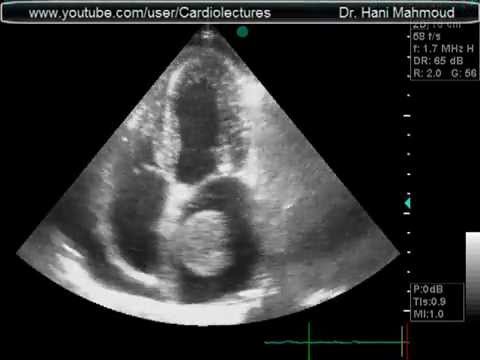
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
LA myxoma
Lipoma
LA thrombus
Angiosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
LA myxoma
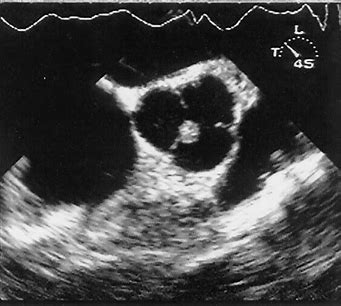
Identify the cardiac pathology demonstrated in the image.
Aortic valve mass
Papillary fibroelastoma
Aortic stenosis
Aortic valve vegetation
Papillary fibroelastoma
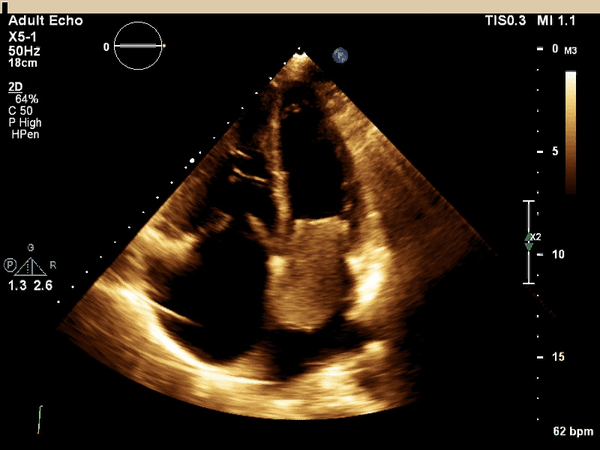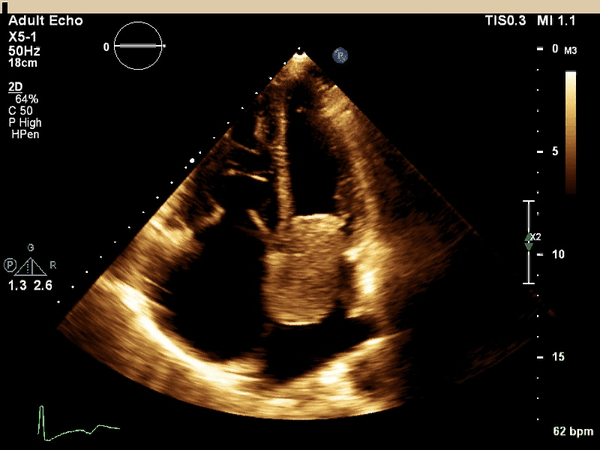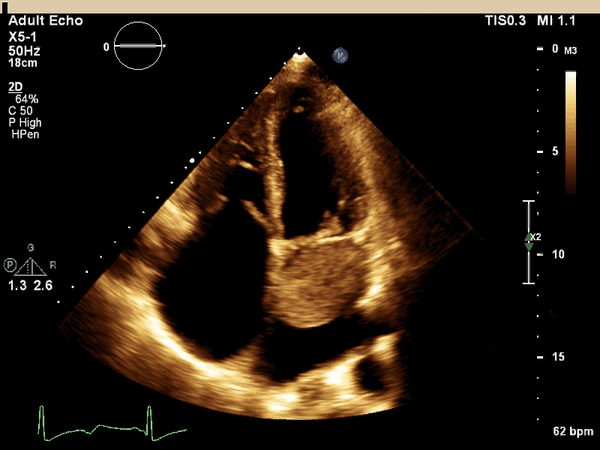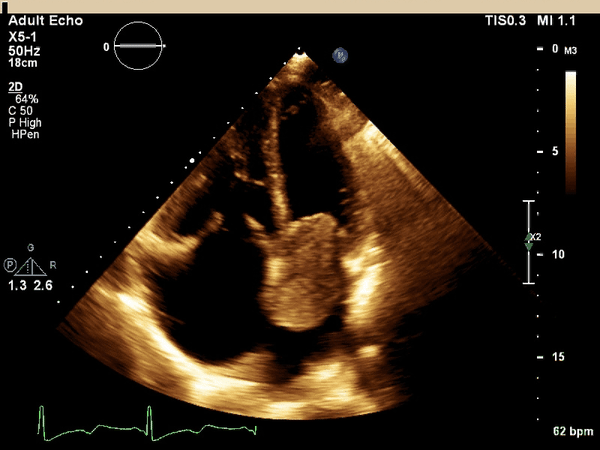
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
LA thrombus
LA myxoma
Lipoma
Angiosarcoma
LA myxoma
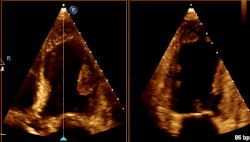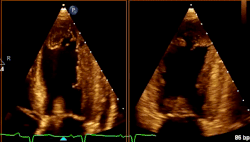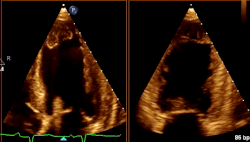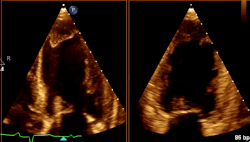
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
LV apical aneurysm
Non-compaction cardiomyopathy
LV Apical thrombus
Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
LV Apical thrombus
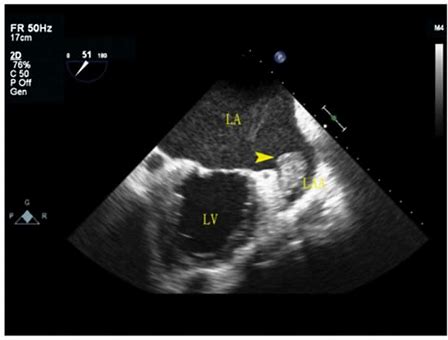
What cardiac condition is demonstrated in this image?
LV Apical thrombus
LA appendage thrombus
LA myxoma
LA appendage thrombus

What cardiac pathology does this m-mode represent?
Mitral stenosis
Left atrial myxoma
Aortic insuffiency
Infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis
The different types of cardiac thrombus include all the following, EXCEPT:
single
layered
pedunculated
multilobulated
thickened
thickened
Virchow's Triad, the risk factors in the formation of a thrombus, include all the following, EXCEPT:
hypercoagulability
vessel wall injury
hyperdynamic wall motion
Blood stasis
hyperdynamic wall motion
Cardiac thrombus form in areas and are found in some pathologies including all the following, EXCEPT:
patients with significant LAE
areas of hypo-akinetic wall motion
Mitral stenosis/Atrial fibrillation
areas of stenosis
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
areas of stenosis