Ap Bio- Cell energetics
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms

CO2 is reduced to form glucose.

Test whether they release O2 in the light.
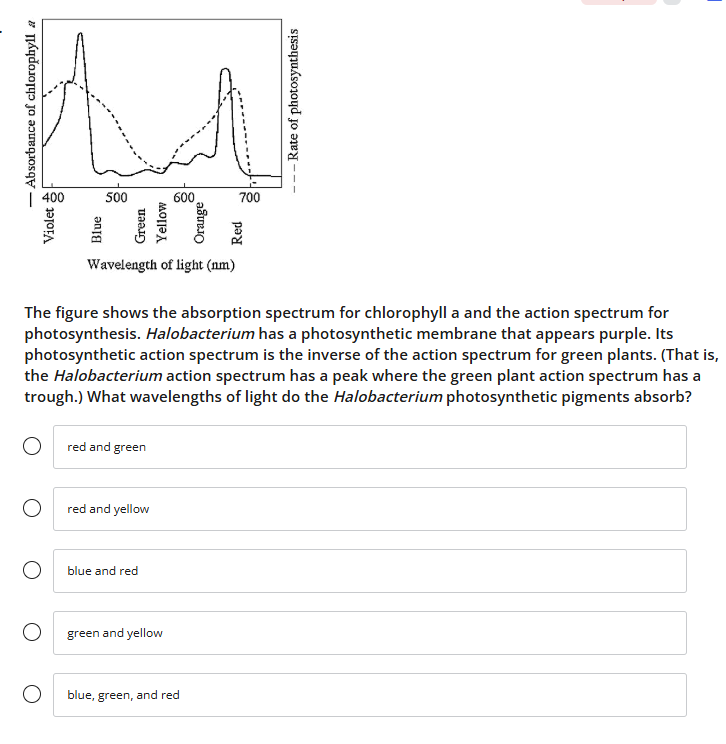
green and yellow

wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis

a. water

to produce simple sugars from carbon dioxide

No pull on water into the plant from evaporation will slow down the photosynthesis rate.

d. In photosynthesis, water and carbon dioxide are reactants. GA3P and oxygen are products.

a. chloroplasts

c. sugars/carbohydrates and oxygen

b. stroma
What is photosynthesis
the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars.
The glucose molecules provide organisms with two crucial resources:
1) Energy
2) Fixed Carbon
The chemical energy in glucose can be harvested through processes like ____
Cellular respiration and Fermentation
Fixed carbon
Carbon taken from inorganic molecules to become apart of a organic molecule through carbon fixation
Photoautotrophs
organisms that make their own food via light to make sugars
Heterotrophs
organisms that can’t convert carbon dioxide to organic compounds themselves
Mesophyll
The cells in a middle layer of leaf tissue
Primary site of photosynthesis
Mesophyll
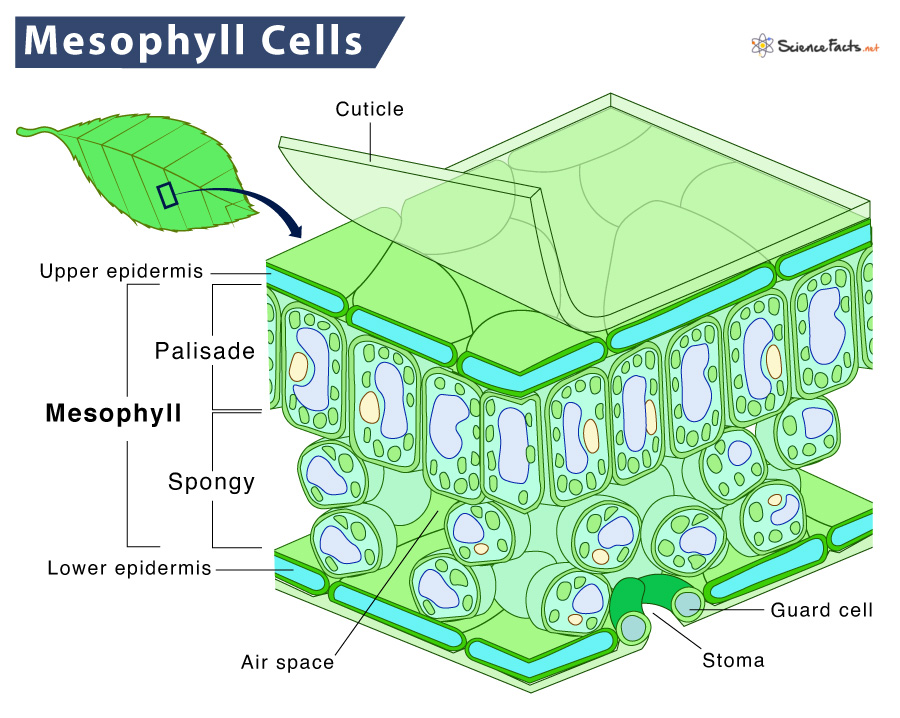
Stomata
Small pores called-singular, stoma-are found on the surface of leaves in most plants, and they let carbon dioxide diffuse into the mesophyll layer and oxygen diffuse out.
Whats in what order
Thylakoid space, chlorophyll →Thylakoid → Granum → Stroma → Chloroplast → Cell → Mesophyll → Leaf → Plan
Each mesophyll cell contains organelles called_____
chloroplasts
Thylakoids
disc-like structures arranged in piles known as grana within each chloroplast
Chlorophyll
Pigments in the membrane of each thylakoid
Stroma
fluid-filled space around the grana
the stage of photosynthesis
1) Light-dependent reactions
2) Calvin cycle
Where do light-dependent reactions take place
thylakoid
Light dependent equation
light + 2H2O + 2NADP+ +3 ADP + 3Pi → O2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Light dependent reaction input
light + 2H2O + 2NADP + ADP + Pi
Light dependent reaction output
O2 + 2NADPH + ATP + 2H+
ATP
A energy storage molecule
NADPH
A electron carrier, used for reducing stuff later
where does the calvin cycle take place
Stroma
Calvin cycle inputs
ATP + NADPH + Co2
G3P
sugars made from calvin cycle that join up to make glucose
ATP and NADPH are used to?
fix Co2 to make G3P
Calvin cycle outputs
ADP + Pi + NADP+ + G3P
Redox reactions
reactions involving electron transfer
Photosystems
large complexes of proteins and pigments that are optimized to harvest light. They can contain chlorophyll
non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Process where electrons are removed from water to pass through PSI and PSII before ending up in NADPH
1st step of light reactions
A photon is absorbed by PSII, excites electrons of pigments that make up PSII
Excited electrons emit photons that are passed around by the pigments within PSII like a pinball machine
Eventually a photon may hit the reaction center complex (RCC)
one of the electrons in one of the chlorophyll of the RCC, instead of going back to ground state, is transferred into the primary electron acceptor
a enzyme supplies a electron to a pigment that is missing one through breaking down a water molecule into O2, 2H+, and 2e-
basically: PSII absorb light, water is broken down into o2, H+, and e-
2nd step of light reactions
Electrons travel down electron transport chain (compounds that are embedded in thylakoid membrane)
H+ move against concentration gradient
Proton pumps bring protons into the thylakoid space (inside thylakoid)
3rd step of light reactions
H+ gradient goes through ATP synthase and ATP is made (something to do with H+ spinning the protein motor)
PSI absorbs light to excite electrons again (electrons lose energy as they travel down chain)
4th step of light reactions
As electrons move through PSI, NADP+ to make NADPH
Net outputs of Light reactions
ATP and NADPH
2 ways electrons flow in photosynthesis
Linear electron flow and cyclic electron flow
Linear electron flow
electrons go from
PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → NADPH
Ratio of ATP and NADPH made in light reactions
1:1
cyclic electron flow
PSI → electron transport chain
makes ATP without making NADPH, important in Calvin cycle cuz there will be an uneven ratio of ATP and NADPH
ATP and NADPH ratio in calvin cycle
9ATP:6NADPH
1st step of calvin cycle
CO2 comes in through stoma and rubsico attaches it to a 5-carbon sugar (ribulose bisphosphate) → makes a unstable 6 carbon molecule → splits into two 3-PGA
(Carbon Fixation)
2nd step of calvin cycle
9ATP and 6NADPH from light reaction are used to reduce 3carbons to become G3P
Each 3-PGA receives a phosphate from ATP and reduced by NADPH to make G3P
3rd step of calvin cycle
Some G3P stay in cycle, and are used to regenerate more Rubsico to start the cycle again
Some G3P leave the cycle to other pathways to make glucose and other compounds
net products of calvin cycle
G3P + NADP+ + ADP
Photosynthesis overall equation
light + H2O + Co2 → C6H12O6 + O2
Light reaction basically
convert light energy (photons) into chemical energy (ATP, NADPH)
Calvin cycle basically
uses chemical energy made from light reactions to make G3P (precursor to glucose)
there are around how much chloroplasts per plant cell?
30-40
1 G3P requires how much ATP and NADPH?
9 ATP, 6 NADPH
The light reactions are basically a sequence of _
redox reactions
How many calvin cycles to make 1 glucose?
6 cycles
Where is ATP made?
outside of thylakoid membrane in stroma (ATP synthase embedded in membrane)
How do H+ travel against the H+ gradient?
They get energy from electrons that lose energy as they travel down the electron transport chain
Chlorophyll 680
P680 is the specialized chlorophyll in Photosystem II (PSII) that absorbs light at 680 nm
how much Co2 to make 1 G3P
3
When a molecule gains an electron, did it gain or lose energy?
gained
waves with shorter lengths have more
energy
wavelength of UV
~400nm
wavelength of infrared
~700nm
phosphorylation
chemical process that involves the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule, which can either activate or inactivate it