A&P Lab Exam 2 Study Guide
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Define osteology
the study of the structure and function of the skeleton and bony structures
List the functions of the skeleton
1. support and protection
2. levers for movement
3. hematopoiesis
4. storage of mineral and energy reserves
5. calcium homeostasis
Describe the number of bones depending on their age.
babies = 300 bones
adults = 206 bones
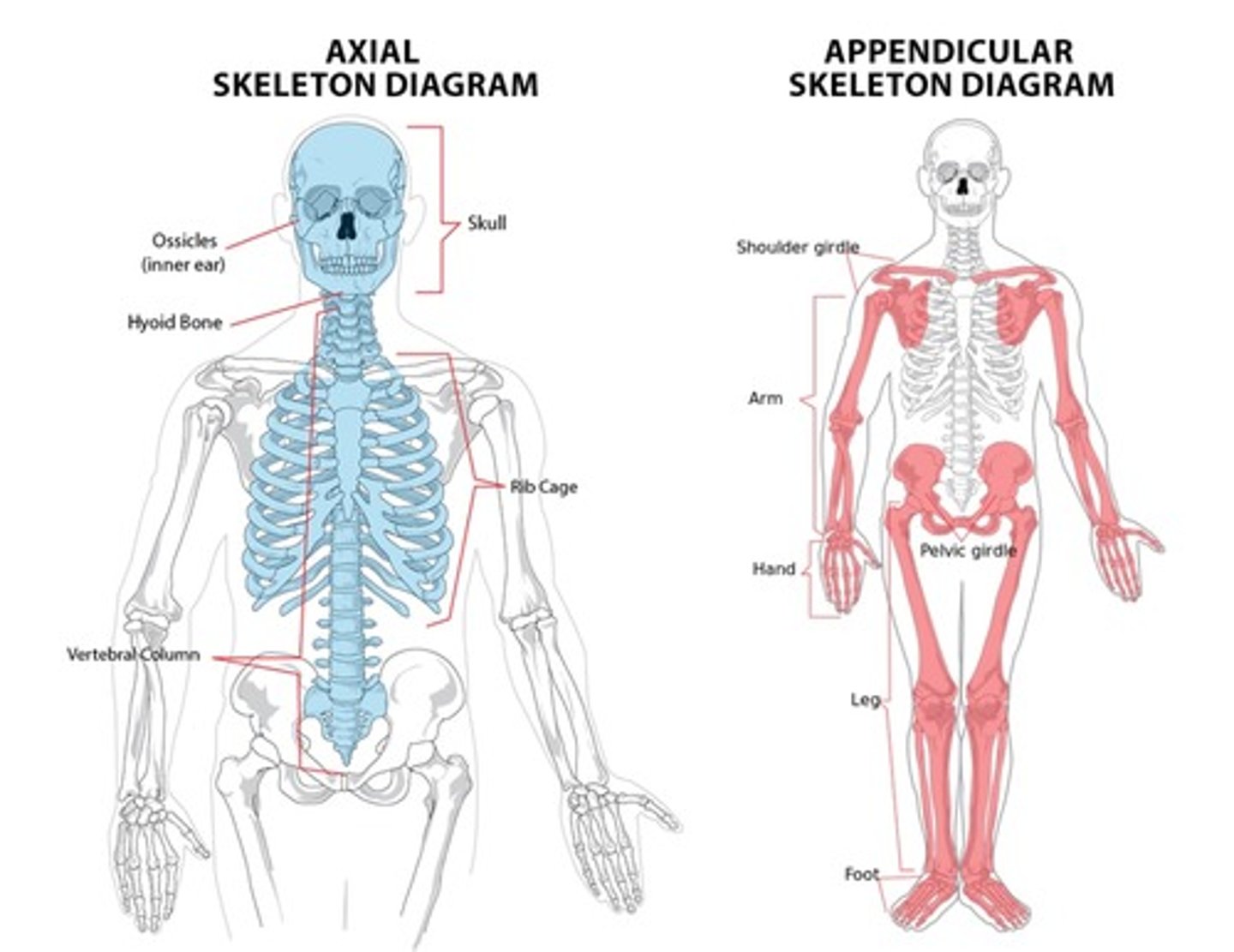
Identify and describe axial skeleton vs the appendicular skeleton
axial = skull, vertebral column, and rib cage
appendicular = all other limbs, pelvic and pectoral girdle
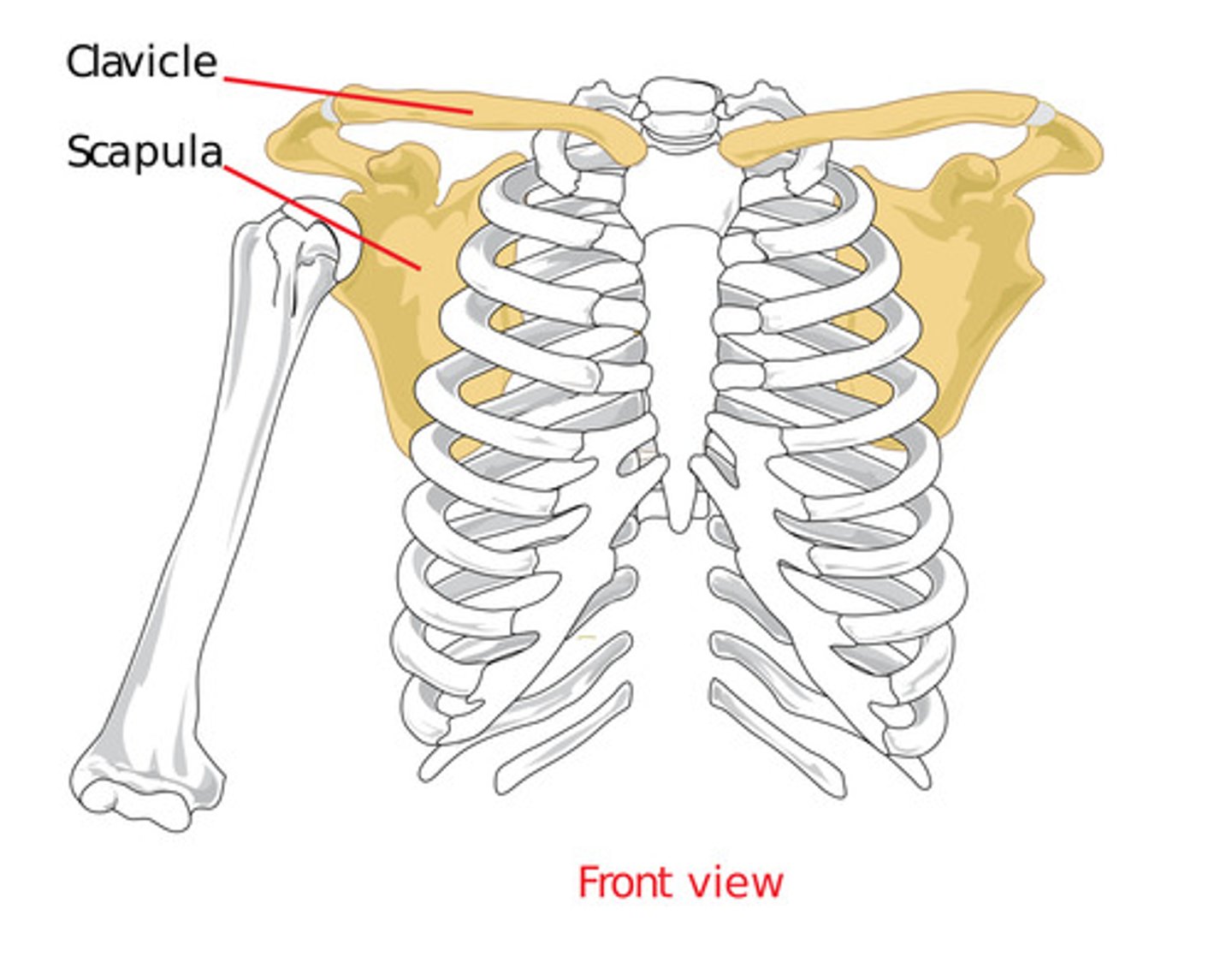
Identify and describe the pectoral girdle
bony structure that connects the arm to the torso
- made up of the clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
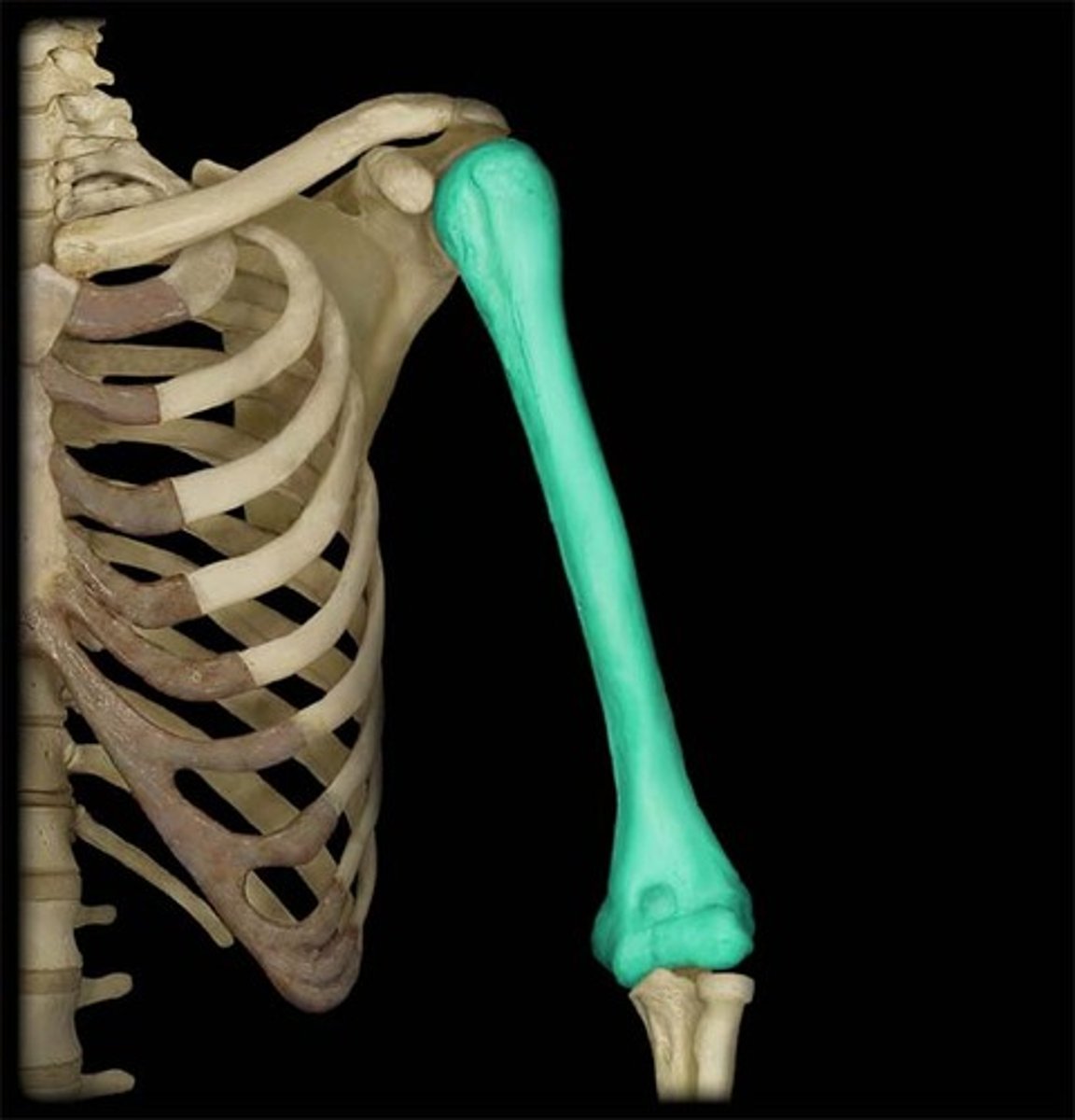
Identify and describe the humerus
long bone of the upper arm
- connects to shoulder and elbow
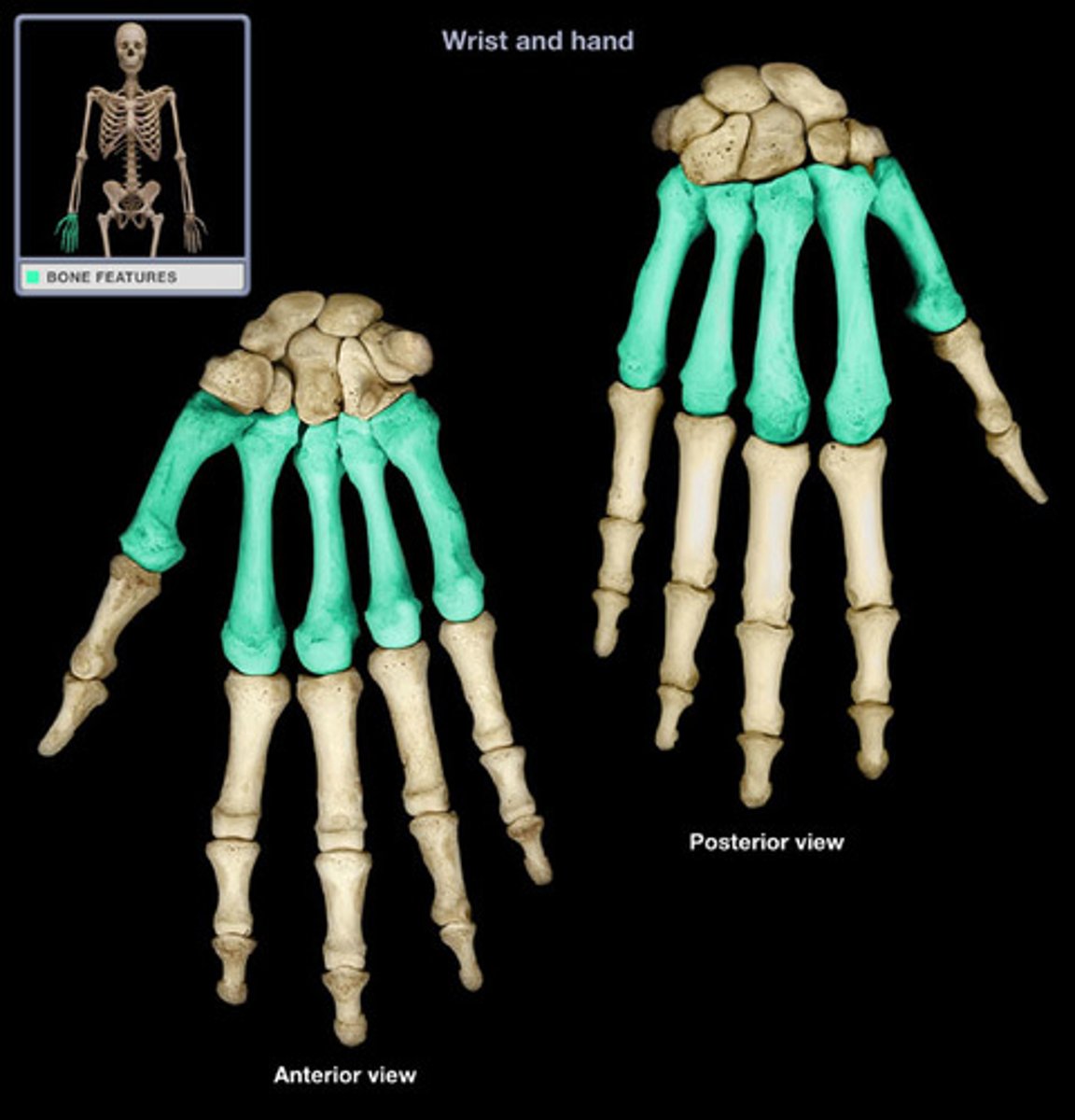
Identify and describe the metacarpal bones
the long bones in the palm that connect the wrist (carpal bones) to the fibers (phalanges)
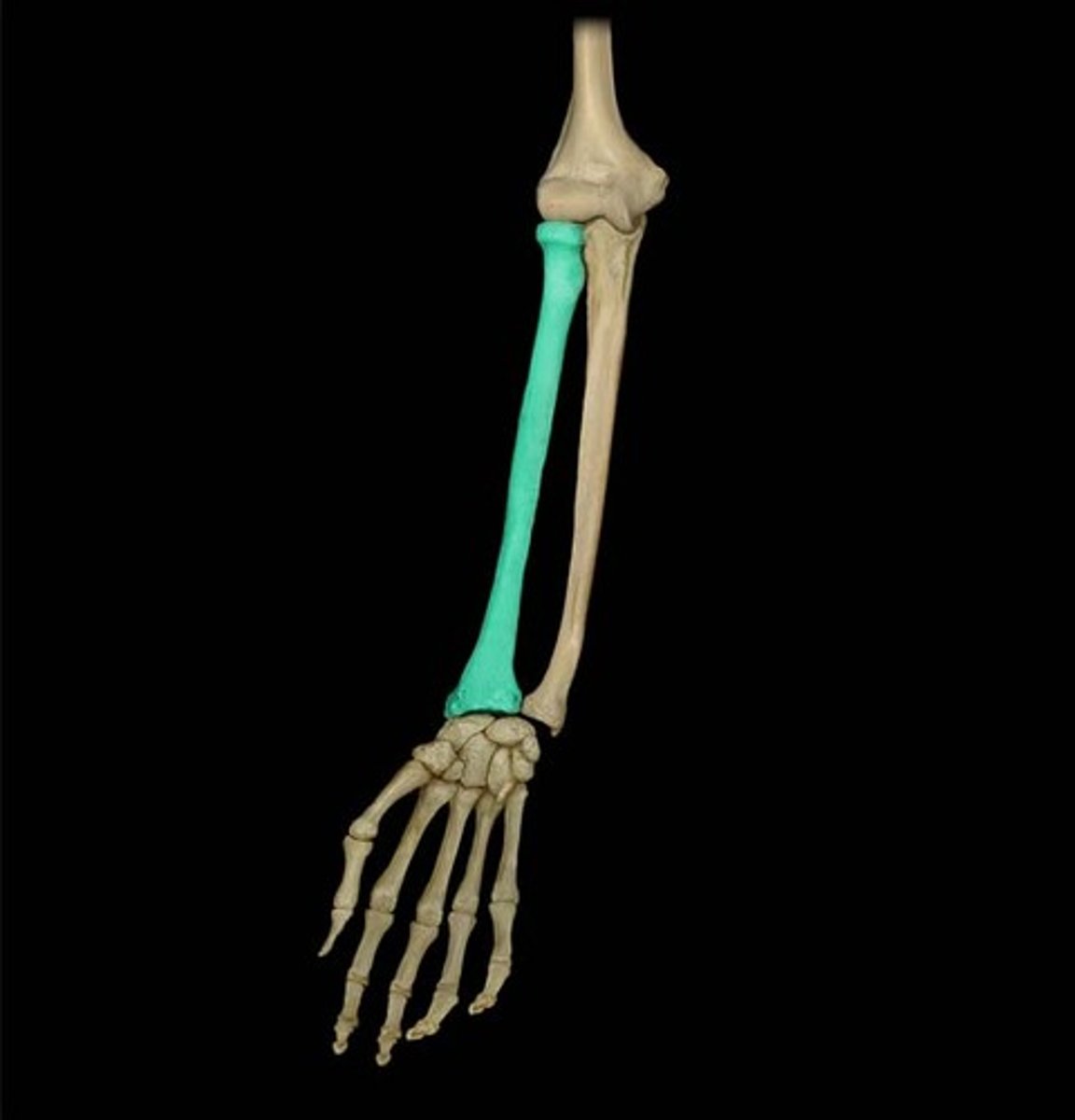
Identify and describe the radius
the larger and thicker bone of the forearm, on the thumb side
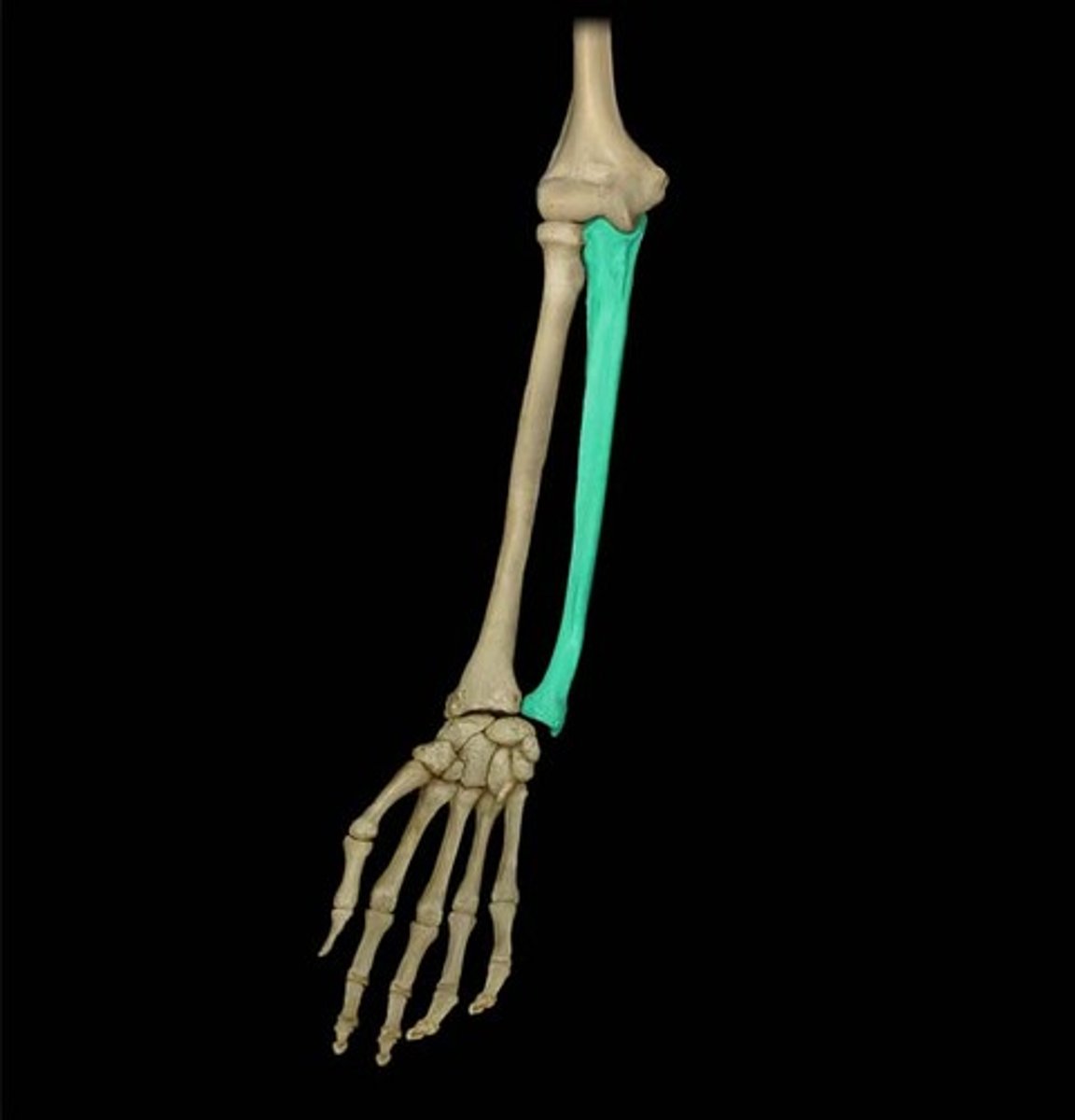
Identify and describe the ulna
the longer bone of the forearm, on the medial (pinky) side
Identify and describe the phalanges
bones of the finger and toes, has 14 bones per hand and foot
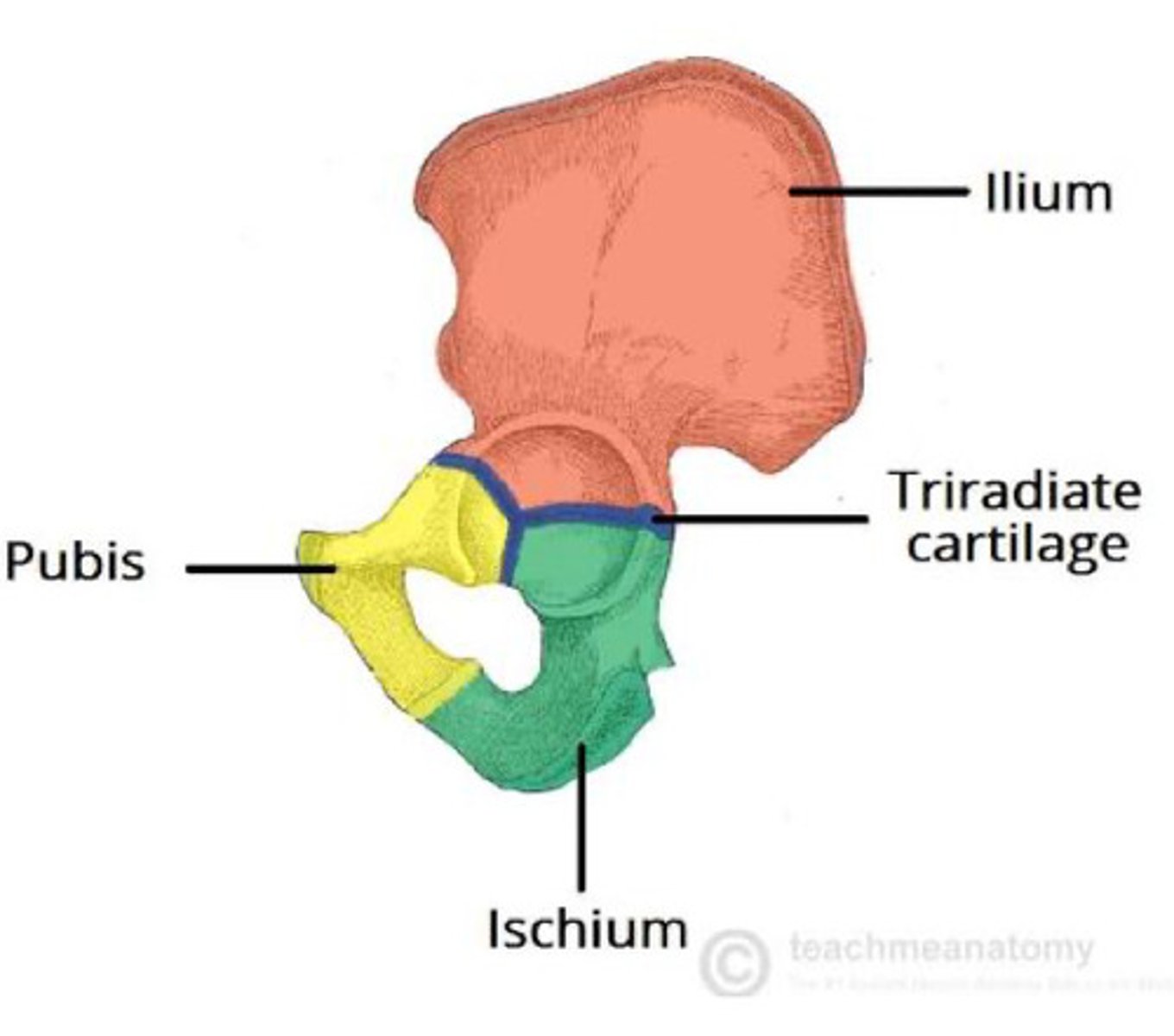
Identify and describe the hip bone
large fused bone forming the pelvis
- connects to spine and legs
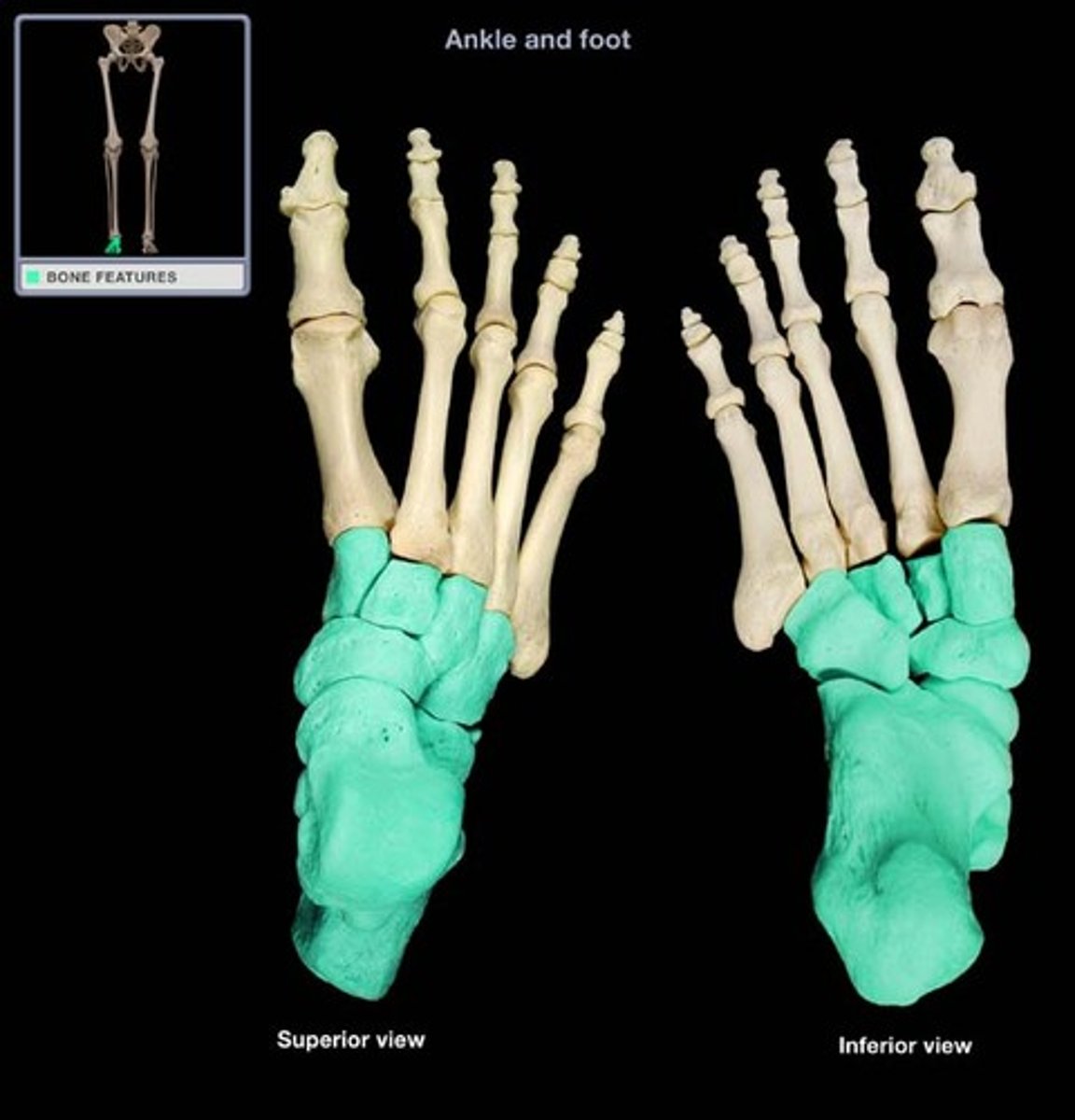
Identify and describe the tarsals
proximal part of the foot, forming the ankle and heel
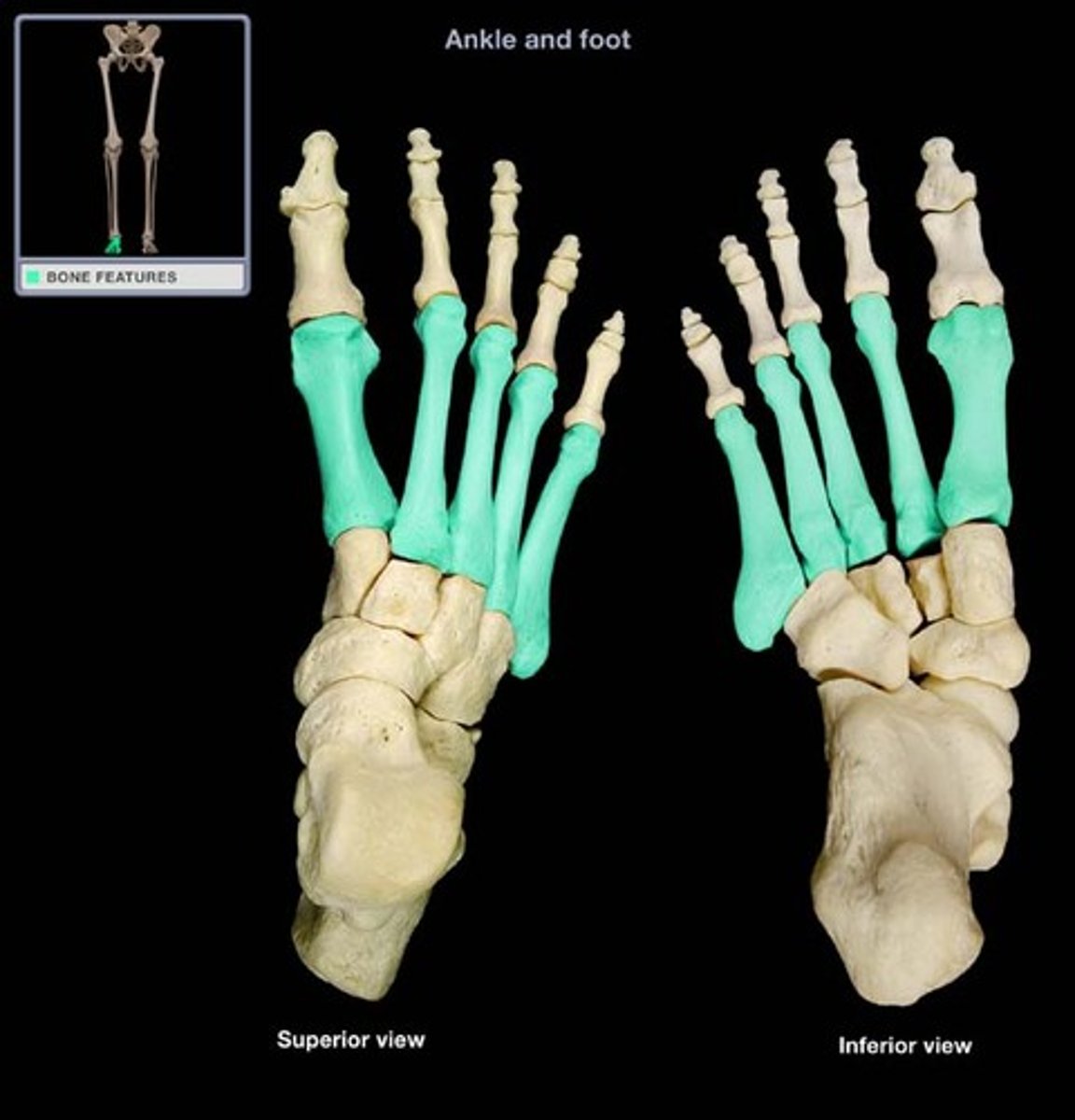
Identify and describe the metatarsal bones
long bones in the forefoot that connect the tarsal bones to the phalanges
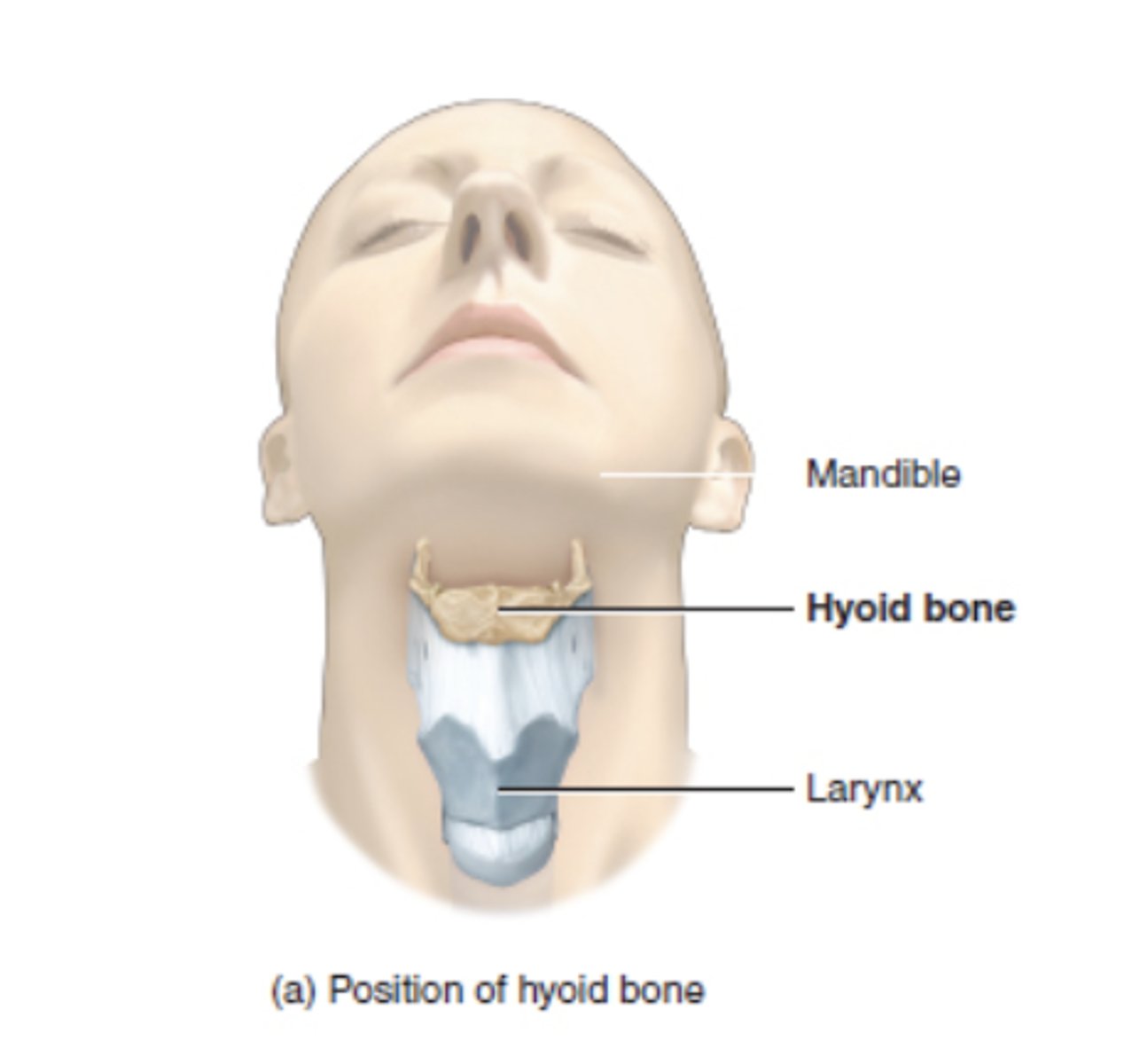
Identify where the hyoid bone is located
in front of the neck, below the jaw, and above the Adams apple
- at the level of C3-C4 vertebrae
- articulates with no other bone
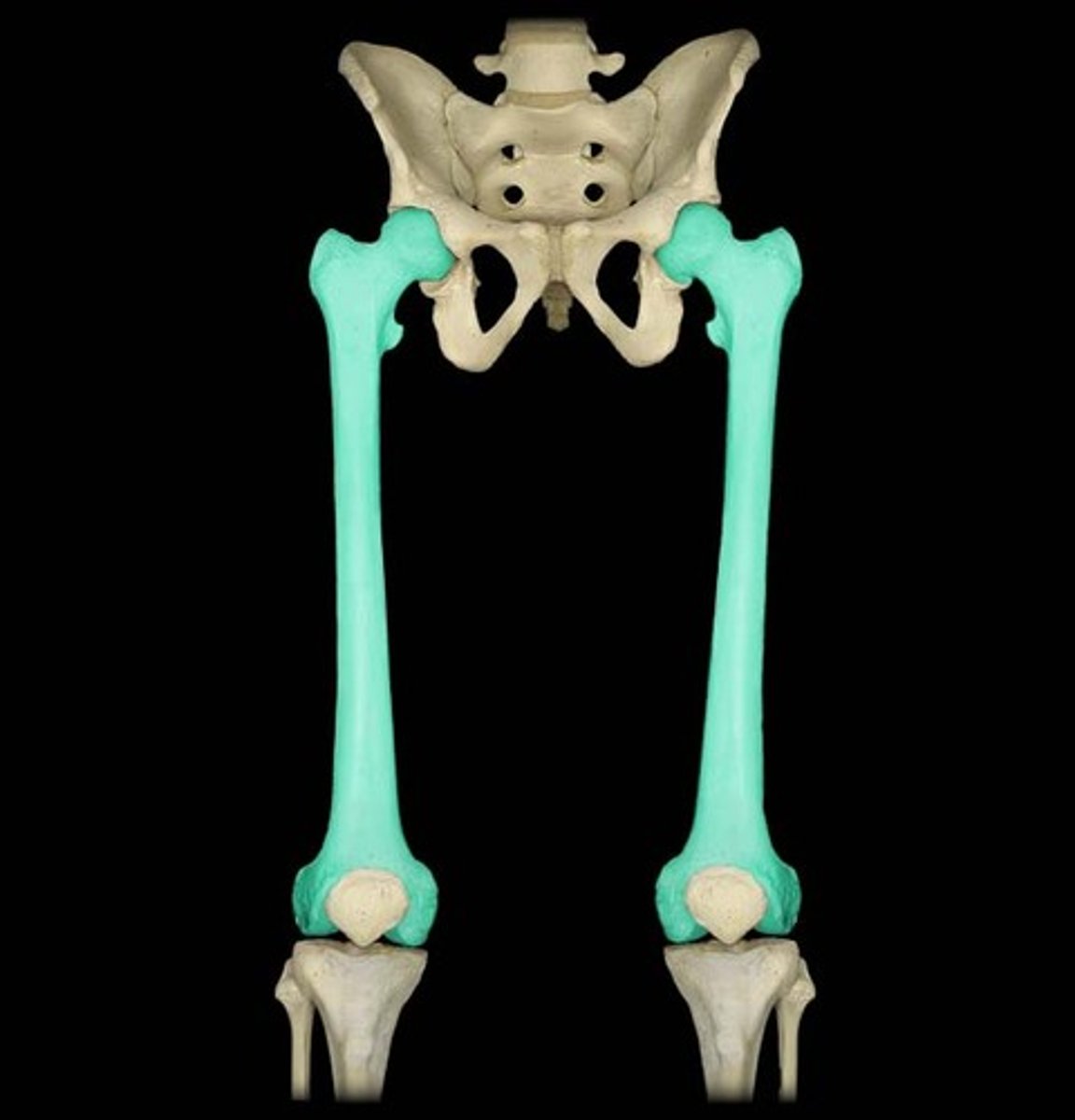
Identify where the femur is located
in the upper leg, extending from hip to knee
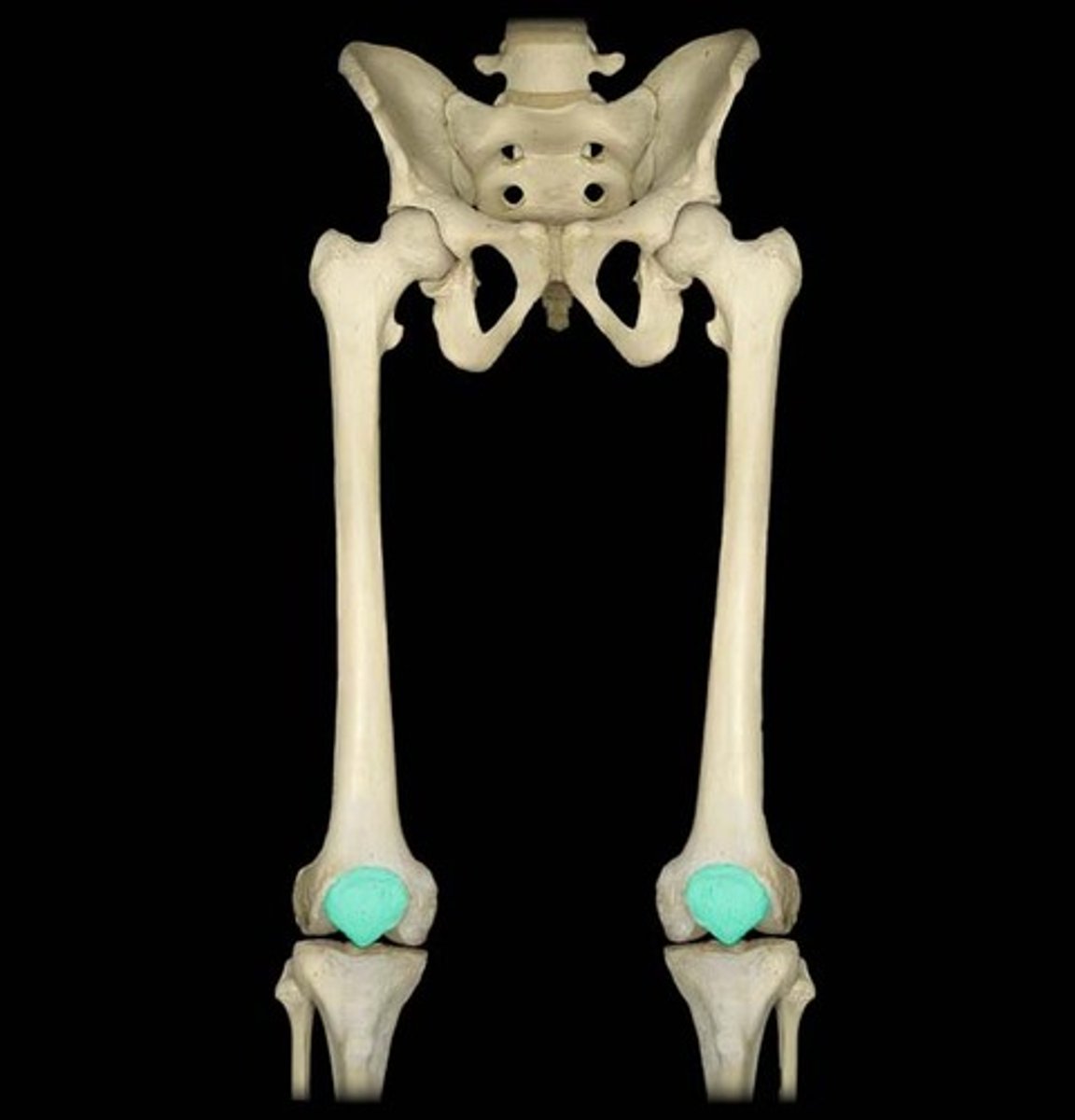
Identify where the patella is located
at the front of the knee joint, within the quadriceps tendon
- the kneecap
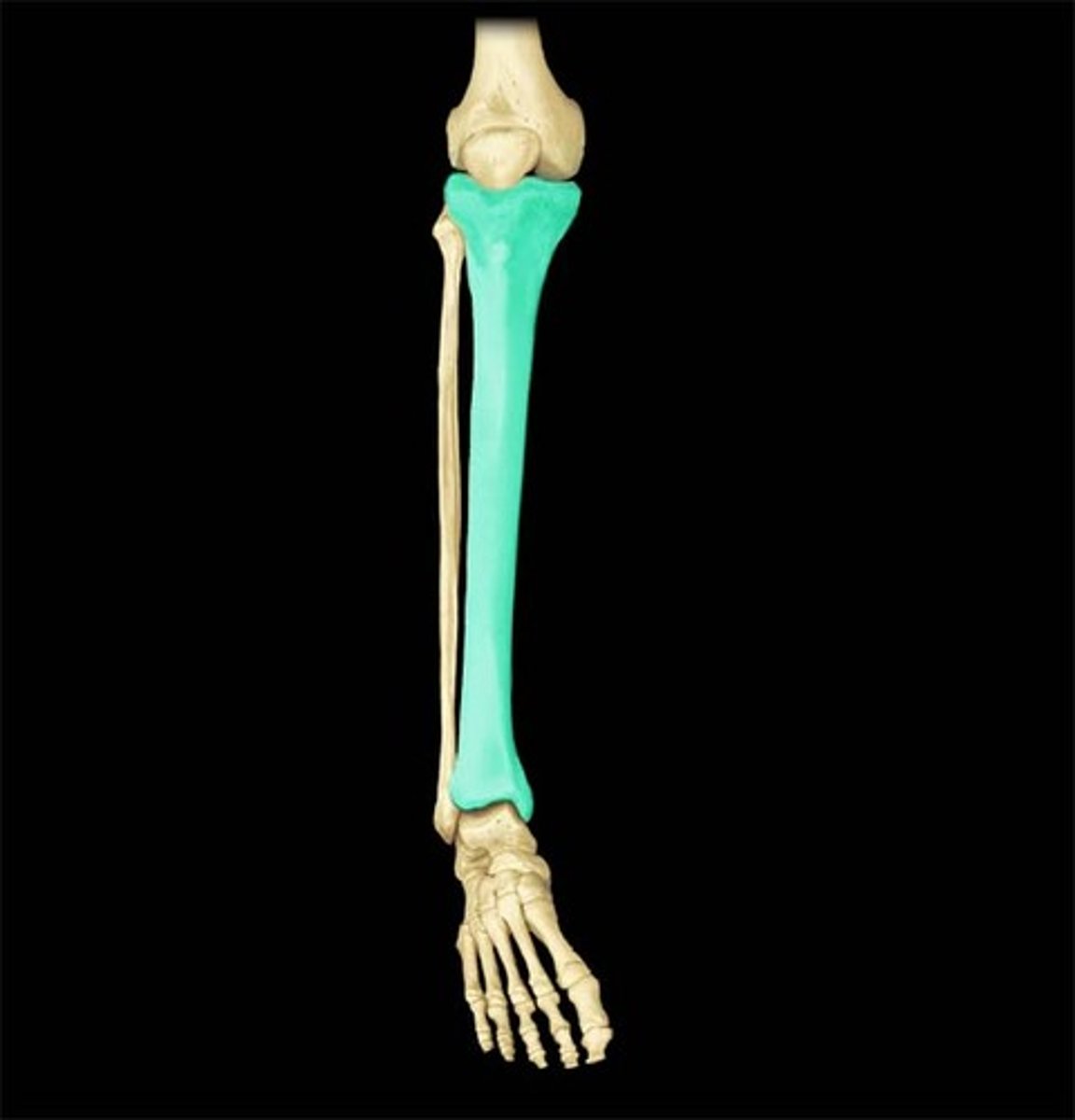
Identify where the tibia is located
larger of the shin bones, on the medial side, connecting the knee to the ankle
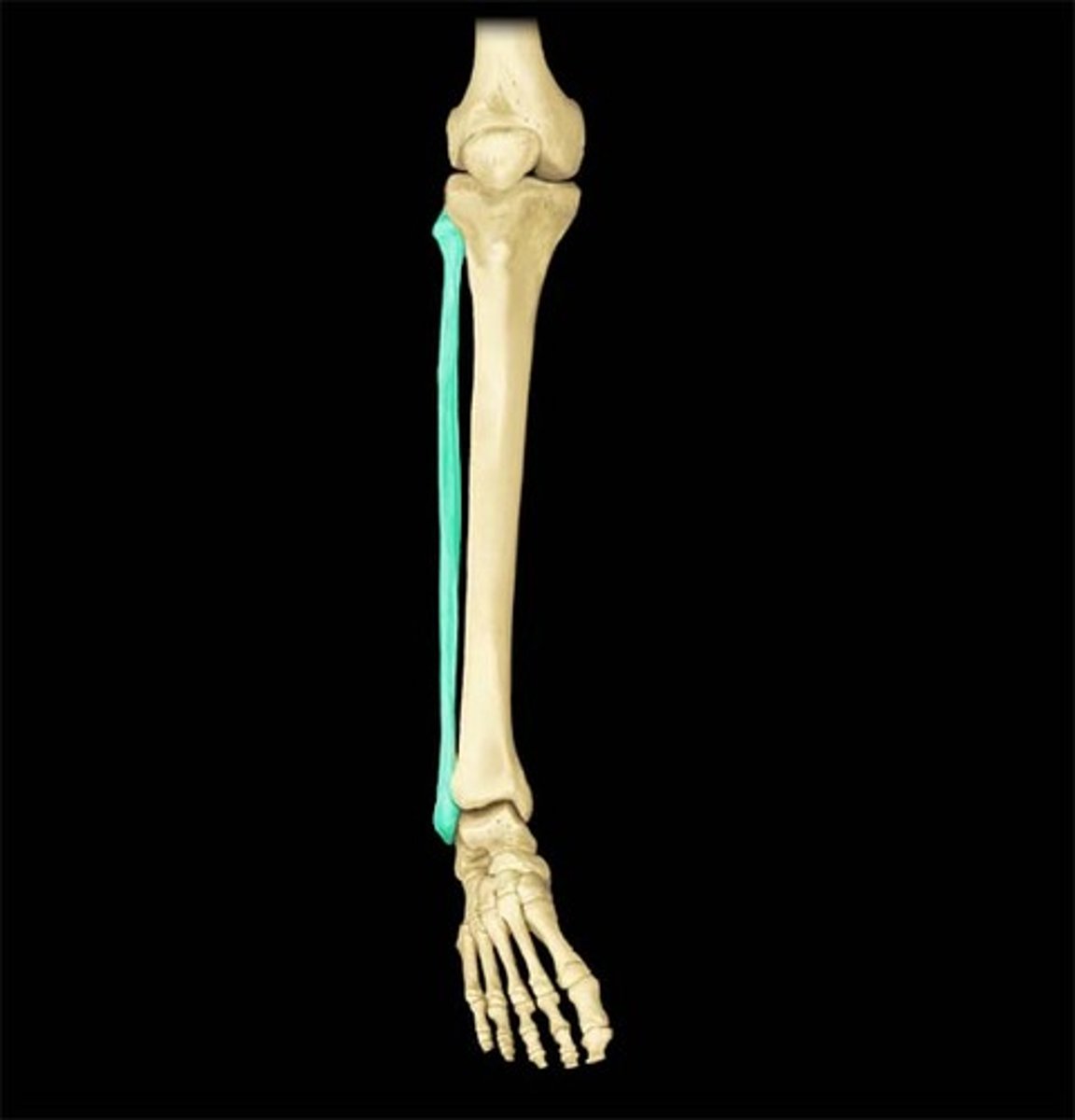
Identify where the fibula is located
skinnier shin bone, on the lateral side
Define excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle
-action potential travels along muscle fiber triggering the release of calcium ions from the SRI
- Release of the ions allows muscle filaments to interact and slide past one another
- causing the muscle to shorten
threshold stimulus
the minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a response
ex. action potential in a neuron or contraction in a muscle fiber
Define maximal stimulus
the minimum force required to recruit all motor units in a muscle, resulting in its maximum possible contraction
- opposite of threshold stimulus
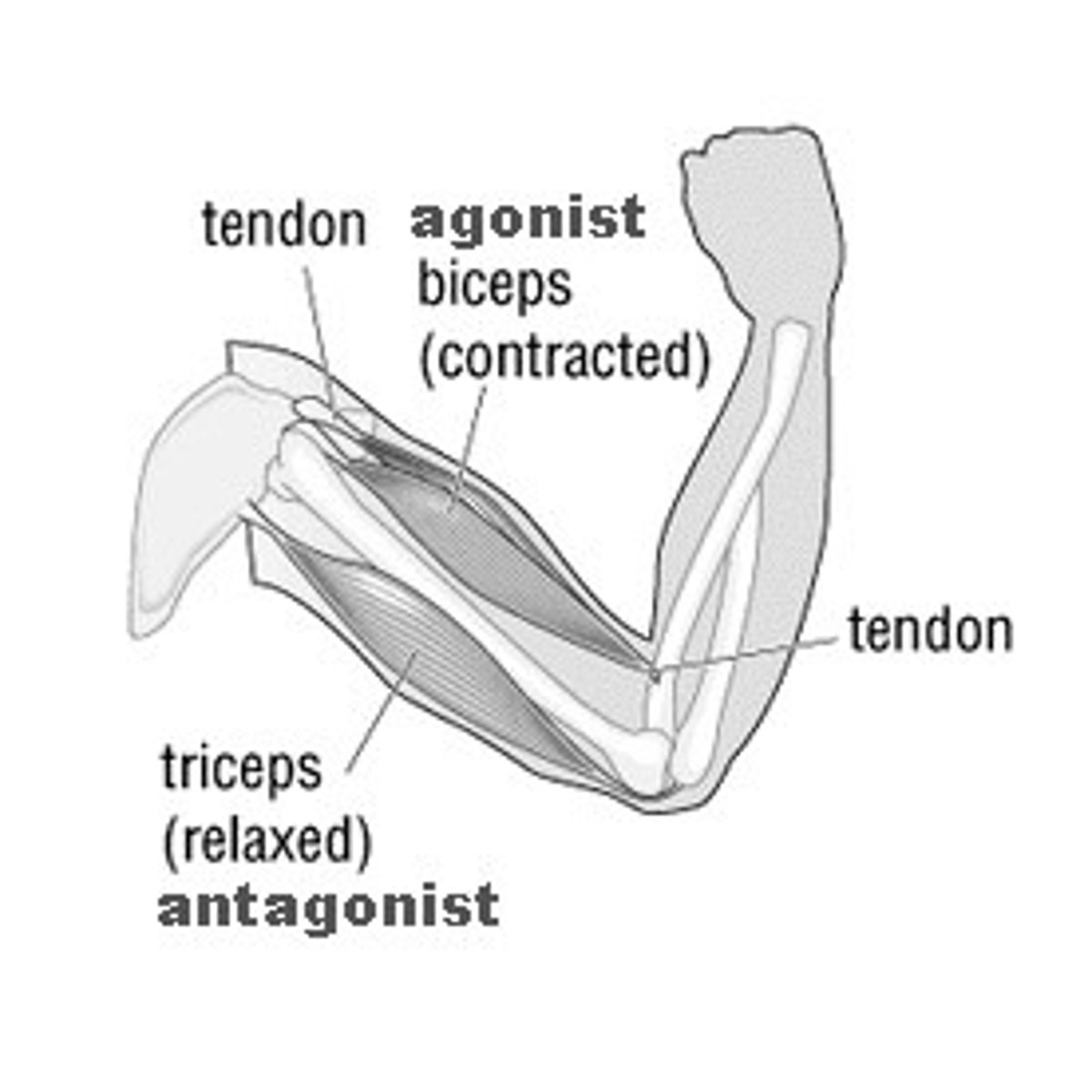
Define the prime mover (agonist), antagonist, and synergist muscles
prime mover (bicep) - provides main force for a movement
antagonist (tricep) - opposes action of agonist
synergist (brachialis brachii)- assists prime mover by stabilizing the joint or making movement more fluid/accurate
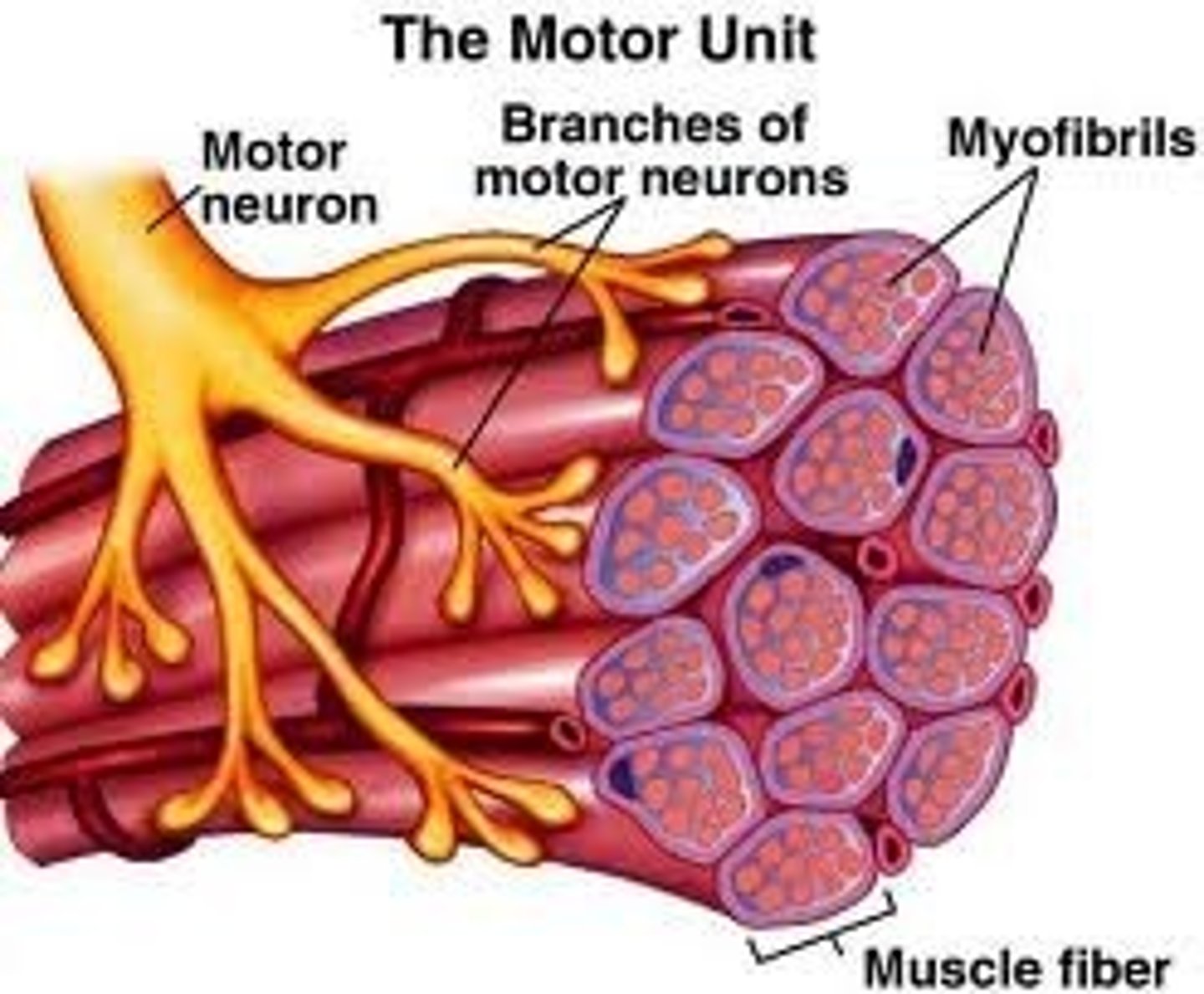
Define motor neuron
a nerve cell forming part of a pathway along which impulses pass from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland
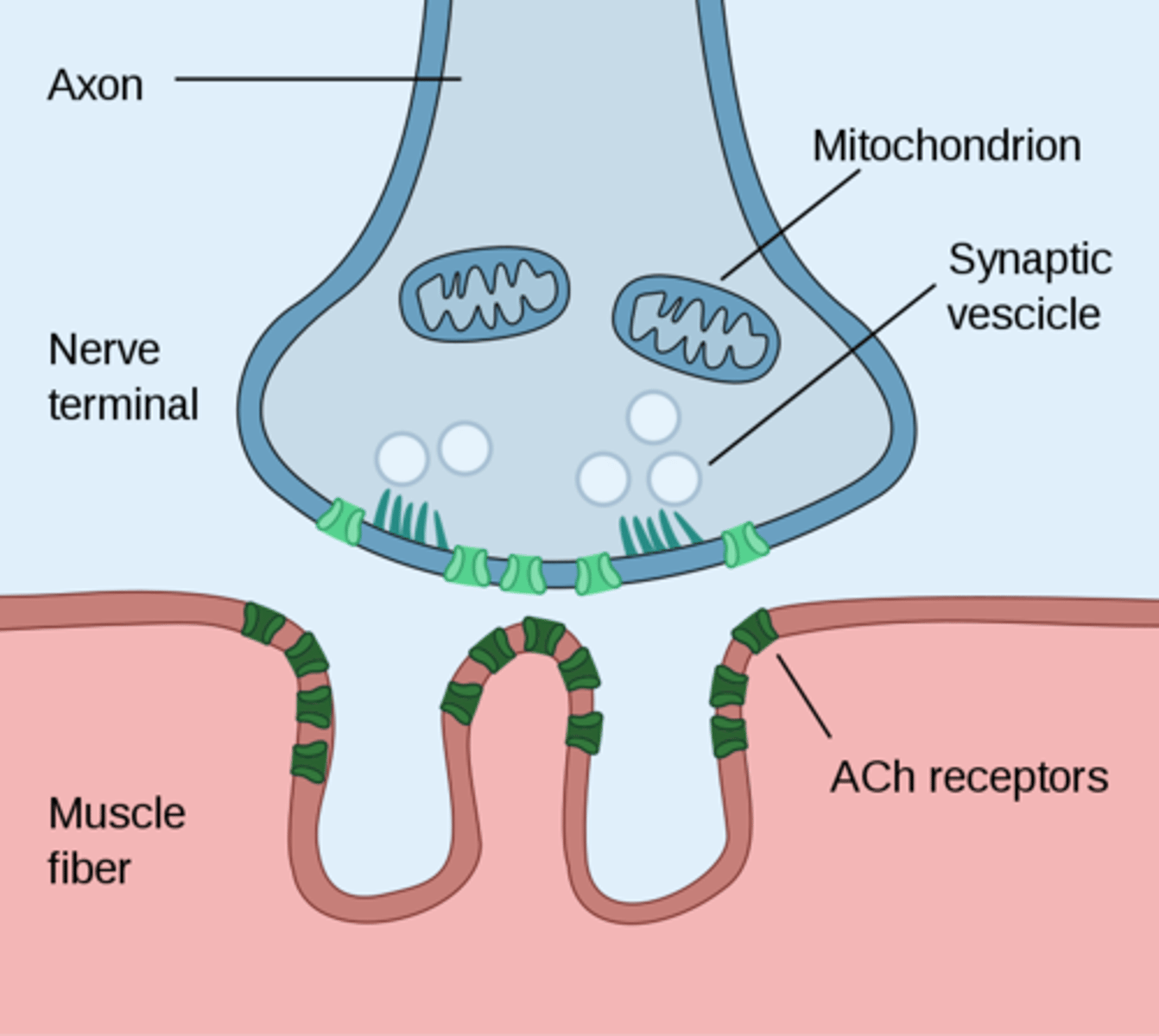
Define neuromuscular junction
specialized synapse where a motor neuron connects with a muscle fiber to transmit a signal, initiating muscle contraction
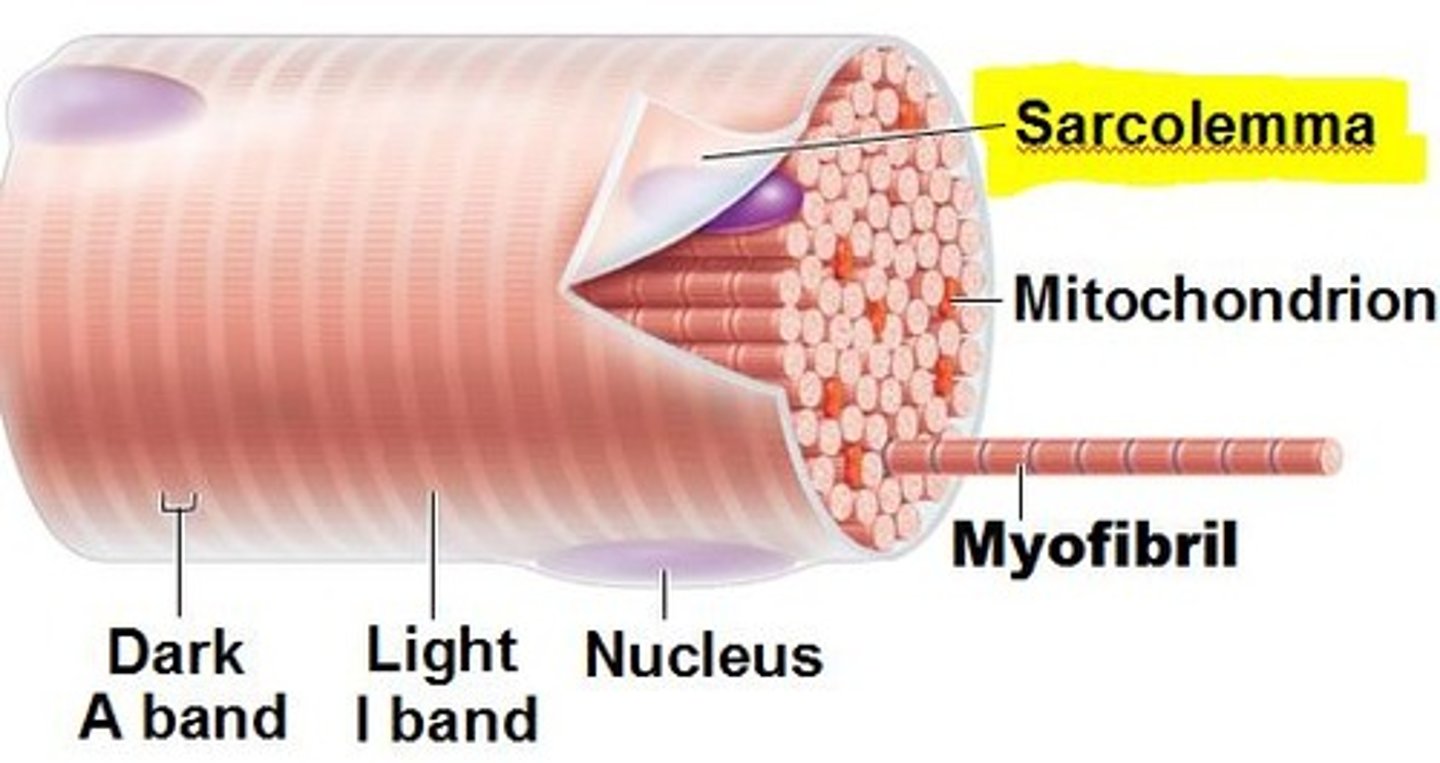
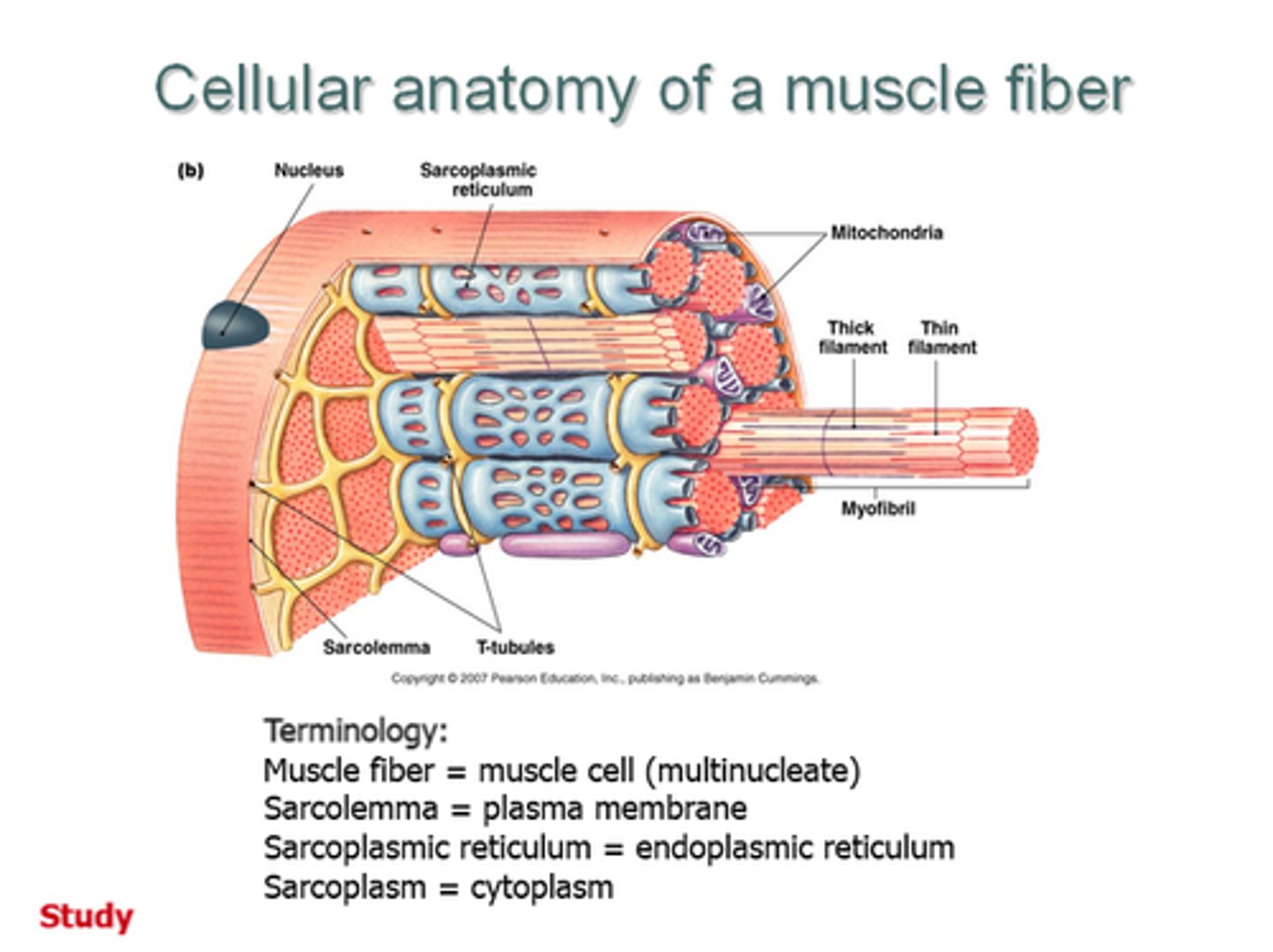
Define sarcolemma
tubular sheath which envelopes the fibers of skeletal muscles
Define sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells
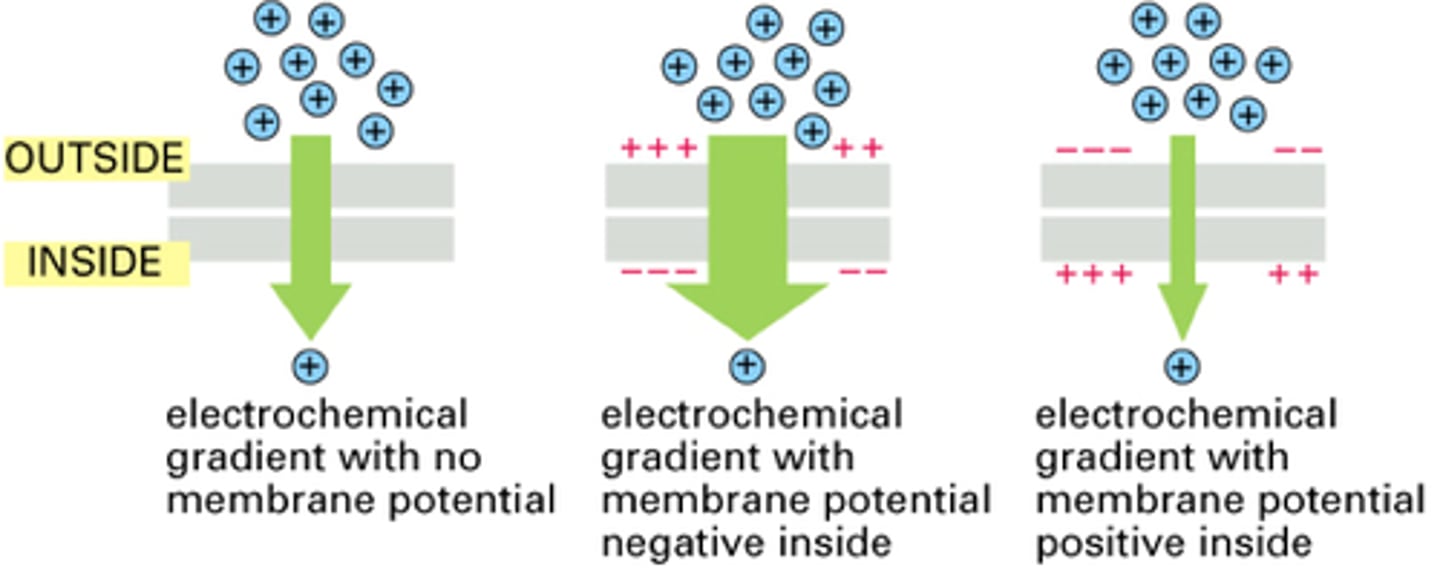
Define membrane potential
electric voltage difference across a cell's plasma membrane
- results from unequal distribution of ions (like sodium and potassium) between inside and outside of cell
Define action potential
a rapid, temporary change in the electrical potential across a cell membrane
- also called a nerve impulse or "spike"
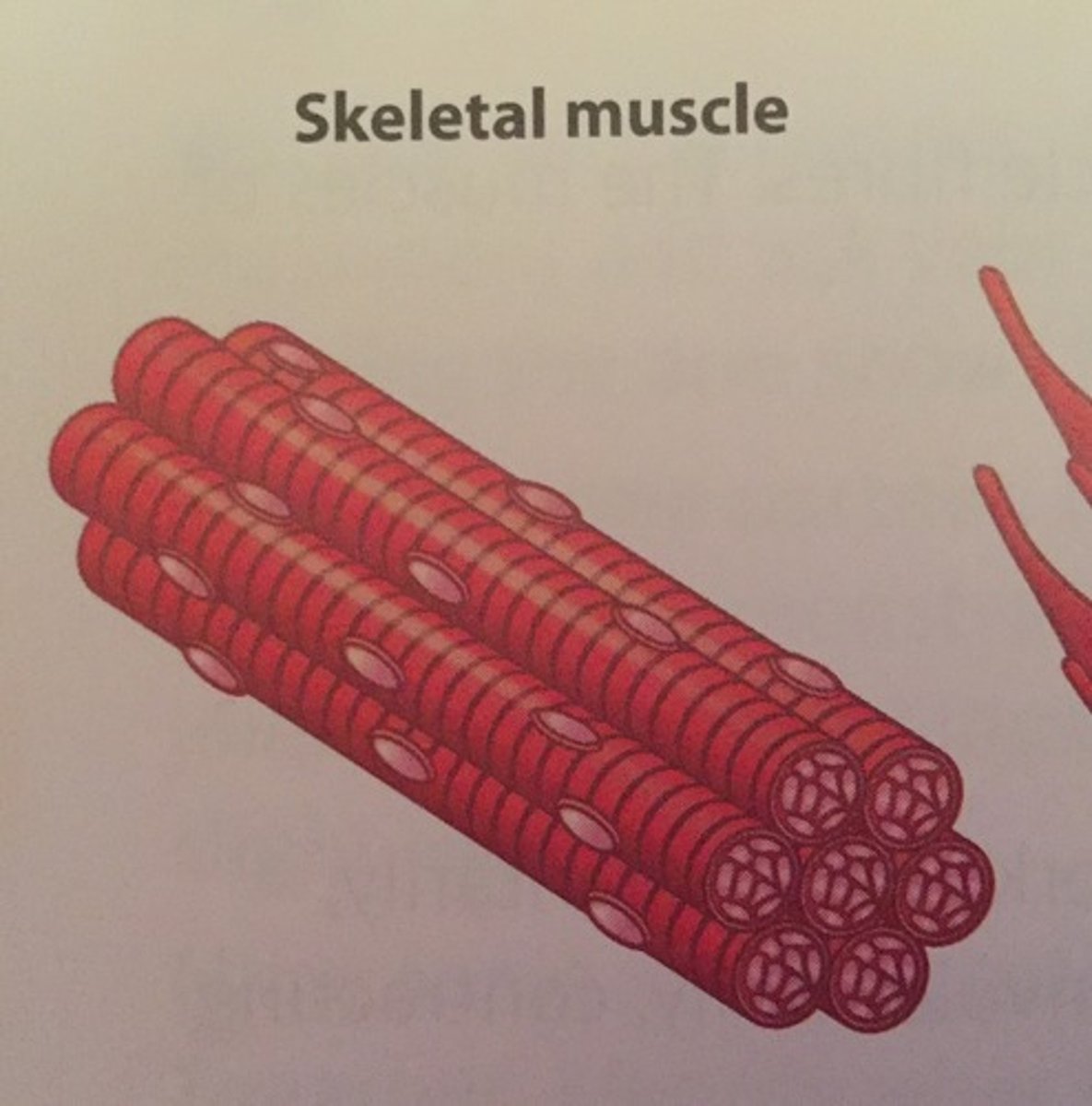
Describe skeletal muscle tissue
- voluntary contractions
- striated and multinucleate
- attached to bones
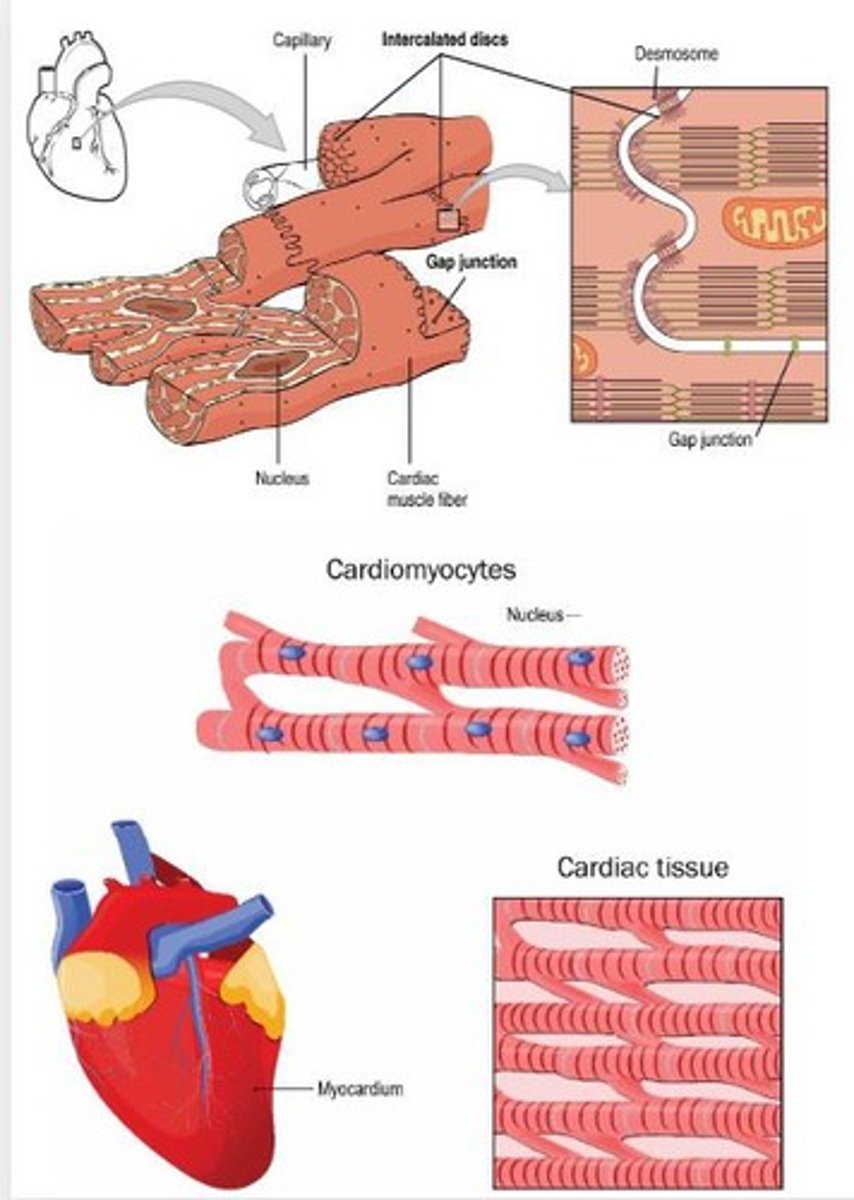
Describe cardiac muscle tissue
- involuntary contractions
- striated, intercalated discs
- found only in heart
Describe smooth muscle tissue
- involuntary contractions
- non striated
- found In walls of organs, blood vessels, and the eye
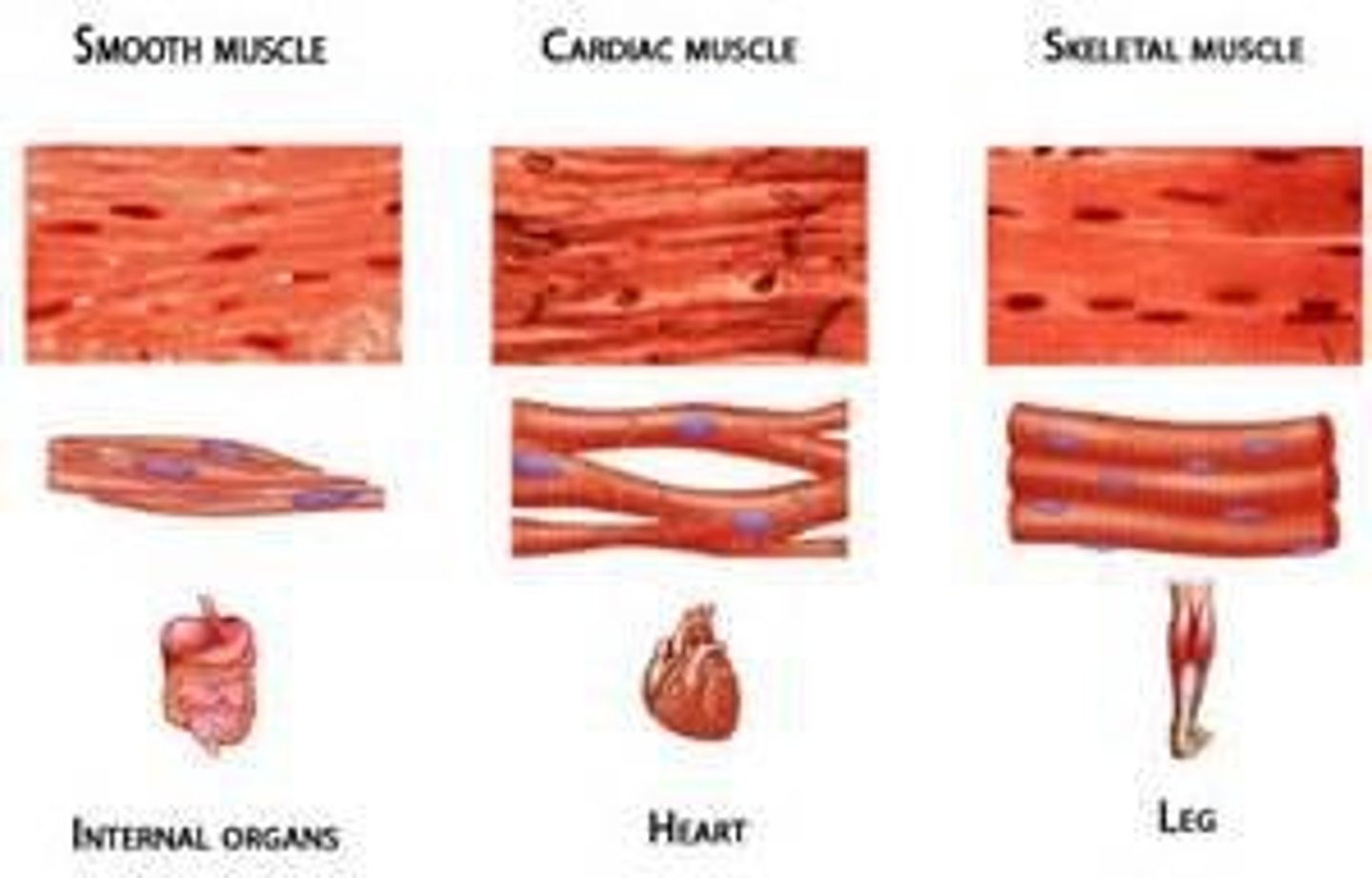
Describe involuntary vs voluntary muscle
involuntary are not under our conscious control, can't make them contract when we think about to (heart muscles)
voluntary ARE under our conscious control (limbs and overall outer physical movement)
Describe the functions of skeletal muscle tissue
- move the body
- maintain posture
- protect and support
- regulate elimination of materials
- produce heat
Define sarcomere
smallest contractile unit of muscle
- generates contractile force in muscle fibers
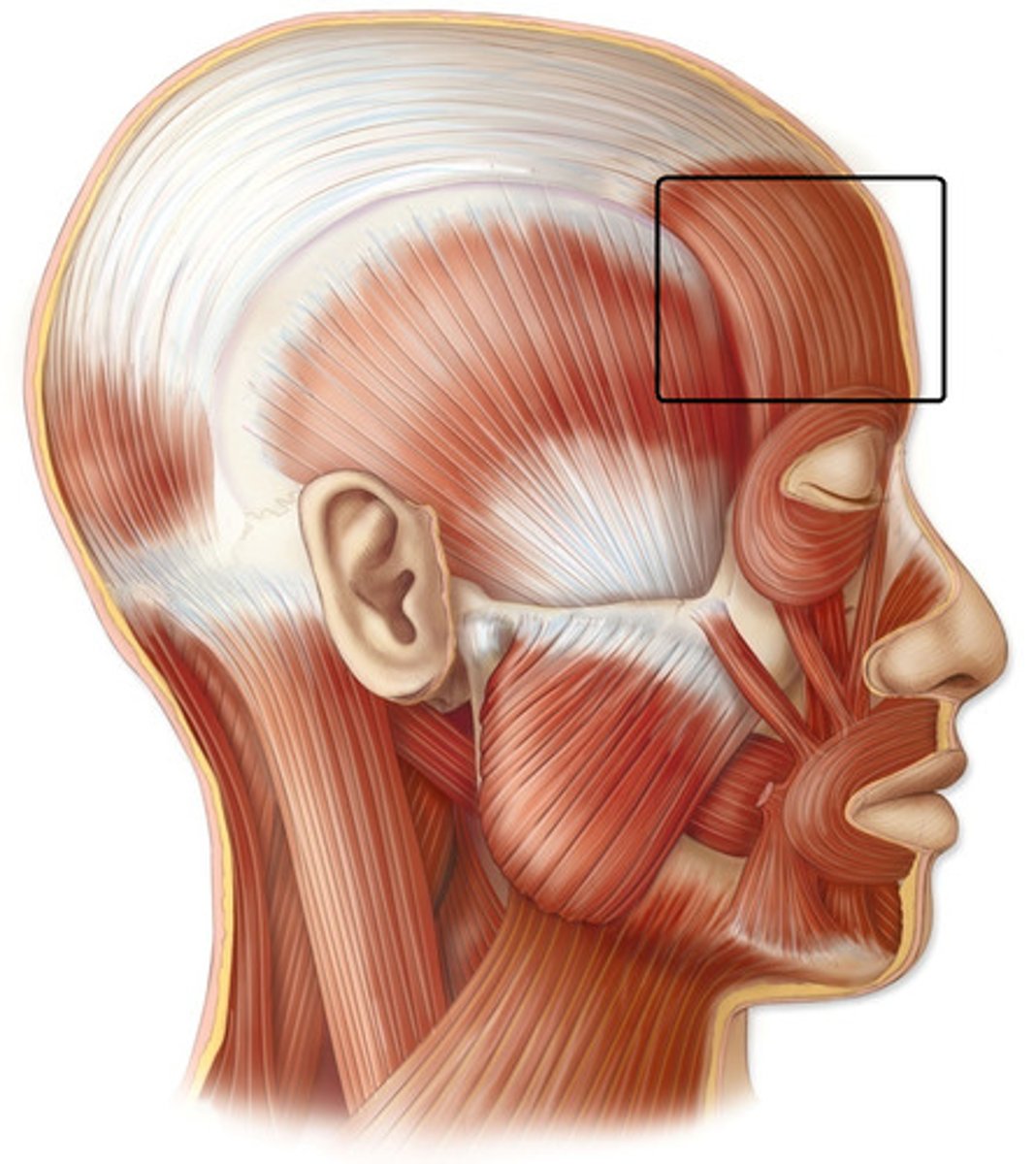
Identify the frontalis muscle
muscle located on front of the head in the forehead
- raises eyebrows, wrinkles the skin of forehead, and pulls scalp forward
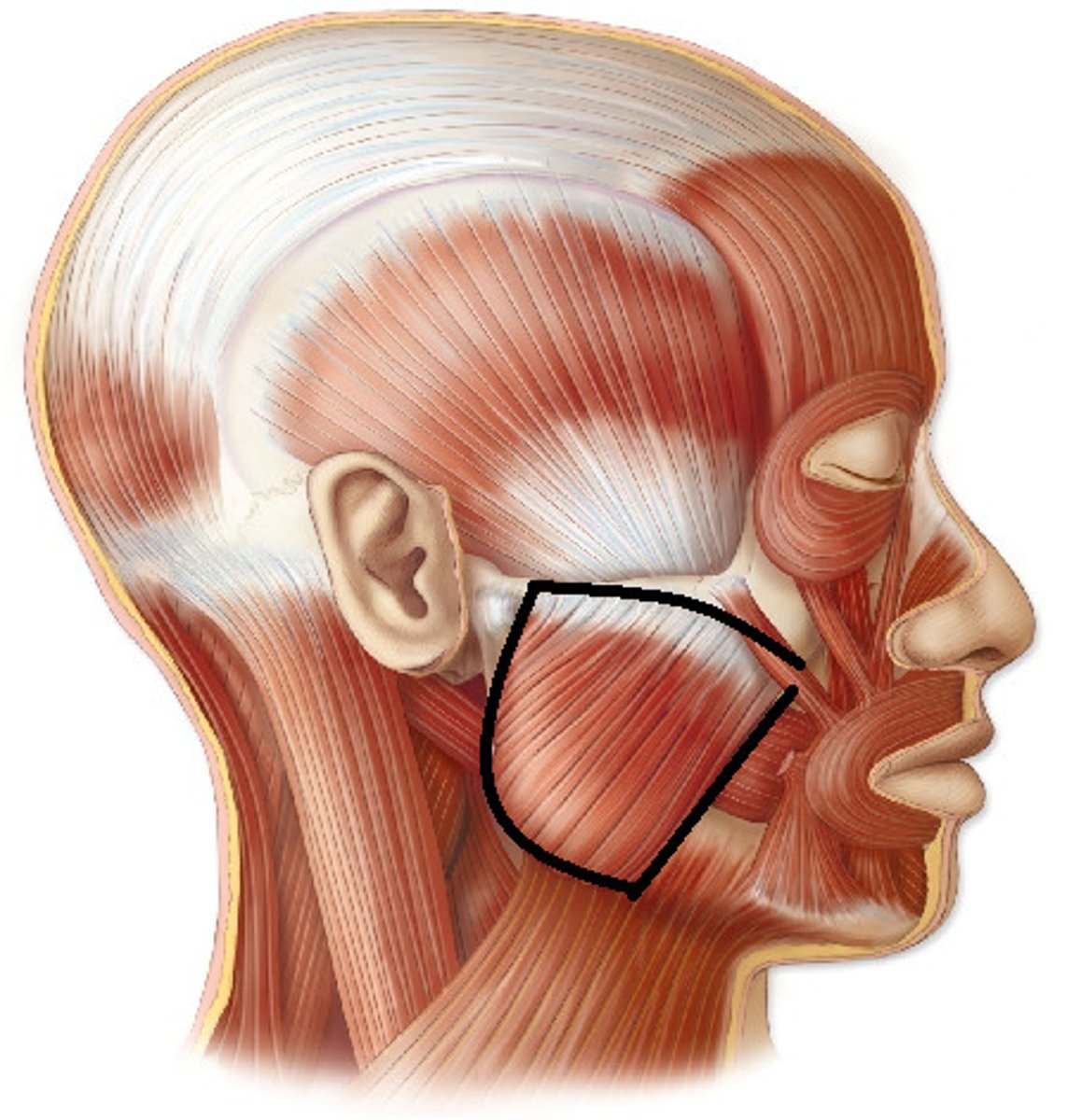
the masseter muscle
muscle located on each side of the jaw in the cheek area
- responsible for chewing
the nasalis muscle
pair of facial muscles located on the nose
- changes the size of the nostrils
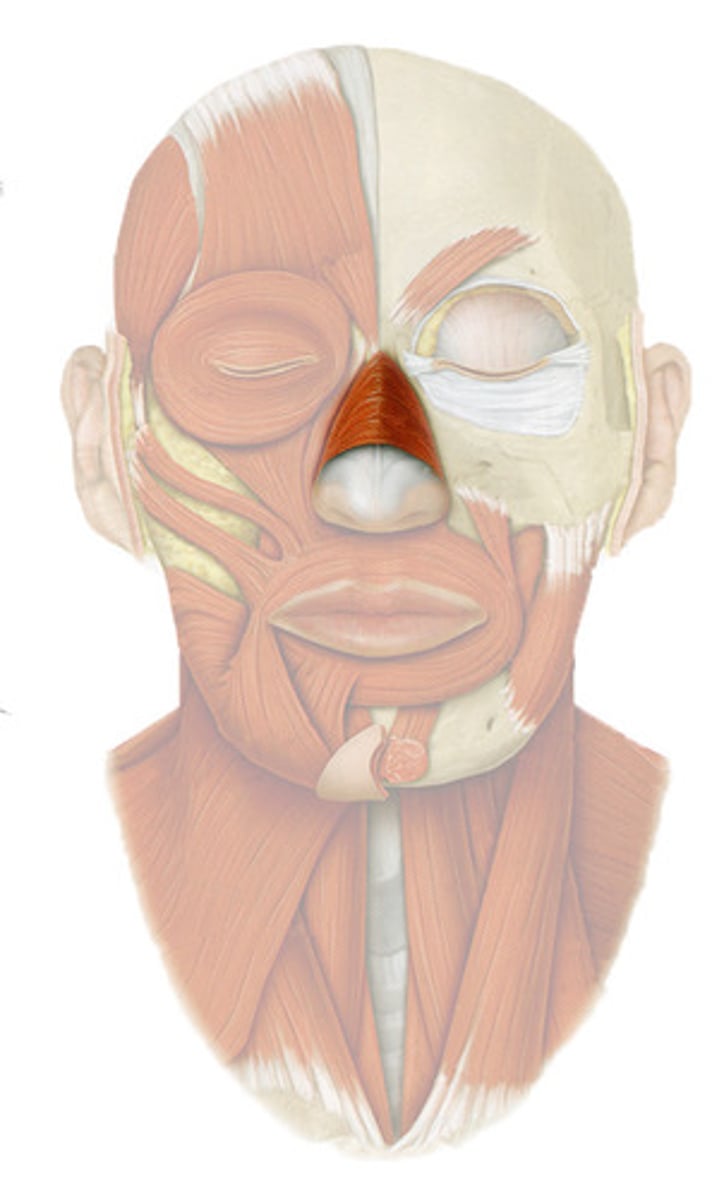
Identify the orbicularis oculi/oris muscles
circular muscles around the eye (oculi) and the mouth (oris)
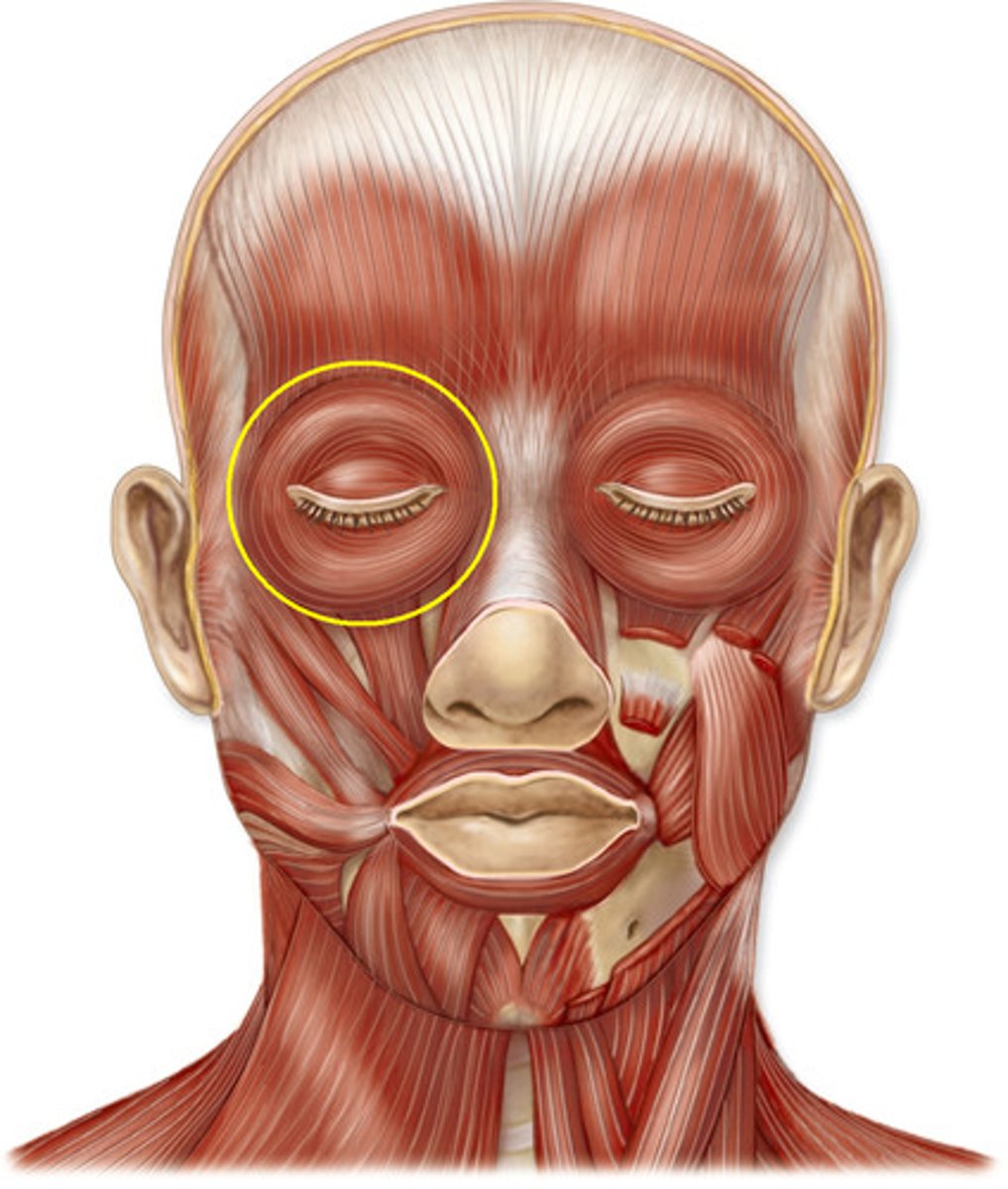
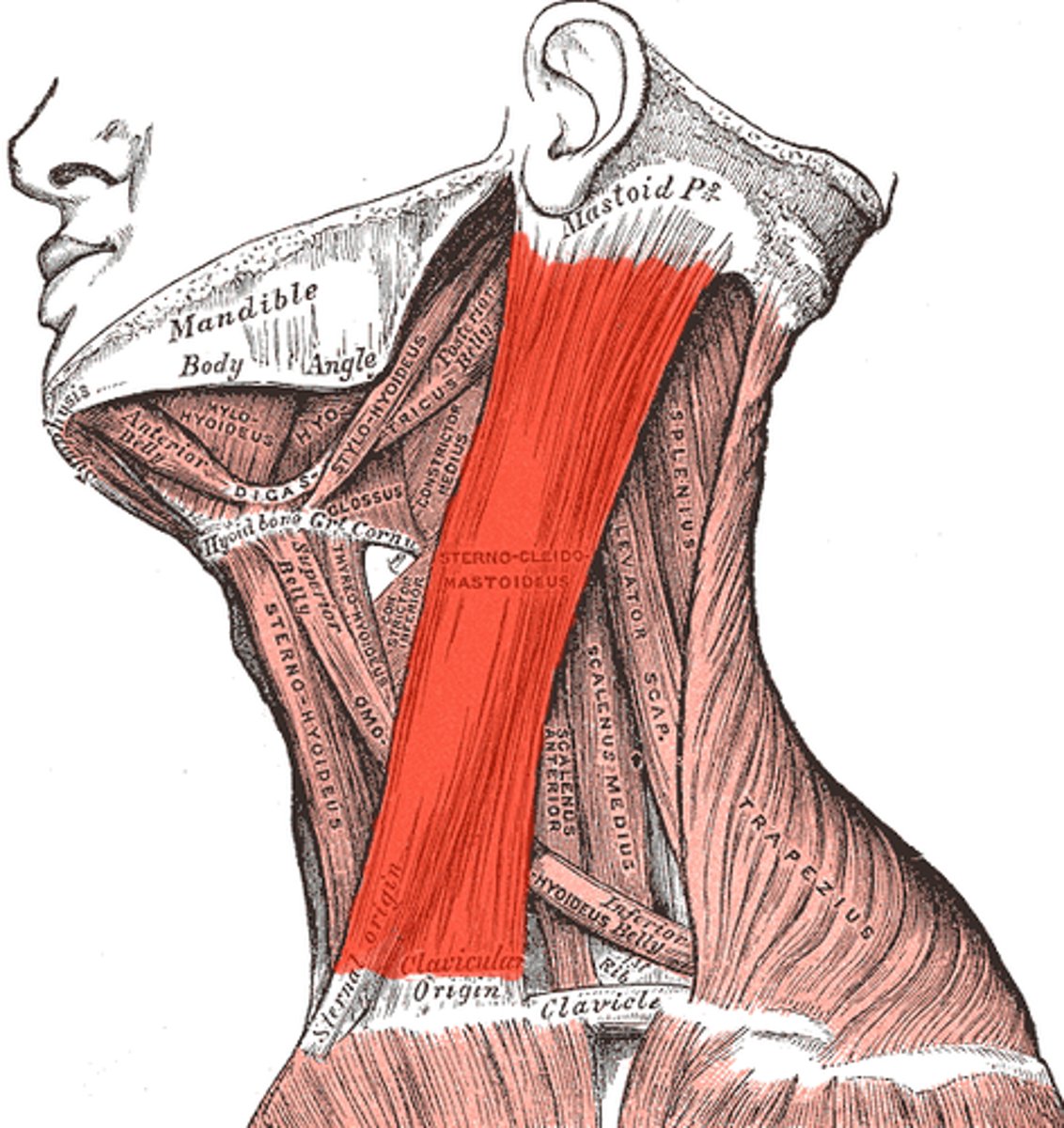
Identify the sternocleidomastoid muscle
a large, superficial muscle in the neck that runs from the sternum and clavicle to the mastoid process of the skull
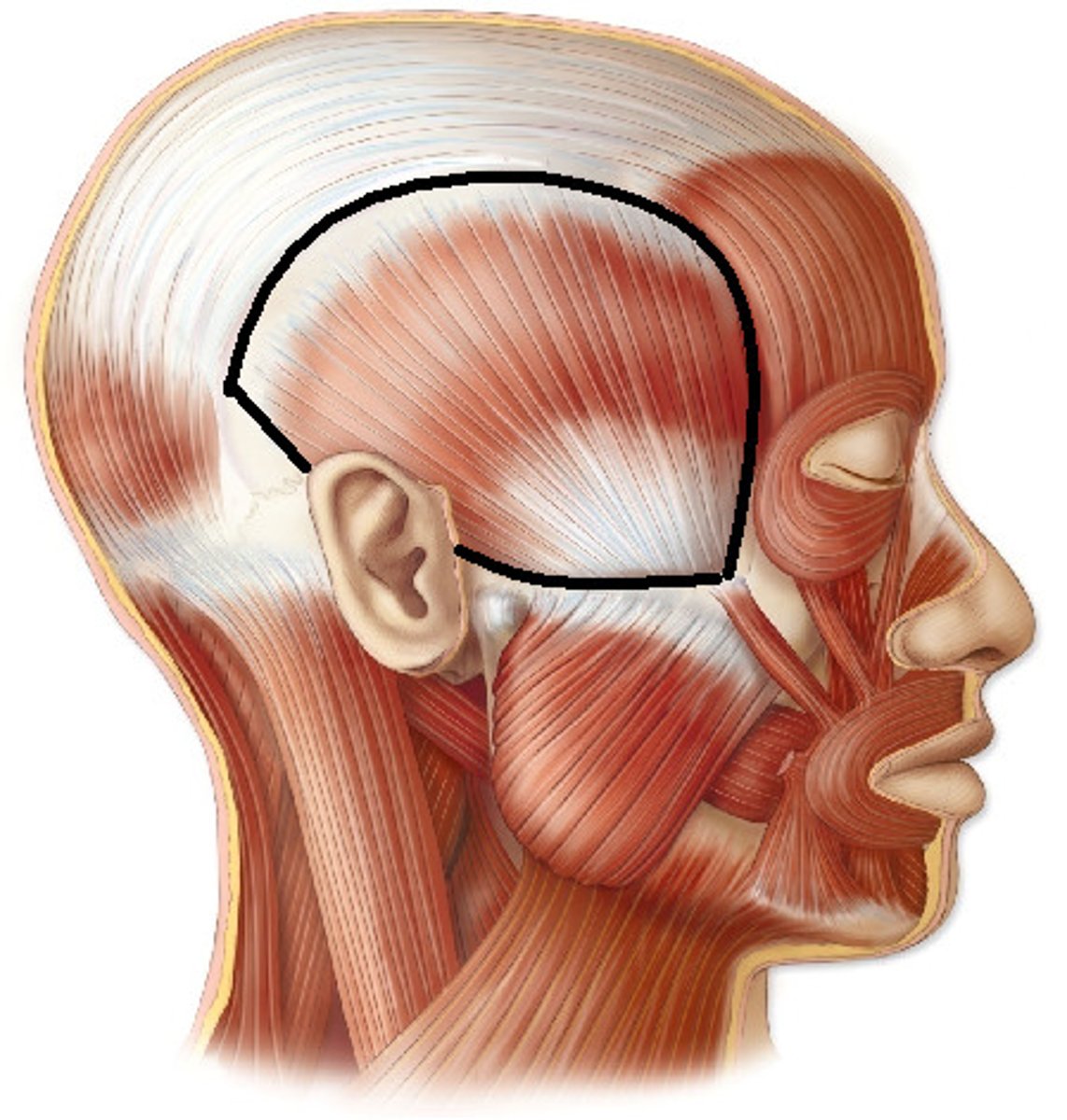
Identify the temporalis muscles
large, fan shaped muscles located on the side of the head
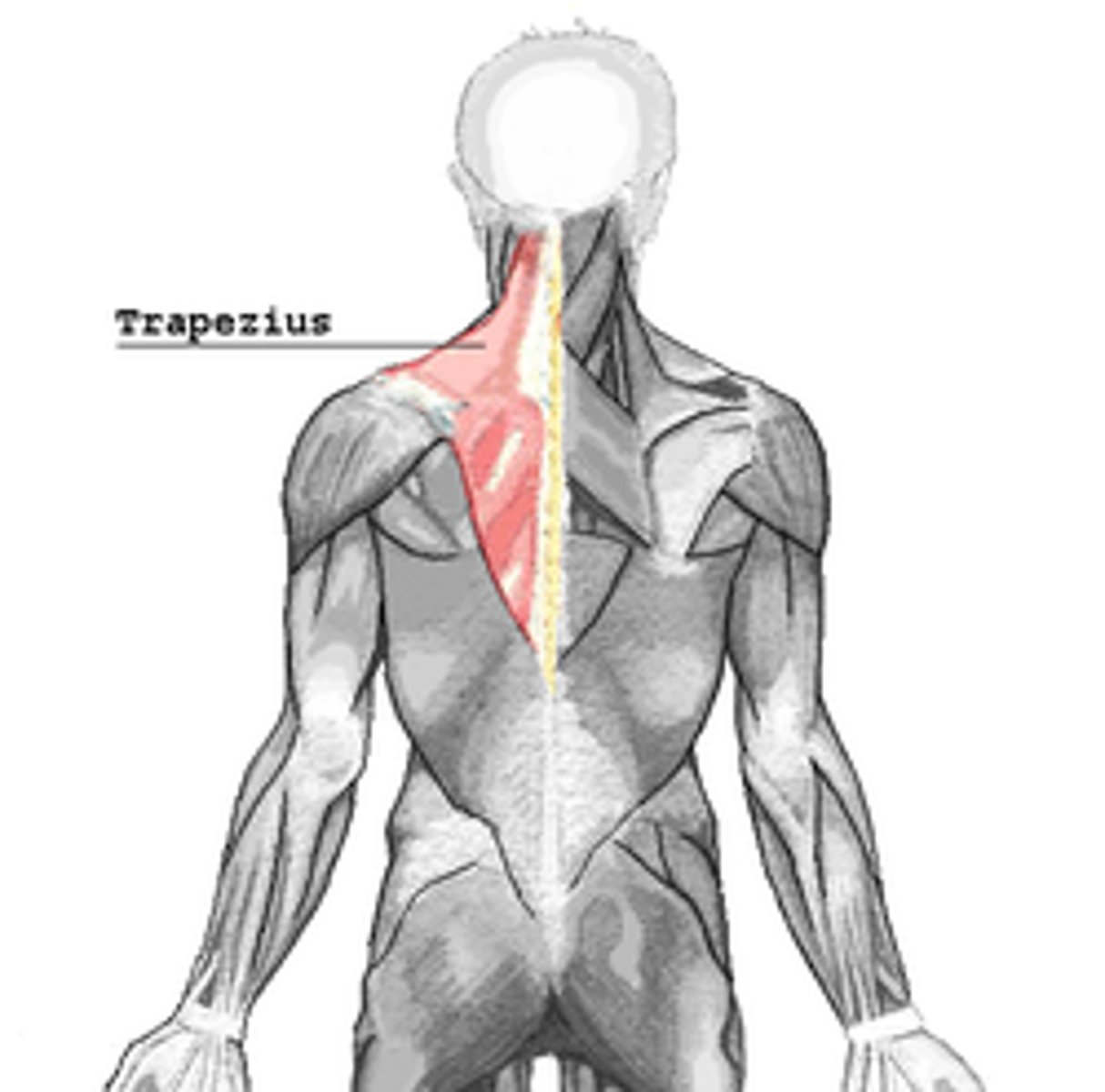
Identify the trapezius muscles
a large, triangular muscle on the upper back and neck
the external abdominal oblique muscle
a wide, thin muscle located on the side of the abdomen
- runs diagonally downward and forward
- outer surface of lower 8 abs
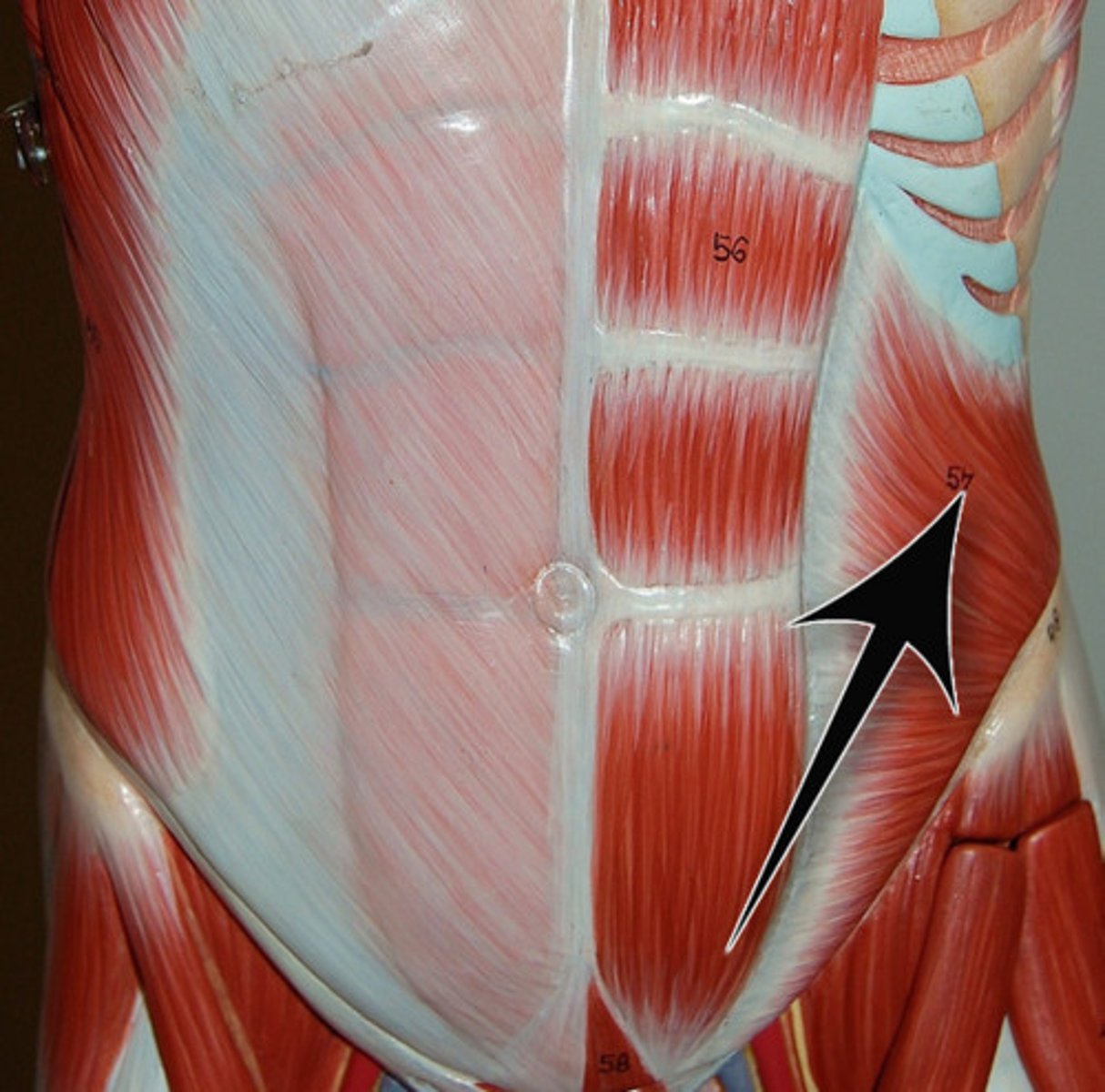
Identify the internal abdominal oblique muscle
a broad, thin muscle of the anterolateral abdominal wall
- directly underneath the external oblique
- superficial to the transverse abdominis
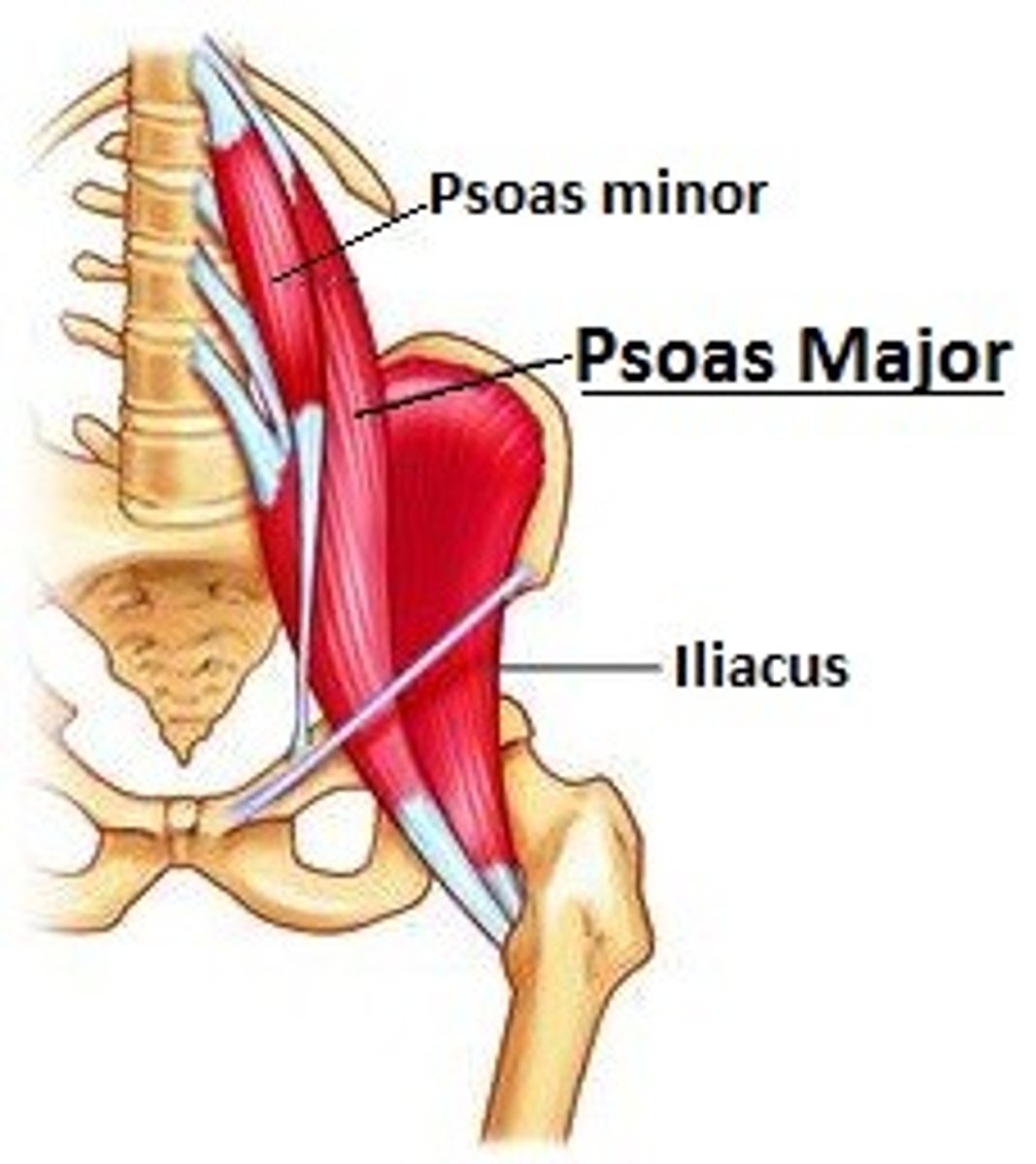
Identify the psoas major muscle
a long, deep muscle in the lower back
- connects the lumbar vertebrae to the inner thigh bone (femur)
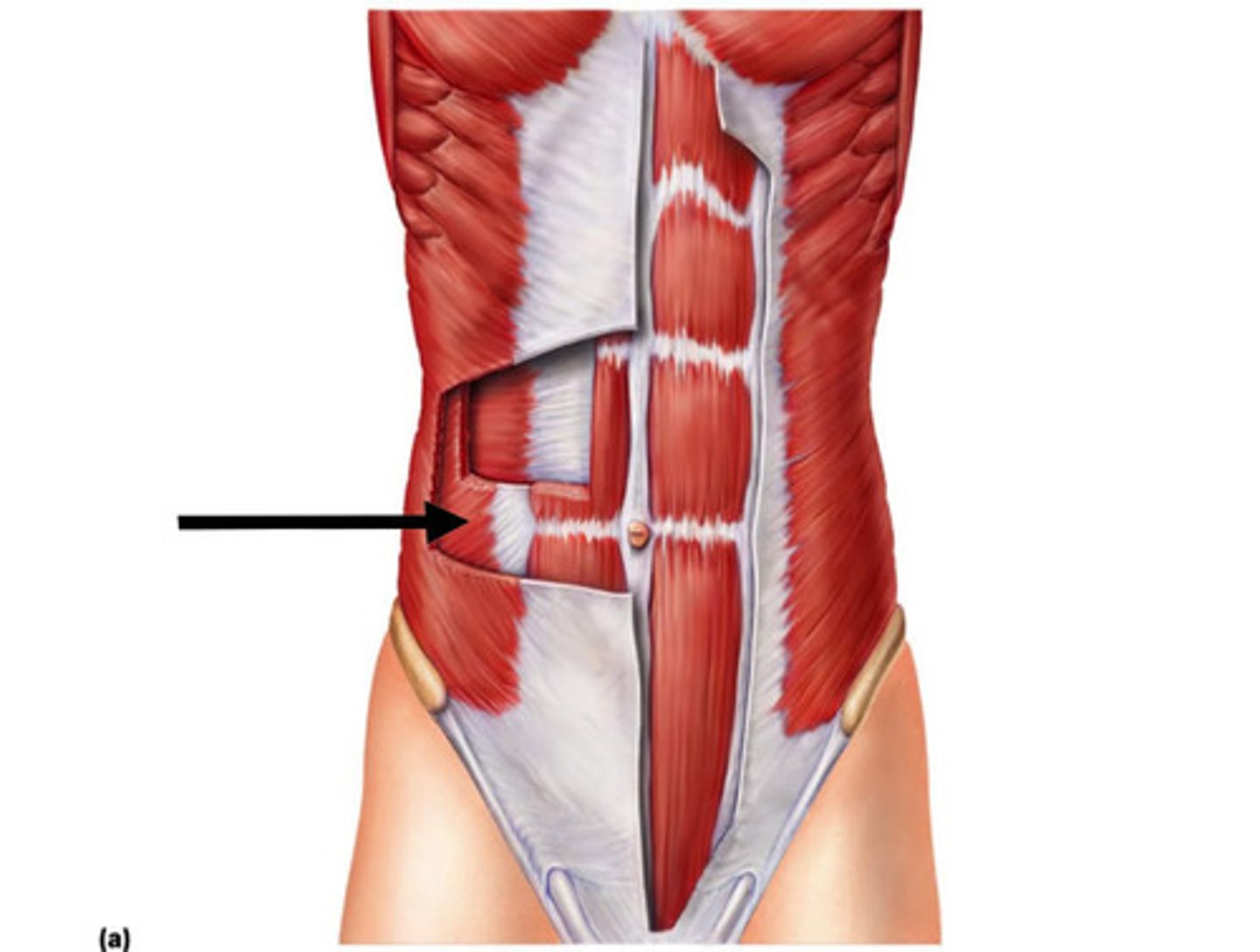
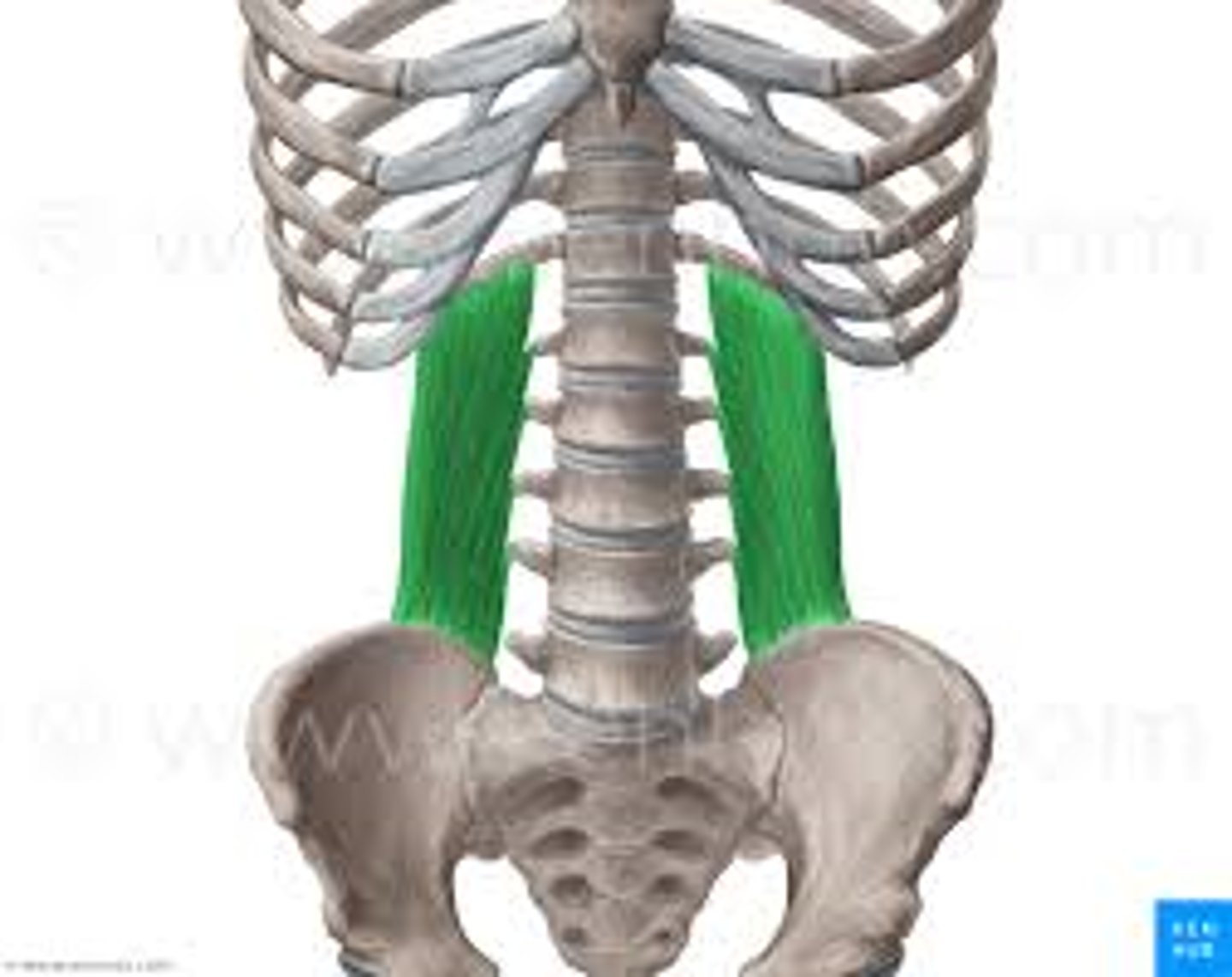
identify the quadratus lumborum muscle
a deep, flat muscle located in the lower back, lateral to the spine
Identify the rectus abdominis muscle
the six pack abs
a long, paired muscle that runs vertically along the front of the abdomen
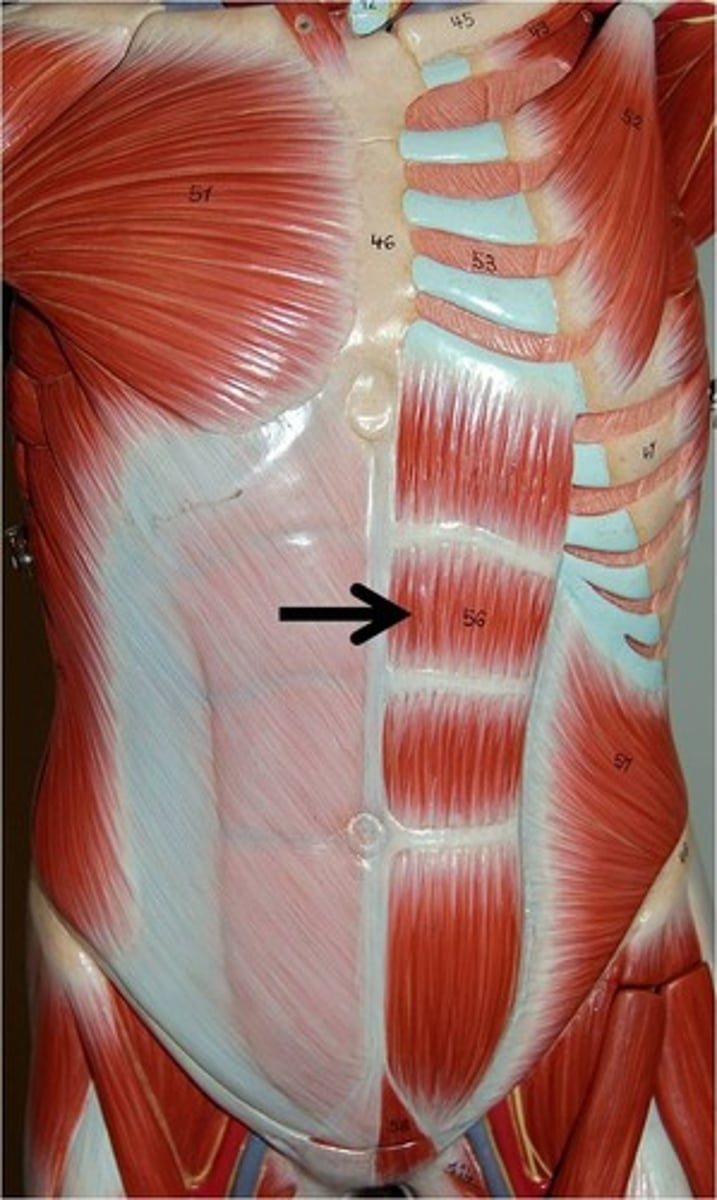
Identify the tendinous intersections of the rectus abdominis
three horizontal fibrous bands that divide the muscle into segments
- give abs their separated appearance
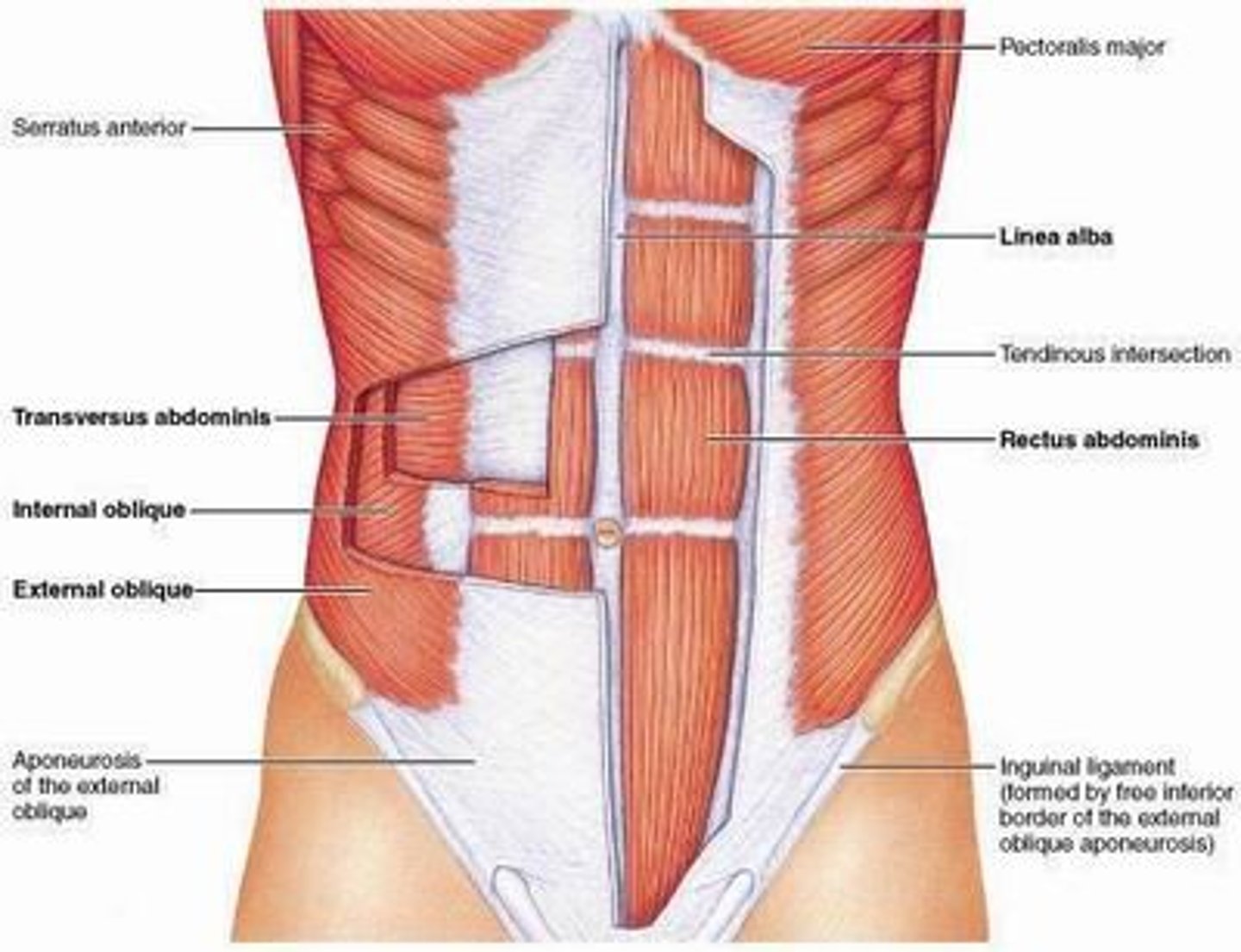
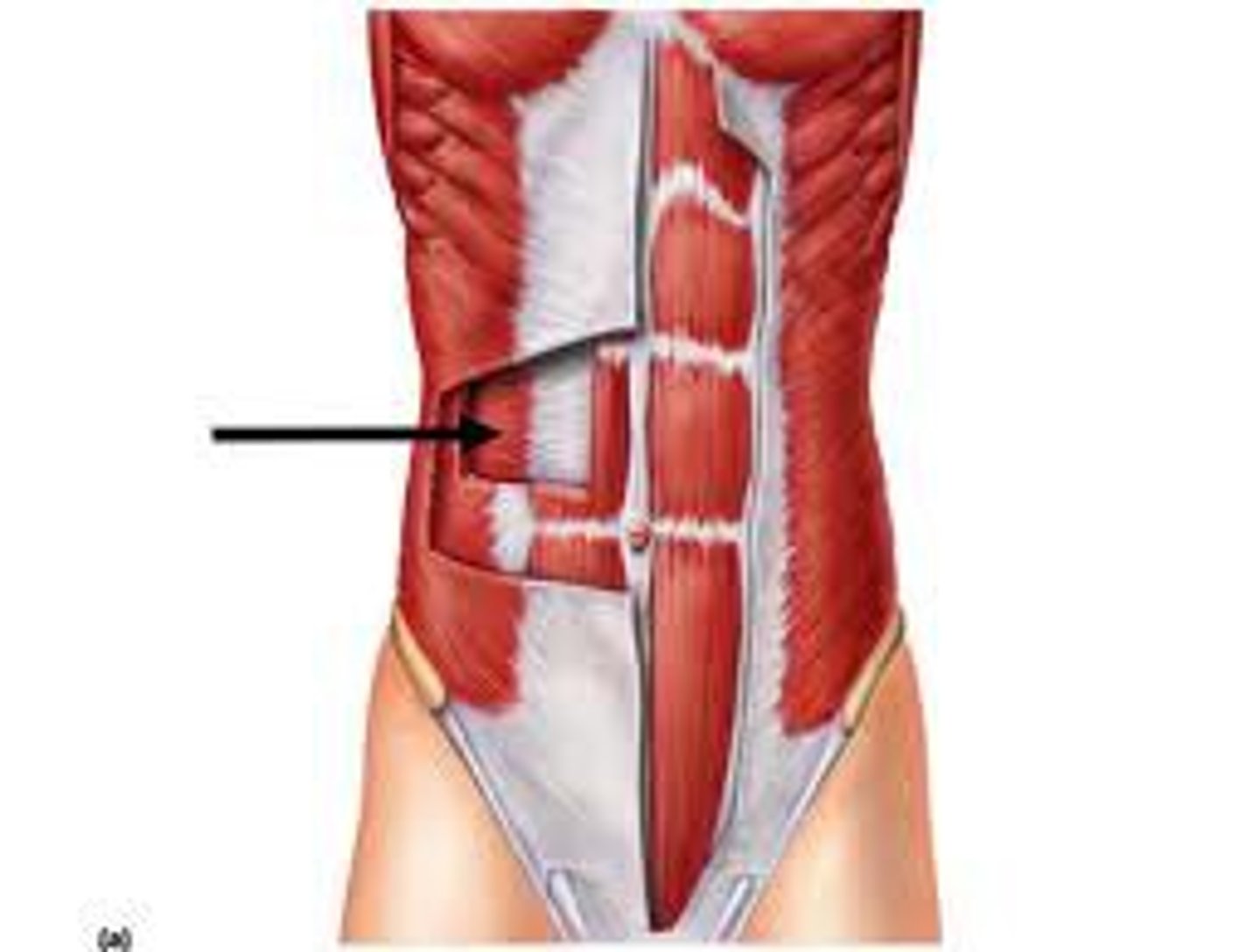
Identify transverse abdominis muscle
deepest abdominal muscle, beneath the internal oblique
- wrap around the torso like a corset
Identify the umbilicus muscle
belly button
the point on the abdominal wall formed by convergence of muscles and fascia
Identify the deltoid muscle
shoulder muscle
large, triangular muscle that forms the rounded contour of the shoulder and covers the shoulder joint
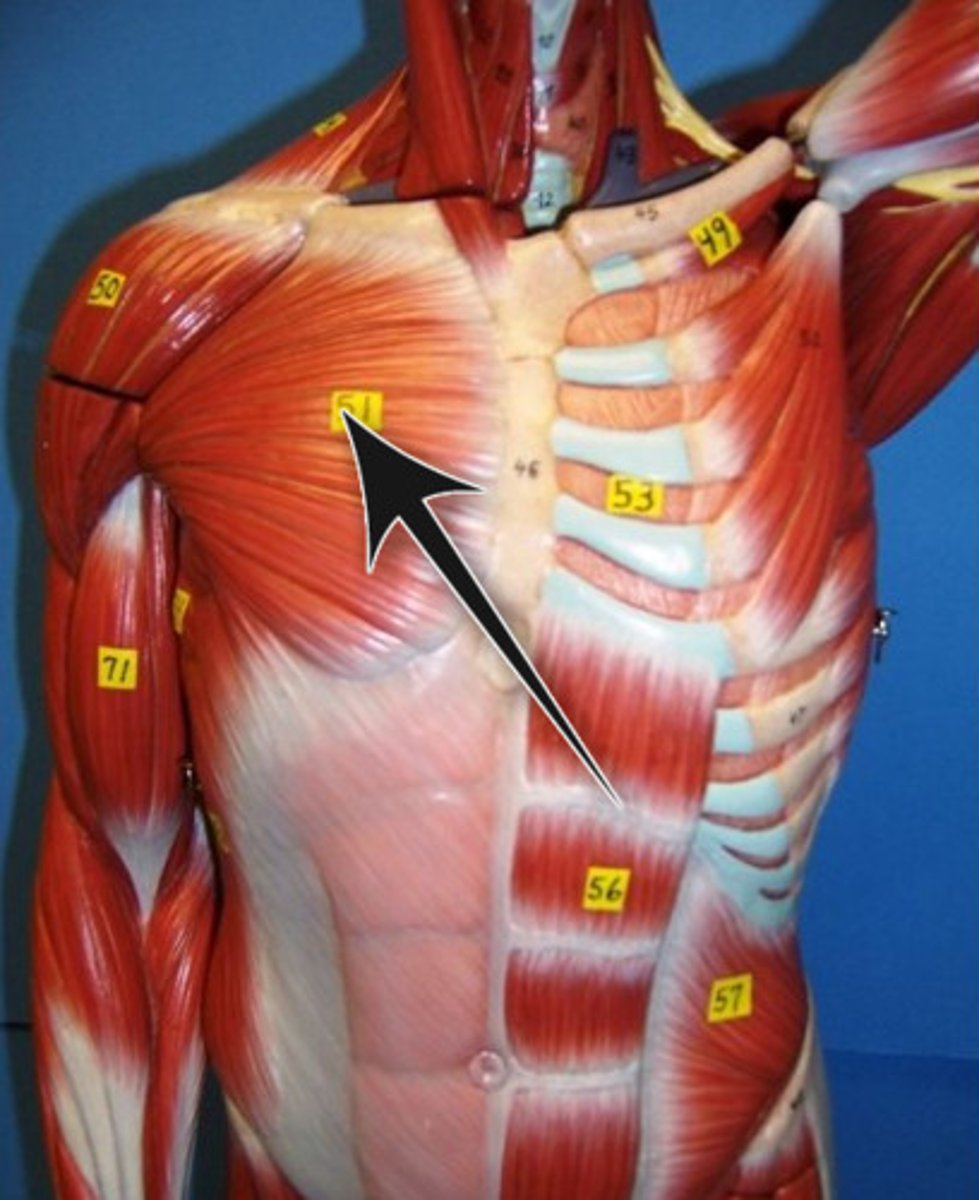
Identify how the external abdominal oblique muscle helps with breathing
assists in forceful exhalation
Identify the external intercostal and membrane internal intercostal muscles
external- outer surface of the ribs with fiber visible from front of body
membrane internal- deeper inside rib cage
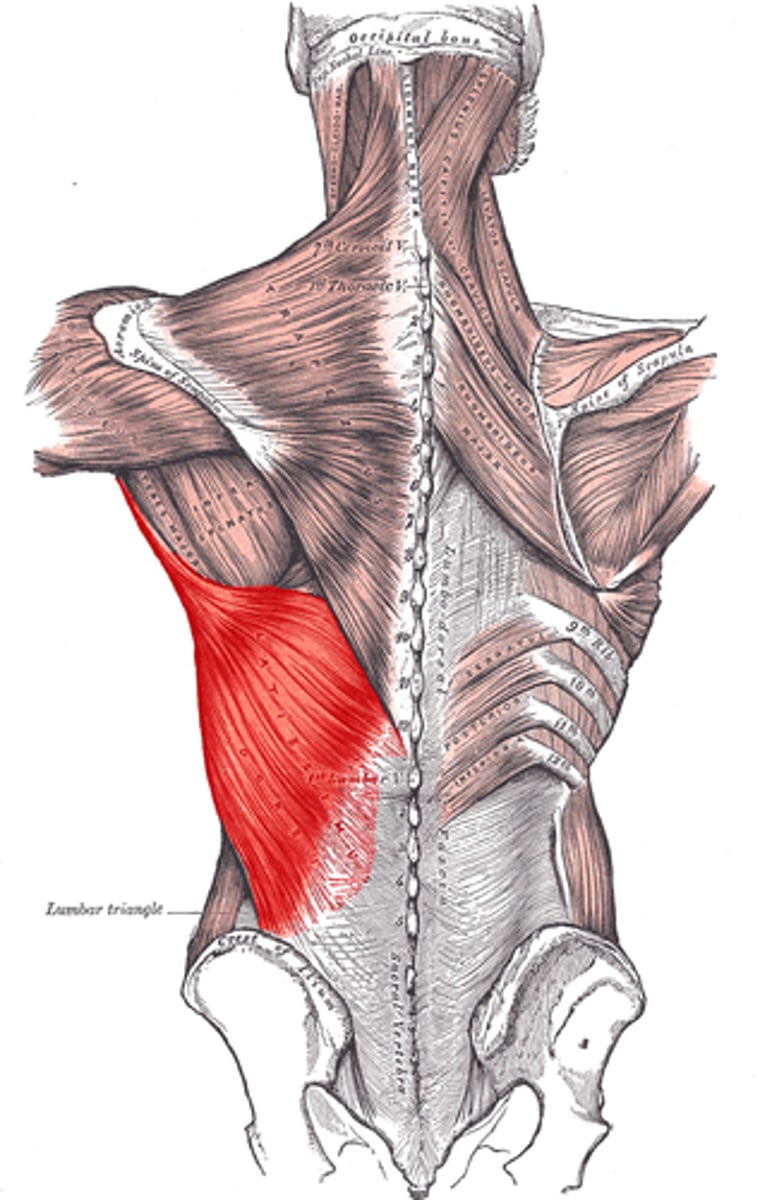
Identify the latissimus dorsi muscles
large, triangular muscles on the back
- located below shoulder blades and either side of the spine
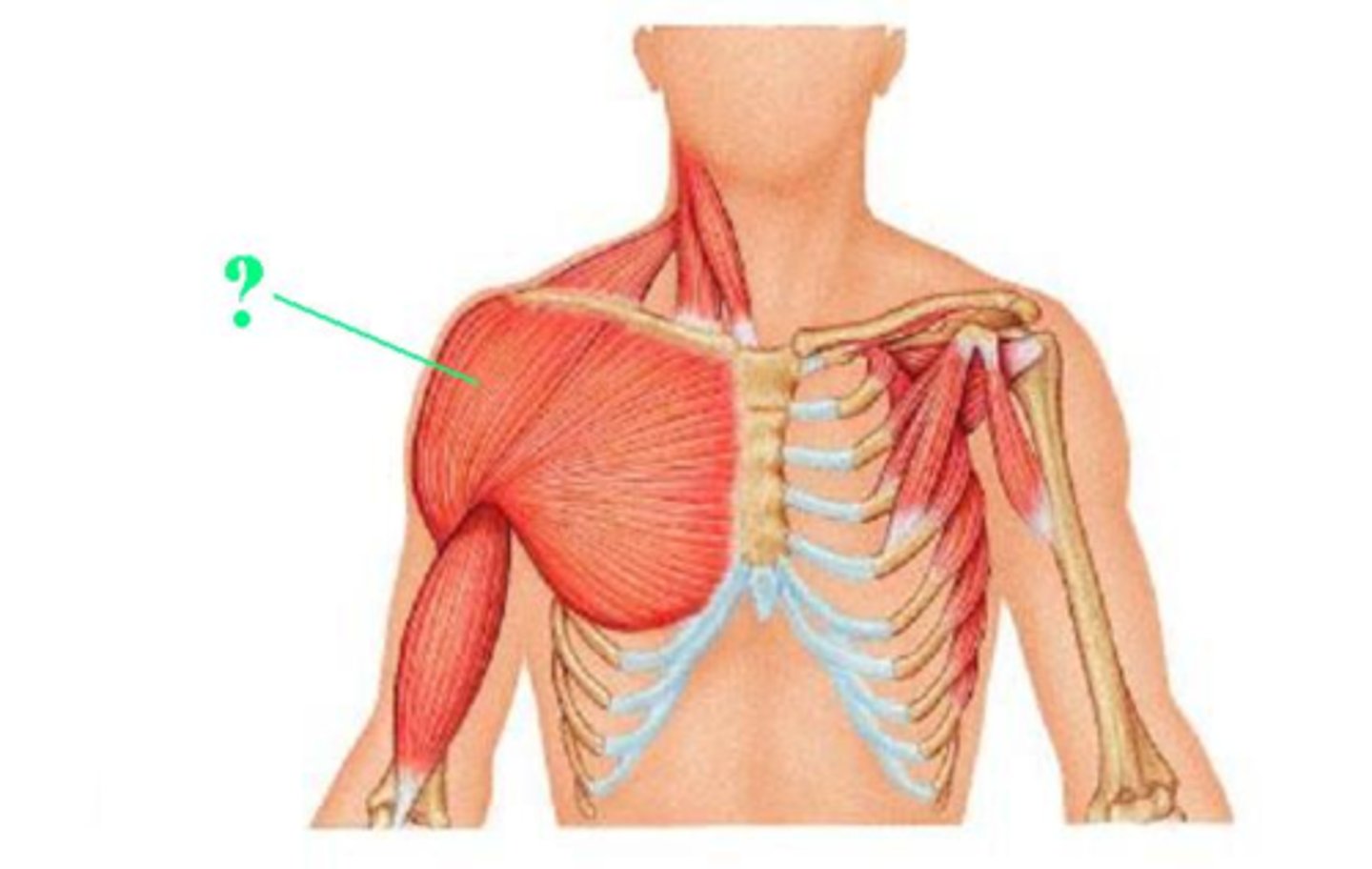
Identify the pectoralis major muscle
fan shaped muscle in upper chest that forms the bulk of the chest muscles
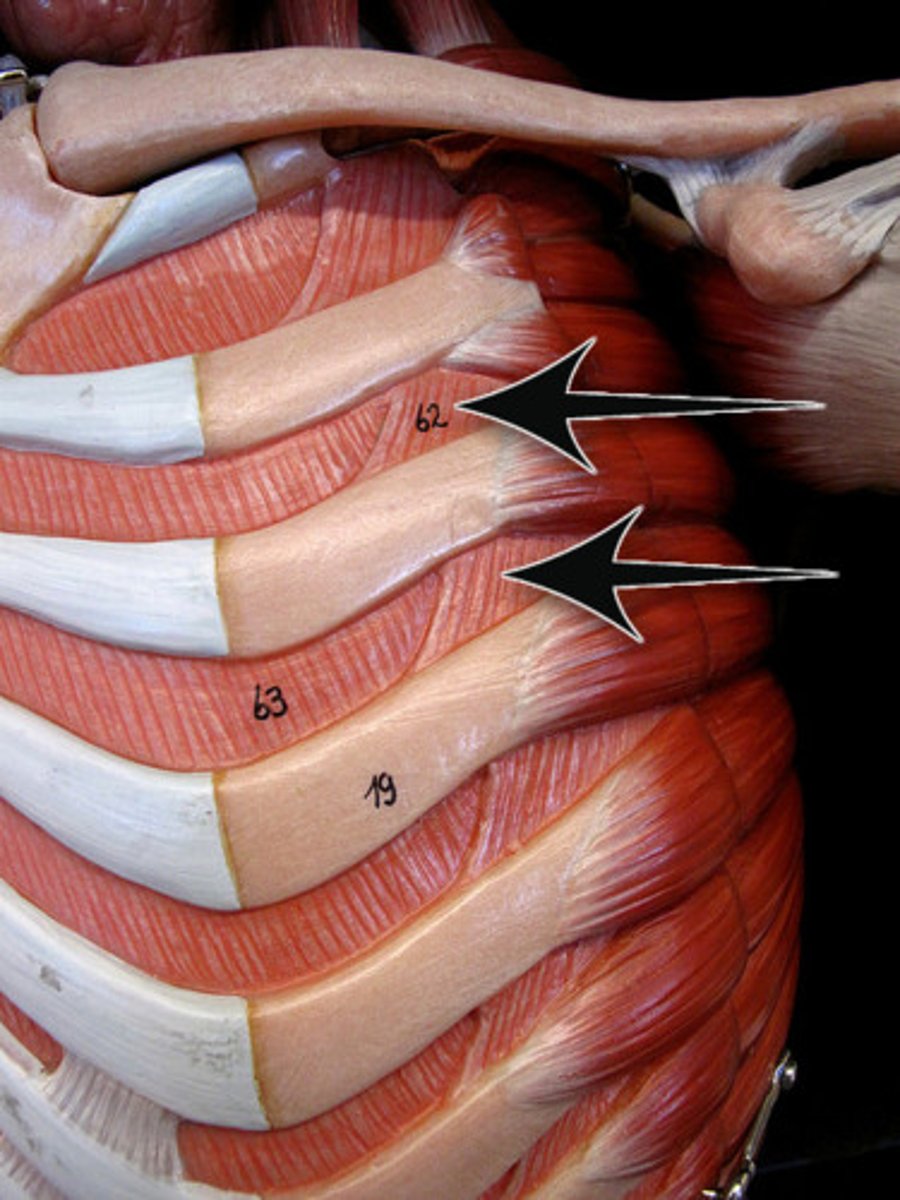
Identify the pectoralis minor muscle
thin, triangular muscle located deep to the pectoralis major in the upper chest
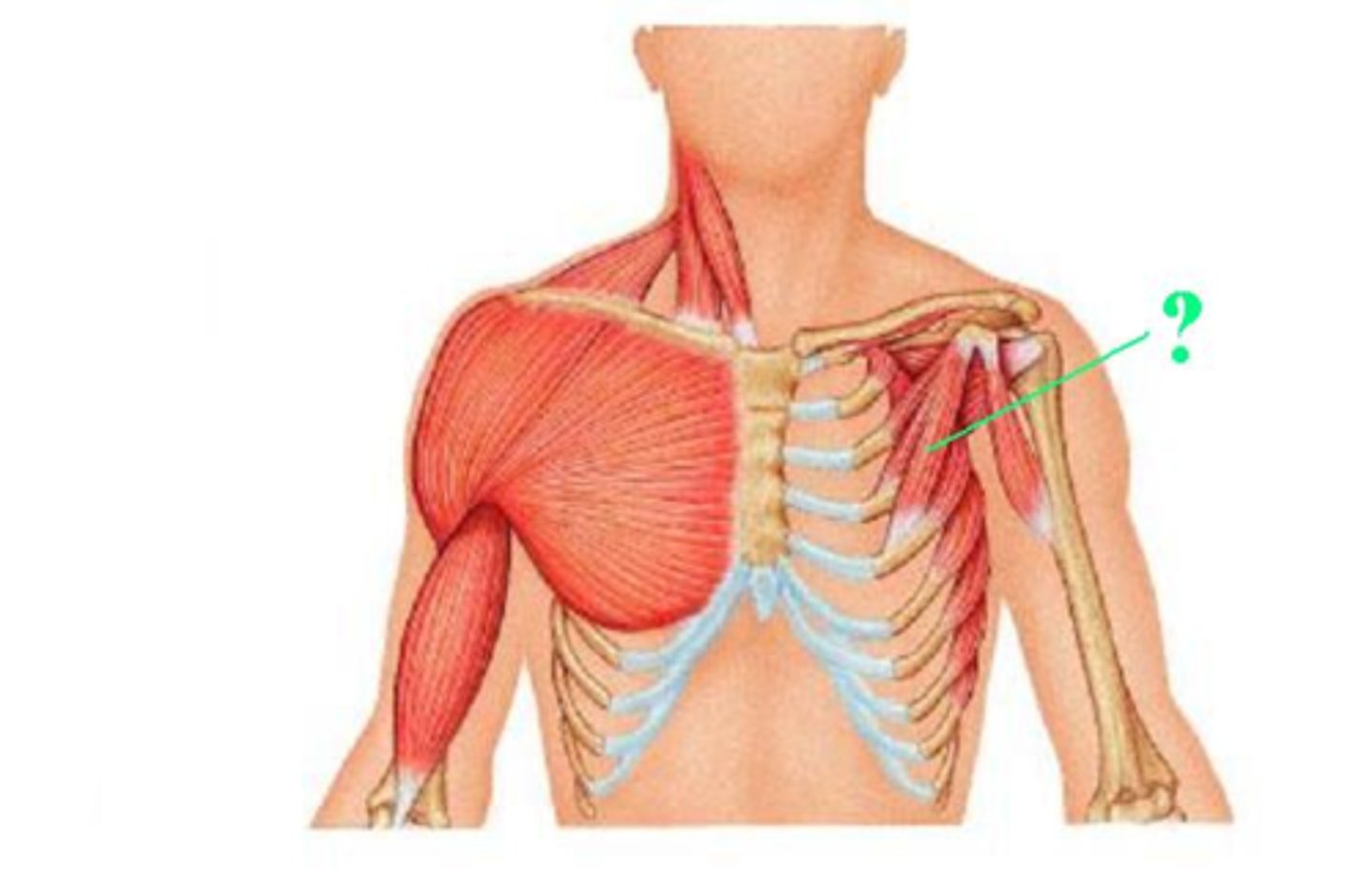
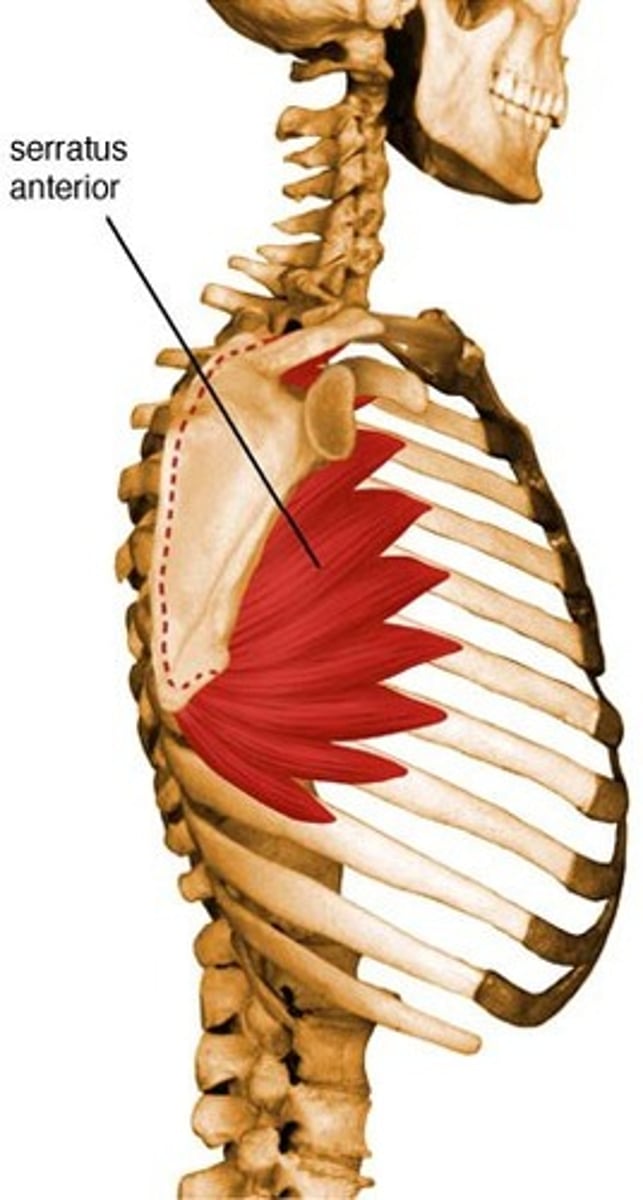
Identify the serratus anterior muscle
fan shaped muscle, located on the side of the chest
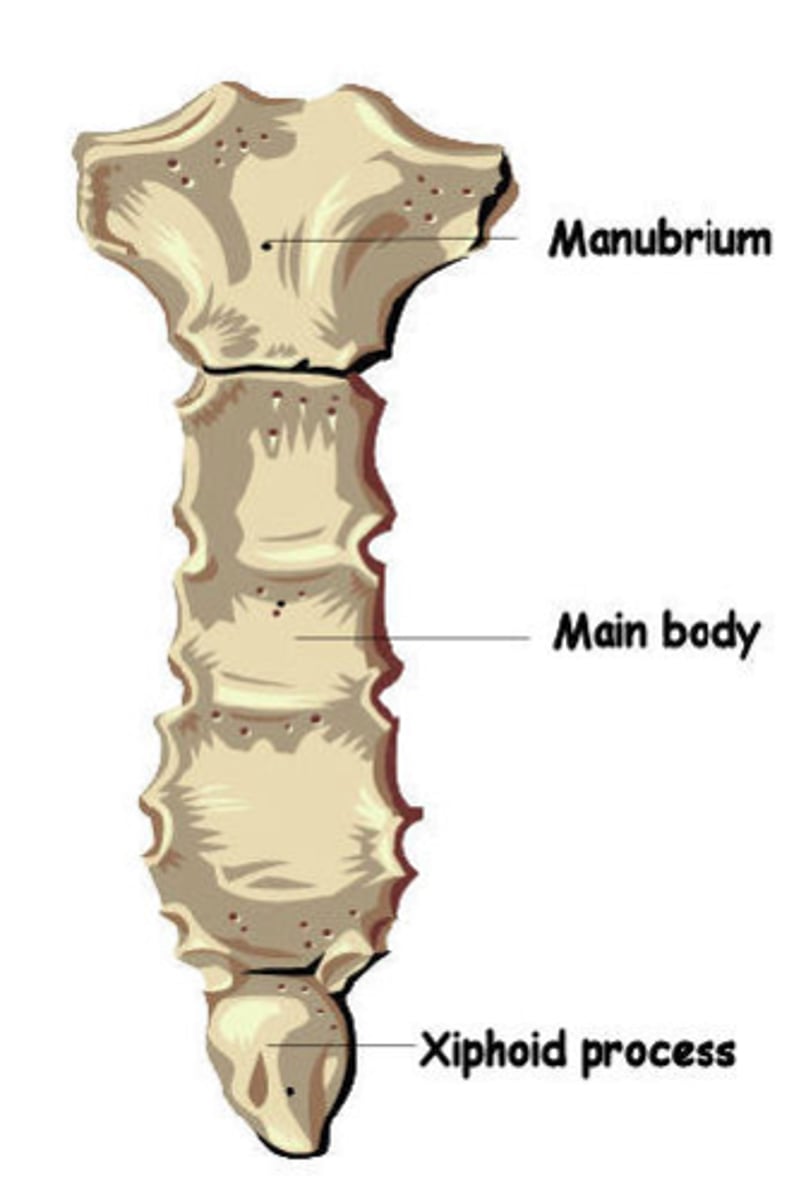
Identify the parts of the sternum
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
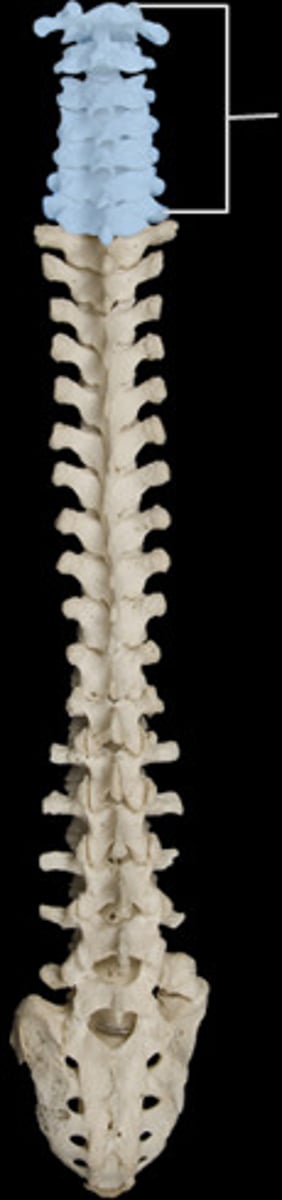
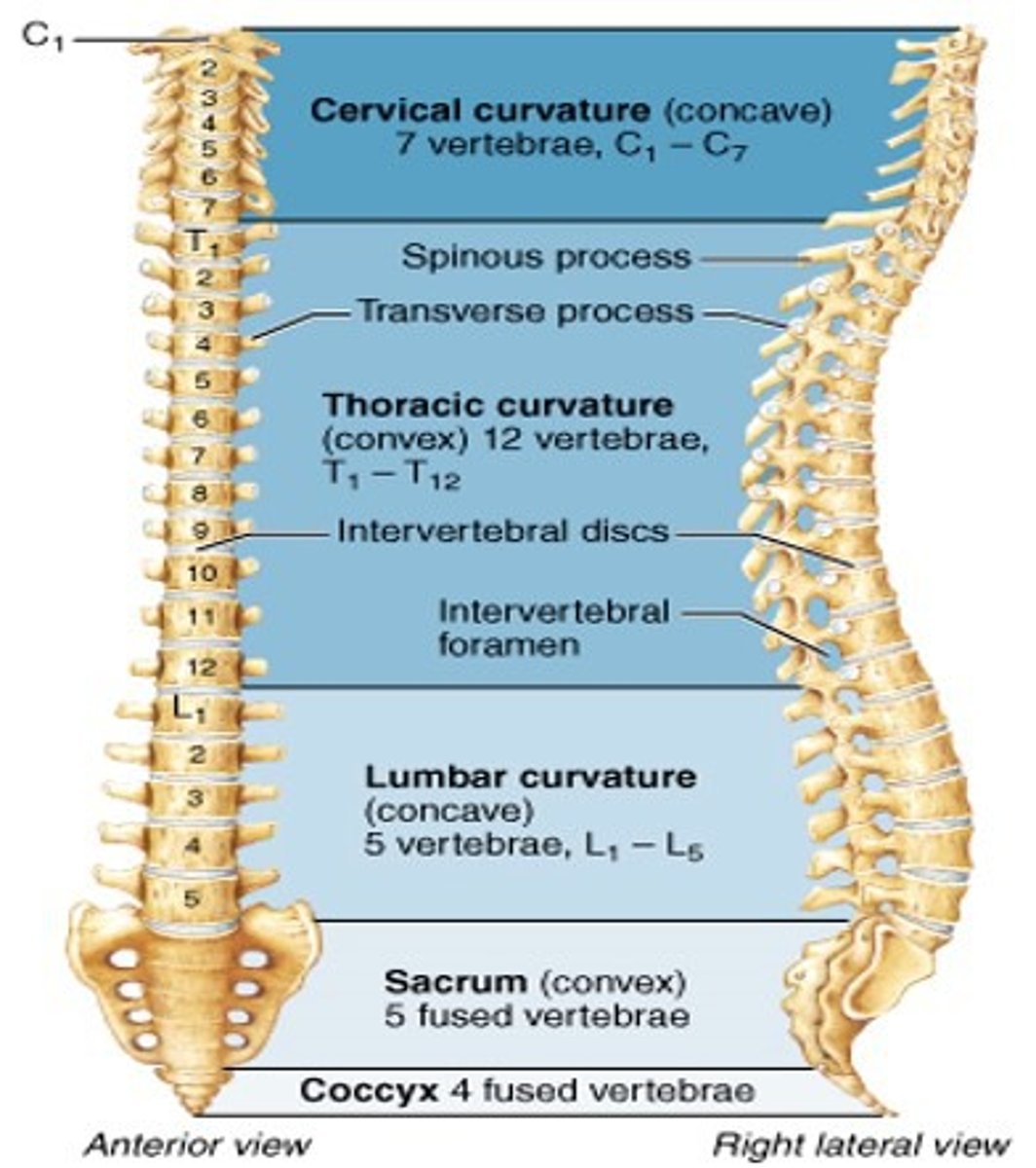
Identify the cervical vertebrae
first 7 vertebrae in the spine
- C1-C7
Identify the clavicle
a pair of long S shaped bones that run horizontally at the base of the neck
- connects the sternum to the shoulder blades
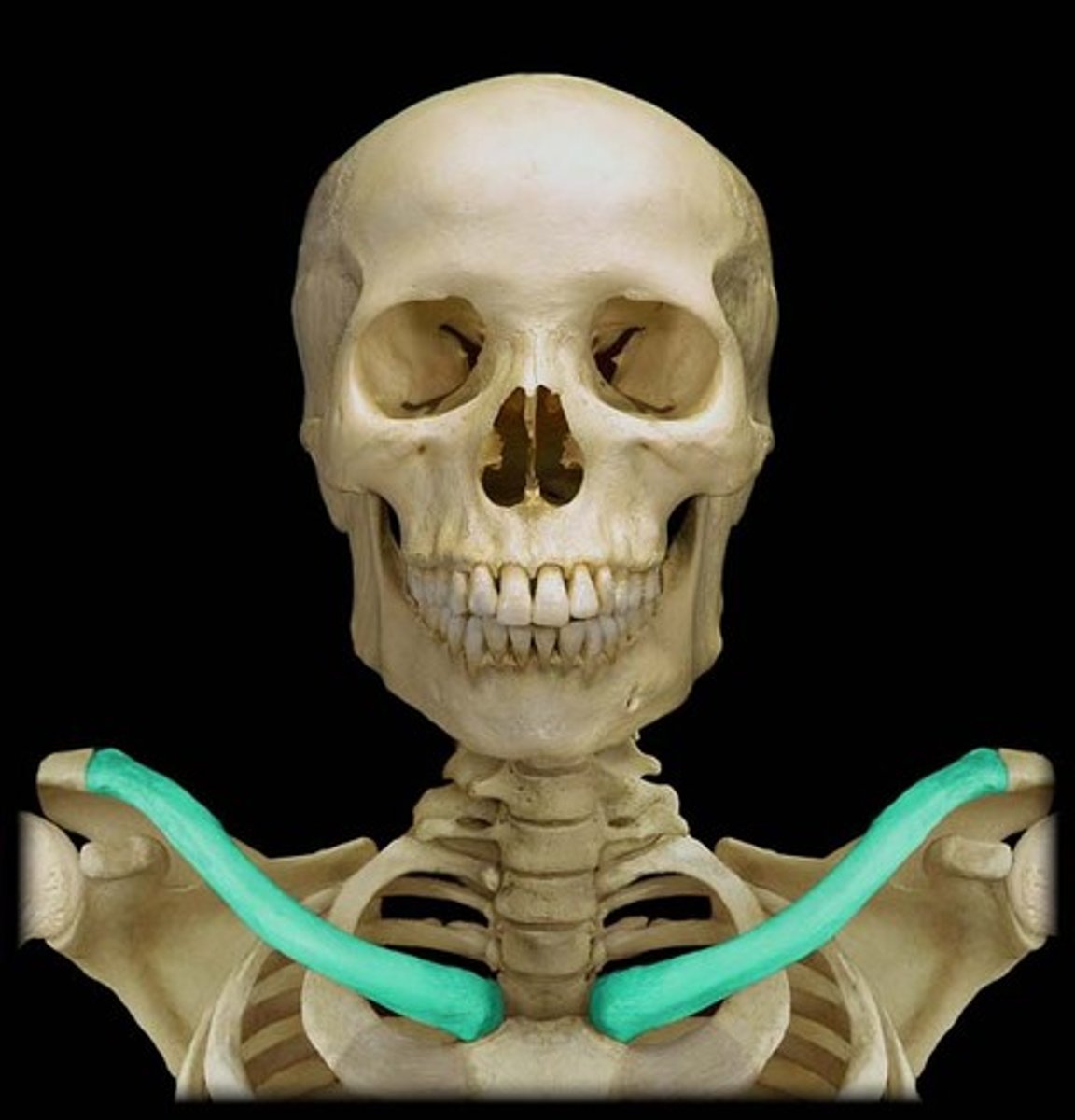
Identify the costal cartilage
hyaline cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum at the front of the thoracic cage
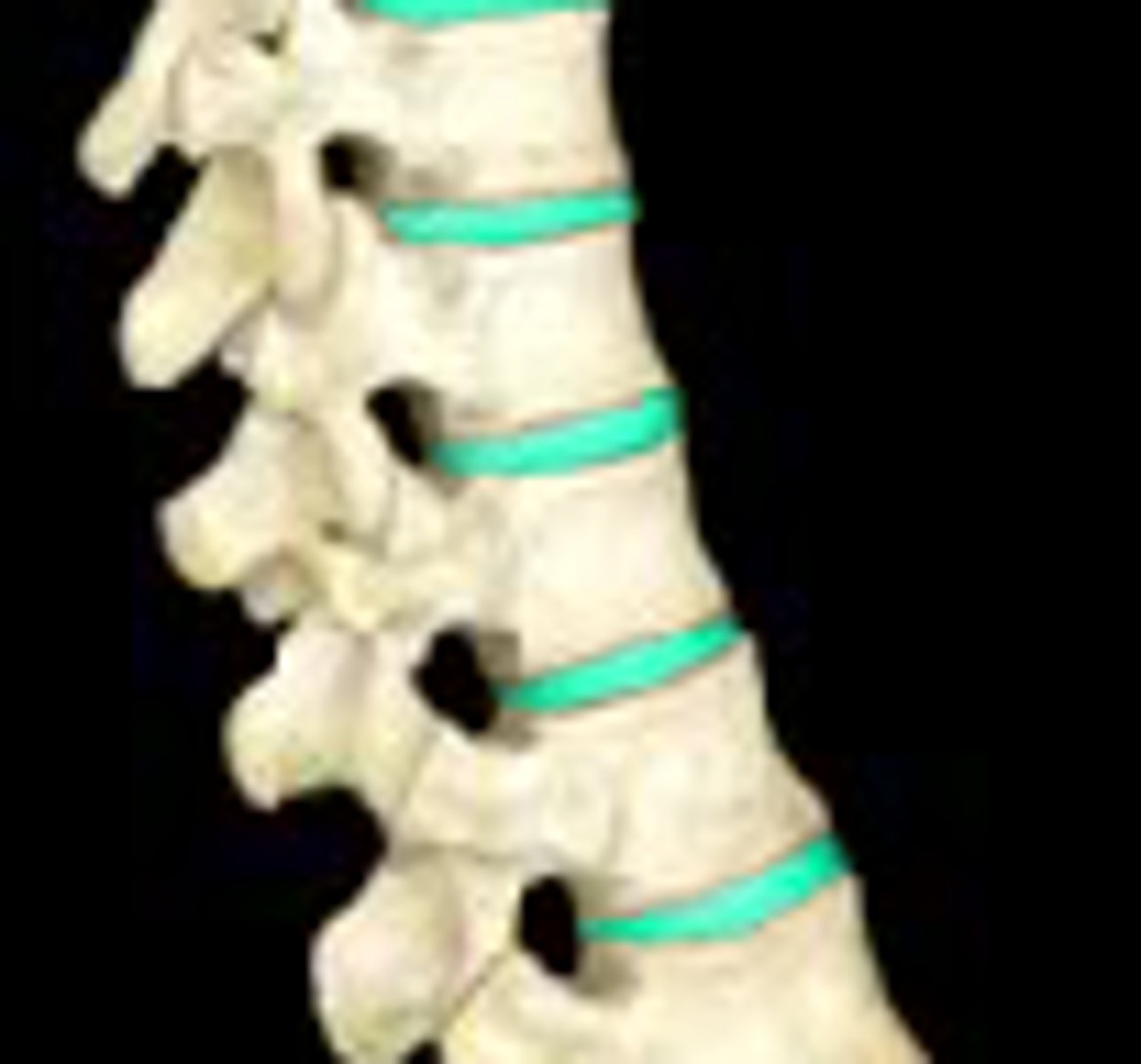
Identify the intervertebral disc
flat, round, cushion like structure located between two vertebrae
- absorbs shock and allows for movement of the spine
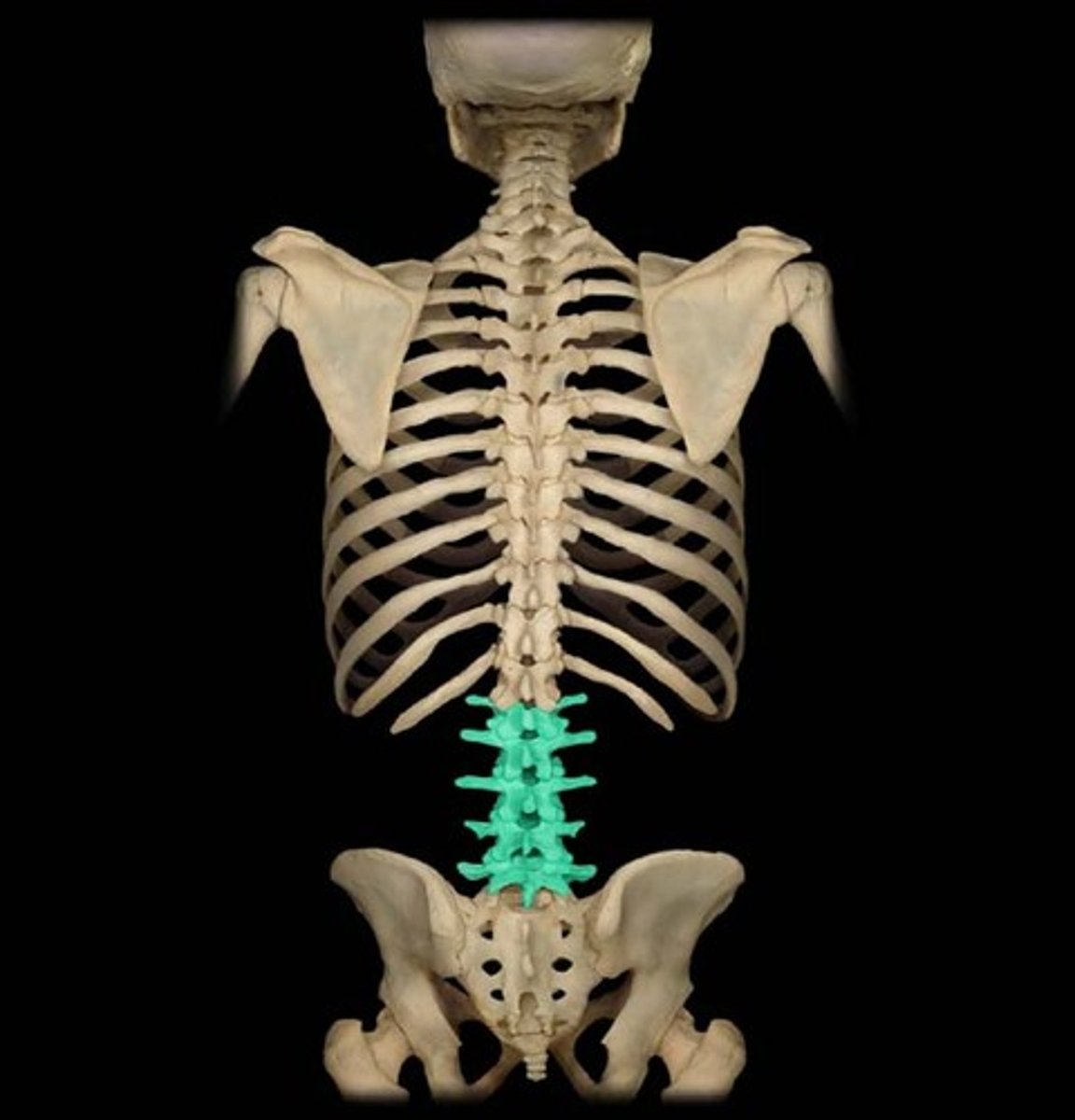
Identify the lumbar vertebrae
the 5 vertebrae of the lower back
- L1-L5
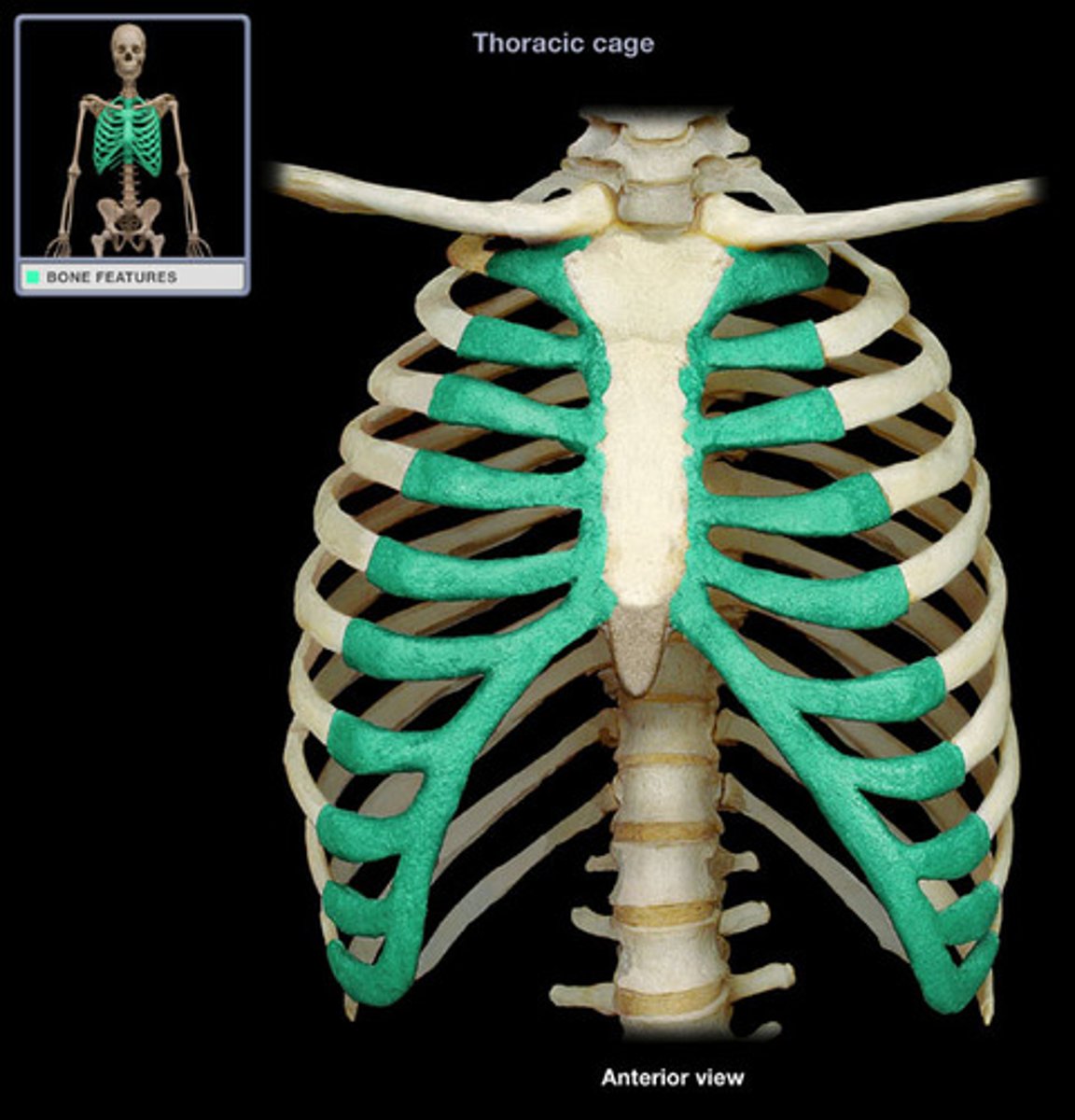
Identify ribs 1-12
true ribs 1-7
false ribs 8-10
floating ribs 11-12
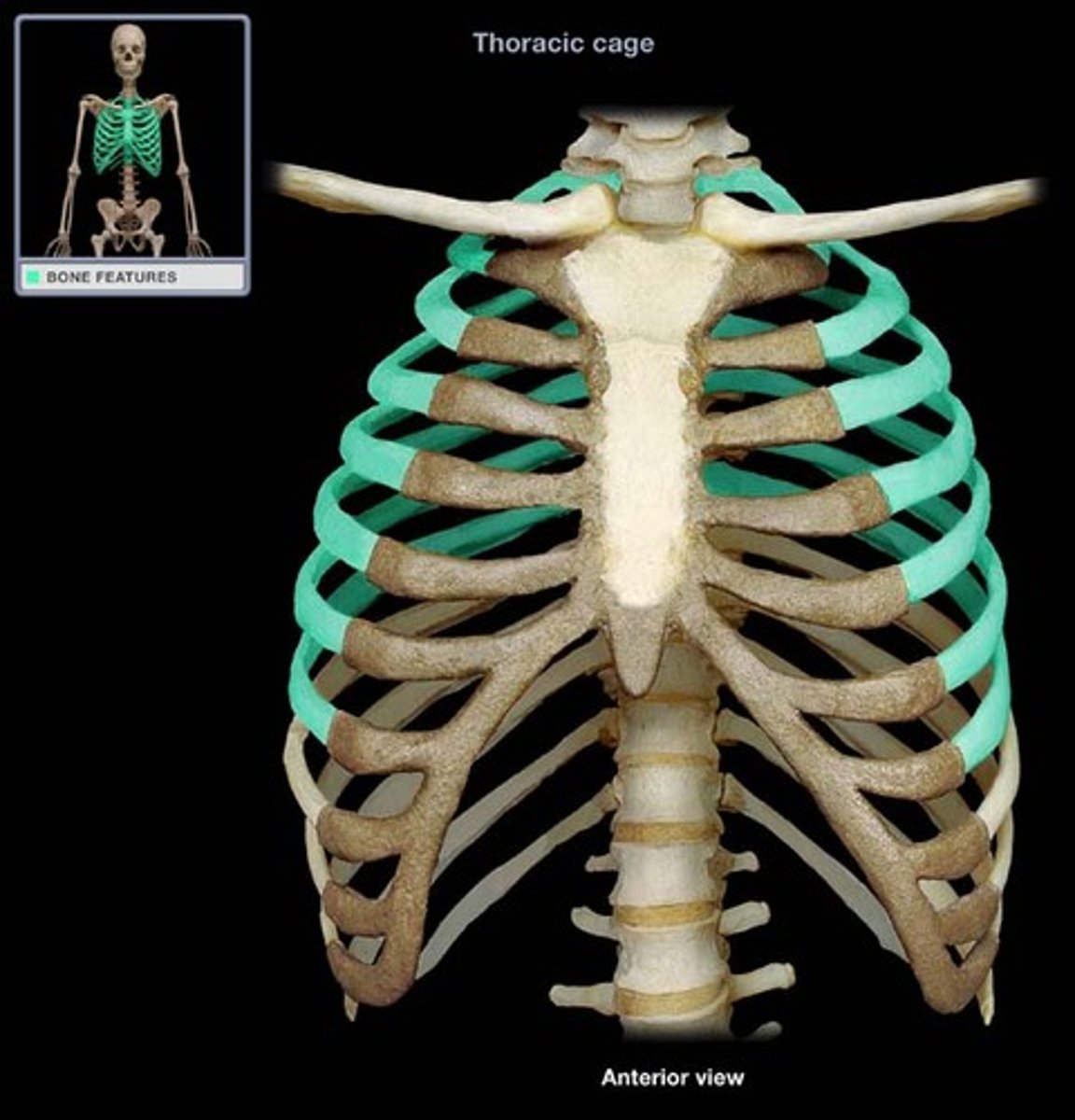
Identify the thoracic vertebra
the 12 vertebrae in the middle section of the spine
- T1-T12
Explain the functions of the nervous system
1. collect information
2. process and evaluate information
3. initiate response to information
Describe the 2 divisions of the nervous system
central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Describe the subdivisions of the PNS
somatic NS- controls voluntary movements
autonomic NS- regulates involuntary movements
What are the 2 divisions of the ANS?
sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest)
Define neuron
nerve cell
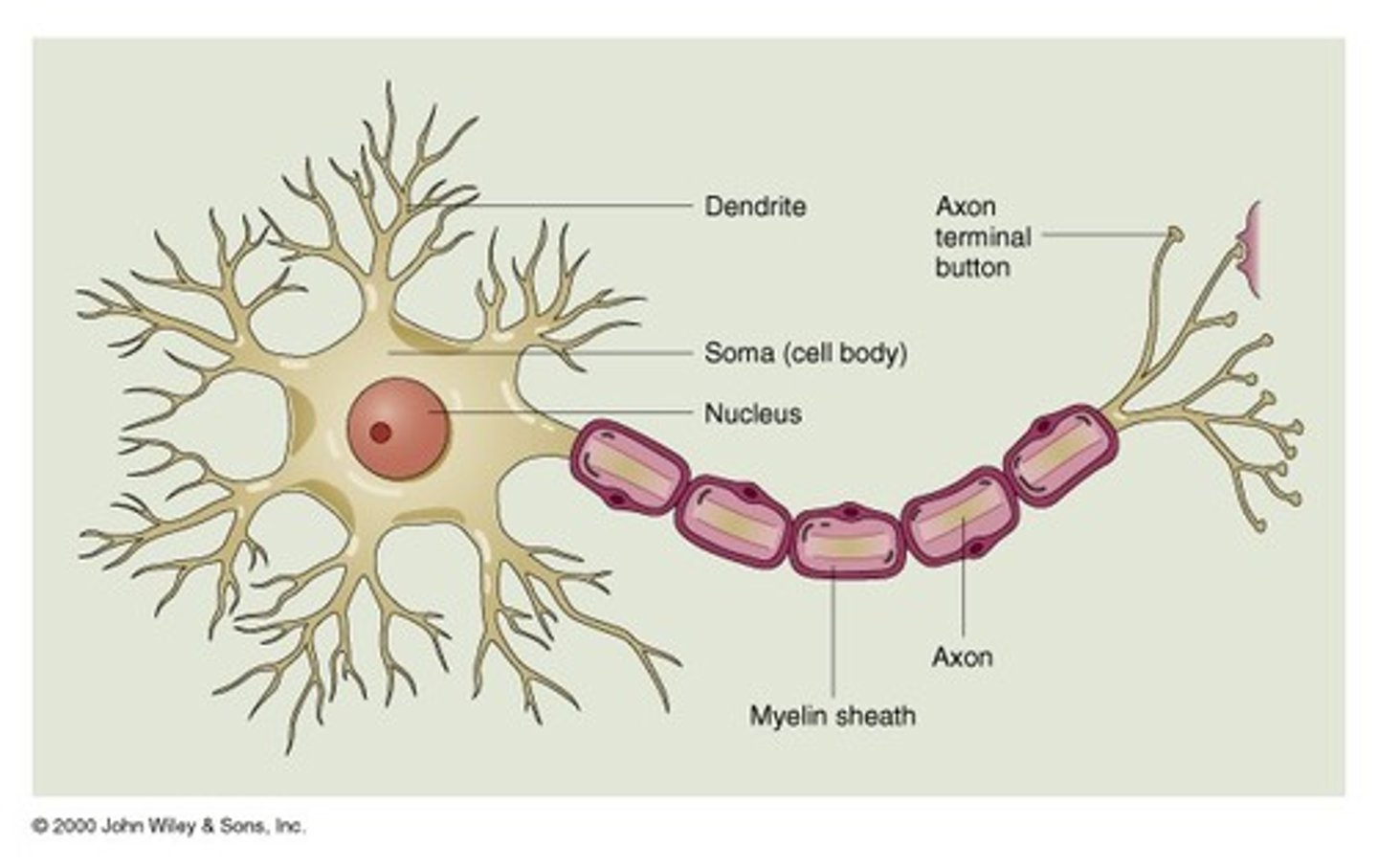
Define dendrites
branching projections of a neuron
- conduct impulses to cell body of neuron
Define axon
elongated projection of a neuron
- conducts impulses away from cell body of neuron
Define what a trigger zone is in the nervous system
specific area in the nervous system where a particular stimulus elicits a specific response
ex. where action potentials are generated in neurons
Differentiate between node of Ranvier and Internodes
nodes of ranvier- gaps in myelin sheath along an axon
internode- insulated segments of the axon between nodes of ranvier gaps
What is the function of myelination?
insulate nerve axons and speed up the transmission of action potentials along nerve cells
Define neuroglia
connective tissue of nervous system, consists of several types of cell associated with neurons
Define astrocytes
star shaped glia cells
- anchor small blood vessels to neurons
Define ependymal cells
lines ventricles of brain/central canal, or spinal cord
- assists in production and circulation of CSF
Define microglia
small cells
- move in inflamed brain tissue carrying on phagocytosis
Define oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheaths around axons in CNS
Define Schwann cells
form myelin sheaths in PNS only
Define satellite cells
electrically insulates PNS cell bodies
- regulates nutrient and waste exchange for cell bodies in ganglia
Define electrical potential
the electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electrical field
- measured in volts
Describe white matter
tissue in the brain and spinal cord that connects different areas of the CNS
- enables communication between the two parts of the CNS
Describe gray matter
the "thinking" part of the brain
- responsible for processing information and performing functions like memory, emotions, and conscious thought
What are the five cerebral lobes?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insular
Identify the diencephalon and it's parts (3)
- thalamus
- hypothalamus
- epithalamus
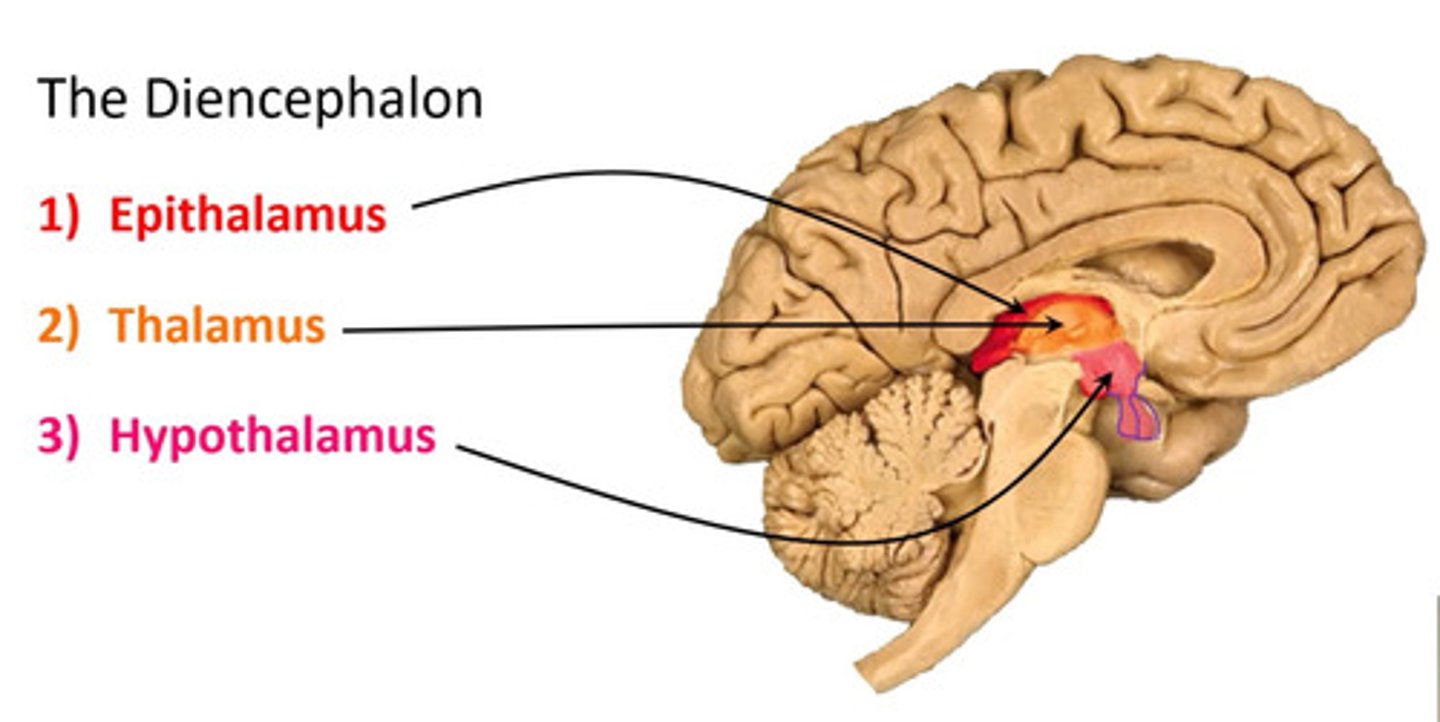
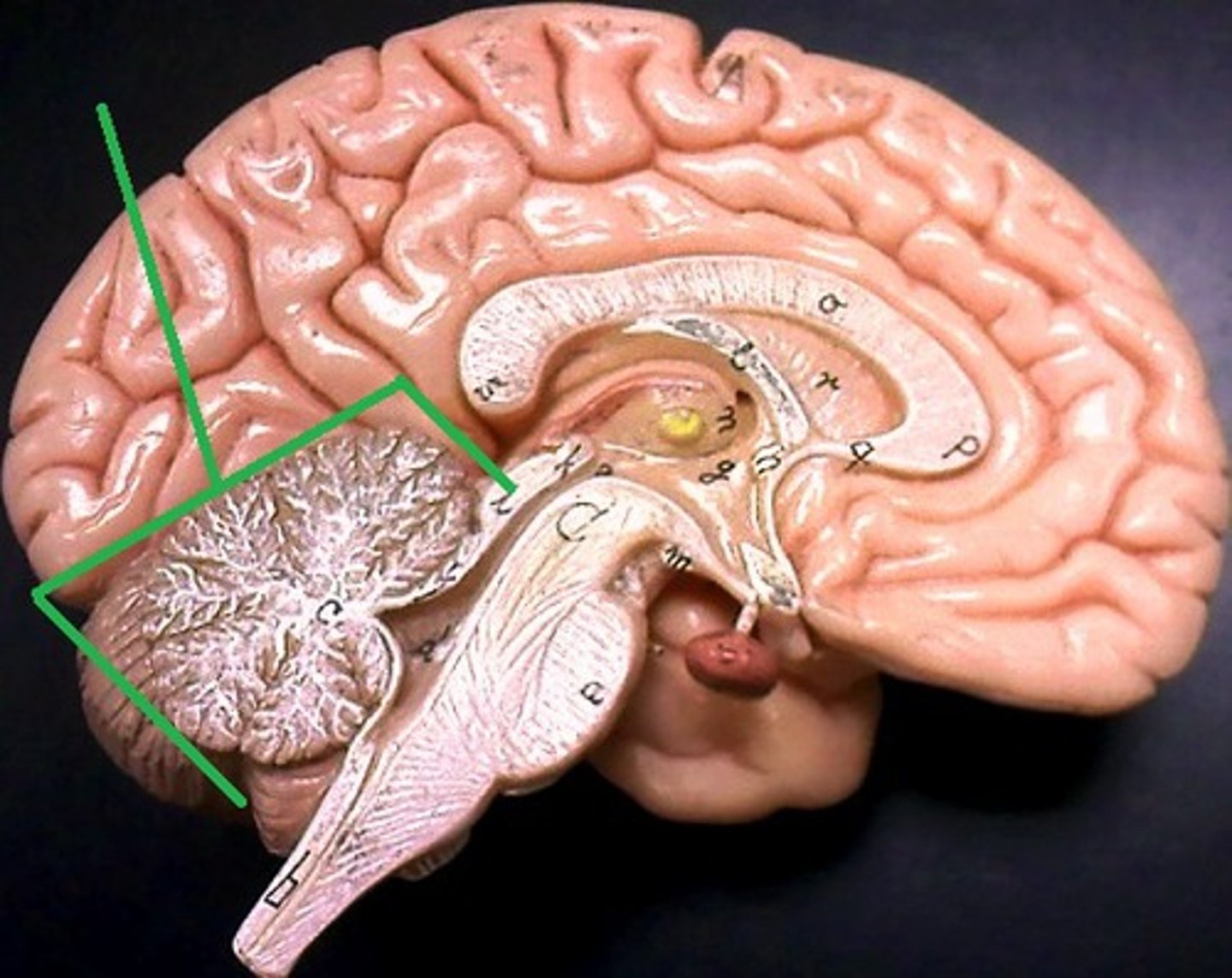
Identify the cerebellum
located at the back of the brain, inferior to occipital and temporal lobes and behind the brainstem