Unit 19. Infectious Diseases Affecting the Genitourinary System
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Defenses of the genitourinary system: Urinary tract:
• the flushing action of the urine flowing out of the system.
• The group of microorganisms that constitute the normal biota in the GI tract
Defenses of the genitourinary system: The defenses of the female reproductive tract
* vary over the lifetime of the woman.
• The vagina has a protective covering of secreted mucus.
• Changes in the pH of the vagina
Normal biota of the urinary tract, both genders
Nonhemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus, corynebacterium, lactobacillus, prevotella, veillonella, gardnerella
Normal biota of the genitourinary system: The male genital tract
microbiome shifts with sexual activity, outer surface of the penis: pseudomonas & staphylococcus; sulcus of uncircumcised penis
Normal biota of the genitourinary system: The female genital tract
varies but often dominated by Lactobacillus (in charge of PH). Candida albicans is commonly present at low levels. Microbial composition shifts throughout life.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Invasion of the urinary system by bacteria or other microorganisms
UTI-Cystitis
infection of the bladder due to reduced urine flow or accidental introduction of bacteria. Symptoms: pain, frequent urges to urinate, and burning pain with urination (dysuria).
• Back pain and high fever are an indication that the kidneys may be involved (pyelonephritis). Can result in permanent damage to the kidneys.
Community-acquired UTIs:
-C: E. coli, Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Enterococcus. both treated via antibiotics
Catheter-associated UTIs:
-catheter is a medical device that allows patients to pee, when inserted, can push bacteria where it shouldnt be.
-c: previous bacteria plus Klebsiella species.
Leptopirosis
• Zoonosis that can affect the kidneys, liver, brain, and eyes. transmitted through contaminated soil or water from an animal
• C: spirochete Leptospira interrogans
Leptospiremic phase of leptopirosis
-pathogen in the blood and CSF.
-Symptoms: sudden high fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, conjunctivitis, and vomiting
Immune phase of Leptopirosis
- blood infection is cleared by natural defenses. Milder fever; headache due to leptospiral meningitis; and Weil's syndrome
-kidneys and liver damage can lead to long-term disability and death
Vaginitis
Inflammation of the vagina that causes itching, burning, and varying types of discharge depending on the causative agent.
Vaginitis caused by Candida albicans:
-most common cause, forms thick, whitish colonies on the walls of the vagina that contribute to a white vaginal discharge. Not invasive In healthy people. Mostly opportunistic
Vaginitis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis
-flagellated protozoa with an undulating membrane. No cyst form.Frequent asymptomatic infections. Men mostly asymptomatics. Women can have vaginitis symptoms, with a white to green, frothy discharge.
-Causes premature labor and low-birth weight infants. Chronic infections increase risk of other infections (HIV) & may lead to infertility. -Linked to increased prostate cancer risk(men)
Vaginosis
• Mixed bacterial infection, STI or oppurtunism
-No inflammatory response; vaginal discharge, fishy odor, itchyness is common
-Complications: pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, more rarely, ectopic pregnancies. Babies born with low birthweights.
Prostatitis
• Inflammation of the prostate gland
-C: GI tract biota
-symptoms: pain in the groin and lower back, frequent urge to urinate, difficulty in urinating, blood in the urine, and painful ejaculation.
• Acute prostatitis:
usually caused by bacteria from normal biota from the GI tract or from a previous urinary tract infection, gives patient fever + flu like symptoms
Chronic prostatitis:
also often caused by bacteria. Can be caused by mixed biofilms of bacteria in the prostate (often unresponsive to antibiotic treatment)
Discharge Diseases: Gonorrhea
• C:Neisseria gonorrhoeae, or the gonococcus that attach to fimbriae
-rare case: bacteria can enter bloodstream(bacteremia) & go to other parts of body
-transmitted via sex & requires mucos membrane entry site
Gonorrhea In males:
can cause urethritis, painful urination and discharge, rarely causes infertility
Gonorrhea In females:
Can cause a mucopurulent or bloody vaginal discharge and painful urination. Complications: Salpingitis, (inflammation of the fallopian tubes), or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) (inflammation of other parts of the upper reproductive tract), that can block the fallopian tubes, causing sterility or ectopic pregnancies
Discharge diseases
infectious agent causes an
increase in fluid discharge in the male and female reproductive tracts.
Discharge Diseases: Chlamydia
-C: Chlamydia trachomatis, an obligate intracellular parasite
-often goes w gonnorea
Chlamydia in males
inflammation of the urethra. Similar to gonorrhea
Chlamydia in females
cervicitis, a discharge, and often salpingitis and Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).Up to 75% are asymptomatic
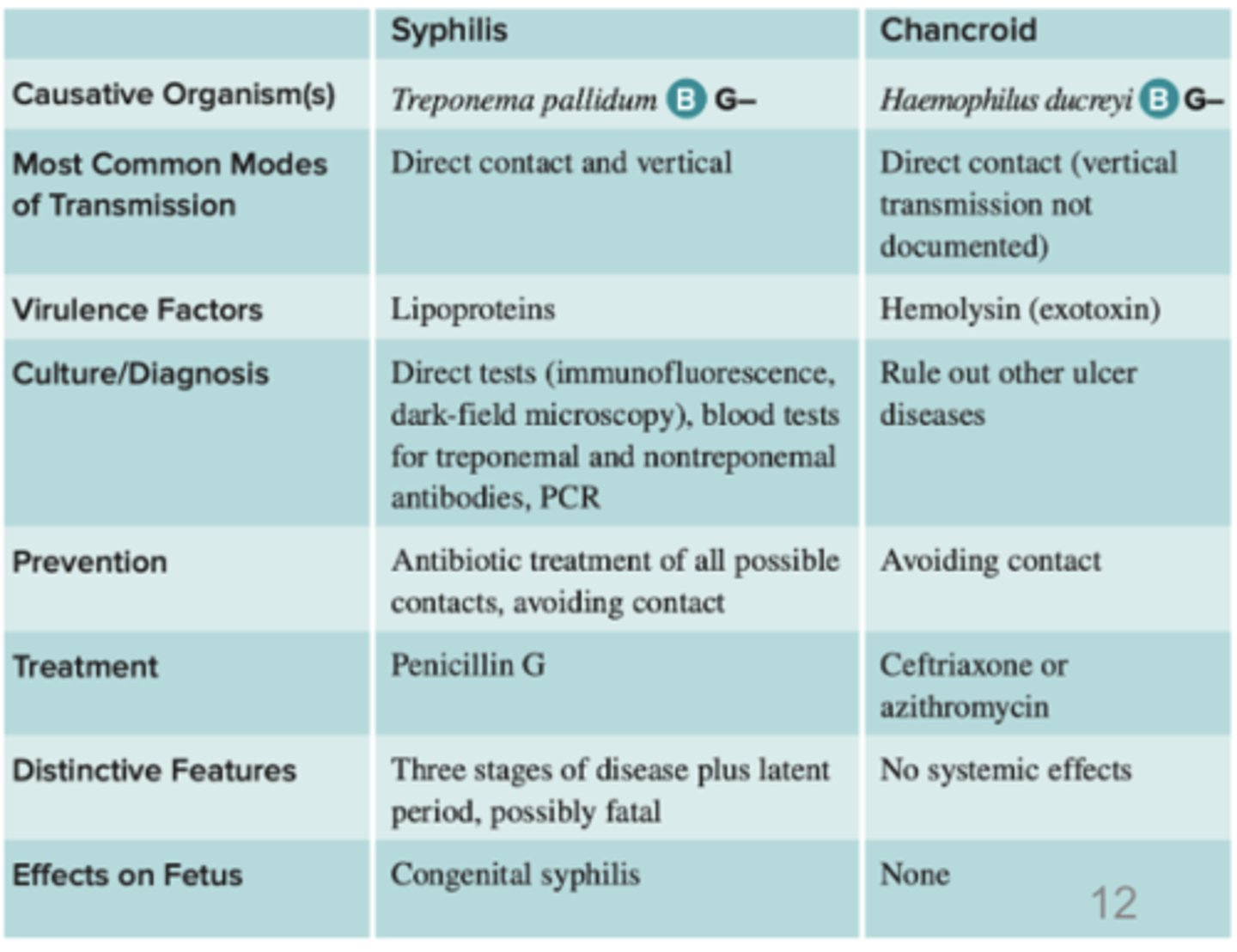
Genital Ulcer Diseases
Syphilis, genital herpes, and Chancroid
Syphilis
-C:Treponema pallidum a thin spirochete. Strict parasite requiring living host cells
-can lead to gummas
-congenital syphilis: bacteria crosses placenta & can cause miscarriage,infant deformaties,etc.
Chancroid
• Caused by a pleomorphic Haemophilus ducreyi.
• Soft papule, or bump, at the point of contact"soft chancre". Inguinal lymph nodes can become very swollen and tender. May be asymptomatic
Genital Ulcer Diseases chart syphilis and chancroid
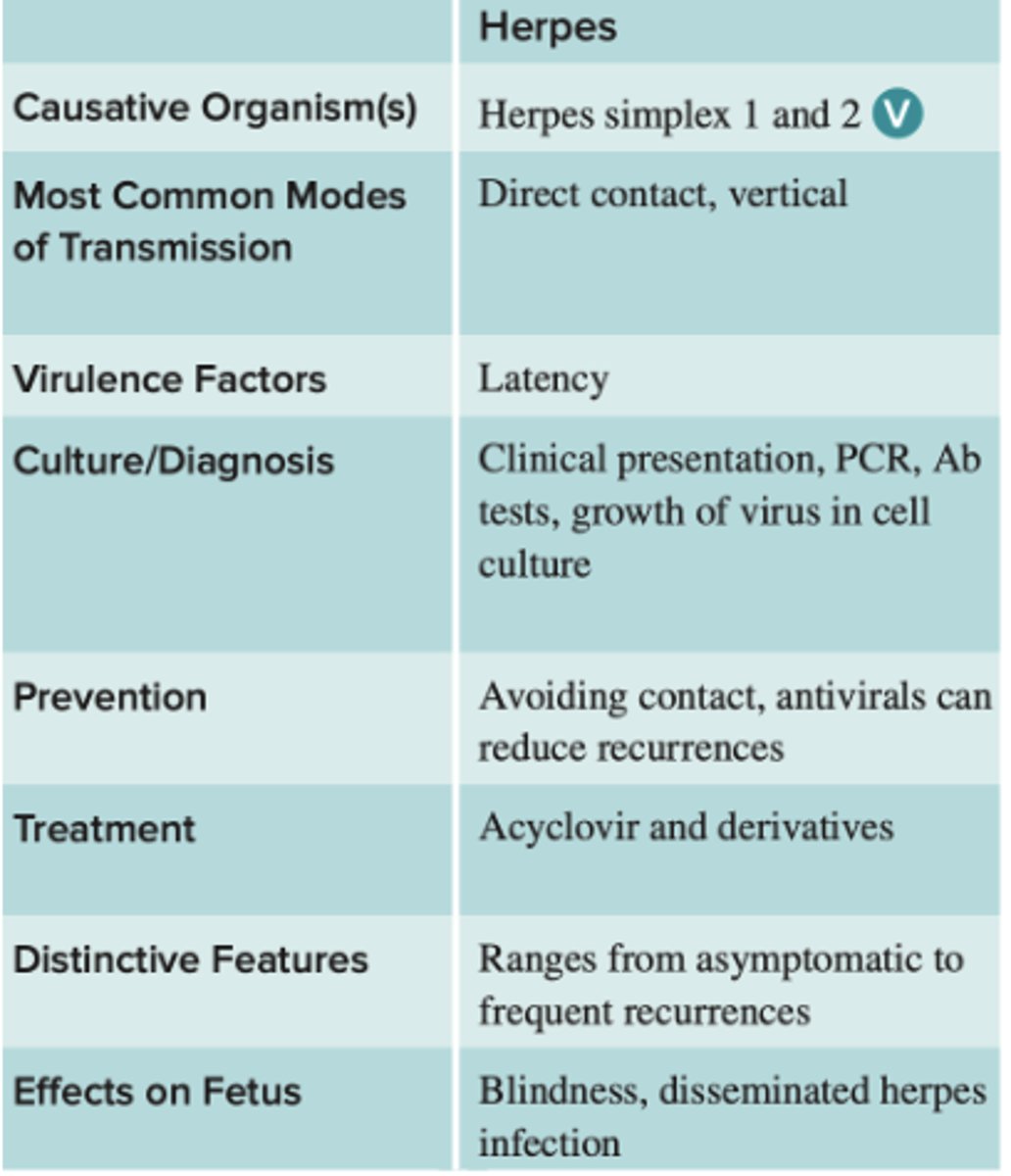
Genital herpes caused by
herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1 or HSV-2). DNA viruses with icosahedral capsids and envelopes containing glycoprotein spikes
Genital herpes can be asymptomatic or cause
small painful vesicles filled with clear fluid. The first time can be accompanied by malaise, anorexia, fever, and bilateral swelling and tenderness in the groin. Occasionally, meningitis or encephalitis can develop. Recurrences are common but usually less severe
Neonatal herpes
in neonates and fetuses HSV infections are very destructive and can be fatal. In infants with disease confined to the mouth, skin, or eyes, the mortality rate is 30%,but disease affecting the CNS has a 50% to 80% mortality rate
Genital herpes for pregnant women procedure
Standard procedure to screen pregnant women for the HSV early
Herpes chart
Wart Diseases
Human Papillomaviruses (HPV), Molluscum contagiosum
Human Papillomaviruses (HPV):
nonenveloped DNA viruses of the Papovaviridae family can cause genital warts or in some cases result in cancer
Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) symptoms
if present, warts on the genitals, including the anal and groin area. May range from tiny, flat bumps to branching, cauliflower-like masses called condiloma acuminata
Other types of HPV infect cells in the female cervix, can lead to
abnormal cell changes and cancer. Cervical cancer greatly reduced by vaccine implementation. Detected in Pap smears
Molluscum contagiosum
molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) in the family Poxviridae,.
• Sexually transmitted skin lesions, found on the mucous membranes or the skin of the genital area
Wart Diseases chart

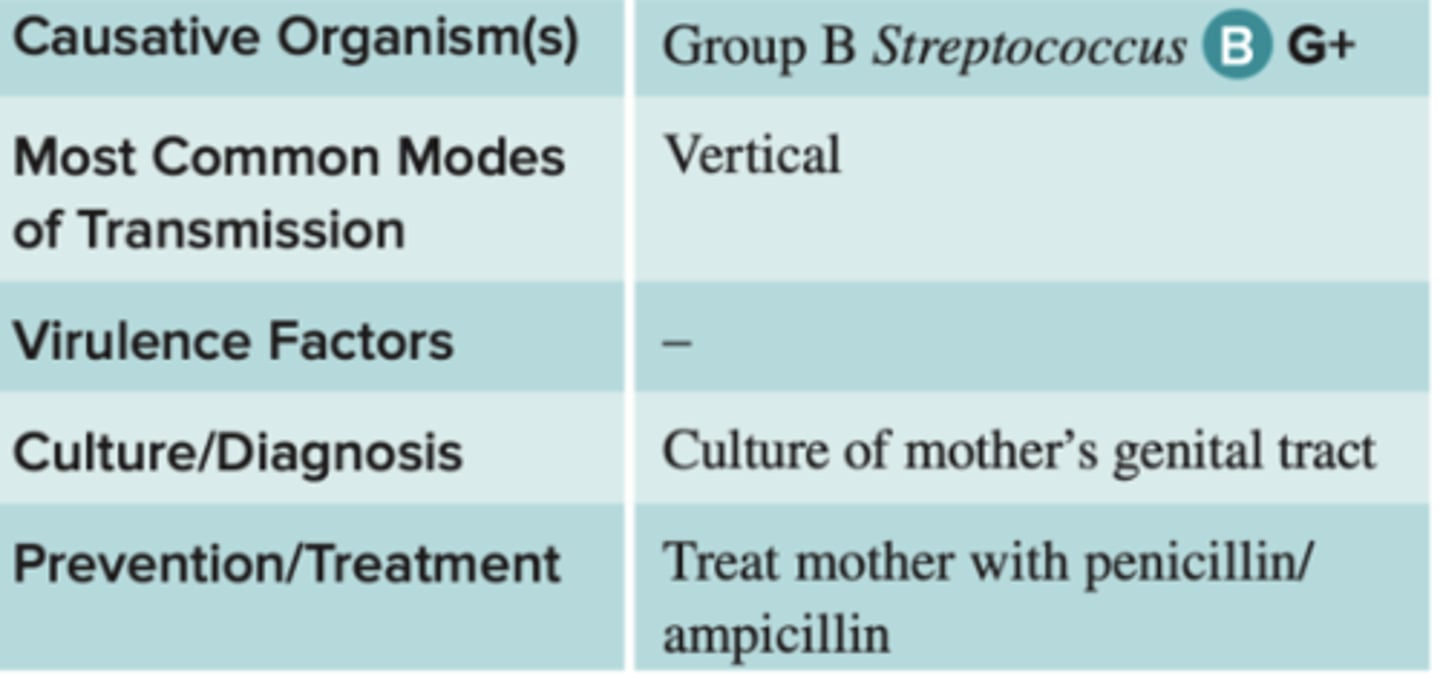
Group B Streptococcus "Colonization"—Neonatal Disease
• Group B Streptococcus (GBS) colonices asymptomatically 10-40% of women in the USA.When they give birth, about half of their infants become colonized by the bacterium
Group B Streptococcus "Colonization"—Neonatal Disease small percentage of infected infants experience
experience life threatening septicemia, meningitis, or pneumonia. If they recover, they may have permanent disabilities such as developmental disabilities, hearing loss, or impaired vision. In some cases, the mothers also experience disease, such as amniotic infection or subsequent stillbirths.
• GBS infections are a major threat to infant morbidity and mortality worldwide
Group B Streptococcus "Colonization"—Neonatal Disease recommended screen for GBS at
35-37 weeks of pregnancy
Group B Streptococcus "Colonization"—Neonatal Disease chart