10.4 Thermodynamic Considerations for Halogenation Reactions
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What determines whether a halogenation is thermodynamically favorable?
The sign of ΔG (must be negative)
What does a negative ΔG indicate?
Products are favored; the reaction is spontaneous/favorable
Why is the entropy term (ΔS) negligible in halogenation?
Because two molecules of reactants form two molecules of products — no major change in disorder.
If ΔS is negligible, what mainly determines ΔG?
The enthalpy change (ΔH)
What two bonds are broken in halogenation of methane?
One C–H bond and one X–X bond.
What two bonds are formed in halogenation of methane?
One C–X bond and one H–X bond.
How is ΔH estimated for halogenation?
ΔH = (bonds broken) − (bonds formed)
Which halogenation is too exothermic and explosive?
Fluorination (F₂)
Which halogenation is most practical and moderately exothermic?
Chlorination (Cl₂)
Which halogenation is slow and slightly endothermic?
Bromination (Br₂)
Which halogenation is not feasible because it’s endothermic?
Iodination (I₂).
Which step type determines ΔH in halogenation?
The balance between energy absorbed in bond breaking and released in bond formation.
What determines whether halogenation is exothermic or endothermic?
The balance between bond energies of bonds broken and bonds formed (ΔH)
Which halogenation is too exothermic to control?
Fluorination (F₂)
Which halogenation is not thermodynamically favorable?
Iodination (I₂), because it’s endothermic.
Which halogenations are practical in the lab?
Chlorination and bromination.
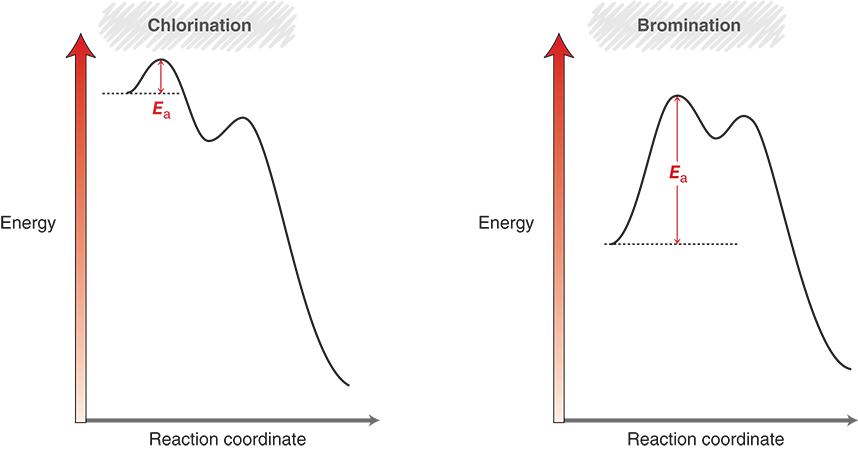
Why is bromination slower than chlorination?
Its first propagation step (H-abstraction) is endothermic, requiring more activation energy.
What is the rate-determining step in halogenation?
The first propagation step (hydrogen atom abstraction)
What is the estimated ΔH for chlorination of ethane?
−117 kJ/mol (exothermic)
What is the estimated ΔH for bromination of ethane?
−50 kJ/mol (exothermic but slower)
How does activation energy (Ea) relate to reaction speed?
Lower Ea → faster reaction; higher Ea → slower reaction.
Why doesn’t iodination of methane occur?
It’s endothermic (ΔH positive → ΔG positive → not spontaneous).
What is the thermodynamic trend among halogens for halogenation?
F₂ >> Cl₂ > Br₂ > I₂ (from most exothermic to least).
Make sure you know this