ch 9 mid and south america
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the most spoken Indigenous languages in Middle and South America?
Nahuatl, Quechua, and Guarani
chinampas
raised agricultural fields that look like floating gardens
terraces
stair-like hillside agricultural plots called
altitudinal zonation
agricultural zoning of crops by elevation
guano
bird dung used as potent fertilizer
Which of the following regions received the largest shares of enslaved African peoples during the Trans-Atlantic Trade?
Brazil and the Caribbean
Which of the following countries have the highest Indigenous populations?
Mexico and Guatemala
The racial mixing of peoples that extensively occurred in Middle and South America is referred to as
miscegenation
Which of the following ideologies incentivized large scale European migration to Middle and South America from 1880-1930?
blanquiamiento
The exchange of plants, animals, and diseases that followed the colonization of the Americas is referred to as...
the Columbian Exchange
What factor best explains the rise of the "pristine myth"?
depopulated landscapes due virgin soil epidemics
Which of the following best describes the significance of the Haitian Revolution?
It abolished slavery before anywhere in the world
What is the geological origin of the Andes mountains?
the subduction of the Nazca Plate underneath the South American Plate
Which Latin American region is the most tectonically active, prone to both earthquakes and volcanic activity?
Western Latin America
Which factor contributes to high number of deaths and high destruction due to Haiti's 2010 earthquake?
the fact that Haiti is the poorest nation in the Western hemisphere
Which of the following is a latitudinal belt of rising air (low pressure system) that brings abundant rain to tropical regions?
the Intertropical Convergence Zone
Mexico City is outlined by a series of volcanoes and is frequently rattled by earthquakes due to...
the subduction of the Cocos Plate
Both the Inca and the Aztec revered mountains, considering them sacred places and the realm of the Gods.
True
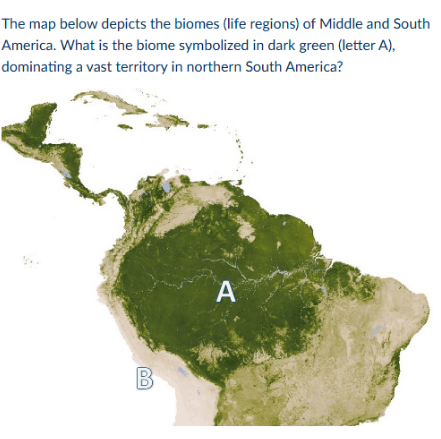
amazon rainforest
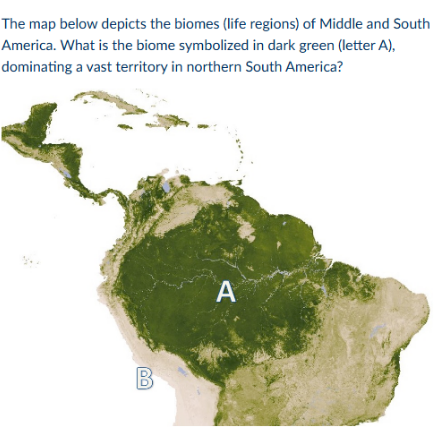
rainshadow effect
TRUE OR FALSE:
Cumulative research suggests that over thousands of years the inhospitable conditions in the Amazon, like warm temperatures and infertile soils, have made it largely uninhabitable by humans. Thus, for millennia, the Amazonian rainforest has been largely empty of people and untouched by human hands.
False
What evidence supports the current scientific conclusions about the historical settlement patterns in the Amazon?
There is evidence of extensive composted soils and geometric earthworks that suggest large settlements existed in the past.
How and why do geographers split Africa into two separate world regions? What are some of the issues with that?
Geographers split Africa into North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa based on historical, cultural, and geographical differences, with North Africa being influenced by Arab-Islamic culture and Sub-Saharan Africa by indigenous and colonial histories. The Sahara Desert acts as a natural boundary, reinforcing this distinction.
However, this division oversimplifies the continent's complexity by grouping diverse cultures, economies, and histories into just two regions, ignoring overlaps in religion, language, and politics. It also overlooks the growing interconnectedness across Africa and fails to capture the unique characteristics of various sub-regions, like West or East Africa.
Describe Africa's latitudinal situation and how it shapes its major biome regions. Identify the major biomes described.
Africa’s latitudinal situation spans from about 37°N to 34°S, placing it mostly within the tropical zone, which significantly shapes its diverse biome regions. This positioning creates distinct biomes like deserts, savannas, rainforests, and temperate regions, influenced by varying rainfall and temperature patterns across the continent.
The major biomes in Africa include the Sahara Desert (arid), Sahel (semi-arid), Savanna (tropical grassland), Tropical Rainforest (humid), Mountain (highland climates), and Mediterranean (mild, wet winters). These biomes are shaped by latitude, altitude, and the distribution of precipitation.
Explain the mechanisms of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) and how it shapes climate and seasonability in tropical regions.
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a band of low pressure near the equator where the trade winds from both hemispheres converge, causing air to rise and leading to high precipitation. This zone shifts north and south with the seasons, affecting rainfall patterns and creating distinct wet and dry seasons in tropical regions.
As the ITCZ moves, it influences seasonality by causing alternating rainy and dry periods; when it is overhead, the region experiences heavy rains, while its departure leads to drier conditions. This shifting pattern significantly impacts agriculture, water availability, and ecosystems in the tropics.
Identify the major river basins of Africa South of the Sahara and their significance.
Major river basins south of the Sahara, such as the Congo, Niger, Zambezi, and Orange, are crucial for providing water, supporting agriculture, enabling transportation, and sustaining ecosystems across the region.
Explain the tectonic dynamics of the Great Rift Valley and some of its geographical features. Where are the highlands of Africa and its tallest peaks?
The Great Rift Valley is a tectonically active region formed by the stretching and splitting of the Earth's crust, resulting in volcanic mountains, deep valleys, and earthquakes, with the East African Highlands hosting Africa's tallest peaks, including Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Kenya.
What are the two scientific truths about human genetics? Describe human origins and migration out of Africa. What explains variations of human hue? What world region contains the greatest human diversity? What is scientific racism?
1. Two scientific truths about human genetics are that all humans share 99.9% of their DNA and that genetic diversity within populations is often greater than between them.
2. Human origins trace back to Africa, with early Homo sapiens migrating out of the continent around 60,000 years ago, spreading across the globe and adapting to diverse environments.
3. Variations in human skin color are primarily caused by adaptations to different levels of ultraviolet radiation, with darker skin protecting against intense sun in equatorial regions and lighter skin aiding vitamin D synthesis in northern latitudes.
4. Sub-Saharan Africa contains the greatest human genetic diversity, reflecting its status as the origin of modern humans and the longest period of human evolution.
5. Scientific racism is the misuse of scientific research or theories to support or justify racial discrimination, claiming that some races are inherently superior or inferior based on biological traits.
Describe West Africa as a cultural hearth. What is the Bantu expansion?
1. West Africa is considered a cultural hearth because it has been a center of early civilization, trade, language, and the spread of agricultural and religious practices that influenced much of the African continent.
2. The Bantu expansion refers to the migration of Bantu-speaking peoples from West and Central Africa to much of Sub-Saharan Africa, spreading languages, agricultural techniques, and cultural practices over several millennia.
Describe the great kingdoms and empires of pre-colonial Africa, the trading networks that enriched them, and the cities central to indigenous African civilizations. What is the significance of Timbuktu?
1. Pre-colonial Africa was home to powerful kingdoms and empires like Ghana, Mali, Songhai, and Great Zimbabwe, whose wealth was derived from control over gold, salt, and trans-Saharan trade routes, with cities like Timbuktu, Cairo, and Kinshasa serving as cultural, political, and commercial hubs.
2. Timbuktu was a center of intellectual and cultural life, known for its wealth, Islamic scholarship, and famous libraries, making it a symbol of African historical achievements in education and trade.
What are some difficulties in reconstructing African history? What is the movement to restitute African artifacts about? How much of it is abroad? Where?
1. Reconstructing African history is challenging due to the lack of written records, the diversity of oral traditions, and the impact of colonialism on indigenous knowledge systems.
2. The movement to restitute African artifacts seeks to return cultural treasures taken during colonial times, aiming to restore heritage and correct historical injustices.
3. An estimated 90% of Africa's cultural artifacts are held abroad, primarily in European museums such as the British Museum, Louvre, and Berlin's Ethnological Museum.
What is protocolonialism? Why are scholars adopting this term to describe the pre-colonial economic relations of African kingdoms with Europeans?
1. Protocolonialism refers to the economic and political relationships between African kingdoms and European powers before formal colonization, characterized by trade, diplomacy, and sometimes exploitation.
2. Scholars are adopting this term to highlight how pre-colonial interactions laid the groundwork for later colonization, showing that European powers often exploited African resources and people long before establishing direct control.
What was the Berlin Conference of 1884? Which African state was never colonized? What period did most African countries gain their independence?
1. The Berlin Conference of 1884 was a meeting where European powers divided Africa into colonies without African representation, formalizing the "Scramble for Africa."
2. Ethiopia (then Abyssinia) was never colonized, successfully resisting Italian invasion and maintaining its sovereignty.
3. Most African countries gained their independence during the 1950s and 1960s, as decolonization movements accelerated following World War II.
Compare and contrast language families and religion contrasts between countries north and south of the Sahara and the processes responsible for their geographic distribution.
1. North of the Sahara, the predominant languages belong to the Afro-Asiatic family, and the region is primarily Islamic, while south of the Sahara, languages belong to the Niger-Congo family, and Christianity and indigenous religions are more common.
2. The geographic distribution of these linguistic and religious differences is influenced by historical processes such as the spread of Islam from the Arabian Peninsula across North Africa and the transatlantic slave trade and European colonialism shaping the south.
Describe how our conventional ways of measuring poverty and wealth tend to underestimate Africa. Use these follow up questions to develop your explanation: Define the GPD p/capita and its omissions, and the poverty rate and its exclusions. What is the multidimensional poverty index (MPI) and how does this measure change our understanding of the global population living in poverty? What is the informal economy? How does it influence our perceptions about the economies of African countries?
1. Conventional measures like GDP per capita and poverty rates tend to underestimate Africa by failing to account for informal economies, subsistence farming, and non-monetary contributions that are significant in many African countries.
2. GDP per capita measures average income but omits factors like inequality, health, and education, while poverty rates exclude non-income deprivations, such as lack of access to education, clean water, and healthcare.
3. The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) expands on income-based measures by considering deprivations in health, education, and living standards, providing a more comprehensive view of poverty.
4. The informal economy includes unregistered, non-taxed activities like street vending or small-scale farming, and it significantly influences African economies, as it provides livelihoods for a large portion of the population not reflected in formal economic statistics.
5. The informal economy challenges perceptions about African economies by showing that official economic indicators often overlook the true extent of economic activity, leading to underestimations of the continent's wealth and development.
Describe the demographic qualities of Africa South of the Sahara. What are the most populous countries in the region? What demographic characteristics and trends can be promising for African economies? (Think female education and demographic dividend)
1. Africa south of the Sahara has a young, rapidly growing population, with high fertility rates and a large proportion of youth under 25.
2. The most populous countries in the region include Nigeria, Ethiopia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Tanzania.
3. Promising demographic trends for African economies include increasing female education and empowerment, as well as the potential demographic dividend from a youthful labor force entering the workforce in the coming decades.
What has propelled rural-to-urban migration in African countries? What African regions have greater share of the population living in cities? What are some of the challenges African cities face?
1. Rural-to-urban migration in African countries has been propelled by the search for better economic opportunities, improved education, healthcare, and the impact of climate change on rural livelihoods.
2. North Africa and Southern Africa have a greater share of their populations living in cities, driven by more developed infrastructure and economies.
3. African cities face challenges such as rapid urbanization, inadequate infrastructure, high unemployment, slum growth, and insufficient access to basic services like water and sanitation.
Describe the apartheid system and how its legacy continues to shape South Africa.
1. The apartheid system was a policy of racial segregation and discrimination in South Africa that lasted from 1948 to 1994, enforcing separate living areas, schools, and job opportunities for non-white South Africans.
2. Its legacy continues to shape South Africa through ongoing economic inequality, spatial segregation, and social divisions, as well as challenges related to land redistribution and access to quality education and healthcare.
Describe mineral wealth in Africa and its importance in the crossroads of history. What is the resource curse? Explain the process that helps shape the vulnerability of African economies to this phenomenon.
1. Africa’s mineral wealth, including vast deposits of gold, diamonds, oil, and rare earth metals, has made the continent a critical player in global trade and a focal point in colonial and geopolitical history.
2. The resource curse refers to the paradox where countries rich in natural resources experience slower economic growth, corruption, and conflict due to over-reliance on resource extraction.
3. African economies are vulnerable to the resource curse because dependence on commodity exports makes them sensitive to global price fluctuations, while weak institutions, corruption, and conflicts over resources hinder long-term development.
Describe some of the impacts of the protocolonial and colonial period on African economies.
1. The protocolonial and colonial periods disrupted traditional African economies by shifting them toward extractive industries, focusing on resource extraction for European benefit and stunting local economic development.
2. These periods also established infrastructure and trade networks that prioritized European interests, leading to economic dependency, social inequality, and the creation of borders that ignored ethnic and cultural divisions.
What motivated the Second Scramble for Africa? What are the enduring outcomes of this period?
1. The Second Scramble for Africa was motivated by European powers' desire for control over Africa’s vast natural resources, new markets, and strategic territories, intensified by industrialization and competition for global dominance in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
2. The enduring outcomes of this period include the artificial borders that divided ethnic groups, long-lasting political and economic instability, and the legacy of colonial exploitation that continues to affect Africa’s development.
Compare and contrast how Freedom in the World and the State of Democracy Indexes are measured and categories defined. What do these indexes say about governance in Africa today? How has it changed overtime? What are the democratic countries in Africa? What is the democracy gap? In other words, what do surveys tell us about African views about autocrats?
1. The Freedom in the World index measures political rights and civil liberties, categorizing countries as "Free," "Partly Free," or "Not Free" based on factors like electoral processes, political participation, and individual freedoms, while the State of Democracy Index evaluates the health of democracy through aspects like electoral processes, functioning of government, political participation, and civil liberties, ranking countries from "Full Democracy" to "Authoritarian Regime."
2. These indexes suggest that governance in Africa remains diverse, with some countries improving in political rights and civil liberties, but many still struggling with authoritarianism, corruption, and weak institutions; overall, governance has improved slightly but remains uneven across the continent.
3. Some of the democratic countries in Africa today include Mauritius, Cape Verde, Botswana, and Ghana, which score higher in both indexes for their stable democratic practices.
4. The democracy gap refers to the disparity between the growing desire for democratic governance among Africans and the continued prevalence of autocratic regimes or poor democratic practices in many countries.
5. Surveys show that while many Africans desire greater democracy and view autocratic leadership negatively, there is also a pragmatic acceptance in some countries of autocrats as a means to maintain stability or economic growth, reflecting mixed views on leadership styles.
How does the resource curse empower autocrats and oppressive armed forces? Explain the discontent behind the #EndSARS movement in Nigeria
1. The resource curse empowers autocrats and oppressive armed forces by providing them with control over lucrative natural resources, which they can exploit to maintain political power, fund military operations, and suppress opposition, often with little accountability to the public.
2. The #EndSARS movement in Nigeria arose from widespread discontent over police brutality, particularly by the Special Anti-Robbery Squad (SARS), highlighting frustrations with government corruption, ineffective governance, and the abuse of power by security forces, prompting calls for reform and accountability.
How is Angola the landmine capital of the world? What is the significance of biodiversity protection in Angola for the Kavango-Zambezi Trans-frontier Conservation Area? What is the impact of landmines in supporting biodiversity and livelihoods?
1. Angola is considered the landmine capital of the world because of the extensive landmine contamination left from the civil war (1975–2002), with millions of mines scattered across the country, hindering development, agriculture, and safety.
2. The Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area (KAZA) is significant for biodiversity protection in Angola as it creates a large, cross-border conservation zone that supports wildlife migration, habitat preservation, and regional ecological stability.
3. The impact of landmines on biodiversity and livelihoods is profound, as landmine contamination not only restricts access to vital land for farming and grazing but also disrupts wildlife corridors, reducing biodiversity and limiting local communities’ ability to thrive.
Describe China’s influence on African countries. How does trade illustrate the bond between the two regions? What is the Belt and Road Initiative? Defined "debt diplomacy" and identify concerns around China’s strategy in Africa. According to surveys, what do Africans think about Chinese influence?
1. China’s influence on African countries has grown significantly through investments in infrastructure, trade, and loans, positioning China as a major economic partner and political player in the region.
2. Trade illustrates the bond between China and Africa through the exchange of African raw materials like oil, minerals, and agricultural products for Chinese manufactured goods, infrastructure projects, and financial investments.
3. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is China’s global infrastructure development strategy aimed at enhancing trade routes and connectivity, which includes major projects in African countries like roads, railways, and ports.
4. Debt diplomacy refers to the practice of using loans to create economic dependence, with concerns about African countries accumulating unsustainable debt to China in exchange for infrastructure projects, leading to potential loss of sovereignty or long-term economic vulnerability.
5. According to surveys, many Africans view Chinese influence positively, particularly in terms of infrastructure development and job creation, though there are growing concerns about debt, labor practices, and the lack of local economic benefits.
Identify the ways that climate change is an economic burden on African countries by describing its impacts on GDP and poverty rates. What is climate vulnerability and how is it projected to impact African countries and peoples?
1. Climate change is an economic burden on African countries by reducing agricultural productivity, damaging infrastructure, and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events, all of which negatively affect GDP and push millions further into poverty.
2. Climate vulnerability refers to the susceptibility of countries and populations to the adverse impacts of climate change, with projections indicating that African countries will face severe consequences like rising temperatures, droughts, floods, and food insecurity, disproportionately affecting poor and rural communities.
What are some of the vulnerabilities in the Sahel? Describe the Great Green Wall, its purpose and potential in building climate resilience.
1. The Sahel is highly vulnerable to climate change due to its arid climate, frequent droughts, desertification, and dependence on rain-fed agriculture, which exacerbate food insecurity, displacement, and conflict.
2. The Great Green Wall is an ambitious African-led initiative to combat desertification and land degradation by planting a mosaic of trees and vegetation across the Sahel, aiming to restore 100 million hectares of land, build climate resilience, and improve livelihoods for local communities.
Scientific evidence supports that humans migrated out of ___________ around 60,000 years ago, dispersing to every corner of the world overtime to eventually arrive in ____________ last at around 12,000 years ago.
Africa; the Americas
Culturally and genetically, the most diverse human population lives in...
Africa
Racial categories used today such as Black, Asian, white, or Indigenous are genetically identifiable categories of human difference.
False
Genetic research suggests that all 8 billion plus humans in the world are closely related and genetically similar, despite our large human population and global geographic distribution.
True
It is more likely that two chimpanzees are more genetically different from one another than two humans.
True
Differences in human hue are a bi-product of naturally occurring mutations in the human DNA, advantageous hues became prevailing features for human populations in different climate regions.
True
Which of the following best describes the studies of Samuel Morton in the early 1900s?
He collected human skulls as faux scientific evidence of the superiority of Europeans.
Pre-Colonial West African Empires reached great wealth based on their trading connections to
the Trans-Saharan trade
About 90 percent of African cultural artifacts are kept in collections outside of Africa
True
Which of the following most influenced the establishment of authoritarianism in African countries?
the Cold War
Landmines in Angola…
are residues of decades of proxy wars funded by international actors
Measuring poverty as the percentage of the population earning $1.90 a day tends to…
underestimate poverty since earning slightly more than $1.90 a day does not end poverty
Most national economies in Africa are largely reliant on...
exports of oil, gold, and/or diamonds
According to the Democracy Index, which of the following countries is a democracy?
South Africa
Which of the following countries is the top trading partner for most African countries today?
China
Which of the following represents an era of protocolonialism in Africa?
the Transatlantic slave trade