Mitosis & Meiosis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Mitosis
Division of somatic cells
Meiosis
Division of sex cells
What does most body cells have?
46 chromosomes → 2 sets of identical chromosomes (diploid aka 2n)
Homologous chromosomes
The same chromosome, one from maternal and the other from paternal (2 identical pairs of 23)
What do gametes (sex cells) have?
Haploid (singular) chromosome number (n) → will join together with either sperm or egg that also has n (to make 46 aka 2n)
What does gamete formation also involve?
Two consecutive cell divisions (meiosis 1 and meisosis 2) → only one round of DNA replication tho → produces 4 daughter cells
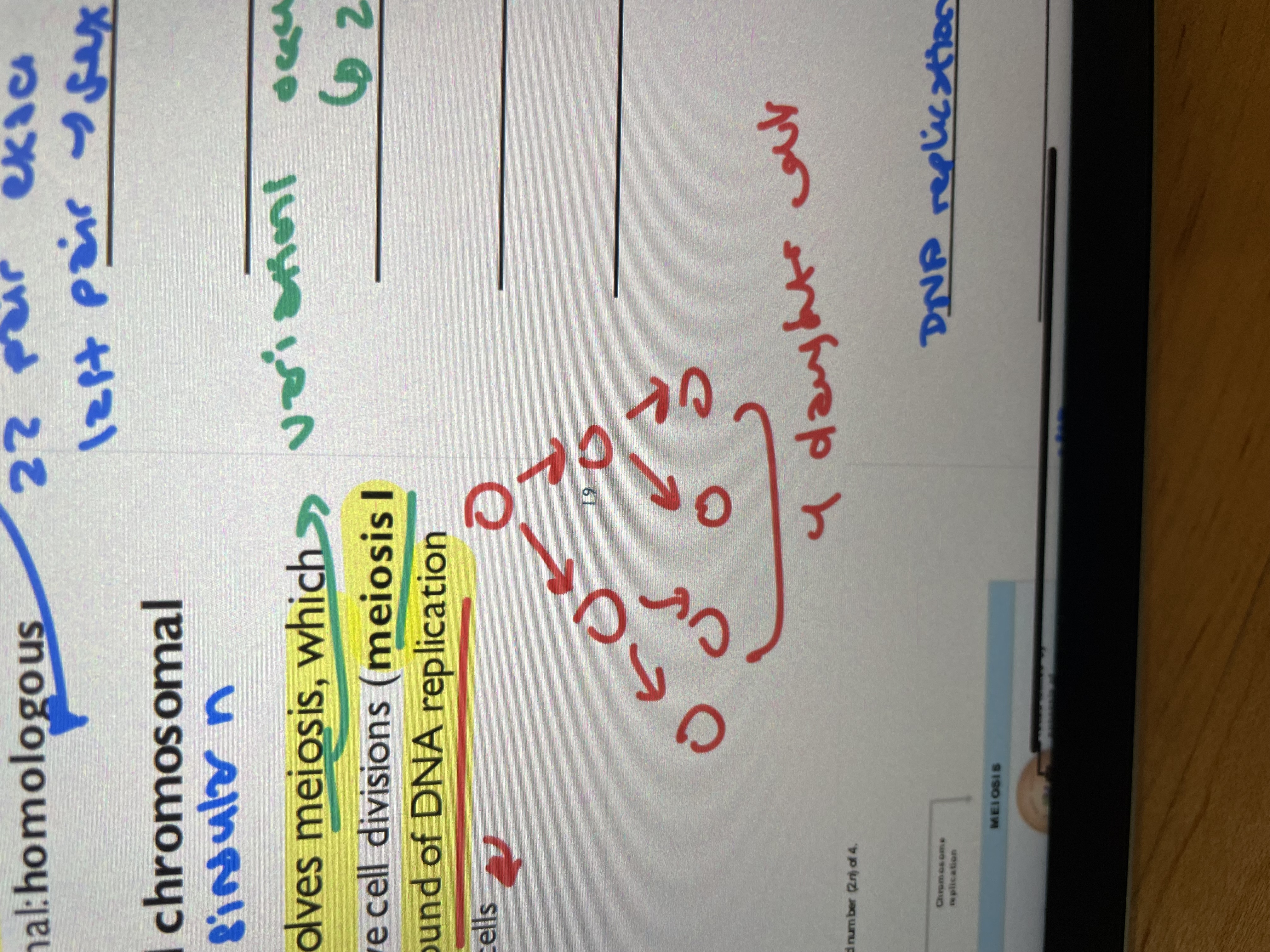
Mitosis simplified
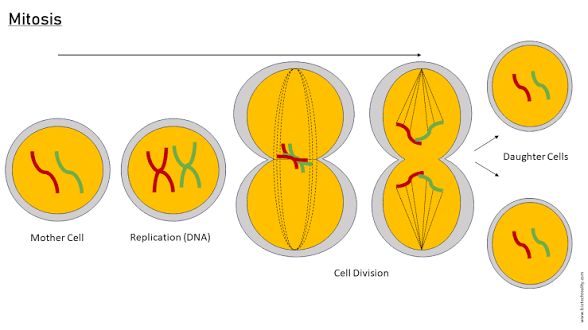
Prophase → replicated chromosome (double DNA)
Metaphase : chromosome align at the metaphase plate (still double DNA)
Sister chromatids (the identical DNA attached by a centromere) separate during anaphase → give Two different daughter cells with 2n each
Meiosis simplified
Prophase I : retard formed by synapsid of replicated homologous chromosomes (double of identical DNA)
Metaphase I : rereads align randomly at metaphase plate (where variation happens)
Homologous chromosomes separate but sister chromatids remain together during anaphase I → two daughter cells that contain 46 chromosomes each
Meiosis II → no further replication but sister chromatids separate during anaphase II → results in 4 daughter cells each contain 23 chromosomes