Measuring enthalpy changes
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
difference between heat and temperature
temperature = measure of average kinetic energy of the particles
heat = measure of energy content of a substance
chemical reactions involve a transfer of energy between the system and the surroundings, while total energy is conserved
enthalpy
total chemical energy inside a substance measured at constant pressure
when reactions happen, enthalpy changes
exothermic reactions
when products have less enthalpy than reactants
heat is given off by the system to the surroundings
temp of surroundings increase, temp of system decrease
ΔH is negative
endothermic reactions
when products have more enthalpy than reactants
heat is taken in by the system from the surroundings
temp of surroundings decrease, temp of system increase
ΔH is positive
energy profiles
shows energies of reactants, transition state and products over time
transition state is stage during reaction when chemical bonds are partially broken and formed, very unstable
activation energy needed to reach transition state
minimum amt of energy needed for reactant molecules to successfully collide and start reaction
standard enthalpy change
ΔHꝊ refers to heat transferred at constant pressure under standard conditions
calculated in kJ mol–1
standard enthalpies

energy transferred as heat equation
no need to convert C into K if given in C
ΔH = - heat energy Q / n

specific heat capacity
energy needed to raise the temp of 1g of substance by 1K
enthalpy changes for reactions in solution
reaction with excess of one reagent, temp is measured over time
assumptions made:
specific heat capacity is same as water
density of solution is same as water (1 gcm3)
negligible heat losses
reaction goes to completion
specific heat capacity of container is ignored
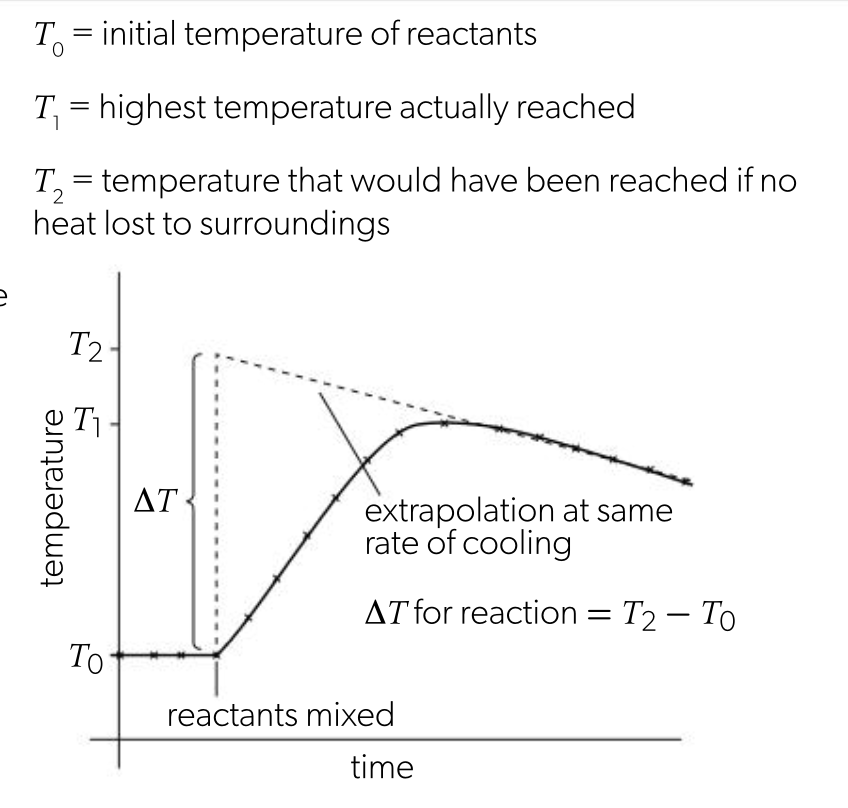
temperature correction graphs
reactions aren’t instantaneous, so there is delay before max temp is reached, during delay substances may be losing heat to surroundings, so true max temp is never reached
graphs are extrapolated to calculate the max temp that couldve been reached
enthalpy of combustion experiments
heat released from combustion reaction used to increase temp of water
to minimise heat loss calorimeter should be placed close to the flame and lid placed over calorimeter
main sources of error
heat losses
incomplete combustion