Cell Communication
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
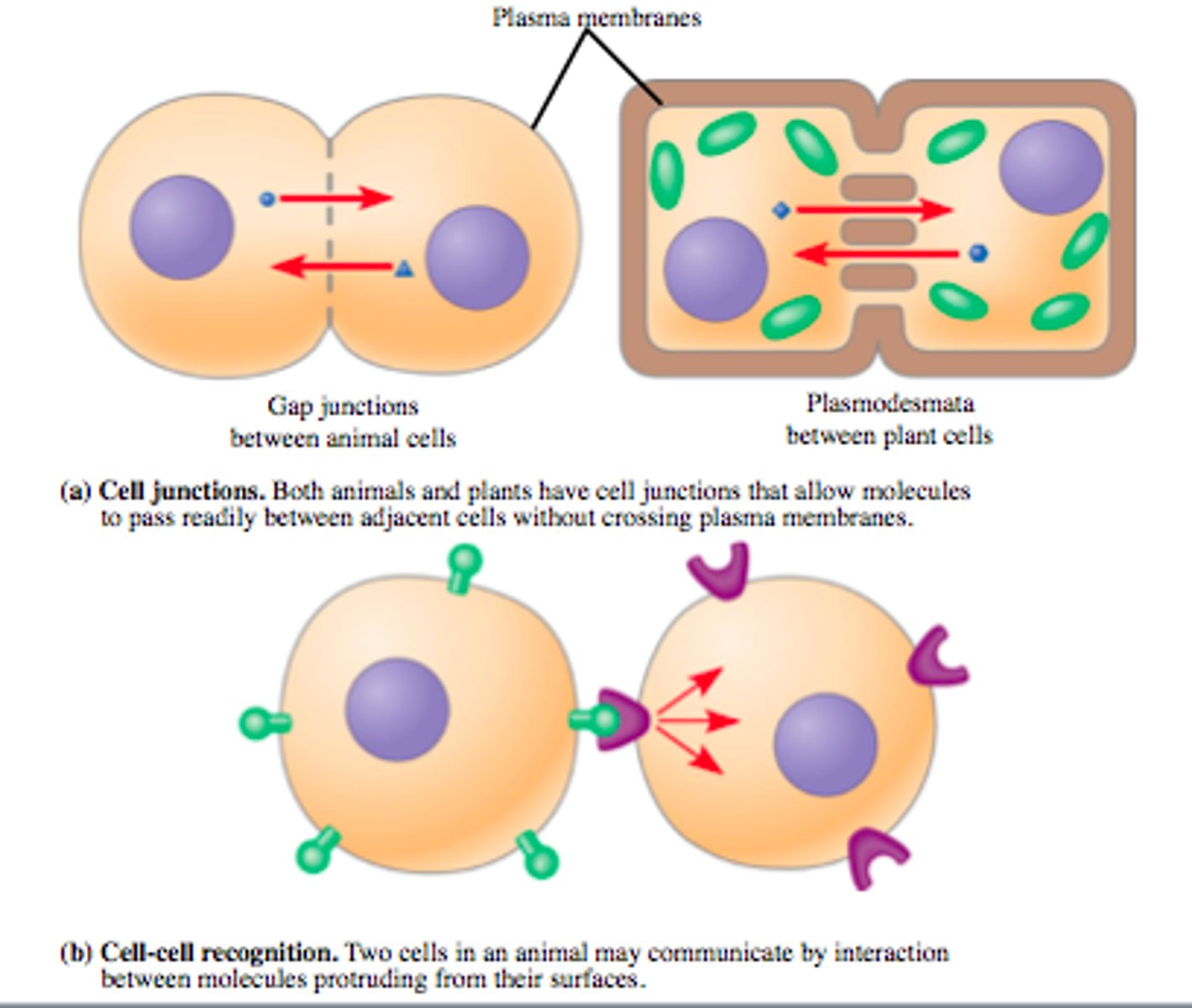
Juxtacrine
Type of cell signaling where cells are touching through cell junctions (plasmodesmata or gap junctions) or surface receptors
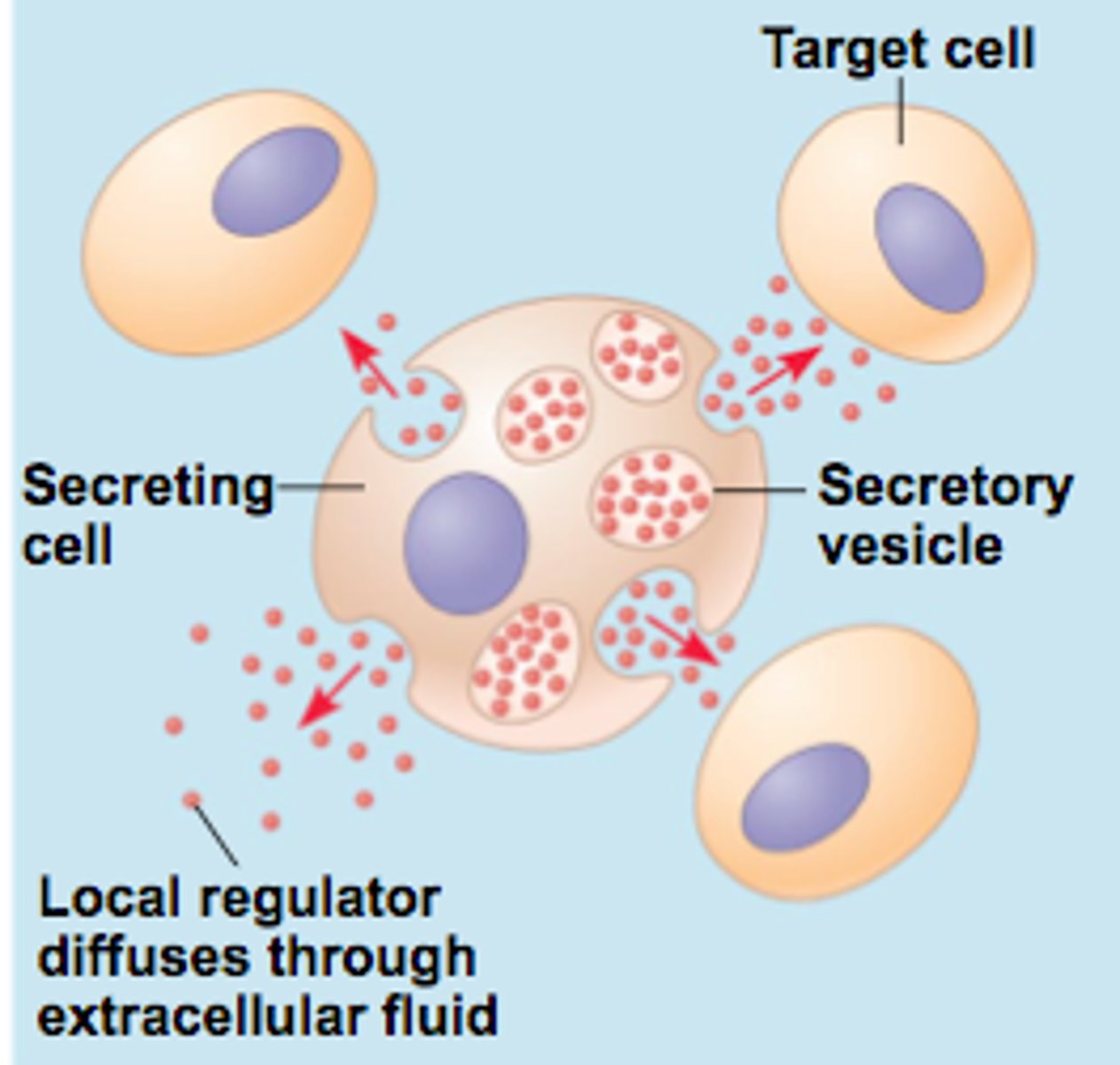
Paracrine
Type of cell signaling between cells that are near each other.
Endocrine
Type of cell signaling between cells that are far from each other. Long distance signaling using hormones.

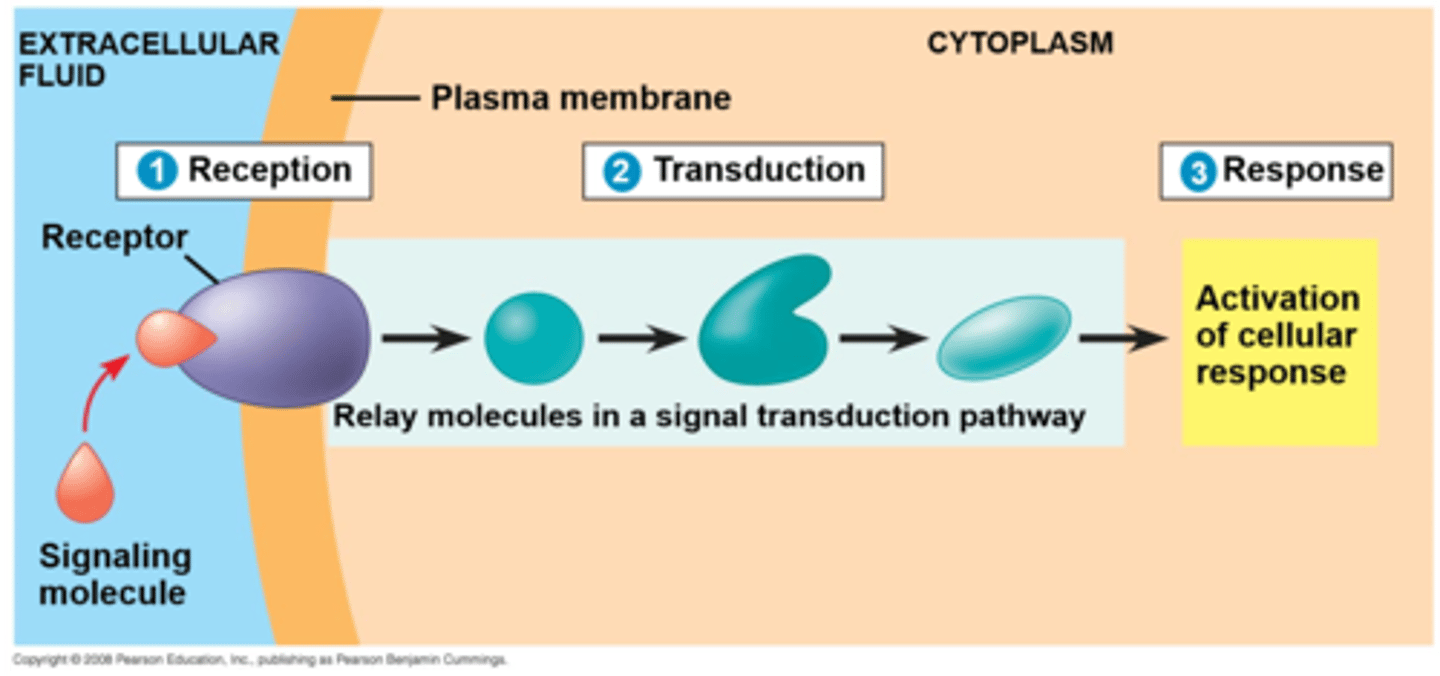
3 stages of cell signaling
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
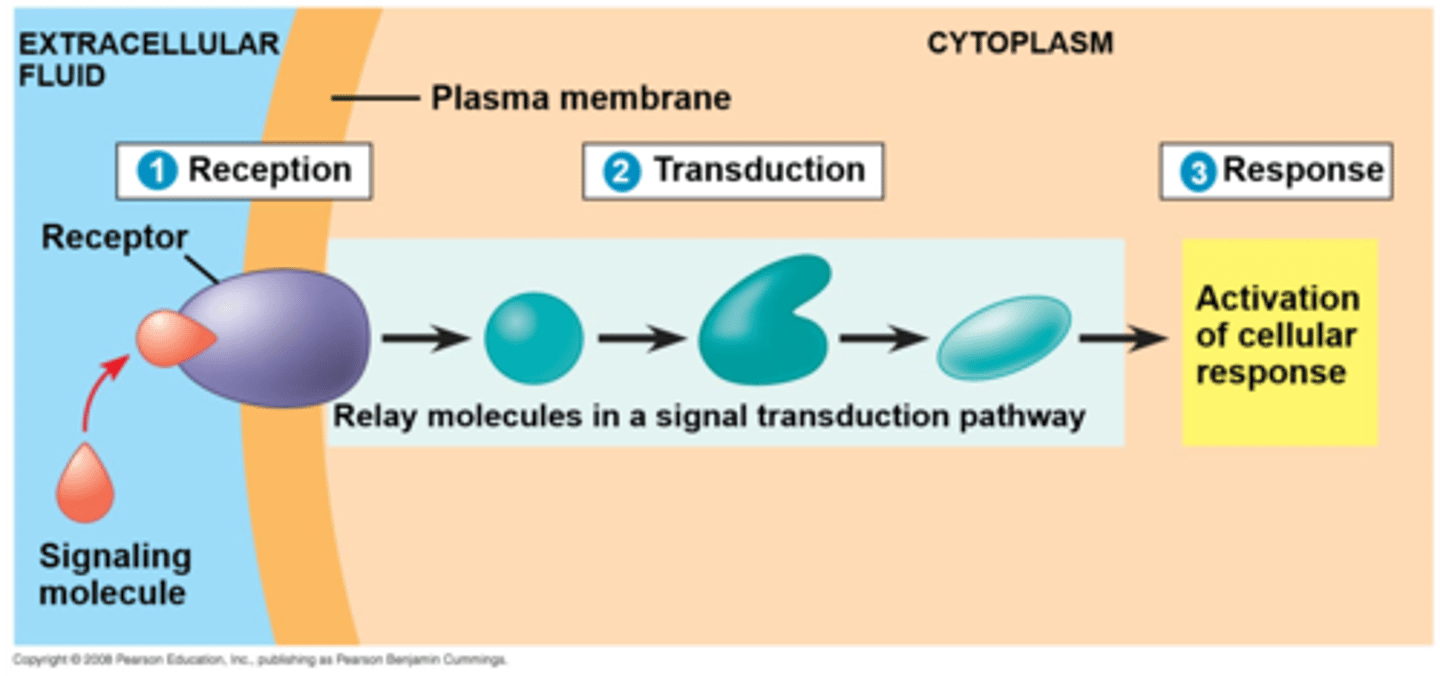
Cell surface receptor
receptors that are embedded in the membranes of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. (A, C, D in image)
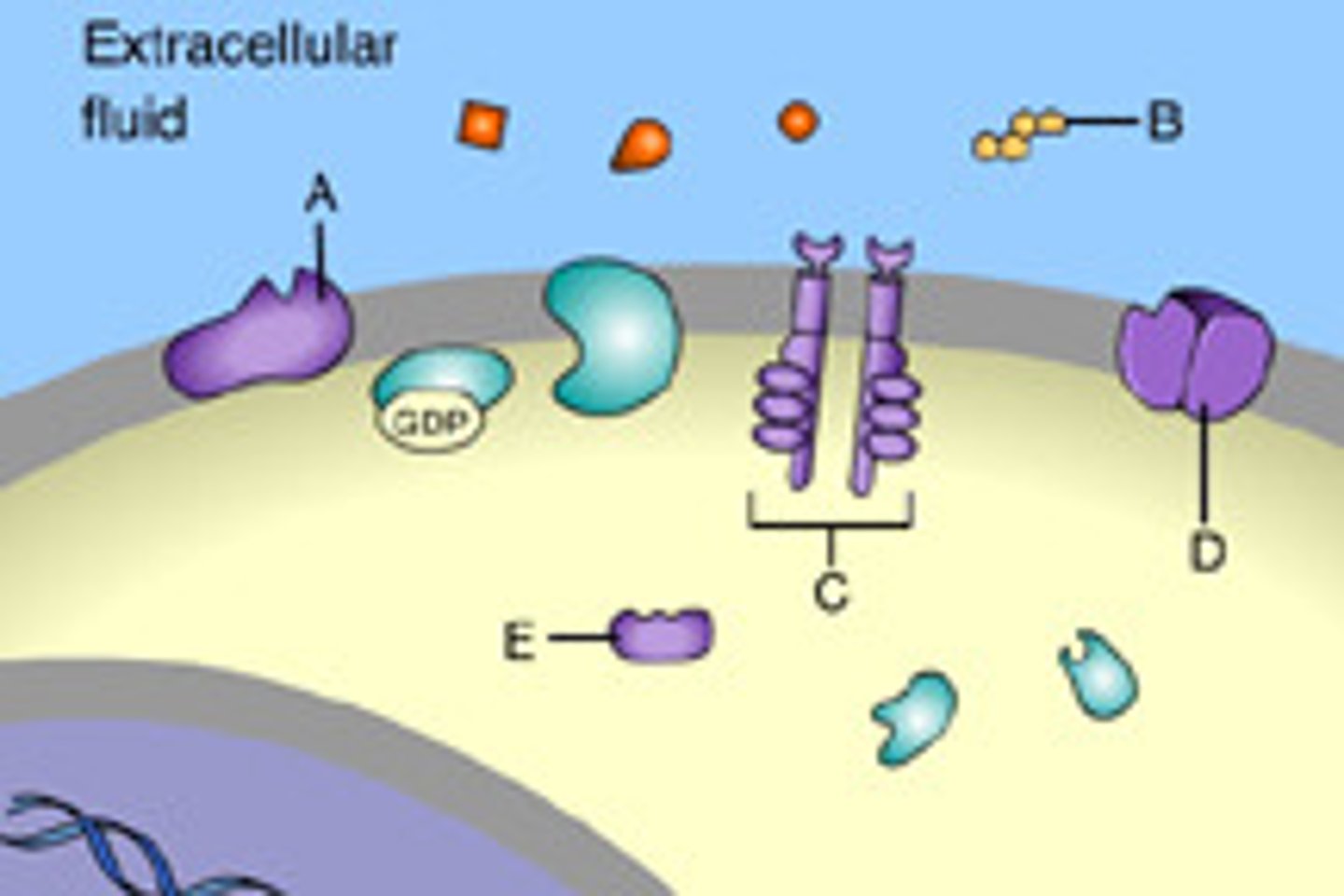
Intracellular receptor
a receptor located inside the cell in the cytoplasm or nucleus. Binds nonpolar, hydrophobic signals.

Signal Transduction Pathway
The spread of a message from the receptor throughout the cell to the response that involves phosphorylation cascades or second messengers.
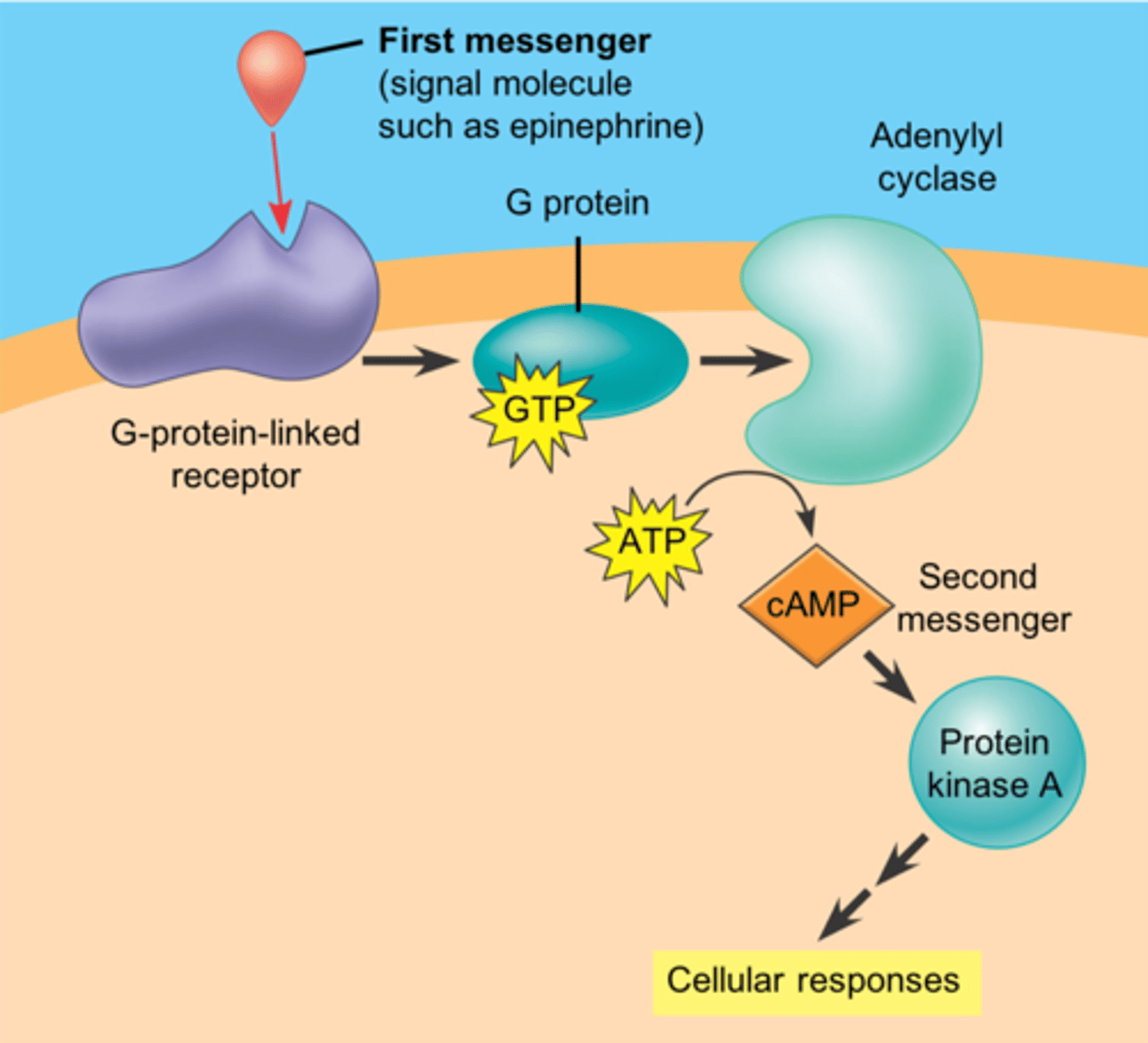
Second messenger
A small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as calcium ion or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signal received by a signal receptor protein. (signal transduction pathway)
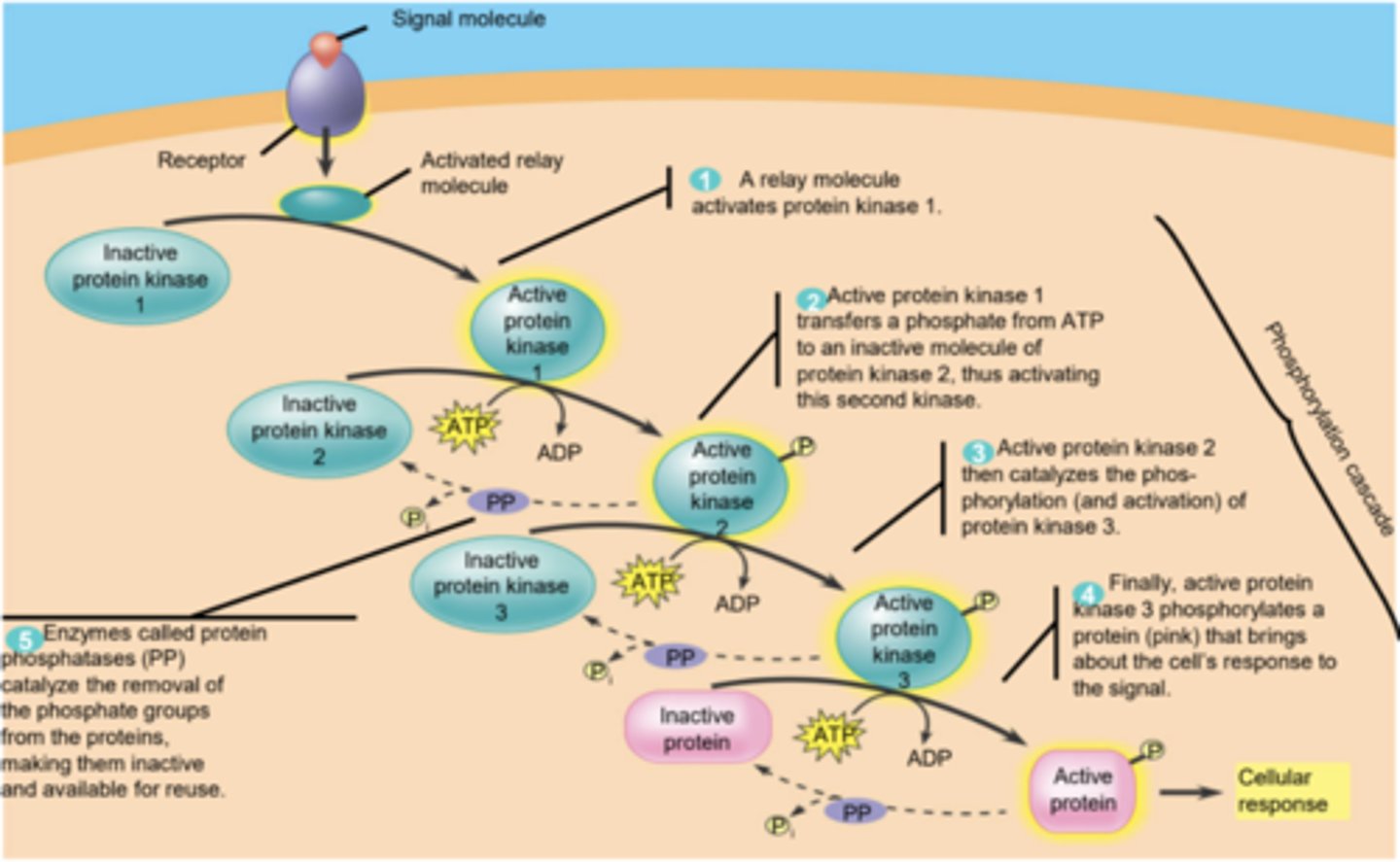
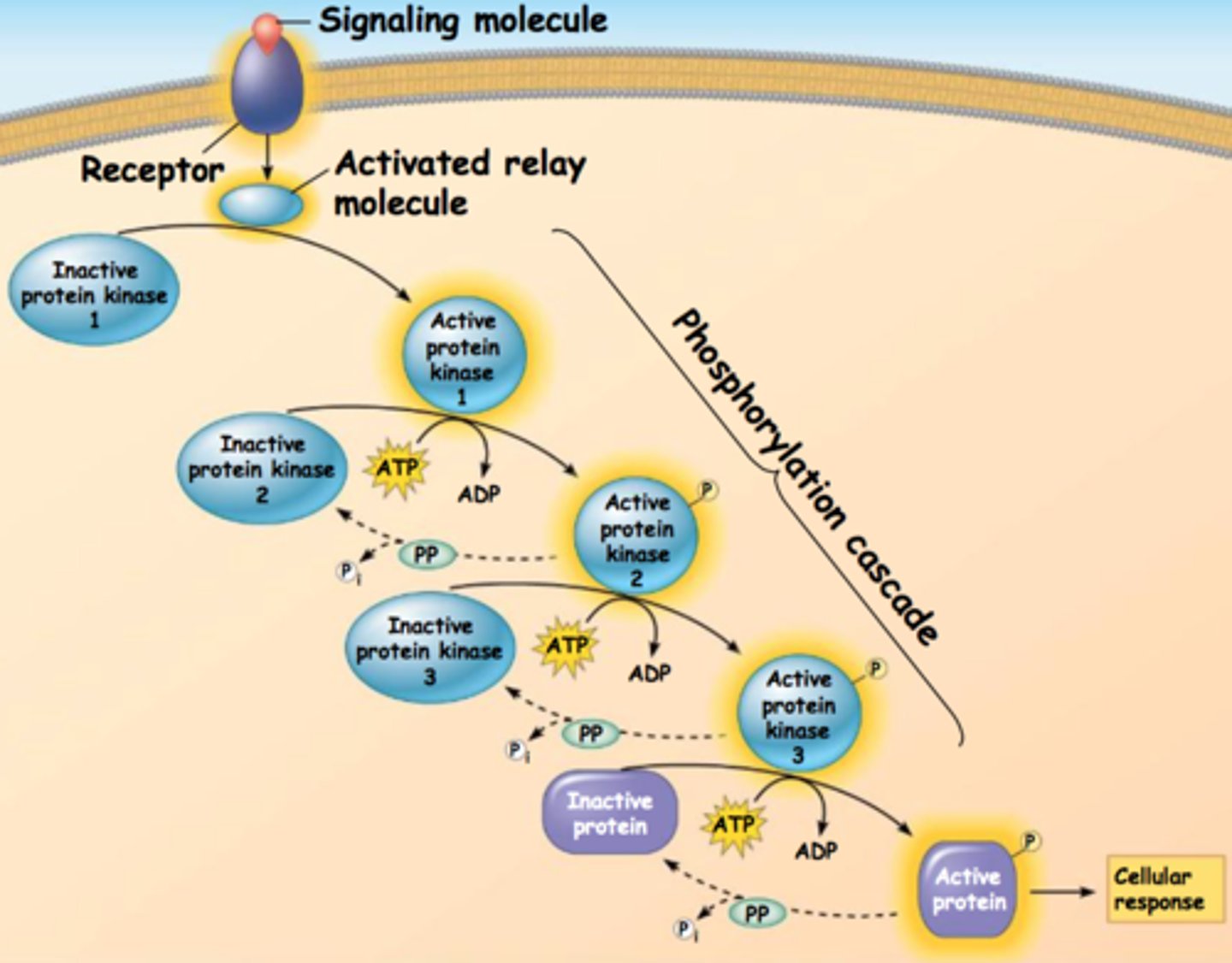
Phosphorylation cascade
a sequence of events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the phosphorylation of thousands of proteins. (signal transduction pathway.)
Cytoplasmic Response
Type of response in cell signaling where there may be activation or inactivation of an enzyme in cytoplasm, activation of cell division, or activation of cell death
Nuclear Response
turning genes on/off to start/stop protein synthesis; if gene is activated, then transcription factors attach to DNA and cause the creation of mRNA and then a protein.

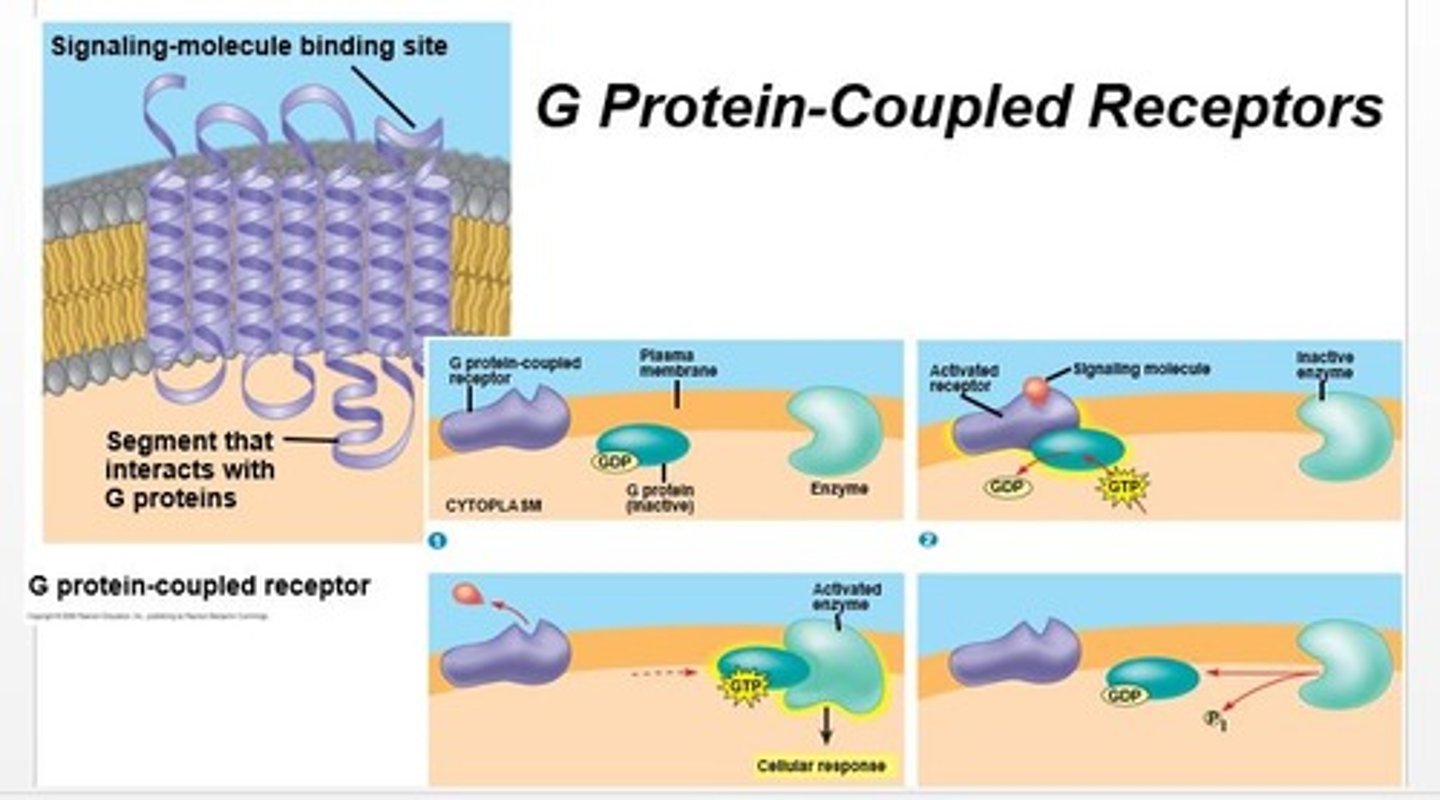
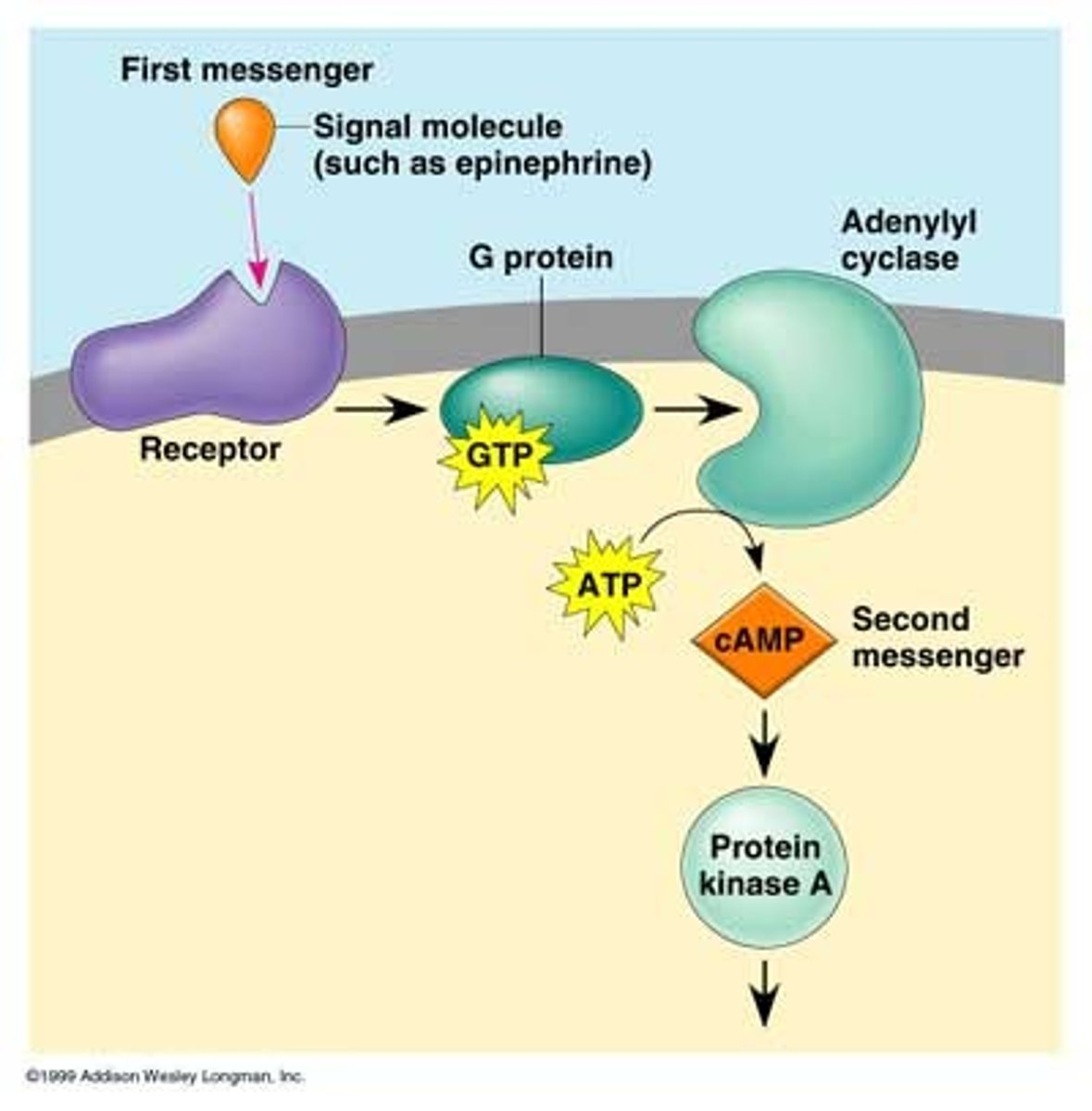
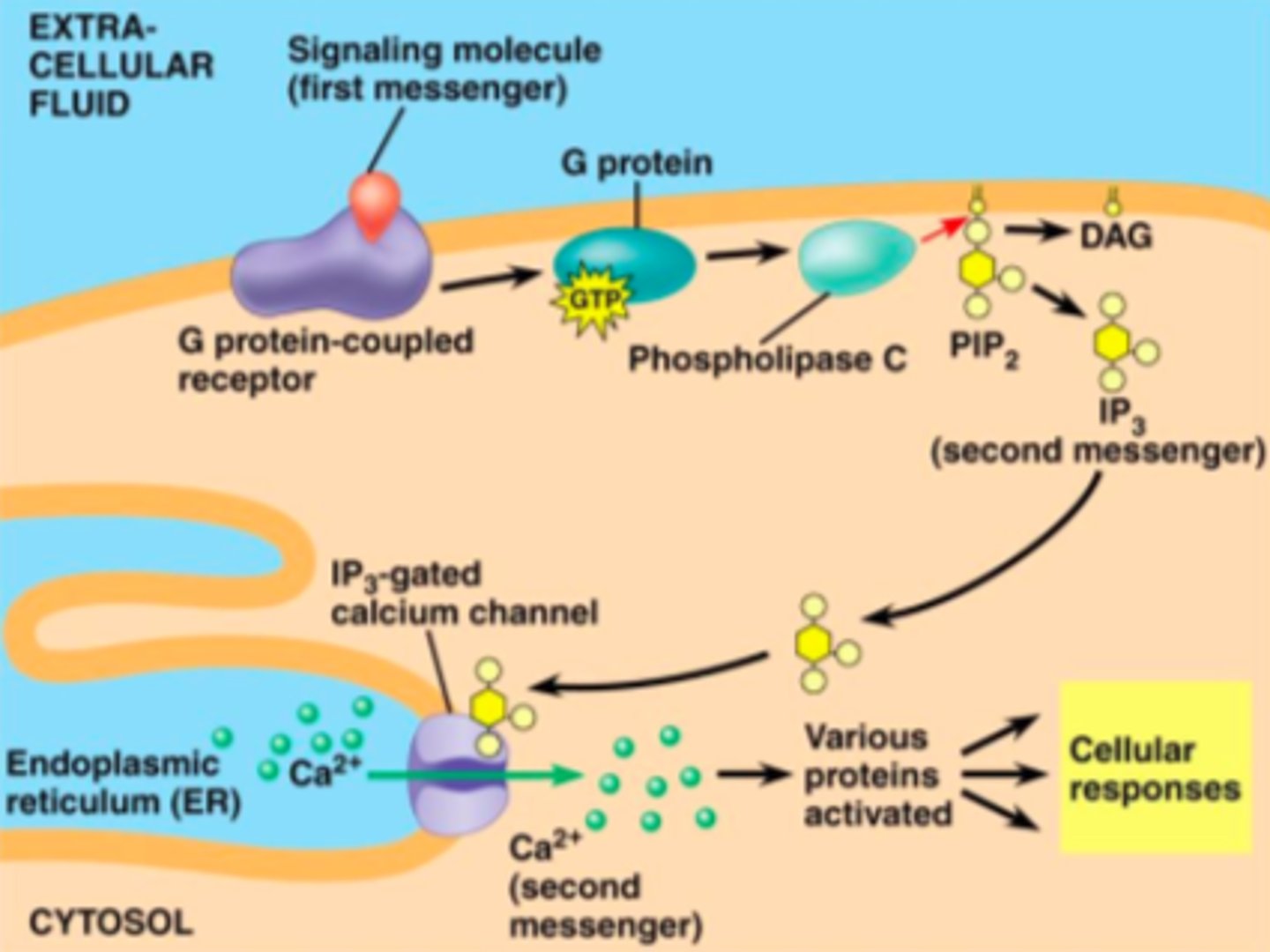
G-protein coupled receptors
A signal receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signaling molecule by activating a G protein. Also called a G protein-linked receptor.
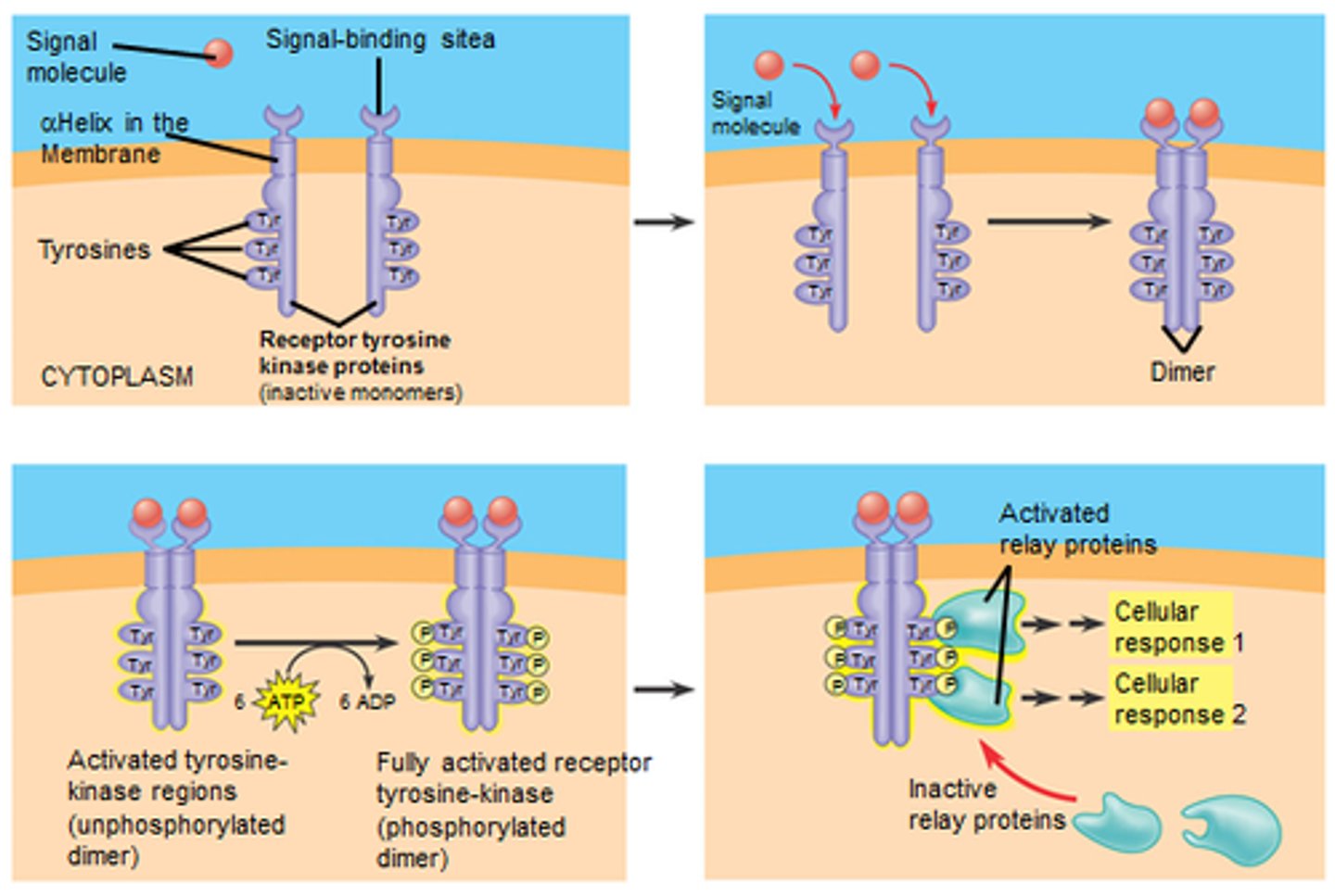
Receptor Tyrosine kinase
A receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signal molecule by catalyzing the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to tyrosines on the cytoplasmic side of the receptor. The phosphorylated tyrosines activate relay proteins within the cell.
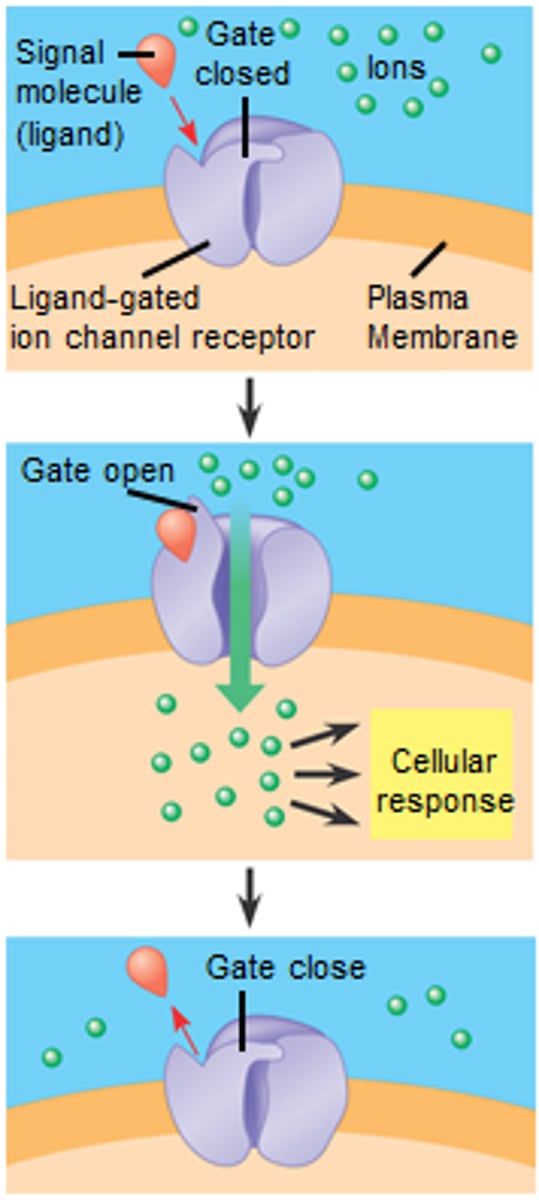
Ion-channel receptors (ligand-gated ion channels)
type of membrane channel receptor containing a region that can act as a "gate" that binds a ligand to the channel receptor causing a conformational change to allow gates to open or close to allow ions to enter or stop entering cell.
Protein kinase
general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein to activate the protein
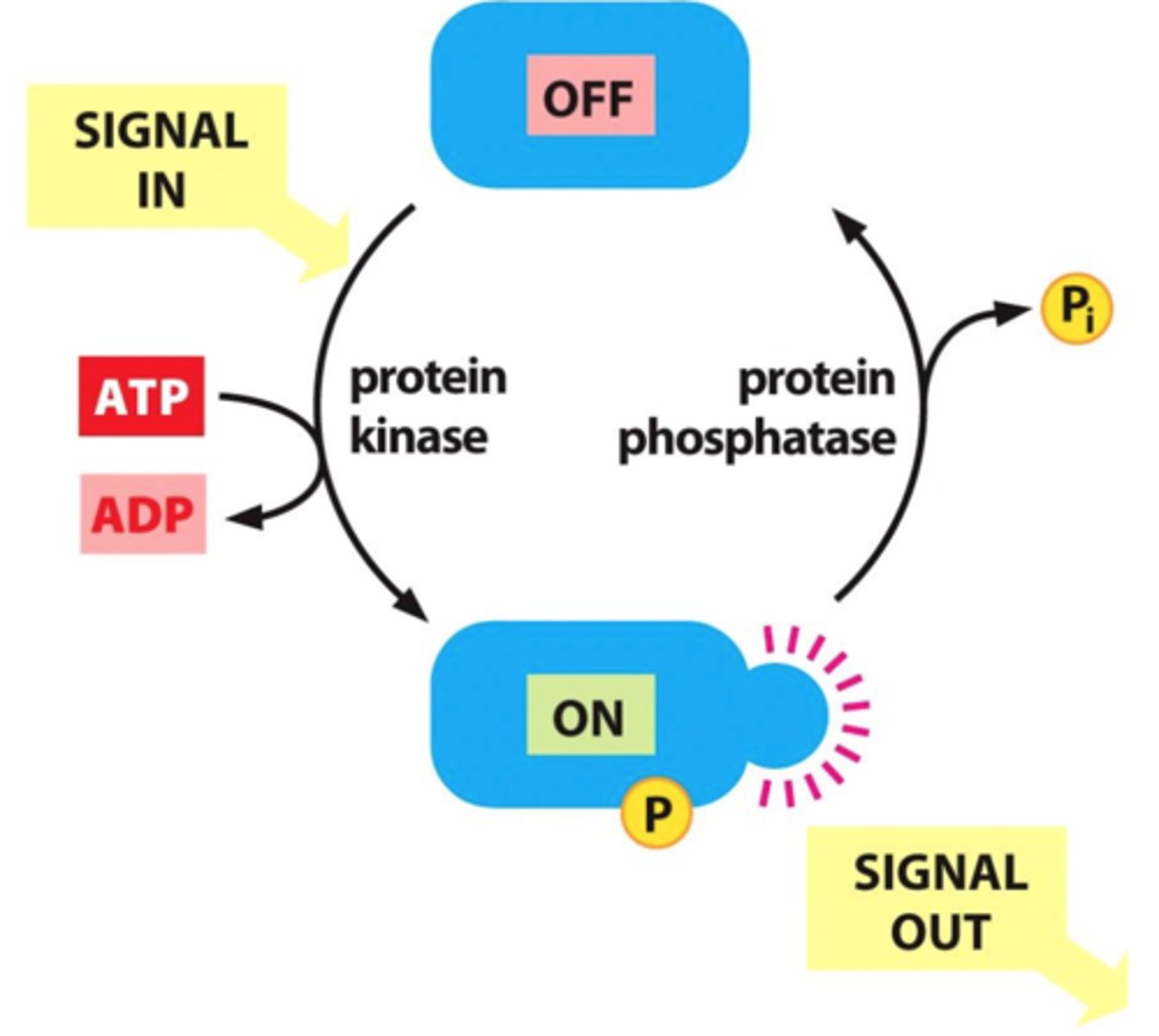
Protein phosphatase
An enzyme that removes phosphate groups from (dephosphorylates) proteins, to deactivate the protein
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
A compound formed from ATP that acts as a second messenger.
Calcium ions
act as a second messenger in many signal transduction pathways in cells to lead to a response.
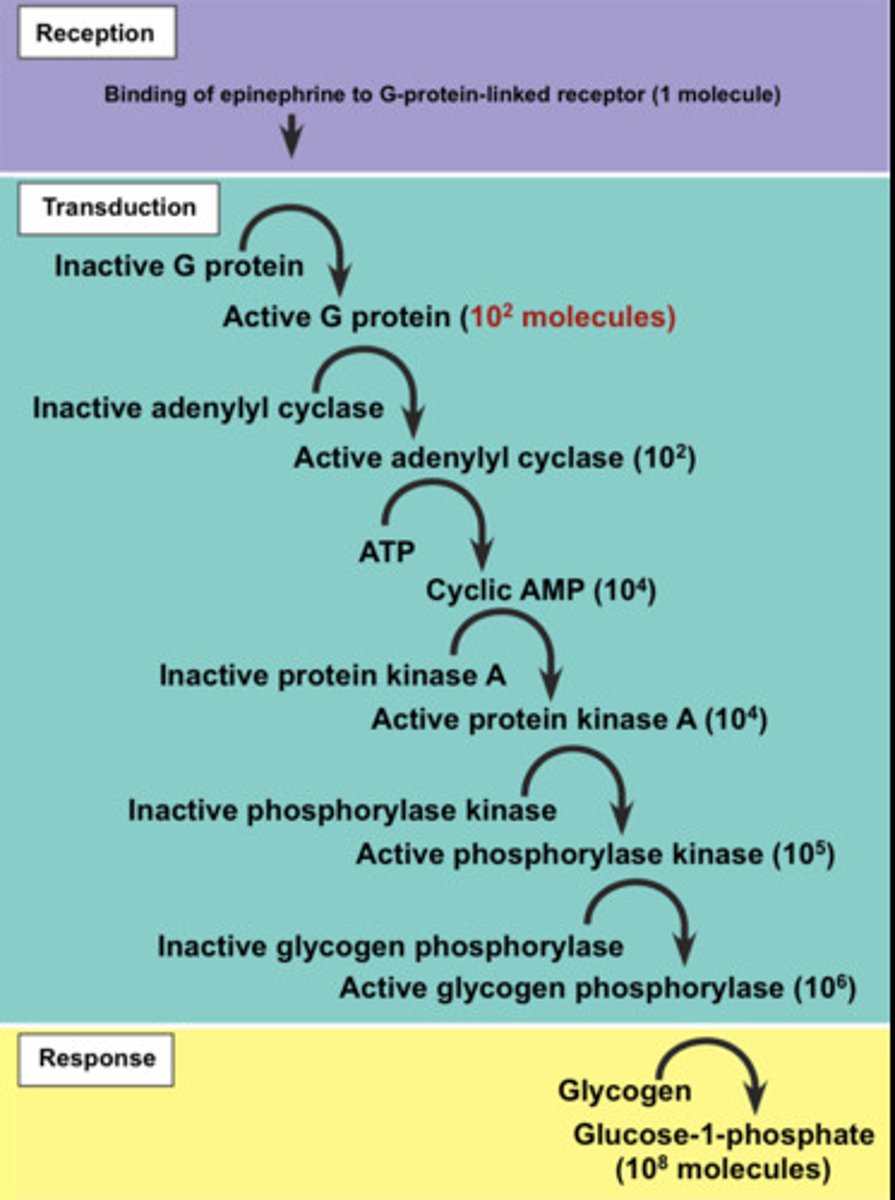
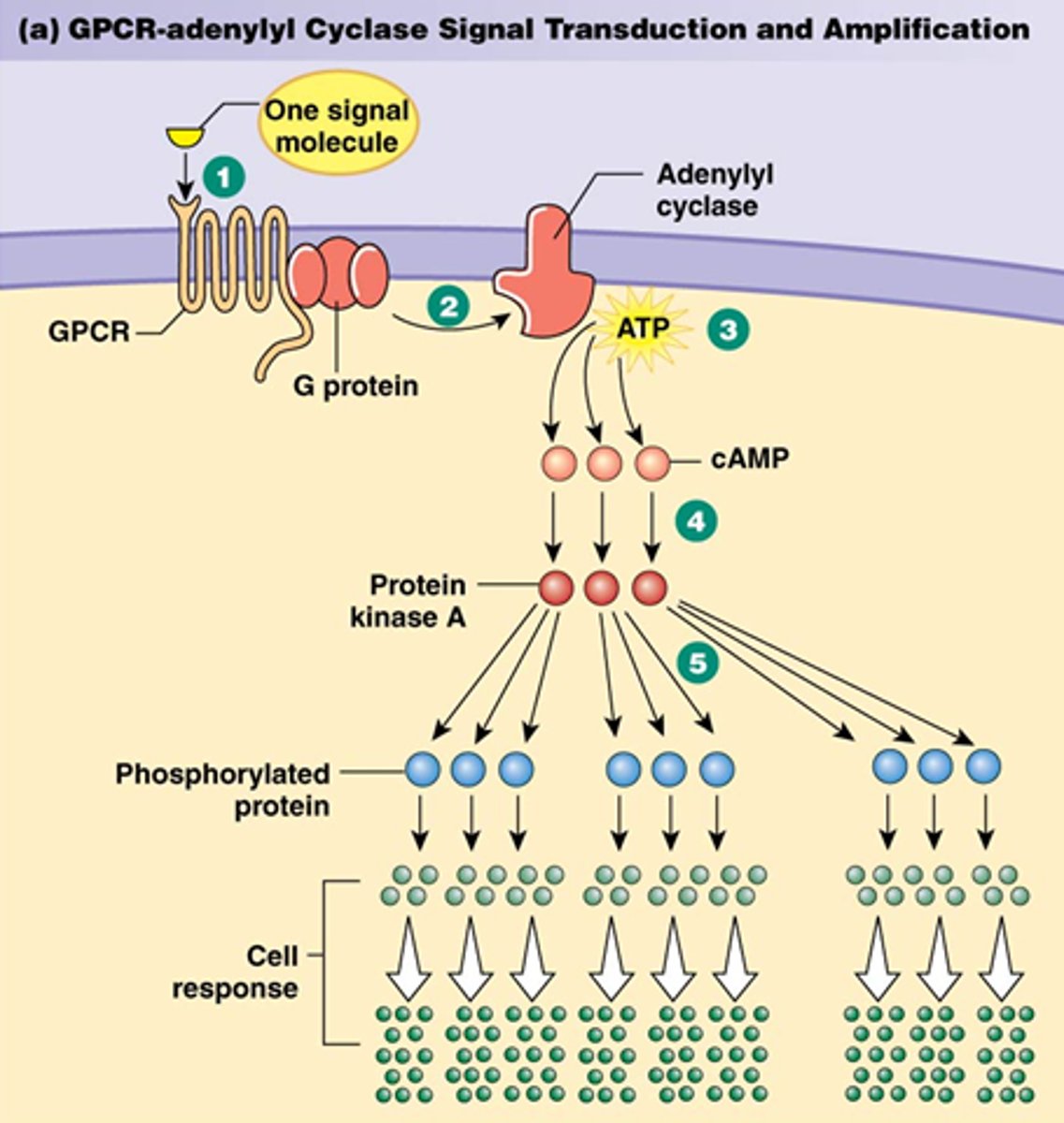
Amplification in signal transduction
when molecules activate other molecules, the number of activated molecules increases in an enzyme cascade. (1 activates several which activate even more to cause a larger/faster response)
Ligand
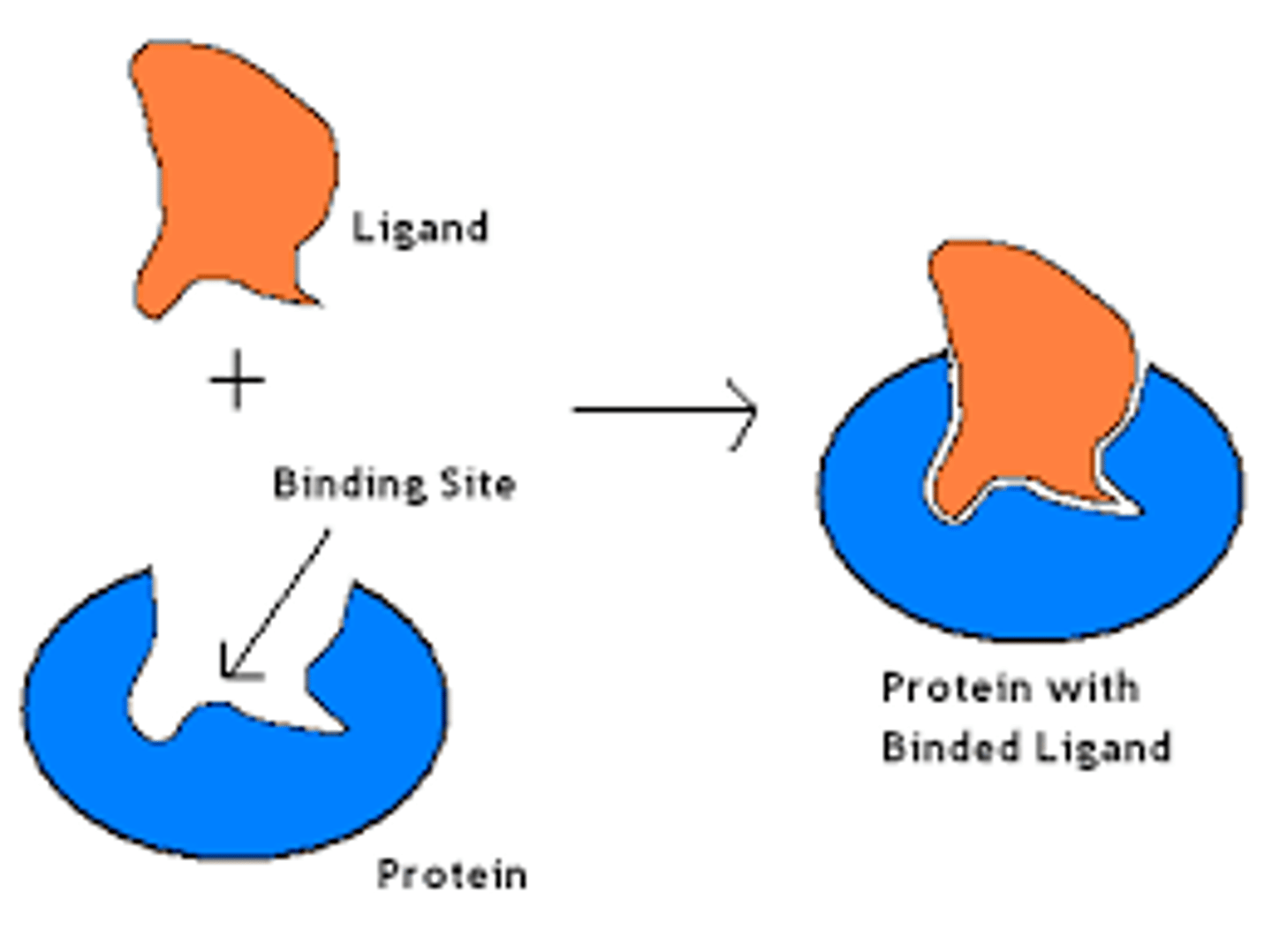
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule. Has unique bonding with receptor because shapes match. May be hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
Quorum Sensing
How bacteria communicate using local signaling. The bacteria detect the presence of other bacteria by secreting signals. If enough bacteria are present then they carry out a group behavior.

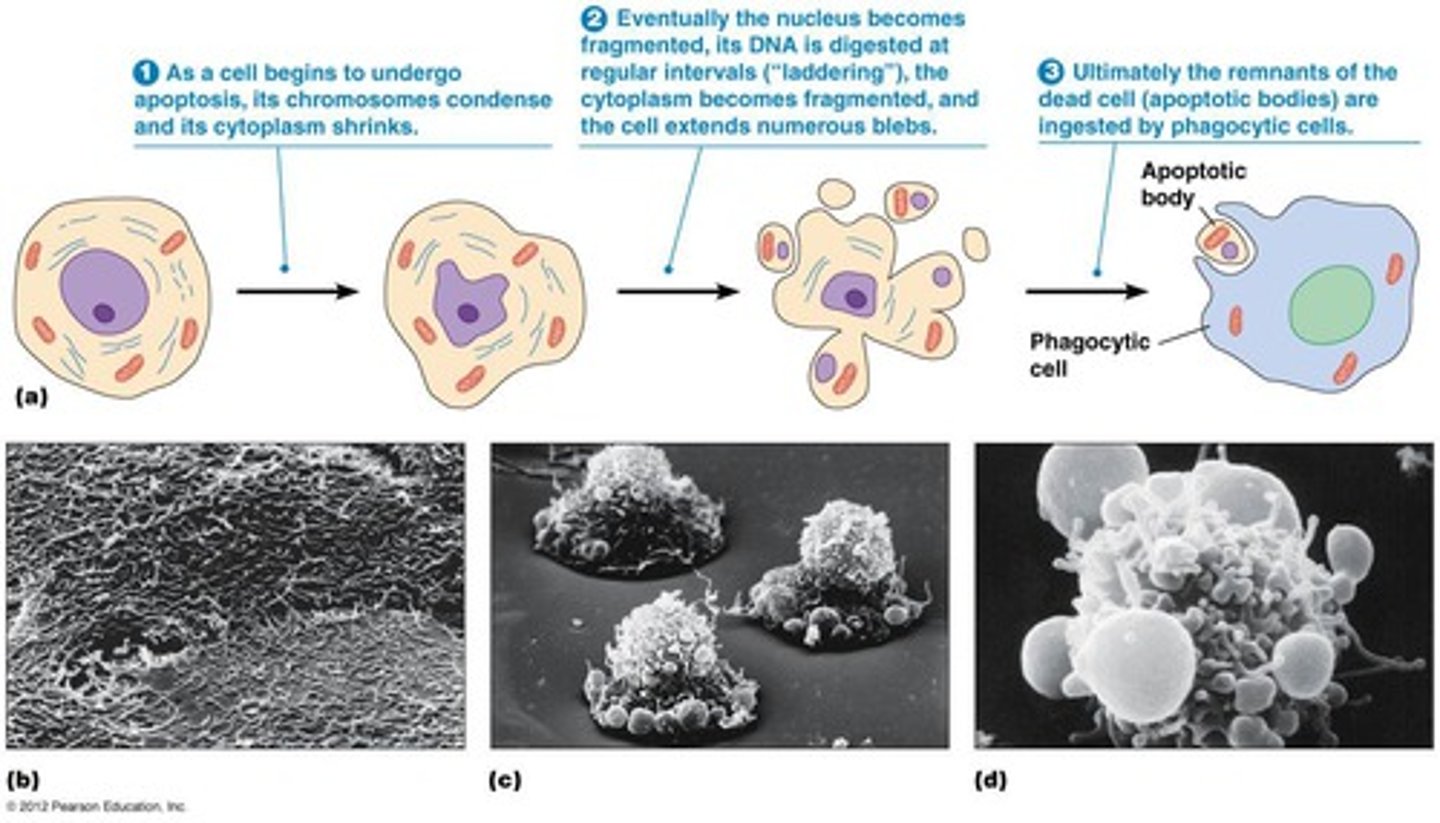
Apoptosis
programmed cell death; cell receives death signal which activates proteins that lead to digestion of DNA, the organelles fragment, cell shrinks and forms blebs, cell is "eaten" by a phagocyte