AP Biology Unit 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
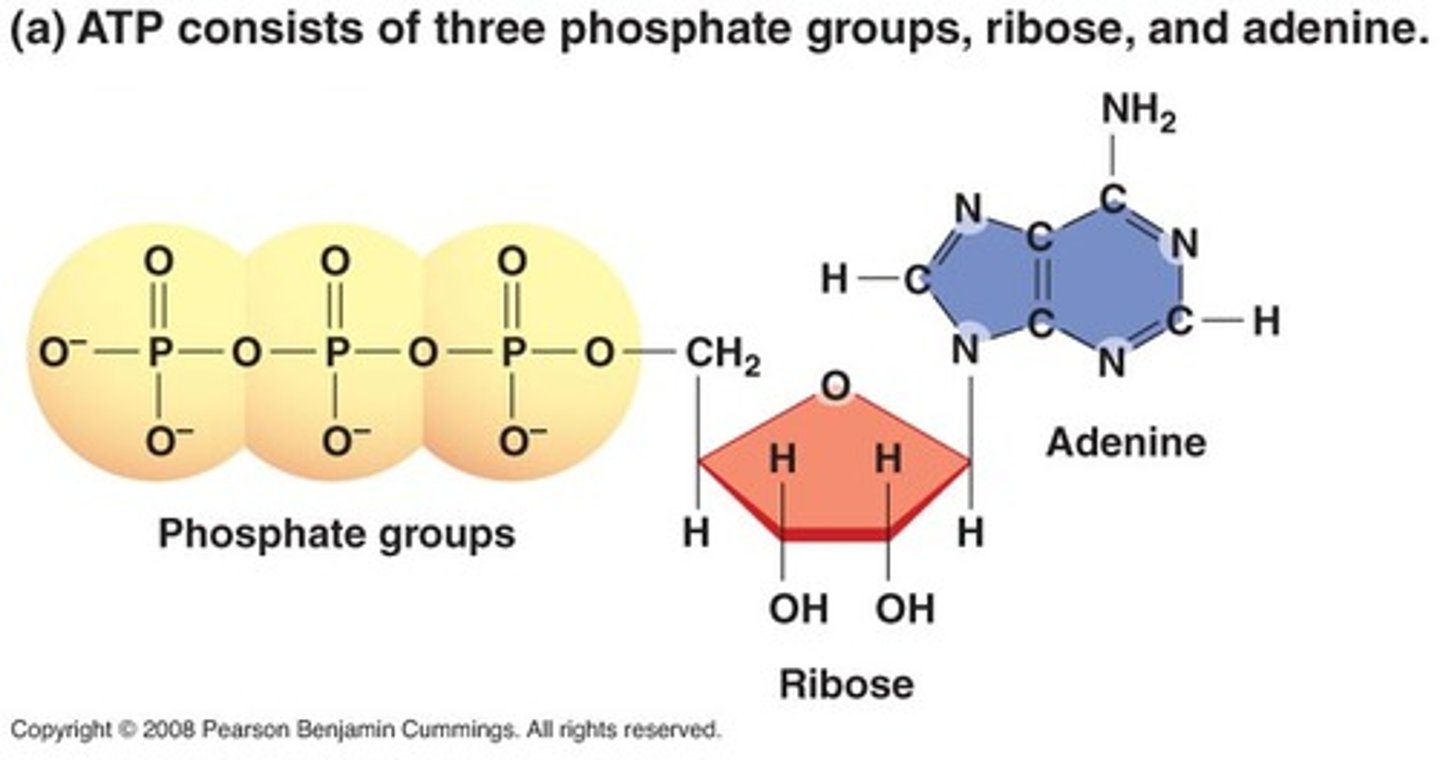
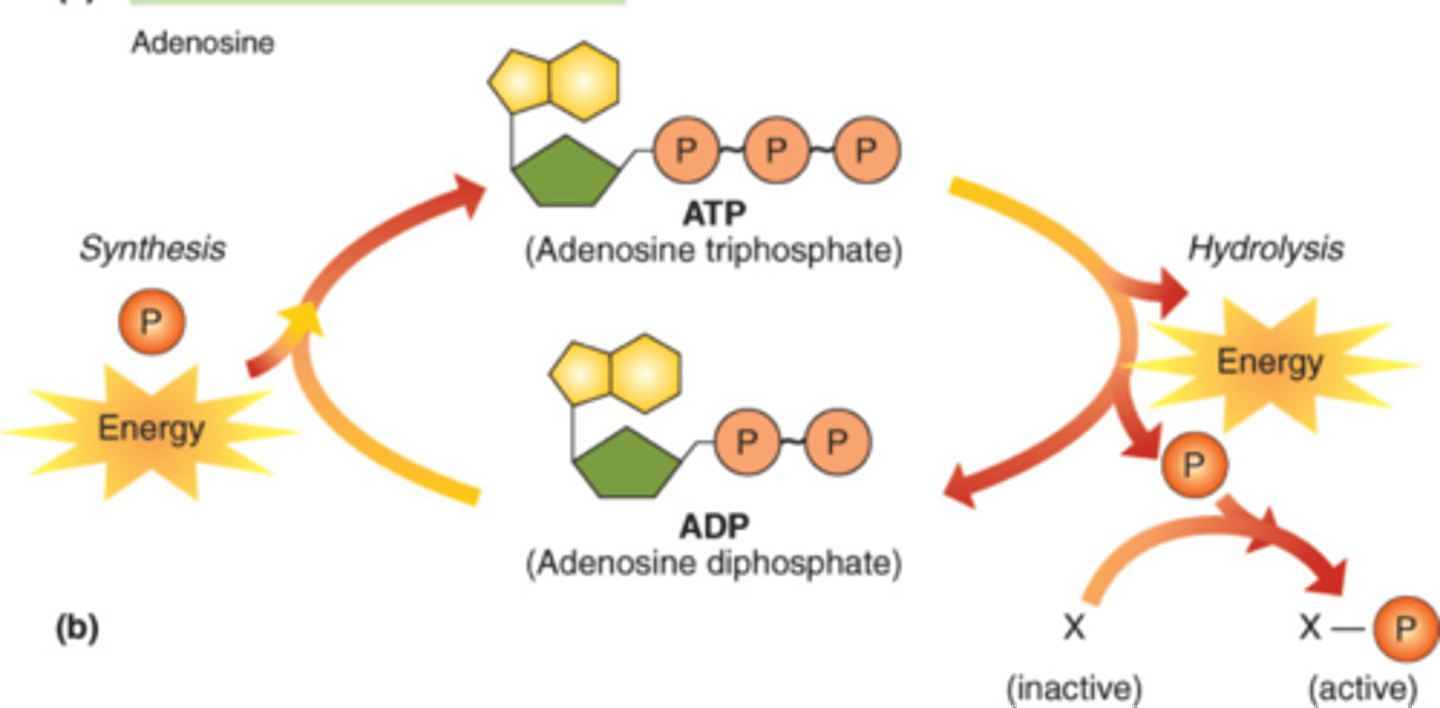
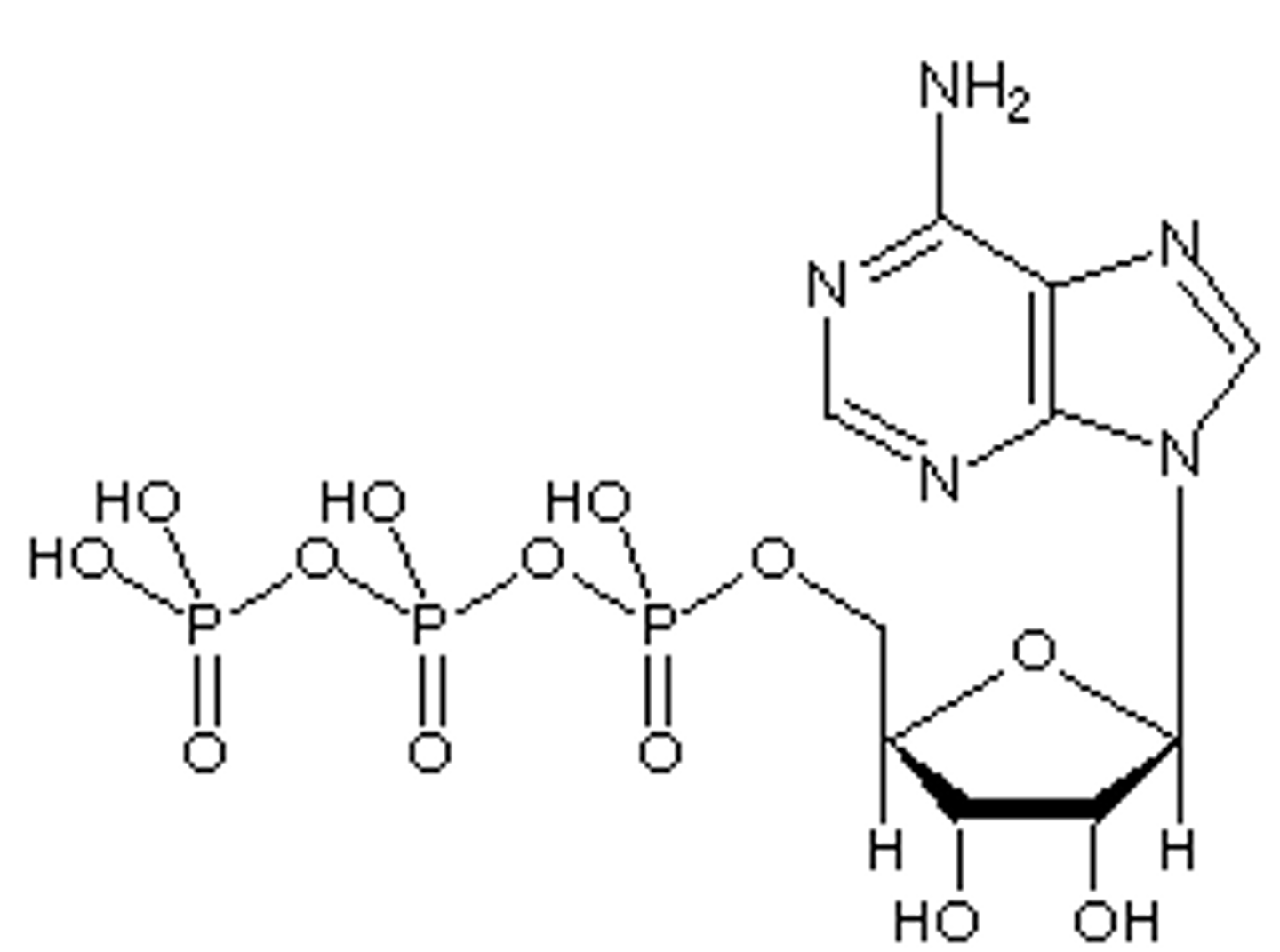
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
ADP
adenosine diphosphate; molecule that ATP becomes when it gives up one of its three phosphate groups
free energy
Chemical energy available to do work

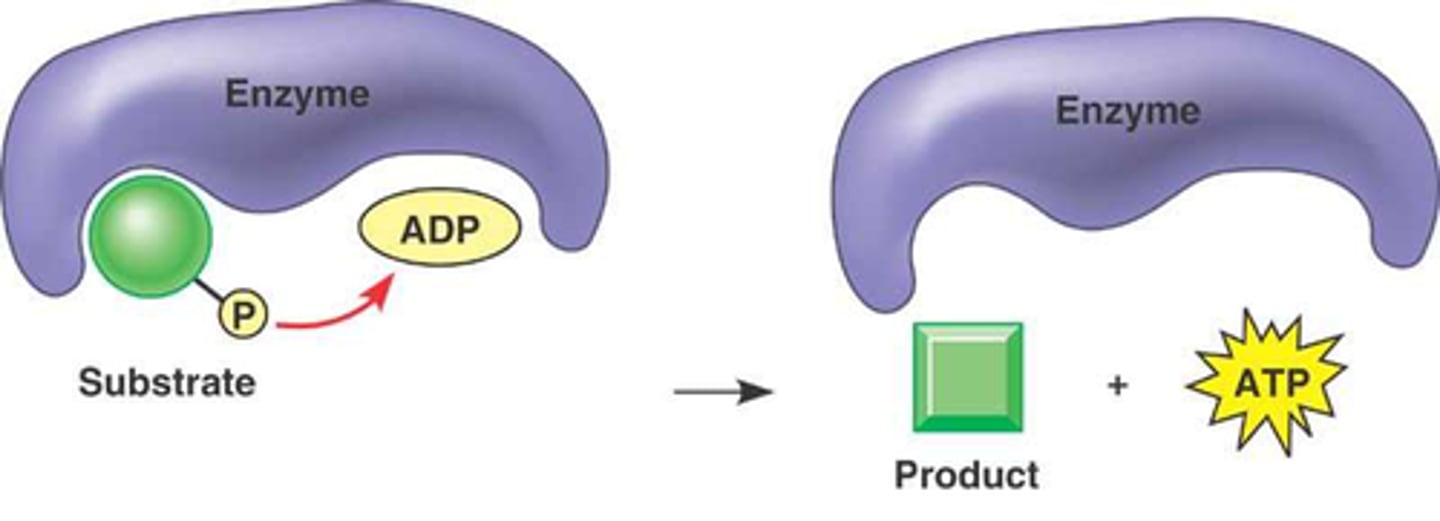
substrate level phosphorylation
the enzyme-mediated direct transfer of phosphate from another molecule (the substrate) to ADP
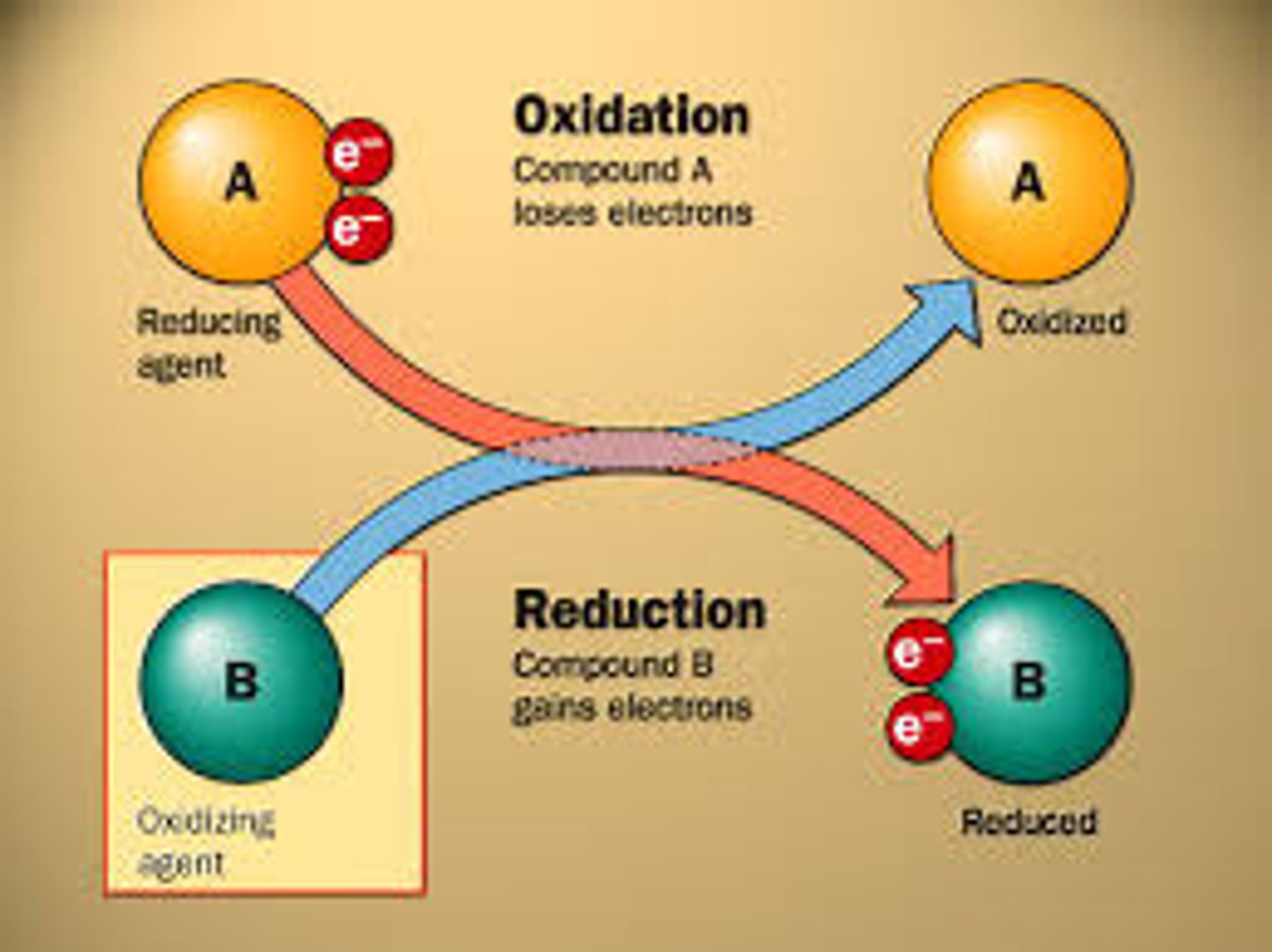
reduction
Gain of electrons by a chemical reactant; any reduction is accompanied by an oxidation.
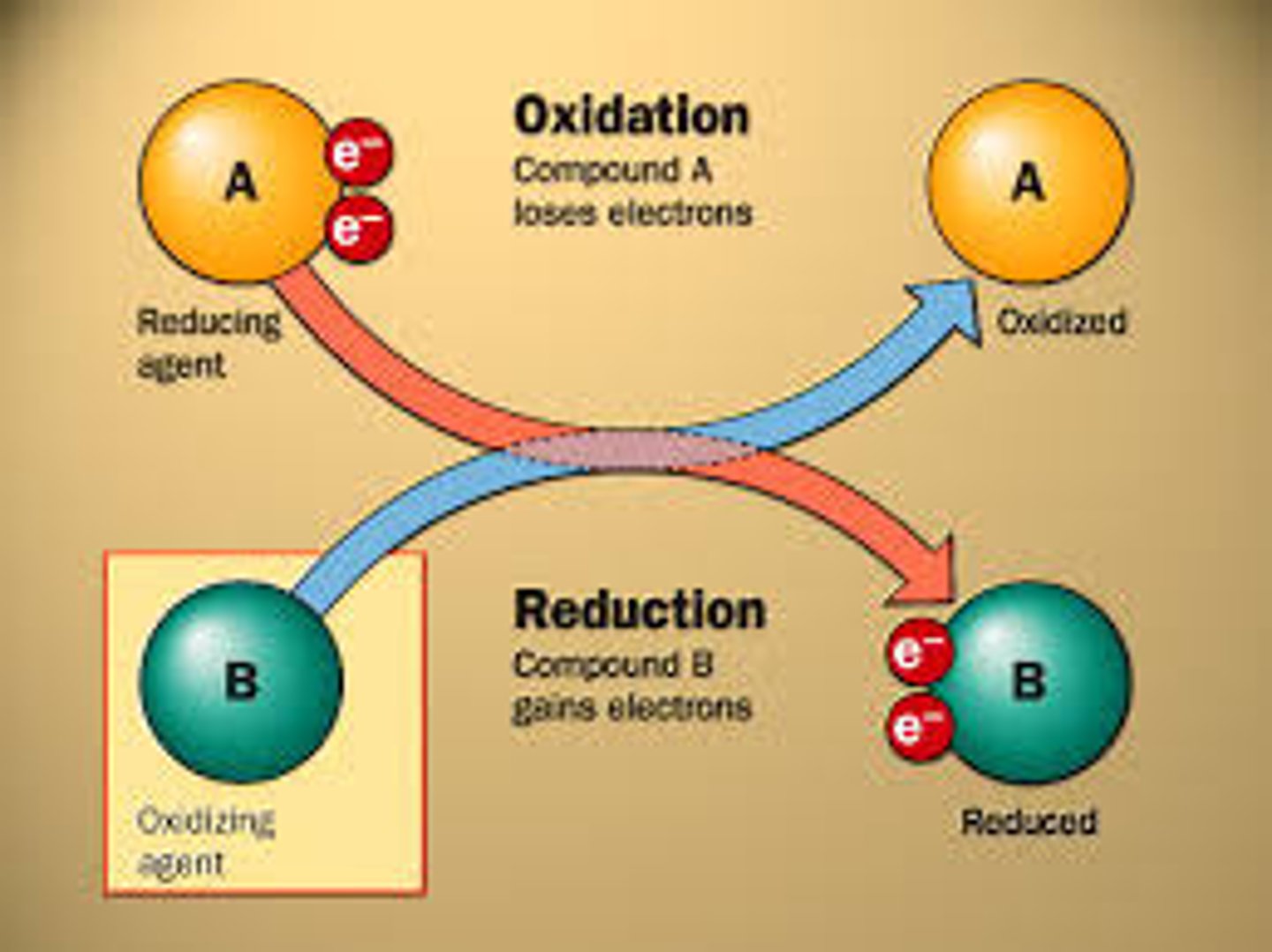
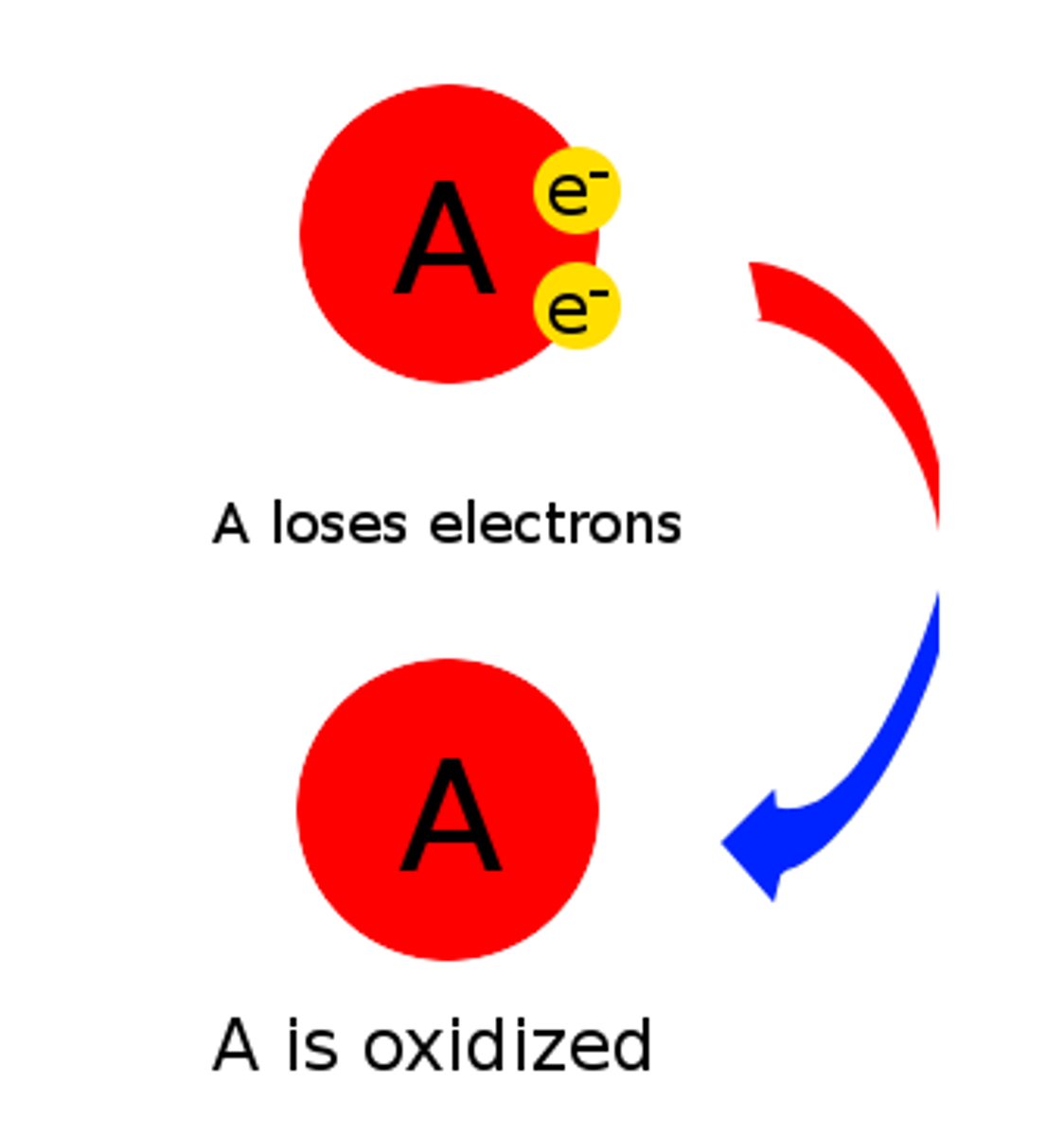
oxidation
Relative loss of electrons in a chemical reaction; either outright removal to form an ion, or the sharing of electrons with substances having a greater affinity for them, such as oxygen. Most oxidations, including biological ones, are associated with the liberation of energy.
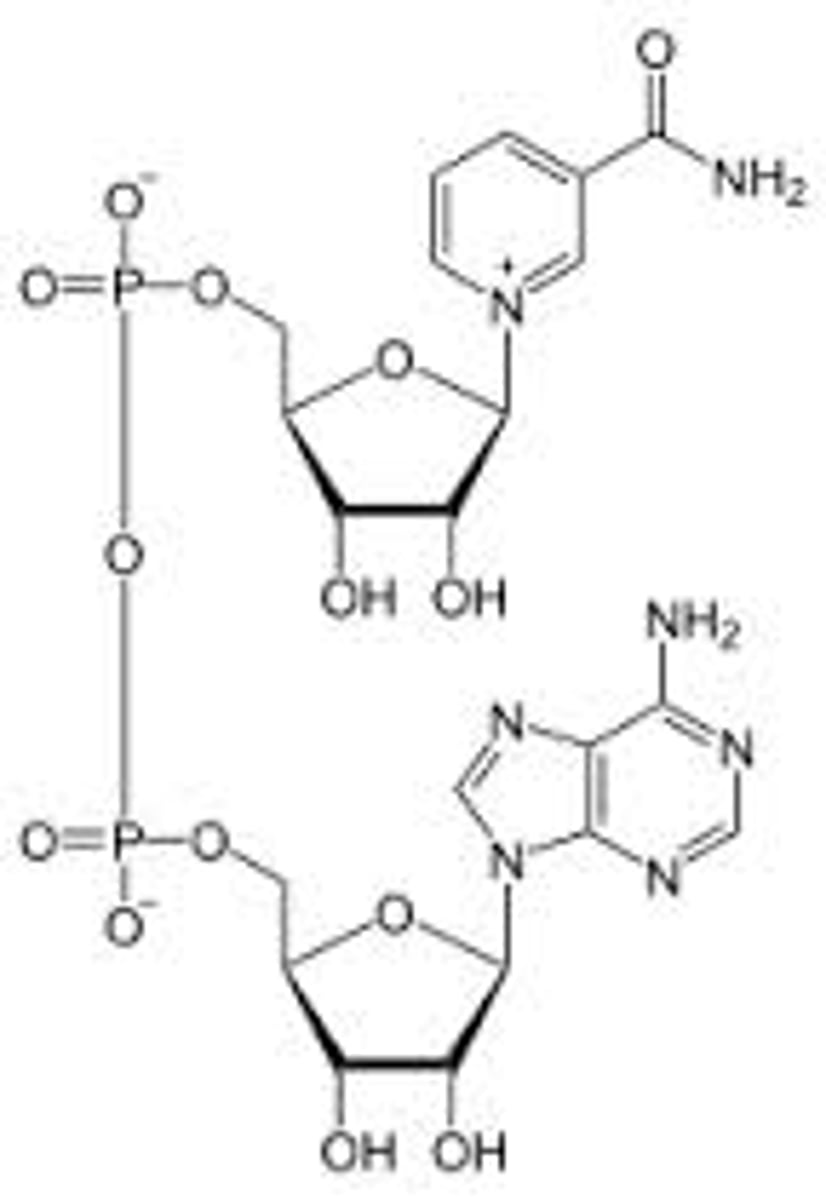
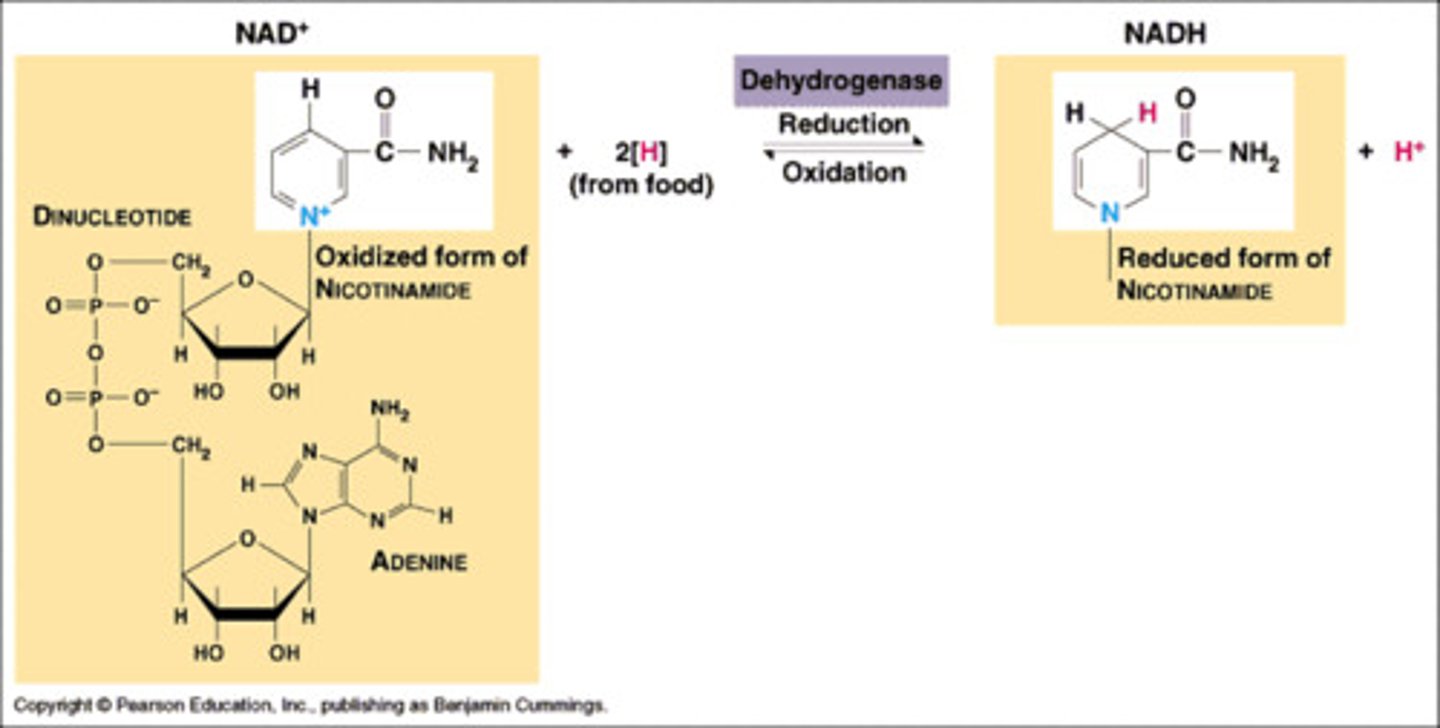
NAD
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - a coenzyme that is an electron carrier; NAD+ is oxidized, NADH is reduced
reducing agent
compound that loses electrons in a reaction
oxidizing agent
compound that gains electrons in a reaction

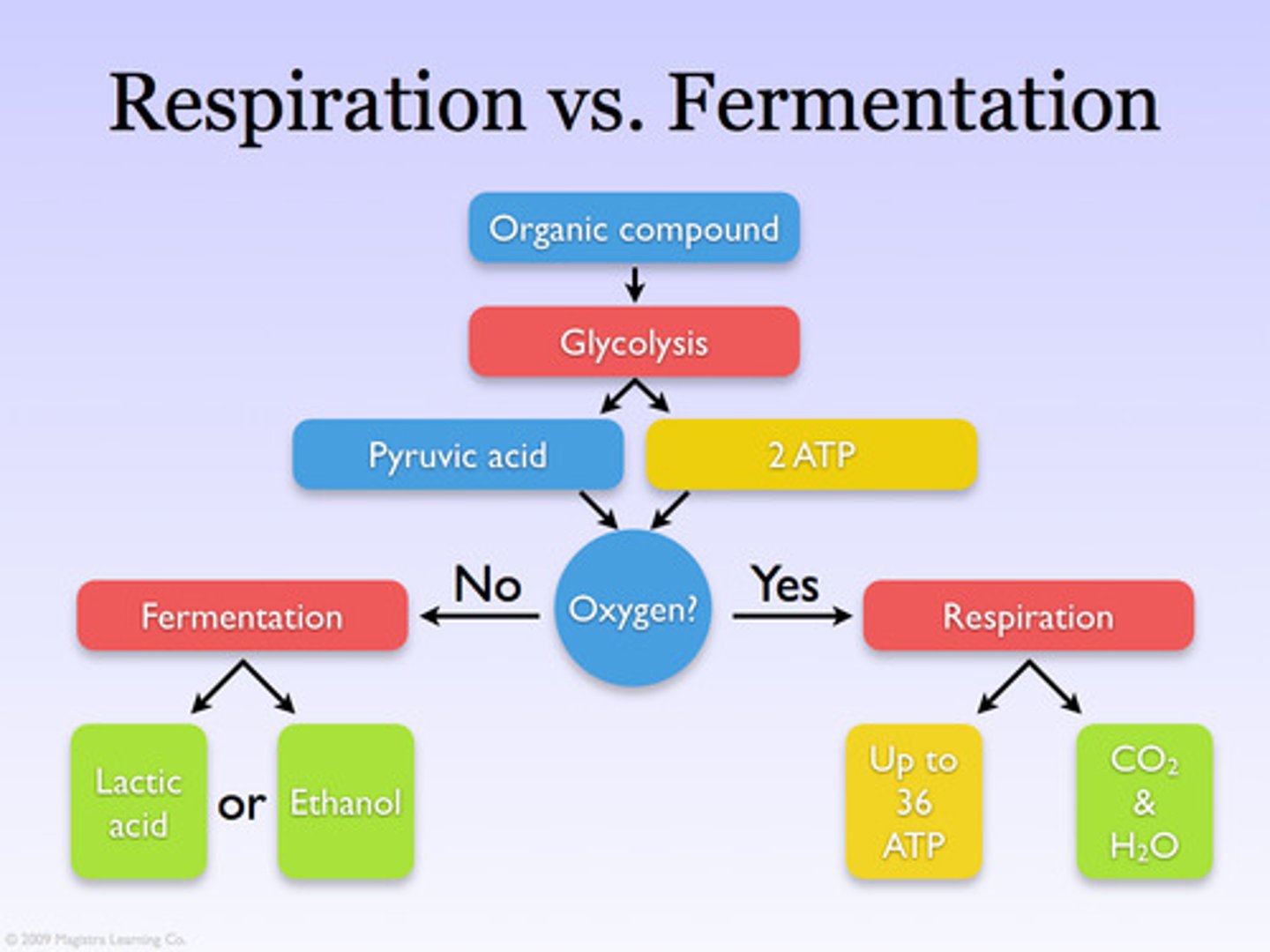
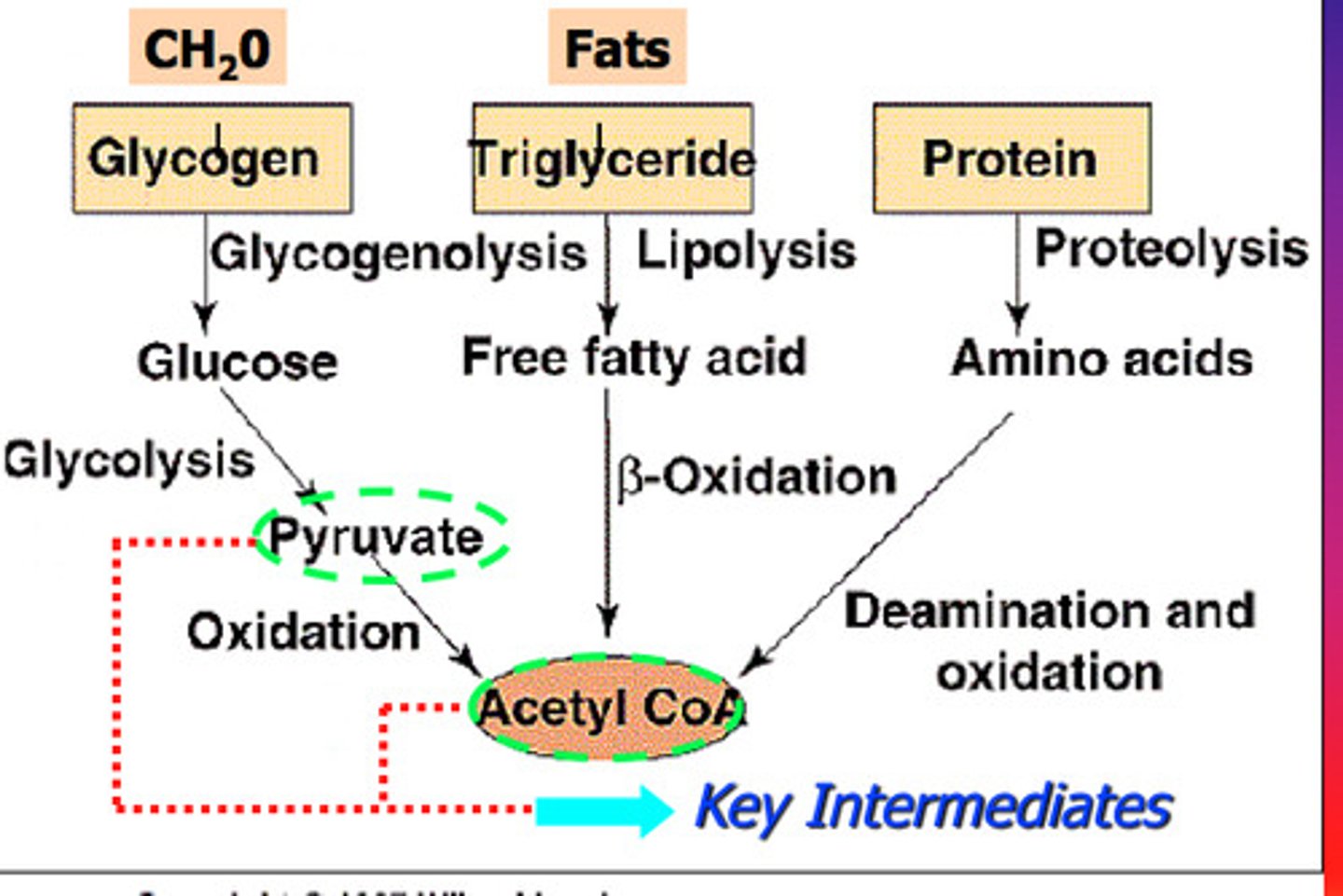
cellular respiration
The catabolic pathways by which electrons are removed from various molecules and passed through intermediate electron carriers to O2, generating H2O and releasing energy.

aerobic
Requiring molecular oxygen, O2
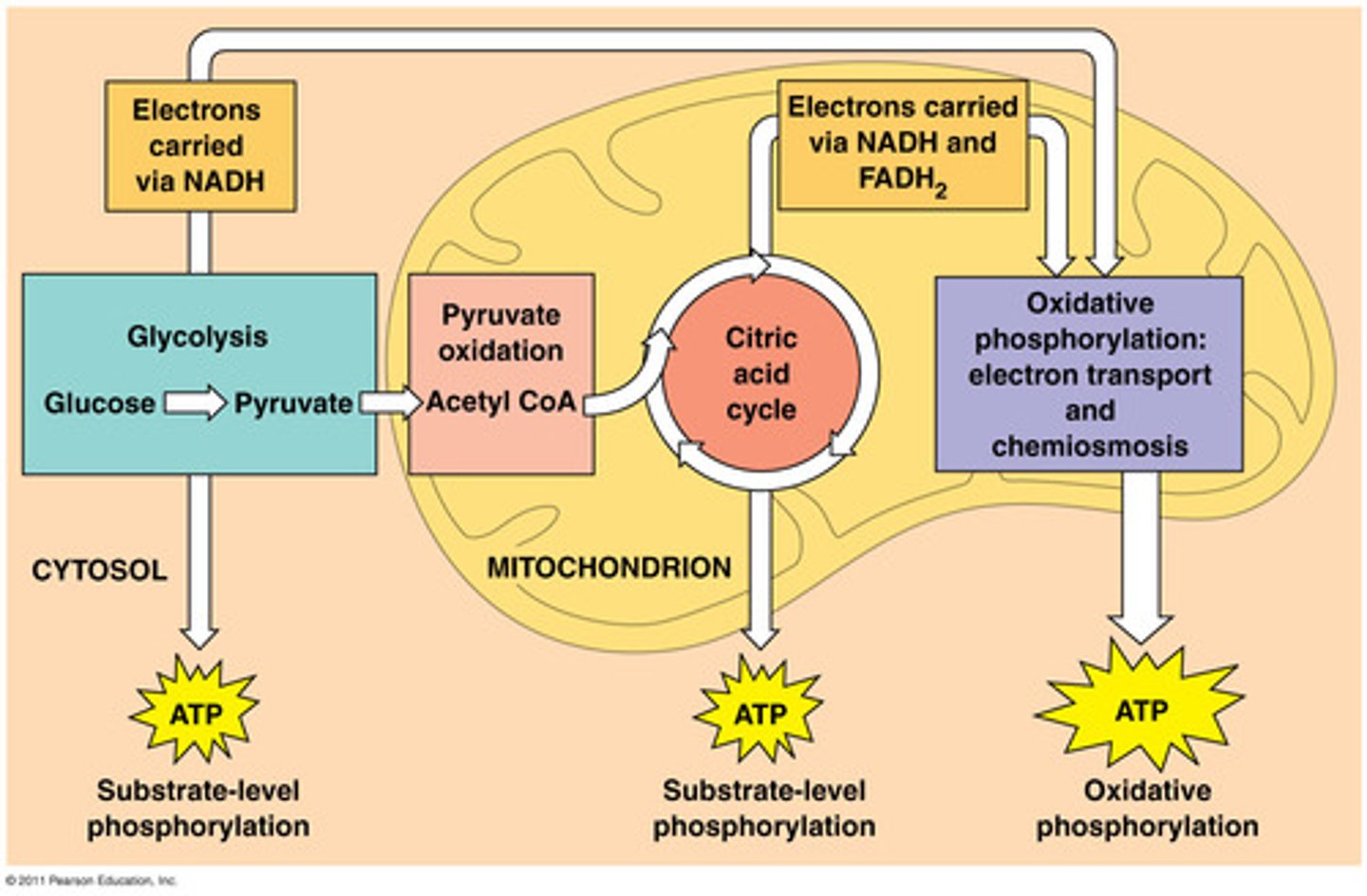
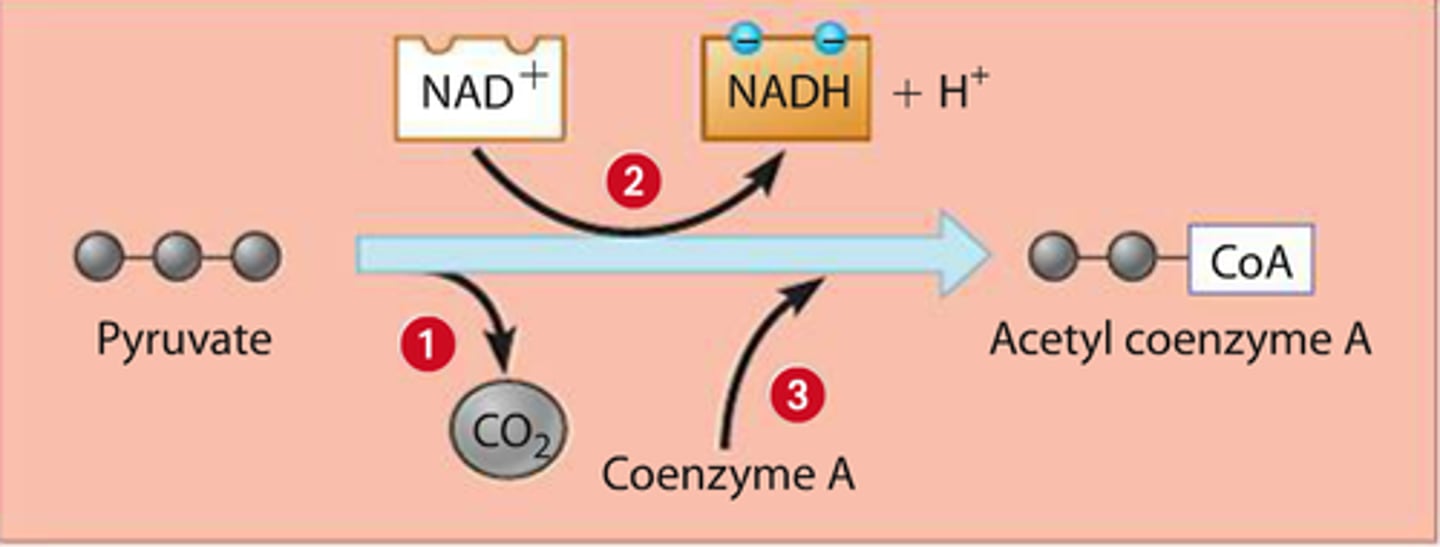
pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate molecules are oxidized and produces acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH
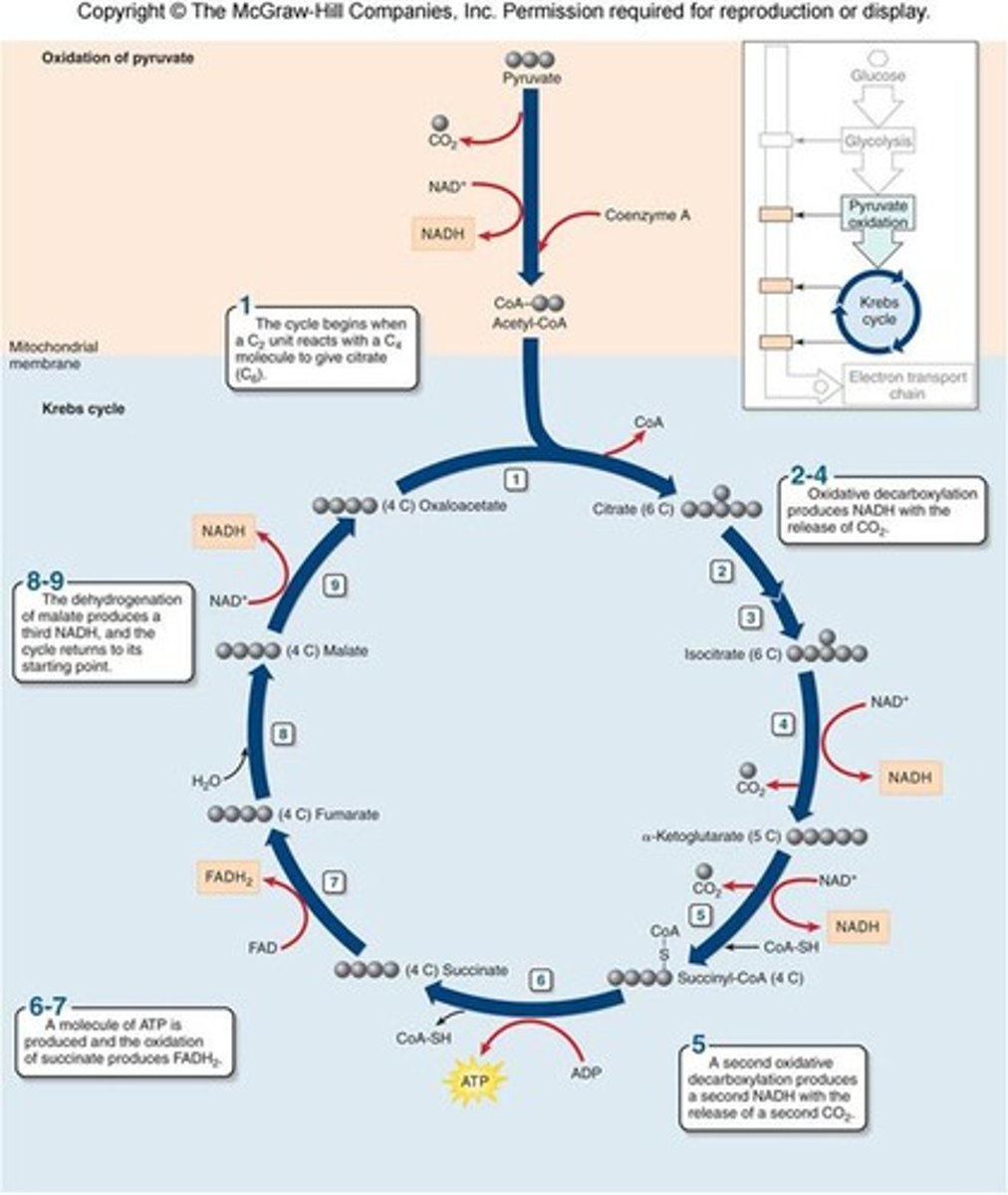
citric acid cycle
In cellular respiration, a set of chemical reactions whereby acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms are stored as NADH and FADH2. Also called the Krebs cycle.
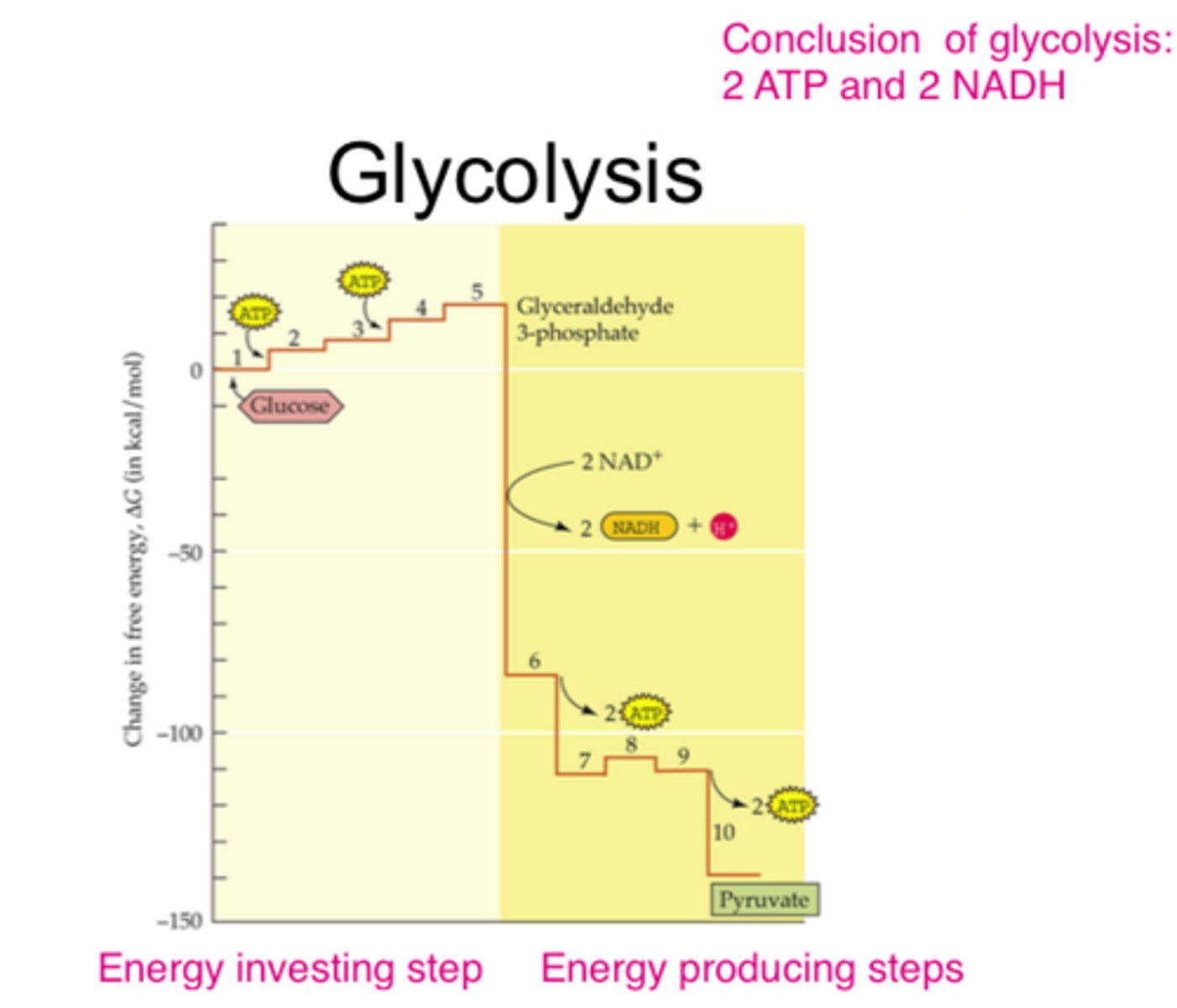
energy-investing reactions
endergonic stage of glycolysis in which glucose is converted into G3P
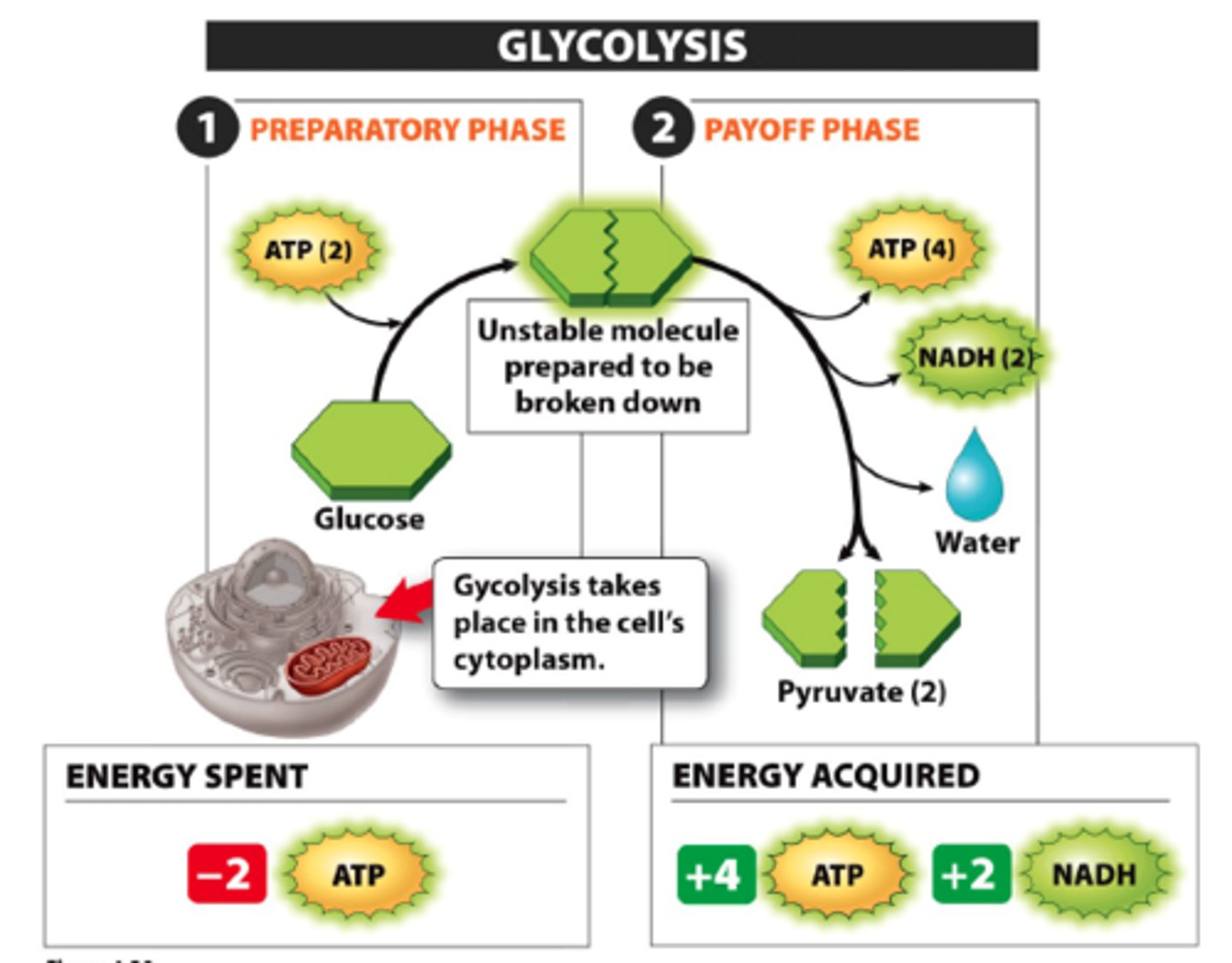
energy-harvesting reactions
exergonic stage of glycolysis in which G3P is converted into two molecules of pyruvate
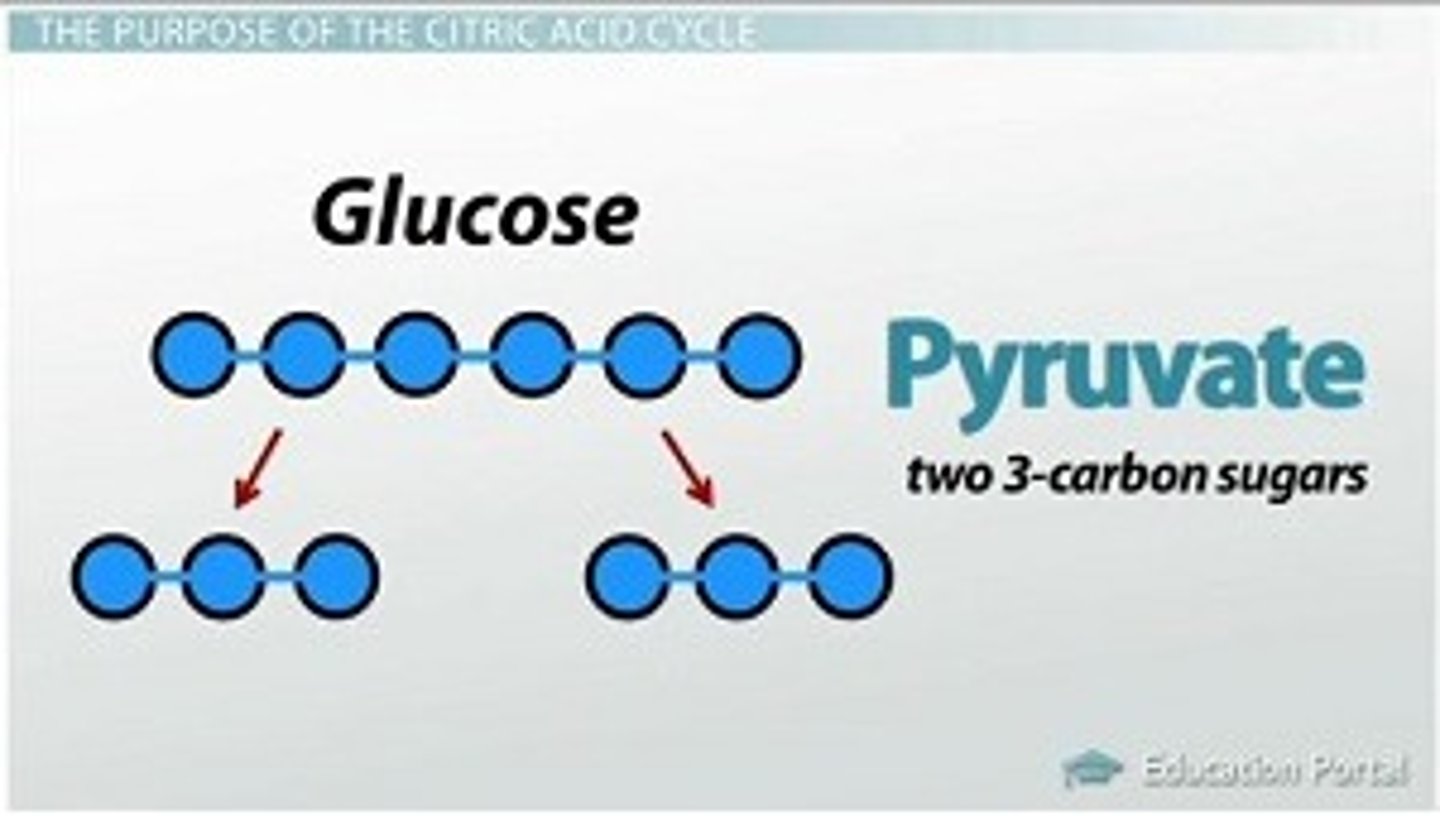
pyruvate
Three-carbon compound that forms as an end product of glycolysis.
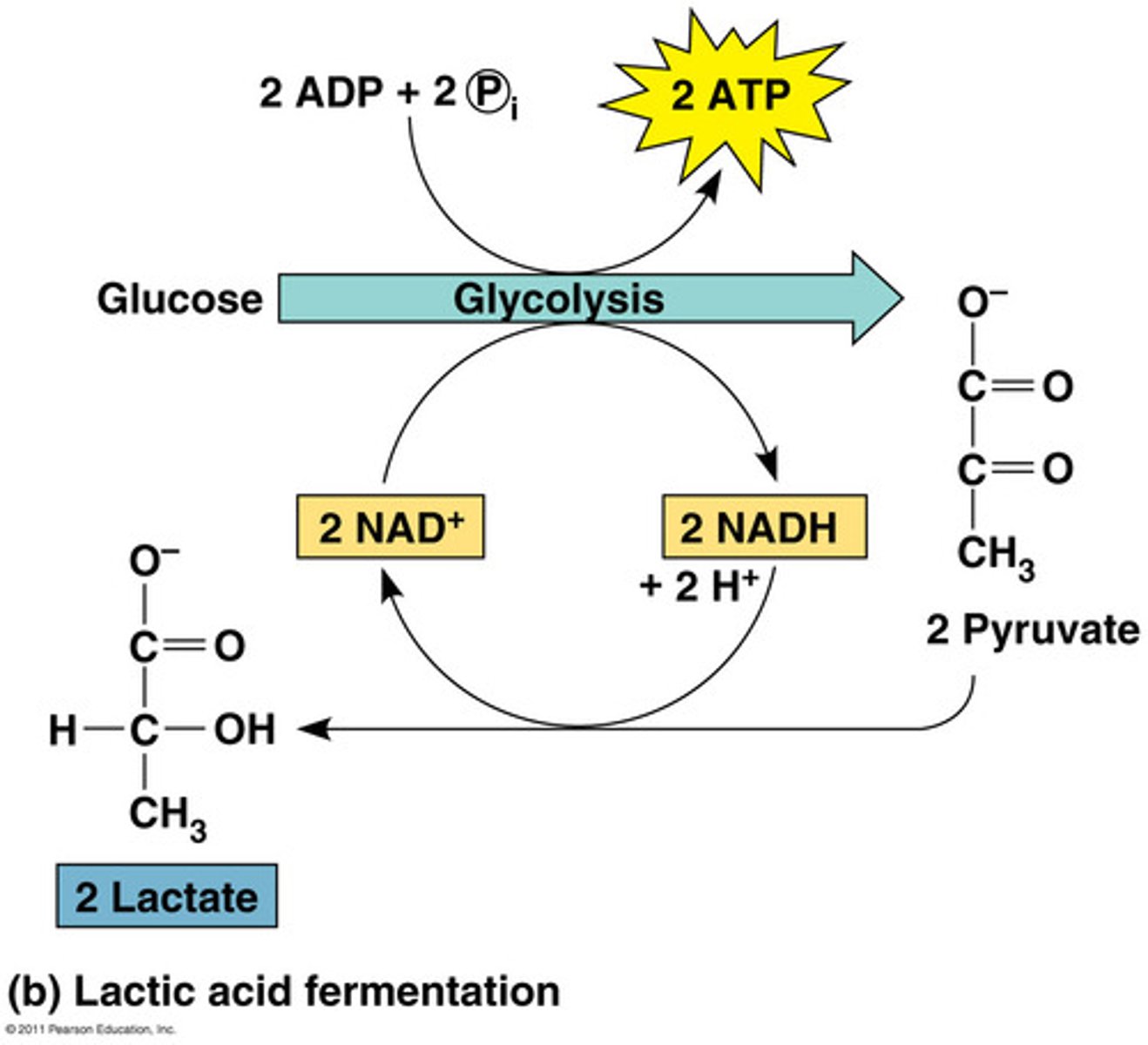
NADH
reduced electron carrier molecule formed in glycolysis
Krebs cycle
another name for the citric acid cycle
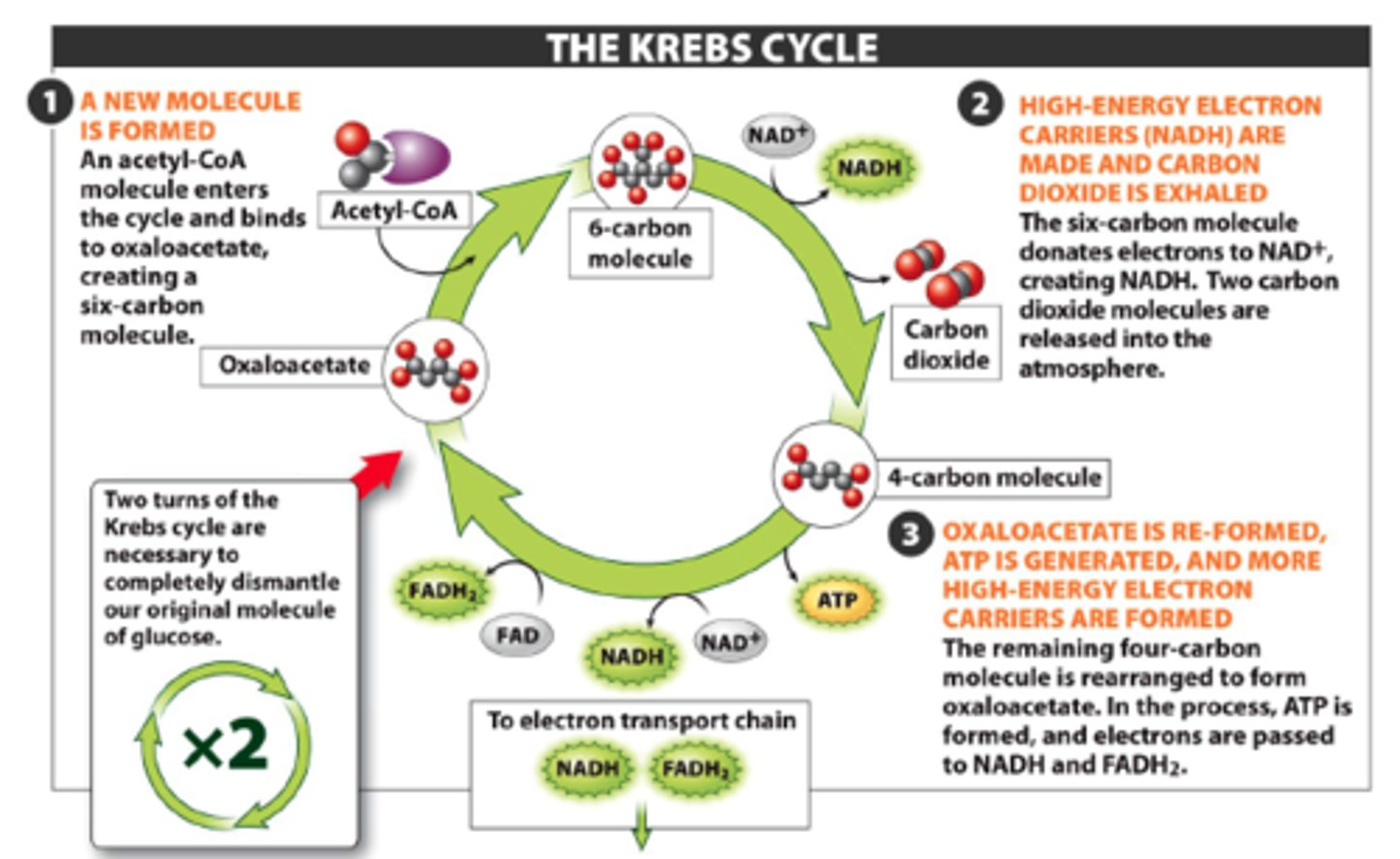
acetyl CoA
molecule formed from the oxidation of pyruvate

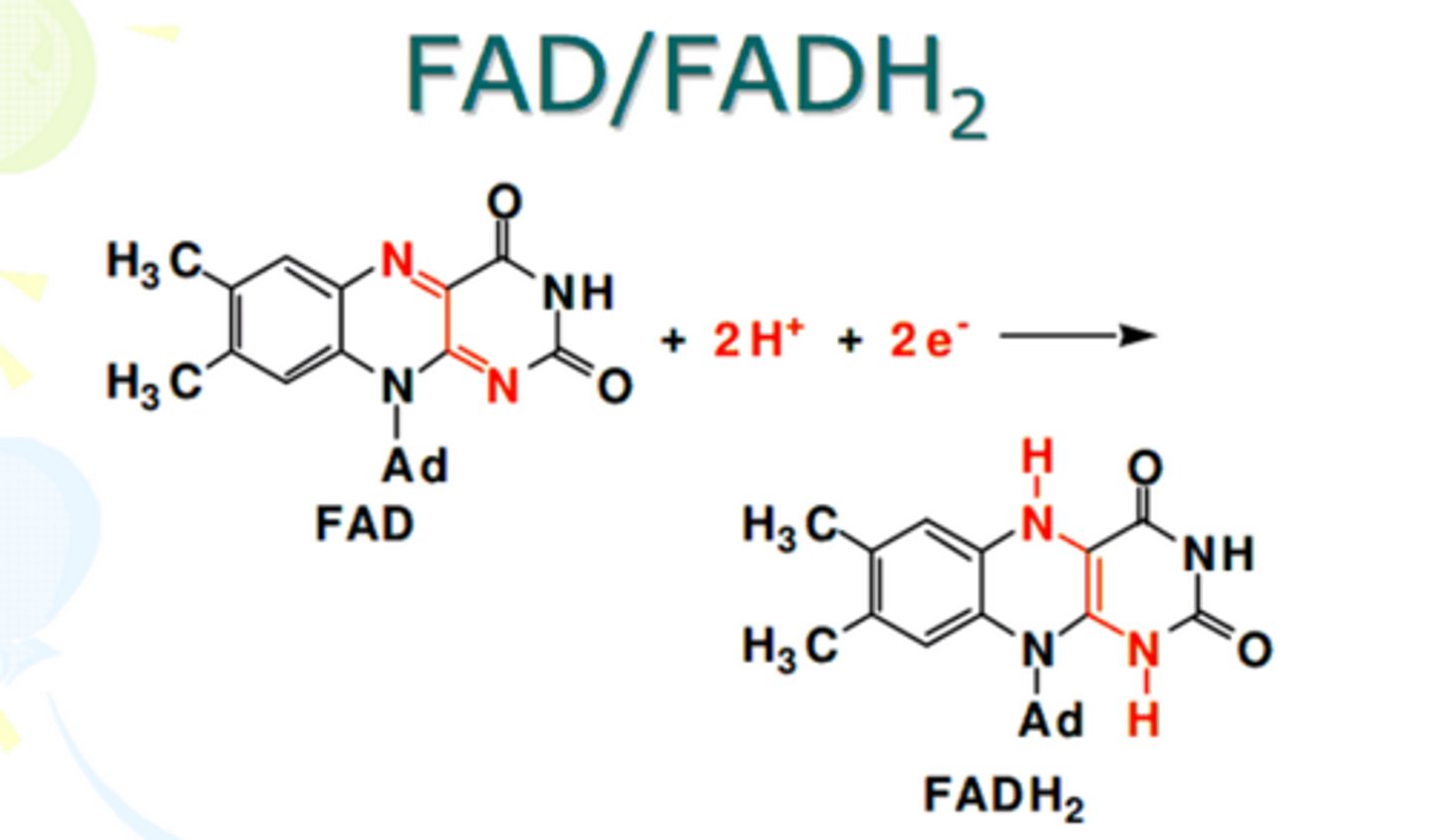
FADH2
a reduced coenzyme similar to NADH, an electron carrier
anaerobic
Occurring without the use of molecular oxygen, O2.
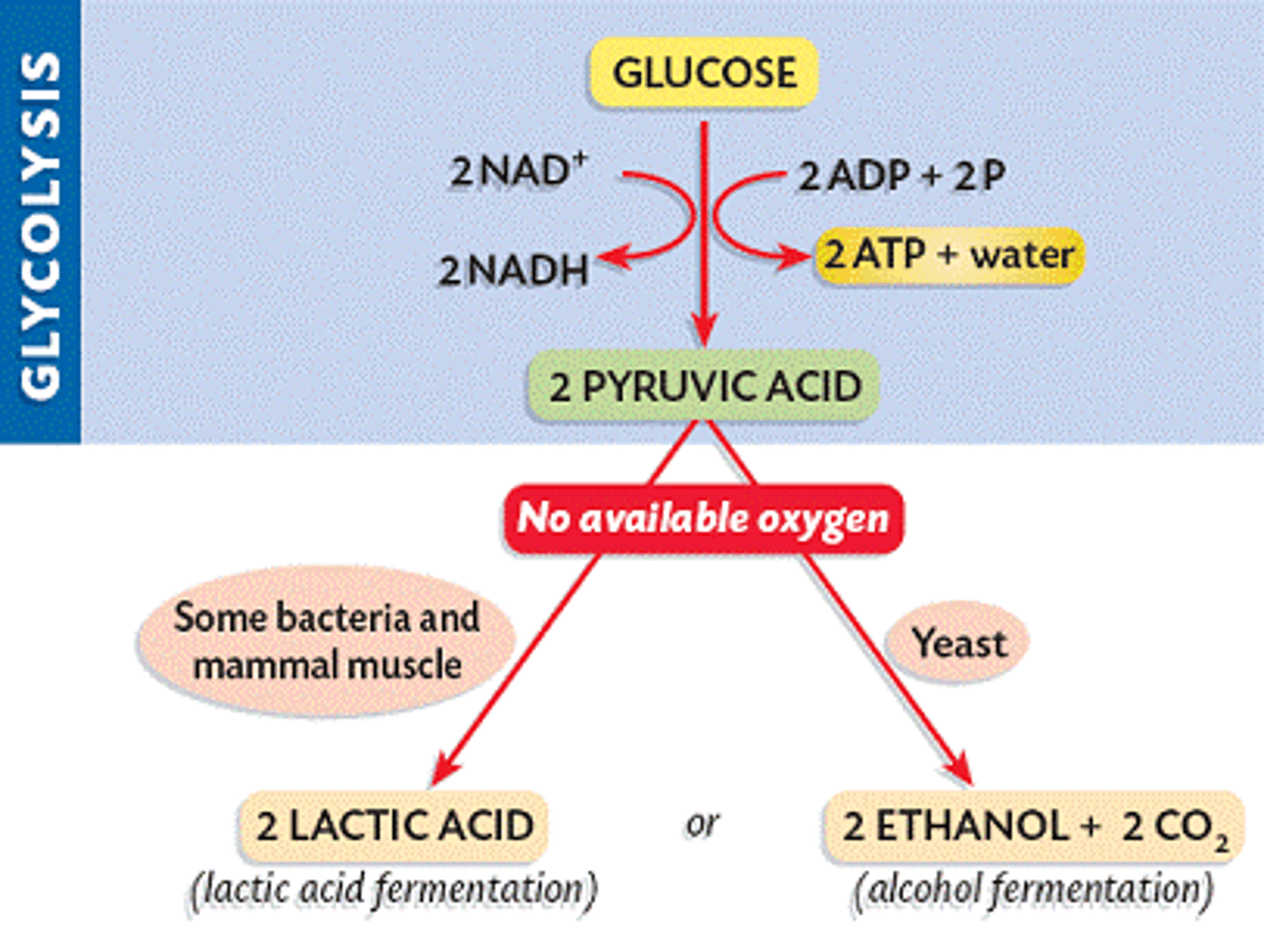
fermentation
Speaking specifically about energy metabolism, the anaerobic degradation of a substance such as glucose to smaller molecules such as lactic acid or alcohol with the extraction of energy. (2) Speaking generally, metabolic processes that occur in the absence of O2.
lactic acid fermentations
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to lactic acid, in some bacteria and animal cells.
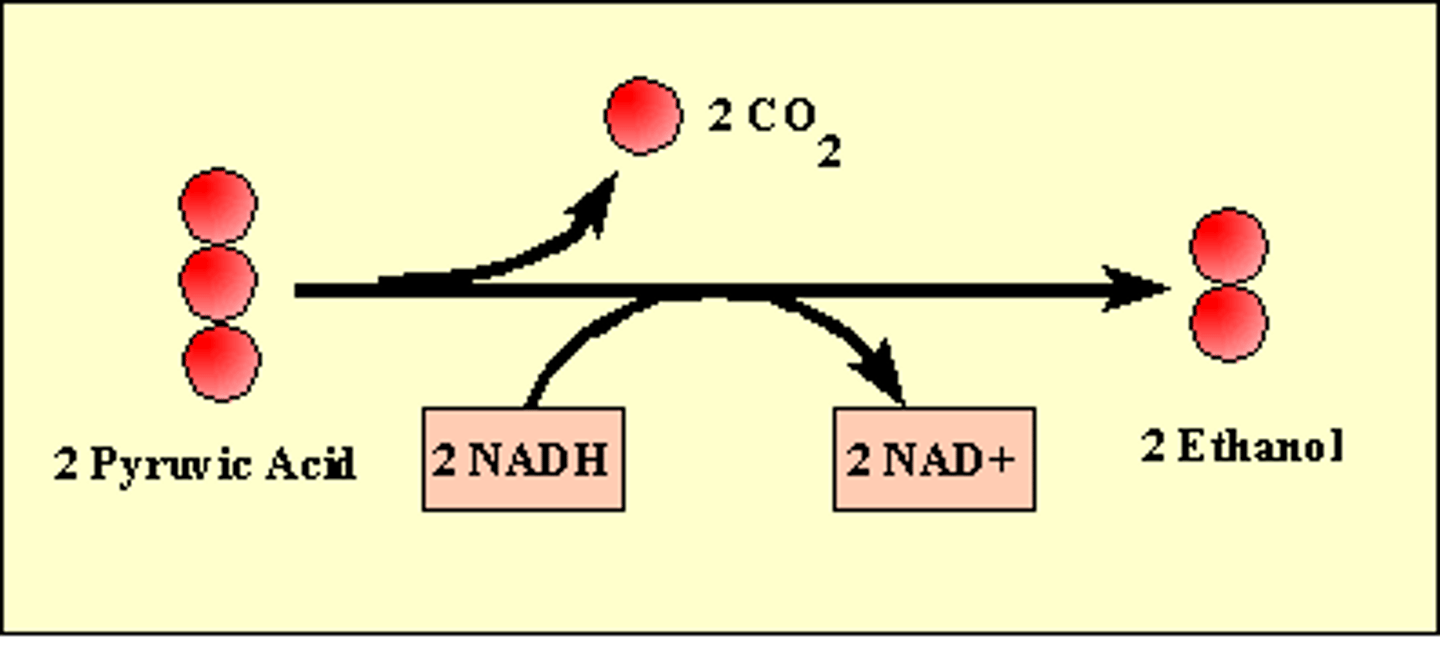
alcoholic fermentation
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide in some plants and yeast cells.
photosynthesis
photosynthesis: Metabolic processes carried out by green plants and cyanobacteria, by which visible light is trapped and the energy used to convert CO2 into organic compounds.
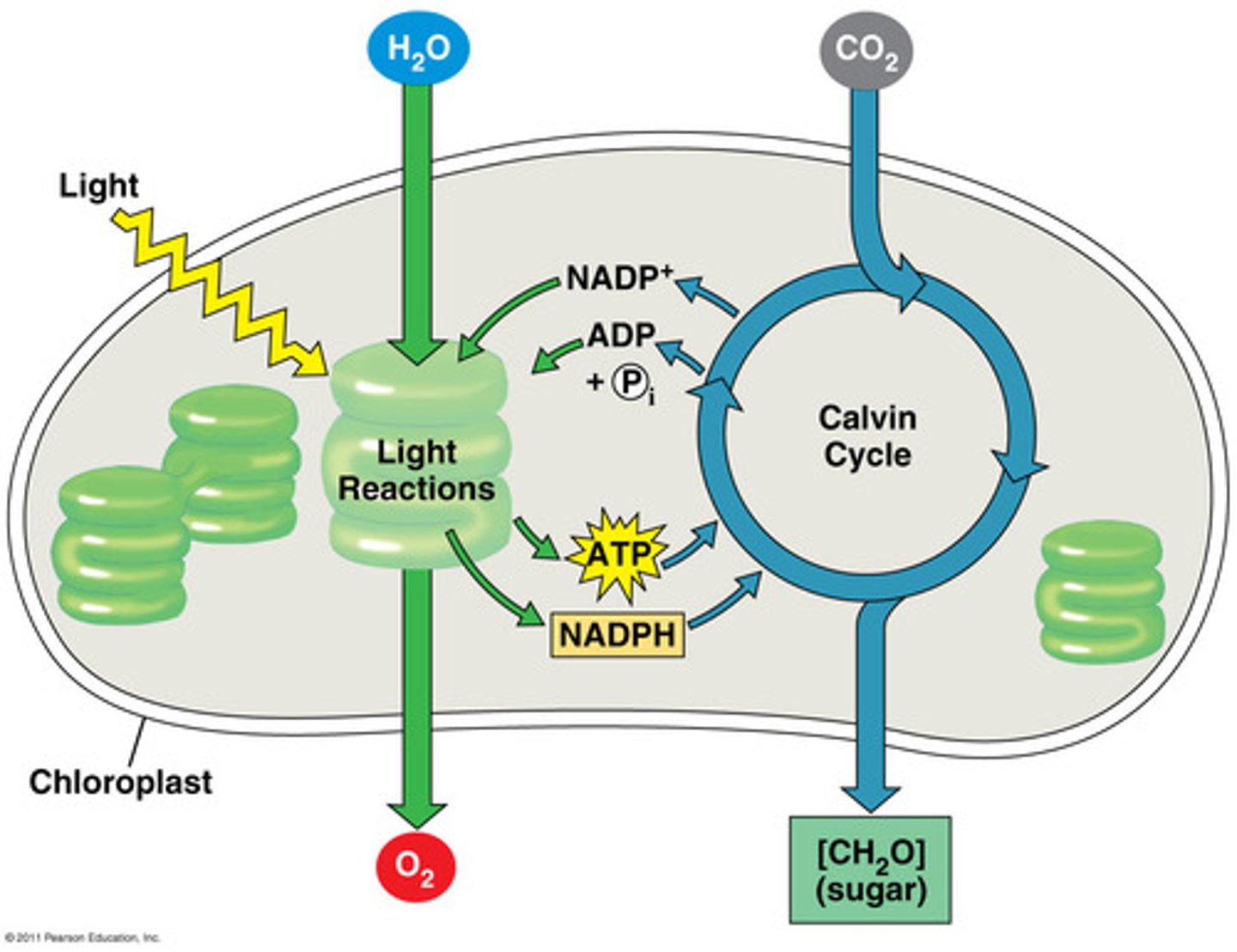
light reactions
The initial phase of photosynthesis, in which light energy is converted into chemical energy.

pigment
A substance that absorbs visible light.

chlorophyll
Any of several green pigments associated with chloroplasts or with certain bacterial membranes; responsible for trapping light energy for photosynthesis.
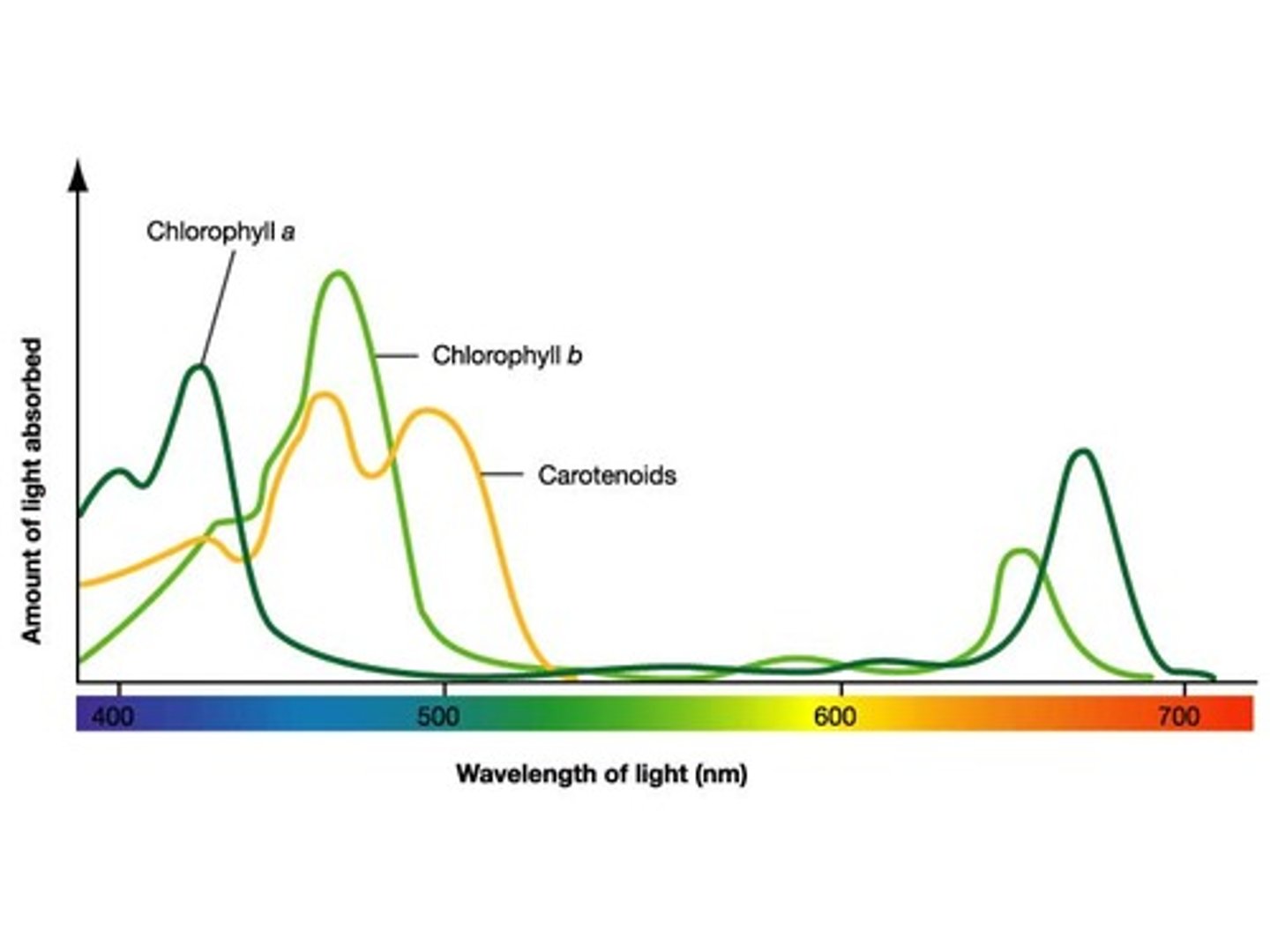
absorption spectrum
A graph of light absorption versus wavelength of light; shows how much light is absorbed at each wavelength.
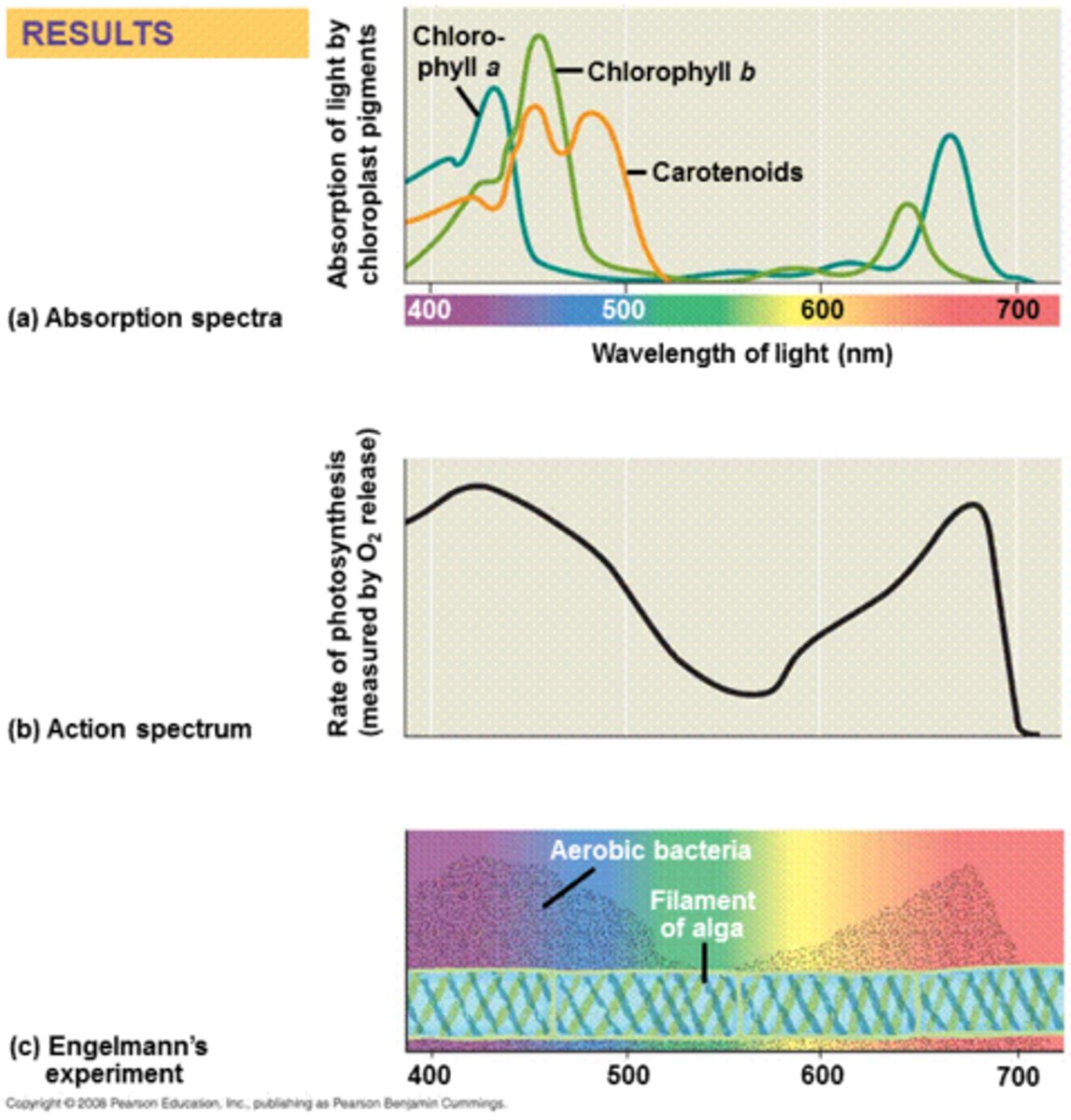
action spectrum
A graph of a biological process versus light wavelength; shows which wavelengths are involved in the process.
photosystem
A light-harvesting complex in the chloroplast thylakoid composed of pigments and proteins.
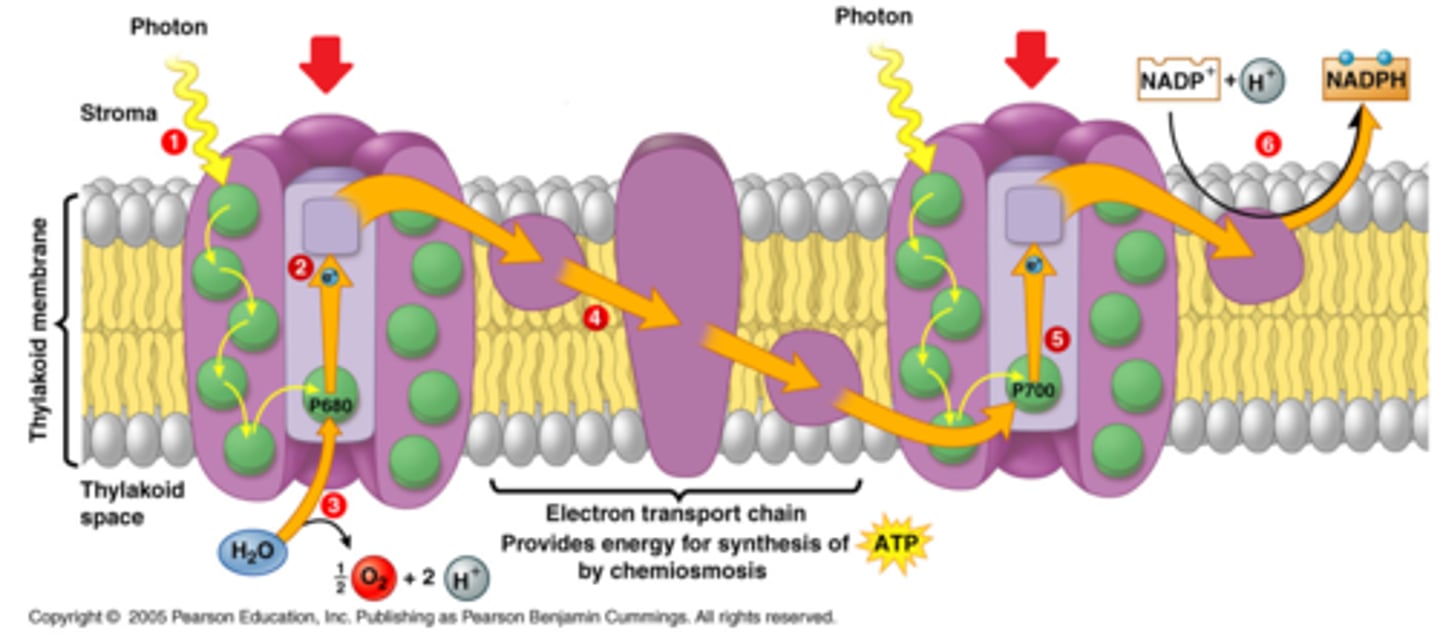
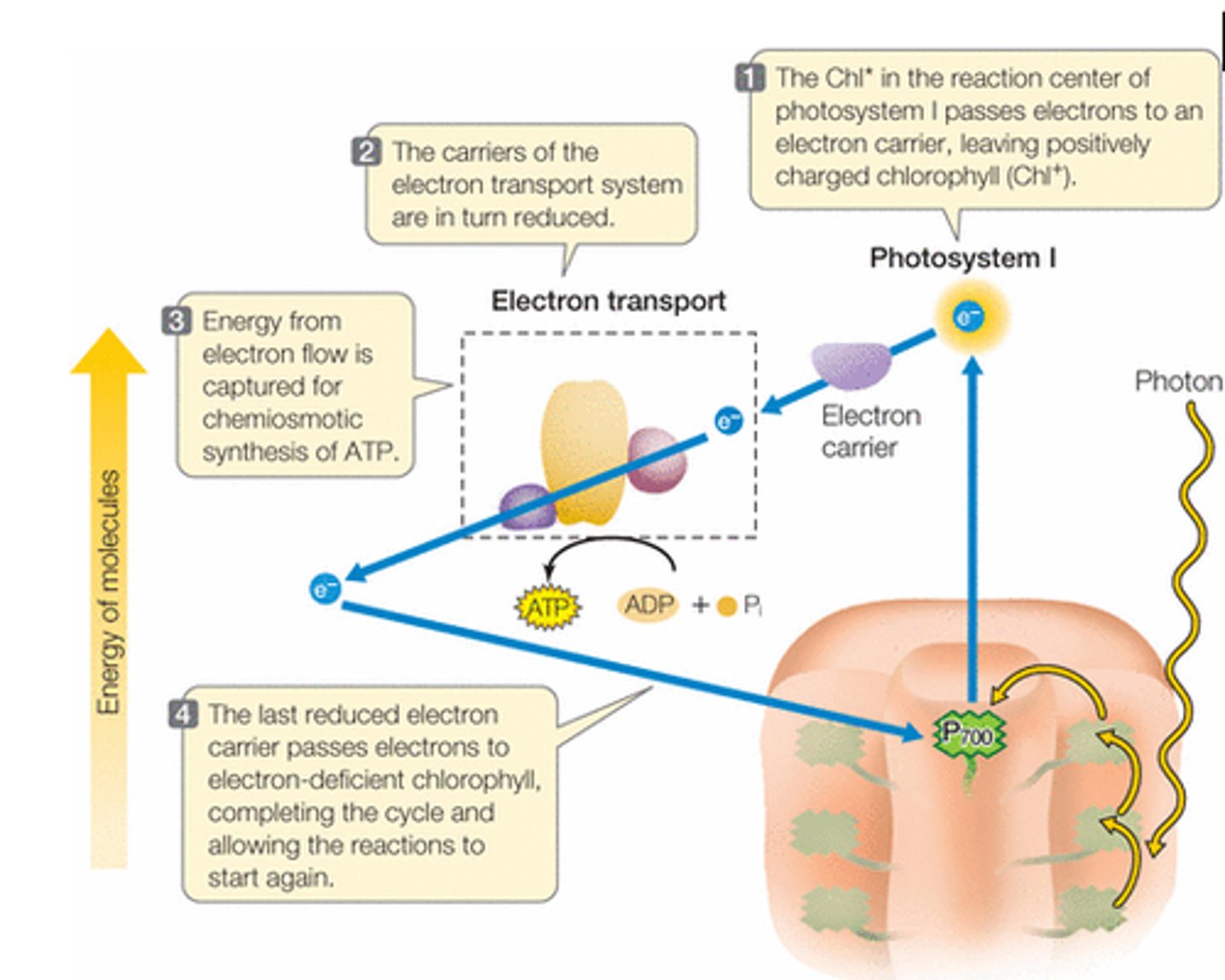
cyclic electron transport
in photosynthetic light reactions, the flow of electrons that produces ATP but no NADPH or O2.
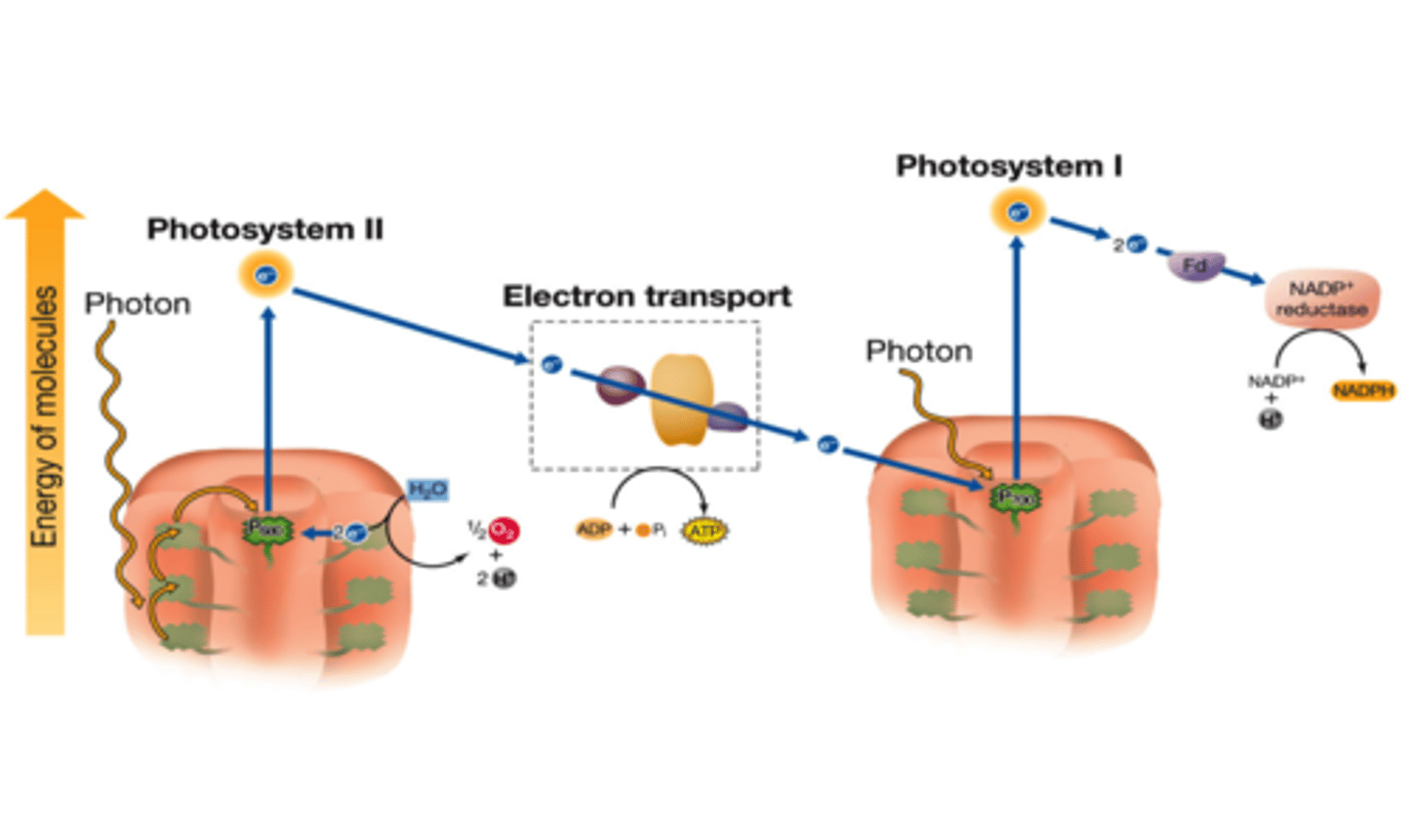
noncyclic electron transport
In photosynthesis, the flow of electrons that forms ATP, NADPH, and O2.
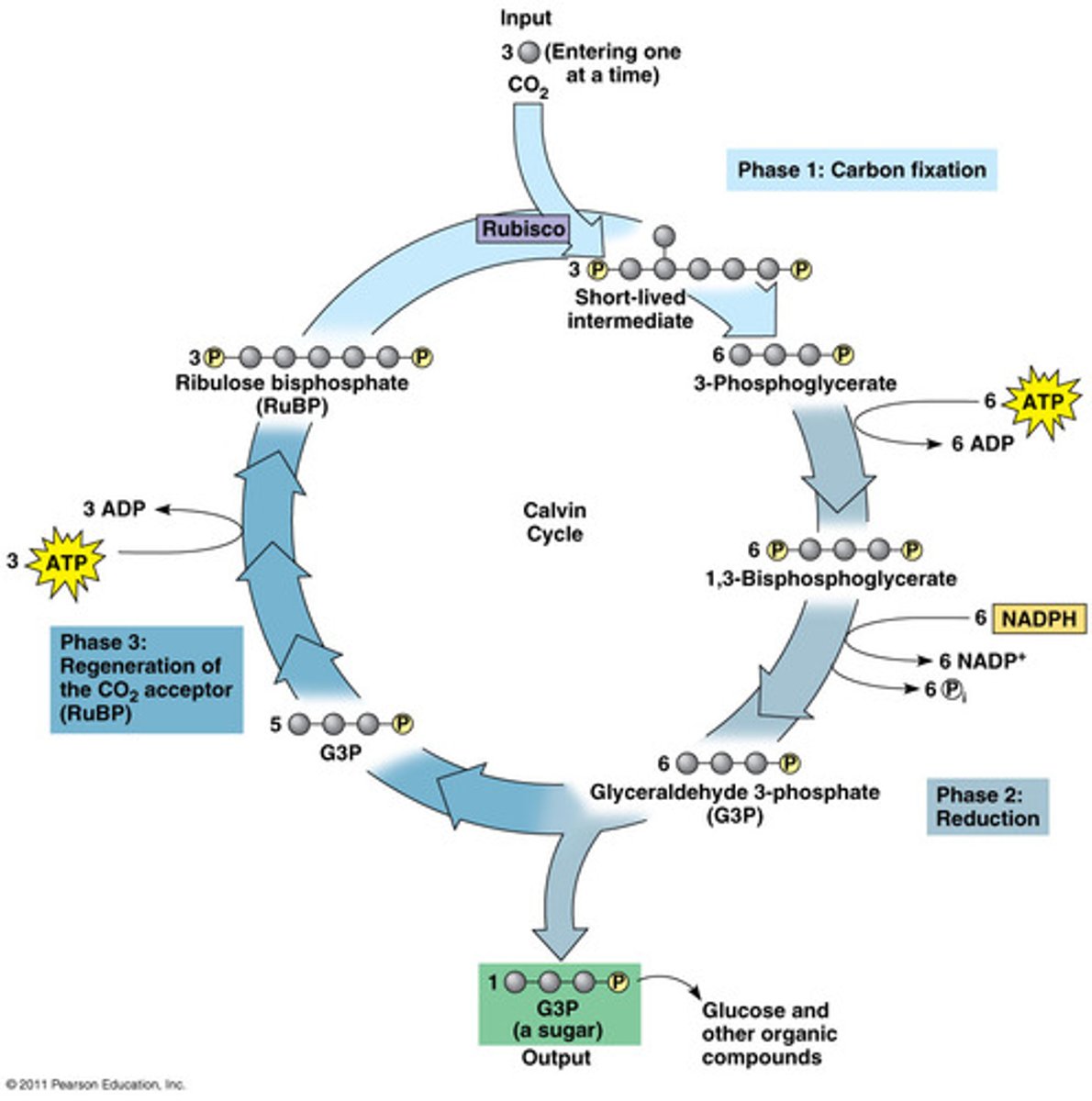
Calvin cycle
a series of enzyme-assisted chemical reactions that produces a three-carbon sugar
metabolism
The sum of the building & breaking reactions occurring in cells
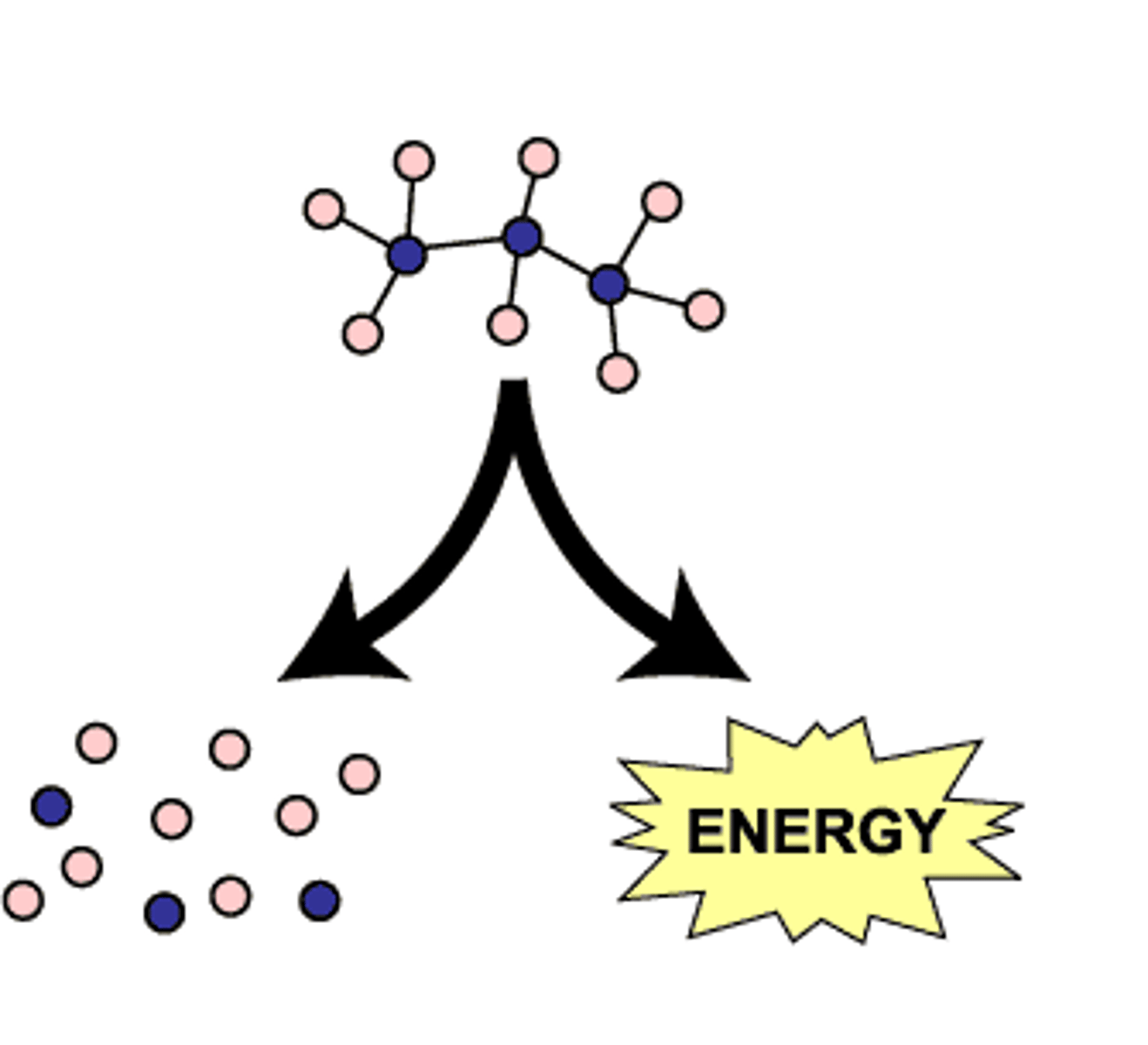
catabolic pathways
Series of reactions that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds.
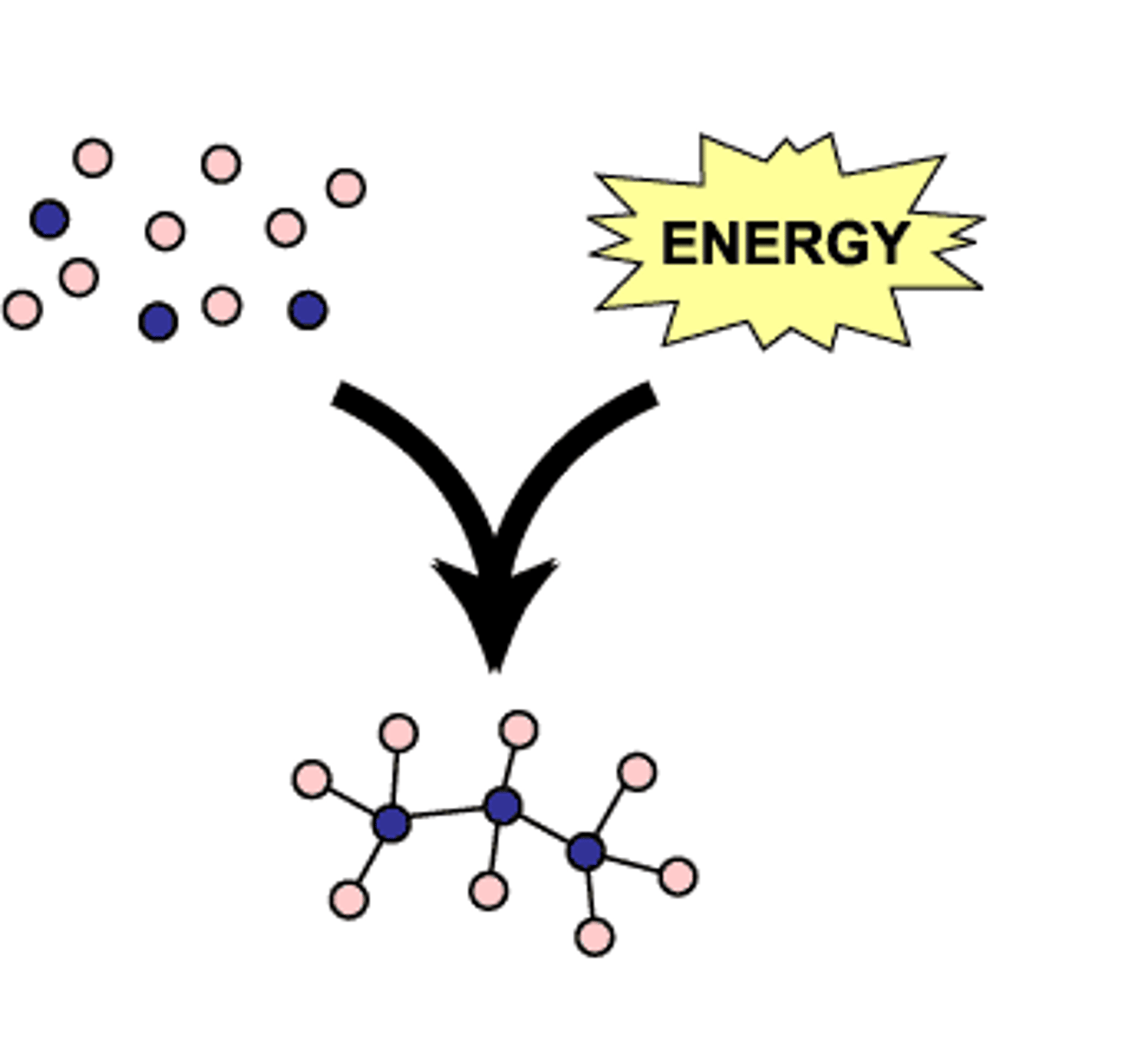
anabolic pathways
Series of reactions that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones.
kinetic energy
Energy associated with relative motion of objects.

thermal energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of molecules or atoms. (heat)

potential energy
Stored energy.

entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness. Tends to increase in the universe.

free energy
Measures the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell.

endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
exergonic reaction
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy.
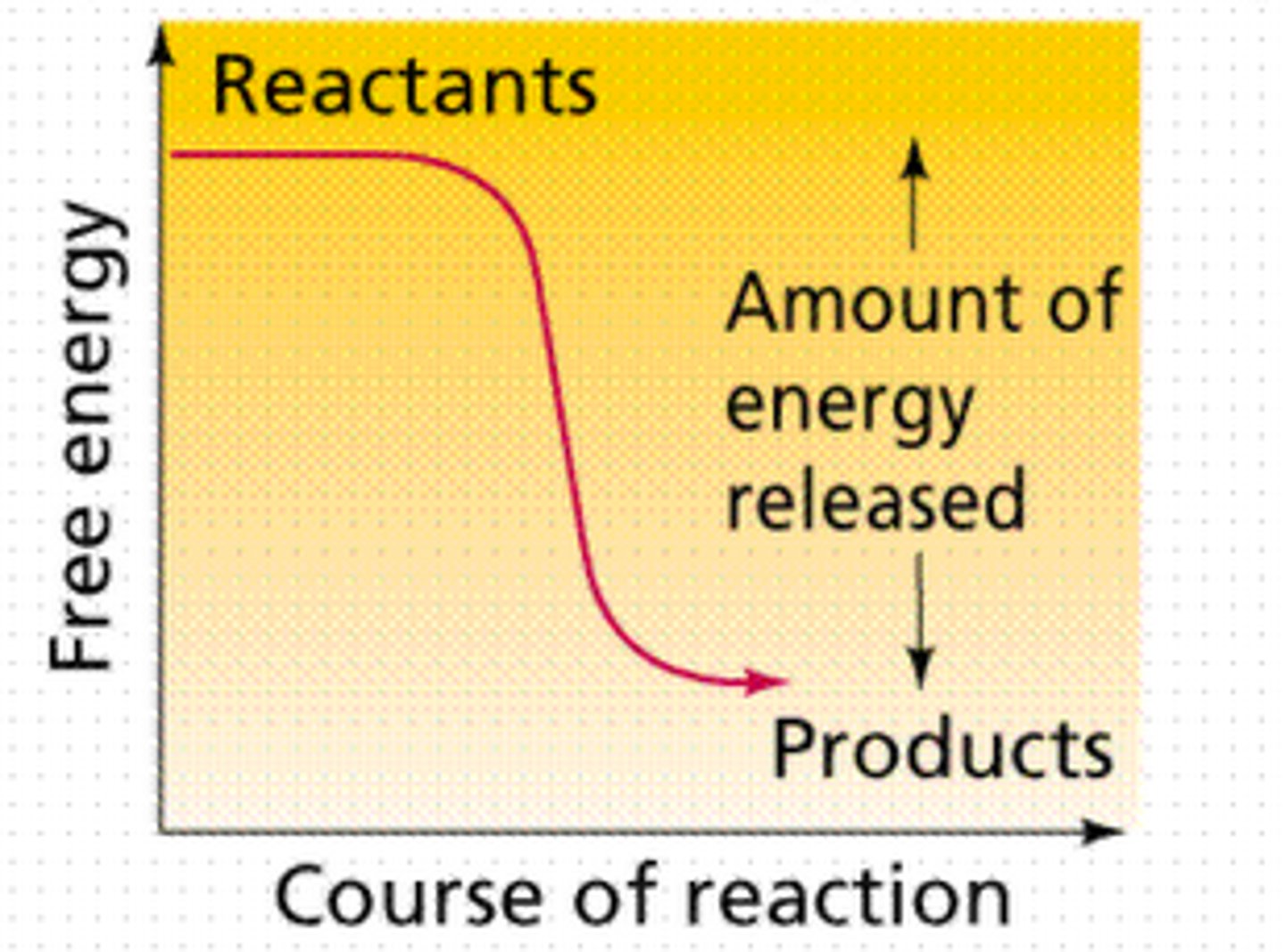
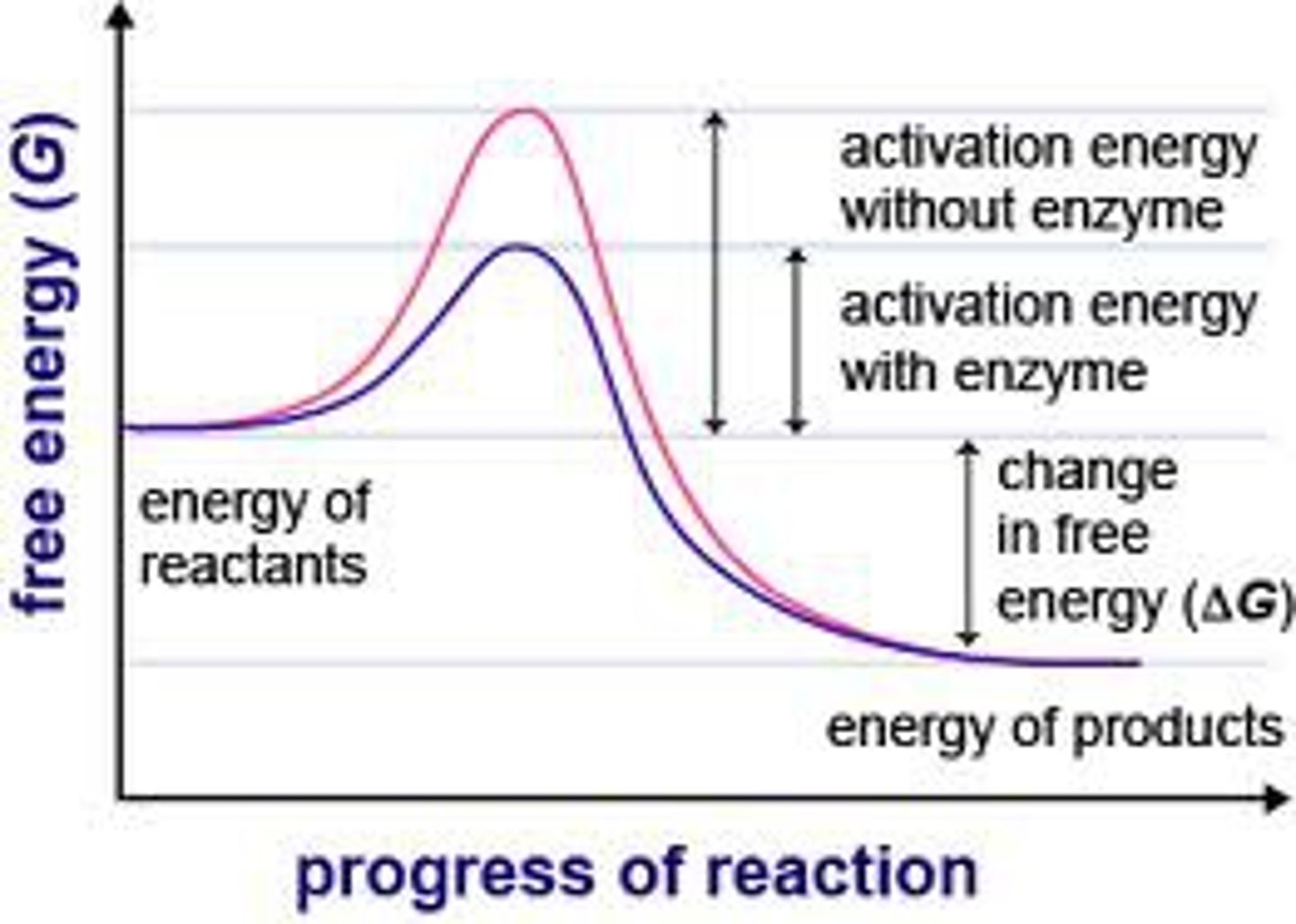
catalyst
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.

enzyme
Protein that speeds up reactions. Typically end in "ase" (ex. Peroxidase, Lipase)

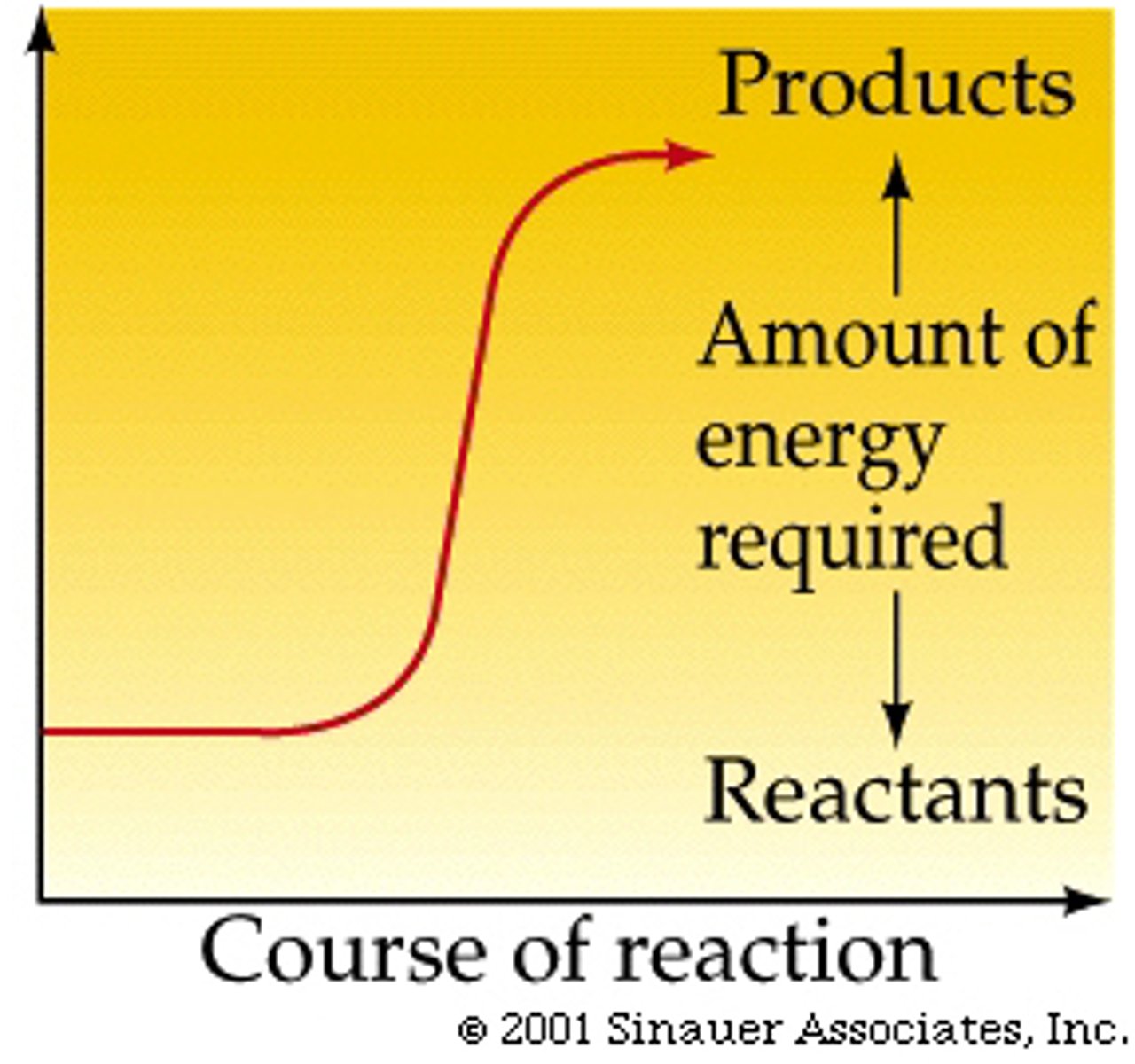
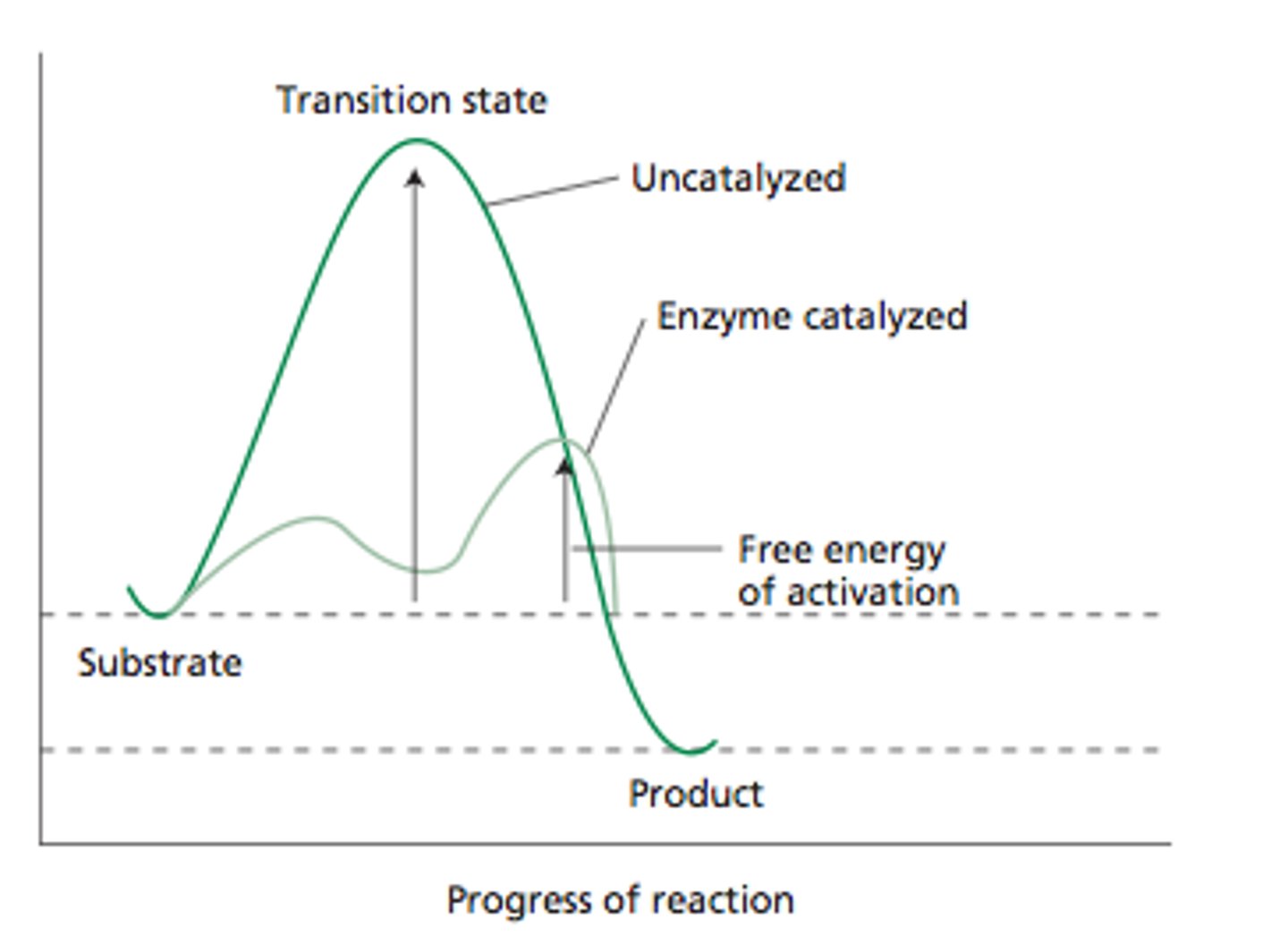
activation energy
The amount of energy needed to push the reactants over an energy barrier.
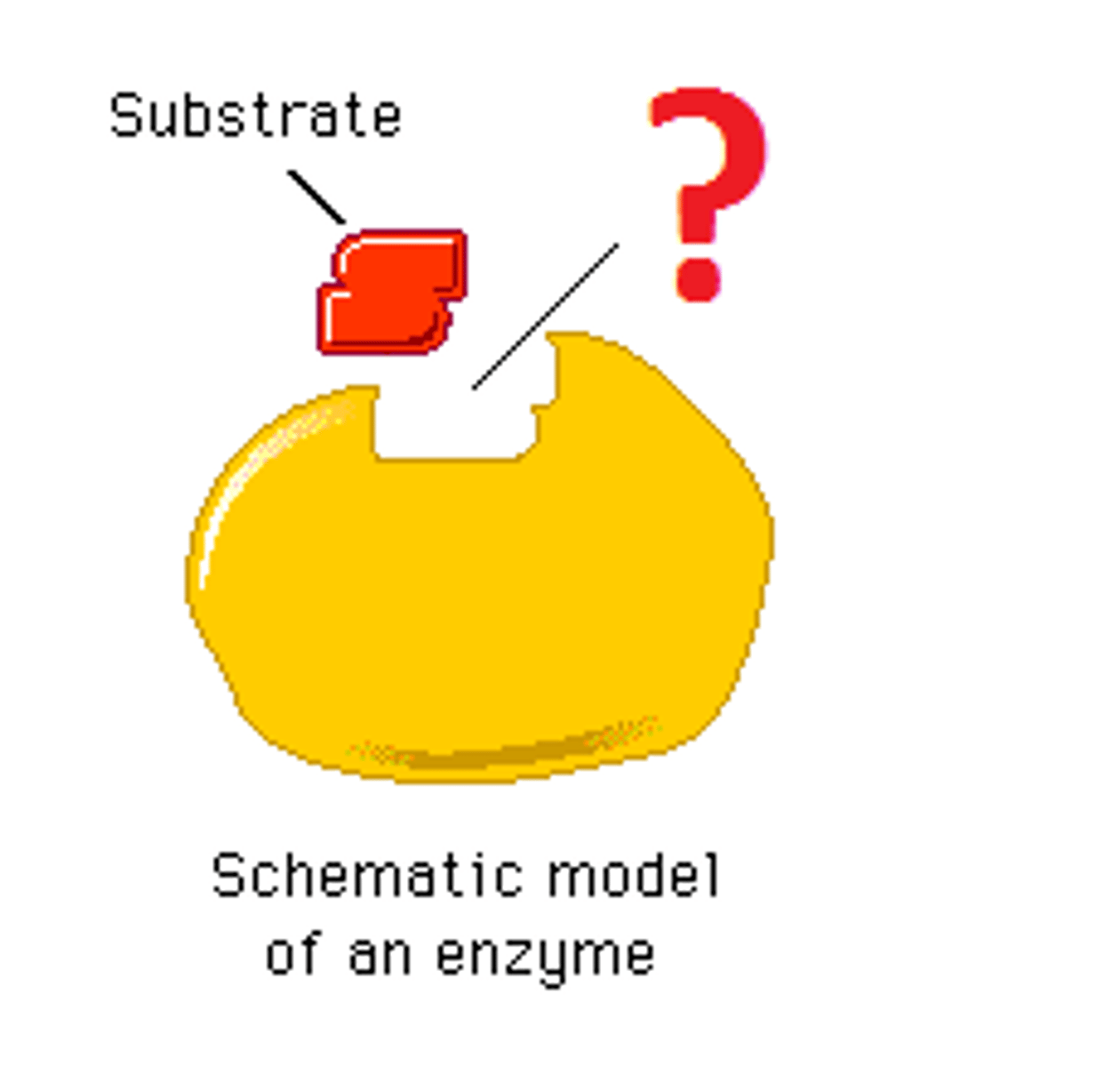
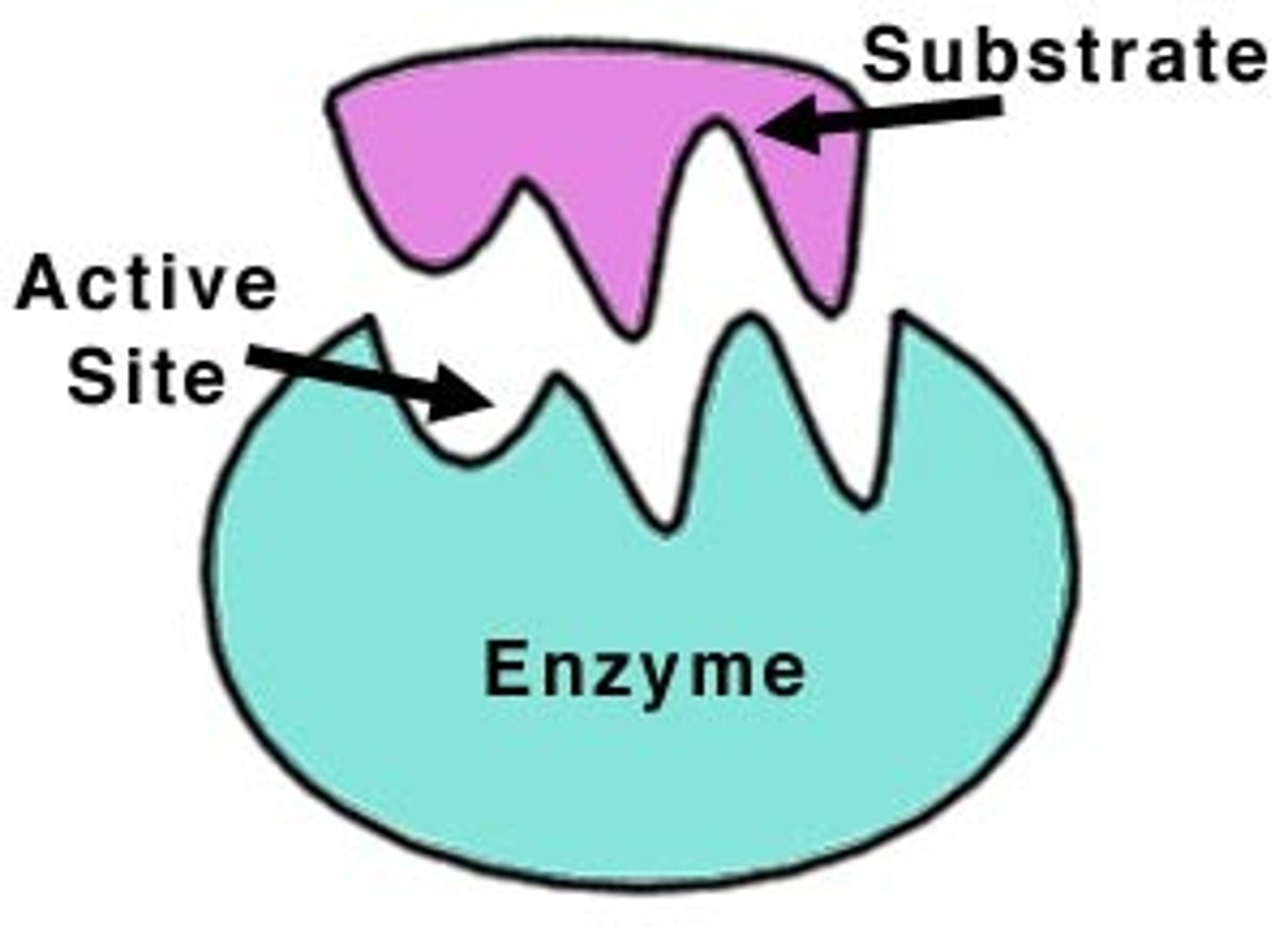
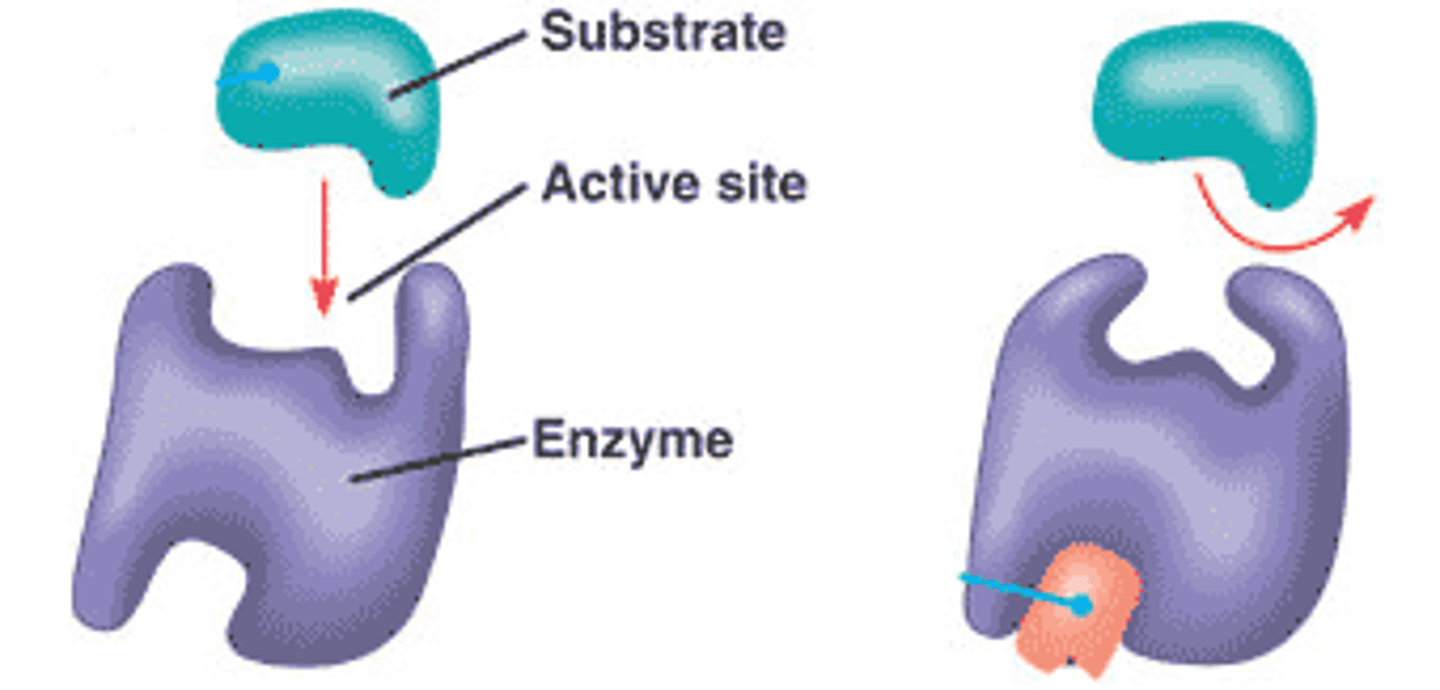
enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms:
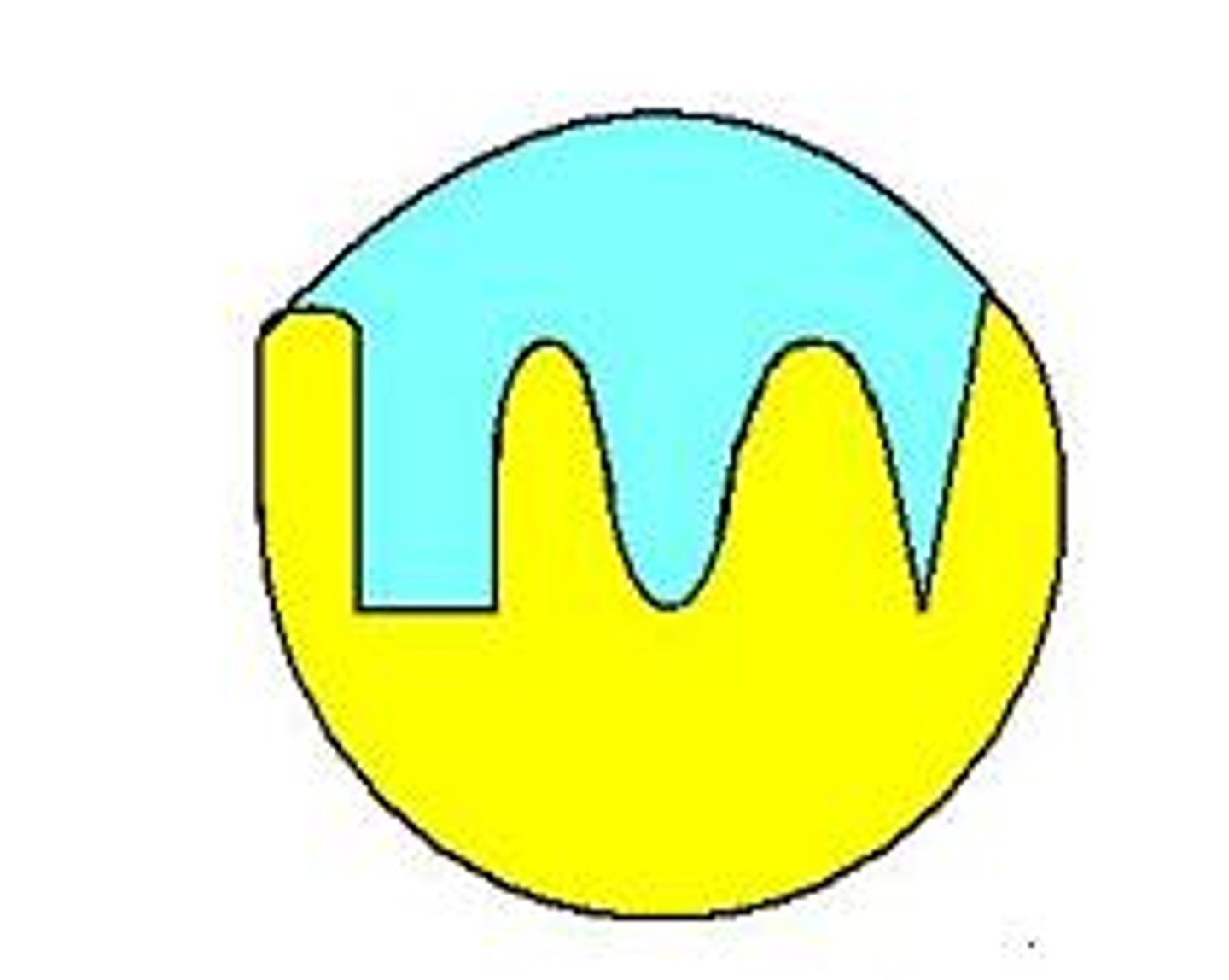

active site
A pocket or groove on the surface of the enzyme where a substrate can bind.
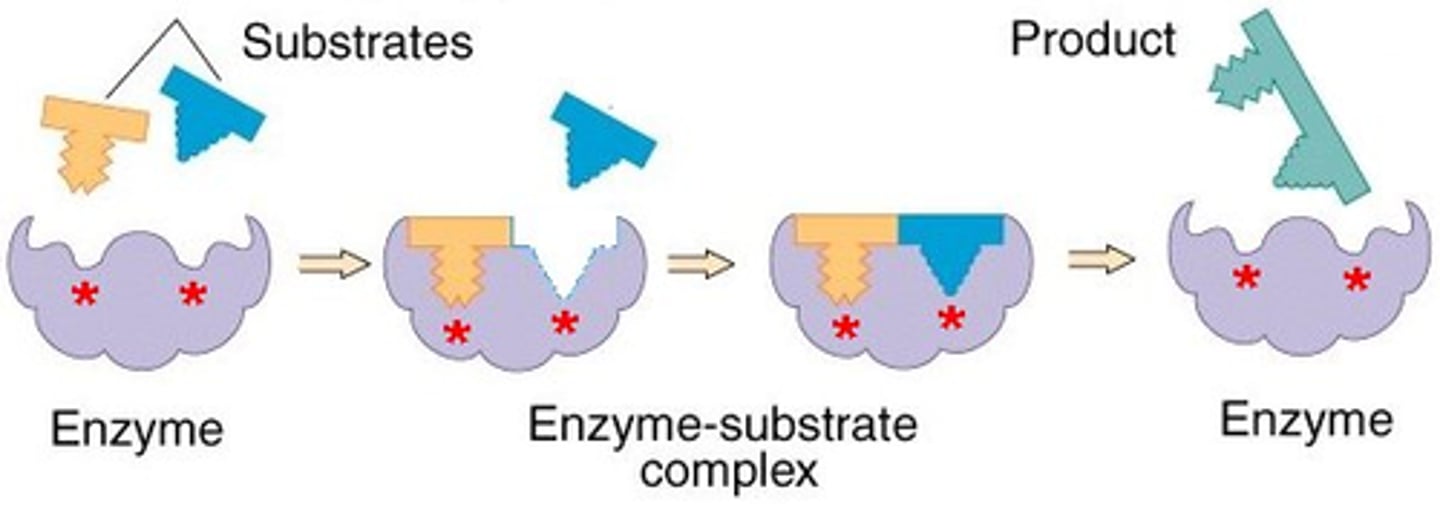
induced fit model
States that the enzyme and substrate undergo conformational changes to interact fully with one another (as opposed to "Lock & Key"
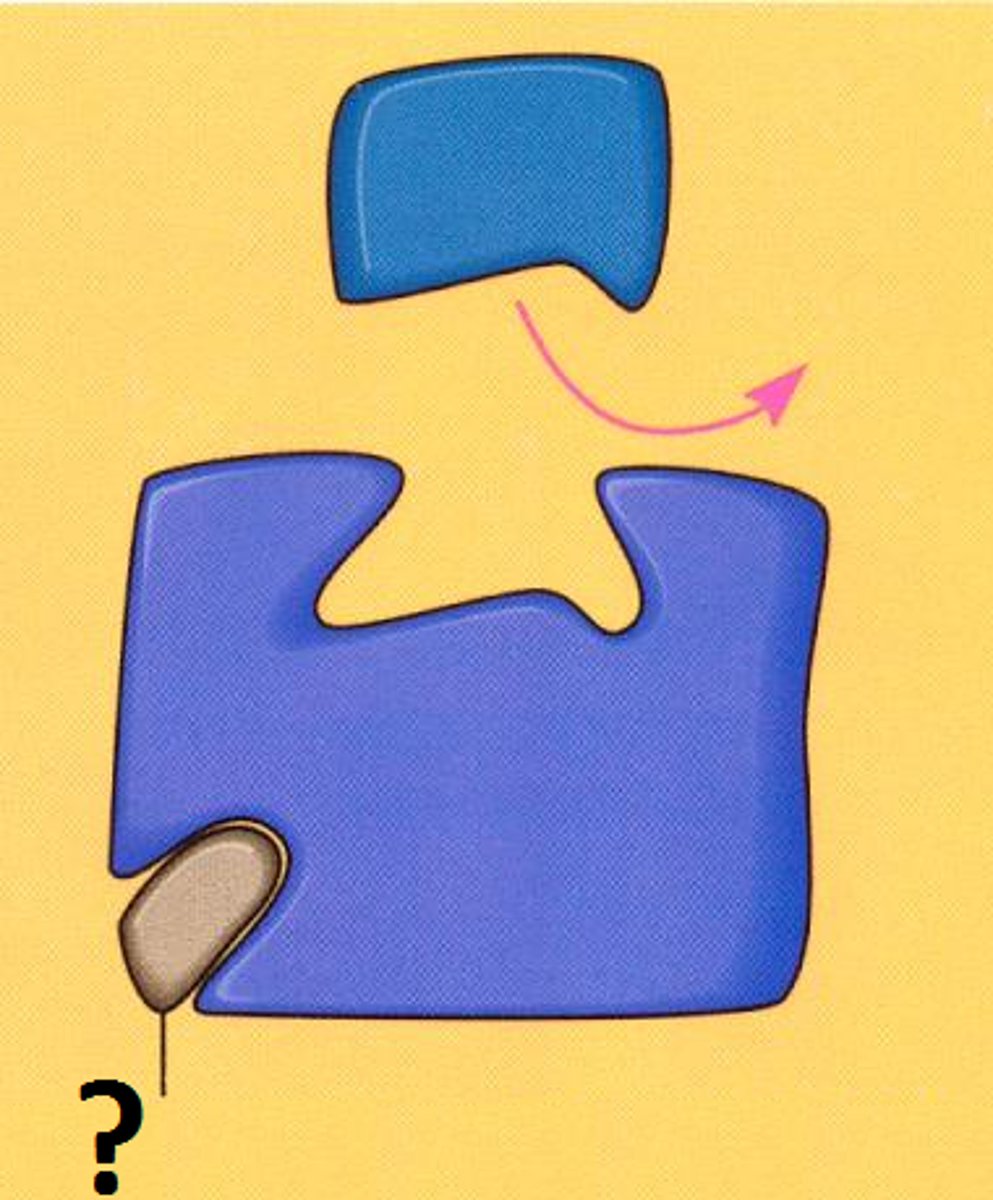
competitive inhibitors
Reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites.
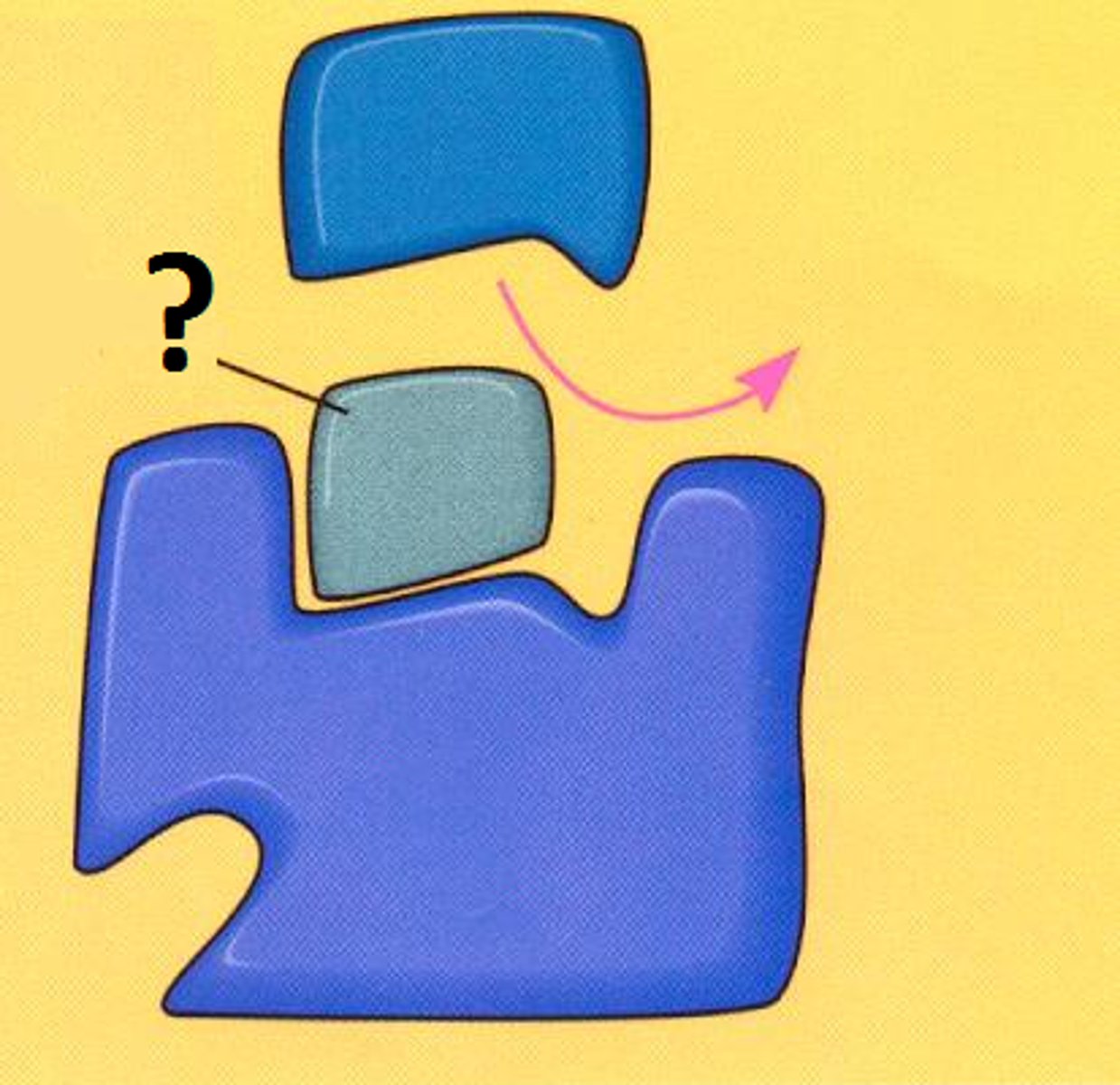
noncompetitive inhibitors
Impede enzymatic reactions by binding to another part of the enzyme (other than the active site).
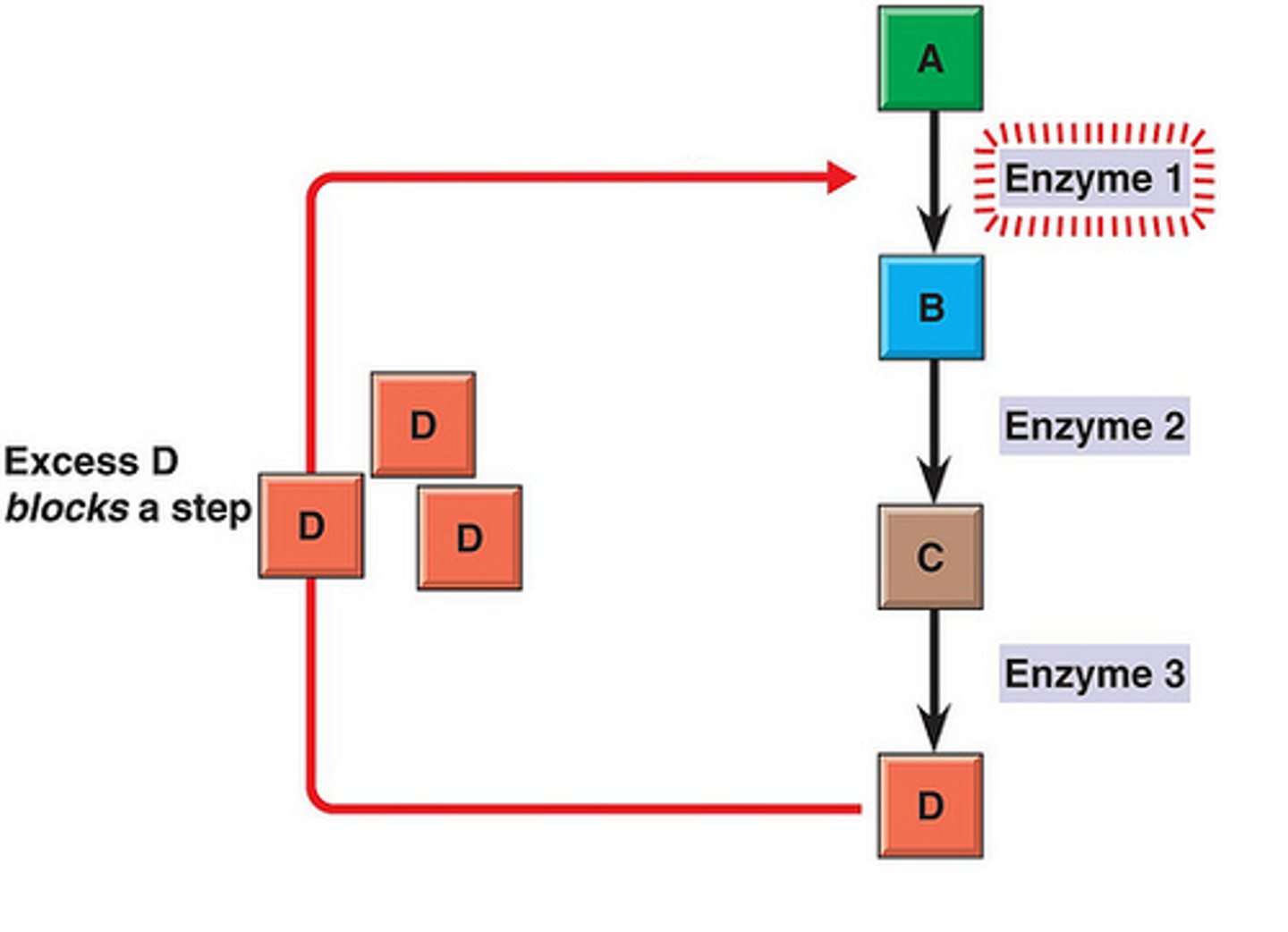
feedback inhibition/negative feedback
A metabolic pathway is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
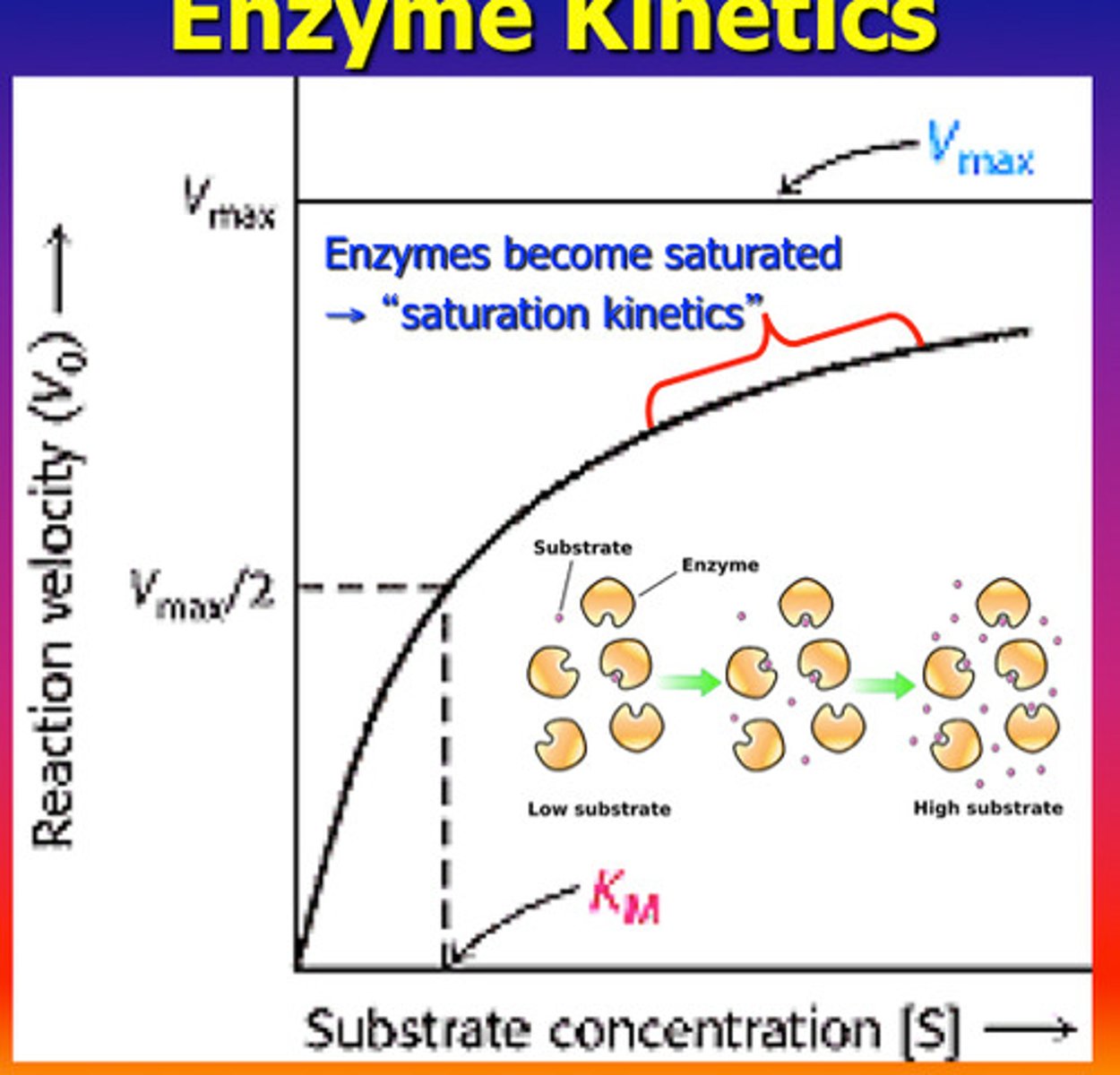
saturated enzyme
Describes an enzyme's maximum activity when every active site is being used.
Chemical Energy
Potential energy trapped in molecular bonds.

Spontaneous Reaction
When a reaction doesn't require energy to proceed it is said to be this - doesn't mean it will be FAST.
Competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
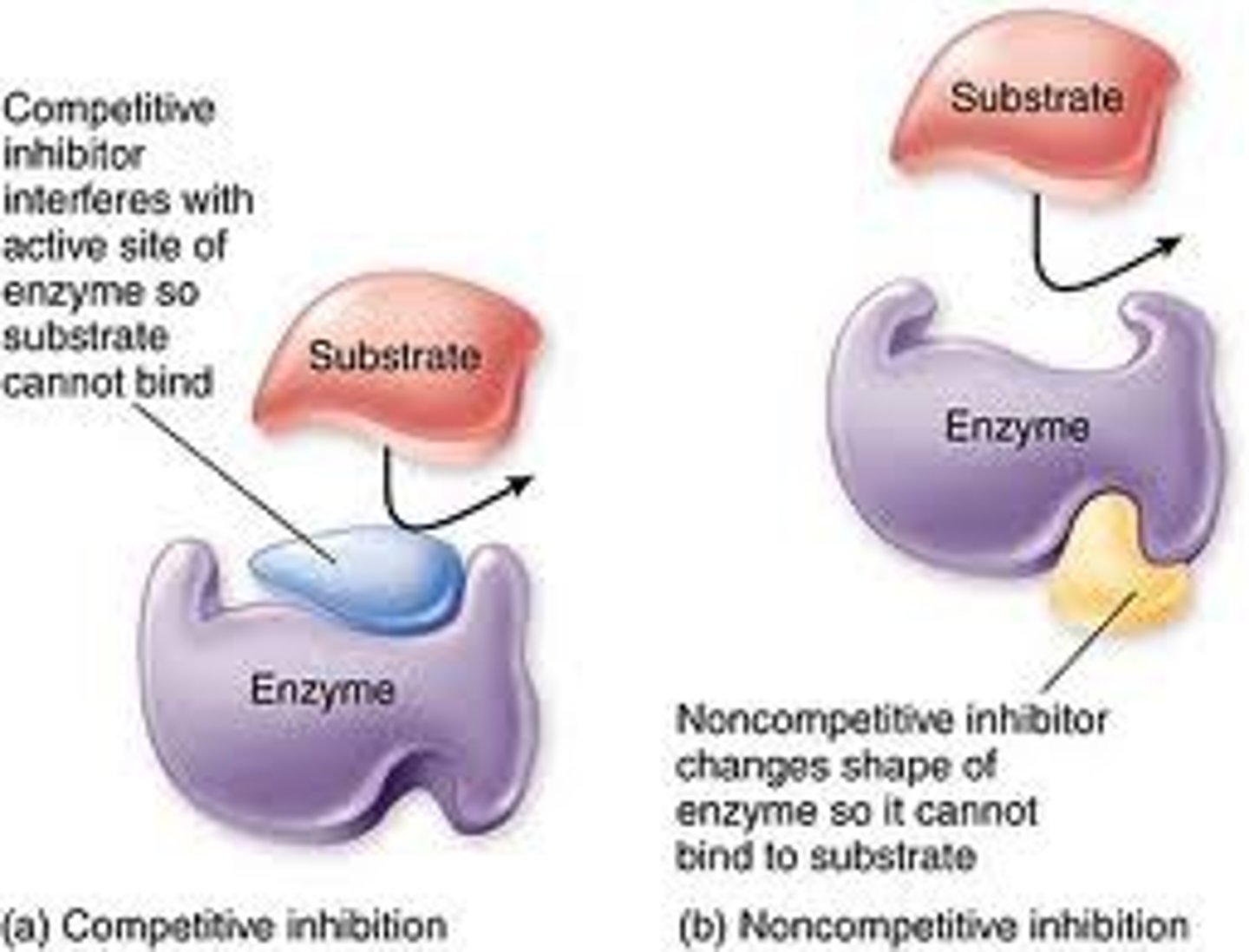
Noncompetitive inhibitor
a chemical that binds to an enzyme but not in the active site. This chemical will change the shape of the enzyme (reversible)
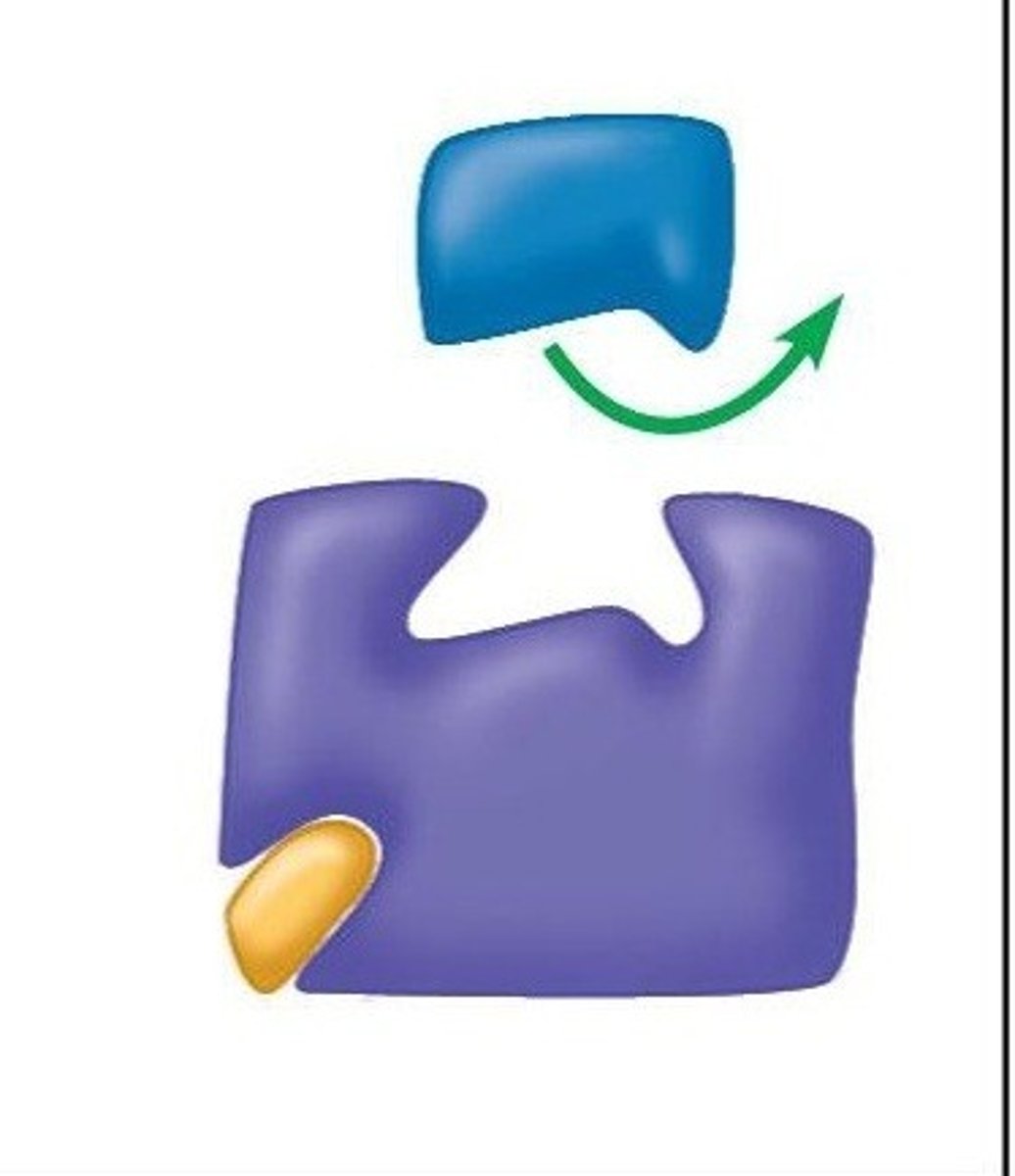

substrate
the substance an enzyme catalyzes, changes.
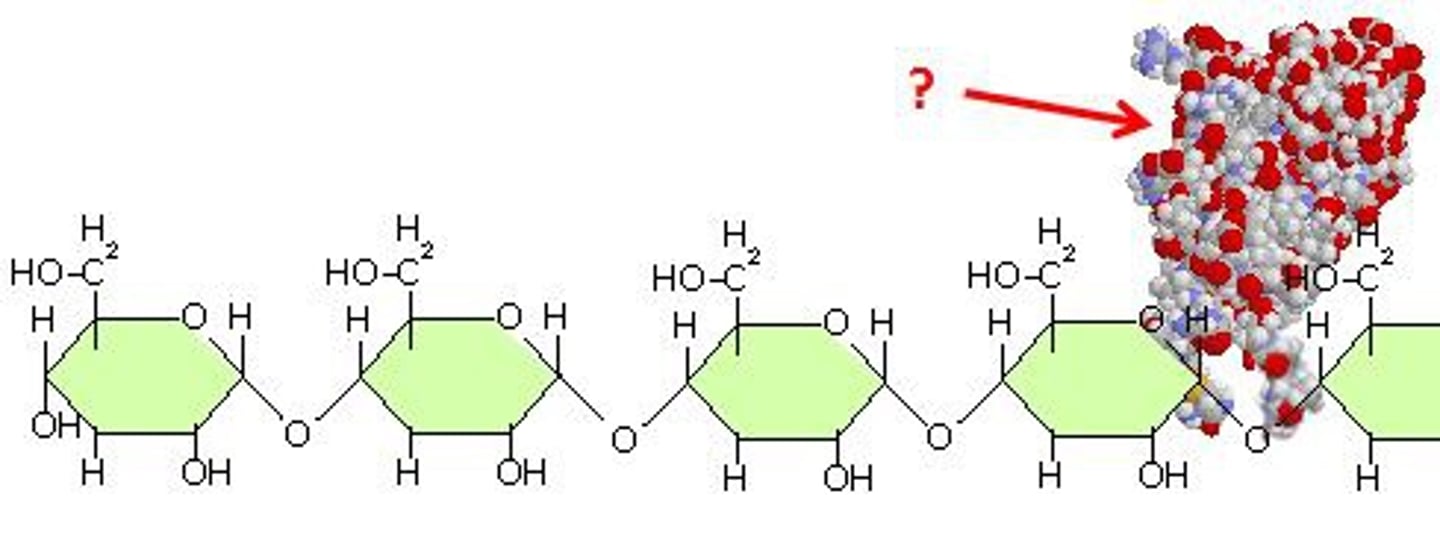
amylase
Enzyme that can break the bonds of starch to form the carbohydrate monomer, glucose.
Denature
Characteristic of proteins; a change in shape that stops the protein from functioning.
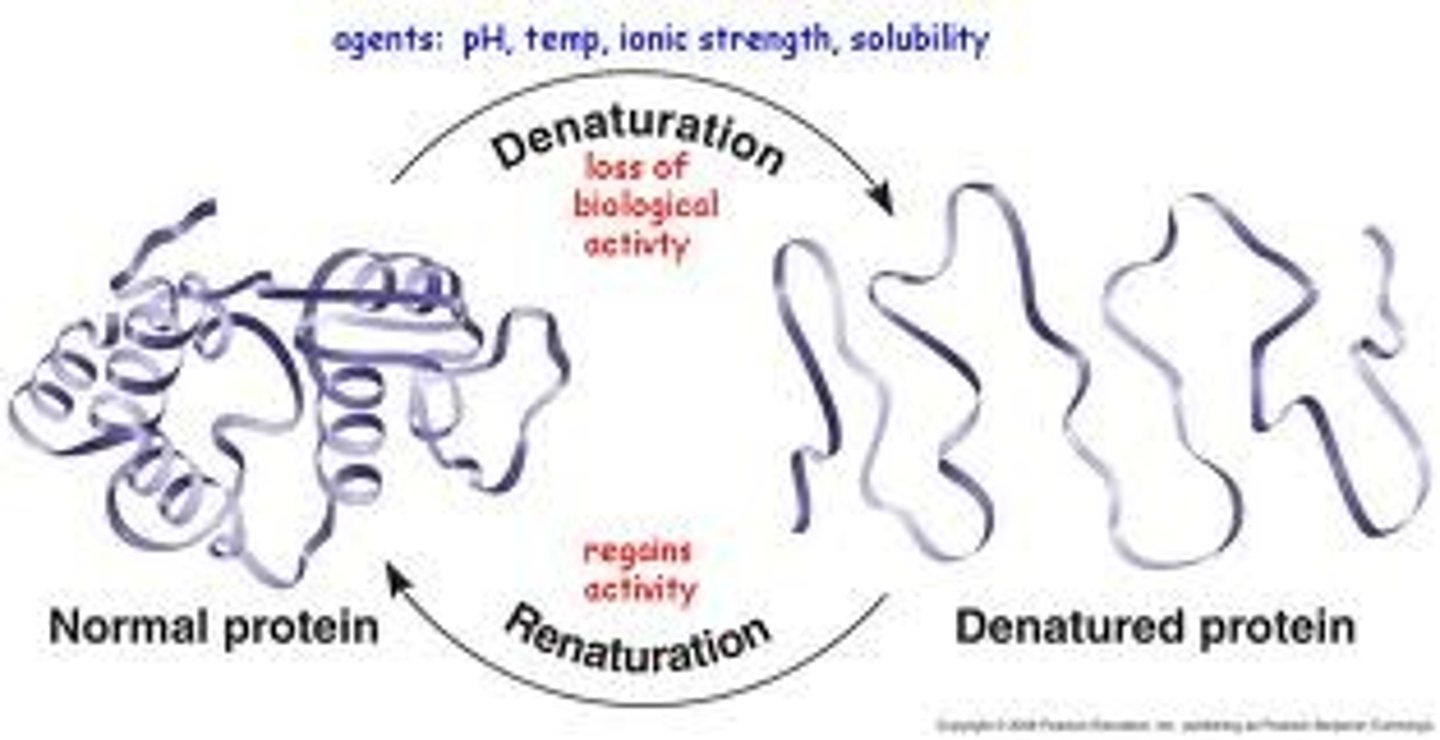
Allosteric
__________ regulation of enzyme occurs when a molecule binds to an enzyme changing the protein's shape
Transition State
The less stable state that occurs and is usually a high-energy state between reactants and products in a chemical reaction
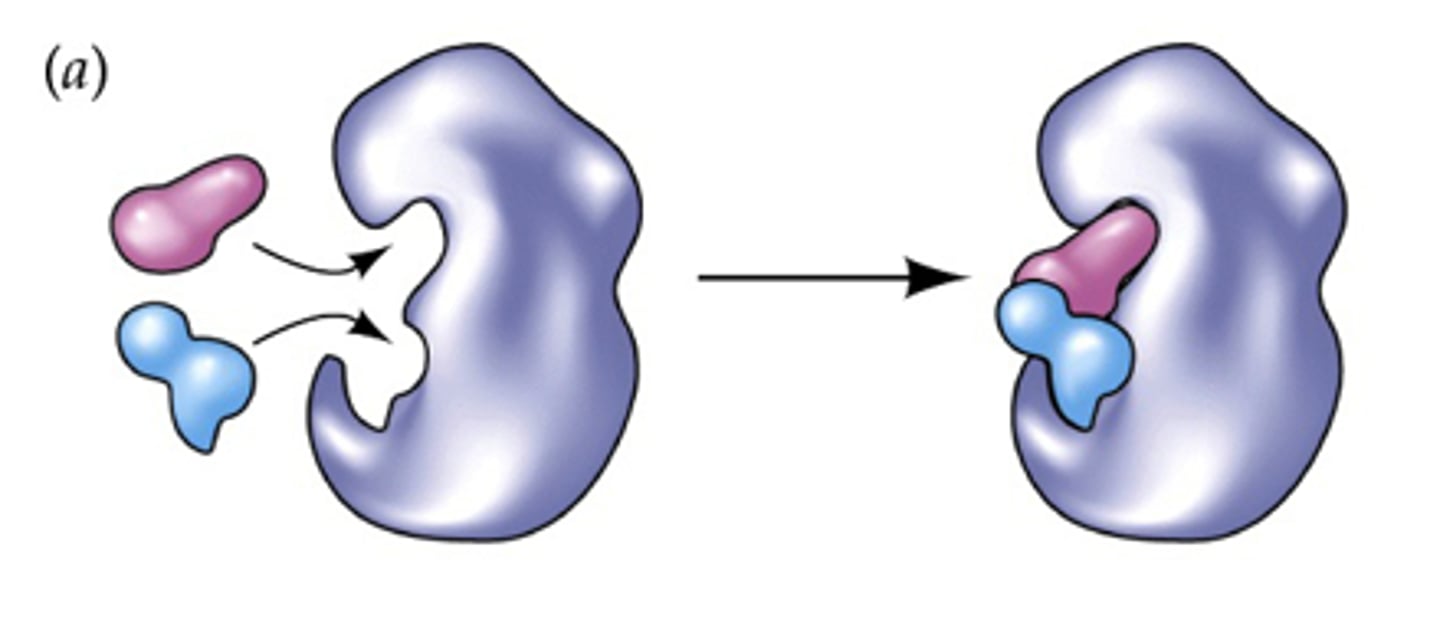
Substrate orientation
When Enzyme bring together specific atoms into a correct position that are otherwise rotating and tumbling so that bonds can form
Temperature
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable:
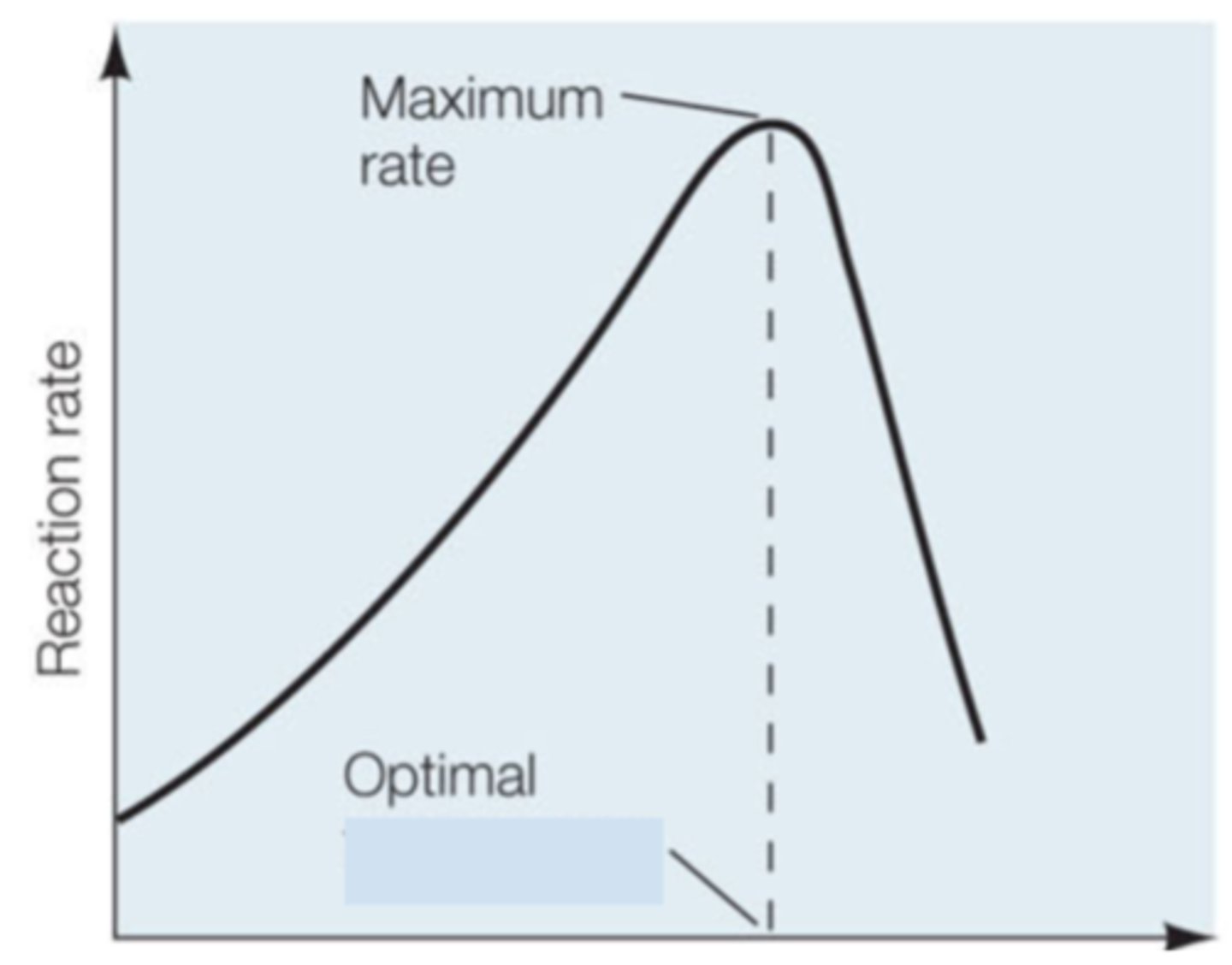
Substrate Concentration
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable:
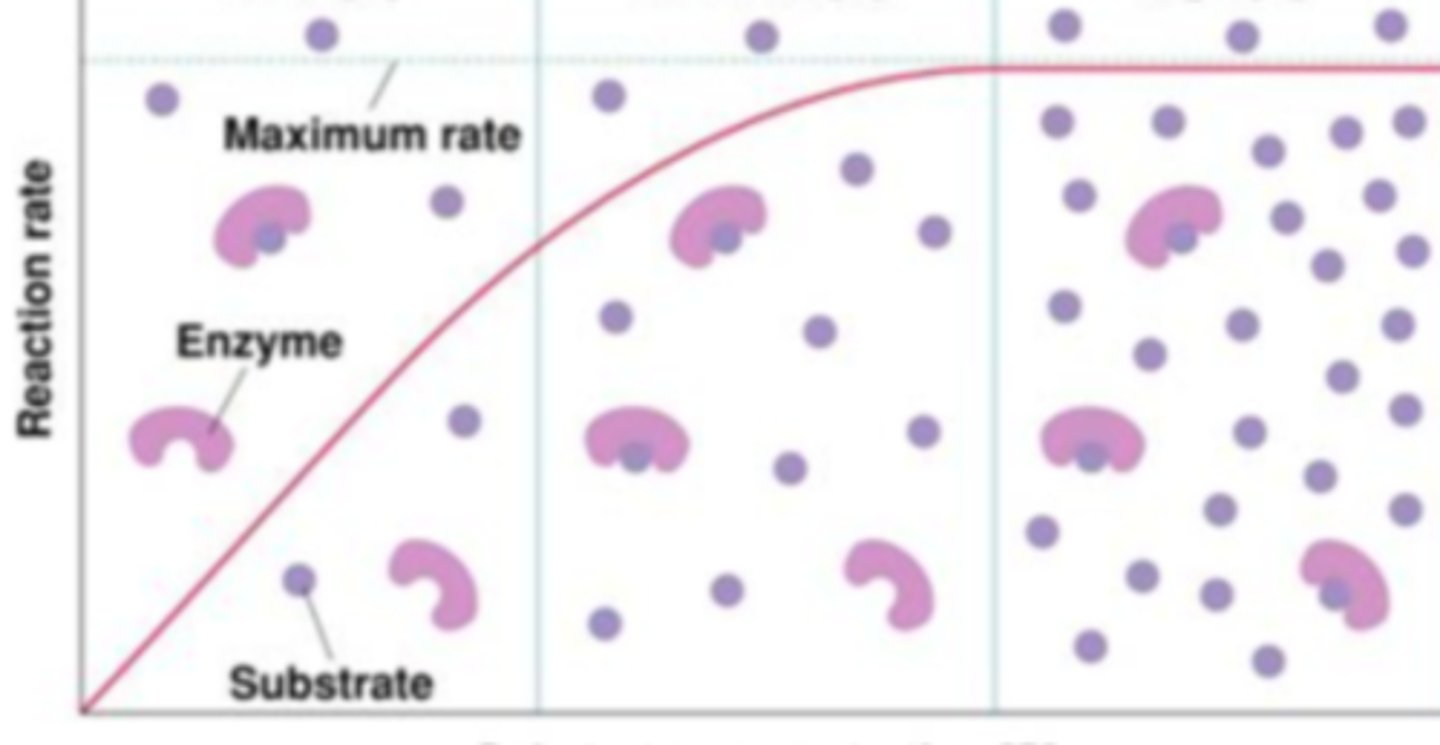
breaks down molecules, negative ΔG
Catabolic
Energy storing, Positive ΔG
Endergonic
builds larger products, Positive ΔG
Anabolic
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Equation for ΔG
symbol G
Free energy
Symbol H
Enthalpy aka system's total energy
symbol T
Temperature
symbol S
Systems total entropy (disorder)
Adenine, ribose, phosphate group
ATP is composed of
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Death
What happens if we have a decrease or disruption in energy?
