Miscellaneous Pulm Disorders
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
obstructive sleep apnea, high altitude pulmonary edema
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
obstructive sleep apnea
recurrent upper airway collapse during sleep that involves cessation of airflow in the presence of breathing
snoring, sleepiness during the day, significant other reports episodes
what are the 3 cardinal symptoms of OSA?
enlarged tongue, tonsils & lateral pharyngeal walls, long soft palate, abnormal positioning of the maxilla and mandible
what anatomic factors of OSA decrease the pharyngeal wall space?
risk patients have an exaggeration of the normal decrease in reflex respiratory activity that occurs during sleep, results in decrease of motor output to upper airway muscles, leads to soft tissue collapse at the level of the soft palate or tongue
neuromuscular factors of OSA that contribute are?
obesity, retrognathia, micrognathia, macroglossia, adenoid or tonsillar hyperplasia, pierre robin syndrome, downs, marfans, hypothyroidism, acromegaly
what are some structural risk factors of OSA?
retrognathia
receding chin
micrognathia
lower jaw is smaller than usual
macroglossia
unusually large tongue
pierre robin syndrome
congenital birth defect characterized by an underdeveloped jaw, backward displacement of tongue and upper airway obstruction
male sex, advanced age, alcohol and sedative use, tobacco
what are some nonstructural risk factors of OSA?
insidiously and may be present for years
symptoms of OSA begin how?
gasping and choking sensations
people with OSA feel what sensations that result in restless sleep with frequent arousals?
supine
OSA is worse in what position?
excessive daytime sleepiness
what aspect of OSA can be very debilitating?
obesity
what is the #1 documented risk factor for OSA?
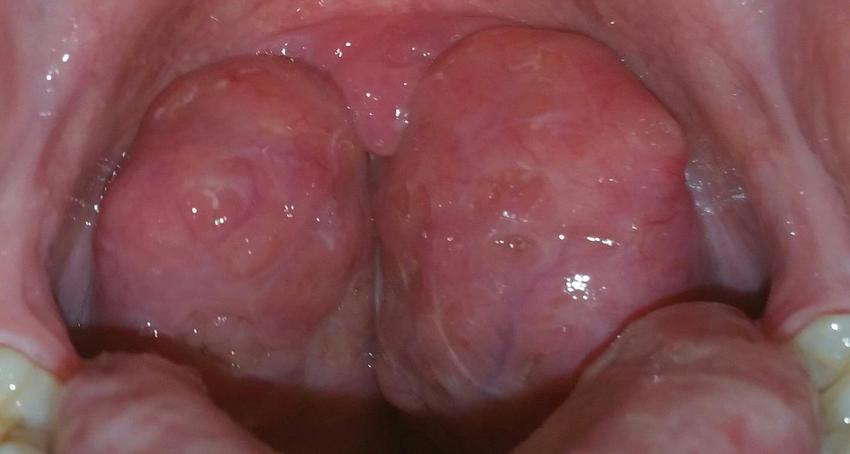
large neck circumference, enlarged “kissing” tonsils, retrognathia, micrognathia, high mallpati score
on physical exam what are the risk factors aside from obesity?
kissing tonsils
polysomnography (sleep study)
what is the study of choice for OSA?
sleep stages recorded via EEG, electroculogram, EMG, oxygen, heart rhythm, leg movements, air flow and chest wall movement, breathing pattern
what is analyzed/monitored during a polymnosography?
cessation of airflow for 10 seconds with persistent respiratory effort
what is considered OSA according to polysomnography?
cessation of airflow for 10 seconds with no respiratory effort
what is considered OSA according to polysomongraphy?
weight loss avoidance of alcohol, sleeping in non-supine position
what is the conservative management of OSA?
nasal CPAP
what is the treatment of choice for OSA?
only if noninvasive methods fail
when is surgery indicated for OSA?
uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
what is the surgery we do if noninvasive methods fail for OSA?
uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
resection of the uvula, soft palate, tonsils and adenoids
tracheostomy
what may patients require in the post op period after their UPPP for their OSA?
nocturnal dysrhythmias, systemic HTN, CAD, pulmonary HTN, cor pulmonale, stroke, DM
what are the complications of OSA?
midnight and 6am
with nocturnal dysrhythmias there is an increase incidence of sudden death between what times?
CPAP
the incidence of complications of OSA is reduced by the use of what?
excellent with use of CPAP
short term outlook of OSA?
unknown
long term prognosis of OSA?
MI and VCA
untreated severe sleep apnea is a significant risk factor for….
MVA due to excessive daytime sleepiness
OSA increases the incidence of what?
high altitude pulmonary edema
form of non-cardiogenic edema that results from high altitude illness resulting from short-term exposure to altitudes >2500
acute mountain sickness, cerebral edema
what is the spectrum of high altitude illnesses?
altitude, rate of ascent, physical activity, individual susceptibility factors
severity of HAPE is influenced by?
reduced
the ambient inspired oxygen concentration is ______ at higher altitudes
increasing their minute ventilation
natives of high-altitude areas compensate long term by doing what?
acute hypoxia resulting in increased capillary permeability and ARDS
non-natives of high altitude areas develop…
young, physically fit patients
HAPE usually occurs in who?
height and rapidity of ascent, physical exertion at high altitude, cold weather, underlying respiratory infection, alcohol & respiratory depressant use
risk factors of OSA?
fatigue, generalized weakness, lightheadedness, headache, nausea, cough & DOE, symptoms more severe at night
what might the history look like in someone who has HAPE?
progressive dyspnea, hypoxia, altered mental status, frothy sputum
untreated disease of HAPE results in….
hangover
early symptoms of HAPE may mimic…
general - respiratory distress, cyanosis
vitals - tachycardia, tachypnea, low O2
lungs - bilateral rales
no evidence of cardiogenic pulmonary edema
what might one find on the physical exam of someone with HAPE?
bilateral thoracic infiltrates
what are the expected chest xray findings of HAPE?
high pH, low pCO2, low HCO3?????
what would be the patient’s expected acid-base findings of HAPE?
descent
what is the most important therapy for HAPE?
2500
HAPE is exposure to altitudes > ______ m
noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
what does the cxr reveal with HAPE?