Porter's Five Forces
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
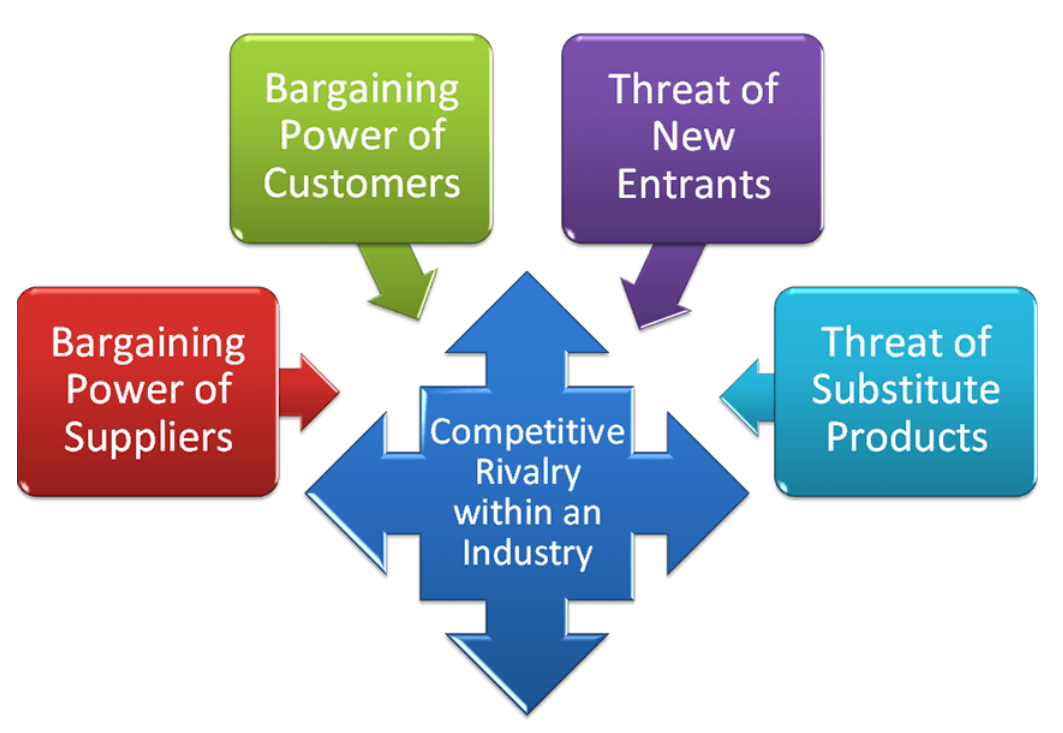
What is the Porter’s Five Forces model?
A framework used to identify and analyse an industry’s competitive forces.
According to Porter, what are the forces that shape the nature of competition within an industry?
Threat of substitute products
Bargaining power of customers
Bargaining power of suppliers
Threat of new entrants
What does the bargaining power of suppliers refer to?
The bargaining power of suppliers relates to the extent to which suppliers can exert influence over the business.
If suppliers have more power, the market may be less attractive, as suppliers can charge higher prices.
When do suppliers have high levels of bargaining power?
When there are only a few, large suppliers
When the resources they supply are scarce
When there are few / no substitute resources available
When the cost of switching to an alternative supplier is high
What does the bargaining power of customers refer to?
The bargaining power of customers relates to the extent to which customers can exert influence over the business.
The higher the buyer power, the lower the potential for the business to set the price themselves. If buyer power is low, then the business is able to set the price high and therefore achieve more profit.
State some factors that determine buyers’ bargaining power.
The amount of bargaining leverage the buyer has - for example, does the customer buy a large proportion of the business’s products/services?
Whether the customer buys in bulk - the larger the order the greater the level of negotiated discount.
Whether the buyer has information on costs/availability of alternative suppliers.
Product USP and exclusivity.
Brand identity and loyalty of the product bought. If the product is branded, the buyer has less control over price paid, they may even be told the price that they can sell the product at.
Price sensitivity of the product - how changes in price affect demand levels (PED)?
If forward vertical integration exists.
What does threat of new entrants refer to?
How easy it is for businesses not currently in the market to set up and become rivals.
If new businesses can enter the market easily then the existing businesses will have a challenge to keep their profits high. New businesses will be attracted to the market if profits are high but if barriers of entry exist, or existing businesses attempt to create barriers to entry, then this can reduce or stop new businesses entering the market.
Give some examples of barriers to entry to businesses.
High capital / investment requirements
Economies of scale of existing businesses
Strong brand identity of existing business’ products and high levels of advertising
Access to factors of production, e.g. raw materials, skilled staff, and components
Access to technologies used in the industry.
What does threat of substitutes refer to?
The availability of alternative products or services that customers could switch to (outside the industry).
If there are more substitutes available, this may limit the price a business can charge, which will lead to reduced profits for the business.
Customer loyalty and availability can limit the extent of this threat.
What are some factors that determine the likelihood of availability of substitute products?
Rate of change of technology – the faster the rate of change of technology, the more quickly substitutes are likely to occur.
Availability of capital for investment – how likely potential producers of substitutes are to be able to raise the capital required for research and development, and production.
Switching costs for customers – cost of changing to substitute.
Level of substitution effect – how close the substitute is, how easily it replaces the original product or service.
Price-performance trade-off of substitutes – how effective the substitutes are in cost and performance, e.g. at the moment electric cars do not offer an effective substitute for petrol engine cars so few people consider them as effective substitutes.
The existence of patents and licenses - to operate in the market.
What factors determine how intense rivalry is within an industry?
The number of competitors in the market.
Market size / growth prospects - competition is more intense in slow-growth / declining markets.
Product differentiation and brand loyalty
More customer loyalty= less intense competition
Less product differentiation= greater intensity of price competition
Exit barriers- if it is difficult or expensive to exit an industry, businesses are likely to remain which adds to competition.
An attractive industry is one that has…
High profitability.
This is due to:
new entrants finding difficulty setting up
few strong competitors – little rivalry
weak suppliers
loyal, but passive customers
lack of competition from substitute products.
An unattractive industry is one that has…
Low profitability.
This is due to:
many substitutes
lack of barriers to entry
strong, well-established competitors
powerful suppliers
well-organised and choosy customers.