General Biology II: Chapter 29
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Land Plants
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Closest living relative of land plants?
charophytes
Which group is considered the first land plant?
bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, hornworts)
Vascular System
tracheophytes, have tissue for conducting water and minerals throughout a plant
Examples of vascular plant groups
clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (conifers), angiosperms (flowering plants)
What did the new adaptation of the vascular system allow?
they allowed plants to grow taller, become independent of water, and efficiently transport water, nutrients and sugar throughout the plant
Seedless Vascular Plants
no seeds, but have xylem and pholeum that help transport water and food
Seed Plants
reproduce using seeds
Nonvascular Plants
no vascular system xylem and pholeum, grow in moist environments
How did seedless plants affect earth and life?
they drove global cooling and creating coal deposits via CO2 removal
What kind of adaptations did plants need to get to survive out of water?
waxy cuticle, stomata, development of vascular tissue, embryos, spores/seeds
How did adaptations of land plants benefit animals and other life?
plants supply oxygen & are the ultimate source of most food eaten by animals, allowed animals to diversify, and create new niches
Difference between spores and seeds
spores are not seeds, all plants have spores, but seed plants make them
Advantages of spores
dispersal, survival, reproduction, allow wide distribution by wind, water or animals
Advantages of seeds
protection, nourishment for embryo, enhanced dispersal capabilities, and ability to remain dormant to survive harsh conditions
Alternation of Generations
life cycle is characterized by this, plants alternate between 2 multicellular adult body forms
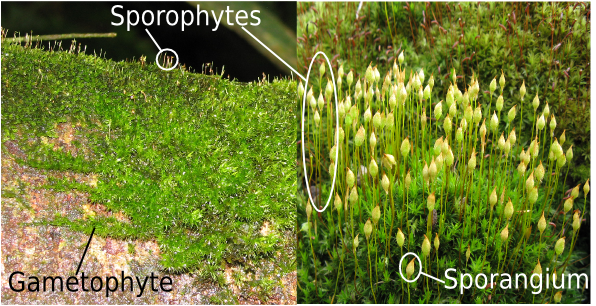
Alternation of generations in mosses
gametophyte n vs sporophyte 2n: gametophyte produces gametes that fuse to form a zygote, develops into sporophyte
Alternation of generations in ferns
diploid sporophyte vs haploid gametophyte: sporophytes produce haploid spores through meiosis
Alternation of generations in vascular plants
dominant, diploid sporophyte, smaller haploid gametophyte
sporophyte from a gametophyte stage
Photosynthesis
plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, making their own food from CO2 and H2O
Stomata
pores that facilitate gas exchange between the outside air and internal plant tissue
What is the risk stomata take by opening up for gas exchange?
excessive water loss