Java main questions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the differences between ArrayList and LinkedList?
• ArrayList: Uses a dynamic array. When the array reaches its capacity, it is resized (usually doubled in size).
• LinkedList: Uses a doubly linked list. Each element (node) contains a reference to the previous and the next node.
Index Access
• ArrayList: Fast (O(1)) because it is based on an array. Elements have fixed indices, allowing direct access.
• LinkedList: Slow (O(n)) as it needs to traverse the nodes to reach the desired index.
Insertion and Deletion
• ArrayList:
• Insertion at the end: Fast (amortized O(1)), unless resizing is required.
• Insertion/deletion in the middle: Slow (O(n)), as elements must be shifted to maintain order.
• LinkedList:
• Insertion/deletion at the start, middle, or end: Fast (O(1)) if you already have the reference to the node. However, finding the node to insert/delete may take O(n).
Memory Usage
• ArrayList: More memory-efficient, as it only stores the data.
• LinkedList: Consumes more memory since each node contains additional references (pointers to the previous and next nodes).
Use Cases
• ArrayList:
• Ideal when frequent access by index and iteration are required.
• A good choice for lists with a predictable size and infrequent insertions/deletions.
• LinkedList:
• Better suited for lists with frequent insertions and deletions, especially at the beginning or in the middle.
• Useful when the list size changes significantly and access by index is not a priority.
What are the key differences between List, Set, and Map in the Java Collections Framework?

What are the key differences between HashMap and TreeMap?
Key Differences Between HashMap and TreeMap:
Structure: HashMap uses a hash table; TreeMap uses a red-black tree. (a self-balancing binary search tree). Entries are stored in sorted order based on their keys.
Ordering: HashMap is unordered; TreeMap maintains sorted order.
Performance: HashMap has O(1) average for get/put; TreeMap is O(log n).
Null Keys: HashMap allows one null key; TreeMap does not allow null keys.
Use Case: HashMap for fast, unordered access; TreeMap for sorted data and range queries
What is the difference between equals() and ==?
==: Compares object references (checks if they point to the same memory location). Used to check if two objects are literally the same instance.equals(): Compares object values (checks if the contents are equal).
Explain the Java memory model (Heap and Stack).
The heap stores objects and class-level variables, shared across threads. The stack holds method-level variables and execution context, faster and thread-safe
What is the purpose of the volatile keyword?
Ensures visibility and ordering of variable updates across threads by preventing caching
What is the difference between String, StringBuilder, and StringBuffer?
String is immutable. StringBuilder is mutable and not thread-safe, faster in single-threaded operations. StringBuffer is mutable and thread-safe, slower than StringBuilder
What is autoboxing and unboxing in Java?
Autoboxing is the automatic conversion of primitives to their wrapper types (e.g., int to Integer). Unboxing is the conversion of wrapper types to their corresponding primitives
What is the difference between Comparable and Comparator?
Comparable defines natural ordering using the compareTo() method. Comparator defines custom ordering using the compare() method
What are checked and unchecked exceptions?
Checked exceptions must be declared or handled (e.g., IOException, SQLException). Unchecked exceptions are runtime exceptions that do not require declaration or handling (e.g., NullPointerException, ArithmeticException)
What is the difference between final, finally, and finalize()?
final is used to declare constants, prevent inheritance, or prevent method overriding. finally is a block used to execute code regardless of exceptions. finalize() is a method used by the garbage collector before reclaiming an object
What are the differences between abstract classes and interfaces?
Abstract classes can have both abstract and concrete methods; interfaces (prior to Java 8) only had abstract methods but now support default and static methods
Explain method overloading vs. overriding.
Overloading allows methods with the same name but different parameters. Overriding changes the implementation of a method in a subclass
What is the purpose of the transient keyword?
Indicates that a field should not be serialized
What is a marker interface?
An interface with no methods (e.g., Serializable), used to signal metadata to the JVM or frameworks
What is the difference between HashSet and TreeSet?
HashSet is unordered and faster for most operations (O(1)). TreeSet maintains a sorted order with O(log n) complexity
What is the difference between shallow copy and deep copy?
Shallow copy duplicates only the references to objects. Deep copy duplicates the objects themselves, creating independent clones
What is the difference between throw and throws?
throw is used to explicitly throw an exception. throws declares exceptions a method might throw
What is the difference between static and instance methods?
Static methods belong to the class and do not require an instance. Instance methods belong to an object and require an instance to be called
What is immutability, and how is it achieved in Java?
Immutability means an object cannot be changed after creation. It is achieved by declaring fields as final and not providing setters
What is the difference between deepToString() and toString() in Arrays?
toString() returns a representation of the array object, while deepToString() gives a detailed representation of nested arrays
What is the difference between Path and File classes in Java?
File represents a file or directory in the filesystem. Path is part of NIO.2 and provides more flexible file and directory path handling
What is a ClassLoader, and how does it work?
A ClassLoader loads classes into memory during runtime. It works in a hierarchical delegation model (parent-first)
What is the purpose of the assert keyword?
Used for debugging to verify assumptions in code; throws an AssertionError if the condition is false
What is the difference between InputStream and Reader in Java?
InputStream reads raw bytes, while Reader reads characters using a specific encoding
What is the difference between try-with-resources and a regular try block?
try-with-resources automatically closes resources (e.g., files) that implement AutoCloseable, reducing boilerplate code
Explain the difference between fork() and join() in Java.
fork() schedules a task for execution, and join() waits for its completion. Used in the ForkJoinPool framework
What is a Callable, and how is it different from Runnable?
Callable can return a value and throw checked exceptions, while Runnable cannot return a value and does not throw checked exceptions
What are weak references in Java?
Weak references do not prevent garbage collection of an object, allowing the JVM to reclaim the memory if needed
What is the purpose of the Default method in Java 8?
It allows interfaces to have method implementations to ensure backward compatibility without breaking existing code
Explain the Java memory model (Heap and Stack).
The heap stores objects and class-level variables. The stack holds method-level variables and execution context. Stack is faster and thread-safe; heap is shared across threads.
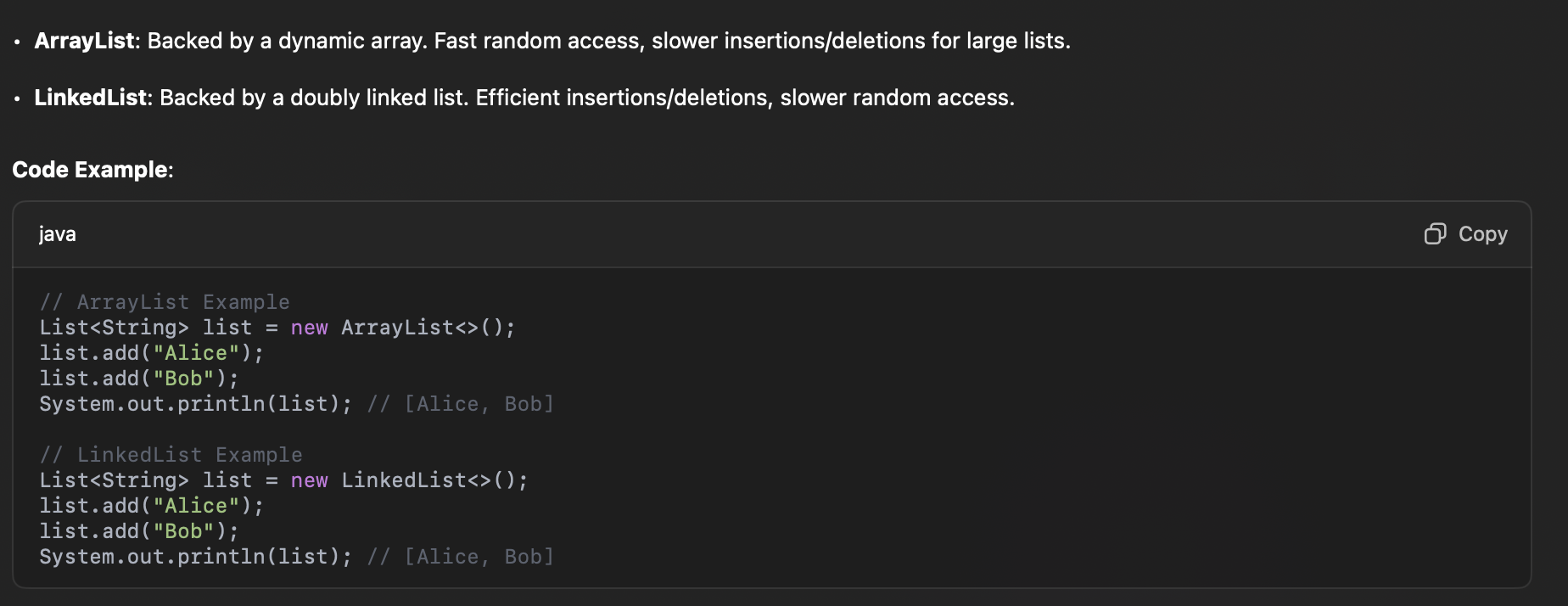
What are the main implementations of List in the Java Collections Framework?
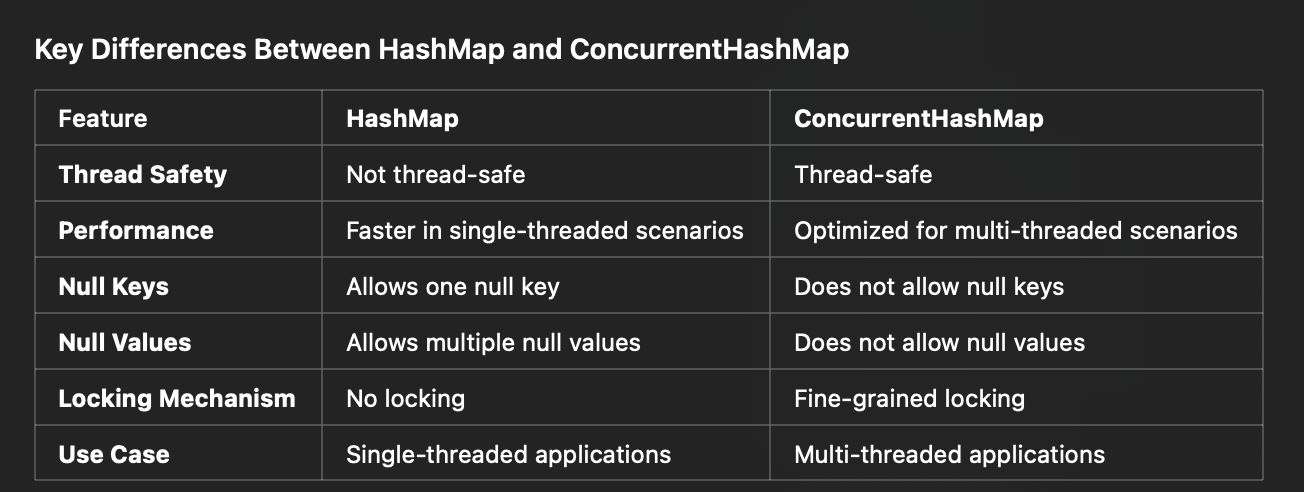
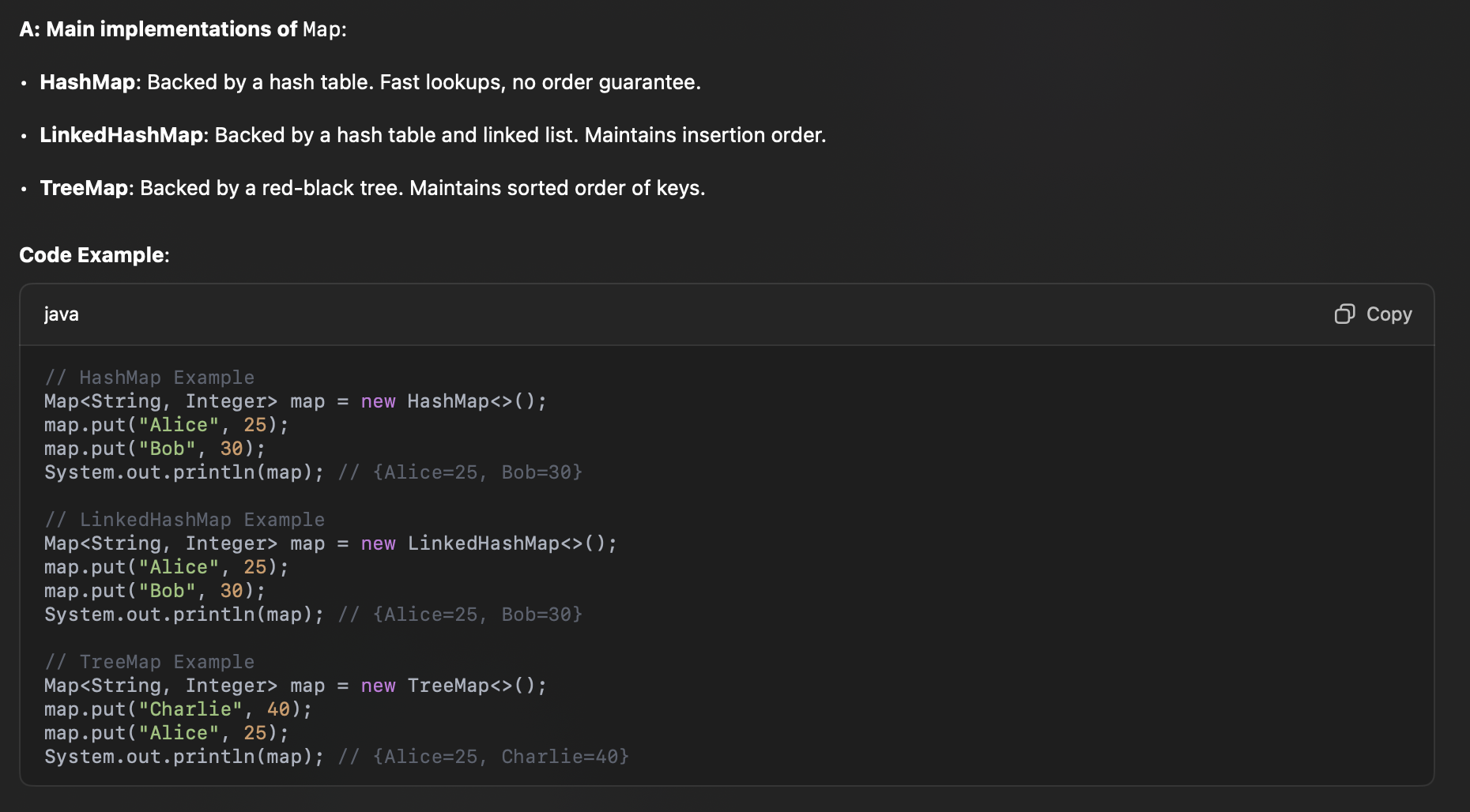
What are the main implementations of Map in the Java Collections Framework?
Key Differences Between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap