physics autumn
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
average velocity
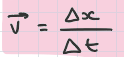
average acceleration
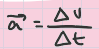
velocity w/ constant acceleration
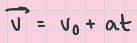
displacement curve equation (translation)
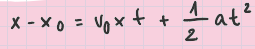
power rule
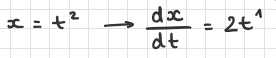
opposite of power rule
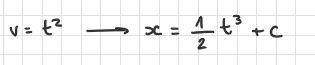
newton’s 2nd law
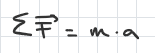
equation for kinetic friction
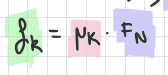
max of static friction
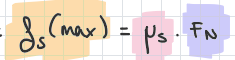
acceleration in a uniform circular motion
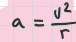
kepler’s first law
Dans le référentiel héliocentrique, les planètes du système solaire décrivent des trajectoires elliptiques, dont le Soleil occupe l’un des foyers.
kepler’s second law
Pendant des durées égales, le segment reliant le Soleil à une planète balaie des aires égales.
A1=A2 over ∆t
kepler’s third law
Le rapport du carré de la période de révolution par le cube du demi-grand axe est constant.
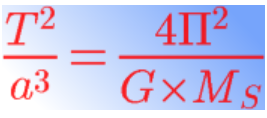
newtonian gravity
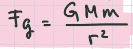
acceleration with newtonian gravity (free fall)

equations for work
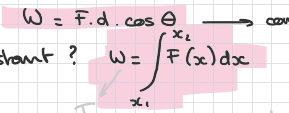
kinetic energy (translation)

potential energy (gravitational for translation)

potential energy (spring for translation)
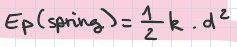
force exercised by a spring
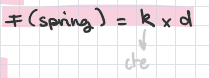
non conservative system
can lose energy (heat/noise)
conservative system
doesn’t lose energy through work
equation for average power

impulse
J = change in momentum
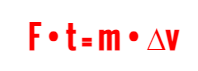
momentum (and how it changes during collision)

elastic collision
all Ec of the object colliding w/ the other object is transfered to the other object
perfectly inelastic collision
Ec is not conserved, the objects move together
center of mass
average position of all the mass in the system

angular velocity
ω
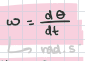
tangential velocity

frequency
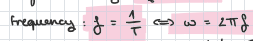
angular acceleration

radial acceleration

tangential acceleration
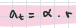
displacement curve equation (rotation)
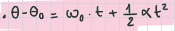
angular velocity with angular acceleration

torque
τ

net torque
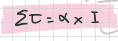
inertia
object’s tendency to keep doing what it’s doing
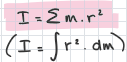
work of torque
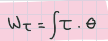
rotational kinetic energy

angular momentum

equilibrium
