Day 6 Endocrine systems
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Endocrine systems
carry info to and from control centers
2 main endocrine systems in animals
neural signals (action potentials)
hormones (blood-borne messengers)
Nervous messages
faster
more specifically targeted
shorter duration
Hormonal messages
slower
more broadly targeted
longer lasting
How are chemical signals classified
distance of travel and their source
How are neurotransmitters classified
by distance of travel
How are hormones classified
by their source
What most hormones activate
membrane bound receptors
What cells hormones reach
reach almost every cell, but not all cells respond
What type of hormone activates membrane bound receptors
hydrophilic
Which type of hormone activates intra-cellular receptors
lipophilic
Lipophilic hormones
pass through the membrane and activate intracellular receptors
change DNA transcription rates
receptors ___ or ____ biochemical pathways
activate or deactivate
Most vertebrate endocrine glands
hypothalamus/posterior pituitary
anterior pituitary
thyroid gland
parathyroid gland
adrenal gland
pancreas
gonads
hormones and other tissue
many other organs secrete hormones in addition to their primary functions
Examples of other organs secreting hormones along with their primary function
GI tract secretes hormones that regulate GI function
Fat cells release hormones that affect energy homeostasis
Heart releases a hormone that affects blood pressure
Kidney and Liver release hormones of various functions
endocrine glands
secrete hormones into the blood
What glands aren’t endocrine
exocrine glands
Exocrine glands
secrete/release a liquid/fluid
Examples of exocrine glands
salivary glands
sweat glands
mammary glands
Is both endocrine and exocrine
pancreas
Anterior pituitary gland
produces hormones that control many systems, including the release of other hormones
Produces hormones that control many systems, including the release of other hormones
anterior pituitary gland
controls the anterior pituitary gland
hormones released by the hypothalamus (neurohormones)
What the hypothalamic - anterior pituitary system controls
gonadal and reproductive function
aspects of metabolism, energy use and growth
Extension of the hypothalamus
posterior pituitary gland
Hormones released by the posterior pituitary
ADH
Oxytocin
ADH
controls water reabsorption in collecting ducts
Oxytocin
promotes contractions during labor and milk “letdown”
Releases hormones for response to danger
anterior pituitary gland
Danger or stress requires the need for
acute responses to support immediate, intense activity (danger)
longer term, sustained increases in activity and alertness (stress)
Acute responses to support immediate, intense activity (danger)
“fight-or-flight” response
What the “fight-or-flight” response is driven by
by the hormone epinephrine (adrenaline)
Longer term, sustained increases in activity and alertness (stress)
also, known as stress response
What the stress response is driven by
by the hormone cortisol
Fight-or-flight response pathway

Stress response pathway

What thyroid hormones help control
metabolic rate
CNS development and activity
protein synthesis
growth
What thyroid hormones trigger in amphibians
metamorphosis
Experiment one to test if thyroid controls metamorphosis
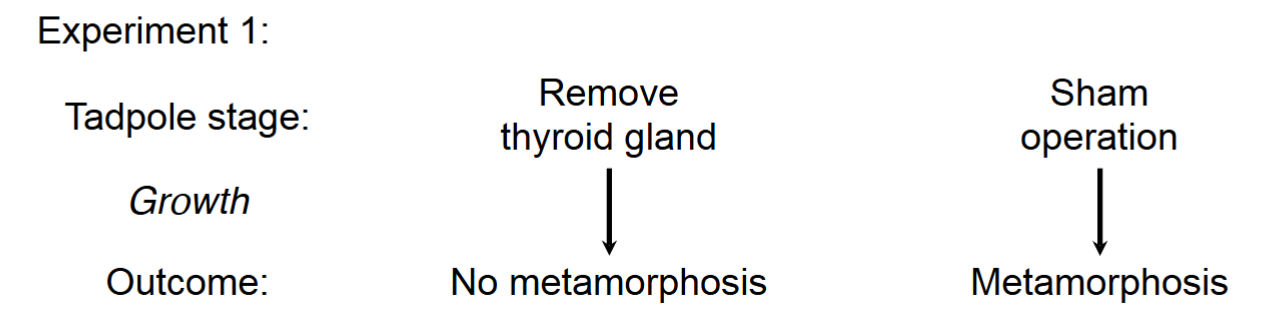
Experiment two to test if the thyroid controls metamorphosis
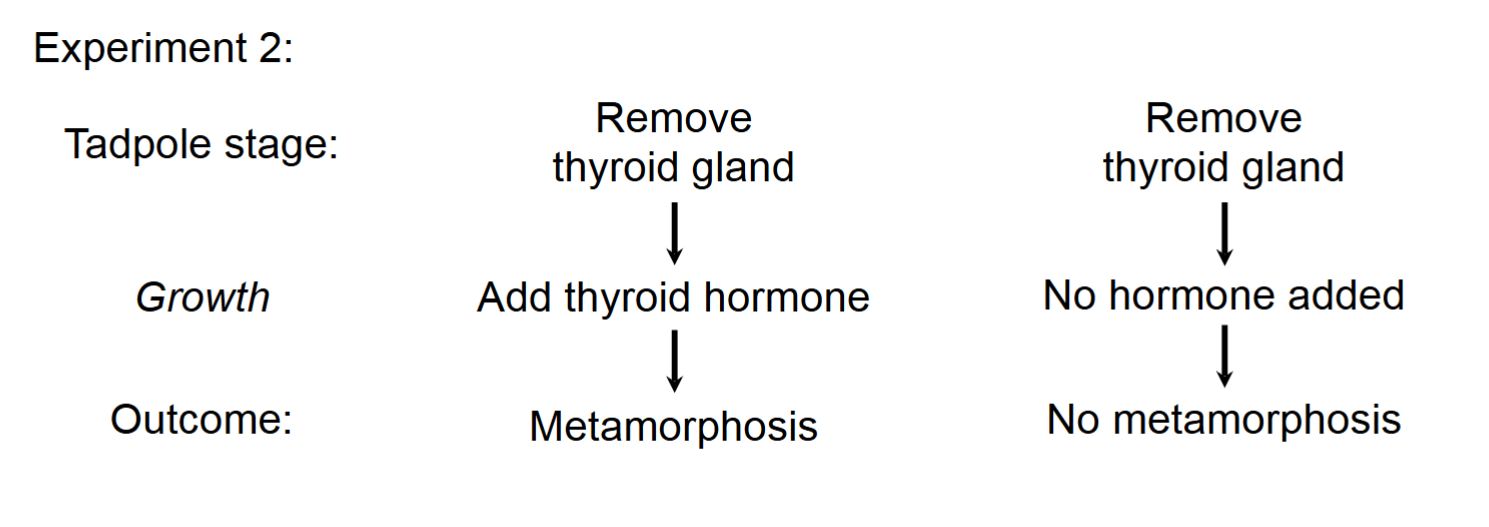
Process/steps of the thyroid in mammals
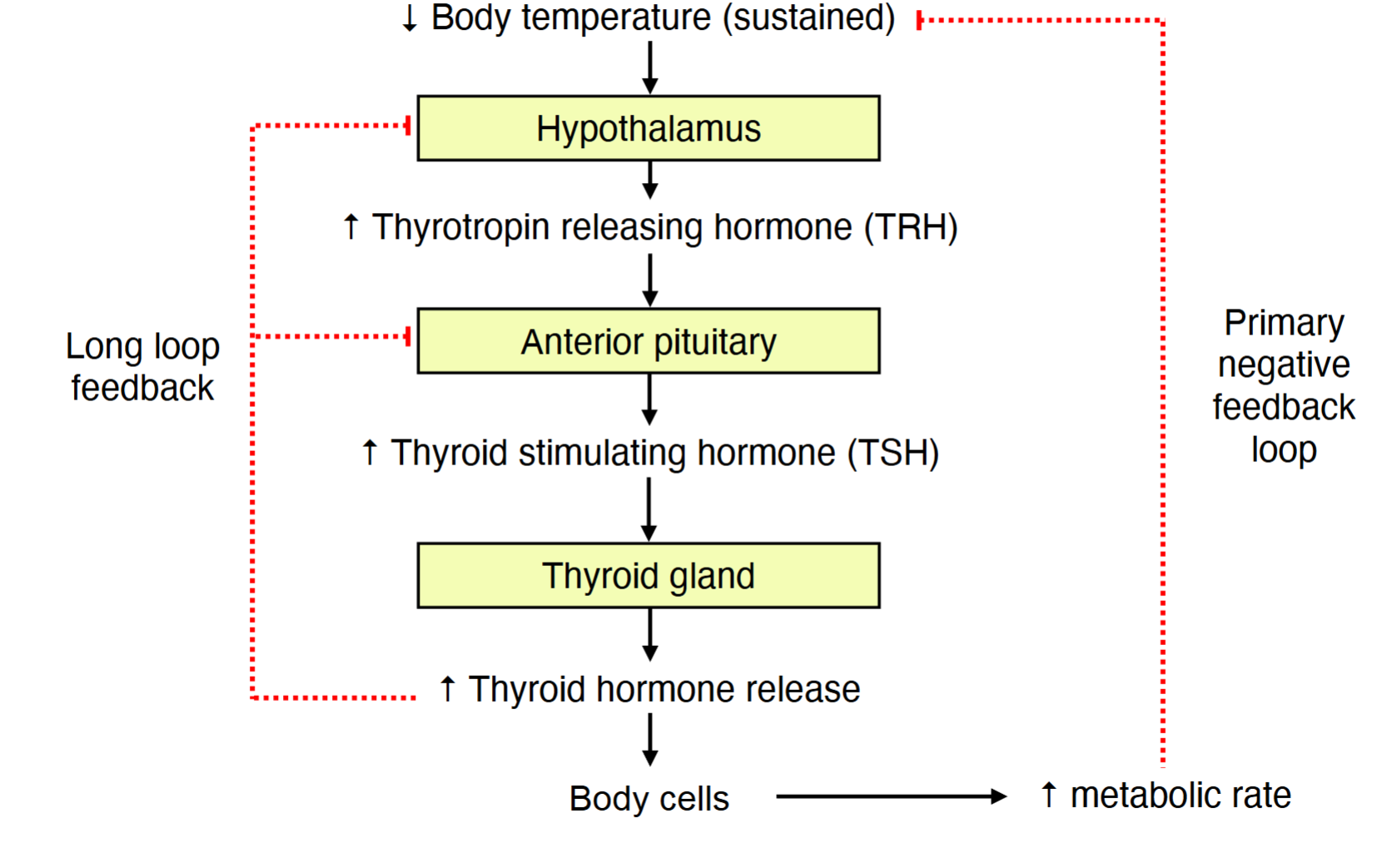
If thyroid hormones are too high
it inhibits TRH and RSH
If thyroid hormones are too low
increases TRH and TSH secretion
How are hormone levels determined
by classic negative feedback loops
How hormone levels are determined
hormones control effectors that influence a variable; the value of that variable helps determine the amount of hormone released
Long-loop feedback
levels of “downstream” hormones have negative effects on levels of “upstream” controlling hormones
Another name for long-loop feedback
feedback inhibition
How can hormone pathways fail
hypersecretion
hyposecretion
hyporesponsive
Hypersecretion
too much hormone secreted
Example of hypersecretion and symptoms
hyperthyroidism
symptoms are overheating, weight loss, and restleness
Hyposecretion
too little hormone released
Example of hyposecretion
Type 1 diabetes - lack of insulin causes failure to metabolize and store glucose from meals
Hyporesponsive
too few hormone receptors (receptors don’t respond well to hormones)
Example of hyporesponsive
Type 2 diabetes (early stage) - lack of insulin receptors leads to milder type 1 effects
In multi-hormone pathways, impact of problems with upstream hormones
problems with upstream hormones will cause problems with downstream hormones
Leptin helps control
the body’s energy stores
What produces leptin
fat cells - more fat stores leads to higher leptin levels
What leptin influences/impacts
influences appetite and metabolic rate
Leptin in vertebrates helps maintain
maintain normal fat reserves
Pathay of leptin

Leptin levels in overweight people
overweight people show high levels of leptin
Overweight people are ____
are hyporesponsive
Growth and metamorphosis in insects involve what hormones
Juvenile hormone (JH)
Ecdysone (from “ecdysis” or molting)
High JH + ecdysone surge =
larval growth (via molting)
Low JH + ecdysone surge =
pupation and metamorphosis
Larval stage
an immature stage that looks very different from the adult
for butterflies the larval stage is the caterpillar
for frogs the larval stage is the tadpole
Pupation
process in which a larva transforms into a pupa, the stage between the larva and the adult
example is when a caterpillar is in its cocoon