Chapter: 8 Photosynthesis
Transfer of Energy
flows in an ecosystem (sunlight - leaves heat)
mesophyll
interior tissues of the leaf
chloroplasts found
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Transfer of Energy
flows in an ecosystem (sunlight - leaves heat)
mesophyll
interior tissues of the leaf
chloroplasts found
stomata
Co2 enters and O2 exits through these microscopic pores
stroma
chloroplasts has an envelope of two membranes surrounding a dense fluid called…
thylakoids
connected sacs in the chloroplast that compose a third membrane system
grana
thylakoids are stacked in collumns
chlorophyll
pigment that gives leaves their green color
in the thylakoid membranes
Photosynthesis Chemical Formula
6 cycles of photosynthesis to build glucose

Cellular Respiration
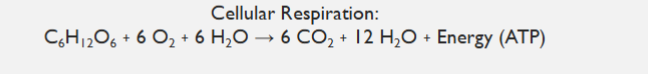
photosynthesis splits water
chloroplasts splits H2O → hydrogen and oxygen → incorporates hydrogen electrons into sugar molecules → oxygen byproduct
Light is a form of energy
can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed
pigments can absorb light
unabsorbed light wavelengths → reflected back → what we see
chlorophyll a
the key light capturing pigment
chlorophyll b
an accessory pigment
carotenoids
a separate group of accessory pigments
photosystem II (PS II)
functions first
reaction-center of chlorophyll a of PS II is called P680 (best at absorbed at a wavelength of 680 nm)
photosystem I (PS I)
best at absorbing wavelength of 700 nm
reaction - center = P700
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (1)
photon hits a pigment in a light-harvesting complex of PS II, and its energy is passed among pigment molecules until it excites P680
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (2)
An exited electron from P680 is transferred to the primary electron acceptor
P680+
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (3)
H20 is split by enzymes, and the electrons are transferred from the hydrogen atoms to P680+, thus reducing it to P680
H+ are released into the thylakoid space
O2 is released as a by product
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (4)
Each electrons “falls“ down an electron transport chain from the primary electron acceptors of PS II to PSI. energy released by the fall drives the creation of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (5)
Potential energy stored in the proton gradient drives production of ATP by chemiosmosis
photophosphorylation
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (6)
In PS I (like PS II), transferred light energy
excites P700, which loses an electron to the
primary electron acceptor
• P700+ (P700 that is missing an electron) accepts an
electron passed down from PS II via the electron
transport chain
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (7)
Each electron “falls” down an electron
transport chain from the primary electron
acceptor of PS I to the protein ferredoxin (Fd)
Steps in Linear Electron Flow (8)
NADP+ reductase catalyzes the transfer of
electrons to NADP+, reducing it to NADPH
• The electrons of NADPH are available for the
reactions of the Calvin cycle
• This process also removes an H+ from the stroma Campbell Biology Figure 10.14
mitochondria
proton movements
matrix > intermembrane space > ATP synthase > matrix
chloroplast
proton movement
stroma > thylakoid space > ATP synthase > stroma
The Calvin Cycle uses…
ATP and NADPH → to reduce Co2 to sugar > G3P
Calvin Cycle (3 Phases)
Carbon Fixation - Carboxylation
Reduction
Regeneration of CO2 acceptor
Carbon Fixation (Carboxylation)
3 carbon dioxide molecules (one at a time)
5C sugar (RuBP) accepts Co2 → converts to an unstable 6C sugar
instability causes a split into 2, 3C molecules
Reduction
Each 3C molecule is phosphorylated to 1 - 3 BPG
NADPH reduces 1 - 3 BPG to G3P
Regeneration
3 Co2 enter per cycle → 6C molecule upon entering the cycle → splits into 2 3C molecules
1 G3P leave the cycle to assemble into glucose or other organic molecules
5 G3Ps used to regenerate RuBP