Introduction to Java Technology and Programming Concepts
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
GREEN
The research project's codename funded/supported by Sun Microsystem in 1991.
C++
The programming language used to create Java.
Oak
The first name of Java.
James Gosling
Creator of Oak/Java.
Java
The name after the name of oak, introduced in May 1995, called after the coffee they drank.
Java Applets
Programs that run spontaneously by a Java compatible browser and can be downloaded without interaction with the user.
Life cycle of Applets
1. Initialization - preparation of information inside applets. 2. Start - Beginning/Starting point of applets. 3. Run - process. 4. Stop / Destroy.
Compiler
A program that translates Java Program to CLASS FILES - bytecodes.
Bytecodes
Compiled format for Java Programs executed by the JVM.
Portability
The ability to run on different operating systems.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
A bridge between the apps to OS that allows Java programs to run from different OS and hardware platforms.
Object Oriented
A feature of Java that focuses on objects rather than function or logic.
Dynamic
A feature of Java where decision making happens.
Multi Threaded
A feature of Java that allows programs to run concurrently/simultaneously with better performance.
Architecture Neutral
A feature of Java that allows it to run on any platform.
Five Phases of Java Programs
1. Creating and Editing - where programmers type the needed rectifications and save the program as .java file extension. 2. Compile - where you compile a program to find errors. 3. Load - placing the program in memory (RAM) before it can implement a process. 4. Verify - ensures the java programs entering over the network do not harm the user's files or system. 5. Execute - bytecodes stated in the program will be executed by the JVM.
Java Application
A computer program that performs when you utilize the Java Command to open the JVM.
Comment Lines
Indicated by //, where the user can insert documentation used to improve readability.
Class Declaration
A class declaration for class Welcome. Java programs must have at least one class declaration that is defined.
Body of a Class Declaration
A { indicates the beginning of the body of a class declaration.
Java Application Starting Point
This shows the starting point of a Java application. Items enclosed in parentheses indicate that it is a program building block called method.
Body of the Method
This left brace starts the body of the method.
Action Directive
This directs the computer to do an action.
End of Class Declaration
The right brace ends each class declaration.
End of Method Declaration's Body
This right brace must end the method declaration's body.
Primitive
Built in fundamental types installed already in Java Program.
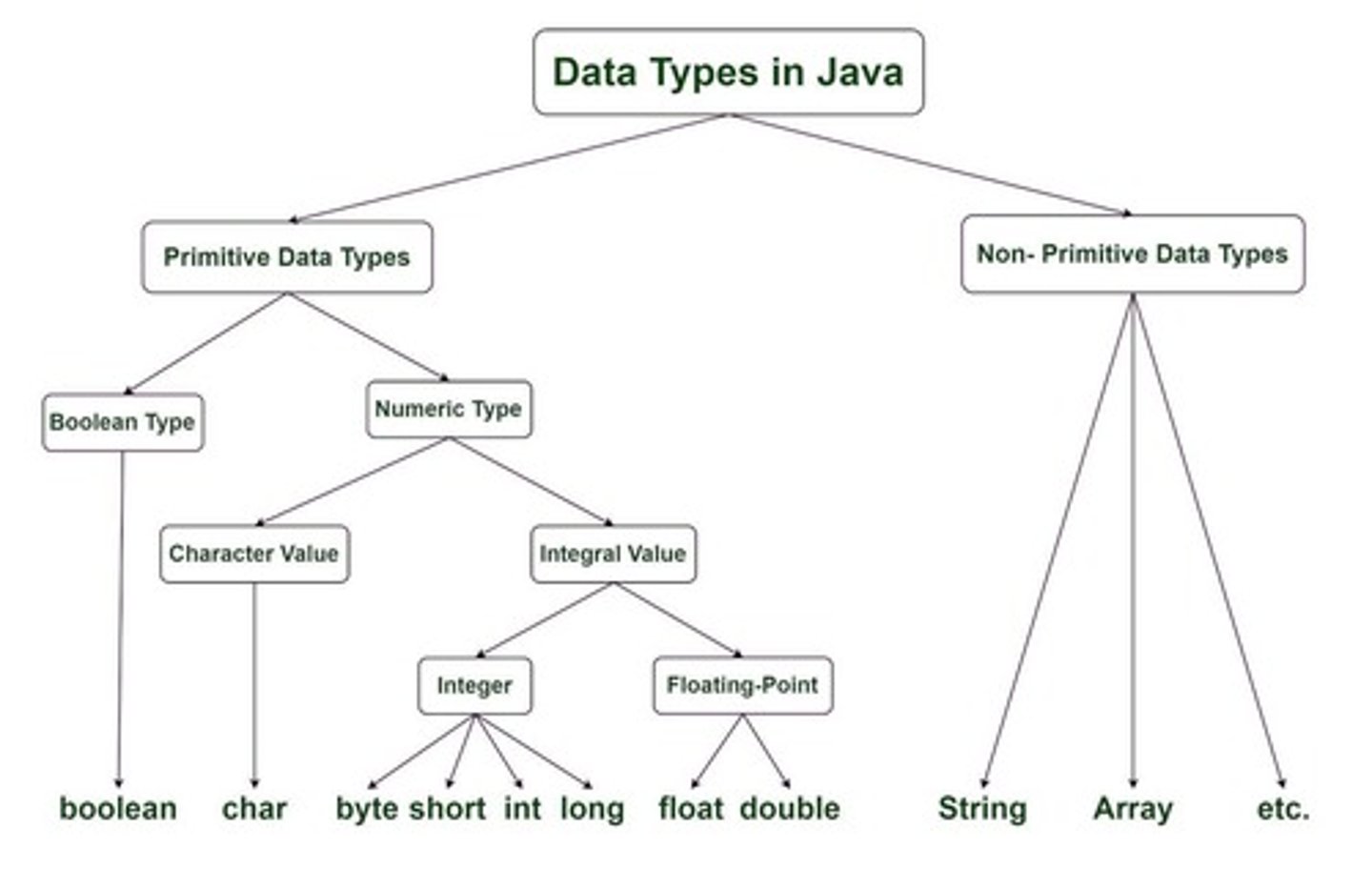
Non Primitive
It is what the programmers created and not built in.
Data Type
Sometimes called Type.
Variable
Memory spaces that utilize value.
Value
Sometimes called Identifiers or Literals; representation of value.
Boolean
If answerable by True or False.
Numeric
Character - used for single letters, numbers and characters and only use 'SINGLE QUOTES'.
Integral
Integers - whole numbers.
Byte
-128 to 127 (8 bit).
Short
-32,768 to 32,767 (16 bit).
Int
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (32 bit).
Long
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (64 bit).
Floating Point
Includes Float - it is up to 1-7 decimal places and Double - it is up to 7 to 15 decimal places.
Packages
Are the best tool for classifying different classes from each other.
User Defined Packages
Made by the programmers.
In Built Packages
Built in packages.
Java.util.scanner
Where we import the scanner class.
Tokens
Series of characters that ends with whitespace (Blank, Tags, Etc.).
Scanner Methods
Methods include in.nextBoolean(), in.nextByte(), in.nextDouble(), in.nextFloat(), in.nextInt(), in.nextLine(), in.next(), in.nextLong(), in.nextShort().
Class Construct
To create an object inside your program.