Chapter 5 What-if Analysis for Linear programming单词卡 | Quizlet
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Which of the following represents the marginal gain in the objective value that would occur if one more unit of a resource were added?
a. Reduced cost
b. Shadow price
c. Allowable increase
d. Allowable decrease
e. Constraint
b. Shadow price
The process of determining the effect of changing objective function coefficients, right-hand side values of constraints, and decision variable values on a linear program is known as
a. change management.
b. process evaluation.
c. what-if analysis.
d. project management.
e. optimization.
c. what-if analysis.
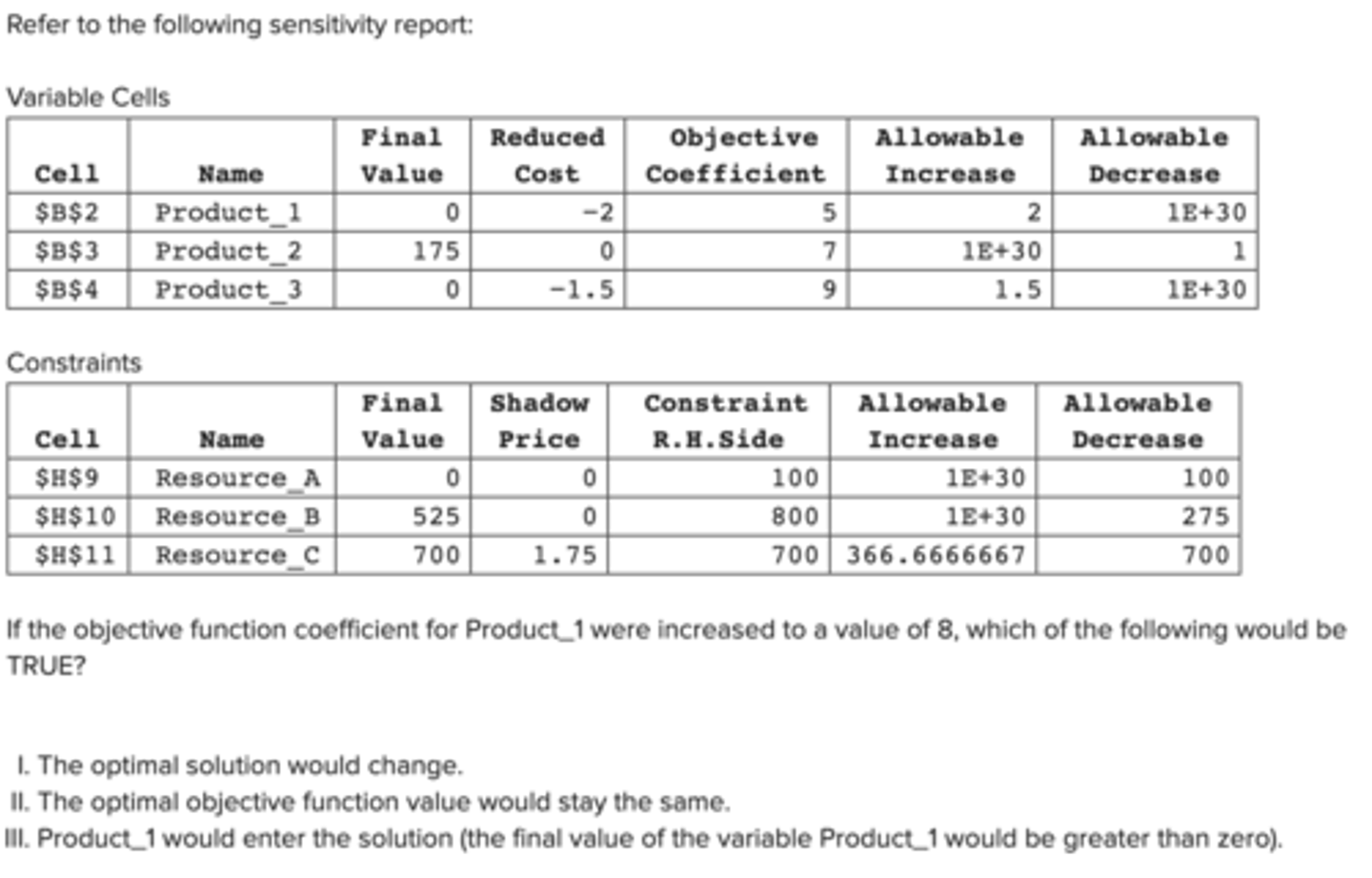
If the objective function coefficient for Product_1 were increased to a value of 8, which of the following would be TRUE?
Only I and III are true
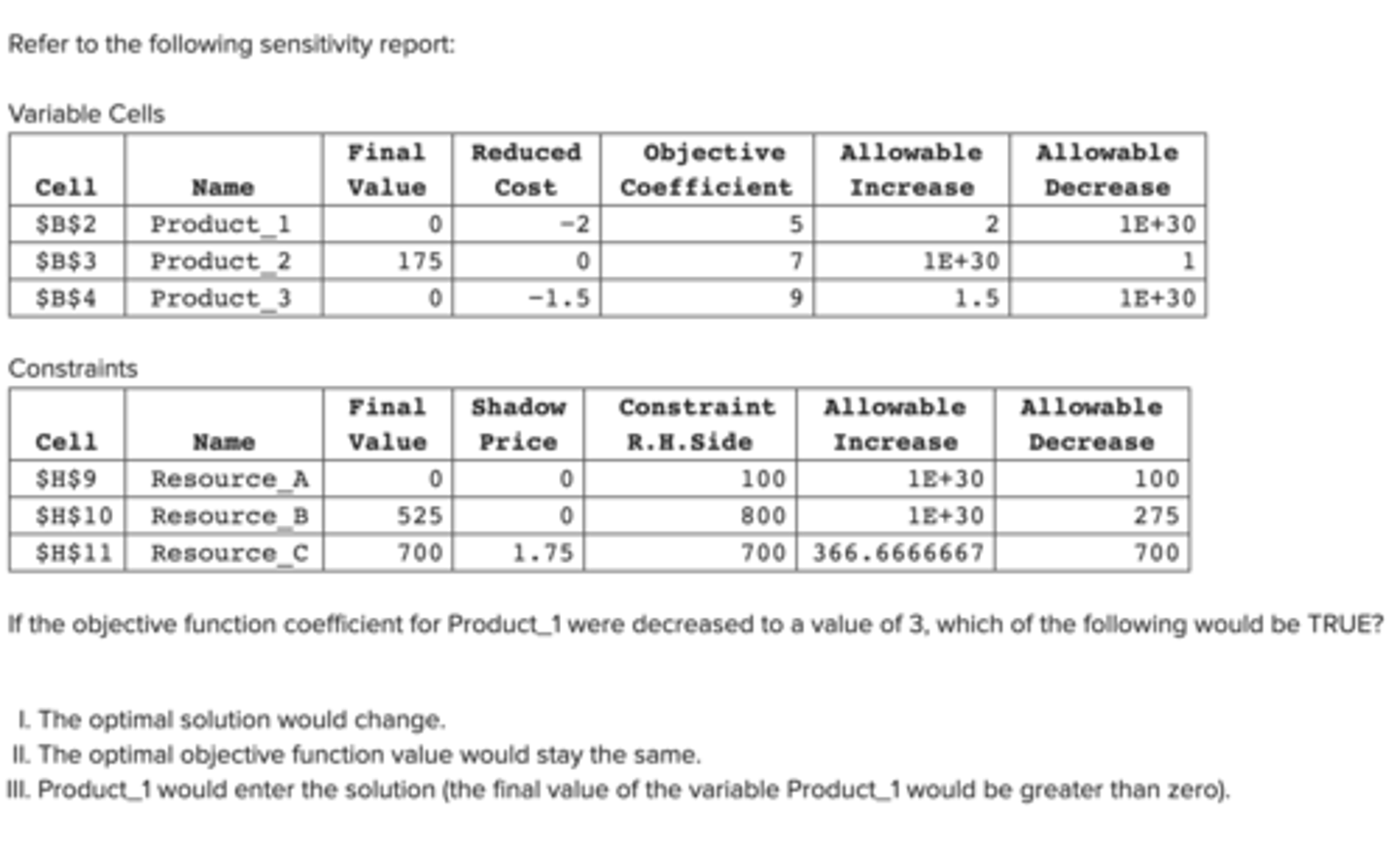
If the objective function coefficient for Product_1 were decreased to a value of 3, which of the following would be TRUE?
II only
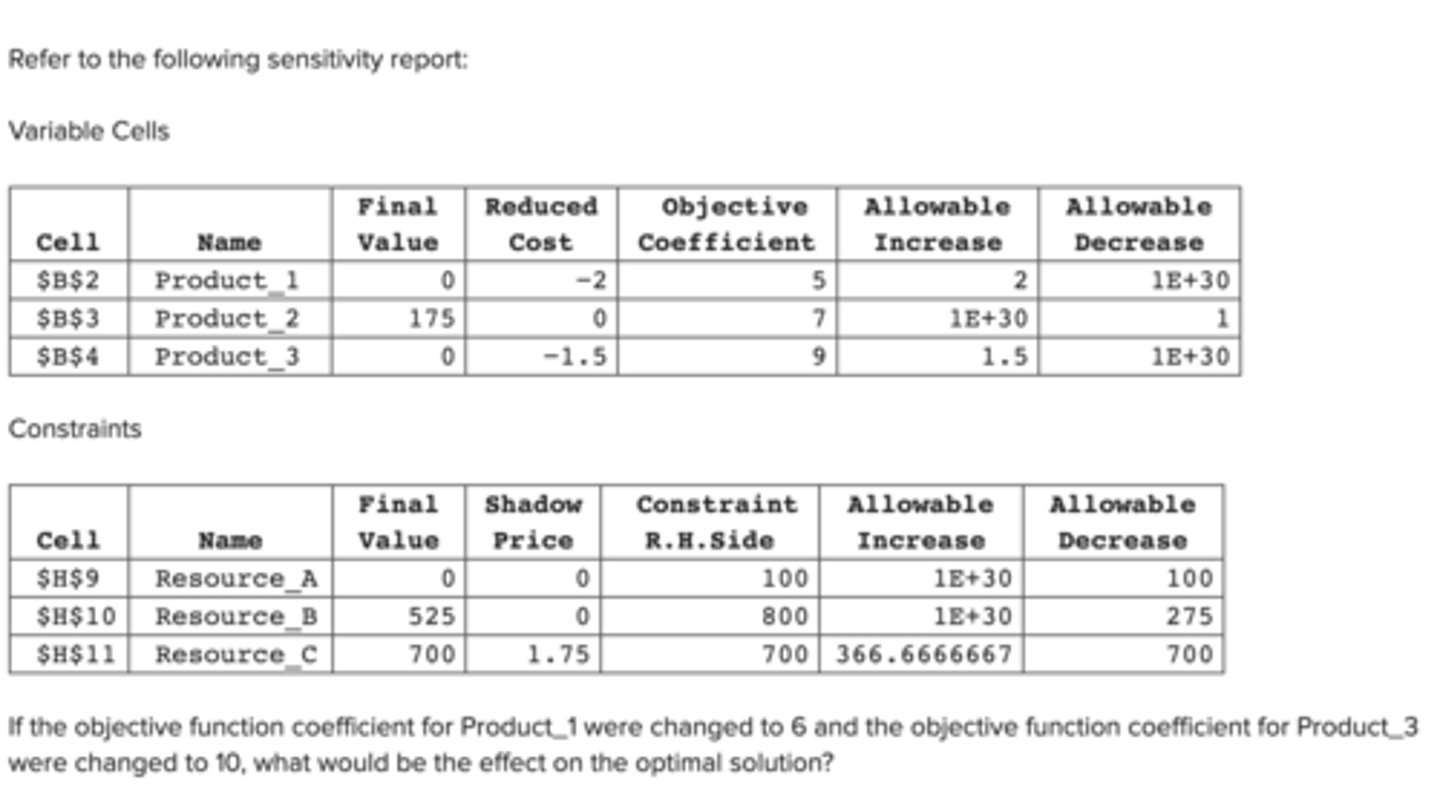
If the objective function coefficient for Product_1 were changed to 6 and the objective function coefficient for Product_3 were changed to 10, what would be the effect on the optimal solution?
a. The optimal solution remains the same.
b. The optimal solution may or may not remain the same.
c. The optimal solution will change.
d. The shadow prices are valid.
e. None of the answer choices is correct.
b. The optimal solution may or may not remain the same. (use 100% rule)
Shadow price analysis is widely used to help management find the best trade-off between costs and benefits for a problem.
t/f
True
The term "allowable range for an objective function coefficient" refers to a constraint's right-hand side quantity.
t/f
False
A shadow price indicates how much the optimal value of the objective function will increase per unit increase in the right-hand side of a constraint.
t/f
True
Changing the objective function coefficients may or may not change the optimal solution, but it will always change the value of the objective function.
t/f
False
Every change in the value of an objective function coefficient will lead to a changed optimal solution.
t/f
False
If the change to a right-hand side is within the allowable range, the value of the shadow price remains valid.
t/f
True
allowable range for an objective function coefficient
the range of values for a particular coefficient in the objective function over which the optimal solution for the original model remains optimal
Allowable range for the right-hand side
The range of values for the right-hand side of a functional constraint over which this constraint's shadow price remains valid.
Sensitivity analysis
the part of what-if analysis that focuses on individual parameters of the model. it involves checking how sensitive the optimal solution is to the value of each parameter
Shadow price
the rate at which the optimal value fo the objective function can be increased by increasing the right hand side of the constraint by a small amount