Electromagnetic Spectrum, Atomic Structure, and Quantum Principles
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What dual nature does light exhibit?
Light acts as both a particle and a wave.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength.
What is the speed of light in meters per second?
The speed of light is approximately 2.998 x 10^8 m/s.
What is Planck's constant?
Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^-34 J·s.
What is the formula for calculating energy of a photon?
Energy (E) = h × frequency (ν).
What does the symbol λ represent?
λ (lambda) represents wavelength.
What are the energy levels in an atom according to Niels Bohr?
Energy levels are defined as shells where electrons reside.
What principle states that electrons fill orbitals from lowest to highest energy?
Aufbau's principle.
What is Hund's rule?
Hund's rule states that electrons will occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up.
What does the Pauli exclusion principle state?
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
What is the formula for calculating frequency?
Frequency (ν) = speed of light (C) / wavelength (λ).
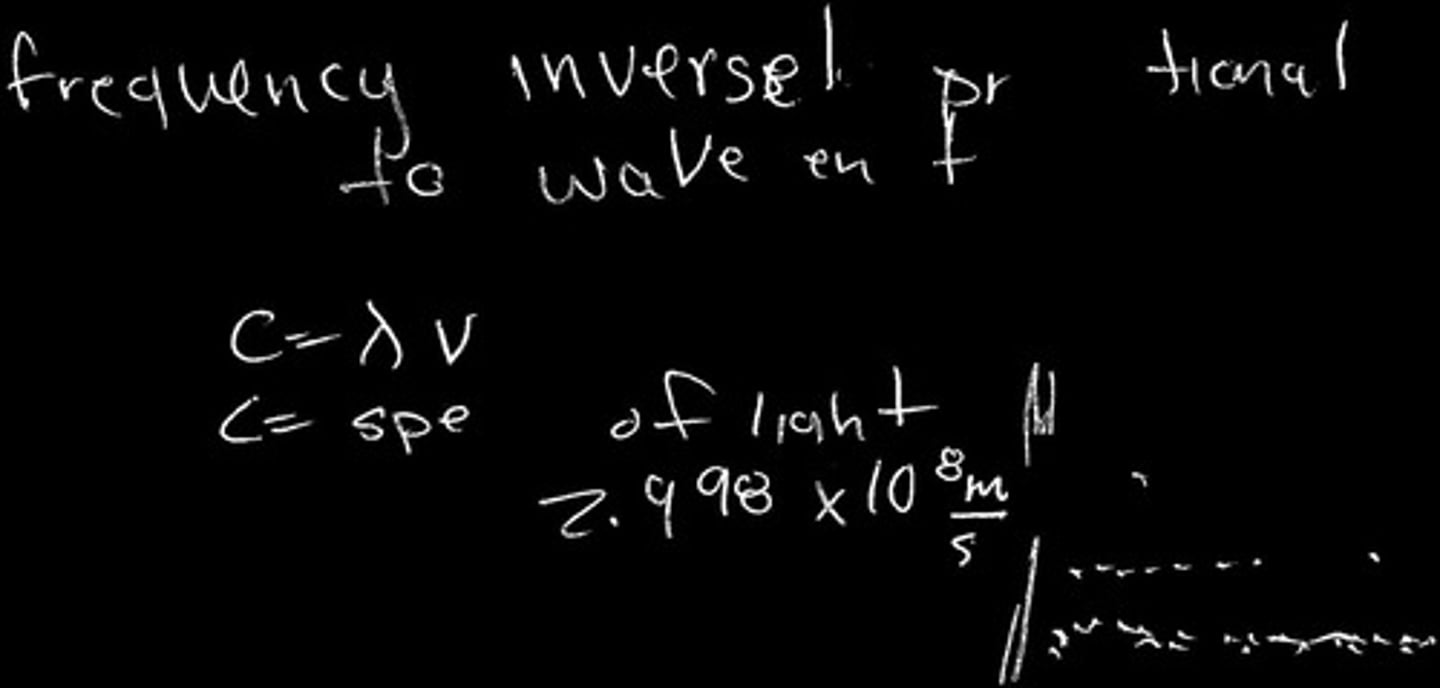
What is the significance of valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons that determine an atom's chemical properties.
What is ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of cations and anions.
What is the octet rule?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons.
What is electron affinity?
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom.
What is a Lewis structure?
A Lewis structure is a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons in a molecule.
What are polar covalent bonds?
Polar covalent bonds occur when two atoms share electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativity.
What is lattice energy?
Lattice energy is the energy released when ions in a gas phase form an ionic solid.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
Polar covalent bonds have unequal sharing of electrons, while nonpolar covalent bonds have equal sharing.
What is the role of core electrons?
Core electrons are the inner electrons that are not involved in bonding and do not participate in chemical reactions.
What is a resonance structure?
A resonance structure is one of two or more valid Lewis structures for a molecule that cannot be represented accurately by a single structure.
What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, UV light, and radio waves.
What does the term 'excited state' refer to in atomic structure?
An excited state refers to an electron that has absorbed energy and moved to a higher energy level.
What is the ground state of an atom?
The ground state is the lowest energy state of an atom, where electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.