Introduction to Research Methods in Psychology: Key Concepts and Validity
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
What is the main focus of PSYC 2100 B?
The course focuses on research methods in psychology.
What are the two main goals of the course?
To become effective producers of knowledge and informed consumers of knowledge.
What methods are used to study self-knowledge?
Surveys/questionnaires, interviews, tasks/morality games, IQ tests, personality assessments, and conversations.
What is the purpose of Wooclap in the course?
To facilitate participation and test students' knowledge during lectures.
What is the textbook for the course?
Research Methods in Psychology, 5th edition by Beth Morling.
What are the office hours for the professor?
Mondays from 11am to 1pm in Loeb B549.
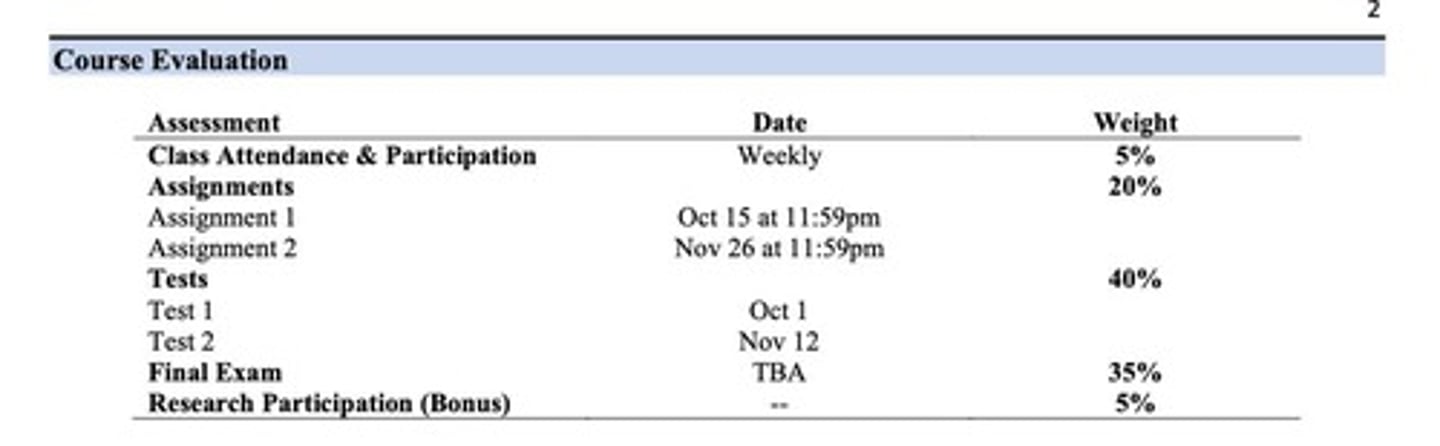
What is the grading breakdown for the course?
5% participation, 20% assignments, 35% tests, and 40% final exam.
What is anecdotal evidence?
Knowledge based on personal experience or stories rather than systematic research.
What is confirmation bias?
The tendency to seek out evidence that confirms existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
What does the availability heuristic refer to?
The bias that occurs when people overestimate the frequency of events that come to mind easily, often because they are vivid or negative.
What is present/present bias?
The failure to consider what is not present, focusing only on the current situation and ignoring other possibilities.
What is the bias blind spot?
The tendency to see others as biased while failing to recognize one's own biases.
What is empiricism in the context of science?
Empiricism is based on systematic, direct, unbiased observations used to draw conclusions about the world.
What is a theory in scientific research?
A set of statements that describe general principles about how variables relate to each other.
What makes a good scientific theory?
It must be testable and falsifiable.
What is pseudoscience?
A theory that is not refutable by any conceivable event, making it non-scientific.
What types of comparison groups are used in scientific research?
Treatment group, therapy group, treatment + therapy group, and control group.
What is the role of authority in knowledge acquisition?
People often trust information from authority figures, but it's important to evaluate the basis of that information.
What is the significance of control groups in research?
Control groups allow researchers to compare outcomes and observe the effects of treatments systematically.
What is the importance of critical evaluation in knowledge consumption?
It enables individuals to assess research designs and interpret findings effectively.
What is the purpose of developing research questions in psychology?
To explore and investigate specific aspects of human behavior and mental processes.
What are the pitfalls of relying solely on personal experience for knowledge?
Lack of comparison groups and potential confounding variables can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
What is the importance of systematic observation in scientific research?
It helps to minimize bias and allows for more reliable conclusions about the phenomena being studied.
What is irrefutability in the context of scientific theories?
Irrefutability is considered a vice of a theory, meaning it cannot be disproven, which undermines its scientific validity.
What is an example of an unfalsifiable theory?
Freud's iceberg theory of the unconscious and repressed memories.
What does 'parsimonious' mean in scientific explanation?
It refers to the simplest explanation that makes the fewest assumptions.
What is Occam's Razor?
A principle stating that if a simple theory explains something as well as a complicated theory, the simpler one should be chosen.
What are the characteristics of a good research question?
It should be relevant to theory, novel, testable, and not too broad.
What is a hypothesis?
A specific prediction about what needs to happen for a theory to be true, which is testable and unique to the theory.
Provide an example of a hypothesis related to narcissism.
Narcissists will compare themselves to people who do worse than them to maintain their self-esteem.
What does it mean that science is probabilistic?
Conclusions are based on probability theory or statistics, rather than absolute proof.
What is the null hypothesis (Hₒ)?
It states that there is no effect or difference, often represented as Hₒ: μ₁ = μ₂.
What is the alternative hypothesis (H₁)?
It states that there is an effect or difference, consistent with the research theory, often represented as H₁: μ₁ > μ₂.
When do we reject the null hypothesis?
When the p-value is less than .05, indicating the observed result is statistically significant.
What does a p-value represent?
The probability of obtaining the observed results or more extreme results if the null hypothesis is true.
What is effect size?
It measures the strength or magnitude of the effect, indicating how meaningful the results are.
What are the three types of scientific research?
Basic research, translational research, and applied research.
What is basic research?
It seeks to understand foundational questions or concepts, such as brain activity during meditation.
What is translational research?
It tests interventions in a laboratory setting before applying them in real-world contexts.
What is applied research?
It tests interventions or treatments in the specific context they are meant for, such as evaluating a school meditation program.
What are the norms of scientific research?
Universalism, communality, disinterestedness, and organized skepticism.
What does it mean for science to be replicable?
Studies must be reported in ways that allow others to replicate the work, ensuring reliability.
What is the significance of the threshold α = .05 in hypothesis testing?
It is the standard for determining statistical significance; p < .05 leads to rejecting the null hypothesis.
What does retaining the null hypothesis imply?
It implies that the p-value is greater than .05, indicating no statistically significant effect.
What is the role of claims in scientific research?
Claims reflect the researcher's assertions about effects or relationships, which may or may not align with reality.
How do researchers assess the truth in science?
Through systematic observations, tests of falsifiable theories, and probabilistic reasoning.
What is the relationship between sleep and test performance based on the study example?
The study suggests a positive relationship, with fewer hours of sleep correlating to worse test performance.
What is a Type 1 error in research?
A Type 1 error (false positive) occurs when a statistically significant result is found (p < .05) when there is no actual effect.
What does a p-value greater than .05 indicate?
It indicates a statistically insignificant result, leading to the retention of the null hypothesis.
What was the purpose of the Tuskegee Syphilis Study?
To understand the effects of untreated syphilis on men, conducted over 40 years without informed consent.
What ethical violations occurred in the Tuskegee Syphilis Study?
Participants were not treated with respect, were harmed, and were part of a targeted, disadvantaged social group.
What are the Belmont Principles in research ethics?
1. Respect for persons, 2. Beneficence, 3. Justice.
What does 'Respect for persons' entail?
It includes the right to informed consent, no coercion, and protection for vulnerable individuals.
What is the principle of Beneficence in research ethics?
To minimize risks and maximize benefits for research participants.
What does the principle of Justice refer to in research ethics?
Equitable distribution of research burdens and benefits, ensuring fairness.
Who sets the ethical guidelines for research in psychology?
The American Psychological Association (APA) and the Tri-Council Policy Statement (TCPS) for Canadian researchers.
What is informed consent?
A process ensuring participants understand the risks and benefits of a study, allowing voluntary participation.
What are the potential issues with obtaining informed consent?
Lack of transparency, undue influence, coercion, and special considerations for individuals with diminished autonomy.
What is passive deception in research?
Omitting information from participants without their knowledge.
What is active deception in research?
Deliberately providing false information to participants.
What is debriefing in research?
Providing full disclosure of the research purpose to participants after the study, especially if deception was used.
What is the concern for welfare principle?
Protecting participants from harm and ensuring their well-being, with risks not outweighing benefits.
What are the Three Rs of Animal Research?
1. Replacement, 2. Reduction, 3. Refinement.
What does 'Replacement' mean in the context of animal research?
Using alternatives to animals when possible, such as computer simulations.
What does 'Reduction' refer to in animal research?
Decreasing the number of animals used while still obtaining valid results.
What does 'Refinement' mean in animal research?
Modifying procedures to minimize pain, stress, or discomfort to animals.
What constitutes research misconduct?
Data fabrication, data falsification, and plagiarism.
What is the difference between data fabrication and data falsification?
Data fabrication involves making up data, while data falsification involves altering existing data to fit desired outcomes.
What types of claims can research make?
Frequency claims, association claims, and causal claims.
What are the types of validity to evaluate in research?
Construct validity, external validity, statistical validity, and internal validity.
What is a variable in research?
A factor that can change or vary; a constant does not change.
What is a manipulated variable?
A variable that the researcher changes or controls, such as the amount of water given to a plant.
What is a measured variable?
A variable that is not manipulated but is measured as it occurs.
What is an operational definition?
It specifies exactly how a conceptual variable is measured or manipulated.
Give an example of an operational definition for relationship satisfaction.
Self-report measures.
What are the three types of research claims?
Frequency claims, association claims, and causal claims.
What is the goal of a frequency claim?
To describe the rate or frequency of a variable.
What type of language is used in frequency claims?
Language such as many, most, or all.
What does an association claim predict?
The relationship between two variables.
What is a correlational study?
A study that measures the relationship between two variables.
What does a correlation coefficient (r) indicate?
The strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
What is the difference between positive and negative associations?
In a positive association, both variables increase together; in a negative association, one variable increases while the other decreases.
What is a causal claim?
It explains the relationship between variables, indicating that one variable causes a change in another.
What are the three criteria for making a causal claim?
Covariance, temporal precedence, and internal validity.
What is covariance in research?
It indicates that cause and effect co-occur.
What does temporal precedence refer to?
The cause must precede the effect in time.
What is internal validity?
It rules out confounding variables or alternative explanations for the findings.
What is random assignment in research?
It ensures every participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any condition.
What is the tradeoff between external and internal validity?
Focusing on internal validity in experimental studies may reduce external validity.
What is construct validity?
It assesses how well a conceptual variable is operationalized.
What does external validity refer to?
The generalizability of findings to other people, contexts, and methods.
What is statistical validity?
The accuracy and reasonableness of a study's statistical conclusions.
What is a Type I error?
A false positive, concluding there is an association when there is none.
What is a Type II error?
A false negative, concluding there is no association when there is one.
Why is a large sample size important in research?
It leads to smaller margins of error, more power to detect effects, and reduces the chance of Type II errors.
What is the difference between independent and dependent variables?
The independent variable is manipulated by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the outcome of interest.
What is the significance of confidence intervals in research?
They provide a range within which the true effect is likely to fall, indicating the precision of the estimate.
What does it mean if a confidence interval excludes zero?
It indicates a significant effect in the relationship being studied.
What are the three types of claims in research?
Frequency, Association, Causal
What does construct validity assess?
How well the variable is measured.