RD22: Memory Allocation III
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Garbage Collection, Memory-Related Issues in C
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is Garbage Collection?
Garbage Collection is a form of automatic memory management that is often employed by implicit dynamic memory allocators to reclaim heap-allocated memory.
Why is Garbage Collection useful?
Adds convenience for the programmer and leads to fewer memory issues.
What’s a key note about Garbage Collection?
Knowing when a piece of dynamically-allocated memory can be freed (cleaning up unnecessary memory and not what’s being used still).
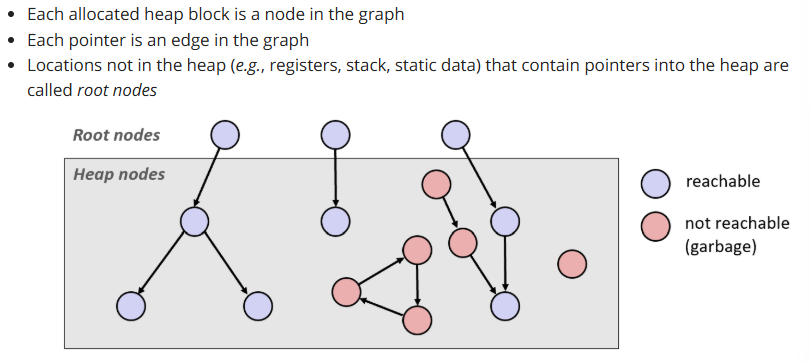
Example of memory as nodes:
Any heap node that is reachable from a root node is considered still in use by the process, while heap nodes that are not reachable from root nodes are considered no longer in use and eligible to be freed.
What assumptions let Garbage Collection work?
The memory allocator knows which data are pointers and which are not.
All pointers to heap nodes point to the start of the payload.
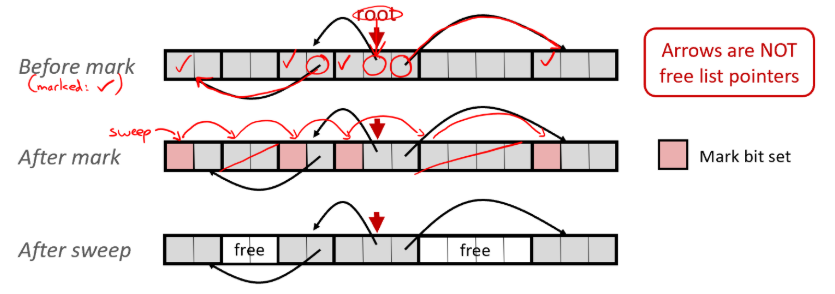
What is makr-and-sweep?
An implementation of garbage collection that requires the use of an extra status bit called the mark bit.
What happens when the garbage collector is invoked?
Recursively follows all of the root nodes into the heap and sets the mark bit for all reachable heap blocks.
Sweeps through the heap forms tart to finish and check mark bit for each block.
If the mark bit is set, then clear it and move on.
If the mark bit is not set, then free the block as it is unused.