polymers
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what is a polymer
a molecule formed from many repeating “monomer” units
what are the two types of polymers
addition and condensation
when drawing repeat units do you need n
yes you do
name the addition polymer formed using ethene
poly ethene
what is a plasticiser
A plasticiser is a substance added to a polymer to increase its flexibility by getting between the polymer chains.
It pushes the chains further apart, weakening the intermolecular forces (like van der Waals or dipole-dipole forces) between them.
This allows the chains to slide past each other more easily, making the polymer softer and more bendy
monomer and use of poly(chloroethene)
what is it commonly known by
why is it suitable for its use
PVC
Monomer: Chloroethene
Uses:
Unplasticised: Hard, brittle material used for drainpipes and window frames
Plasticised: Flexible material used for electrical cable insulation, flooring tiles, and clothing
monomer and use of Poly(ethene)
Monomer: Ethene
Uses:
Plastic bags
Bottles
Washing-up bowls
monomer and use of Poly(propene)
Monomer: Propene
Uses:
Crates
Ropes
Textiles
Moulded objects
state the two ways of making a polyester
with a dioic acid and a diol
hydroxy carboxylic acid
when drawing the repeating structure of a polyester what is lost from each monomer to form the polyester
when drawing the repeating structure you lose the OH from the carboxylic acid group and the H from the alcohol group.
what is the equation in terms of n for the number of waters formed from condensation reactions forming polyesters
what does n represent?
(2n-1) H2O
n is the number of monomers in the polymer
state the two ways of making a polyamide
dioic acid and diamine
amino acid
how are esters named
the prefix from the alcohol and suffix from carboxylic acid.
when naming methyl groups, count away from the ester functional group. this is the only instance where u can get 1-methyl…
when drawing the repeating structure of a polyamide what is lost from each monomer to form the polyamide
when drawing the repeating structure you lose the OH from the carboxylic acid group and the H from the amine group.
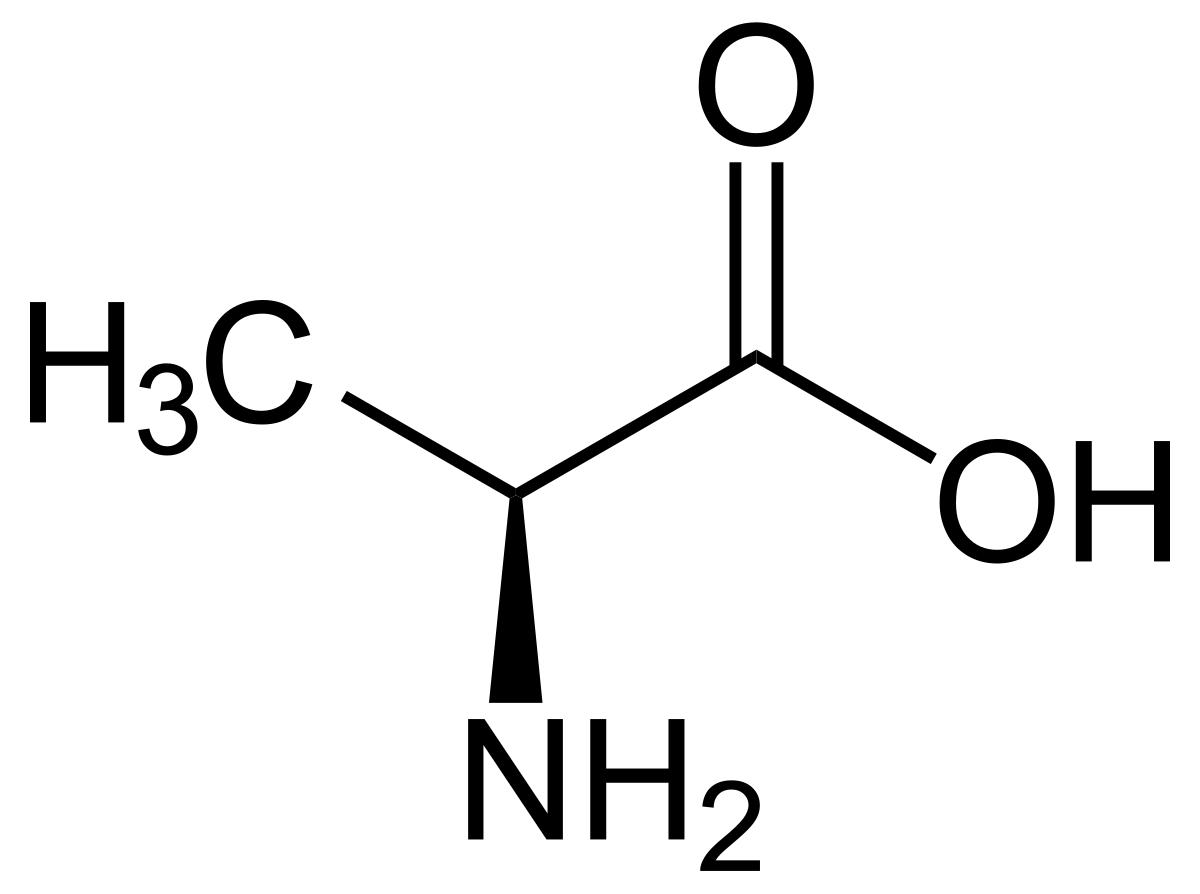
what is the IUPAC name for alanine
2-amino propanoic acid
what is the equation in terms of n for the number of waters formed from condensation reactions forming polyamides
(n-1) H2O
give the monomers properties and uses of Terylene
monomer 1- Benzene-1,4-dioic acid
monomer 2- ethane-1,2-diol
properties- strong, resistant to corrosion, lightweight, high melting and boiling point (PDD forces)
uses- used for water bottles
give the monomers properties and uses of Kevlar
monomer 1- Benzene-1,4-dioic acid
monomer 2- Benzene-1,4-diamine
properties- very strong (hydrogen bonding due to N-H), High melting and boiling points
uses- bullet proof vests
give the monomers properties and uses of Nylon 6-6
monomer 1- Hexane dioic acid
monomer 2- Hexane-1,6- diamine
properties- strong (hydrogen bonding), high melting and boiling points
uses- in stretchy materials such as tights and parachutes
how are nylons named
they are named with the prefix “nylon” and then the two numbers are from the length of the carbon chain of each monomer
side note- a nylon Is a straight chained polymer made of amines and something else. if it has a benzene It cannot be a nylon as it is not straight chained.
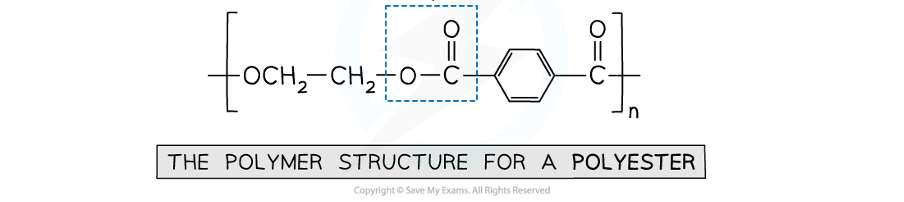
what is the type of link in this polymer
an ester link between an alcohol and carboxylic acid monomer
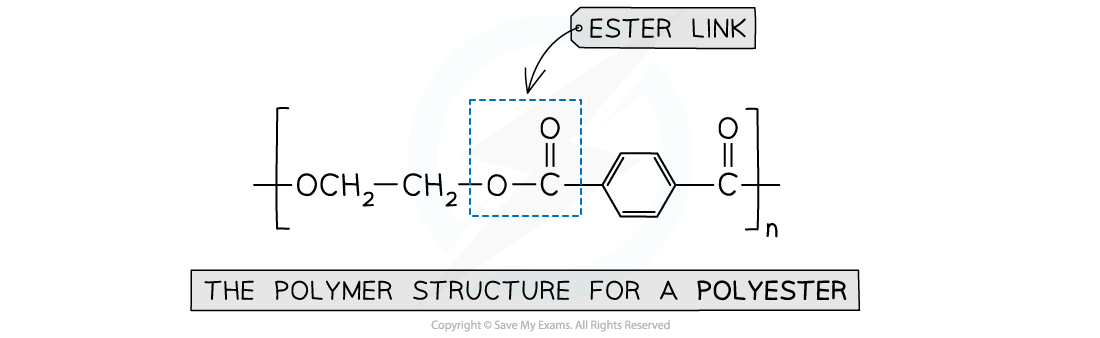
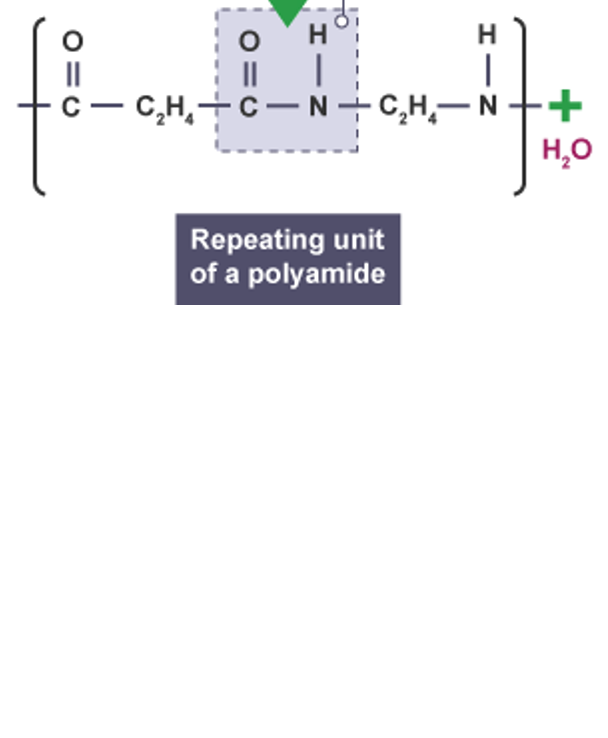
what is the type of link in this polymer
amide link between amine and a carboxylic acid
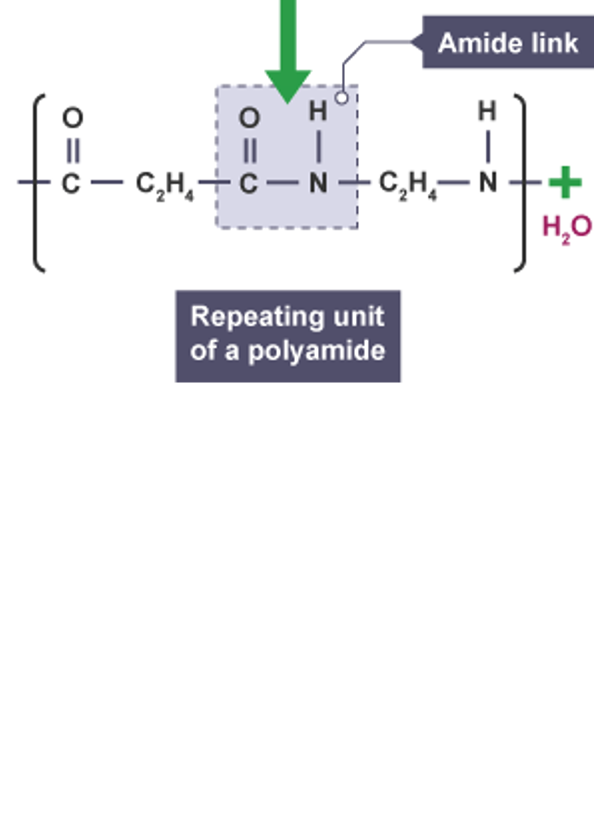
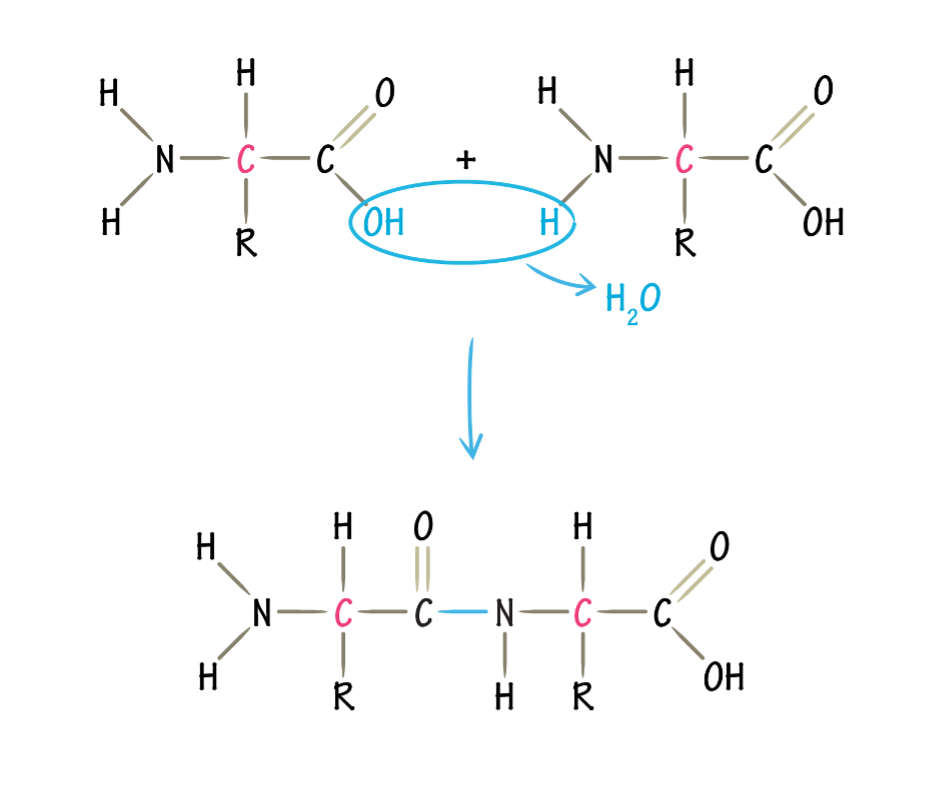
what is the type of link in this polymer
a peptide bond between amino acids
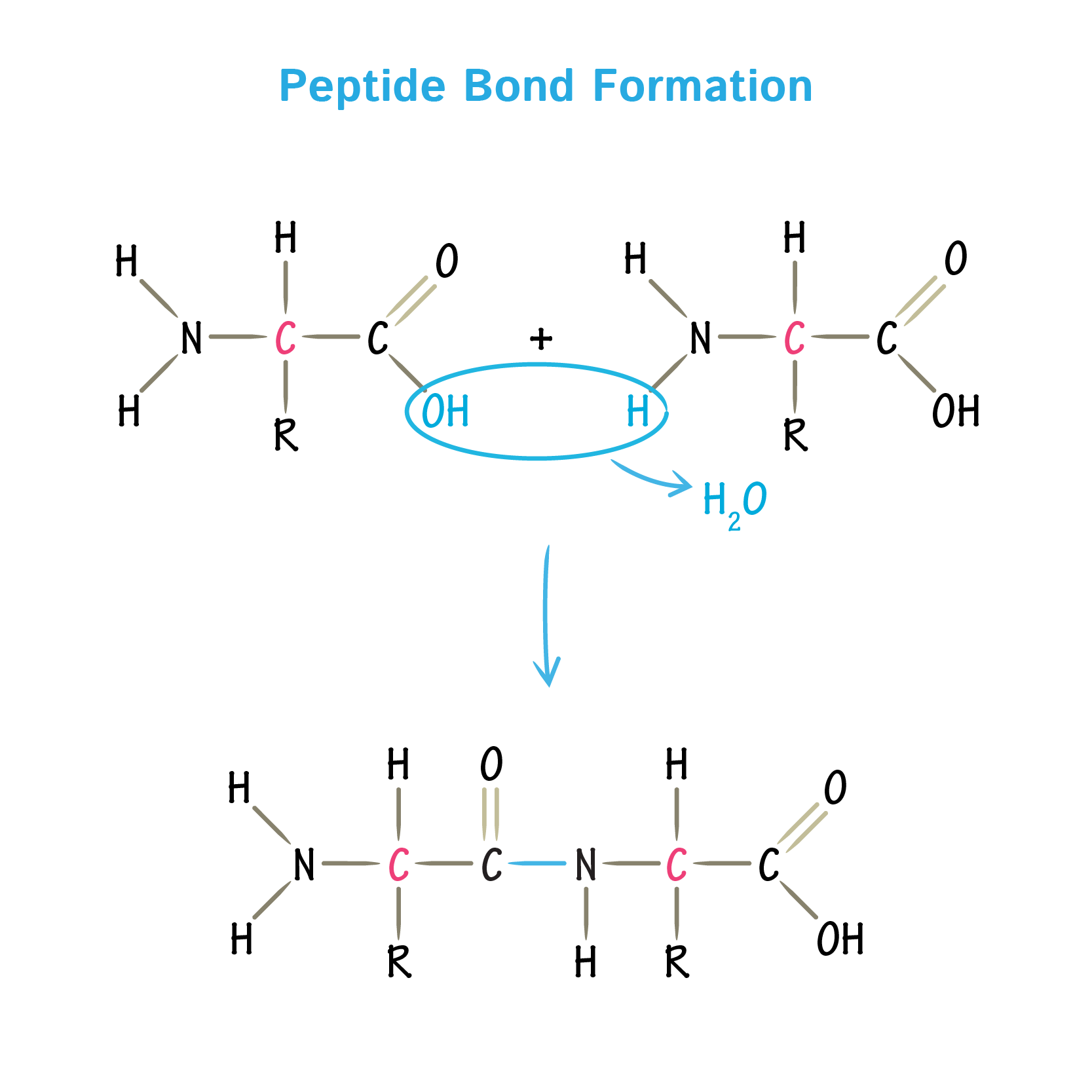
why are polyesters and polyamides not broken down by pure water?
the hydrolysis of polyesters and polyamides is too slow to be useful so an acid or base catalyst is required
what are the products of acid and base hydrolysis of polyesters
which is faster?
Acid hydrolysis of polyesters breaks ester bonds using dilute acid to form a dicarboxylic acid and a diol (orriginal monomers)
base hydrolysis uses a strong alkali (like NaOH) to form a dicarboxylic acid salt and a diol.
Base hydrolysis is generally a faster reaction than acid hydrolysis. Both reactions are methods of breaking down polyesters into their original monomer components.
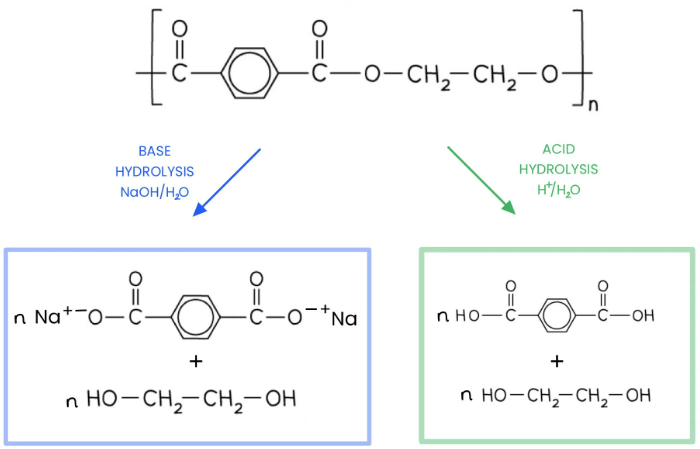
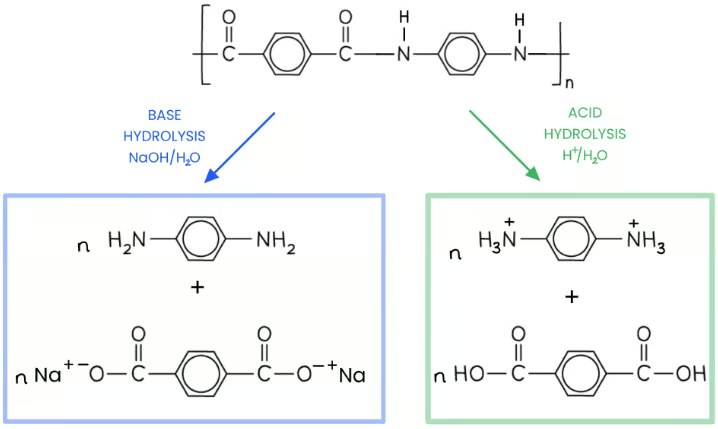
what are the products of acid and base hydrolysis of polyamides
acid hydrolysis uses hot aq HCL and (2n-1) H2O to hydrolyse the amide links. this produces a dicarboxylic acid and an ammonium salt
Hydrolysis with hot aqueous base (e.g., NaOH) and (2n-1) H2O. this forms a Dicarboxylate salt and a diamine
the ammonium salt in acid hydrolysis forms a dative covalent bond with H+ ions to form NH3 but in the base hydrolysis it stays as NH2 as it doesn’t react with a base as it is already a base.
state the three ways of disposing of polymers
landfill (quick and easy but polymers will be dug up in years to come)
burnt/ incinerated- (quick and easy but relics toxic gas)
recycling
advantages and disadvantages of recycling
advantages
reduces amount of plastic in landfill
conserves crude oil
disadvantages
expensive sorting costs
plastics must be collected, sorted and recycles which takes time and money
state why addition polymers are non-biodegradable
they are inert and contain a C=C
they are non polar
so not easily attacked by nucleophiles
state why condensation polymers are biodegradable
condensation polymers have polar bonds
these bonds can be hydrolysed by nucleophiles
can acyl chlorides form condensation polymers
yes