kms (Ch3 Midterm Psych)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
somatic nervous system (SMS)
Transmits sensory signals and motor signals between the central nervous system and the skin, muscles, and joints
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
transmits sensory signals and motor signals between the CNS and the body’s glands and internal organs
responsible for homeostasis
sympathetic
prepares the body for situations requiring the expenditure of energy
parasympathetic
directs the storage of energy
endocrine system
comprised of glands that release chemical messengers known as hormones into the bloodstream to comunicate with other body parts
Responds to input from the nervous system, esp hypothalamus
Involved with arousal, metabolism, growth, and sex
pituitary
“master gland”, many of the hormones it releases activates the body’s other glands
Regulated by hypothalamus, which lies directly above it
pineal
helps regulates body rhythms and sleep cycles
thyroid
regulates the rate of metabolism in the body
adrenal
secretes hormones that arouse the body, help with adjustment to stress, regulate salt balance, and affect sexual functioning
pancreas
release insulin to regulate blood sugar and hunger
nature
contributions of genetic inheritance
nurture
contributions of learning and environment
genes
the units of heredity that help determine the characteristics of an organism
Humans have 23 pairs
gene expression
whether a particular gene is turned on or off and in what location in the body
genome
the master blueprint for making an entire organism
chromosomes
structures within the cell body that are made up of DNA, segments of which comprise individual genes
DNA
a double stranded helix, made of four nucleotide bases
A, T, G, C
the four nucleotide bases in DNA
genotype
entire genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype
outward expression of genes
allele
alternative form of same gene for a trait
dominant gene
a gene that is expressed in the offspring whenever it is present
recessive
a gene that is expressed only when it is matched with a similar gene from the other parent
genetic drift
Any change in the allele frequencies in a population that is due to chance. Beetle example, 3 green and 3 orange in a population, but 2 of the 3 orange get stepped on, by chance the allele frequencies have now changed
Founder effect
Extreme example of genetic drift; occurs when a small, random sample of a population settles separate from the rest of the population and interbreeds
EX: the Blue Fugates
importance of sexual reproduction
Increasing genetic diversity, important for survival in changing environments, provides the variability needed for evolution, (with founder effect) the variation is too small —> genetic drift
Behavioral genetics
the study of how genes and environment interact to influence psychological activity
dizygotic twins
fraternal twins; shares 50% of DNA (like regular siblings)
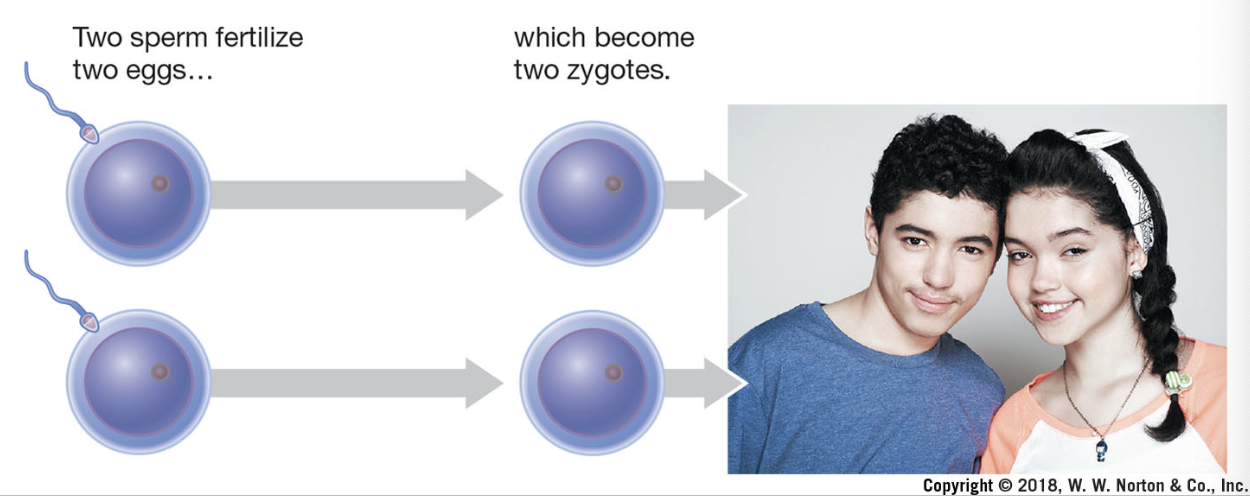
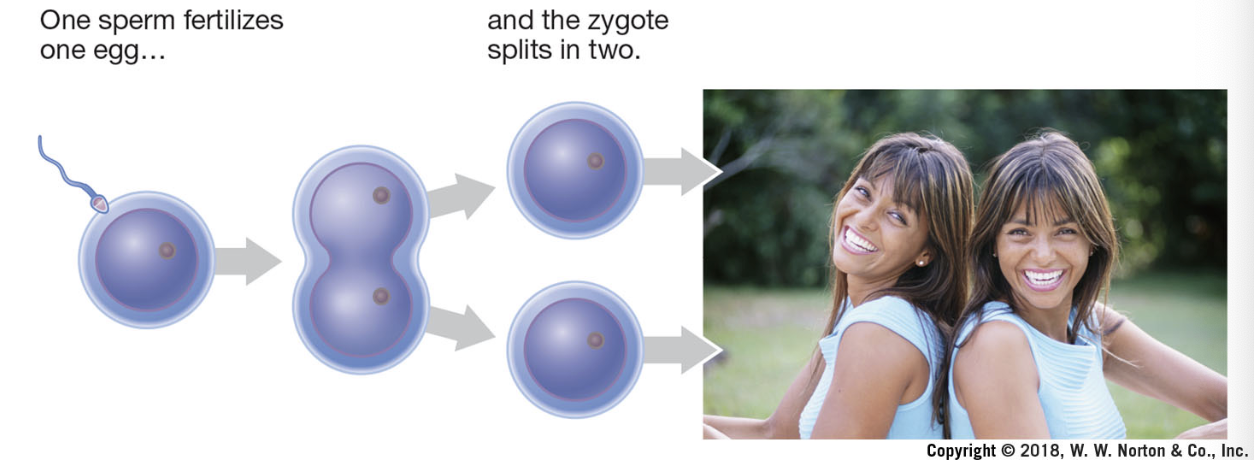
monozygotic twins
identical twins; share 100% of DNA
heredity
transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring through genes
heritability
a statistical estimate of the extent to which variations in a trait within a population is due to genetics
Refers to populations, not to individuals.