Control of cell growth and repair
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Stem Cells
Adult stem cells
Many adult tissues contain stem cells
More restricted differentiation capacity
Located in niches, which differ in varying tissues
Bone marrow stem cells
Have a larger differentiation capacity
[...]
specific differntiation -- give rise to all blood cell lineages
[...]
capable of differentiation into various lineages
Hematopoietic stem cells
Stromal cells
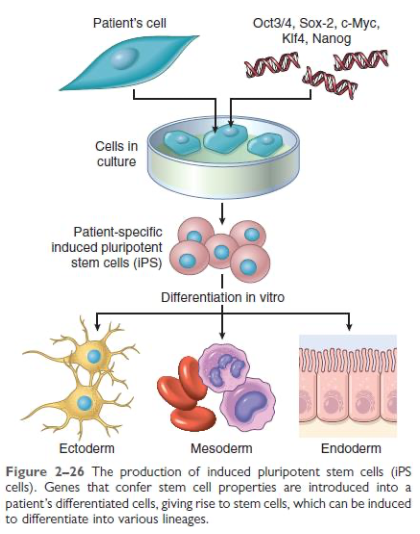
Stem Cells
Adult stem cells
[...]
the multiplicity of stem cell differentiation options (greatest in bone marrow stem cells)
Developmental plasticity
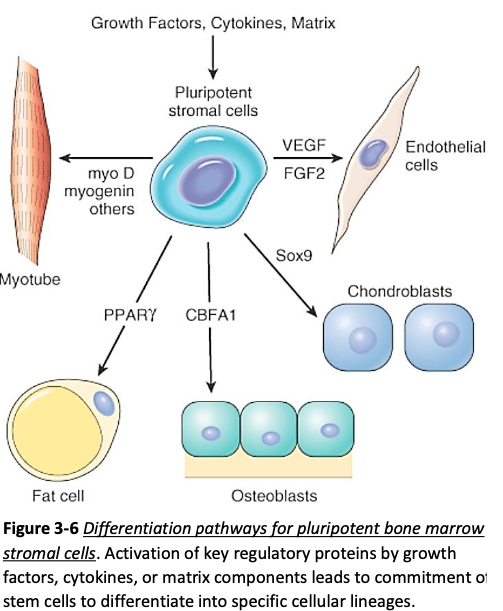
Stem Cells
Adult stem cells
[...]
a change in stem cell differentiation from one cell type to another
Transdifferentiation
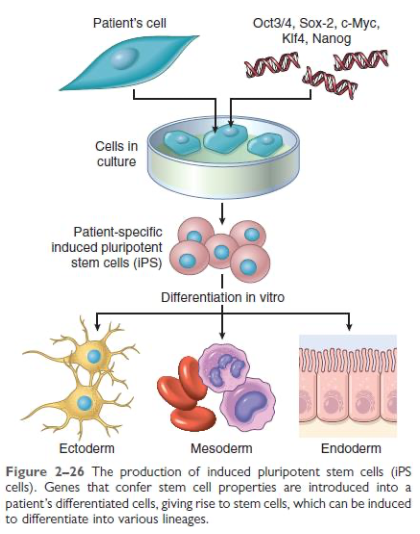
Stem Cells
Characterized by:
[...]
[...]
After each cell division, some progeny enter a differentiation pathway, while others remain undifferentiated
Self-renewal capacity
Asymmetric replication
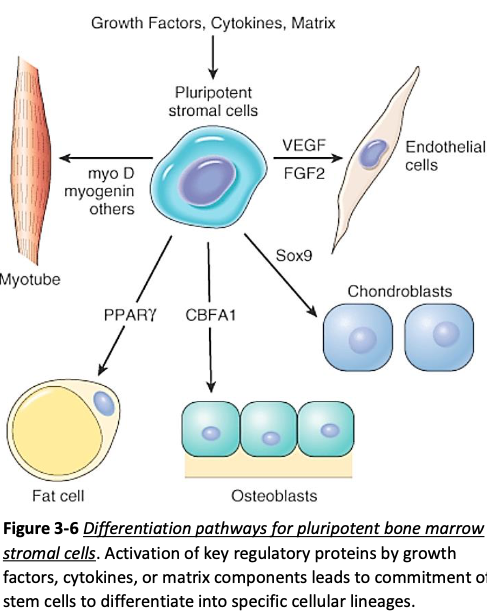
Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells
Embryos contain [...] stem cells which can produce all the tissues of the human body
Can be found in the umbilical cord
pluripotent
![<p>Regenerative Capacity of Cells</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Labile, Quiescent, or Nondividing?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Proliferate throughout life</p></li><li><p>Continuously replacing dying cells</p></li><li><p>Examples:</p><ul><li><p><strong><u>Epithelia</u></strong> (skin, oral cavity, vagina, GI tract, transitional epithelium of urinary bladder) </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0b1868e5-5ae9-4e55-b6f6-b04eb81b0c74.png)
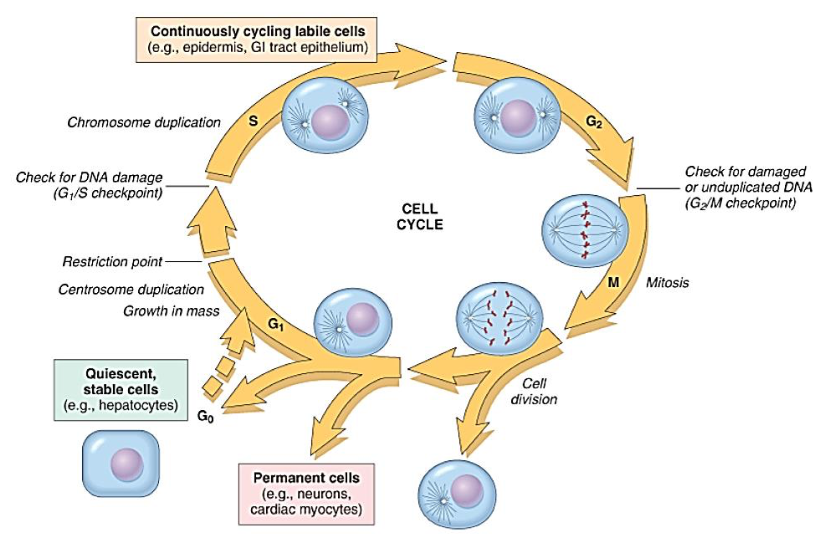
Regenerative Capacity of Cells
[Labile, Quiescent, or Nondividing?]
Proliferate throughout life
Continuously replacing dying cells
Examples:
Epithelia (skin, oral cavity, vagina, GI tract, transitional epithelium of urinary bladder)
Continuously dividing (labile) cells
![<p>Regenerative Capacity of Cells</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Cannot undergo further mitotic division in postnatal life</p></li><li><p>Whatever proliferative capacity may exist, it isn’t enough to produce tissue regeneration after injury</p></li><li><p>Example:</p><ul><li><p><strong><u>Cardiac muscle </u></strong></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ec82ae6a-8906-41ca-9304-c4e28c58fcb1.png)
Regenerative Capacity of Cells
[...]
Cannot undergo further mitotic division in postnatal life
Whatever proliferative capacity may exist, it isn’t enough to produce tissue regeneration after injury
Example:
Cardiac muscle
Permanent (nondividing) cells
![<p>Regenerative Capacity of Cells</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Labile, Quiescent, or Nondividing?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Low level of replication</p></li><li><p>At baseline in G0</p></li><li><p>Can be driven into G1 when needed</p></li><li><p>Examples:</p><ul><li><p><strong><em><u>Liver, kidney, pancreas</u></em></strong>, vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/411f8a67-500b-4cb5-a5ca-9d75d621ea82.png)
Regenerative Capacity of Cells
[Labile, Quiescent, or Nondividing?]
Low level of replication
At baseline in G0
Can be driven into G1 when needed
Examples:
Liver, kidney, pancreas, vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts
Stable (quiescent) cells)
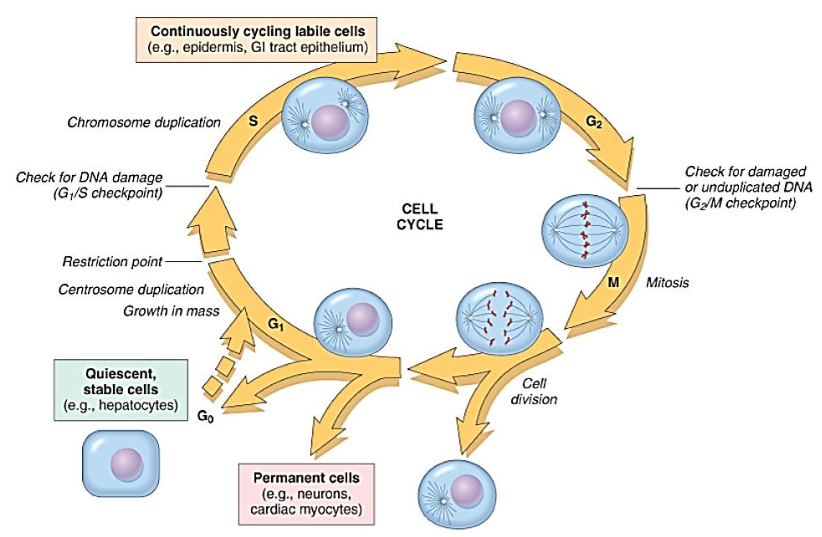
Normal Cell Proliferation
Entry and progression of cells through the cell cycle
Controlled by [...]
Changes in levels
Changes in activities
Work by complexing with and activating [...]
cyclins
cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs)
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
Check points
Surveillance mechanism
Between G1/S and G2/M
Ensures that critical transitions occur correctly and in proper order
Cell cycle is delayed & problem corrected
if not possible the cell undergoes [...]
apoptosis
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
Epidermal growth factor family (EGF) -- EGF-α
[...]
has similar biologic activities and uses the same receptor
TGF- α
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
Growth inhibition
[...]
cell stops growing if it is contacting others on all sides
[...]
Some polypeptide growth factors
example: [...]
Contact inhibition
Growth suppression
TGF-β
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
[...]
In vitro (in lab)
Mitogenic for a variety of epithelial cells and fibroblasts
In vivo (body)
Causes hepatic cell division
Widely distributed
Epidermal growth factor family (EGF) -- EGF-α
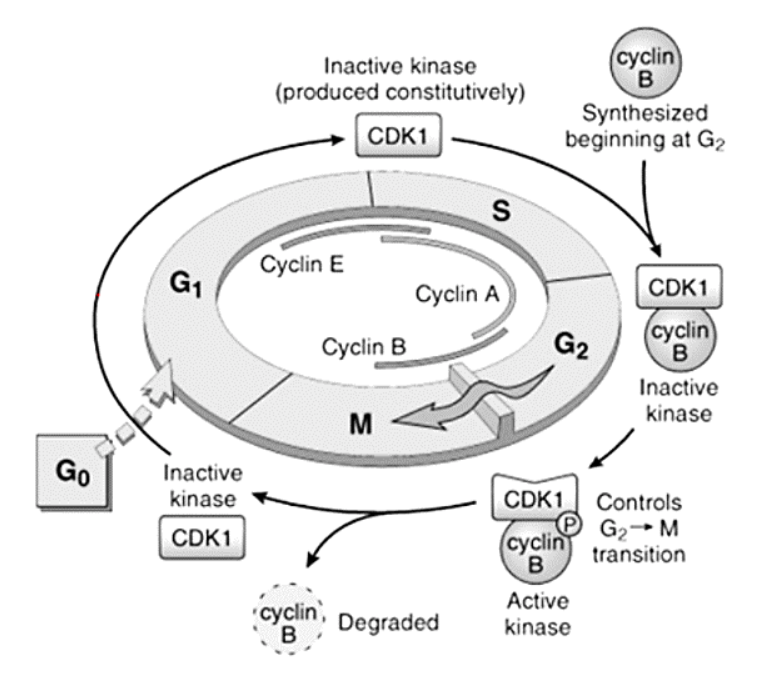
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
Epidermal growth factor family (EGF) -- EGF-α
In vitro (in lab)
Mitogenic for a variety of [...] and [...]
In vivo (body)
Causes [...]
Widely distributed
epithelial cells and fibroblasts
hepatic cell division
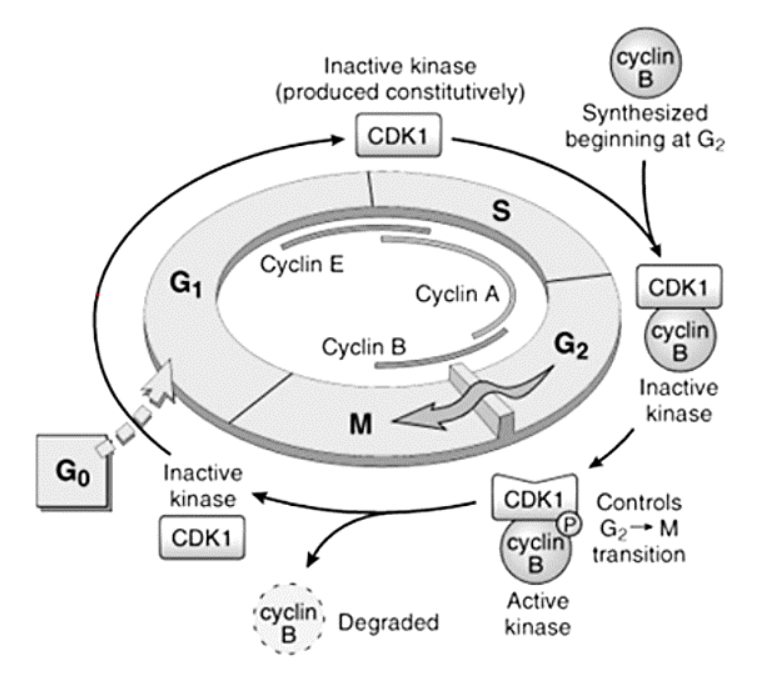
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
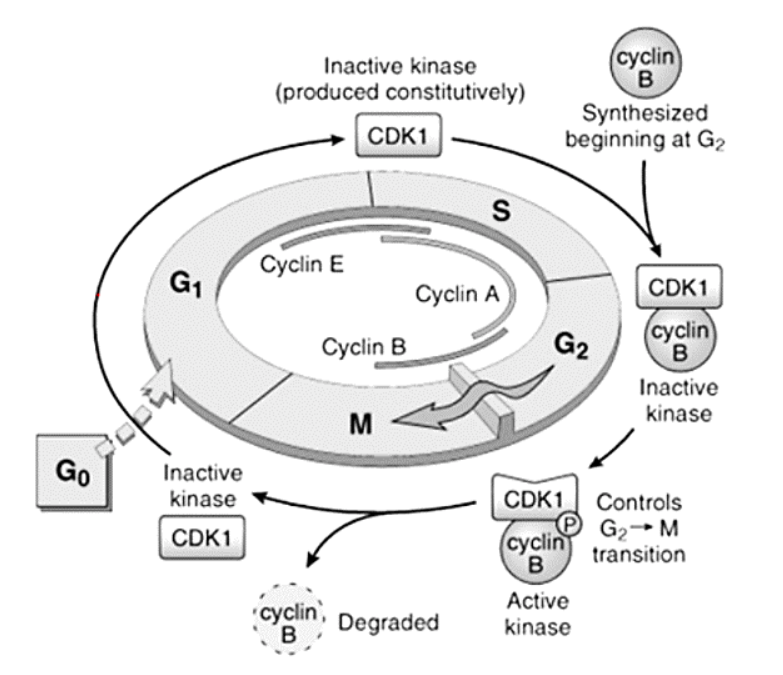
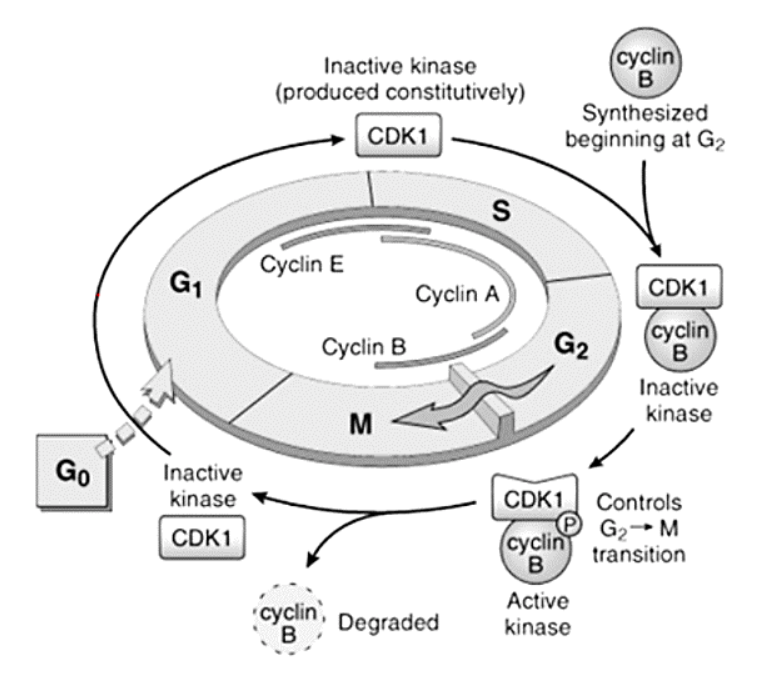
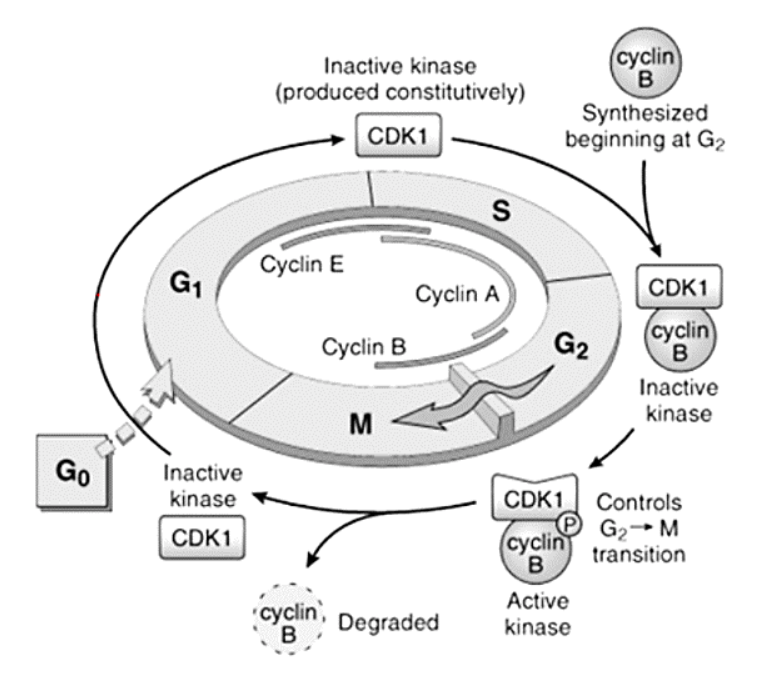
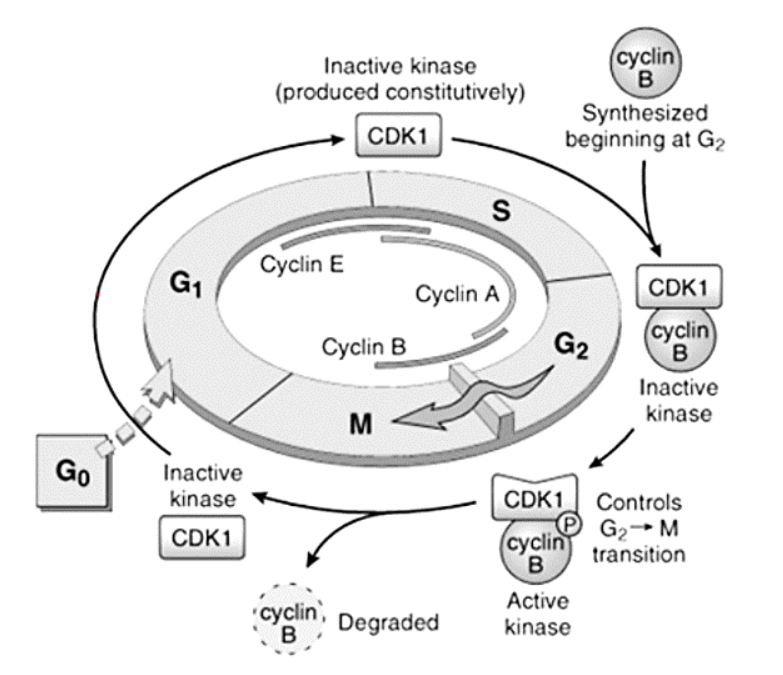
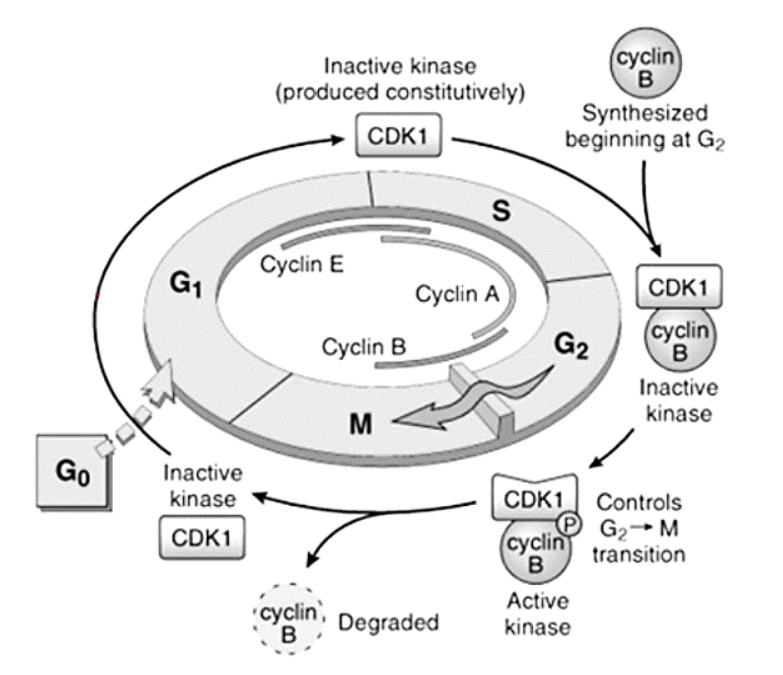
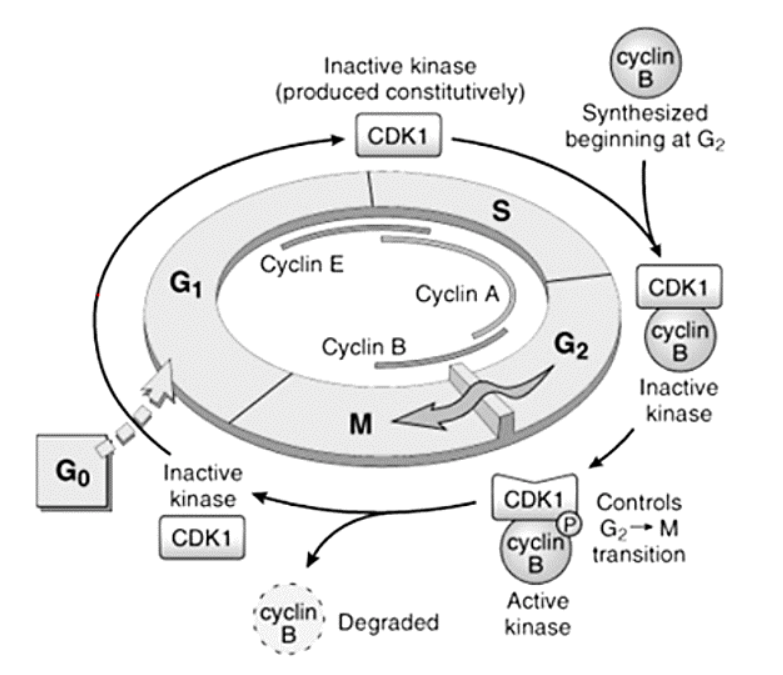
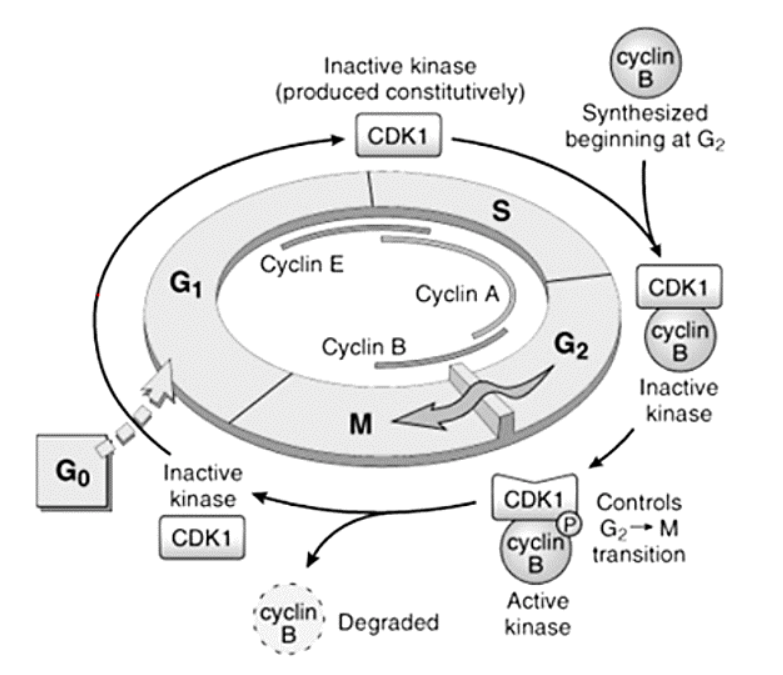
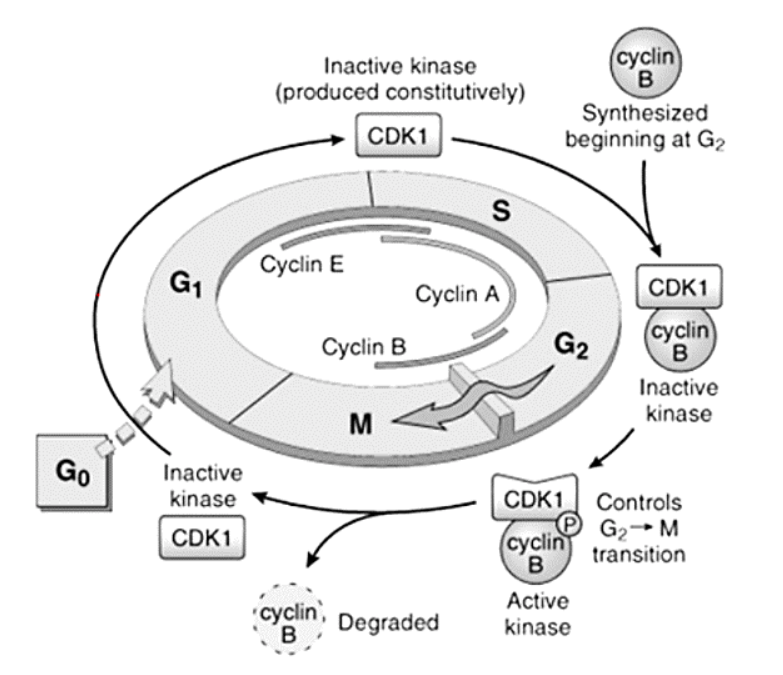
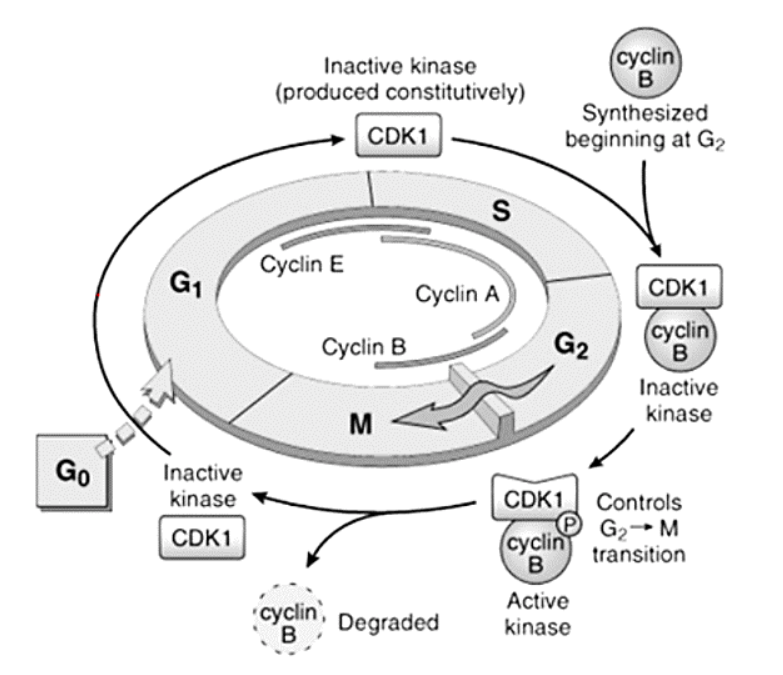
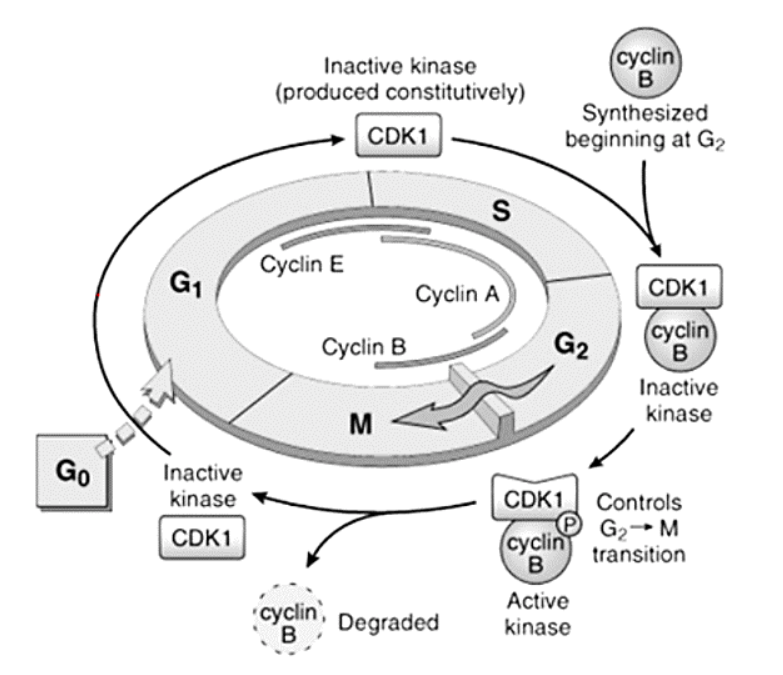
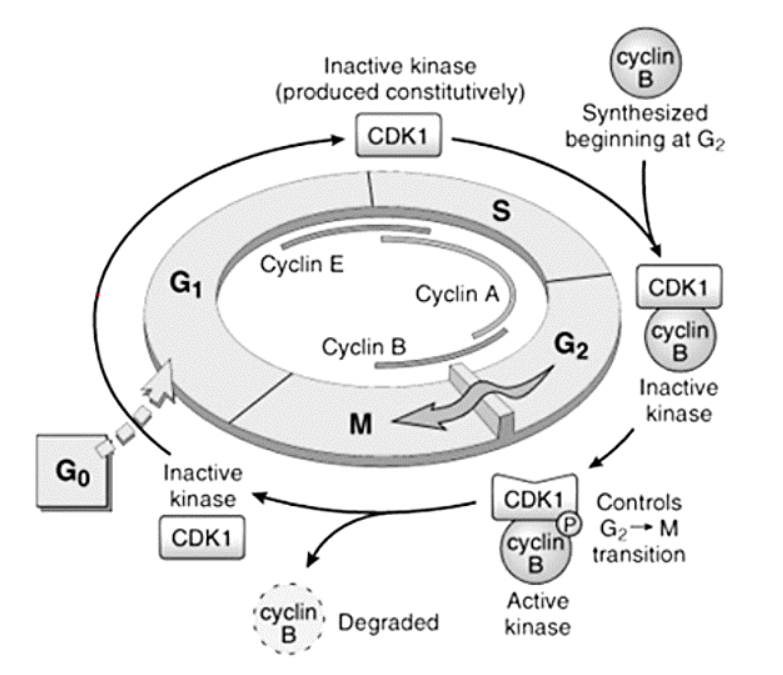
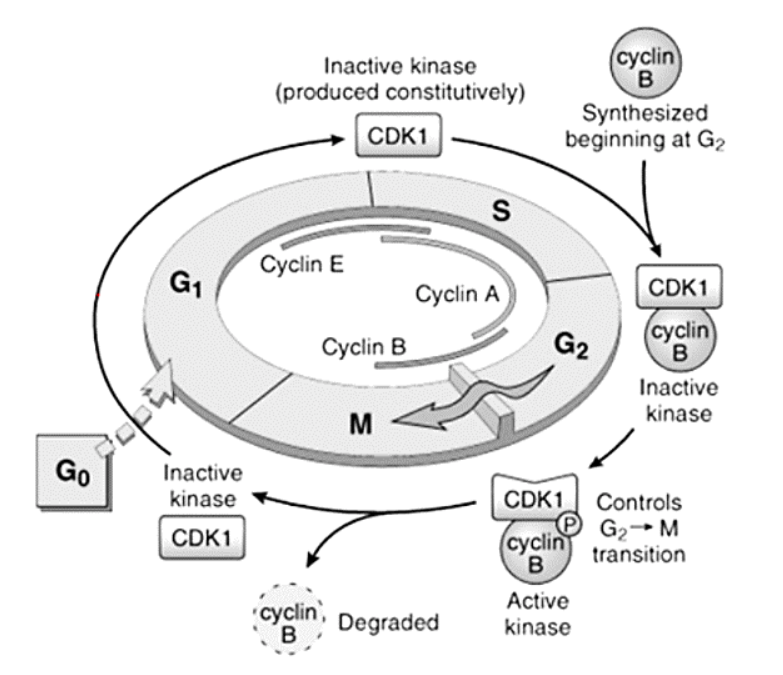
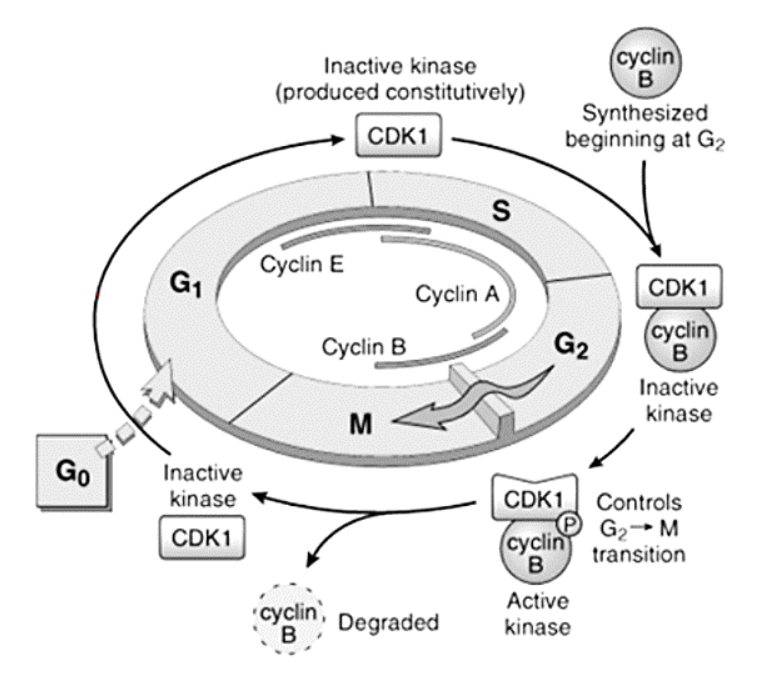
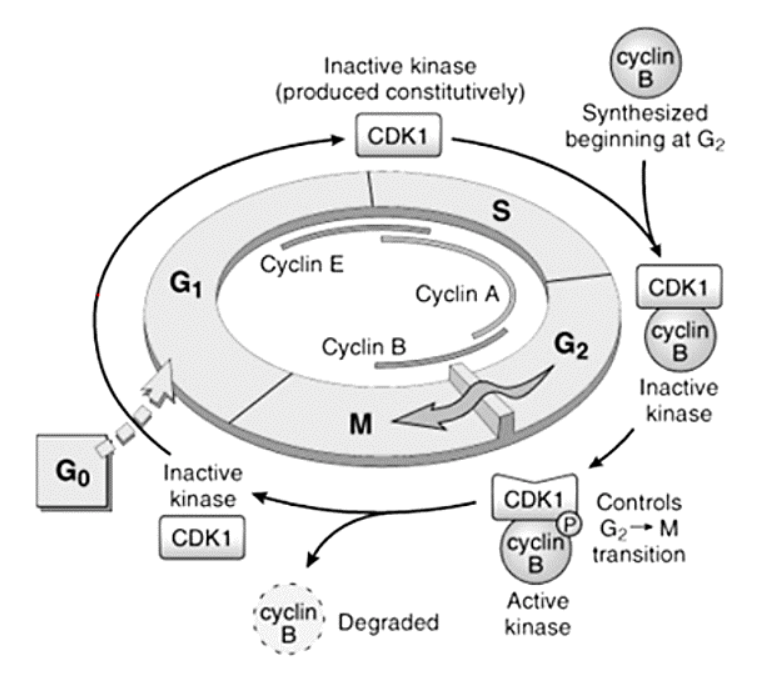
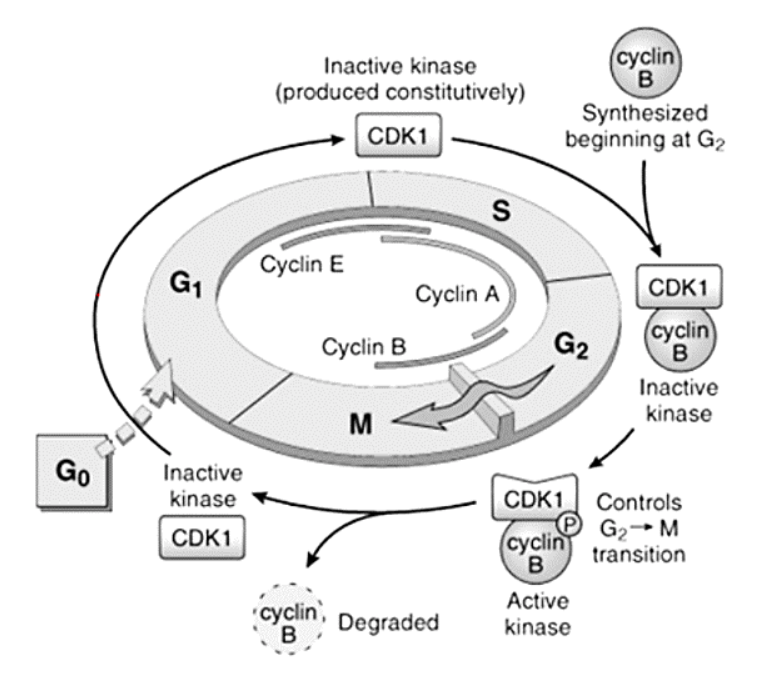
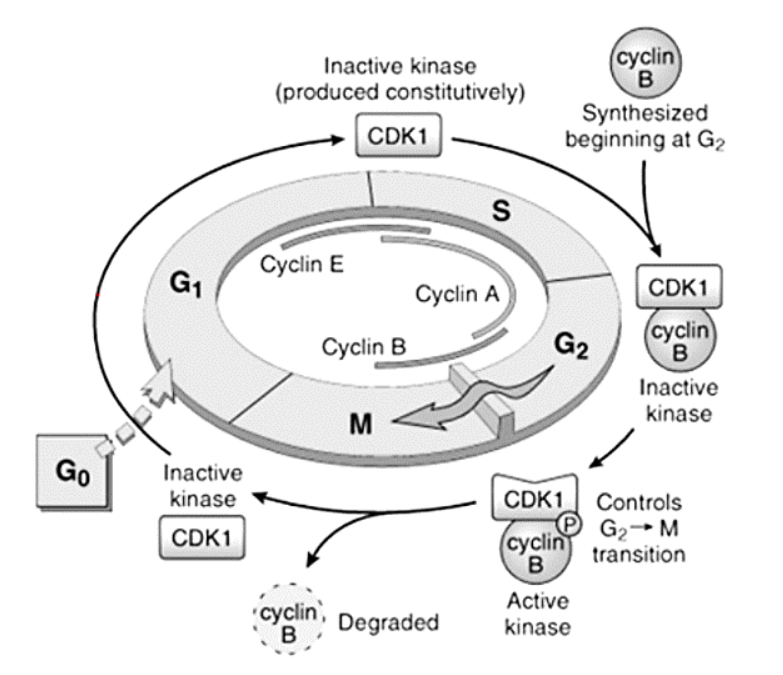
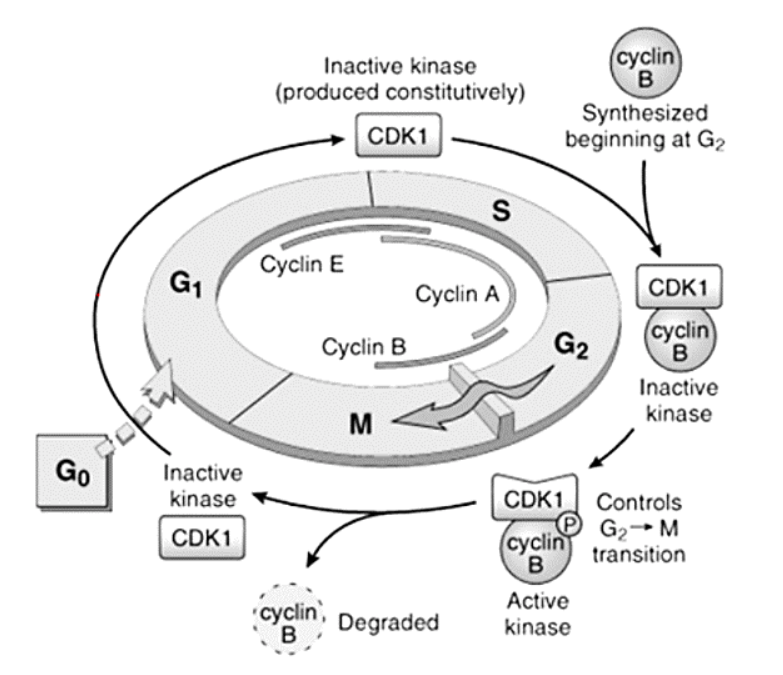
Cyclins – A, B, and E
E
[...] to [...]
A
[...] to [...]
B
[...] to [...]
G1 to S
S to G2
G2 to M
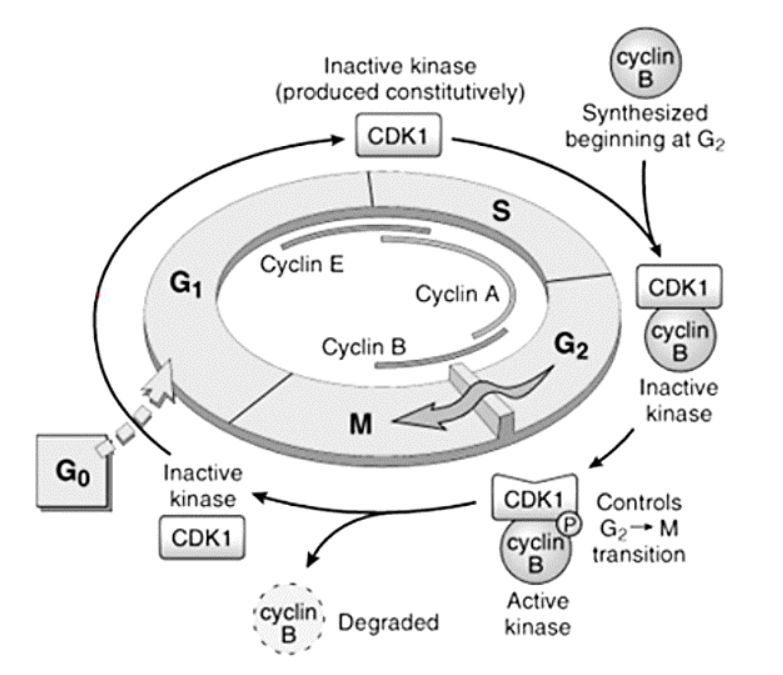
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
Cyclins – A, B, and E
[...]
G1 to S
[...]
S to G2
[...]
G2 to M
E
A
B
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
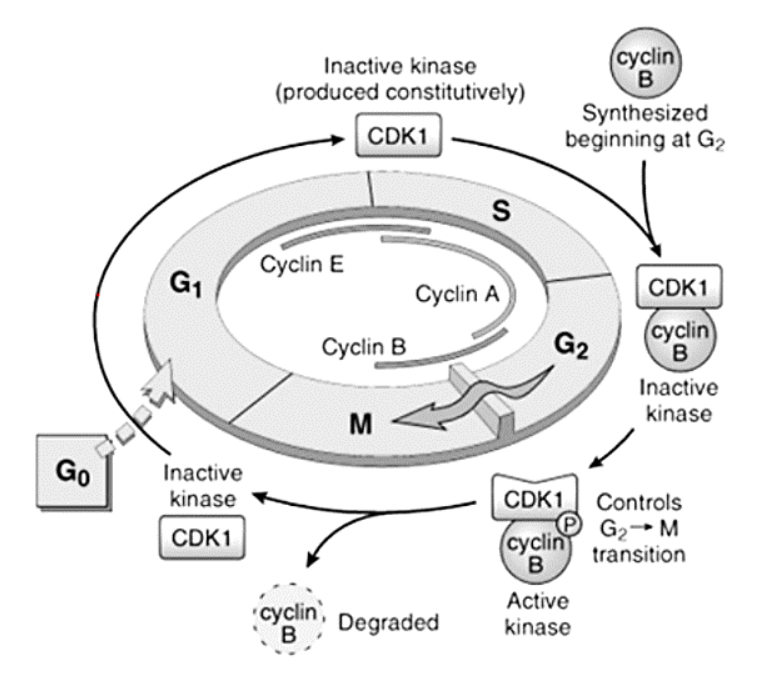
Cyclins – responsible for what functions?
[...]
[...]
[...]
DNA replication
Depolymerization of nuclear lamina
Formation of mitotic spindle
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
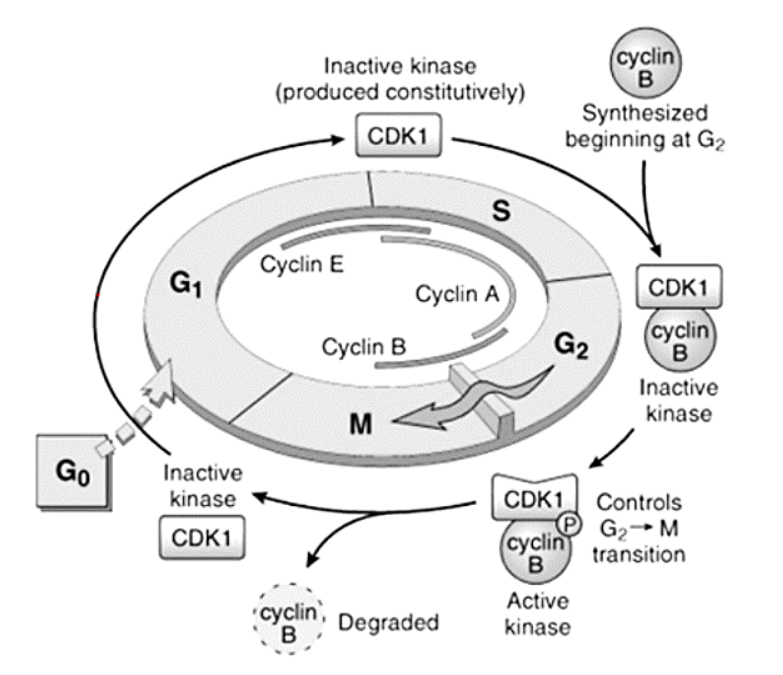
[...]
Cyclins form complexes with them to perform their functions
Cyclin-dependent kinases
Cell Cycle and the Regulation of Cell Division
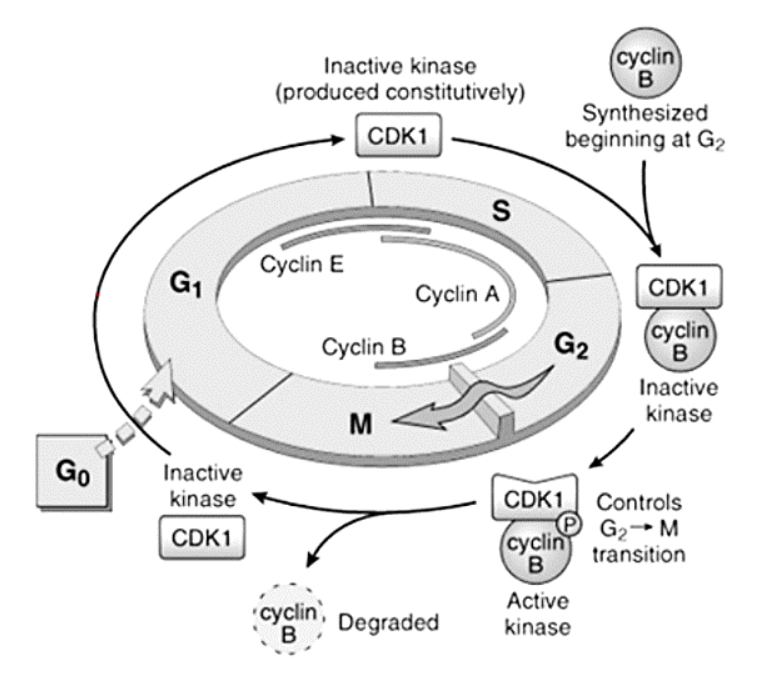
[...]
Control the entry and progression of the cell through the cell cycle
Cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases
Cell Receptors
Classes of cell surface receptors
[...]
[...]
[...]
Receptors with intrinsic kinase activity
Receptors without intrinsic kinase activity
G-protein linked receptors
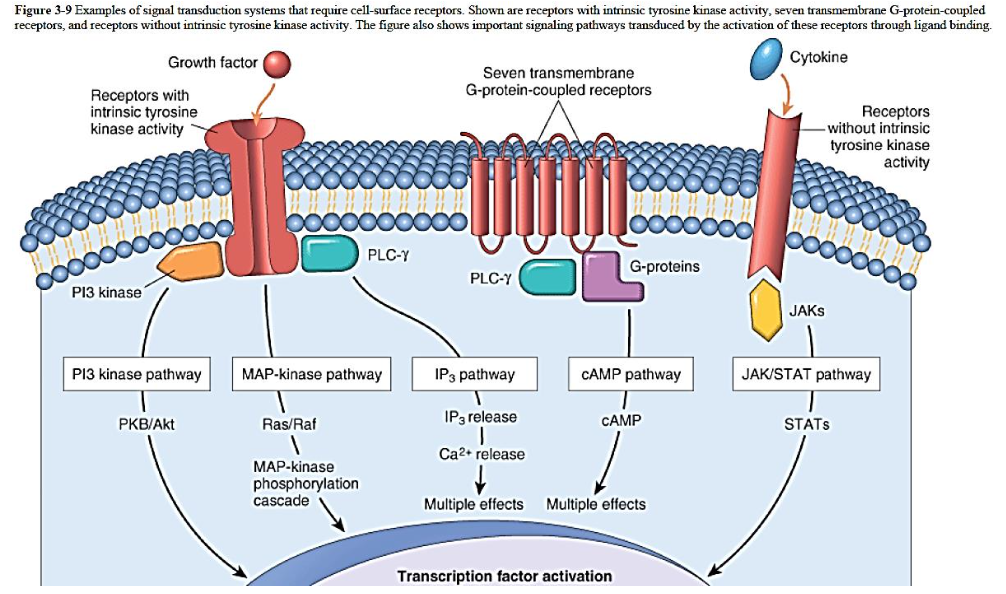
Cell Receptors
Location:
on [...]
in the [...]
in the [...]
on surface
in the cytoplasm
in the nucleus
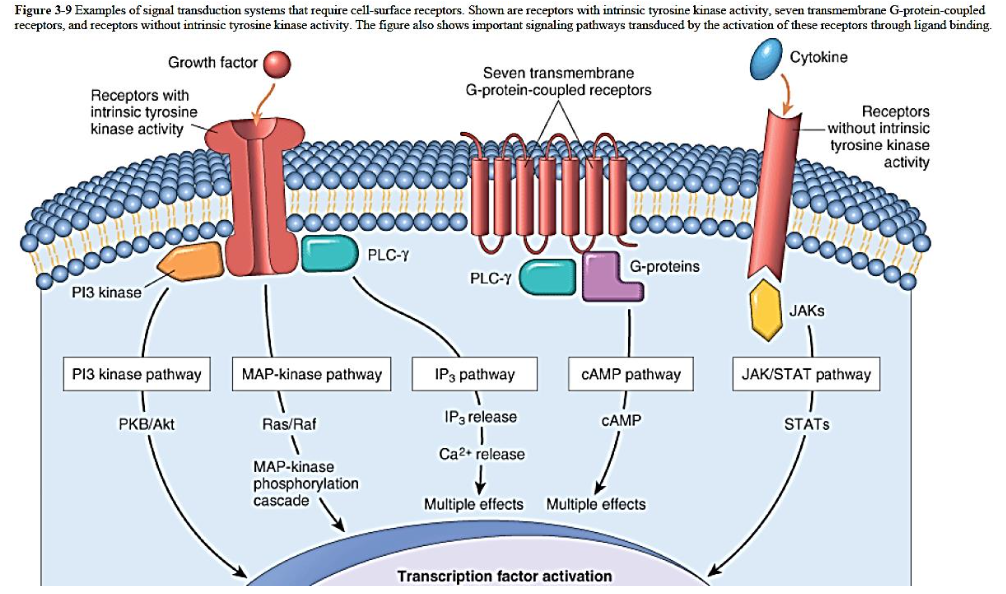
Cell Receptors
Receptor activation
Receptors with intrinsic kinase activity
Ligand binding causes:
[...]
[...]
Others
Recruit cytosolic kinases or
activate other pathways to generate second messengers
dimerization of the receptor (causing amplification)
autophosphorylation
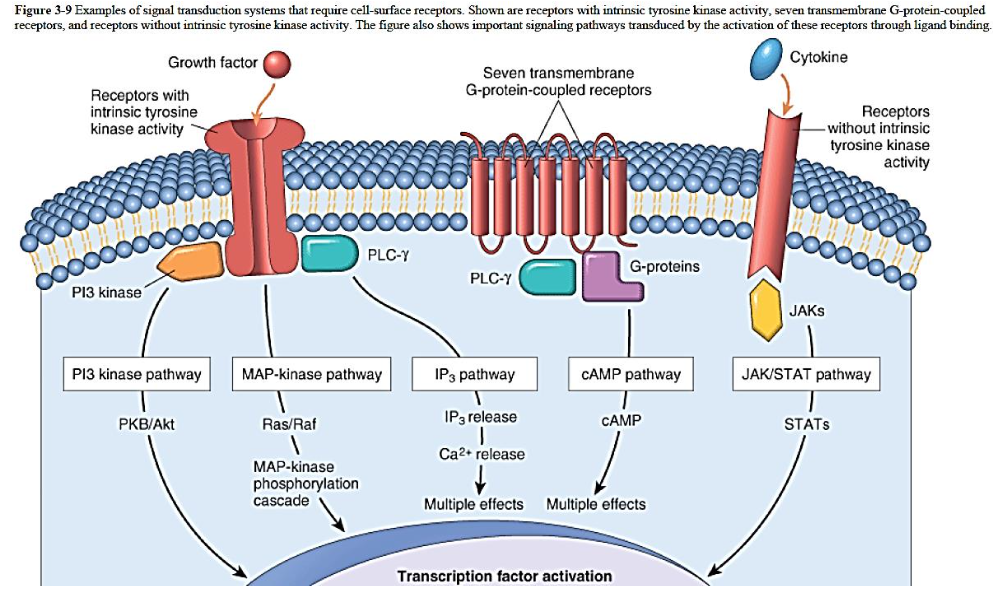
Cell Receptors
Receptor activation
Receptors with intrinsic kinase activity
Ligand binding causes:
dimerization of the receptor (causing amplification)
autophosphorylation
Others
Recruit [...] or
activate other pathways to generate [...]
cytosolic kinases
second messengers
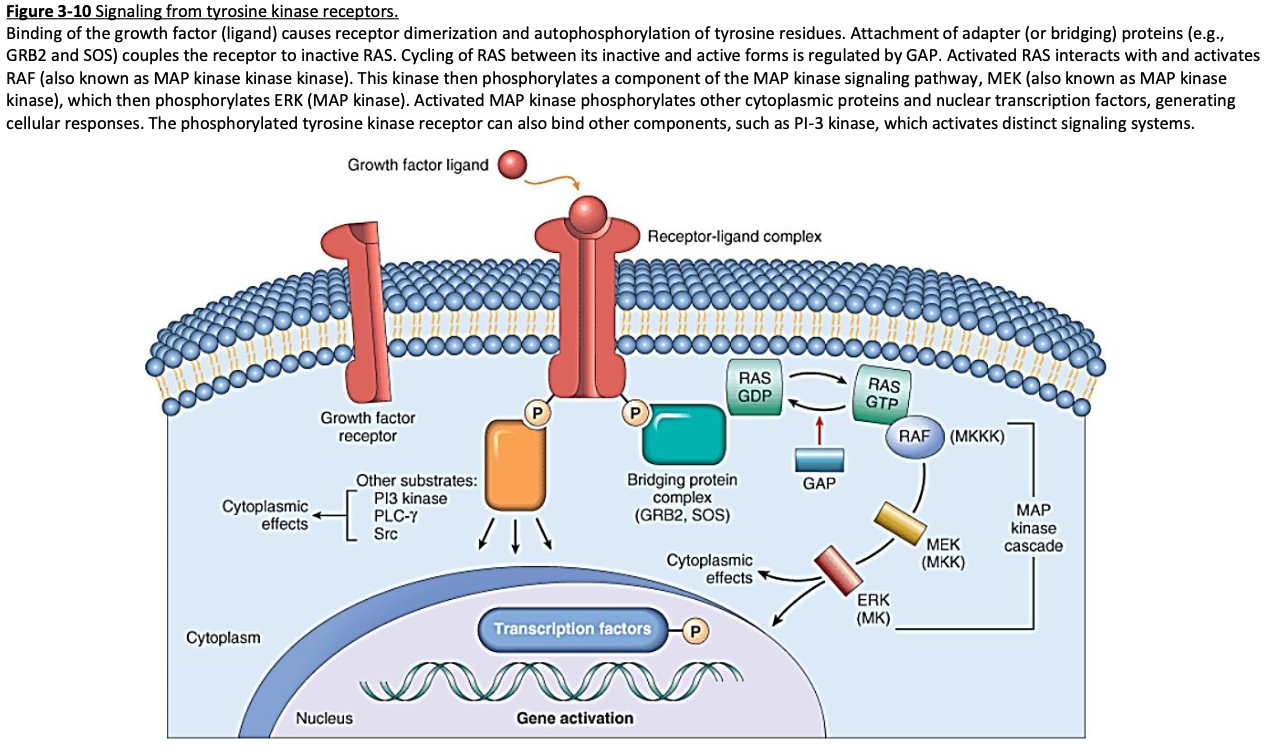
Cell Receptors
Signal Transduction & Second Messengers – transfer information to the nucleus
Ras activation and MAP-kinases (mitogen-activated protein)
[...] is a frequently mutated gene found in human tumors
Ras
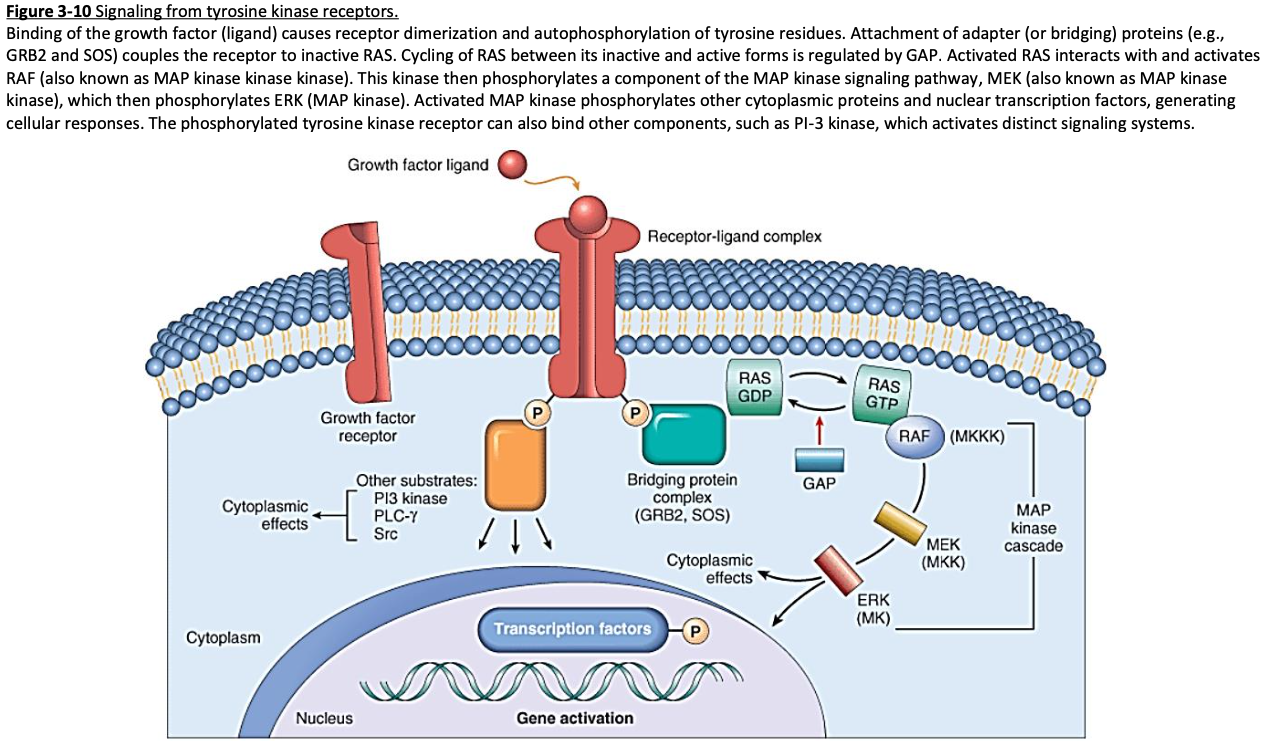
Cell Receptors
Signal Transduction & Second Messengers – transfer information to the nucleus
[...]
frequently invovled in tumor growth
[...]
[...]
[...]
Ras activation and MAP-kinases (mitogen-activated protein)
IP3 pathway (inosol 1,4,5-triphosphate)
PI3 kinase pathway (phosphoinositide-3-kinase)
Phospholipase C-γ
Ras is a frequently mutated gene found in human tumors
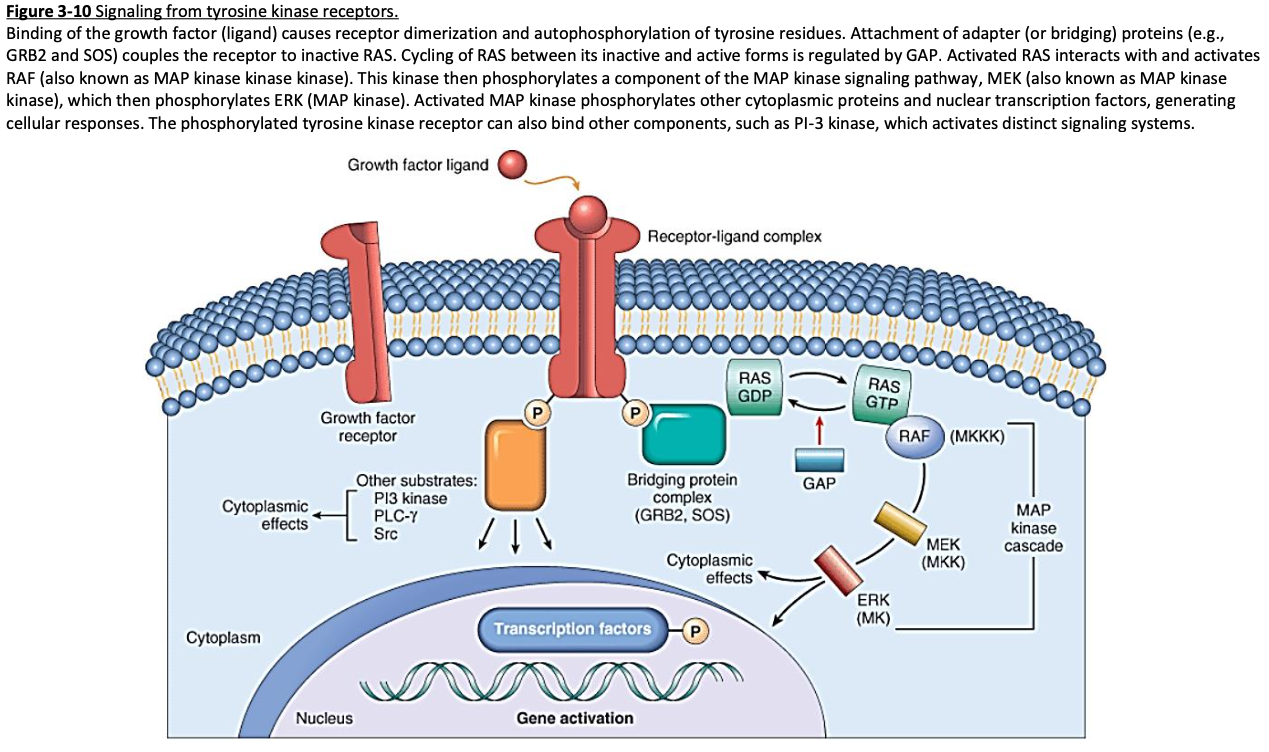
Cell Receptors
Transcription Factors
Control the transcription of genes
Bind to DNA and either increase or decrease transcription
Includes:
[...]
[...]
Proto-oncogenes
Tumor suppressor genes
Cell Receptors
[What type of] binding
Binding of a growth factor to its specific receptor
Ligand-Receptor
Growth Factors
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
Binds tightly to [which drug]
Made by a variety of cells
heparin (anti-coagulation drug)
Growth Factors
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
FGF activities
[...]
by bFGF
Stimulates the proliferation of endothelial cells
[...]
Macrophage, fibroblast and endothelial cell migration
Development
[...] development and [...] formation
[...]
Angiogenesis
Wound repair
Skeletal muscle
lung
Hematopoiesis
Growth Factors
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
FGF activities
Angiogenesis
by [a or b]FGF
Stimulates the proliferation of endothelial cells
Wound repair
Macrophage, fibroblast and endothelial cell migration
Development
Skeletal muscle development and lung formation
Hematopoiesis
b
Growth Factors
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
Two forms:
[...] (aFGF or FGF-1)
[...] (bFGF- or FGF-2)
acidic
basic
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
Belongs to a family of homologous polypeptides including TGF- β1, - β2, β3 and other cytokines like bone morphogenetic proteins
[Which] isoform is widely distributed and is usually referred to as TGF- β
TGF- β1
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
Stimulates production of:
[...]
[...]
[...]
Inhibits collagen degradation by:
Decreasing metalloproteinase activity
Increasing the activity of TIMPs (Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases)
collagen
fibronectin
proteoglycans
Example: Collagenase is a metalloproteinase enzyme that removes type III collagen
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
Stimulates production of:
collagen
fibronectin
proteoglycans
Inhibits collagen degradation by:
[Increasing or decreasing] metalloproteinase activity
[Increasing or decreasing] the activity of TIMPs (Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases)
Decreasing
Increasing
Example: Collagenase is a metalloproteinase enzyme that removes type III collagen
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
Stimulates production of:
collagen
fibronectin
proteoglycans
Inhibits collagen degradation by:
Decreasing [...] activity
Increasing the activity of [...]
metalloproteinase
TIMPs (Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases)
Example: Collagenase is a metalloproteinase enzyme that removes type III collagen
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
TGF- β -- Has many and often opposite effects
Can promote or inhibit growth depending on the cell type and its metabolic state
Promotes growth
in [high or low] concentrations
Induces synthesis and secretion of [...]
Inhibits growth
in [high or low] concentrations
Inhibits [...] expression
low
PDGF
high
PDGF
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
TGF- β
Levels in the tissue are regulated by:
Post-transcriptional activation of [...]
Rate of secretion of the active molecule
Factors in the ECM (most notably [...]) that enhance or diminish TGF- β activity
latent TGF- β
integrins
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
TGF- β
The factor binds to two cell surface receptors with serine-threonine kinase activity
Triggers phosphorylation of transcription factors called [...]
Smads
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
[Stimulates or Inhibits] lymphocyte proliferation and activity of other leukocytes
Inhibits
Needed for transition from an inflammatory process to repair process
Growth Factors
Transforming growth factor- β (TGF- β)
[What is its role in the inflammation process?]
Is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that serves to limit and terminate inflammatory response
Needed for transition from an inflammatory process to repair process
Growth Factors
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Family or related growth factors
VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D, -E and placental growth factor
[Which one] is just referred to as VEGF and is the major inducer of angiogenesis after injury and in tumors
VEGF-A
Growth Factors
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Family or related growth factors
VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D, -E and placental growth factor
VEGF-A is just referred to as VEGF and is the major inducer of [...] after injury and in tumors
angiogenesis
Growth Factors
[...]
Induce fibroblast proliferation
Chemotactic for fibroblasts
Stimulate the synthesis of collagen and collagenases (for remodeling)
Cytokines (IL-1 and TNF)
Growth Factors
[...]
Stored in platelet α granules and produced by a variety of cells
Causes migration and proliferation of:
fibroblasts
smooth muscle cells
monocytes
Chemotactic for neutrophils
Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF)
Growth Factors
Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF)
Stored in platelet α granules and produced by a variety of cells
Causes migration and proliferation of:
[...]
[...]
[...]
Chemotactic for [...]
fibroblasts
smooth muscle cells
monocytes
neutrophils
Growth Factors
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Stimulates the migration of [...]
Promotes vasodilation by stimulating production of [...]
endothelial cells
NO
Growth Factors
[...]
Stimulates the migration of endothelial cells
Promotes vasodilation by stimulating production of NO
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
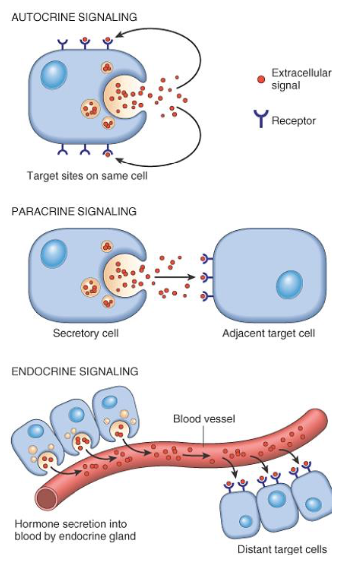
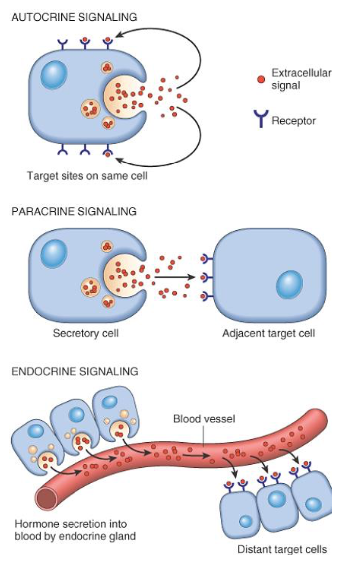
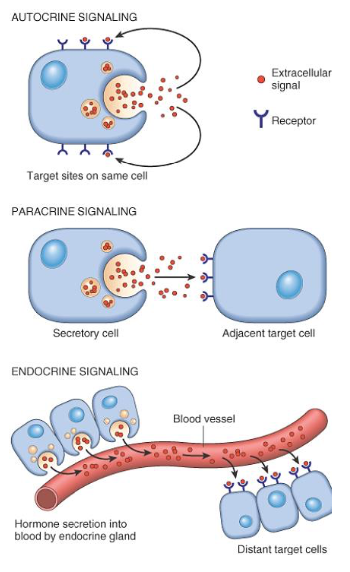
Polypeptide growth factors
Mechanisms of action
[...]
Target site on same cell
[...]
For cell adjacent to GF producing cells
[...]
For distant cells producing GF
Autocrine
Paracrine
Endocrine
Pleiotropic: Producing or having multiple effects from a single gene
Polypeptide growth factors
Most growth factors have pleiotropic (multiple, unrelated) effects
Stimulate
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
Cell proliferation
Migration
Differentiation
Synthesis of specialized proteins
Pleiotropic: Producing or having multiple effects from a single gene
Polypeptide growth factors
Target the function of [...]
proto-oncogenes
Proto-oncogenes: A gene involved in normal cell growth
Pleiotropic: Producing or having multiple effects from a single gene
Repair
Cell Cycle
G1
[...]
S
[...]
G2
[...]
M
[...]
G0
[...]
presynthetic
DNA synthesis
Premitotic
mitotic
quiescent cells
Repair
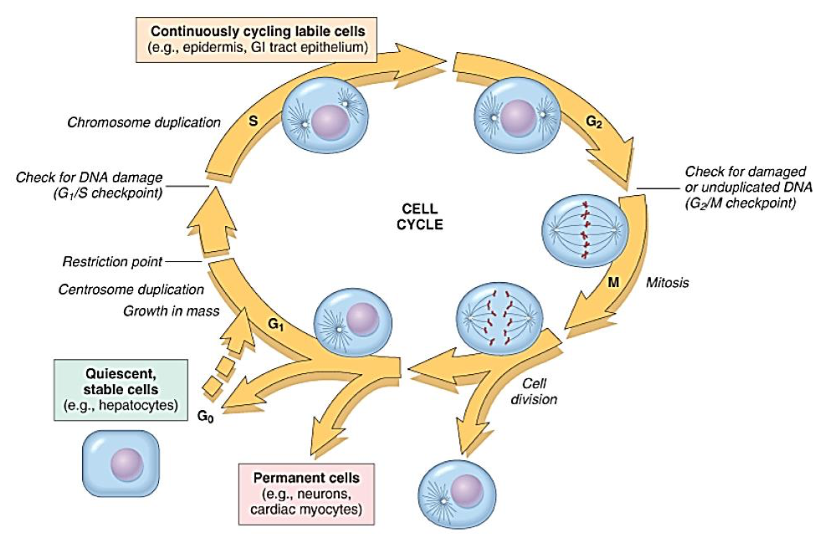
Cell Cycle
[...]
presynthetic
[...]
DNA synthesis
[...]
Premitotic
[...]
mitotic
[...]
quiescent cells
G1
S
G2
M
G0
Repair
Regulation of Cell Population
Increasing rate of [...]
Decreasing rate of [...]
Changing rate of [...]
Changing rate of [...]
cell death
cell death
proliferation
differentiation
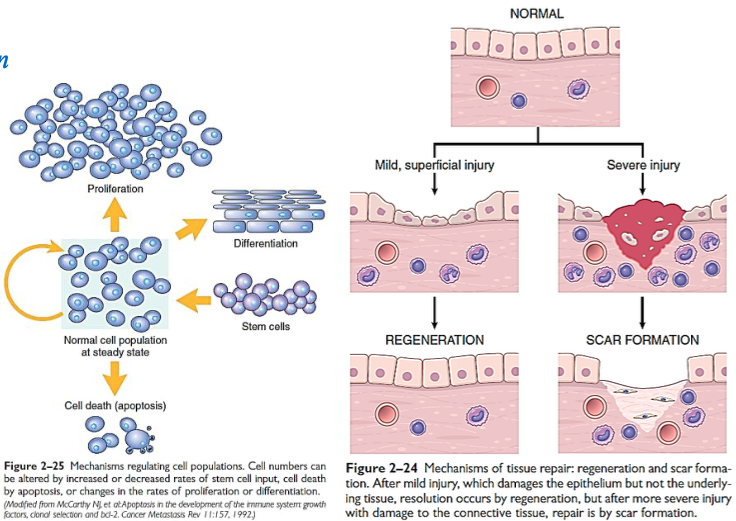
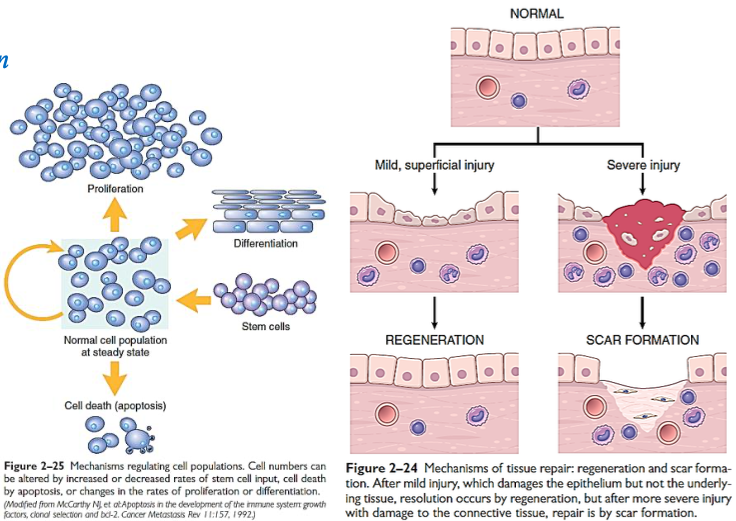
Repair
Has two possible outcomes:
[...]
[...]
Regeneration → tissue returns to normal (common with mild, superficial injuries)
Replacement by connective tissue → scar formation (common with deeper, more severe injuries)
[...]
Exaggeration of process of contraction in secondary union
Results in deformities
Compromise the movement of joints
Frequently seen on the palms, soles, and following burns
Contractures
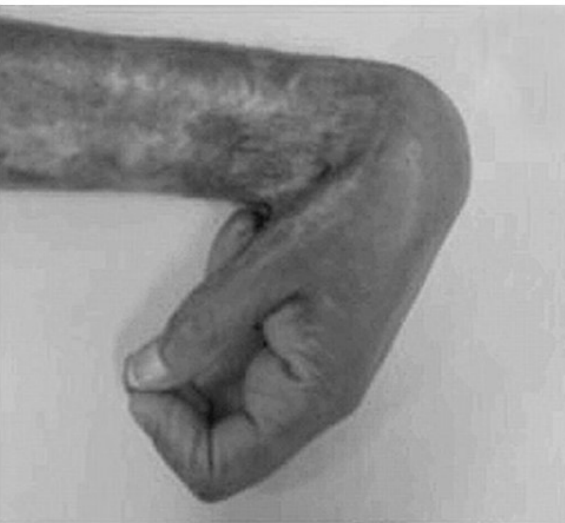
Contractures
Exaggeration of process of contraction in secondary union
Results in deformities
Compromise the movement of joints
Frequently seen on the palms, soles, and following [...]
burns