Psych Unit I-II
1/228
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
Case Study
An observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
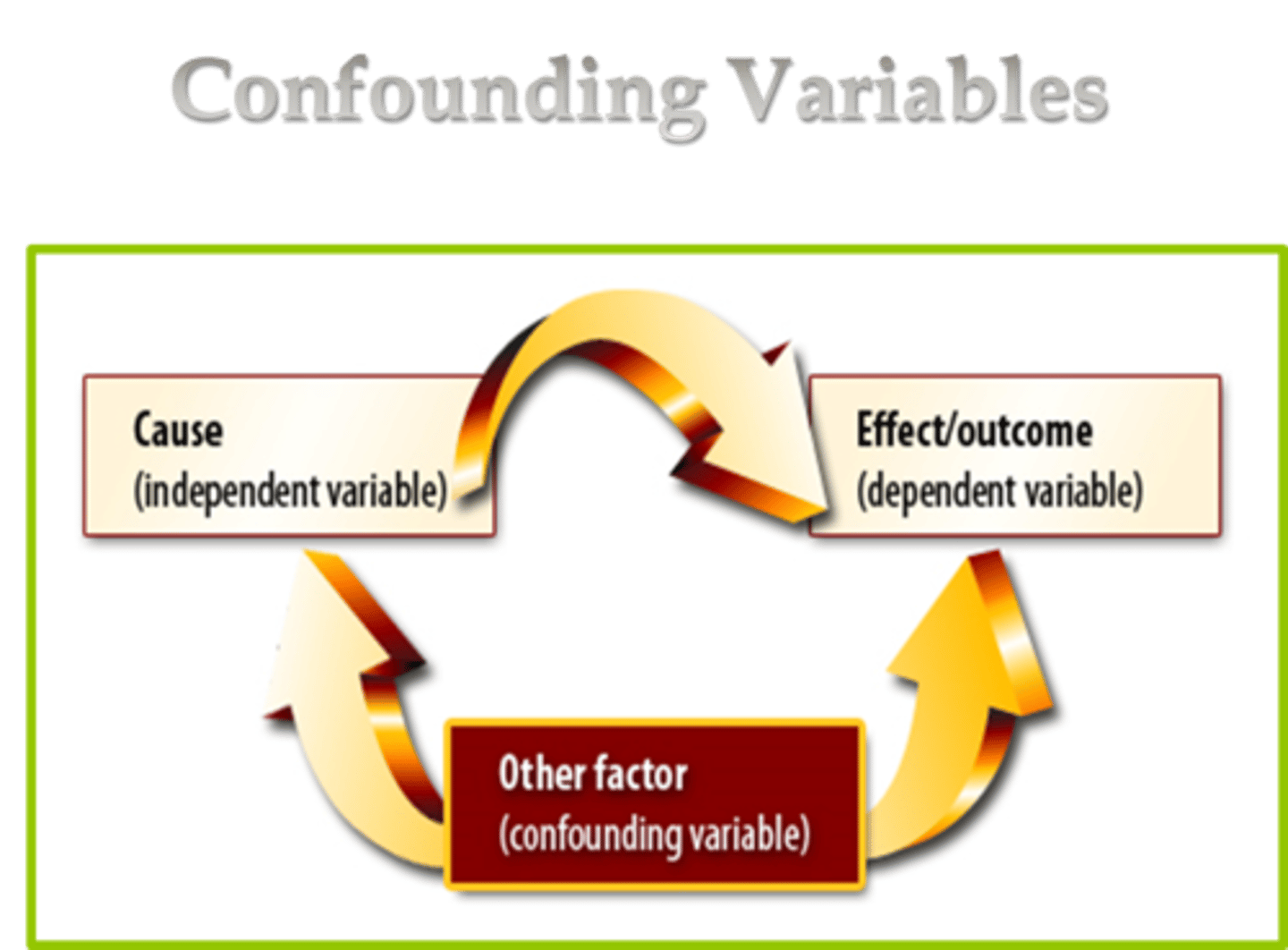
Confounding Variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment.
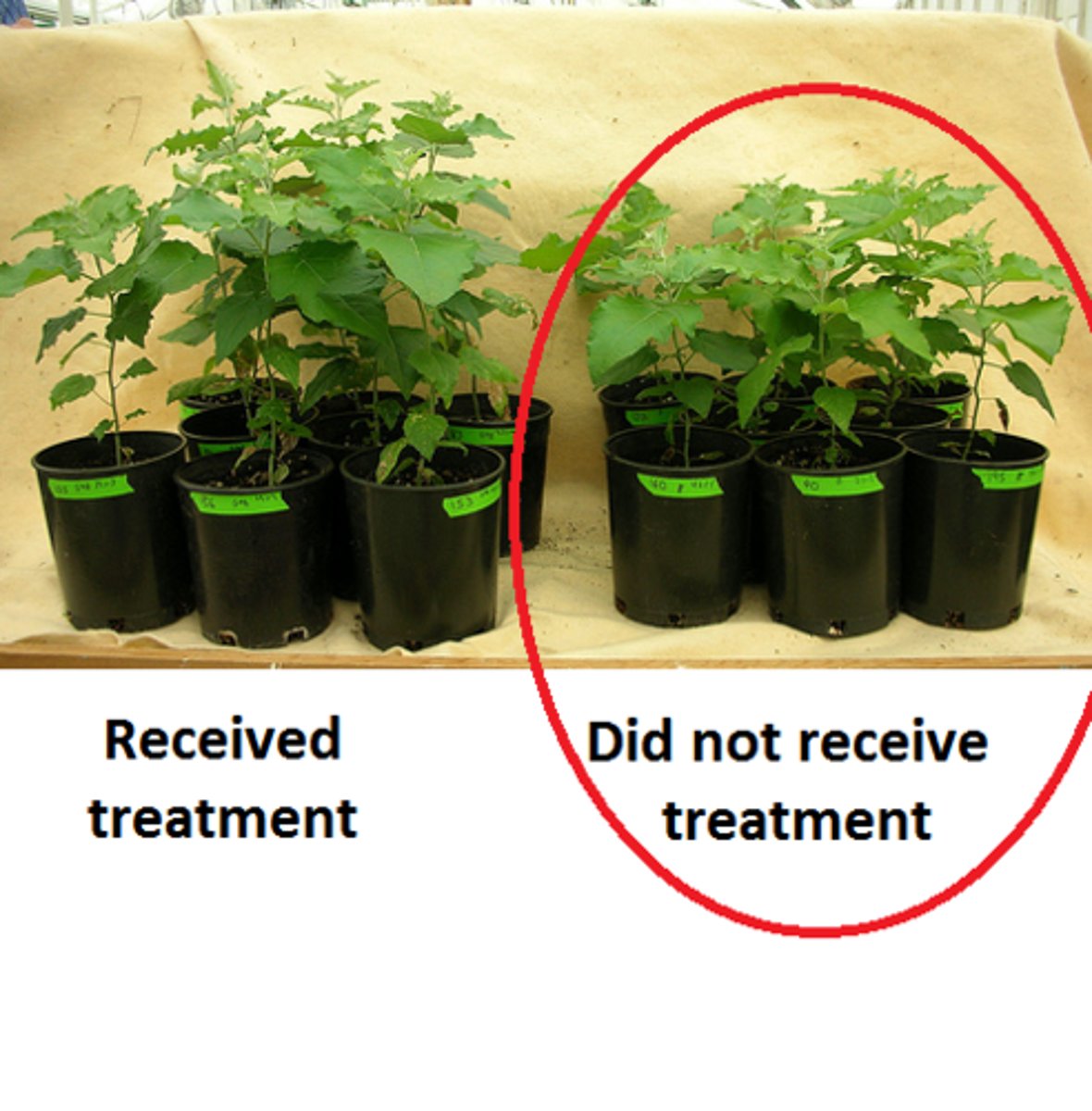
Control Group
in an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.

Correlation Coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1); r is used to represent value
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other. The correlation coefficient (r) is the mathematical expression of the relationship, ranging from -1 to +1
Critical Thinking
thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather, it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions.

Culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, and traditions shared by a large group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
Debriefing
the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
Dependent Variables
The outcome factor, what is being measured -- the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable
Descriptive statistics
Used to describe the basic features of the data in a study.
Experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effects on some behavior or mental process (the dependent variable). By random assignment of participants, the experimenter aims to control other relevant variable
Experimental Group
in an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it (I-Knew-it-all-along phenomenon)
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship where none exists (i.e., athletes and rituals or superstitions)

Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated--the variable whose effect is being studied
Inferential Statistics
numerical methods used to determine whether research data support a hypothesis or whether results were due to chance
Informed Consent
an ethical principle requiring that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Kenneth and Mamie Clark
Used dolls to study children's attitude towards race. Their findings were used in the Brown vs. Board trial.

Mean
The arithmetic average of a distribution, obtaining by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
Measures of Central Tendency
Mean, Median, Mode
Measures of Variation
Range, Variance, Standard Deviation
Median
The middle score in a distribution--half the scores are above it and half are below it
Mode
The most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
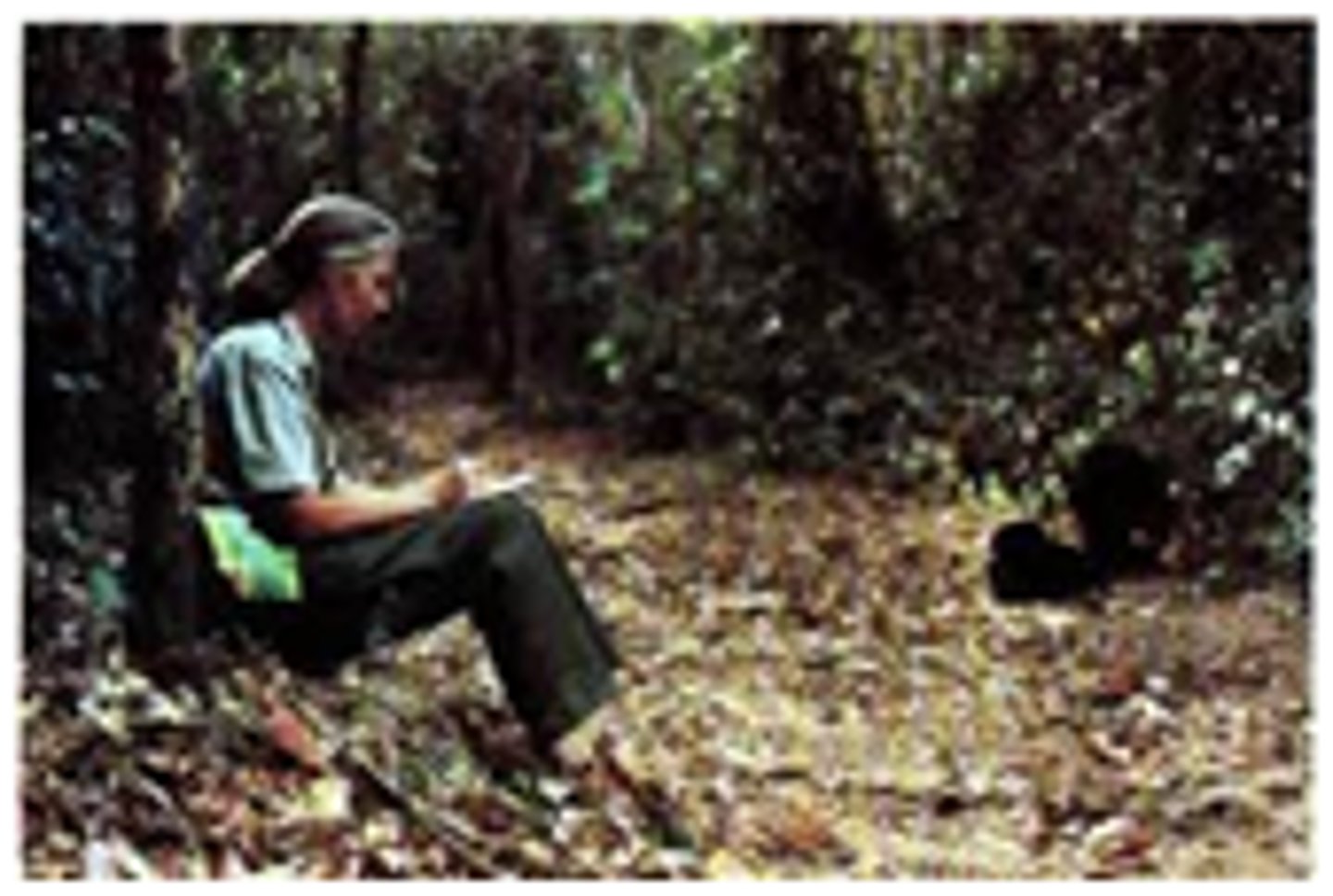
Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation

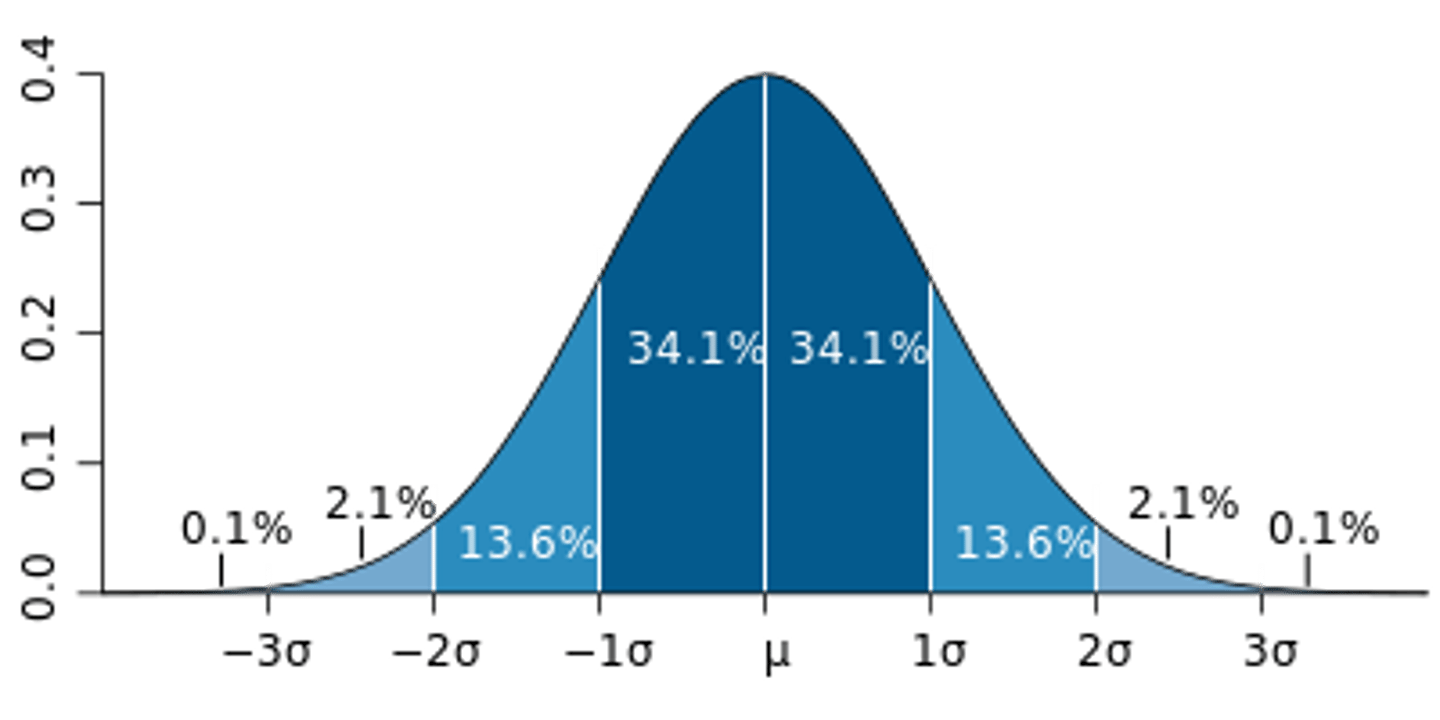
Normal Curve/distribution
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean (68% fall within one standard deviation of it) and fewer near the extremes
Operational Definition
A statement of the procedures used to define research variables. Ex human intelligence -- what an intelligence test measures. (remember the fidget!)
p value
0.05 for statistical significance; ≤ .05 (5%)
Placebo Effect
any effect that seems to be a consequence of administering a placebo
Placebo
a pill/inert substance used for the "affect" of a drug; often times a sugar pill
Population
all the cases in a group, from which samples may be drawn for a study
Psuedo-Psychology
is a false or unscientific form of Psychology.
r
value to signify correlation coefficient
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
Random Sampling
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Regression toward the Mean
the tendency for extremes of unusual scores or events to regress toward the average. (i.e. Baseball player hits 240 normally, now hits 305, eventually will go back to 'normal' hitting average)
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Scientific Attitude
curiosity (passion for exploration), skepticism (doubting and questioning) and humility (ability to accept responsibility when wrong)
Single Blind Procedure
Study in which either the researcher OR the experimenter are "blind" to the treatment being used; NOT both!
Standard Deviation
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score (i.e., average error of different scores are)
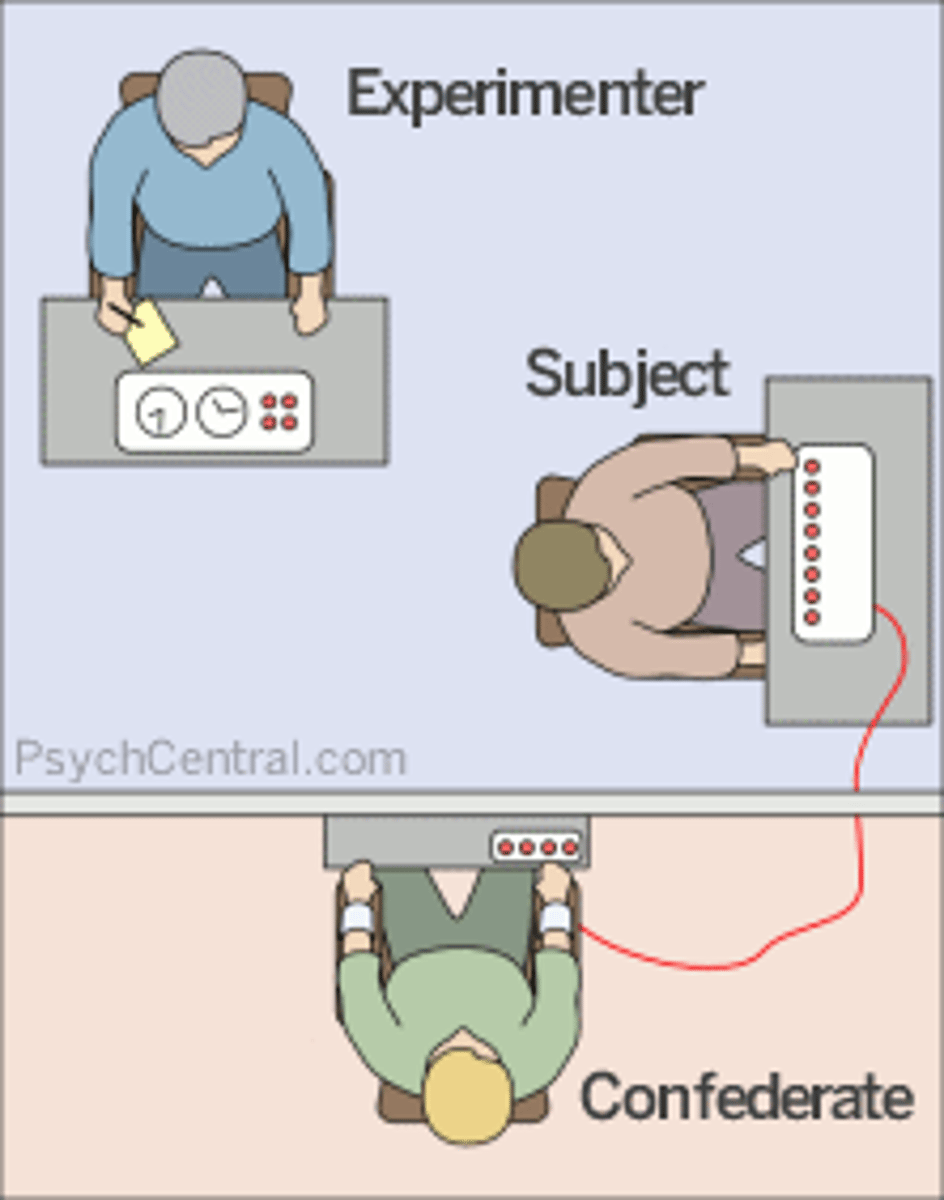
Stanley Milgram
Yale University Psychologist, notable study in the 1960s on Obedience (Experimenter, Teacher and Learner - Teacher doesn't know what is happening.) How willing will the teacher be to "shock" the person learner?
Statistical Significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance; p ≤ .05 (5%)
Survey
A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of people, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of them
Theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations
Variance
Mathematical computation that shows how spread out data points are from mean.
Empirical Approach
Letting the facts speak for themselves/scientifically proven
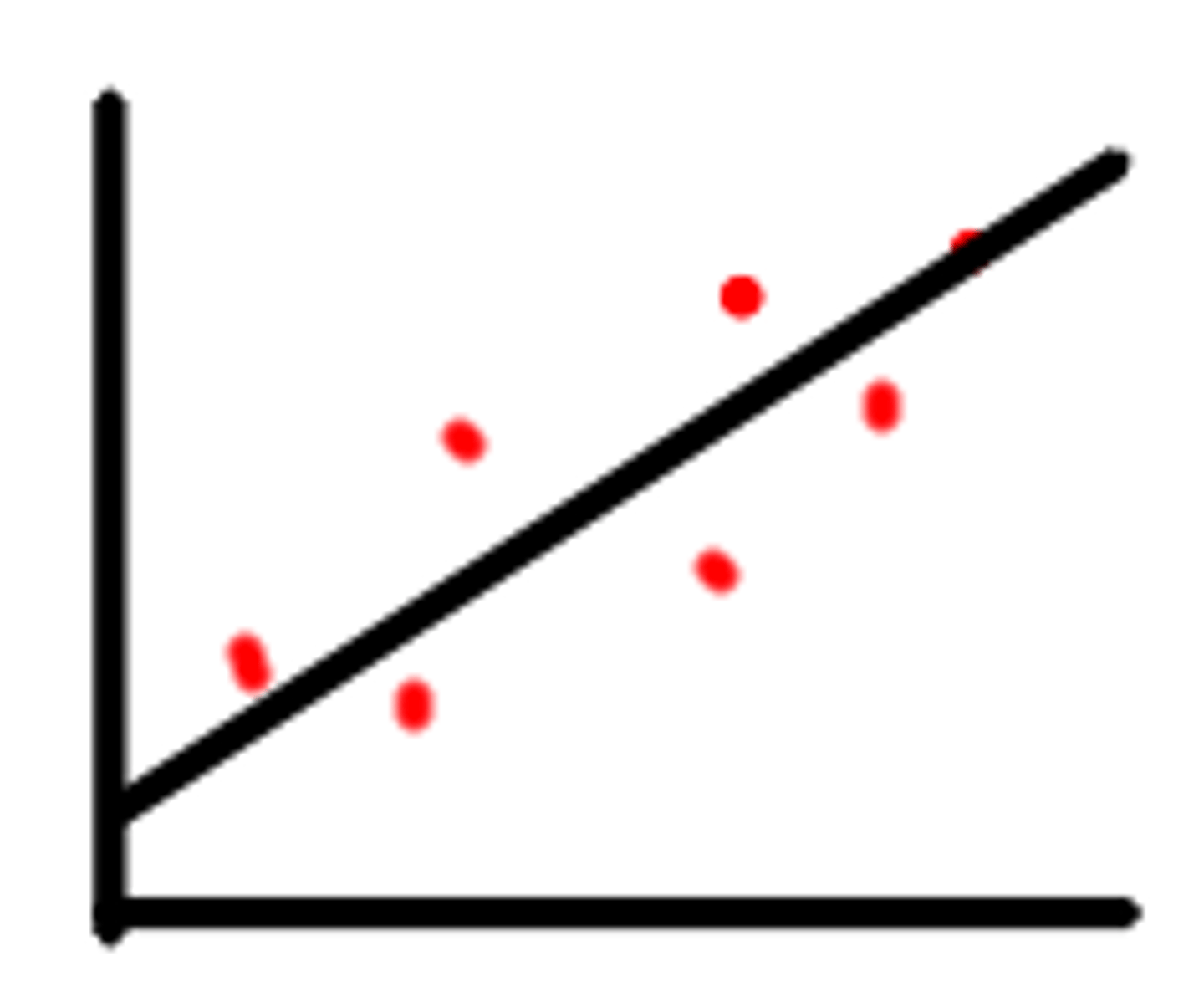
Scatterplots
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the value of 2 variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation.
Double Blind Procedure
testing procedure, designed to eliminate biased results, in which the identity of those receiving a test treatment is concealed from both administrators and subjects until after the study is completed.
skewed distribution
a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value (can be either positive or negative -- the mean is what MOVES the skew)
Experimenter (Researcher) bias
occurs when a researcher's expectations or preferences about the outcome of a study influence the results obtained
sampling bias
exists when a sample is not representative of the population from which it was drawn
variable
A factor that can change in an experiment
Scatterplot
name for a graph of data points in a two variable correlation
Validity
Actually measuring exactly what you intend to measure
Histogram
a bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
meta-analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
Sleep
Periodic natural loss of conciousness
Circadian rhythm
Regular bodily rhythms that occur in 24 hour cycle (Our biological clock)
Examples of circadian rhythm
Body temperature, thinking, memory
REM sleep characteristics
Rapid eye movement, vivid dreams, muscles relaxing, active body system. Gets longer as night progress. Sleep paralysis can occur in this stage
Alpha waves
Slow brain waves of a relaxed awake state
NREM sleep
non-rapid eye movement sleep, every other sleep stage other than REM
Hallucinations
False sensory experiences
Hypnagogic sensations
Bizarre feeling such as falling or floating while transitioning to sleep
Delta Waves
Large slow brain waves associated with deep sleep of NREM-3
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
Pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm
NREM-1 characteristics
Hypnagogic sensations and hallucinations,
NREM-2 characteristics
Sleep spindles, stage gets longer as night goes on
NREM-3 characteristics
Delta waves, grows shorter and disappears as night goes on
Sleep paralysis causation
Motor cortex is active, but brainstem blocks it’s messages
Melatonin production is (increased/d
Melatonin production is (increased/decreased) in the night
Increased
Why do we sleep?
Protection
Immune system restoration and repair brain tissue
Restore and rebuild fading memories
Feeds creative thinking
Supports growth
Insomnia
Recurring problems in falling asleep or staying asleep
Narcolepsy
Sudden attacks of heavy sleepiness often triggered by strong emotions
Sleep apnea
Stopping breathing while sleeping
Sleepwalking
doing normal waking activities while asleep
When does sleepwalking occur?
NREM-3
When does sleeptalking occur?
Any sleep stage
Night terror
Appearing terrified, talking nonsense, or walking around during NREM-3 sleep (NOT THE SAME AS NIGHTMARES)
Effects of insomnia
Chronic tiredness, reliance on alcohol or sleeping pills, reduced REM sleep
Effects of sleep apnea
Fatigue and depression, associated with obesity especially among men
Effects of night terrors
Doubling of child’s heart and breathing rate during the attack

Dream
Sequence of images, emotion, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person’s mind
Manifest content
Remembered storyline of a dream (According to Freud)
Latent content
underlying meaning of a dream (According to Freud)
REM rebound
tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
Psychoactive drug
Chemical substance that alters perception and mood
Substance use disorder
Disorder characterized by continued substance use despite significant life disruption
Tolerance
Brain’s chemistry adapts to offset drug effect, leading to larger doses required to experience same effect
Withdrawal
Discomfort following discontinuing addictive drug or behavior
Depressants
Reduces neural activity and slow body function
Barbiturates
Drugs that depress CNS, reduces anxiety but impairs memory and judgement
Opiates
Depresses neural activity, temporarily lessens pain and anxiety
Stimulant
Drug that excite neural activity and speed up body function
Nicotine
A stimulating and highly addictive psychoactive drug
Cocaine
Powerful and addictive stimulant derived from coca plant
Amphetamines
Drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing accelerated body functions and associated with energy and mood changes
methamphetamine
drug that stimulates the CNS with accelerated body functions and associated energy and mood changes; reduces baseline dopamine levels