Histology of Cardiovascular System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Memorize the structure of the heart:
Right ventricle: blood to the lungs
Left Ventricle: blood to the rest of the body
Right atrium: recieves blood from body
Left atrium: recieves blood from pulmonary veins
What three major layer/tunics are in the walls of the four heart chambers?
ENdocardium (internal)
Myocardium (contains cardiac muscle) (middle)
Epicardium (external) (also know as visceral pericardium)

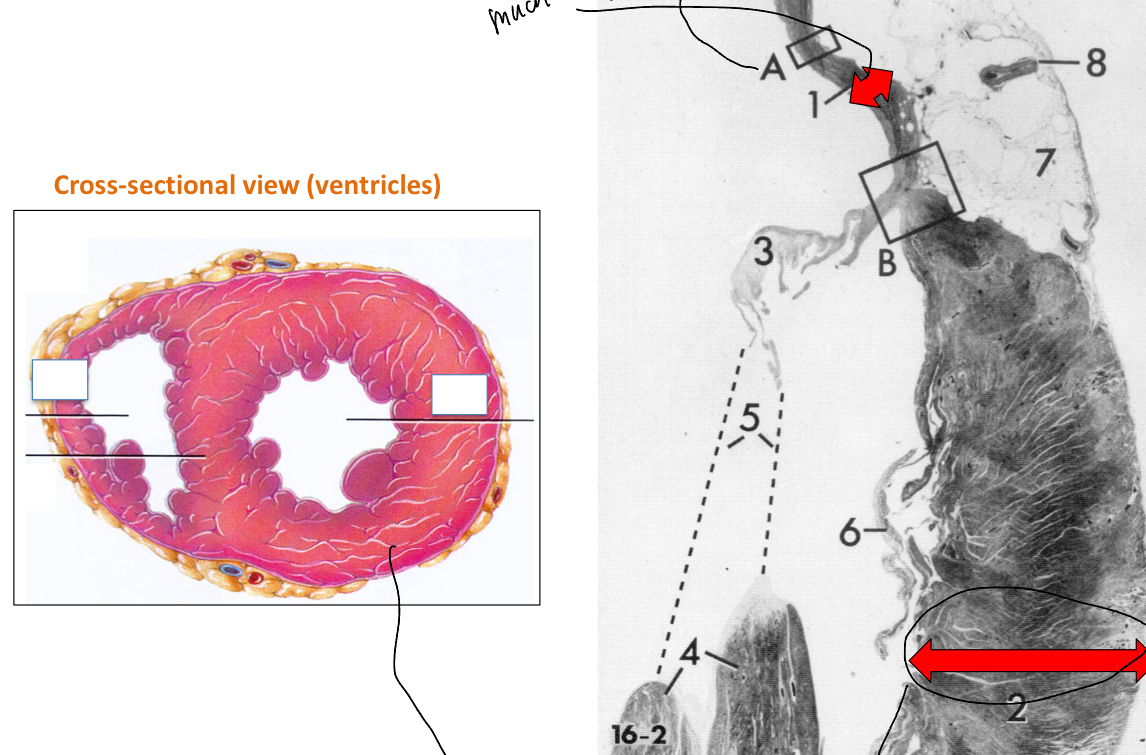
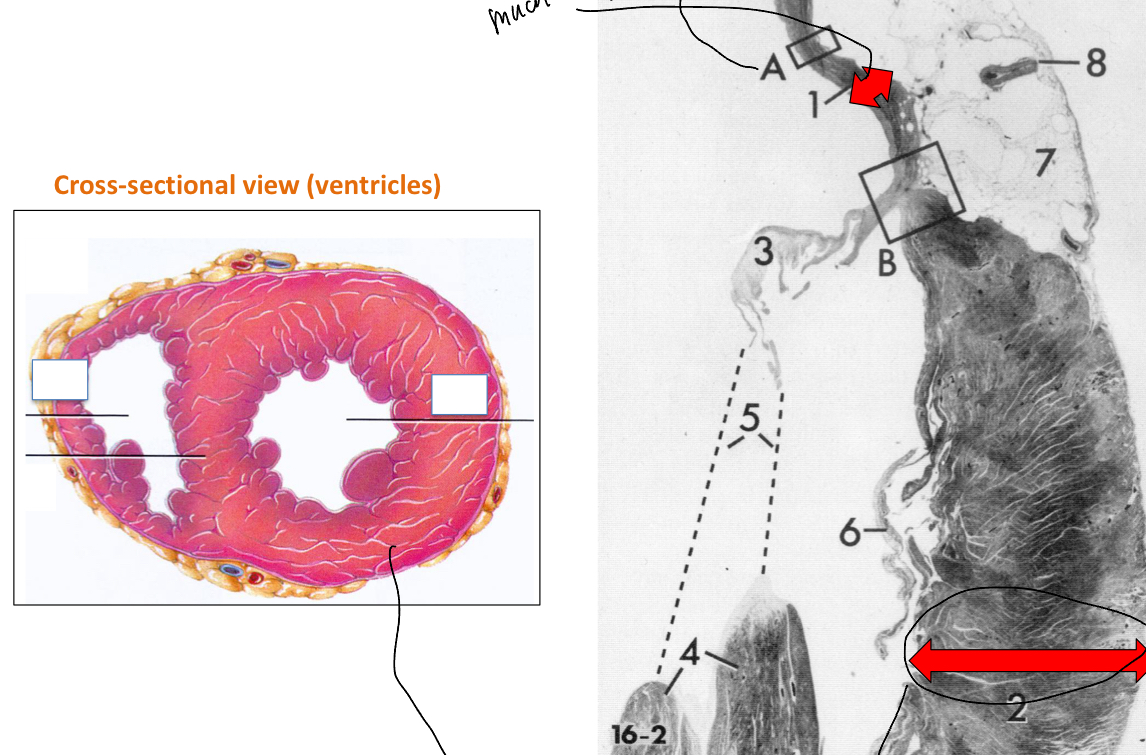
Explain the image depicted of the heart‘S ventricular walls
Top red arrow: atrium wall
Bottom red arrow: Ventricle wall
The ventricle has a thicker wall than the atrium because it has a thicker myocardium since it is in charge of ejecting blood out of the heart.
HOwever, the left ventricle will be thicker than the right one because instead of pumping blood just to the lungs (right ventricle), the left ventricle must pump the blood out to the rest of the body
Describe the Endocardium in detail
It is composed of:
Endothelium: simple squamous epithelium (outermost layer)
Subendocardial layer: a thin layer of loose connective tissue containing:
elastic and collagen fibers
Some smooth muscle cells,
microvasculature
nerves
branches of the impulse conducting system of the heart from the purkine fibers
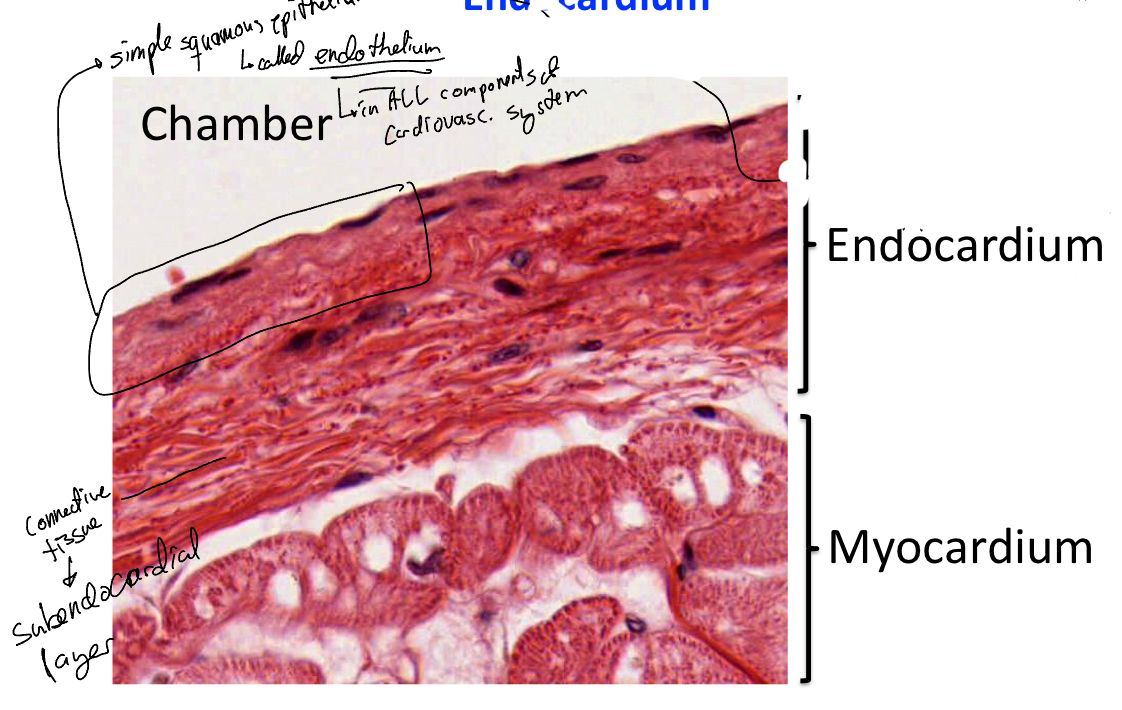
Describe the myocardium in detail
Composed of cardiac muscle arranged in a spiral fashion to contract and propel blood into the arteries for distribution to the body. It is highly vascularized and has an intercellular collagen network that acts as scaffolding

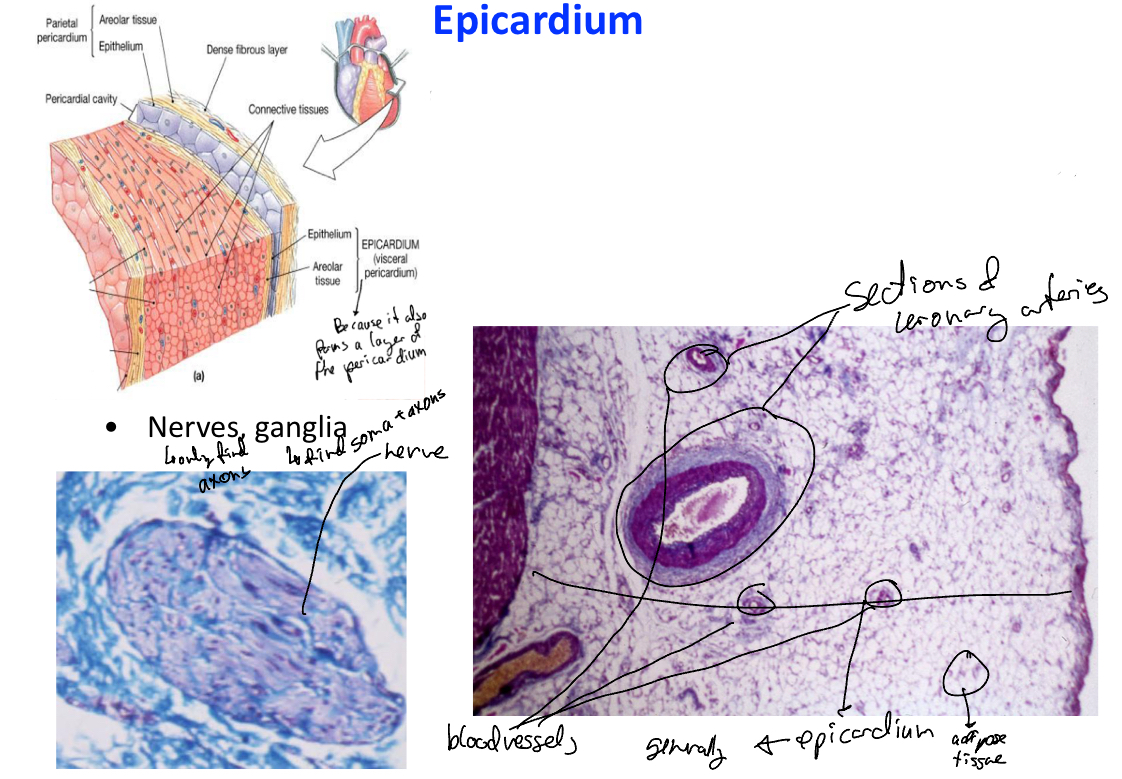
Describe the epicardium in detail
Outermost layer of the heart (visceral layer of the pericardium). Has:
mesothelium: simple squamous epithelium (external surface)
Submesothelial layer: FIrboblastic connective tissue with
Adipocytes
Coronary vessels
Lymphatic vessels
Nerves/ganglia
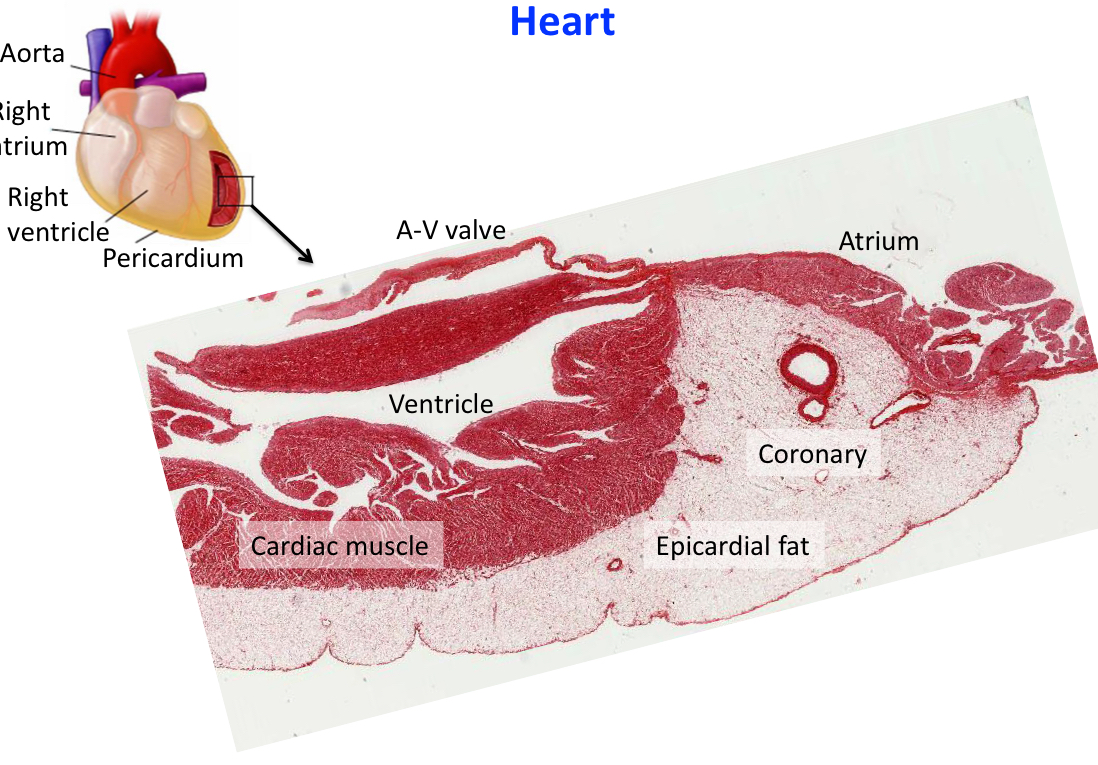
Remember this is how th heart is seen histologically:
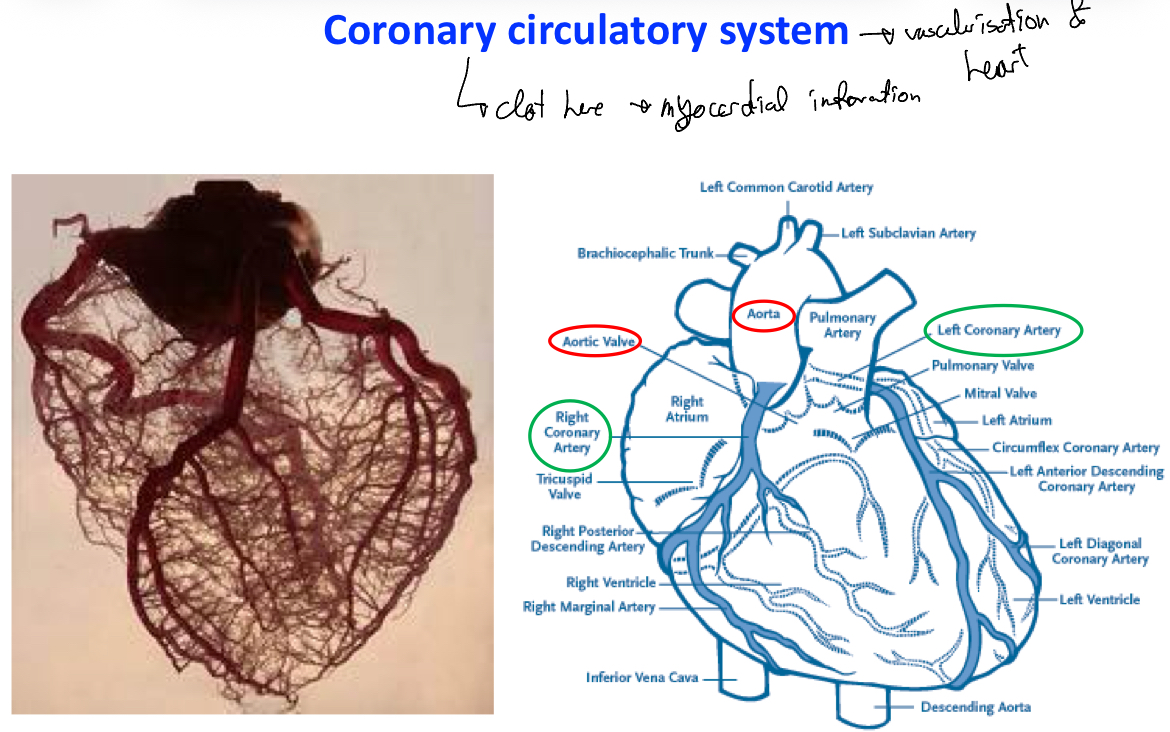
Remember this is how the heart is vascularised:
What is the pericardium?
A double walled sac
With epicardium (which is visceral pericardium), the pericardial cavity (with epricardial fluid (****whiche acts as a lubricant to faciliatte the heart’s movements****) and parietal pericardium (mesothelium and loos connective tissue)
Pericarditis is too much pericardial fluid in the cavity due to inflammation (low blood pressure)
Explain the cardiac valves in general
Stop backflow
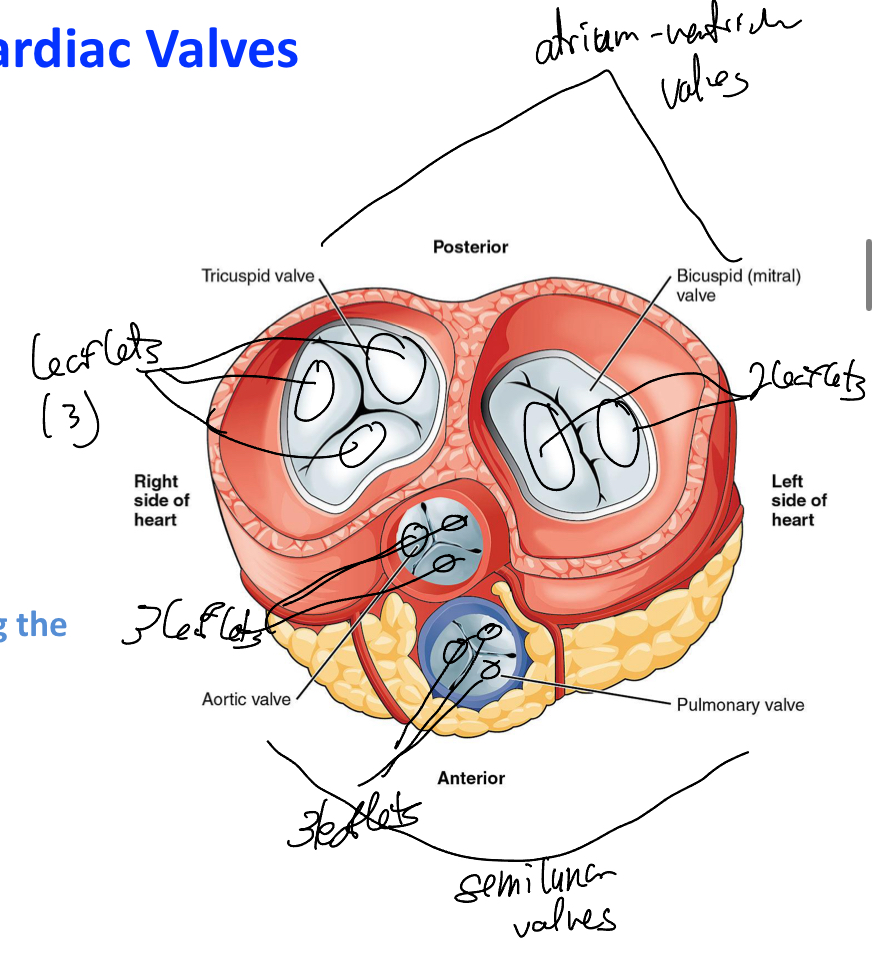
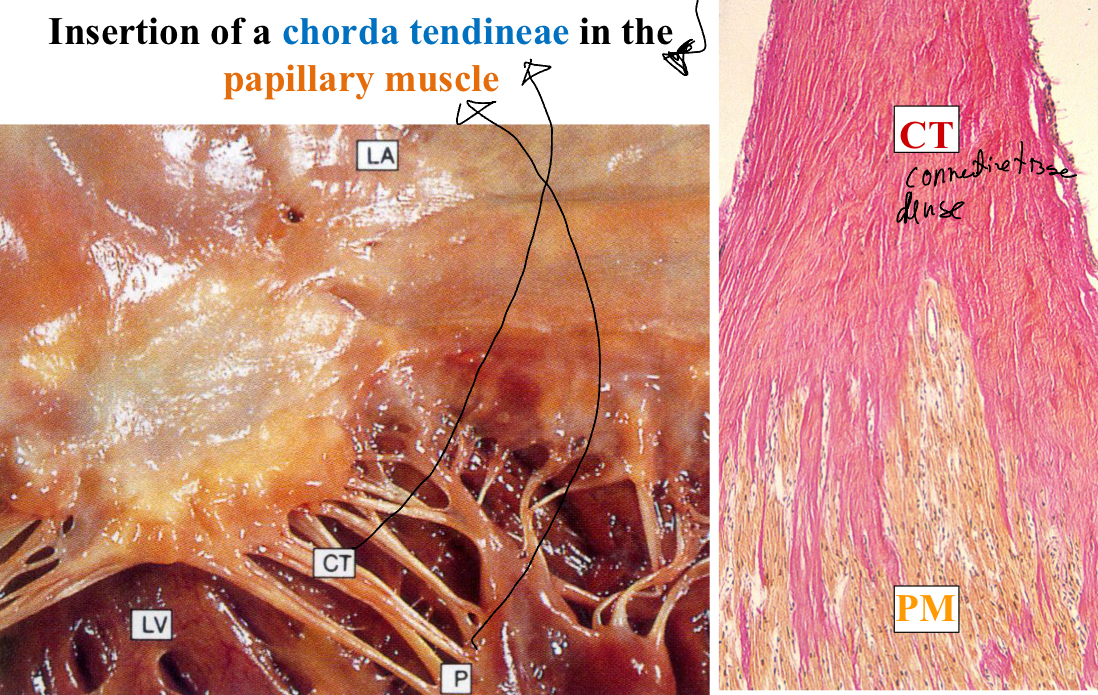
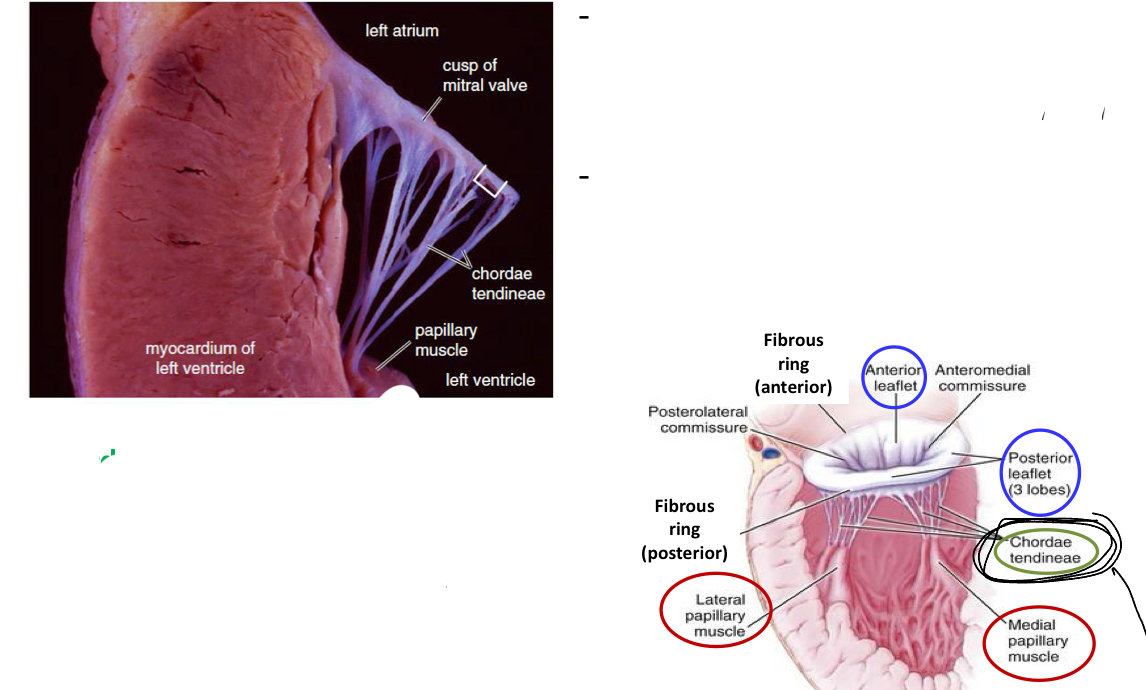
Explain the atrioventricular valves histologically
They have:
central core (dense fibrous connective tissue w/ collagen and elastic fibers)
Endothelial layers lining on both side
Chordae Tendinae( dense connective tissue (lined by endocardium) whichi binds valve leaflets to papillary muscle (prevents regurgitation))
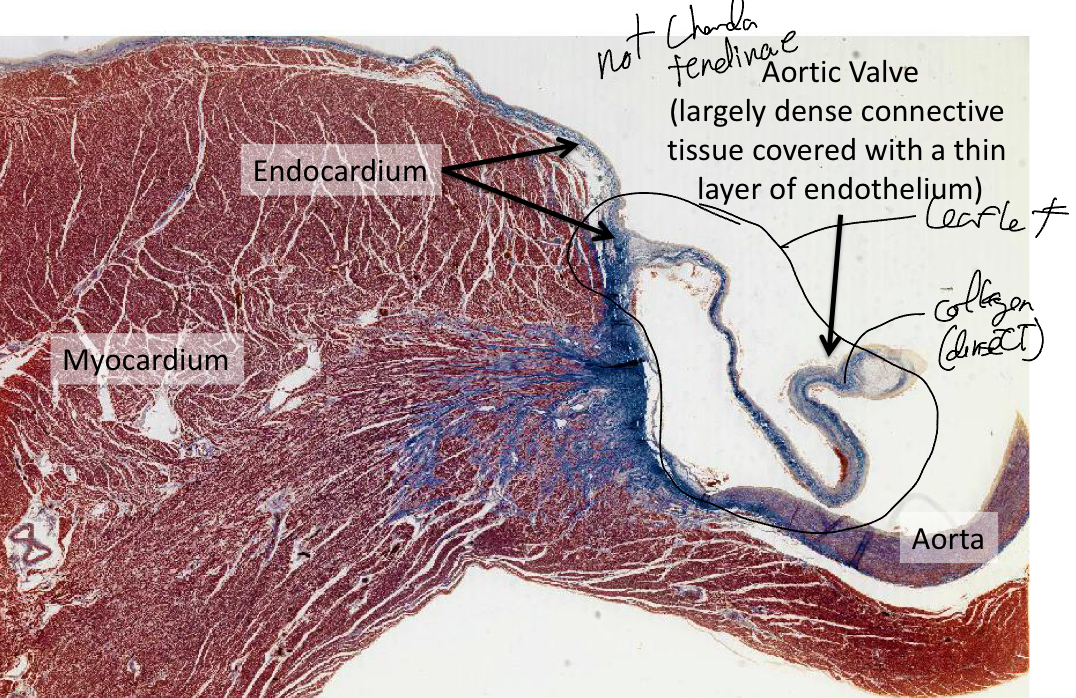
Explain the aortic valve histologically
Largely dense connective tissue covered with athin layer of endothelium, NO chorda tendinae.. mostly made of collagen(stained blue)
Explain the intrinsic regulation of heart rate
Main components+functions
Sinoatrial (pacemaker)node: small mass of modified cardiac muscle cells, they are fusiform, smaller and have less myofibirils than neighboring muscle cells.
Atrioventricular node: like sinoatrial node but with cytoplasmic projection that branch in various directions, forming a network.
Bundle of His (originates from sinoatrial node, passing along interventricular spetum and splits into left and right budnles, branhcing further to both ventricles. They are modified cardiac muscle cells functionally integrated by gap junctions(purkinje fibers)
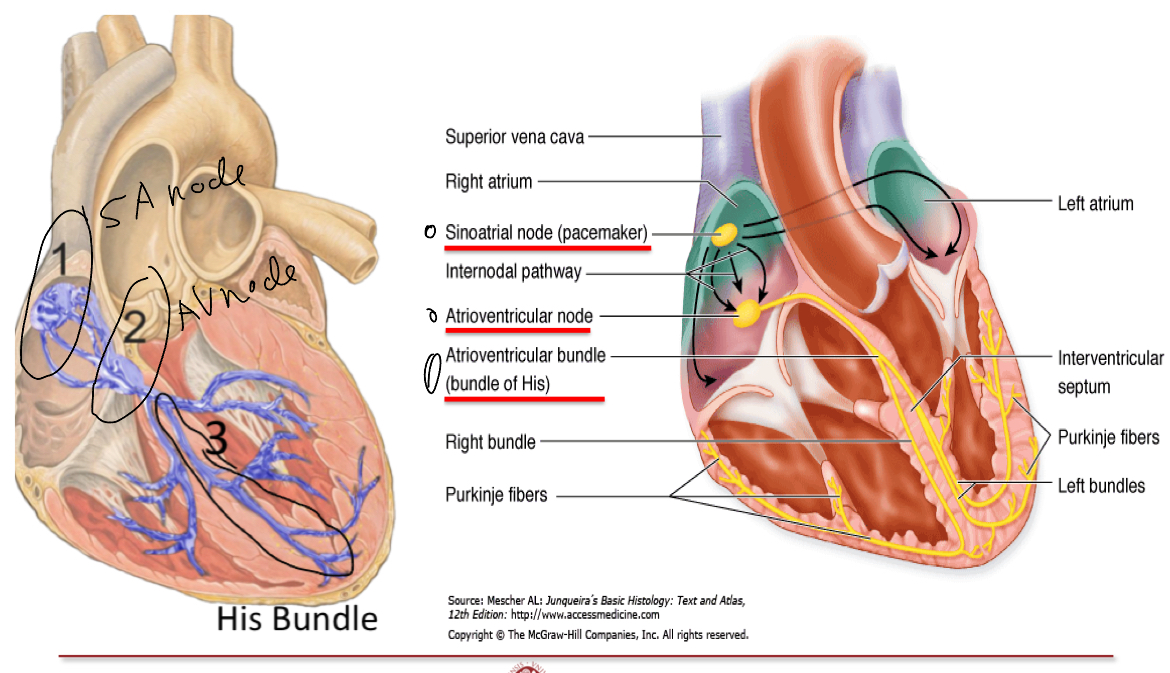
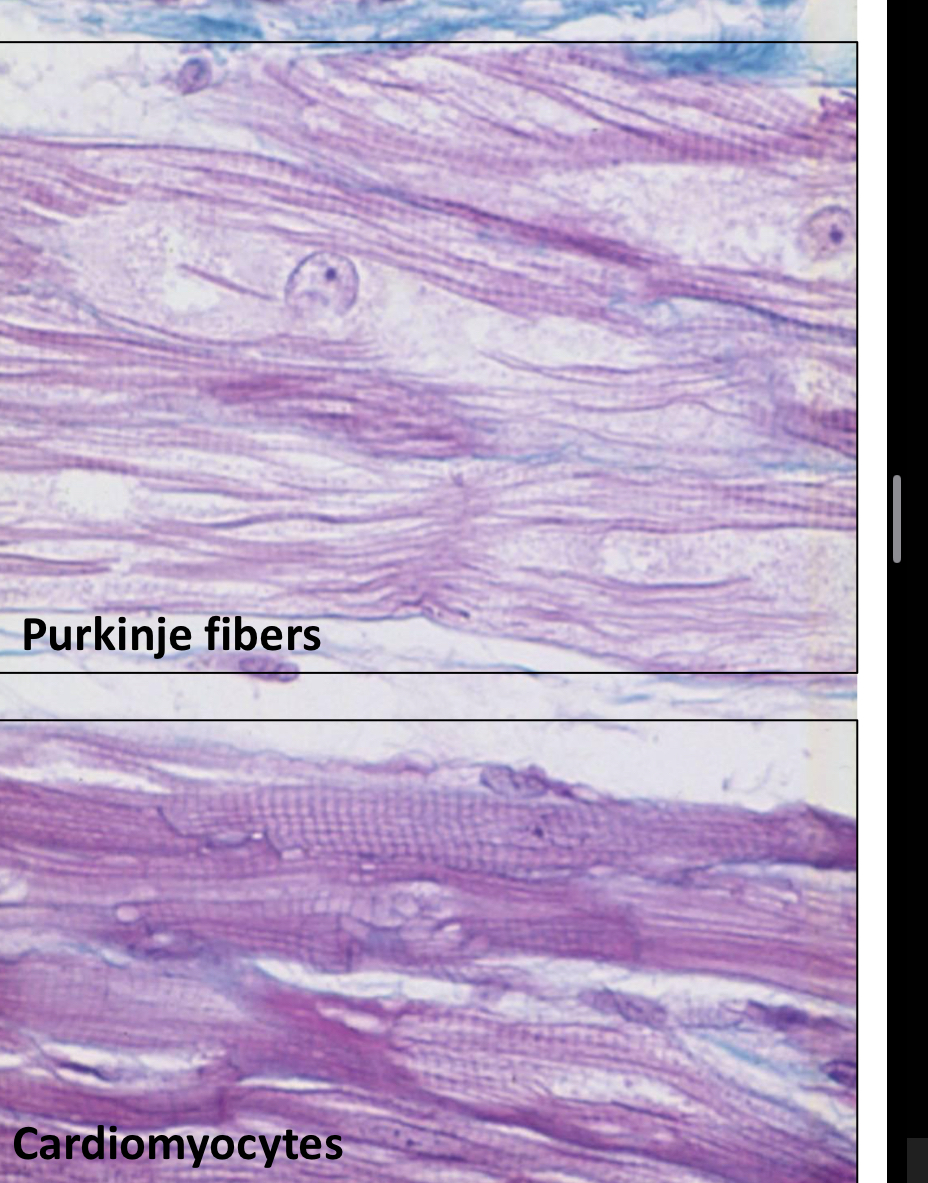
What are the purkinje fibers?
Modified cardiac muscle cells in the bundle of His that transmit the pacemaker impulse. They are larger than normal cardiac muscle, one or two central nuclei, cytoplasm is rich in mitochondria and glycogen, has less myofibrils

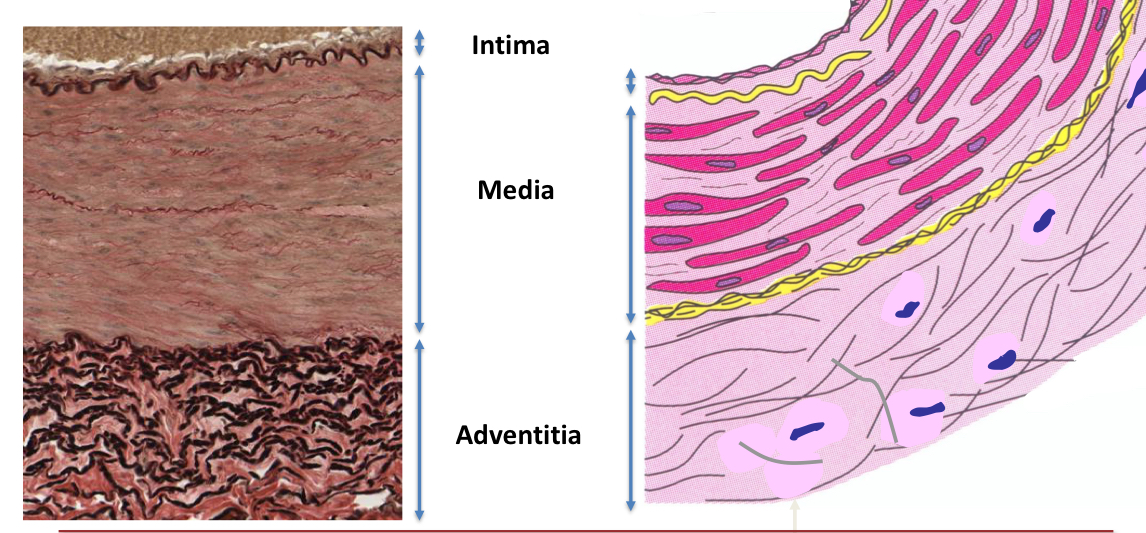
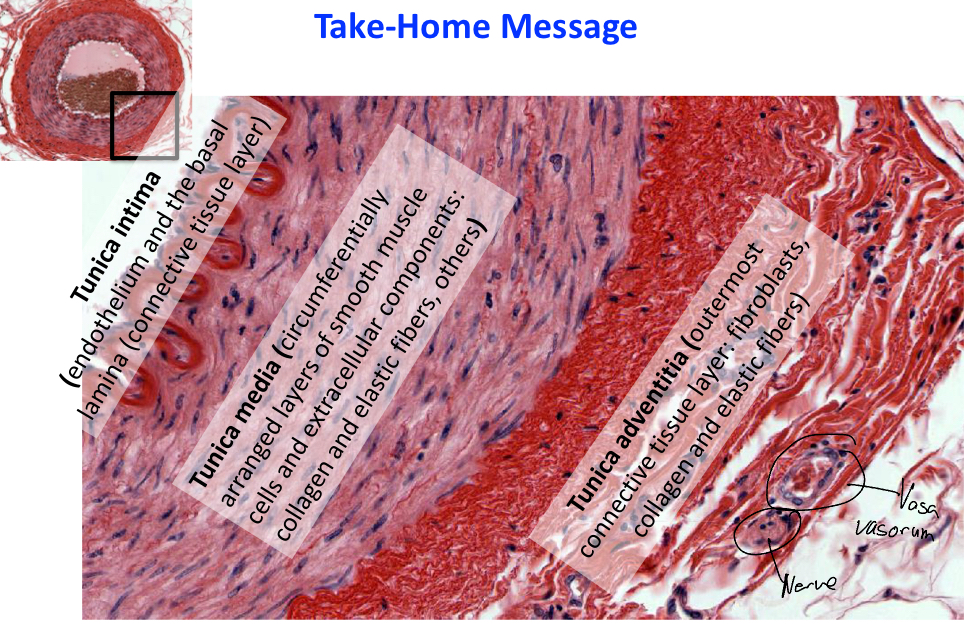
Explain what the blood vessel tunica intima is
It is the innermost lining of the blood vessel.
lined by endothelium (simple squamous epithelium)— these cells have th efollowing:
Basememt membrane (on basal side)
Developed cytoskeleton (intermediate filaments of desmin, vimentin or both for support)
Joined together by Fasciae occludens (tight junctions), with some desmosomes and gap junctions
Many pinocytotic vesicles- for transcytosis (nutrients enter in formo lumen, or wastes excreted out to lumen) +++synthesises hormones
+++++ monitors/mediates exchnage of small molecules.
Underlying connective tissue— when the vessel is very small (capillary) there is no connective tissue
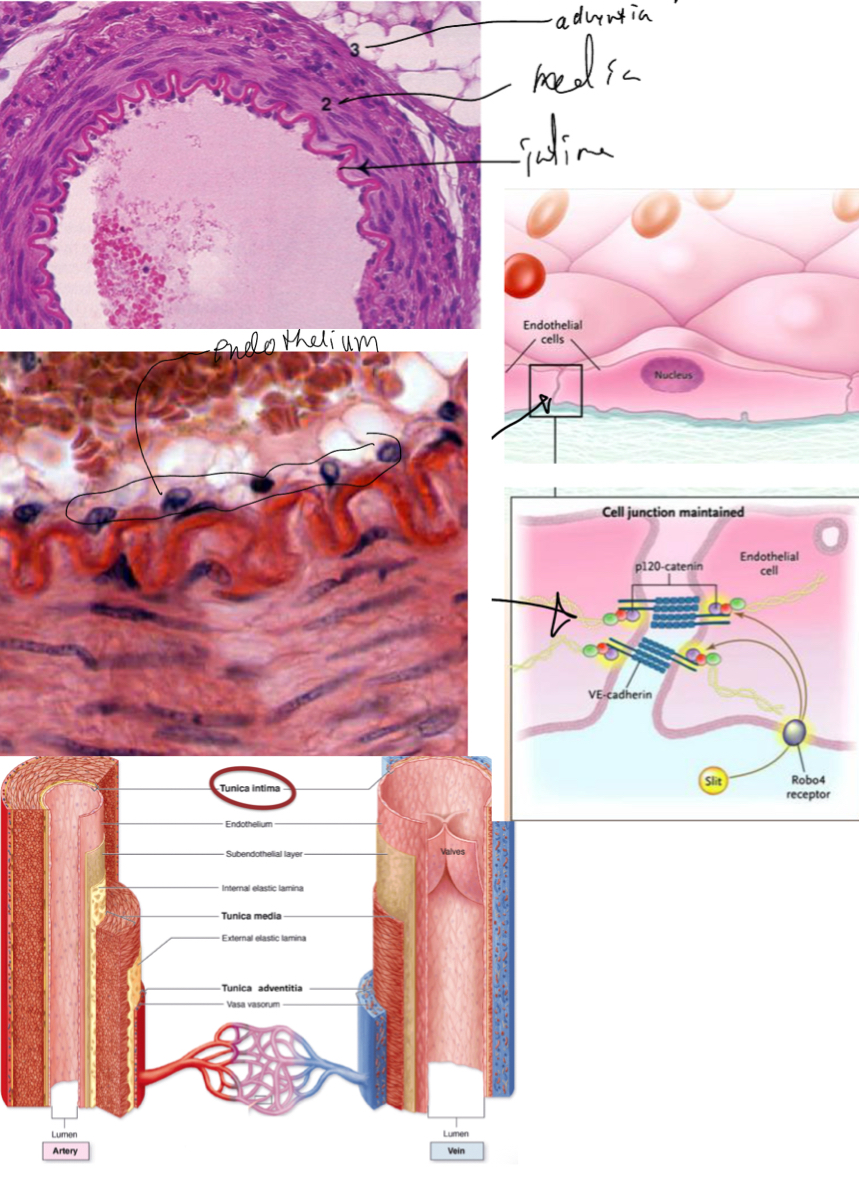
What is the internal elastic membrane
It is a membran ethat marks the boundary between the tunica intima and tunica media (better distinguished in arteries)
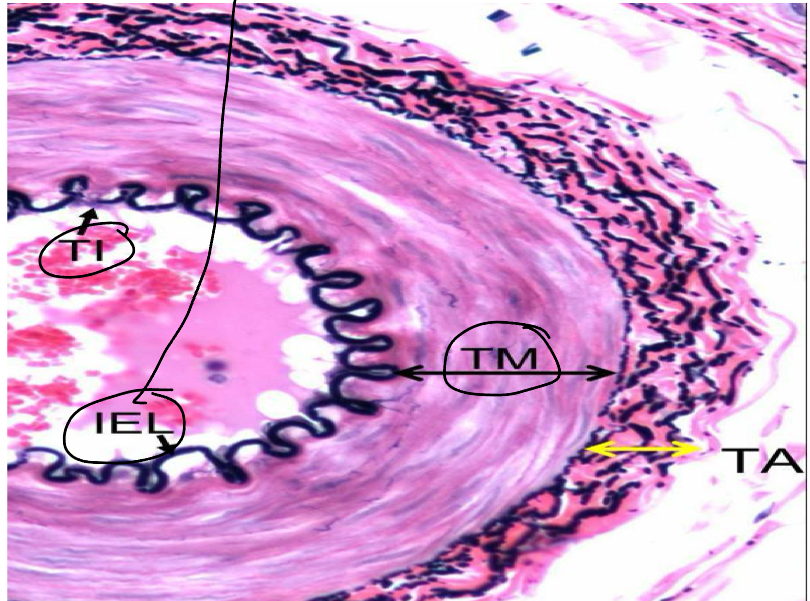
Explain what the blood vessel tunica media is
The middle layer, it contains concentric sheets of smooth muscle cells with extracellular matrix
Myocytes (smooth muscle)
Regulate vessel lumen—modify bloodflow/pressure
Matrix
Collagen fibers+elastic fibers+proteoglycans
Provide resiliency elasticity and cohesion
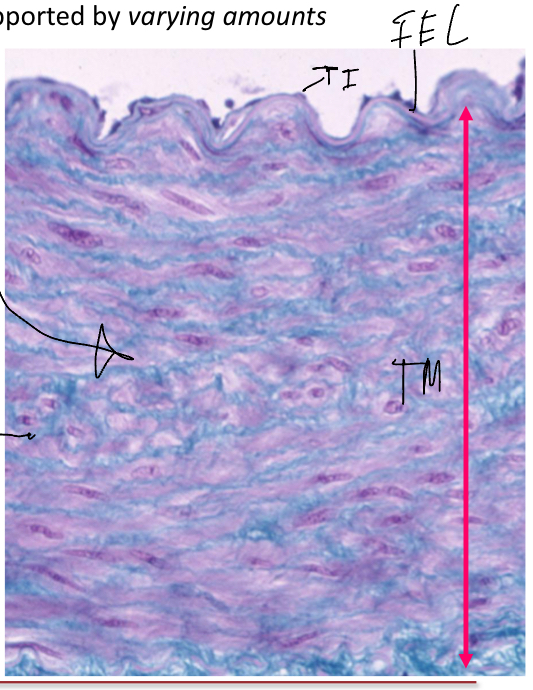
What is the external elastic membrane?
Some arteries have an outer layer of elastic tissue ( the external elastic membrane) which marks the boundayr between the tunica media and the tunica adventitia
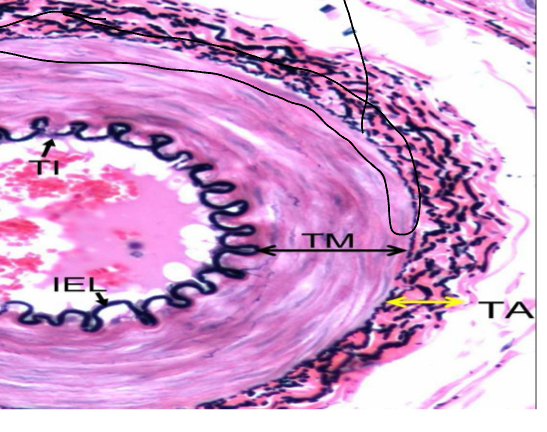
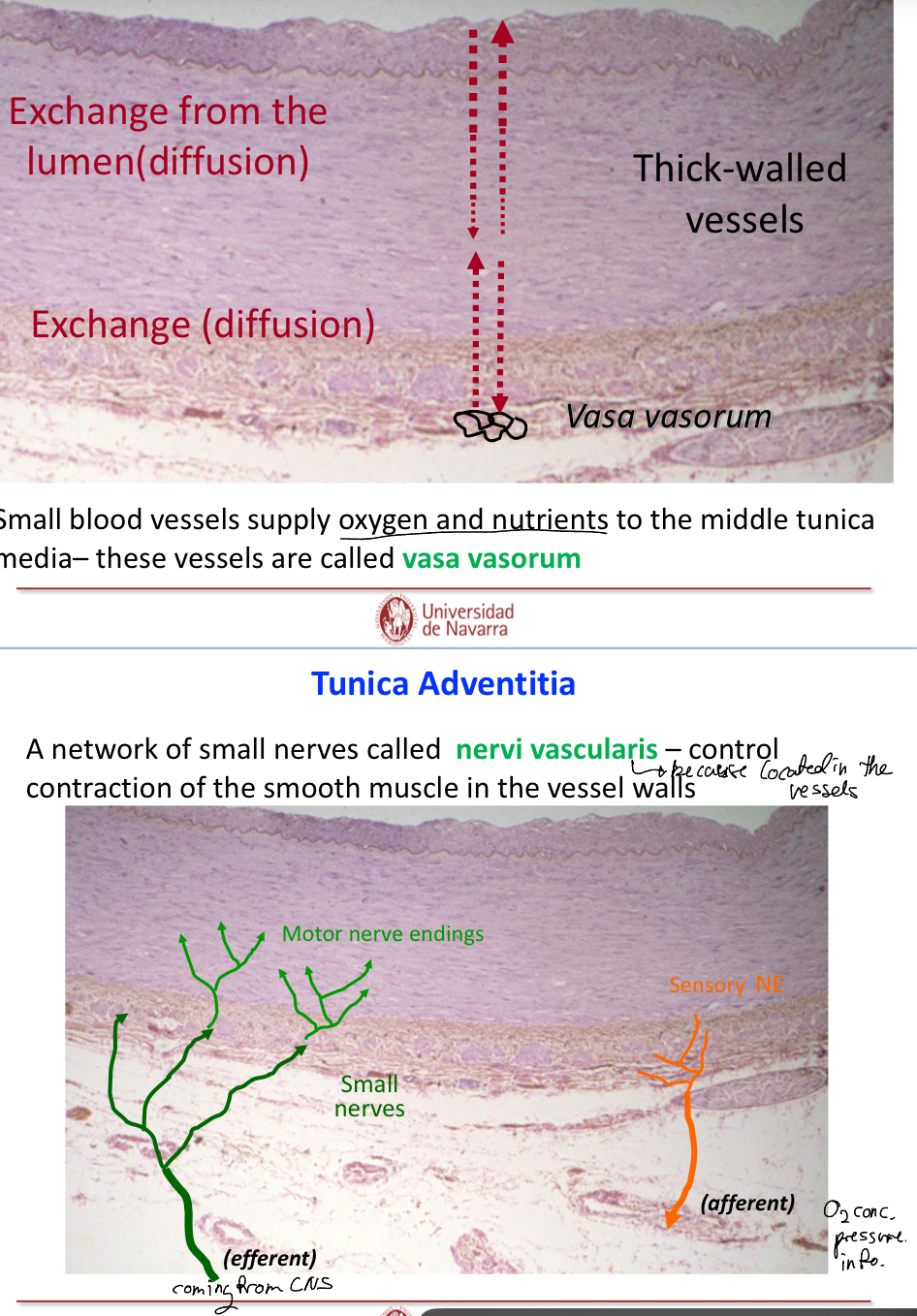
Explain what the blood vessel tunica adventitia (externa) is
Connective tissue that forms the outermost layer of the vessel, these fibers often blend into those of the surrounding tissues to stabilze the position of the vessel.
Vasa vasorum (small blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the middle tunica media
Nervi vascularis (control contraction of smooth muscle in the vessel walls)
Overall keep in mind:
How are arteries generally classified?
Elastic, muscular arteries and arterioles
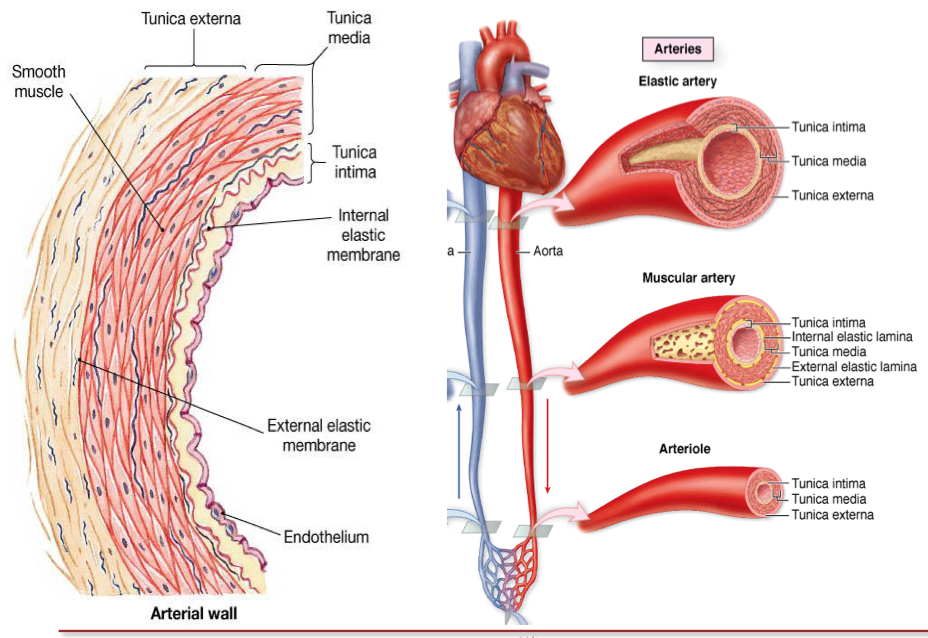
Explain elastic arteries composition
Aorta (oxygenated blood to whole body) and pulmonary (brings oxygenated blood to heart) arteries and their main barnches are elastic arteries. They have:
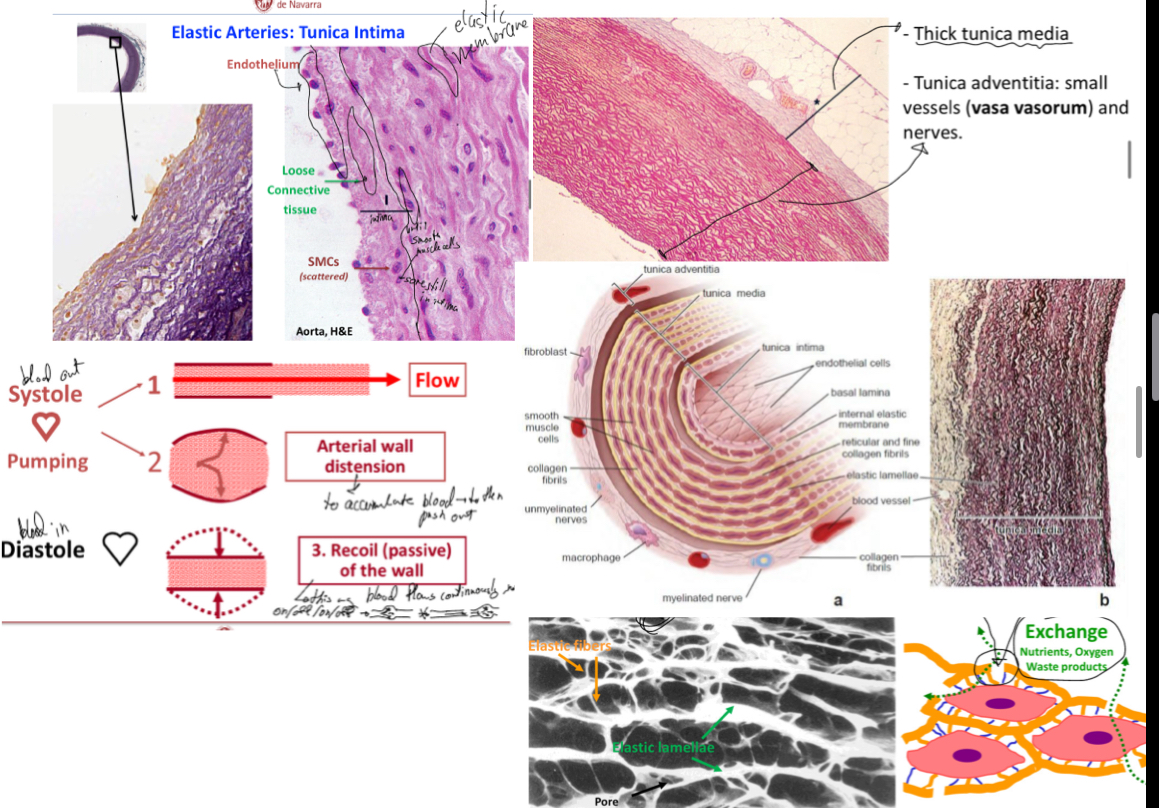
Thick tunica media
Tunica media has small vessels (vasa vasorum) and nerves (nervi vascularis)
It has multiple layer of smooth mucle cells separated by elastic lamellae (seen in histology as thick and concentric sheaths)
The elastic lamellae are fenestrated to facilitate the diffusion of subtances within the arterial wall— the number and thickness of these is related to blood pressure and age.. they aid in elasticity
Collagen fiber and elastic fibers and ground subatnce (poretoglycans), synthesized and secreted by smooth muscle cells
Arterial wall distension and recoil to maintain a continous flow of blood (think of vid shown in class of the balloon and the hose)
Explain muscular arteries
Most oif the named arteries of the body.. medium sized muscular arteries are smaller than elastic arteries but larger than arterioles… They have
endothelium, but thinner subendothelial connective tissue layer than in elastic
A more prominent internal elastic lamina
Composed almost entirely of smooth muscle cells (Arranged in spiral fashion internal elastic lamina arterial wall, their contraction helps maintian blood pressure
Very little elastic material (elastic fibers)
Collagen
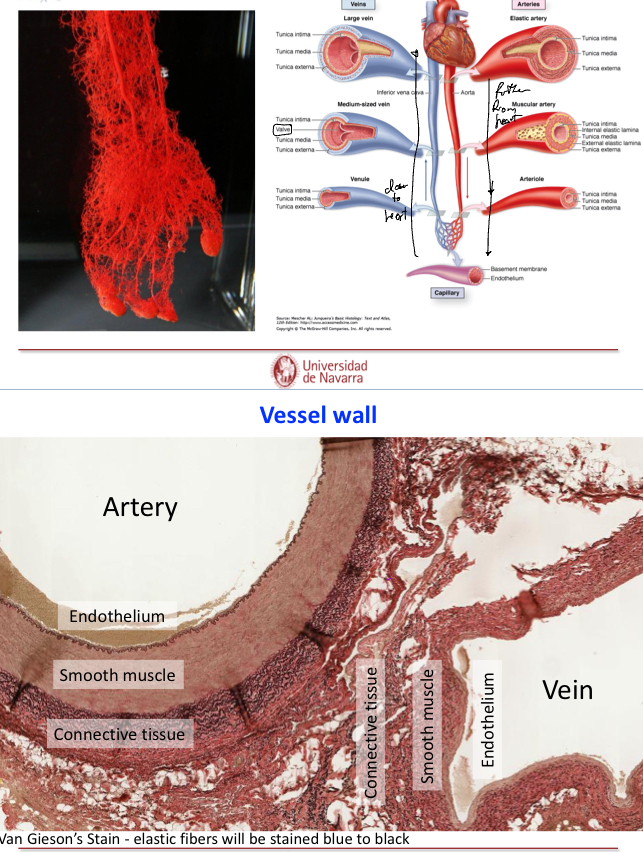
Explain vessels composition
Tunica intima: Endothelium+subendothelial connective tissue
Tunica Media: Smooth muscle cells+extracellular matrix
Tunica adventitia (externa): Connective tissue